
Geography at Our Lady of the Rosary




For the LORD gives wisdom; from his mouth come knowledge and understanding.
Proverbs 2:6






The teaching of Geography at Our Lady of the Rosary Catholic Primary School aims to inspire curiosity and fascination about the world and its people together with a deep respect for our environment that will remain with all pupils for the rest of their lives. Children are equipped with knowledge about diverse places, people, resources and natural and human environments along with a thorough understanding of key physical and human processes. Children learn how to collect, interpret and communicate information enabling them to deepen their understanding of the interaction between physical and human processes, and of the formation and use of landscapes and environments. Geographical knowledge, understanding and skills provide the frameworks and approaches that explain how the Earth’s features at different scales are shaped and provide a strong base to understand interdependence and change over time.




We aim to ensure that all pupils:
• develop contextual knowledge of the location of globally significant places – both terrestrial and marine
• identify and explain physical and human characteristics.
• understand the processes that give rise to key physical and human geographical features of the world, how these are interdependent and how they bring about spatial variation and change over time.

We equip children with the geographical skills needed to:
• collect, analyse and communicate with a range of data gathered through experiences of local fieldwork.
• interpret a range of sources of geographical information, including maps, diagrams, globes and aerial photographs
• communicate geographical information in a variety of ways, including through maps, numerical and quantitative skills and writing at length.









1. From Space to Staines
To talk about similarities and differences in relation to places, objects, materials and living things.
(The WorldELG)

To talk about the features of my own immediate environment and how environments might vary from one another. (The World – ELG)
To look closely at similarities and differences, patterns and change. (The World 40-60)
Our Lady of the Rosary school
Our Lady of the Rosary church
I can identify my school and our church on an aerial photograph.
I know that I live in Staines that is in England.
I can talk about my journey to school, naming some buildings or places I pass by.
I can talk about how other places can be different to Staines.
I can identify similarities and differences between my life here and someone else’s life in another country (through stories, & video clips)
I can suggest how to look after our environment.
I can use a map to navigate a simple route.
I can make my own map of a familiar place. I can use a map, globe and atlas to point out land and sea.
I can use directional language to give directions (forwards, sideways, backwards)
I can use positional vocabulary (e.g. next to, behind, above, below)
Where would you take a friend to visit in Staines?
1. Nursery and beyond! To describe my surroundings to others.
To know that there are different places and that they can be different to where I live.
Our outdoor area
The school playground I can recognise photos of my school and home.
I Know that there are different countries in the world.
I can talk about things and features I see in my immediate environment.
I can talk about the differences between countries that I have experienced or seen in photos. I am to beginning to understand the need to respect and care for the natural environment and all living things.
I can use small world setting such as farms, a garage or a train track in my play.
I can use some positional language (under, in front of, behind)
What is different between here and another country?




1. Places near and farMexico
1. All about Staines
2. Weather and Maps
To be able to ocate countries on an atlas or map (digital or paper)
To develop and use appropriate geographical language to describe a location.

