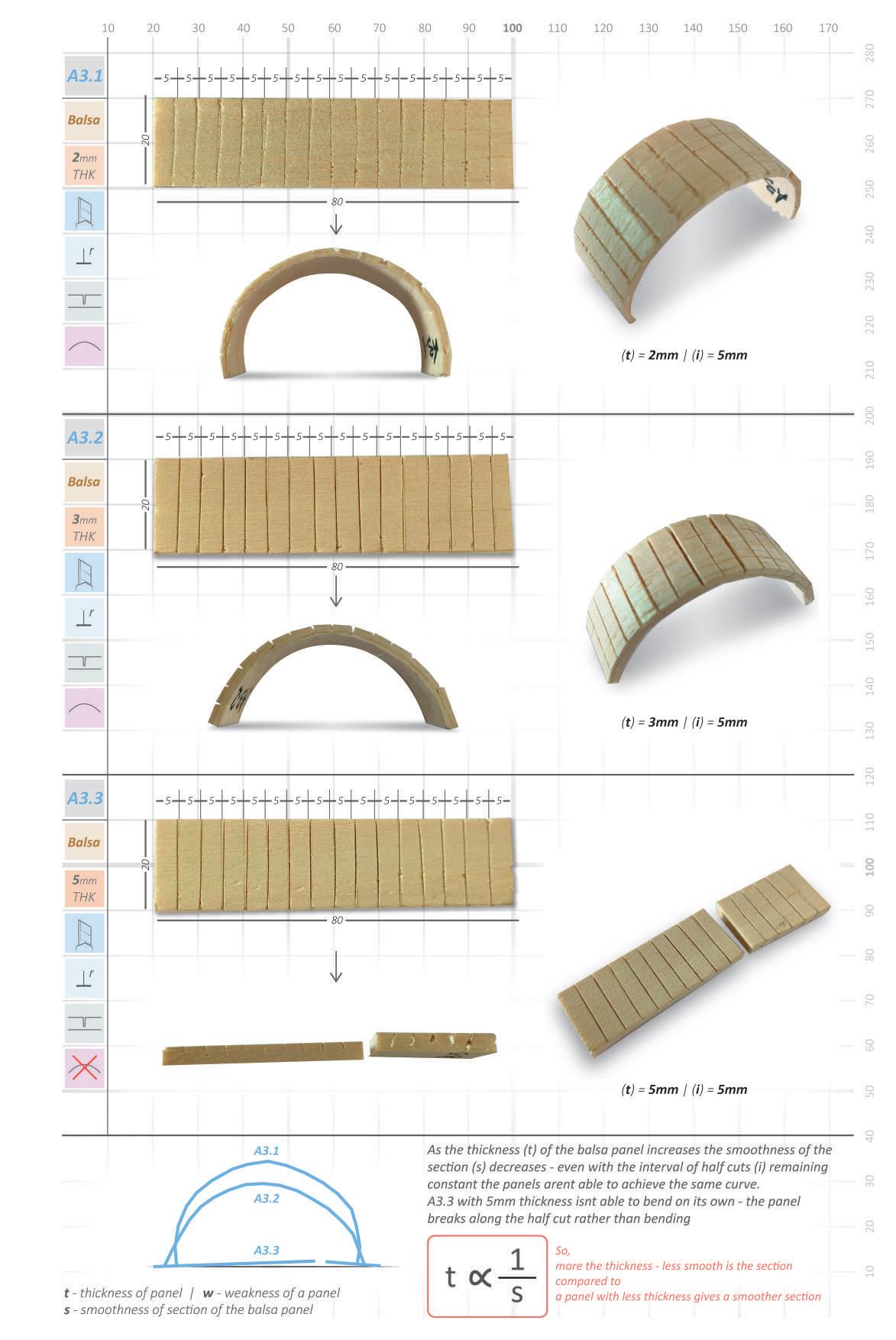
Balsa Experiements 1.


