Architecture Portfolio
Selected work 2019-2023

1
Luis Mendez
RIBA Part 1 Graduate
Projects



Pages 2-16
Youth Centre
Pages 17-26
Social Housing
Pages 27-33
2 Table of
Environmental Learning Centre
P2 P3
P1
Additional works
Group Modelling
Pages 34-35

Sketches and Renders
Pages 36-49

Photography
Pages 40-41

3 Contents
Revit, Photoshop, Twinmotion
2
RIBA
P.1
Luis Mendez
Part 1 Graduate

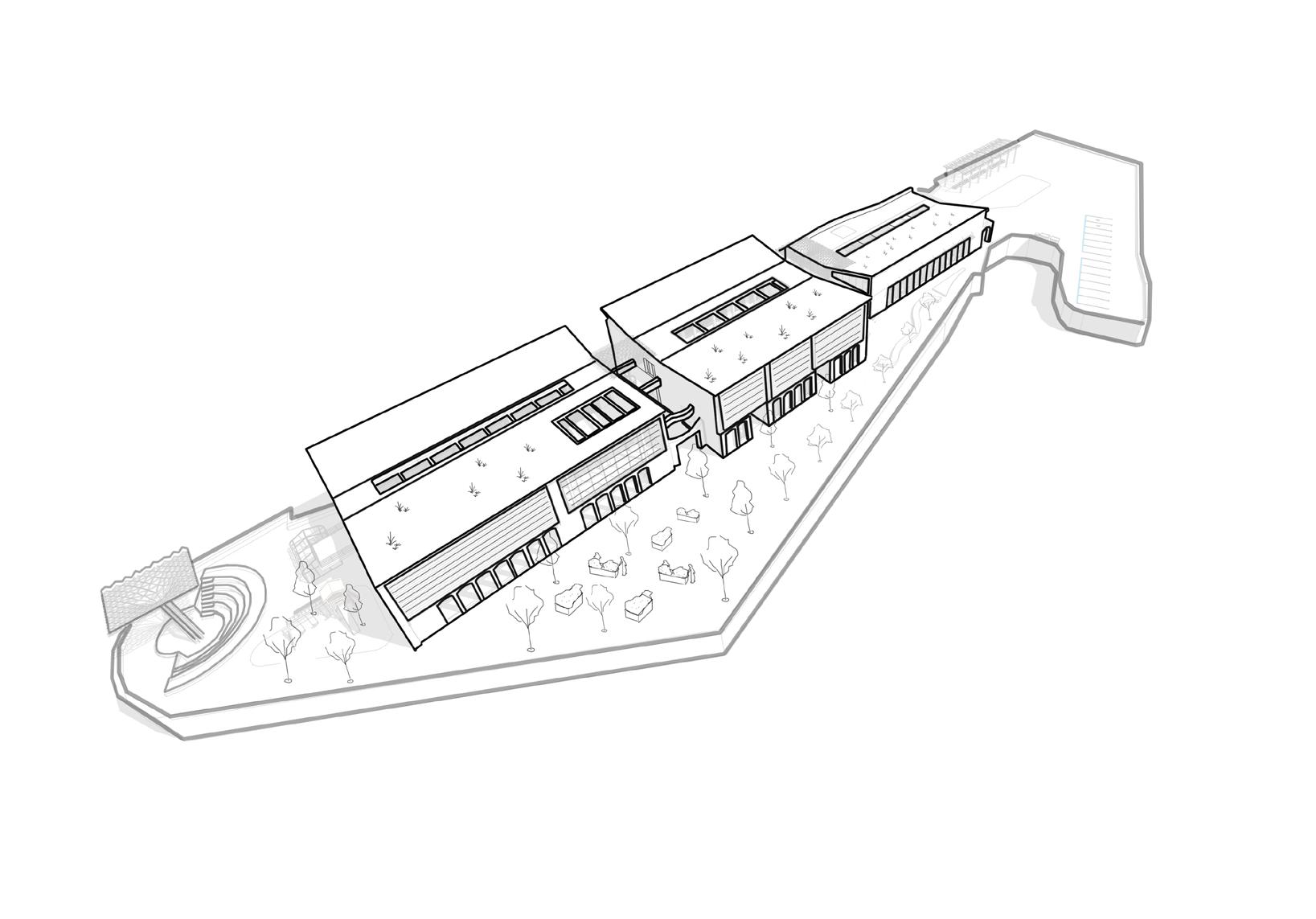
Bristol Environmental Learning Centre
Univeristy of the West of England 2022-23
This project, based in the Cumberland Basin, is a learning centre designed to serve as a community hub for environmental awarness and education. It aims to reconnect people with nature in innovative ways, fostering positive lifestyle changes. The centre will offer spaces for farming and growing natural foods, as well spaces for artisanal workshops. Additionally, it will educate the public about the surrounding ecosystem and teach them how to preserve and protect endangered species. The main objective is to transform outdated notions about nature, encouraging greater appreciation and empathy for the natural world.
3



