most of Braille Institute’s members are low income, they use free gps smartphone apps for commuting
product must be affordable for the average LA local
Based off qualitative insights from a six month study of the visually impaired in Los Angeles, (learning commute patterns, daily habits, benchmarking aid-devices), I designed a wearable device that better assists them through their first-mile last-mile urban commute

“ You can’t get a feel of Downtown using rideshare for every little trip, I want to see Los Angeles up close. ”
still, many choose to not venture outside, as their walking sticks, service dogs, and bulky devices are both visually loud and stigmitized
gps apps are highly distracting and exhausting to use through their constant input via earphones
a visually subtle product will boost confidence in its users product can’t limit the user’s ability to ‘sound marker’ their nearby environment
user-dependency grows through app usage, simple directional commands don’t provide any sense of urban orientation
GPS apps fail to update in depth or real-time ie: construction zones, traffic congestion
create a system that teaches users their selected path
create a safer commute by predicting external outcomes through a public IoT network
obstacle-avoidance guides users around their immediate urban environment ( 10 ft )

turn-by-turn directions help navigate users through the smaller dynamics of their trip
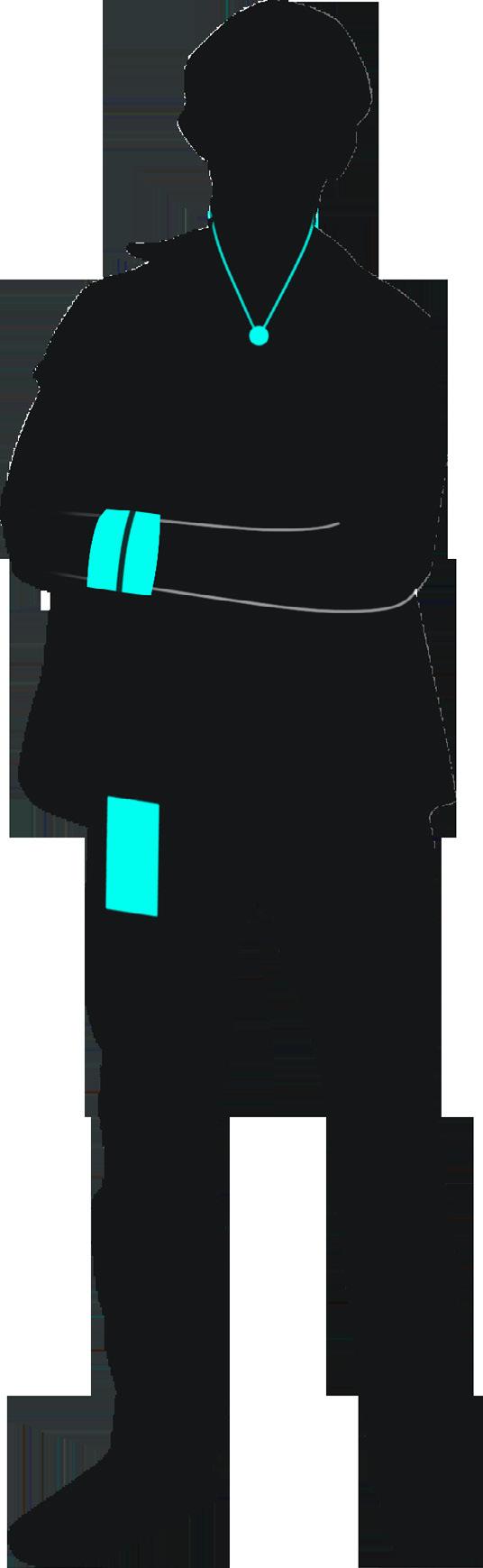
necklace has camera and sonar sensors to contextualize the 2D into 3D for the app
bracelet communicates various urban commute features by touch
app also links to nearby IoT nodes, rerouting the path if need be
compass-orientation lets users learn their urban enviornment at a more macro level
all systems-computing is done through the user’s smartphone