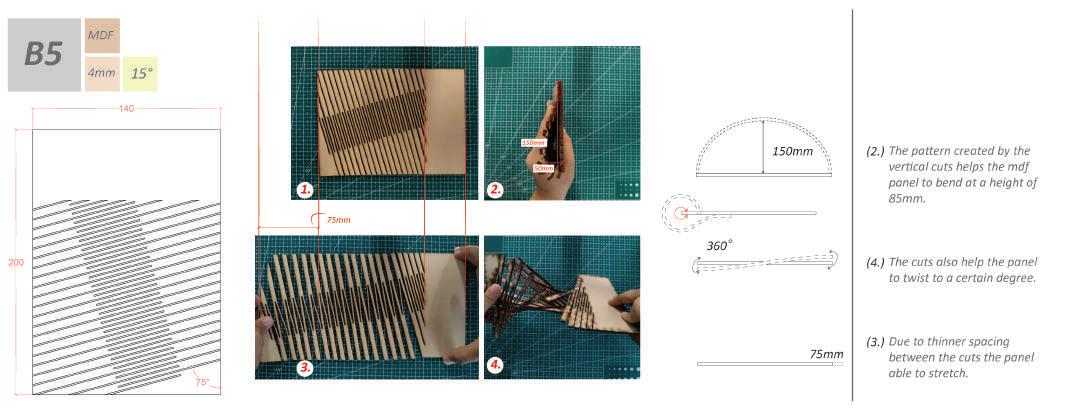
. Kerfing - cutting throught the thickness








AI explorations 3.
‘Two wooden members curved using removal of material to create a pavilion in a solid white background.’


2
‘Two wooden members curved using removal of material to create a pavilion that mimics forms of nature in a solid white background.’


3
‘Two wooden members curved using removal of material to create a minimalistic pavilion that mimics forms of nature in a solid white background.’


4
‘Wooden members curved using removal of material to create a minimalistic pavilion that mimics a tree in a solid white background.’






5
'A pavilion made of curved wooden members that mimics a tree with a central trunk and branches curving towards the ground creating shade and seating spaces in a solid white background.’


6


‘A pavilion made of curved wooden members that mimics a single tree with a central straight trunk and branches from the trunk connecting the ground creating seating spaces in a solid white background.’ 7
‘A minimalistic simple pavilion made of 4 curved wooden members that mimics a single tree with a central straight trunk and branches from the trunk connecting the ground creating seating spaces in a solid white background.’


'A minimalistic simple pavilion made of 8 curved wooden members that mimics a single tree with a central straight trunk and branches from the trunk connecting the ground creating seating spaces in a solid white background.’


'A minimalistic simple pavilion made of 2 curved wooden members that mimics a single tree with a central straight trunk and branches from the trunk connecting the ground creating seating spaces in a solid white background.’


'A minimalistic simple pavilion made of 8 curved wooden members that mimics a single tree with a central straight trunk and branches from the trunk connecting the ground creating seating spaces in a solid white background.’

9 10 11

'A minimalistic simple pavilion made of 8 curved wooden members that mimics a single tree with a central straight trunk and branches from the trunk connecting the ground creating seating spaces in a solid white background.’


4. Spheres & Hexagons


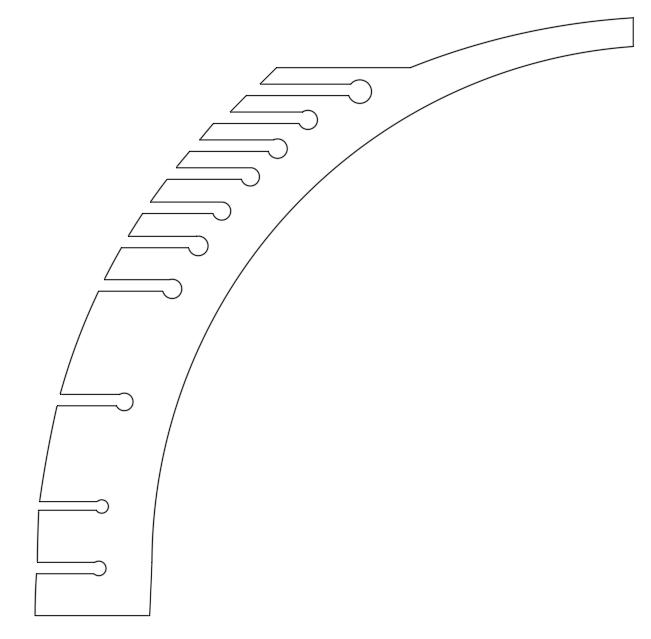
cutting through the thickness
pattern of cuts creating a singluar axis

Conclusion:
This iteration takes in learnings from the previous experiements that explored kerf patterns and distance between 2 kerfs - to a circular patterned, where a continuous cut helps create a different pattern, based on how they are arranged.
The pattern created by alternating the cut helps create a singular axis that passes throught the centre of the circle. The circular piece is able to twist along this axis. However, the pattern fails to make the piece into a rigid shape making it difficult to create a sphere out of this pattern.



Conclusion:
Using spacers to make the C1 iteration stable - and achieve a spherical shape. The spacers have slots which help the circular piece to achieve the desired shape, they act as ribs for the sphere.
Even, after adding spacers on both sides the shape still remains unstable.