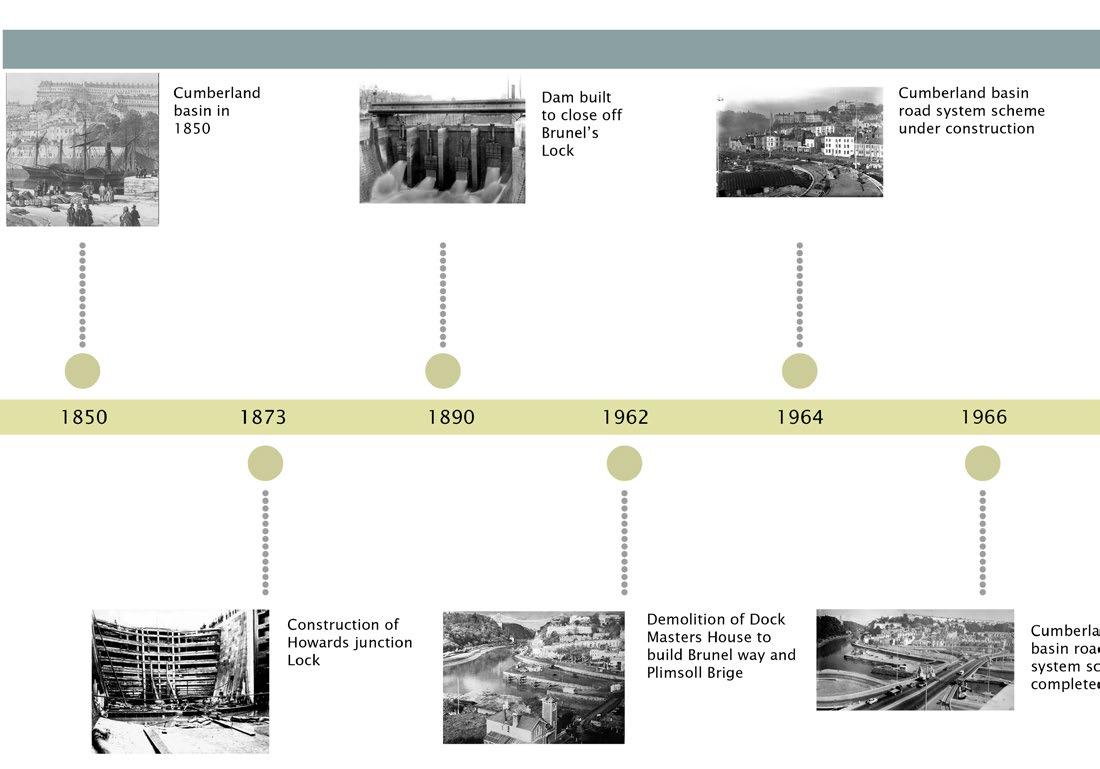
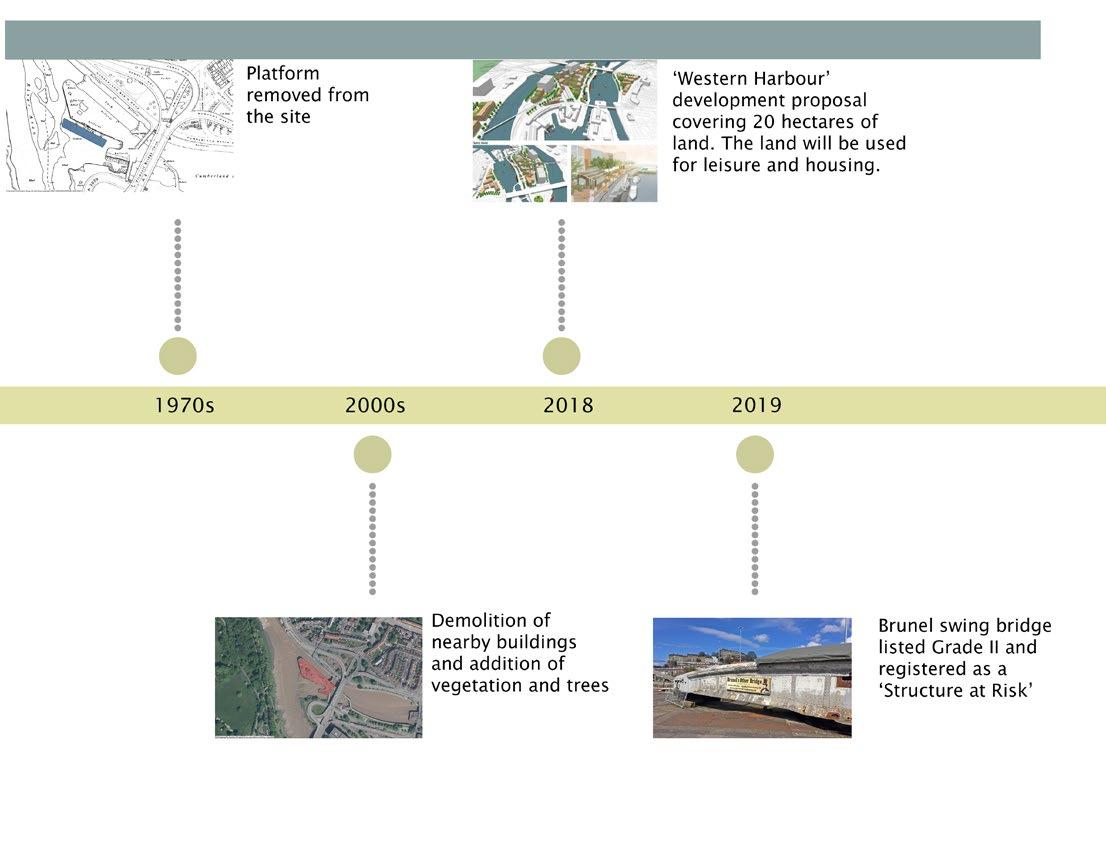
Cumberland Basin