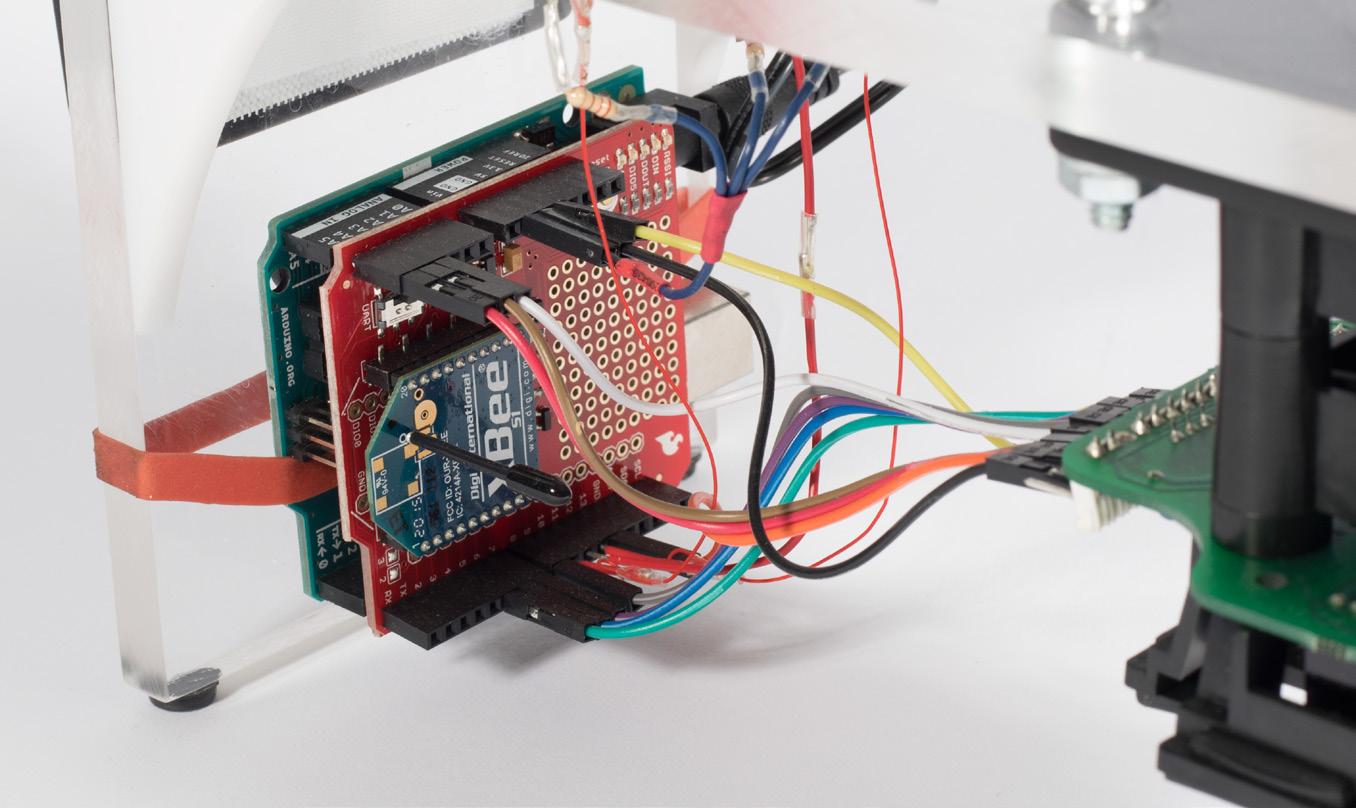
49-way joystick communicates position of oncoming obstacles relative to subject B ’s position

subject A can see which of the three commute features subject B selected, joystick operations will then adjust accordingly
AND
subject A operates the joystick nearby obstacles (acting subject B is blindfolded the his urban space via sense
subject B ’s wearable device offers two rows of vibration motors, these help communicate the height of oncoming obstacles high low both

