The Physical Universe, 15th Edition Test Bank –

Konrad Krauskopf
To download the complete and accurate content document, go to: https://testbankbell.com/download/the-physical-universe-15th-edition-test-bank-konra d-krauskopf/
Multiple Choice Questions
1. The nucleus of an atom cannot be said to A. contain most of the atom's mass.
B. be small in size.
C. be electrically neutral.
D. deflect alpha particles that come near it.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.01
Topic: Nuclear Physics
2. Of the following particles, the one with the smallest mass is the A. electron.
B. proton.
C. neutron.
D. neutrino.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.02
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
3. Of the following particles, the one with the greatest mass is the A. electron.
B. proton.
C. neutron.
D. neutrino.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.02
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
Chapter
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
4. Of the following particles, the only one that is not stable outside an atom is the A. electron.

B. proton.

C. neutron.
D. neutrino.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
5. The atomic number of the nucleus is
A. 4.
B. 5.
C. 9.
D. 13. Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Bloom's Level: 3. Apply
Section: 08.02
Topic: Nuclear Physics
6. The mass number of the nucleus is
A. 4.
B. 5.
C. 9.
D. 13. Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Bloom's Level: 3. Apply
Section: 08.02
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
7. The number of protons in the nucleus is A. 4.
B. 5.
C. 9.
D. 13.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand Bloom's Level: 3. Apply
Section: 08.02
Topic: Nuclear Physics
8. The number of neutrons in the nucleus is
A. 4.
B. 5.
C. 9.
D. 13.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Bloom's Level: 3. Apply
Section: 08.02
Topic: Nuclear Physics
9. The chemical behavior of an atom is determined by its
A. atomic number.
B. mass number.


C. binding energy.
D. number of isotopes.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.02
Topic: Atomic Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
10. The atoms of the isotopes of a given element have the same number of A. protons.
B. neutrons.
C. nucleons.
D. nuclides.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.02
Topic: Nuclear Physics
11. Which of the following is not an isotope of hydrogen?




Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.02
Topic: Nuclear Physics
12. The number of neutrons in a nucleus
A. is less than the number of protons it contains.
B. is the same as the number of protons it contains.
C. is more than the number of protons it contains.
D. Any of the above, depending on the nucleus.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.02
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
13. Which, if any, of the following elements have no radioactive isotopes?
A. Hydrogen.
B. Potassium.
C. Uranium.
D. All of these elements have radioactive isotopes.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
14. A molecule of heavy water contains
A. two oxygen atoms instead of one.
B. three hydrogen atoms instead of two.
C. deuterium atoms instead of hydrogen atoms.
D. a deuterium atom instead of an oxygen atom.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.02
Topic: Nuclear Physics
15. The nucleus of a helium atom is called
A. an alpha particle.
B. a beta particle.
C. a gamma ray.
D. a quark.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
16. The electromagnetic waves emitted by a nucleus are called
A. ultraviolet rays.
B. X-rays.
C. gamma rays.
D. quarks.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
17. A particle never emitted in beta decay is the
A. neutron.
B. neutrino.
C. electron.
D. positron.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
18. The mass of a positron is
A. equal to the mass of an electron.
B. more than the mass of an electron but less than the mass of a proton.
C. equal to the mass of a proton.
D. more than the mass of a proton.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.03
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
19. Which one or more of the following statements is true in general?
A. Alpha particles are more able to penetrate matter than beta particles and gamma rays.
B. Alpha particles are less able to penetrate matter than beta particles and gamma rays.
C. Alpha particles are less able to penetrate matter than beta particles but more able to do so than gamma rays.
D. Alpha particles are more able to penetrate matter than beta particles but less able to do so than gamma rays.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Figure: 08.08
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
20. The atomic number of a nucleus decreases when it emits
A. a proton.
B. a neutron.
C. an electron.
D. a positron.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.02
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
21. When a nucleus undergoes radioactive decay, its new mass number is
A. always less than its original mass number.
B. always more than its original mass number.
C. never less than its original mass number.
D. never more than its original mass number.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.02
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
22. A nucleus with too few neutrons for stability may decay radioactively with the emission of
A. a neutron.
B. a proton.
C. an electron.
D. a positron.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Figure: 08.09
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
23. As a sample of a radioactive nuclide decays, its half-life
A. decreases.
B. remains the same.
C. increases.
D. Any of these choices could be correct, depending upon the nuclide.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.04
Topic: Nuclear Physics
24. If radium and chlorine combine to form radium chloride, the compound is
A. no longer radioactive.
B. half as radioactive as its radium content.
C. as radioactive as its radium content.
D. twice as radioactive as its radium content.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Bloom's Level: 3. Apply
Section: 08.04
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
25. Most known nuclides
A. are stable.
B. are radioactive.
C. can undergo fission.
D. have more nuclear mass than the total mass of their constituent nucleons.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
26. The sievert is a unit of
A. radioactivity.
B. half-life.
C. particle energy.
D. radiation dosage.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.05
Topic: Nuclear Physics
27. The most important single source of radiation dosage received by an average person in the United States is
A. medical x-rays
B. nuclear reactors.
C. radon.
D. radium.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Figure: 08.12
Section: 08.05
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
28. By far the most dangerous diagnostic x-rays in medicine are
A. dental x-rays.
B. chest x-rays.
C. CT scans.
D. mammograms.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Figure: 08.12
Section: 08.05
Topic: Nuclear Physics
29. The radiation dosage due to cosmic rays is greatest
A. in orbiting spacecraft.
B. in airplanes at high altitudes.
C. at sea level.
D. underground.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.05
Topic: Nuclear Physics
30. Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
A. Joule.
B. Kilowatt-hour.
C. Ampere-hour.
D. Electron volt.
Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze
Section: 08.06
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
31. The unit in which atomic masses are usually expressed is the
A. gram.
B. eV.
C. u.
D. quark.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.06
Topic: Nuclear Physics
32. An atomic nucleus has a mass that is
A. less than the total mass of its constituent nucleons.
B. the same as the total mass of its constituent nucleons.
C. more than the total mass of its constituent nucleons.
D. Any of theses choices could be correct, depending on the nucleus.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Figure: 08.13
Section: 08.07
Topic: Nuclear Physics
33. Nuclear fission and fusion reactions give off energy because
A. the binding energy per nucleon is least for nuclei of intermediate size.
B. the binding energy per nucleon is greatest for nuclei of intermediate size.
C. they result in the production of neutrons.
D. they result in the production of plutonium.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Figure: 08.15
Section: 08.08
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
34. A chain reaction does not occur in
A. ordinary nuclear reactors.
B. breeder reactors.
C. fusion reactors.
D. fission nuclear weapons.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.09
Section: 08.13
Topic: Nuclear Physics
35. A nuclear reactor itself does not produce
A. electricity.
B. neutrons.
C. radiation.
D. plutonium.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.10
Topic: Nuclear Physics
36. The moderator in a nuclear reactor
A. slows down neutrons emitted during fission.
B. reduces the production of plutonium.
C. reduces the production of radiation.
D. prevents explosions.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.10
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
37. Enriched uranium contains