To learn and use simple field work and observational skills to study a familiar local place.
To identify and describe weather types and relate this to our UK seasons.
Our Lady of the Rosary church Rail station High street Leisure centre
I can name and locate the four countries making up the British Isles, with their capital cities.
I can name the surrounding seas of the United Kingdom.
I can locate Staines on a map.
can recognise similarities and differences of geographical features in my own immediate environment.
can talk about people and places within my local environment.
can compare Staines with a contrasting place in the UK.
can identify the key features of a location in order to say whether it is a city, town or village, coastal or rural area
I can identify land use around the school.
I can use geographical vocabulary such as forest, hill, beach, mountain, river, city, town, village, factory, farm, house, office and shop to describe physical and human features
I can talk about weather in the UK, what happens in different seasons and how weather changes on a daily basis.
I can identify hot and cold places in relation to the Equator and the North and South Poles.
I can use maps, atlases, globes and digital / computer mapping to locate the UK its countries and their capital cities.
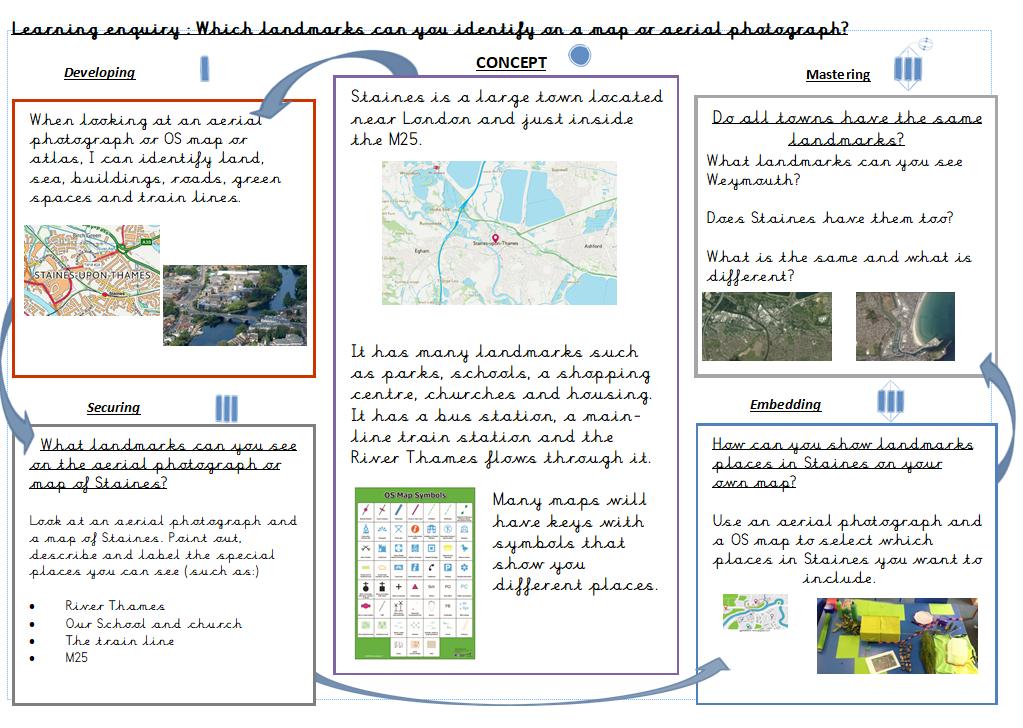
I can use aerial images to recognise landmarks and basic physical features (river, parks, hills) of my locality.
I can use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of my school and its surrounding environment.
What makes Staines a great place to live?
How does the weather vary in each season?
What does a map show us?
2. Maps, keys and compasses –Geographical skills
To understand geographical similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography of a small area of the United Kingdom, and of a small area in a contrasting nonEuropean country.
To name and locate the 7 continents and 5 oceans of the world.
To use fieldwork skills to collect information about the physical and human features of my local area
I can name and locate each continent on a world map.
I can name and locate the five oceans on a world map.
I can name and locate the four countries making up the British Isles, their capital cities and surrounding seas.
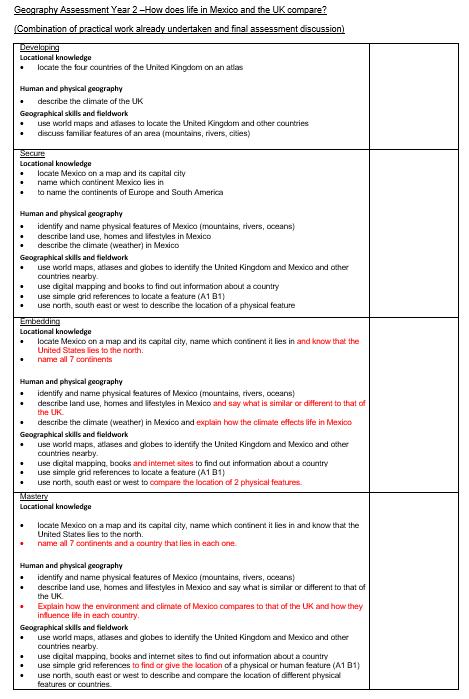
I can find Mexico on a map, name which continent it is in and its capital city.
I know that Mexico is in the continent of N.
America and that the USA lies to its North.
I can use correct geographical vocabulary to describe the physical and human features on a map.
I can understand and use a key.
I can devise a simple map and construct symbols for a key.
Where is Mexico?
I can identify the key features of a location in Mexico and say whether it is a city, town, and village, coastal or rural area.
I can identify similarities and differences between England and Mexico. (the environment and land use, homes and lifestyles)
I can describe the climate of Mexico.
I can name and describe some physical features of Mexico.
(mountains, rivers)
I can read a compass. (North, South, East and West)
I can read and follow a simple route on a map using compass directions.
I can use simple compass directions and directional language [e.g. near and far; left and right], to describe the position of features and describe routes on a map.
I can use simple grid references (A1, B1)
What special features can you find in Mexico?
How is life same and different to ours?
Do Mexico and England have the same climate? How well can use compass directions to find a location or plan / follow a route?