Historical Context
5
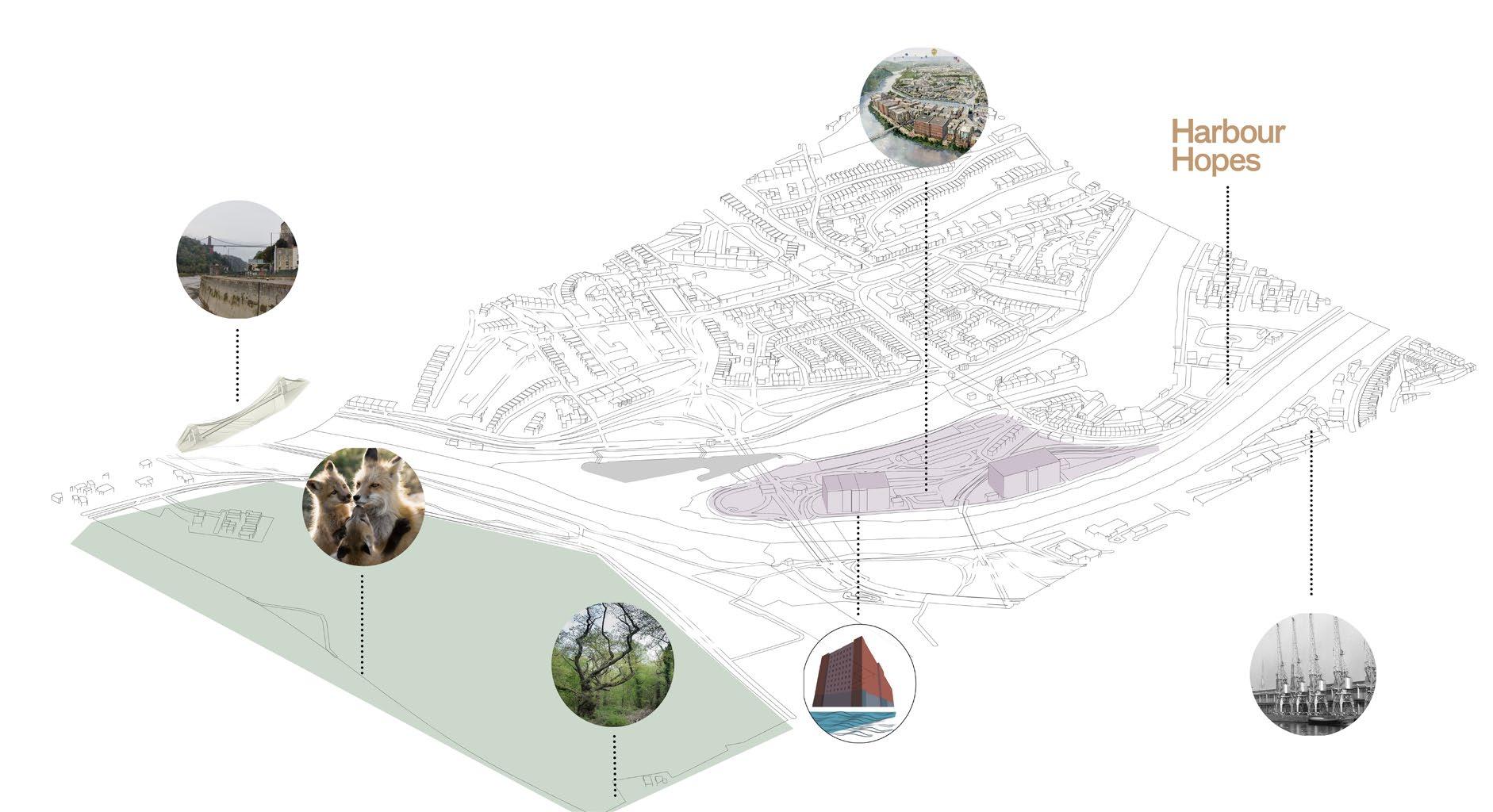
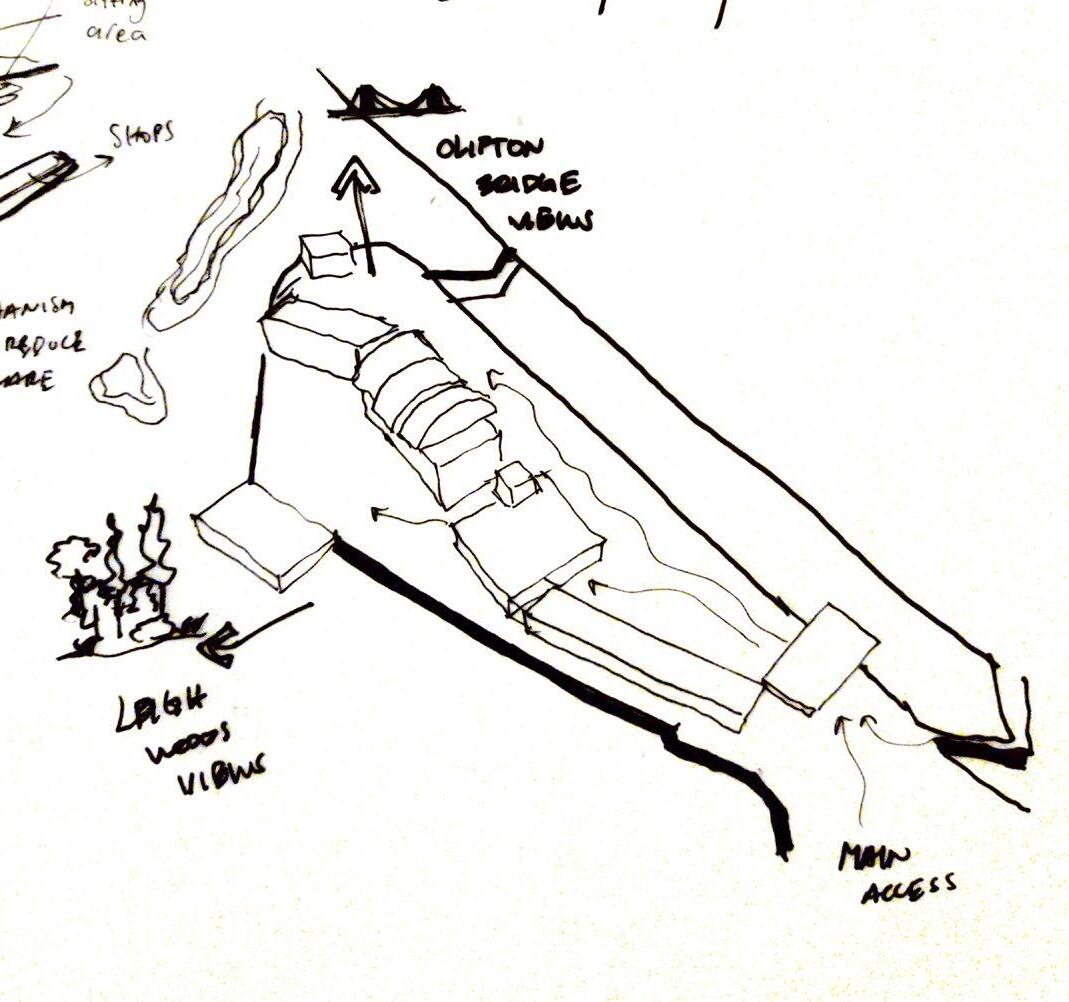
Contextualisation | Cumberland Basin
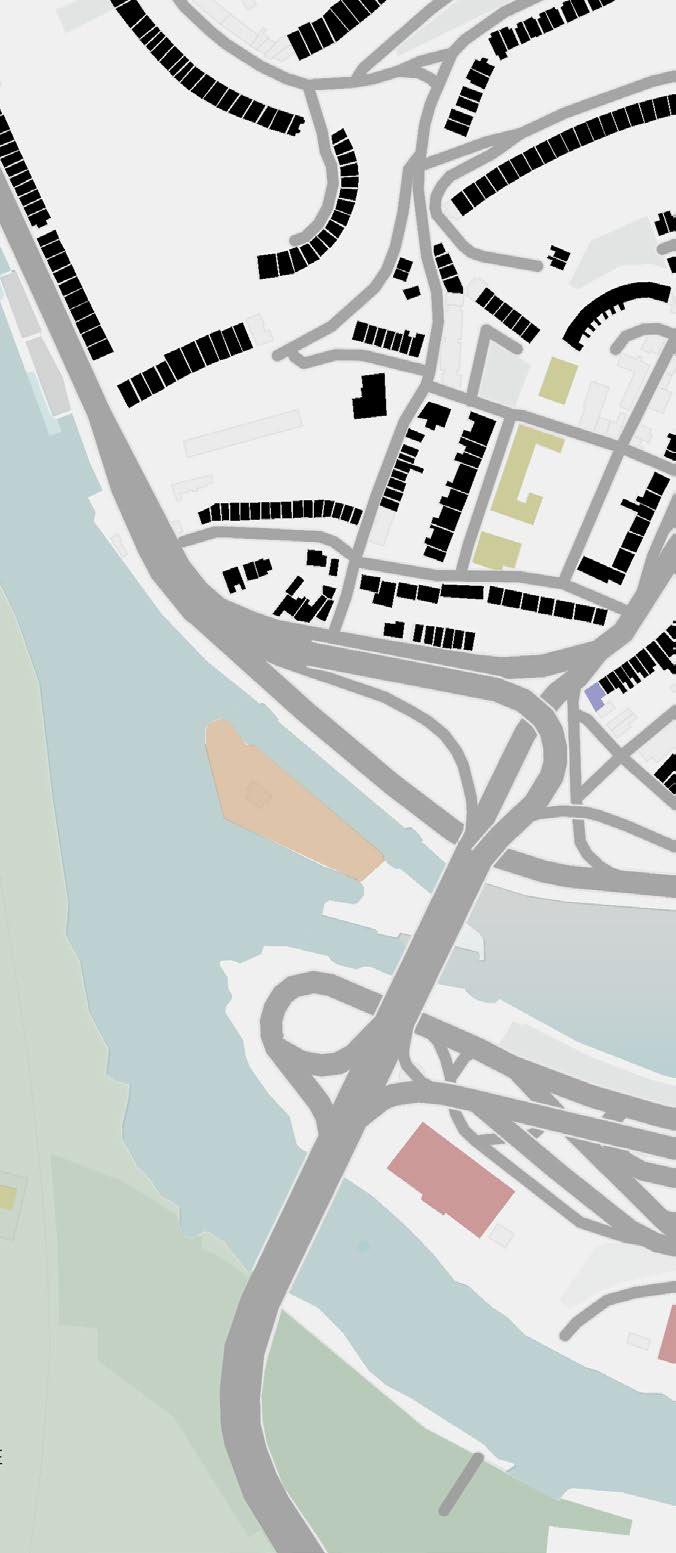
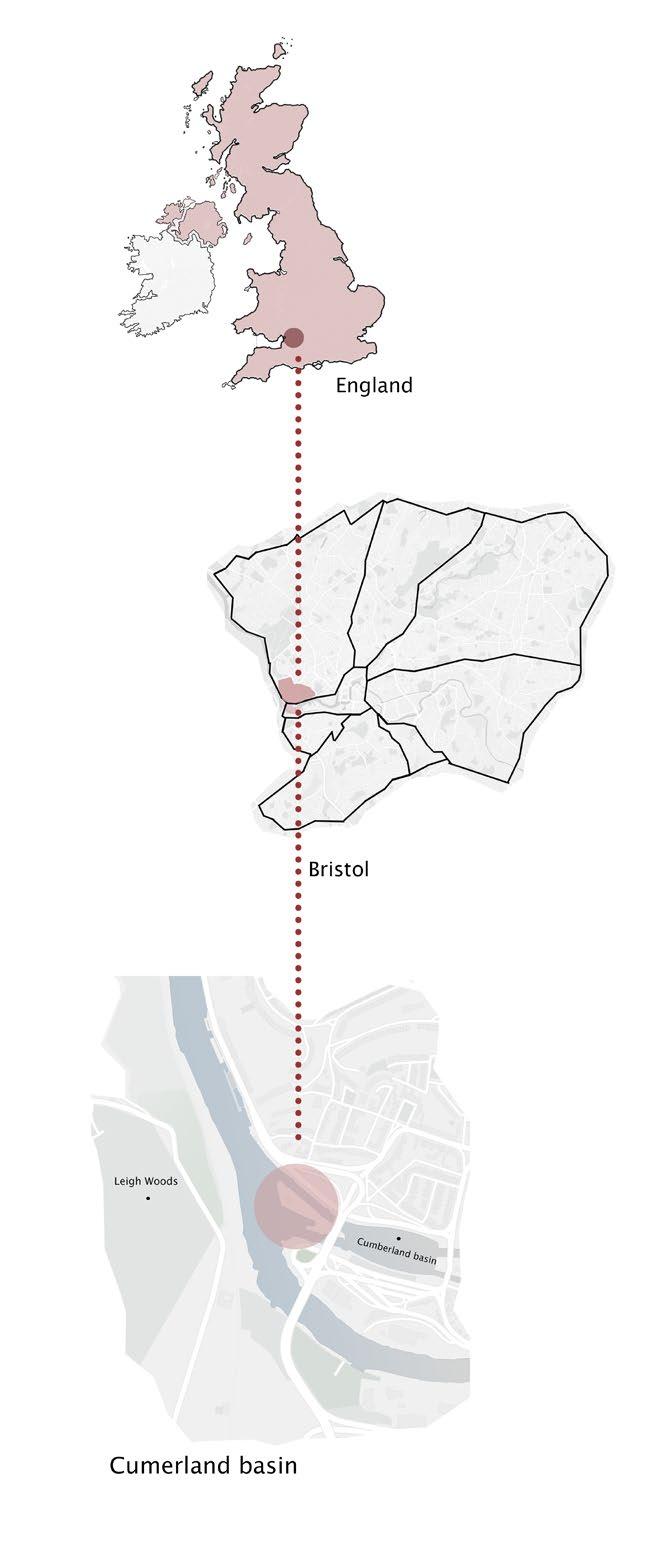
The site is located 10-minute walking from the popular area of Clifton. It is surrounded by the natural landscape of Leigh Woods. Although limited in size, it features three small bridges connecting the islet to the mainland. The main disadvantages of the site are its isolation from the rest of the city and its restricted size. However, the site provides excellent views of both the natural and urban landscapes.