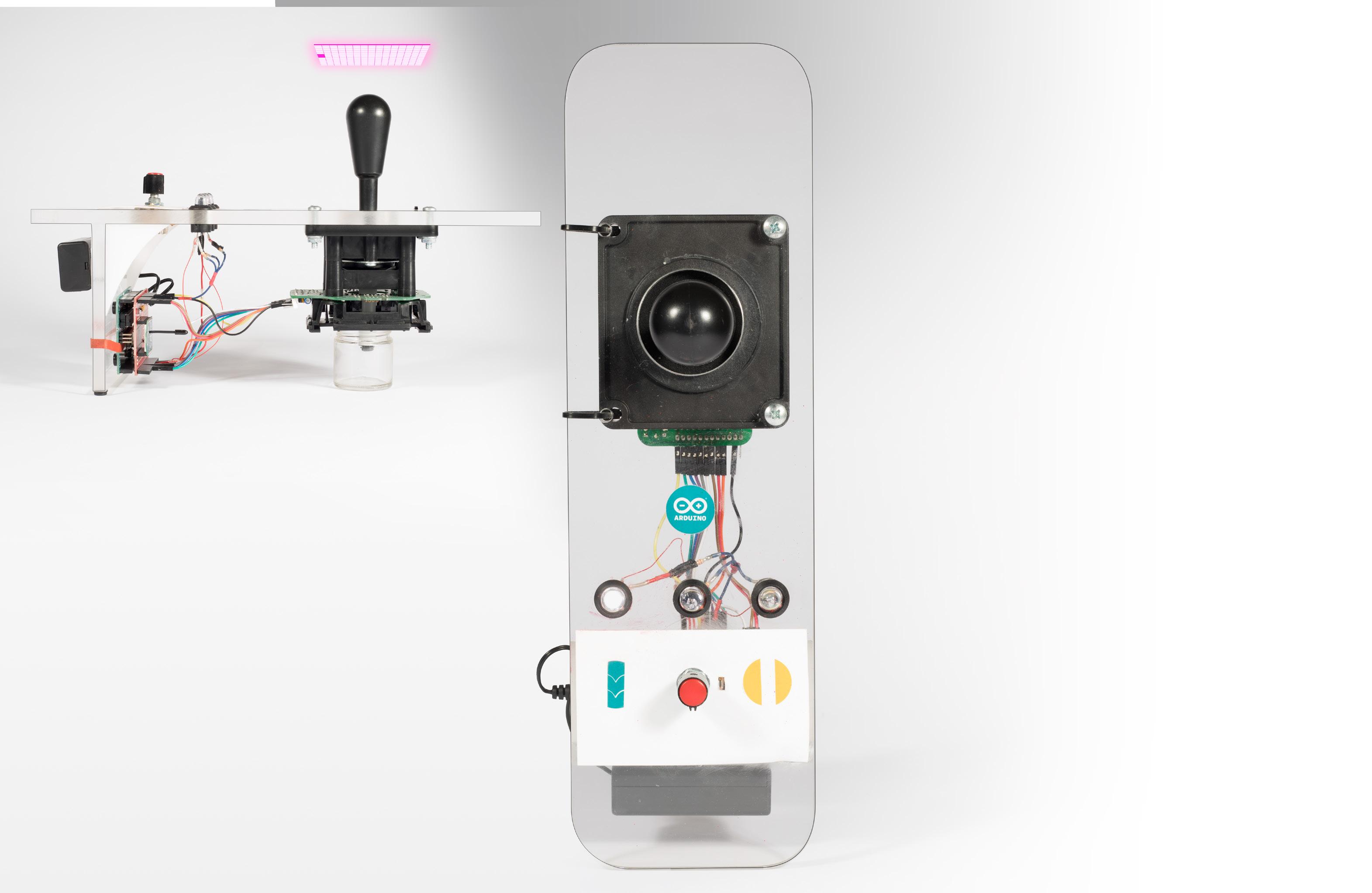
joystick while monitoring for as the app and necklace)
the entire time, navigating of touch from the bracelet



three features help the user learn new routes

obstacle avoidance turn-by-turn direction destination orientation