Topic Why?
1. Local study –Geographical skills
To use fieldwork to observe, measure, record and present the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs, and digital technologies.
I can name and locate counties and cities of England using a map.
I can describe how the locality of my school has changed over time.
I can ask and answer questions about the physical and human characteristics of a location.

2. Comparing France and England.
To understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom, a region in a European country
I can locate and describe different topography land uses in and around Staines.
I can name and locate some countries in Europe.
I can locate France, its capital city and identify some neighbouring European countries.
I can describe the physical geography of a location in the UK and an area in an European country.
I can talk about land use and settlements in these two locations.
I can explain how people’s lives and work are influenced by their physical location.
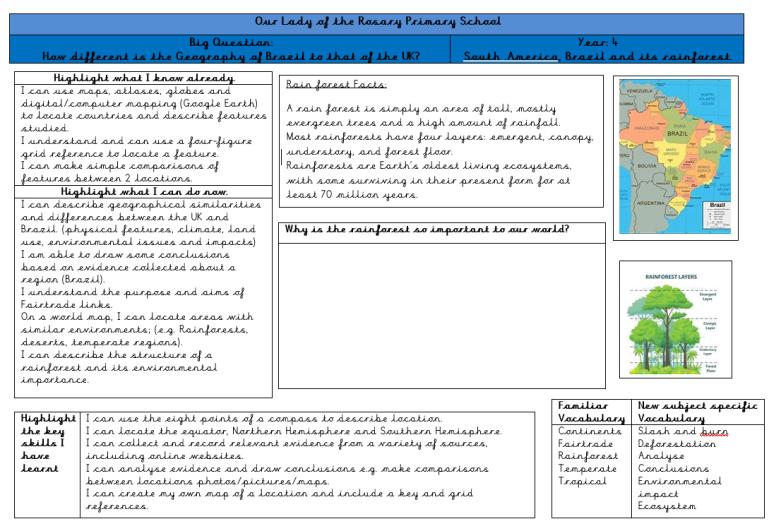
1. South America, Brazil and its rainforest.
To locate the Equator, N. Hemisphere, S. Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle
I can locate Brazil on a map and identify its main physical features.
I can offer and explain my views of an area / region.
I can use maps, atlases, globes and digital mapping to locate counties in the UK and some countries in Europe.
I can use locational and directional language to describe the relative location of features on a map.
I can use internet searches and other sources to collect information.
I have learnt field work skills to gather, record and present information. (Including sketch maps and plans, graphs and IT)
I can describe landmarks location using letter / number co-ordinates.
I can use maps, atlases, globes and digital mapping to gather information about European countries and their key physical features.
What is the geography of Staines?
How has lnad use changed over time?
How can we collect information about an area?
What is the same and what is different about life in England and life in France?
Do France and England have any similar physical features?
2. Extreme Climates
To understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom, and a region within North or South America.
To describe and understand key physical aspects of extreme climates / biomes.
I can describe human and physical differences between the UK and Brazil (topography, climate, land use, environmental issues and population.)
I can describe some features of areas within the Northern Hemisphere, Southern hemisphere and on the equator.
I can locate the Sahara, Gobi and Antarctica deserts on mapping media.
On World maps, I can locate areas with similar environments (E.G. rainforests, deserts, temperate regions)
can understand the purpose and aims of Fairtrade links.
can describe the structure of a rain forest and its environmental importance. can formulate questions to research about the physical or human geography of Brazil / UK.
can describe factors that lead to the creation and expansion of deserts.
can infer how land use and life styles are influenced by climate.
I can use the 8 points of a compass to describe location.
I can collect and record relevant information from a variety of sources to include internet sites.
I can analyse evidence and draw conclusions (ie- make comparisons between locations using maps, photos and other data sources)
I can create my own map to include a key and grid references.
I can name, identify and locate geographical regions with similar physical characteristics.
I can locate the Equator, Northern and Southern Hemispheres, the Arctic and Antarctic Circles and the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn.
What are the main physical features of Brazil?
How does life compare between the UK and Brazil?
Do we need Fairtrade?
Why are rainforests important?
How does a desert form? How do climate and environment influence people’s lives?