6
Site map 1:200
Site Location Diagram
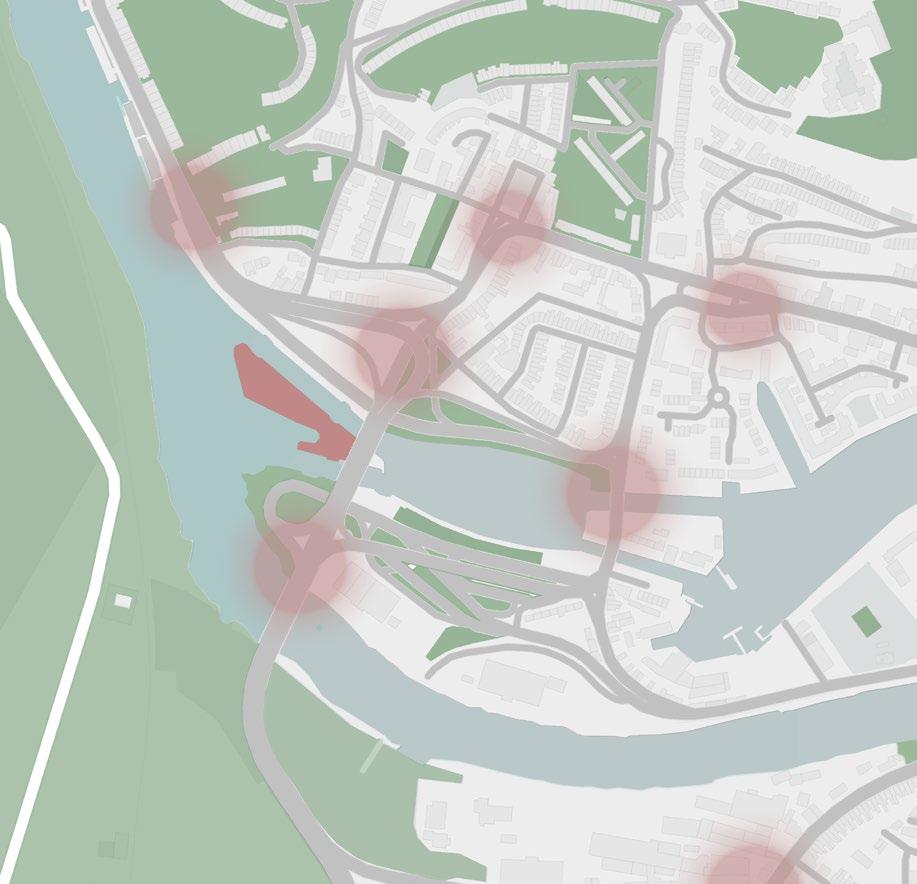
Key site features
Site’s traffic congestion points
Project Intervention & Considerations
Sustainable development goals Interventions

