JavaMethodsandFunctions:Building ModularandReusableCode
InJavaprogramming,methodsandfunctionsplayacrucialroleinbreakingdowncomplextasks intosmaller,manageablepiecesofcode.Theyenablecodereuse,enhancemodularity,and improvetheoverallstructureofyourJavaprograms.Inthisblog,wewillexplorethefundamentals ofJavamethodsandfunctions,theirsyntax,usage,andbestpractices.Bymasteringtheartof creatingandutilizingmethodsandfunctionseffectively,youcanwritecleaner,moremaintainable, andhighlyefficientcode
UnderstandingMethodsandFunctionsinJava
ThissectionwillprovideanintroductiontomethodsandfunctionsinJava.InJavaprogramming, methodsandfunctionsarefundamentalconceptsthatallowdeveloperstobreakdowncomplex tasksintosmaller,manageablepiecesofcode.Understandinghowmethodsandfunctionsworkis essentialforwritingclean,modular,andreusablecode.Methodsandfunctionsactasreusable blocksofcodethatcanbecalledandexecutedwheneverneeded.
DeclaringandInvokingMethods
InJavaprogramming,declaringandinvokingmethodsisafundamentalaspectofwritingmodular andreusablecode Methodsallowyoutoencapsulateasetofinstructionsthatperformaspecific
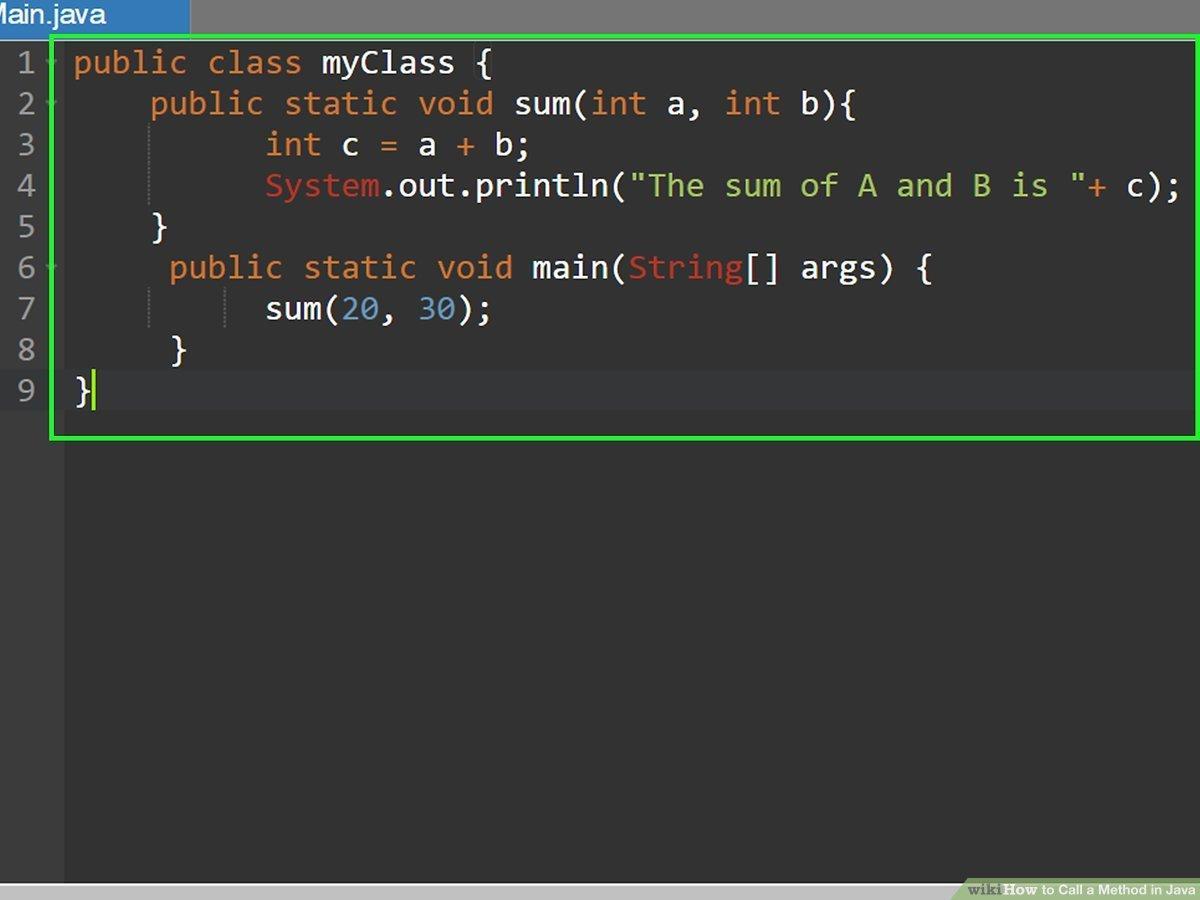
task,makingyourcodemoreorganizedandefficient.Inthissection,wewillexplorethesyntaxand techniquesinvolvedindeclaringandinvokingmethodsinJava.