To describe and understand key aspects of:
Topic Why? Locational Knowledge Place Knowledge Human and Physical Geography Geographical skills and fieldwork Big Questions
Take three countries –a comparison
To locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities
I can name and locate countries in Europe and in North and South America.
I can describe similarities and differences between the climates, key physical features and land use of a region in the UK, in Europe and in North or South America.

To describe and understand key aspects of:
physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and topography
human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water
I can locate and discuss the significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night)
I can explain how locations around the world are changing and offer reasons why.
I can name and describe the natural resources indigenous to each region and discuss the impact they have on human life.
I can infer how physical geography (including natural resources) has influenced human settlements, trade and migration.
I can describe how regions or countries are interconnected and interdependent.
I can identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night)
I can use 4-6 figure grid references.
I can create maps to identify patterns such as land use, climate / biome, population densities and topography.
I can select appropriate geographical resources to collect and analyse information, statistics and other data to draw my own conclusions.
What geographical similarities do the UK, Europe and North America share?
How is life influenced by the environment where people live?
How does the saying, “No man is an island” relate to the relationships between countries?
Settlements –How and Why?
physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes.
human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water.
I can locate countries within Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America.
I can identify their key physical and human characteristics, (countries, major cities, topographical features and land use)
I can describe how these aspects have changed over time.
can name and locate areas where plate tectonic activity is evident (to include N. America)
can explain how locations around the world are changing and offer geographical reasons to explain this.
I can explain what continental drift is and how volcanic islands and mountain ranges are formed.
I can describe the causes and processes of activities associated to plate tectonic activity (earthquakes, volcanoes)
I can describe the push and pull factors influencing migration.
I can describe how settlement evolved in Staines and how its has changed over time under the influence of factors such as trade, resources and travel links.
I can use different mapping media to identify significant physical features relating to continental drift.
I can analyse and give views of the effectiveness of different mapping media.
I can create maps of locations or annotated diagrams describing the features and processes of physical features such as volcanoes and earthquakes.
I can use different types of fieldwork (random and systematic) to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in my loca area.
I can use the eight points of a compass and 4-6 figure grid references to describe relative locations.
I can research land use, economic activity and the distribution of resources over time and in relation to other areas.
What is Pangea?
How has plate tectonics shaped our world?
How does continental drift influence population and settlement? Why did people choose to create a settlement in the Staines area?
How has Staines changed over time?




Each geography lesson will begin with a retrieval activity – What did we learn last time / in our last geography topic? This will enable children to commit their learning to their long term memories.
All children will have a knowledge organizer showing them what they will learn and new vocabulary and skills needed. As they complete each lesson, they can mark off the learning enquiry covered.

Teachers will use a variety of geographical resources to help deliver a lesson and to enable the children to use them independently for their research and recording.



After the main teaching input, Solo Taxonomy is used to provide children with a range of challenging, engaging and motivating tasks to consolidate and move their learning on as well as giving them practice at using associated geographical skills.

Teachers adapt lessons to support any pupils who have additional SEND needs so that they can fully access the lesson.



Teachers monitor pupils within every lesson to make sure that they are reaching the required outcome by the end of the topic. In the early years, this is primarily through observation, discussion and targeted questioning.
As the children move through the school, written or recorded assessments are used to determine the depth of knowledge attained. Once a unit of work is completed, we make a summary judgement of the work of each pupil by carrying out an final assessment where the children answer a, ‘big question’. Teachers then complete an overview grid specifying the attainment reached by each child.





Year One children learnt how to use an aerial photograph as well as a school map to follow a route around the school. Later in the term, they completed a field work challenge to determine whether our playground is a litter free zone and what we should do if it isn’t.
Children through out the school learnt how the importance of keeping our oceans pollution free.







Year 1 – I like geography because we can do field work and we learn about maps. I liked making a big map of Staines with my friends.
Year 4 – I like researching topics online and using maps.

If I am unsure, I look at the concept box on the D4D to help me.





Bespoke planning –

In English, Year 2 were using the text, “The Bee who spoke” which prompted us to wonder how bee friendly our school is. Consequently, as part of their geography learning, the children surveyed our outdoor areas to see where bee friendly places were located and whether we could create new areas.
Adapted planning and teaching to cater for the needs of all learners.