—Provide access to safe and inclusive green spaces and public spaces.
—Reduce the mortality from non-communicable diseases and promote mental health.

—Combat desertification and restore degraded land and soil.
—Take urgen action to end poaching and trafficking of protected species.

—Reduce food waste (from producers, retailers and consumers).
—Reduce the release of chemicals and waste into the air and soil.

—Innovate and adopt technological solutions to mitigate and adapt to climate change.
—Protect the most vulnerable against climate change impacts.
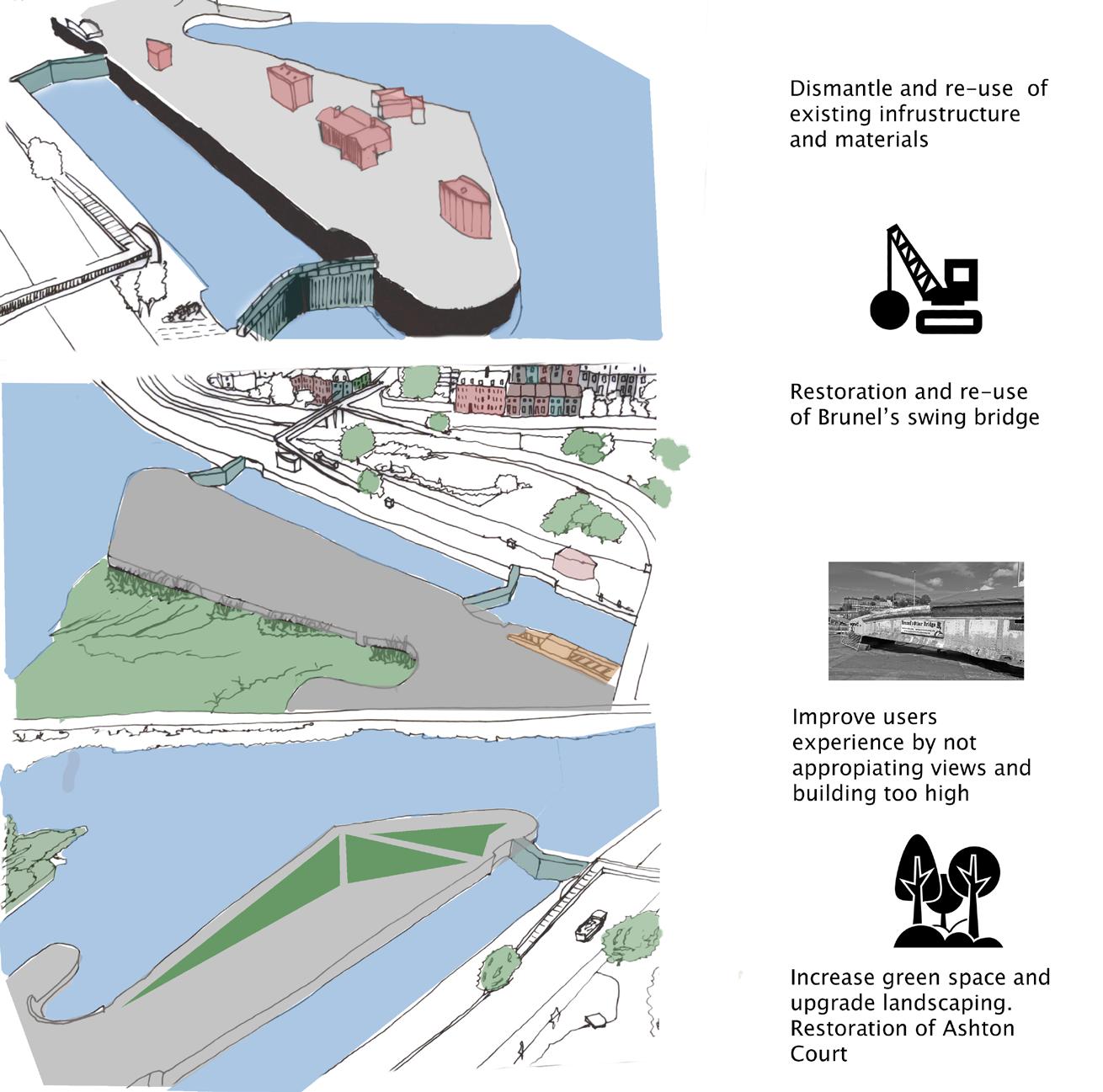
Advantages of the typology
Potential future housing development: Opportunity to teach the new tenants about Bristol’s nature, ecology and sustainable ways of living.
Suspension bridge may attract more visitors and locals to the learning centre
Large and well preseved natural areas. Great area to explore and learn about the ecosystem
Educational Facilities - Bristol archives (Accessible Historic knowladge)
Pro-active and engaging community that wants to enhance the living conditions of Cumberland basin and see the area thrive.
7
Biodiveristy found near the site, Asthon court and Leigh woods
Close proximity to Bristol’s Industrial museum
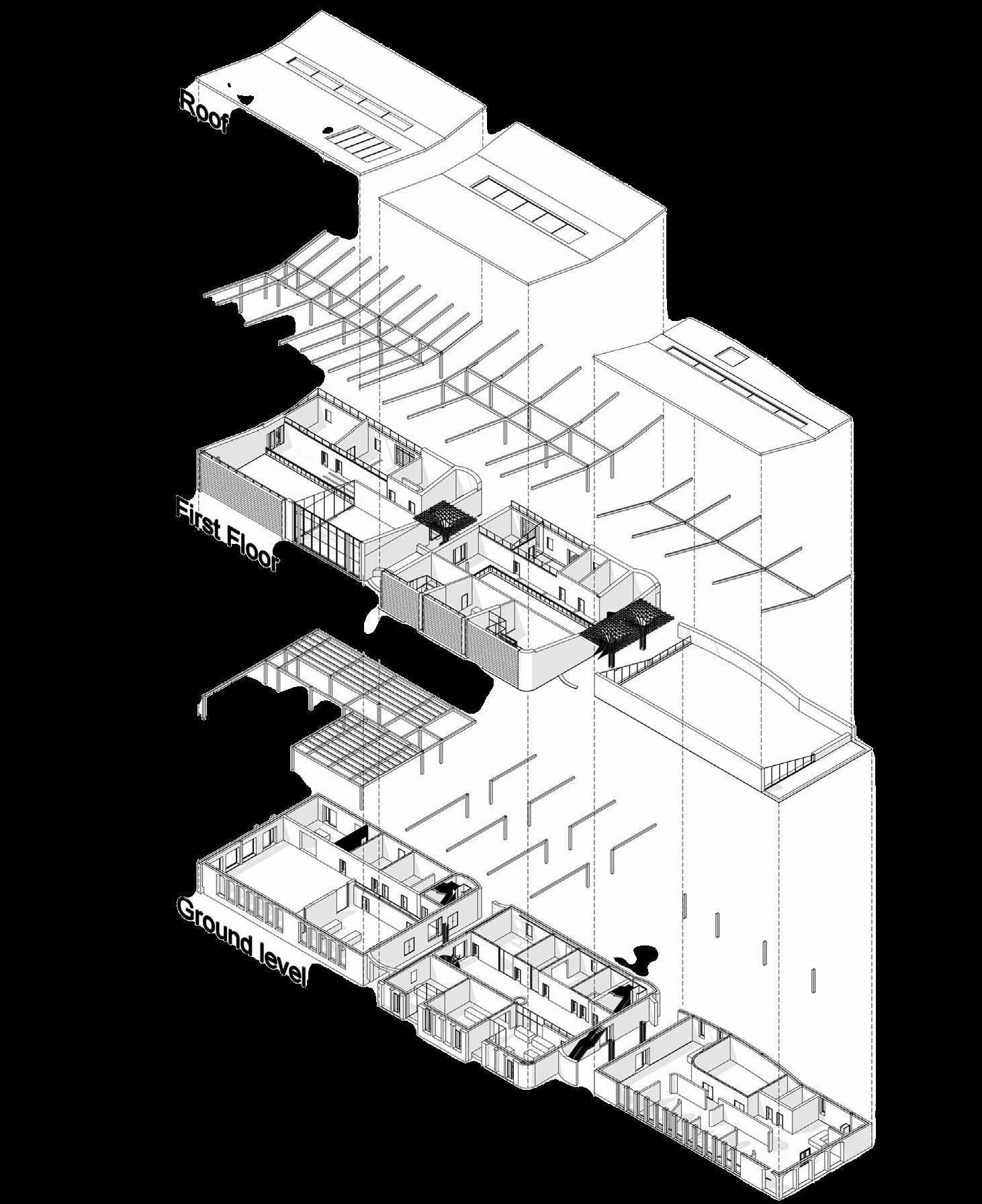
Portfolio | Structure