1. DeclaringMethods:
Declaringamethodinvolvesspecifyingitsname,returntype,andparameters.Themethod declarationdefinesthemethod'ssignatureandservesasablueprintforhowthemethodshould becalledandwhatitshouldreturn Here'sthegeneralsyntaxfordeclaringamethod:
<accessmodifier><returntype><methodname>(<parameterlist>){
//Methodbody
//Codetobeexecuted
//Optionally,areturnstatement
● AccessModifier:Determinestheaccessibilityofthemethod(e.g.,public,private, protected,ordefault).
● ReturnType:Specifiesthedatatypeofthevaluereturnedbythemethoda�erexecution. Usevoidifthemethoddoesnotreturnavalue.
● MethodName:Adescriptivenamethatrepresentsthepurposeoractionperformedbythe method.
● ParameterList:Comma-separatedlistofparameters(inputvalues)thatthemethod receives Parametersareoptional,andyoucanhavemultipleparametersofdifferenttypes
2. InvokingMethods:
Invokingorcallingamethodistheprocessofexecutingtheinstructionswithinthemethodbody. Toinvokeamethod,youneedtospecifythemethodnamefollowedbyparenthesescontainingthe arguments(ifany)requiredbythemethod.Here'sthesyntaxforinvokingamethod:
<methodname>(<arguments>);
● MethodName:Thenameofthemethodyouwanttoinvoke
● Arguments:Valuespassedtothemethod'sparameters(ifany) Argumentsmustmatchthe parametertypesandorderdefinedinthemethoddeclaration
MethodParametersandReturnValues
InJavaprogramming,methodscanacceptparameters(inputvalues)andreturnvalues(output values).Methodparametersallowyoutopassdataintoamethod,whilereturnvaluesenable methodstoprovideresultsbacktothecaller.Understandinghowtoworkwithmethodparameters
andreturnvaluesisessentialforwritingflexibleandfunctionalcode.Inthissection,wewill exploretheconceptofmethodparametersandreturnvaluesinJava.
1. MethodParameters:
Methodparametersarevariablesthataredeclaredaspartofthemethodsignatureandreceive valuespassedfromthemethodcaller Theyallowyoutoprovideinputdatatoamethod,which canbeusedwithinthemethod'sbody Herearesomekeypointstounderstandaboutmethod parameters:
● Declaration:Parametersaredeclaredwithintheparenthesesfollowingthemethodname. Youspecifytheparametertypeandgiveitaname.
● DataPassing:Wheninvokingamethod,youprovidetheactualvalues(arguments)forthe parametersdefinedinthemethoddeclaration.Theargumentsmustmatchtheparameter typesandorder.
● MultipleParameters:Youcandefinemultipleparametersbyseparatingthemwithcommas inthemethoddeclaration
● PassingbyValue:Javapassesparametersbyvalue,meaningacopyoftheargumentvalue ispassedtothemethod Modifyingtheparameterinsidethemethoddoesnotaffectthe originalargument.
2.ReturnValues:
● Returnvaluesallowmethodstoprovideresultsordatabacktothecaller.Thereturntype ofamethoddeterminesthedatatypeofthevaluethatthemethodreturns.Hereare importantaspectsofreturnvaluesinJava:
● Declaration:Thereturntypeisspecifiedinthemethodsignature Itcanbeaprimitivetype (eg,int,boolean)oranobjecttype
● ReturnStatement:Insidethemethodbody,youusethereturnkeywordfollowedbyan expressionorvariablethatevaluatestothedesiredreturnvalue.Onceareturnstatement isencountered,themethodexecutionterminates,andthevalueispassedbacktothe caller.
● VoidReturnType:Ifamethoddoesnotreturnavalue,thereturntypeisspecifiedasvoid. Insuchcases,themethodperformsanactionbutdoesnotprovidearesult.
