SF | DERMATOLOGY
42
October 2021 | Vol. 21 No. 10 www.medicalacademic.co.za
Photo credit: Shutterstock.com
This article was independently sourced by Specialist Forum.
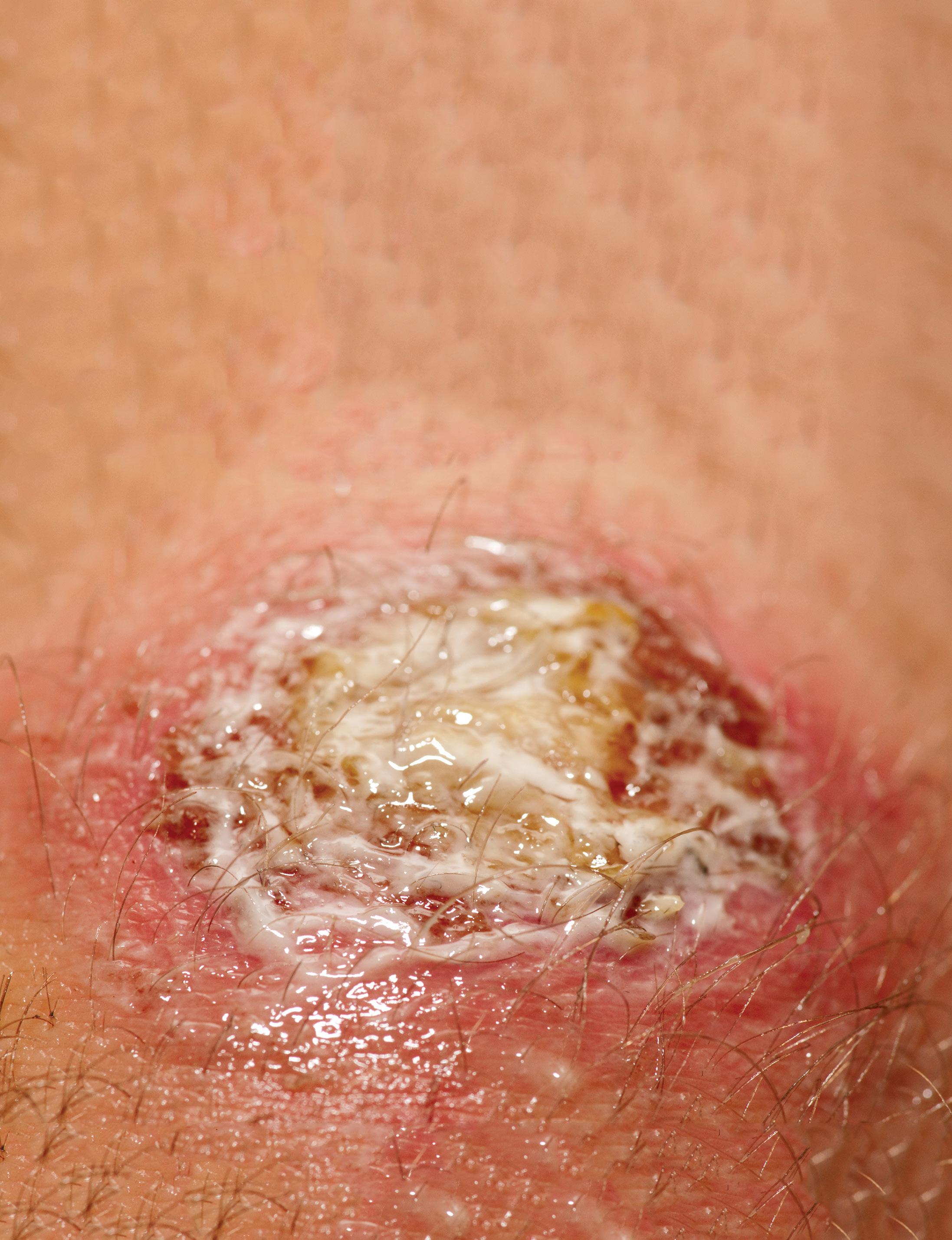
Fusidic acid – first-choice option in the treatment of skin infection
The skin is the largest, and arguably, the most vulnerable organ in the human body. Scratches, scrapes, bites, and puncture wounds can all lead to pain, swelling, and infection. Patients with dermatological conditions such as atopic dermatitis are at great risk of infections due to an impaired skin barrier.1,2,3
T
he skin is the body’s first line of defence against microbial infection by secreting low pH, sebaceous fluid, and fatty acids to inhibit growth of pathogens and by possessing its own normal flora, thus deterring colonisation by
other pathogenic organisms. Unfortunately, once an organism penetrates the skin barrier, it can cause tissue damage and incite an inflammatory response. 2 Bacteria, initially in low numbers, colonise different layers of the skin architecture (eg
epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous and adipose tissues, and muscle fascia). As bacteria increase in number where the skin barrier is disrupted, invasion by these colonising bacteria ensues and an infection develops. 2 The main culprits in causing infections