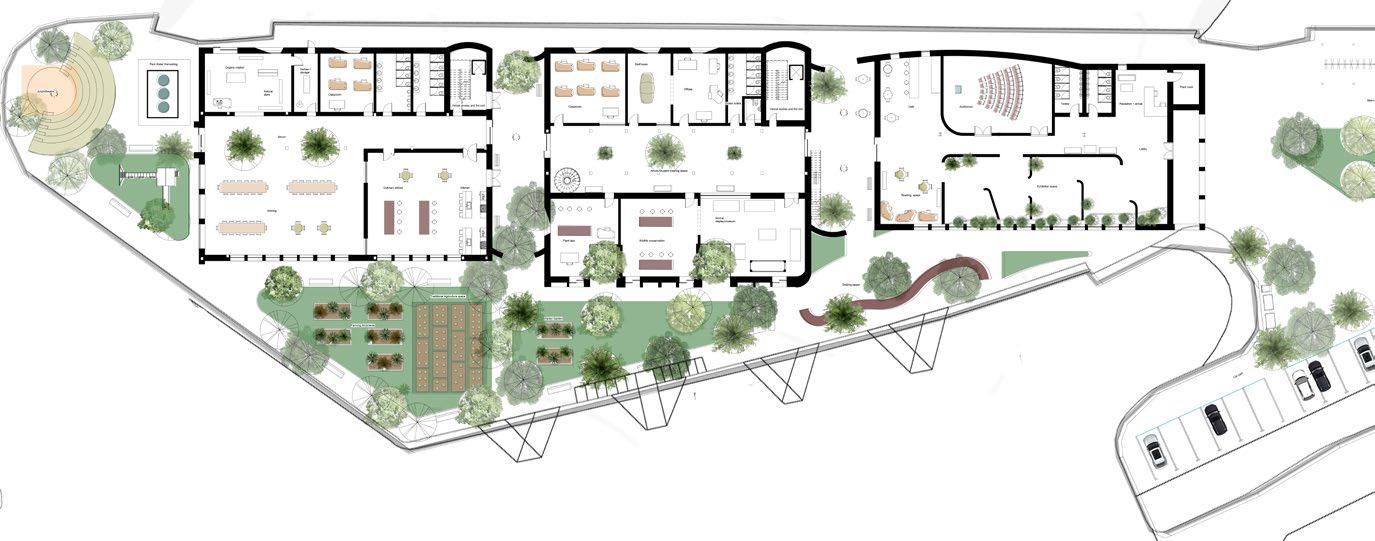


Ecological Centre | Floor plans Roof plan Ground Floor First Floor
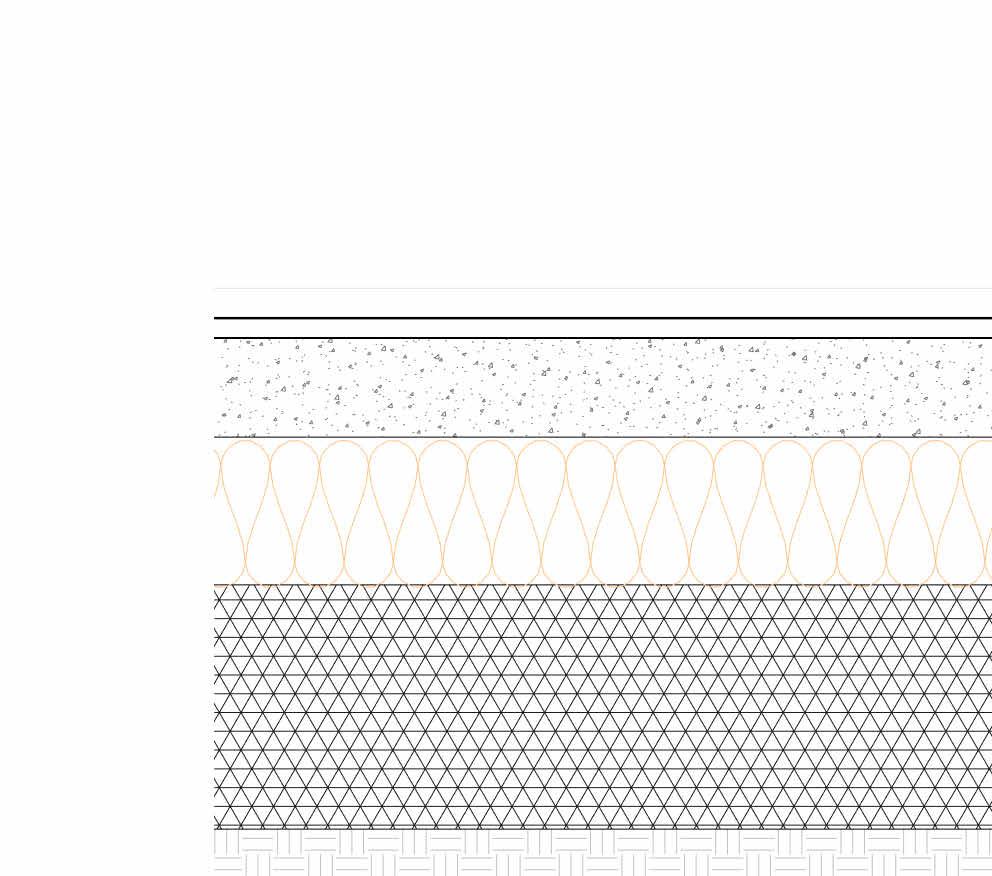
Damp
Vapour Barrier

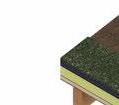
Green roof
- Vegetation
- Growing medium
- Water resorvoir
- Root barrier
- Waterproof membrane
- 150mm Rigid Insulation
- VPC
- 80mm CLT panel
Exterior Wall
- 250mm Reinforced Rammed earth wall
- VCL
- 120mm Polyiso insulation
- 250mm Reinforced Rammed earth wall
Foundation
- 20mm Wood laminated floor
- 100mm Cement screed with radiant heating
- Vapour Barrier
- 120mm EPS Rigid insulation
- Damp proof membrane
- 200mm Hardcore Gravel
- Reclaimed Concrete footing 1:20























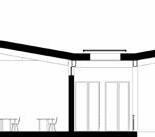

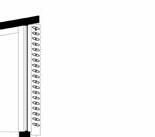



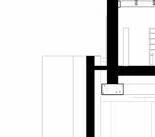
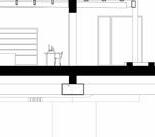
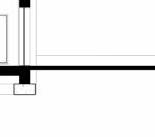

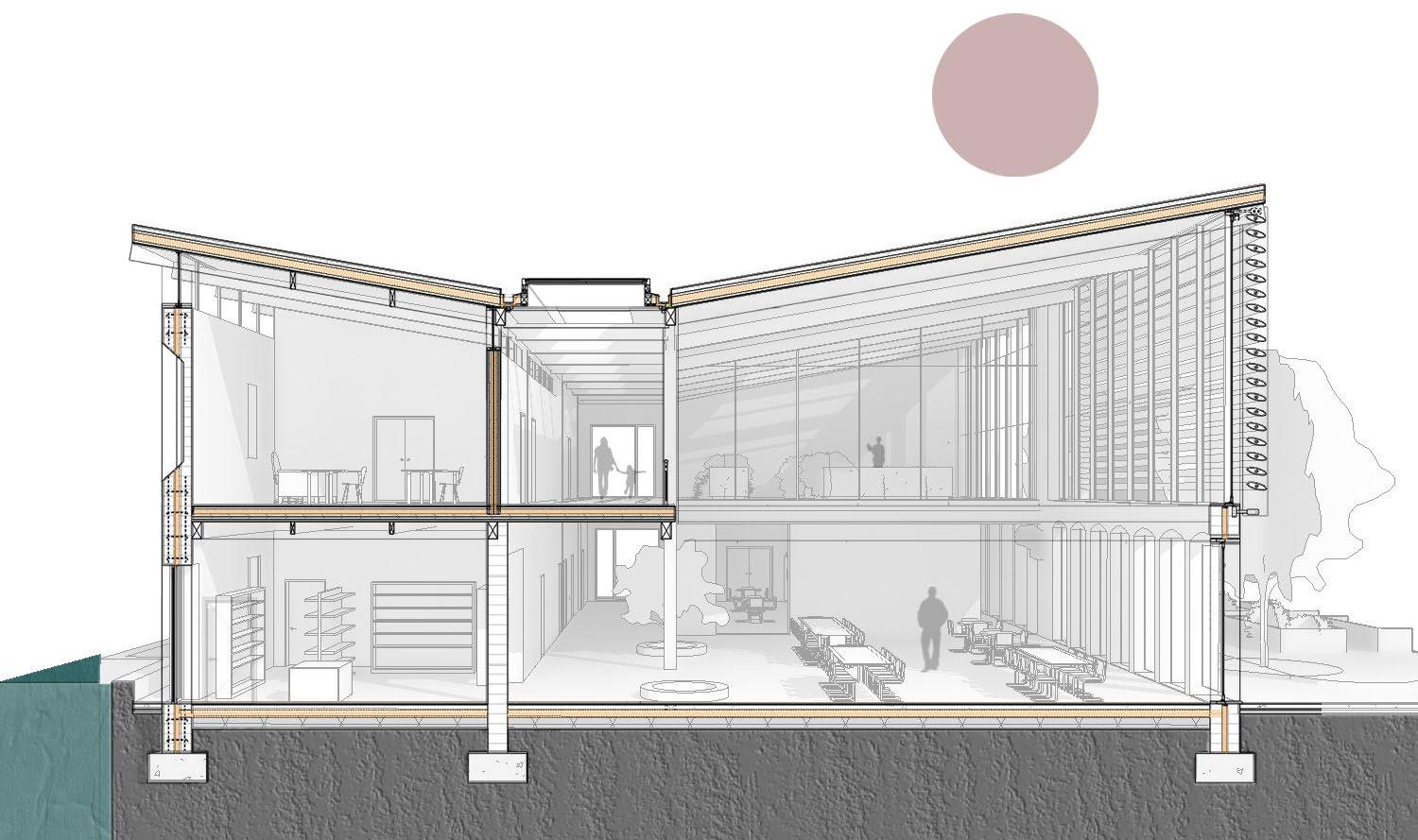
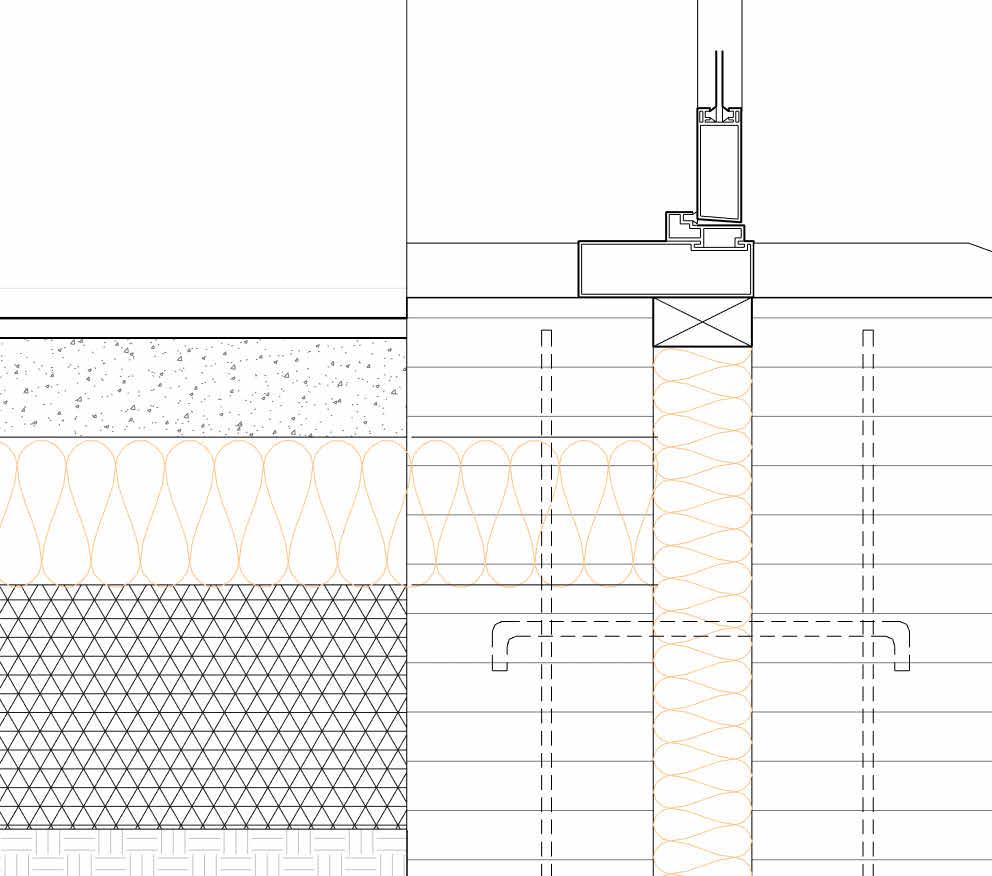
proof membrane Portfolio | Luis Mendez
technical detail
Facade




