A. more than natural uranium.
B. more than natural uranium.
C. plutonium.
D. tritium.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.10
Topic: Nuclear Physics
38. Slightly enriched uranium can be the energy source of which of the following?
A. Nuclear fission reactors.
B. Nuclear fusion reactors.
C. Nuclear weapons.
D. X-rays.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.10
Section: 08.13
Topic: Nuclear Physics
39. A breeder reactor is designed to produce more nuclear fuel than it consumes. The new fuel is in the form of
A. .
B. .
C. plutonium.
D. tritium.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.12
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
40. The number of major accidents that have occurred at nuclear power plants is
A. 3.
B. 12.
C. 20.
D. 88.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.14
Topic: Nuclear Physics
41. A possible fuel for a fusion reactor is
A. .
B. .
C. plutonium.
D. tritium.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.13
Topic: Nuclear Physics
42. The particle that most resembles the proton is the


A. positron.
B. neutron.
C. antiproton.
D. quark.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.14
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
43. The process of pair production cannot produce
A. a proton and an antiproton.
B. a neutron and an antineutron.
C. a neutron and a neutrino.
D. an electron and a positron.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.14
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
44. Protons and neutrons are held together to form nuclei by the
A. gravitational interaction.
B. strong interaction.
C. weak interaction.
D. electromagnetic interaction.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Figure: 08.29
Section: 08.15
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
45. The strongest of the fundamental interactions is the
A. gravitational interaction.
B. strong interaction.
C. weak interaction.
D. electromagnetic interaction.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.15
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
46. The electromagnetic interaction is
A. the fundamental interaction with the shortest range.
B. responsible for the structures of atoms, molecules, liquids, and solids.
C. responsible for holding nucleons together to form nuclei.
D. responsible for radioactive decays.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Figure: 08.29
Section: 08.15
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
47. The number of quarks in a proton or a neutron is
A. 1.
B. 2.
C. 3.
D. 4.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Figure: 08.32
Section: 08.16
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
48. Quarks are not present in
A. electrons.
B. protons.
C. neutrons.
D. hadrons.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.16
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
49. All known charged particles have electric charges that are multiples of e except for

A. electrons.
B. positrons.
C. protons.
D. quarks.
Bloom's Level: 1. Remember
Section: 08.16
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
50. A proton is annihilated when it interacts with which one or more of the following particles?



A. An electron.
B. A neutron.
C. An antineutron.
D. An antiproton.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand
Section: 08.14
Topic: Elementary Particle Physics
51. The product of the alpha decay of the uranium isotope is

A. .
B.
C. .
D.
Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze
Bloom's Level: 5. Evaluate
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
52. The helium isotope undergoes beta decay with the emission of an electron. The product of the decay is





.
B. .
C. .
D. .
Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze
Bloom's Level: 5. Evaluate
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
53. The bismuth isotope, decays into the polonium isotope by


A. emitting an electron.
B. capturing an electron.
C. emitting a positron.
D. emitting an alpha particle.
Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze
Bloom's Level: 5. Evaluate
Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
54. When a nucleus of the copper isotope captures an electron, it becomes










.
.
. D.
Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze Bloom's Level: 5. Evaluate Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
55. When a nucleus of the copper isotope emits a positron, it becomes
.
D.
.
Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze Bloom's Level: 5. Evaluate Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
56. The product of the gamma decay of the strontium isotope is

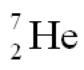






.
.
.
Bloom's Level: 2. Understand Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
57. The nuclide that decays by electron capture to become is


.
. D.
Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze Bloom's Level: 5. Evaluate Section: 08.03
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
58. After 2 h has elapsed, one-sixteenth of the original quantity of a certain radionuclide remains undecayed. The half-life of this radionuclide is
A. 15 min.
B. 30 min.
C. 45 min.
D. 60 min. Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze Bloom's Level: 5. Evaluate
Section: 08.04
Topic: Nuclear Physics
59. The half-life of tritium is 12.5 years. If we start out with 1 g of tritium, after 25 years there will be
A. no tritium left.
B. 1/4 g of tritium left.
C. 1/2 g of tritium left.
D. a total of 4 g of tritium.
Bloom's Level: 4. Analyze Bloom's Level: 5. Evaluate Section: 08.04
Topic: Nuclear Physics
© 2014 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwarded, distributed, or posted on a website, in whole or part