MethodOverloadingandOverriding
InJavaprogramming,methodoverloadingandoverridingarepowerfulfeaturesthatallowyouto definemethodswiththesamenamebutdifferentbehaviors.Theseconceptsenableyoutowrite moreflexibleandreusablecodebyprovidingdifferentwaystoperformsimilartasksormodify
inheritedbehaviors.Inthissection,wewillexploremethodoverloadingandoverridingindetail.
1 MethodOverloading:Methodoverloadingallowsyoutodefinemultiplemethodswiththe samenamebutdifferentparameterswithinthesameclass Eachoverloadedmethod performsasimilartaskbutmayhandledifferentdatatypesornumbersofarguments Here aresomekeypointsaboutmethodoverloading:
● Signature:Overloadedmethodshavethesamenamebutdifferentparameterlists. Theparametertypes,order,ornumberofparametersmustbedifferentto distinguishbetweentheoverloadedmethods.
● ReturnType:Thereturntypeofamethoddoesnotaffectitsoverloading.Methods canbeoverloadedeveniftheyhavedifferentreturntypes
2. MethodOverriding:Methodoverridingoccurswhenasubclassprovidesitsown implementationofamethodthatisalreadydefinedinitssuperclass.Thesubclassmethod hasthesamename,returntype,andparametersasthesuperclassmethod.Herearesome importantpointsaboutmethodoverriding:
● Inheritance:Methodoverridingisbasedoninheritance,whereasubclassinherits methodsfromitssuperclassandmodifiestheirbehaviorasneeded.
● @OverrideAnnotation:Itisabestpracticetousethe@Overrideannotationwhen overridingamethod Ithelpscatchpotentialerrorsatcompile-timeifthe overriddenmethoddoesnotmatchthesuperclassmethodcorrectly
BestPracticesforWritingMethods
WhenwritingmethodsinJava,it'simportanttofollowbestpracticestoensureyourcodeis readable,maintainable,andefficient.Well-designedmethodscontributetotheoverallqualityof
yourcodebaseandmakeiteasierforotherstounderstandandworkwithyourcode.Learn Writing MethodswithBestJavaTraininginIndore,hereyoucangetskillsinjavamethods.. Inthissection, wewilldiscusssomebestpracticesforwritingmethodsinJava
● MethodNaming:Choosedescriptiveandmeaningfulnamesforyourmethodsthat accuratelyconveytheirpurposeandfunctionality Usecamelcasenotation,startingwitha lowercaseletter.Makesurethenamesareconcisebutstilldescriptiveenoughto understandtheirpurposewithoutexcessivecomments.
● MethodLengthandComplexity:Keepyourmethodsconciseandfocusedonasingle task.Longandcomplexmethodscanbedifficulttounderstandandmaintain.Aimfor methodsthatfitonasinglescreenwithoutexcessivescrolling Ifamethodbecomestoo longorcomplex,considerrefactoringitintosmaller,moremanageablemethods
● MethodDocumentation:Provideclearandconcisedocumentationforyourmethods usingcomments.Documentthepurpose,inputparameters,returnvalues,andany exceptionsthrownbythemethod.Gooddocumentationhelpsotherdevelopers understandhowtouseandinteractwithyourmethodseffectively.
● MethodParameterDesign:Designyourmethodparameterstobemeaningfuland self-explanatory Avoidusinggenericnameslike"a"or"value"thatprovidelittlecontext Usedescriptivenamesthatindicatethepurposeormeaningofeachparameter Additionally,considerusingdatatypesthatprovidetheappropriatelevelofabstraction andrestrictinputvalueswherenecessary.
● MethodReturnValues:Ensurethatyourmethodshaveaclearandconsistentreturn value.Ifamethodperformsacomputationorreturnsaresult,makesurethereturntype accuratelyreflectsthenatureoftheresult.Ifamethoddoesnotneedtoreturnanyvalue, usethevoidreturntype.Avoidreturningnullunlessithasaspecificmeaninginthecontext ofyourmethod
● ErrorHandling:Handleerrorsandexceptionsappropriatelywithinyourmethods Use try-catchblockstocatchexceptionsandhandlethemgracefully.Avoidcatchingexceptions toobroadly,asitmaymaskpotentialissuesandmakedebuggingmorechallenging. Considerthrowingspecificexceptionsorcreatingcustomexceptionstoprovide meaningfulerrormessages.
