What is Blockchain? How is it revolutionizing everyday life?
What is Blockchain? Why do we need it? In recent years, Blockchain has always been a hot topic in the technology world as it has opened a new trend for fields such as finance and banking, electronics and telecommunications, logistics, accounting and auditing… In today’s article, we will find out about this revolutionary technology and how it is applied in everyday life.

I. What is Blockchain?
To have a deep understanding about this technology, let’s start by figuring out its definition.
1.1. Definition: What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized database that stores information in blocks that are linked together by encryption and expanded over time to form a chain. Each block in the Blockchain will be linked to the previous block, containing information about the time that block was created along with a timecode and transaction data.
It can be understood simply that Blockchain is an electronic ledger distributed on many different computers, storing all transaction information and ensuring that information cannot be changed in any way. The information stored on that ledger will be verified by a series of computers connected in a common network, no machine can change, overwrite or delete the data in that ledger.
1.2. History of Blockchain
Blockchain was born in 2008 with the first announcement of invention and design by Satoshi Nakamoto, this technology was accomplished the following year after the introduction of Bitcoin, when Blockchain technology acted as a ledger for all transactions. Through the use of a peer to peer network and a decentralized data system, the Bitcoin Blockchain is managed fully automatically.
The invention of Blockchain and its application to Bitcoin made it the first digital currency to solve the problem of Double Spending. This technology of Bitcoin has become the inspiration for a series of other applications in many different fields.
II. Structure of Blockchain
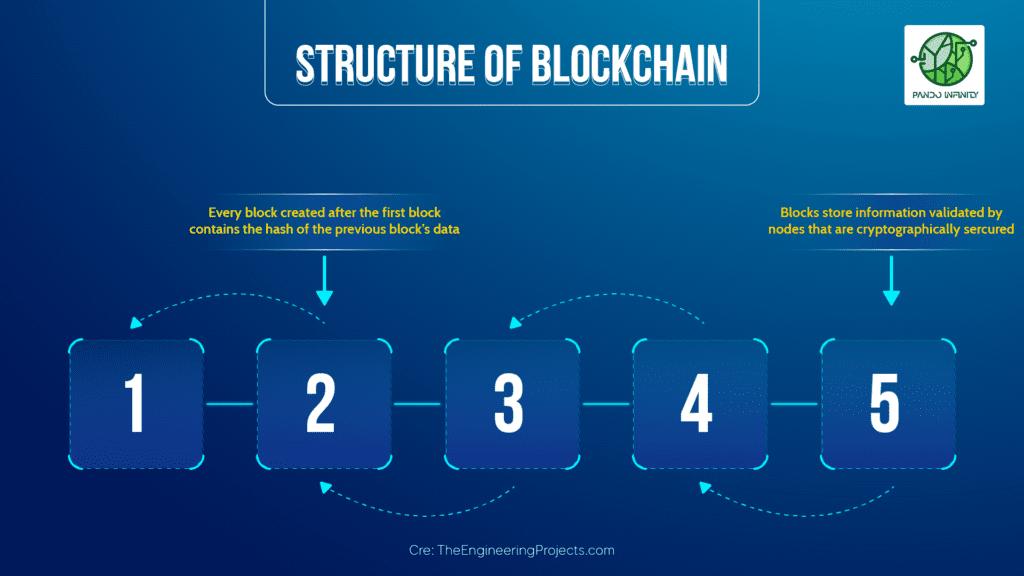
Blockchain consists of 2 main parts:
Block: you can imagine it as a box that is responsible for storing data.
: blocks containing data link together to form a chain. It also indicates that these blocks are linked together to form an inseparable link. The creation of the chain (chain) is also the way that the Blockchain can resist the modification of data information contained in the blocks (Block).
Each block consists of 3 main components: Data , Hash Code of the current and previous block.
III. What problem does blockchain solve?
Blockchain was originally created with the main purpose of transparently and sustainably storing data over time. To have a better understanding of the importance of blockchain in human life, let’s take a look at how the change in the transaction system has taken place!

3.1. Agreements and papers
In the past when technology was not developed yet,
transaction between person A and person B was an agreement on paper. This document will then be verified by a third person (C) and recorded as evidence.
The limitation exists
can possibly turn into a fake transaction.
can deteriorate over time.
one can guarantee
the third party’s reputation.
Therefore, at this stage, the transaction between person A and B has a lot of risks to ensure the interests of both parties, which completely depend on the third party.
3.2. Banks as Financial Intermediaries
Over time, technology has helped society develop to a new level. To be more specific, computer technology has been applied in the banking and financial system. Transactions are now not recorded on paper, but instead, information will be stored on a bank’s server.
At this stage, technology has made the information stored in a more secure way and the security will be guaranteed by banks and governments.
However, a major problem that still exists is that all data is stored on one main server. Therefore, this will be a “prey” that hackers can exploit and edit data. As can be seen, the most important issue remains unresolved.
3.3. The invention of Blockchain has solved these difficult problems
Information is seen as the key element to solve these existing problems. So the question is:
How can I store that information in the most sustainable way?
How to keep the information safe, no one can affect it?
Through the process of changing the above transaction system, it can be seen that with the support of technology, the bank’s transaction system is still not really complete. This is the reason for the next step of development Blockchain.

As in the definition, Blockchain is a database stored distributed on computers. The data will be stored in blocks and these blocks will be linked together, lasting forever. In particular, no one can modify them.
IV. How does Blockchain work?
Until now, we must have understood what is Blockchain and the important characteristics that make it be expected to be an essential change for the future. In this part, let’s figure out how a Blockchain works!
Stage 1: Person A makes a transaction to Person B on Blockchain. Information will be recorded on the system in the form of a Record
Stage 2: This Record will be encrypted and validated by participating Nodes to put data on the block. Specifically, the nodes will verify the amount of assets that person A transfers to person B, put on the network and compare to see if the balance in the wallet is reasonable or not and then proceed to approve the transaction.
Stage 3: Transaction is validated, data is encrypted and put into block.
Stage 4: After being filled with data (transactions between person A and B and others’ transactions), a new block is created and linked to the blockchain.

V. Advantages and disadvantages of Blockchain
This technology also has advantages and disadvantages which are briefly listed below.
5.1. Advantages
It is impossible to forge and destroy the chains: In theory, only quantum computers can decode Blockchain, and this technology will only disappear when there is no Internet in the world.
Immutable: Data in Blockchain cannot be changed (can be edited but will leave a trace) and will be stored forever.
Security: The information and data in the Blockchain are distributed and absolutely safe.
Transparency: Anyone can track data going from one address to another and can track the entire history on that address.
Smart Contracts: are digital contracts embedded in If This Then That (IFTTT) code, allowing them to self execute without 3rd person.
5.2. Disadvantages
Transactions limit per second: Blockchain depends on a larger network to approve transactions so there is a limit on how fast it moves.
High energy costs: Making all nodes active to verify transactions consumes more electricity than a single database or spreadsheet. This not only makes blockchain based transactions more expensive, but also places a greater burden on the environment.
Risk of asset loss: Some digital assets are secured by a cryptographic key like cryptocurrency in a blockchain wallet. You need to carefully protect this key. If the owner of a digital asset loses the private cryptographic key that gives them access to their asset, there will be no way to recover it and the asset will be gone forever.
Potential of illegal activity: Decentralization of blockchain adds privacy and security. This unfortunately makes it attractive to criminals. It’s harder to track illegal transactions on the blockchain than it is through banking transactions that tied to a name.
Read the full article in our Blog here: https://pandoinfinity.com/what is blockchain and how is it revolutionizing everyday life