By repeating the pattern 2 times it creates 2 axes perpendicular to each other



cuts in between 2 primary cuts helps create a stable axes
Conclusion:
By adding another axis perpendicular to the C1 iteration - by repeating the pattern 2 times - helps stablize the shape to a much greater extent. This shows how adding more axes helps create a stable sphere.
To lock in the shape and create a rigid sphere, spacers are used similar to C1.1




Conclusion:
Trying a different approach to lock in / freeze a kerfed pattern to achieve the desired shape. This iteration uses a variation of the C2 iteration by increasing the distance between kerfs to increase the strength of the shape.
Instead of using spacers as a means to make a sphere - this iteration uses beam like shapes to act as spacers. However, this method doesnt allow to achieve a smoother sphere.



Conclusion:
After multiple iterations, the C2 variation is the most stable and is able to achieve a smoother curve compared to other versions. To make the final sphere 2 - of these hemispheres were combined and interlocked using the same spacers as used earlier to act as ribs to the circular piece.
Both pieces create dia-grid like structure that helps create a stable sphere.

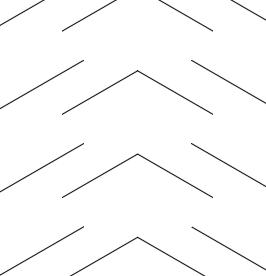
pattern of cuts creating a singluar axis
Conclusion:
Using the patterns from C1 and C2 on a hexagonal shape to see how a change in shape creates a different effect on the base. By creating a pattern that forms a singular axis - helps the hexagonal base to only twist.
The singular axis restricts the motion of the pattern perpendicular to the shape.



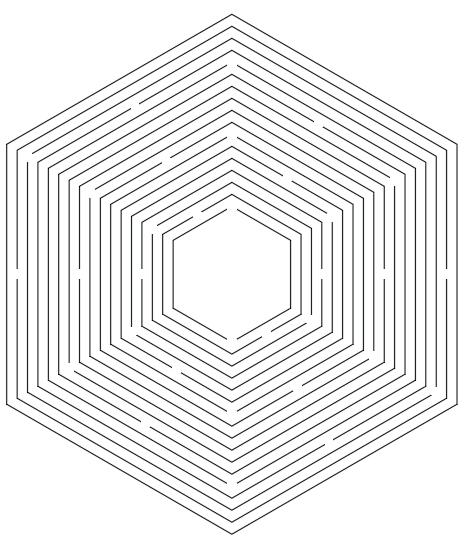
pattern of cuts creating two axes perpendicular to each other

Conclusion:
By creating 2 axes the the shape becomes more stable - and it allows the shape to both twist and extrude.
This shows how adding more axes increases stability of the overall shape.
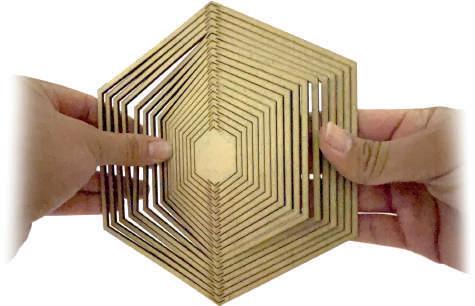
Conclusion:
pattern of rotating axes


Multiple axes creates more resistance for any type of motion - extrusion or twist.
The multiple axes cancel each other out - hence, C4 with 2 axes perpendicular to each other is stable with giving the shape more extrusion and twisting motion
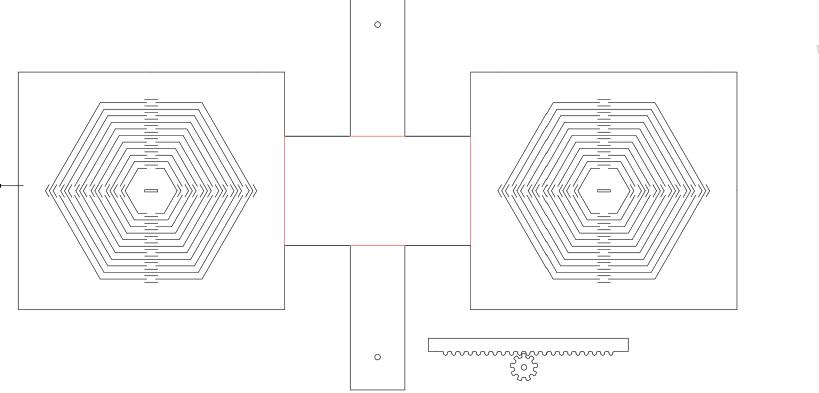


Conclusion: Two C4 hexagonal base attached paralel to each other - move in sync with help of the gear and gear rail.
However, the setup is unstable and needs more supports to help the motion take place seamlessly.