● MethodModifiers:Usetheappropriatemethodmodifiers(public,private,protected) basedontheintendedaccesslevel Limitthevisibilityofyourmethodstoonlywhatis necessary Encapsulatetheinternalworkingsofyourclassbymakingmethodsprivate wheneverpossible.
● MethodCohesion:Ensurethatyourmethodshavehighcohesion,meaningtheyshould performasingle,well-definedtask.Avoidmethodsthattrytodotoomuchorhave unrelatedfunctionalities.Splittingcomplexmethodsintosmaller,focusedmethods improvesreadability,reusability,andmaintainability.
● MethodTesting:Writeunittestsforyourmethodstoverifytheircorrectnessandbehavior UseatestingframeworklikeJUnittocreatecomprehensivetestsuitesthatcoverdifferent scenariosandedgecases Testboththeexpectedbehaviorandanypotentialerror conditionsorexceptions.
● MethodReusability:Designyourmethodstobereusableacrossdifferentpartsofyour codebase.Avoidhard-codingspecificvaluesordependencieswithinmethods.Instead, makethemmoregenericandadaptablebyusingparametersandexternalizing dependencies.
CommonUseCasesandDesignPatterns
Designpatternsareprovensolutionstorecurringproblemsinso�waredesign Theyprovidea structuredapproachtosolvingcommonchallengesandpromotecodereuse,maintainability,and extensibility.JavaTrainingCourseinIndoreisthebestlearningInthissection,wewillexploresome commonusecasesanddesignpatternsinJava.
● SingletonPattern:TheSingletonpatternisusedwhenyouneedtoensurethatonlyone instanceofaclassiscreatedthroughouttheapplication.Itiscommonlyusedforcreating globalaccesspointsormanagingsharedresources TheSingletonpatternrestrictsthe instantiationofaclasstoasingleobjectandprovidesaglobalpointofaccesstothat instance
● FactoryPattern:TheFactorypatternisusedwhenyouwanttocreateobjectswithout exposingtheinstantiationlogictotheclient.Itprovidesacentralfactoryclassthat encapsulatestheobjectcreationprocess.Thefactoryclassdecideswhichimplementation tocreatebasedoncertainconditionsorparametersprovidedbytheclient.
● ObserverPattern:TheObserverpatternisusedwhenyouneedtoestablisha one-to-manyrelationshipbetweenobjects Inthispattern,thesubjectmaintainsalistof observersandnotifiesthemautomaticallyofanystatechanges.Observerscanregisterand unregisterthemselves,andtheyarenotifiedwhenthesubject'sstatechanges.
● DecoratorPattern:TheDecoratorpatternisusedtodynamicallyaddnewbehaviorstoan objectwithoutmodifyingitsoriginalstructure.Itprovidesawaytowrapanobjectwith oneormoredecorators,eachaddingadditionalfunctionalitytotheobject.Thispattern allowsforflexibleanddynamiccompositionofobjects
● StrategyPattern:TheStrategypatternisusedwhenyouwanttodefineafamilyof interchangeablealgorithmsorbehaviorsandencapsulateeachone.Itallowsyoutoselect astrategyatruntimewithoutcouplingtheclientcodetoaspecificimplementation.This patternpromotesflexibilityandenableseasyextensionandmodificationofalgorithms.
● IteratorPattern:TheIteratorpatternprovidesawaytoaccesstheelementsofacollection sequentiallywithoutexposingitsunderlyingrepresentation Itencapsulatesthetraversal logicwithinaniteratorobject,whichprovidesmethodslikenext(),hasNext(),and remove().Thispatterndecouplestheclientcodefromthecollection'simplementation details.
● BuilderPattern:TheBuilderpatternisusedtocreatecomplexobjectsstepbystep.It providesaclearseparationbetweentheconstructionprocessandtherepresentationof theobject.Thebuilderclasscontainsmethodsforsettingtheobject'sattributes,andit returnsthefinalobjectwhentheconstructioniscomplete Thispatternsimplifiesthe objectcreationprocessandimprovescodereadability
Conclusion:
JavamethodsandfunctionsareessentialbuildingblocksinJavaprogramming,allowingfor modular,reusable,andefficientcode Byunderstandingtheirsyntax,usage,andbestpractices, youcanwritewell-structured,maintainablecodethatpromotescodereuseandscalability Leveragingthepowerofmethodsandfunctionsempowersyoutobreakdowncomplextasks, improvecodeorganization,andcreaterobustapplicationsinJava.
Regenerateresponse