Green roof
- Vegetation
- Growing medium
- Water resorvoir
- Root barrier
- Waterproof membrane
- 150mm Rigid Insulation
- VPC
- 80mm CLT panel
Internal Wall
- 20mm Wood laminated flooring
- Service void
- 100mm Rock Mineral wool Insulation
- 150mm CLT wall
- 200mm x 350mm - Glulam secondary beam
- 200 x 350 Main Glulam Beam
Foundation
- 20mm Wood laminated floor
- 100mm Cement screed with radiant heating
- Vapour Barrier
- 120mm EPS Rigid insulation
- Damp proof membrane
- 200mm Hardcore Gravel


















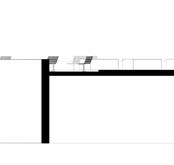




- Reclaimed Concrete footing














Ecological Centre | Luis
1:20 Internal technical detail
Mendez





Timber Shade louvre
40mm Steel bar to support louvre
Timber support panels
Rough Plywood Buck







250mm Rammed earth wall [Reinforced]
120mm Polysio Insulation

250mm Rammed earth wall [Reinforced]
Drip Groove 25mm
Clazing wall




Scale Bar (mm)
Rough Plywood Buck
Glazing Foundation water proofing
10mm Horizontal Rebar
10mm Vertical Rebar


Reclaimed Concrete footing
Scale Bar (mm)


500 1000
0 500 1000
0 500 1000
Technical Details 1:5
Scale Bar (mm)
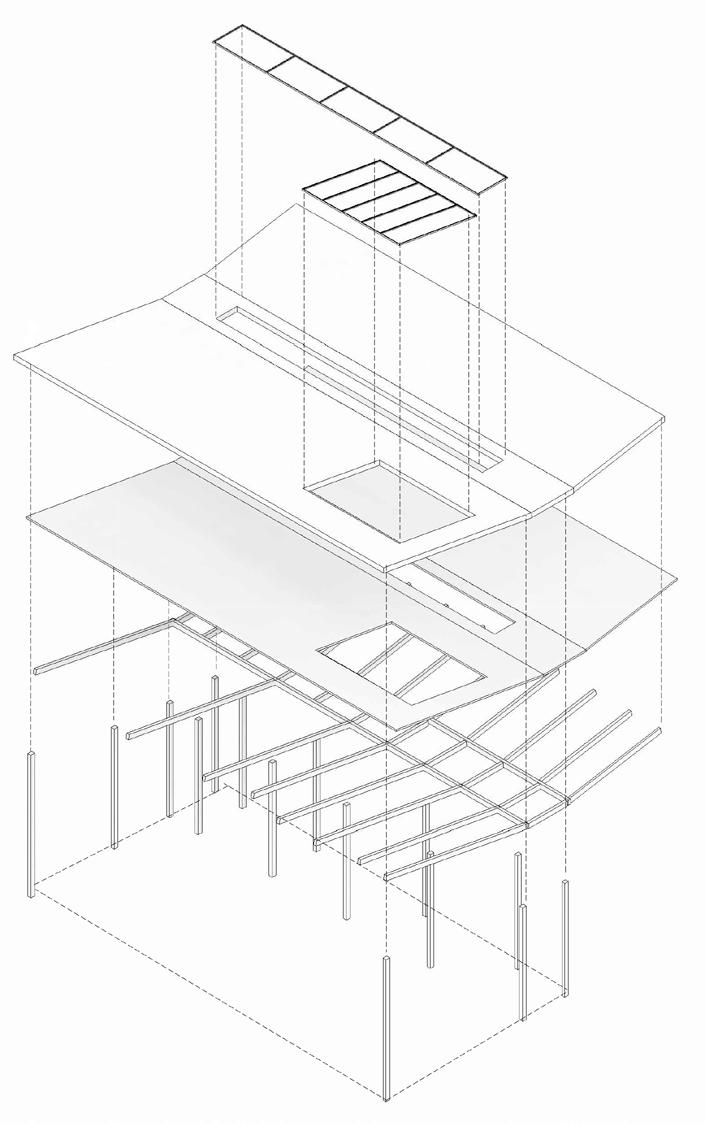
Structural strategy
Key
1. Light Vegetation/Grass
2. Growing medium
3. Water Resorvoir
4. Roof barrier
5. Rockwool Mineral insulation
6. Vapour Control Layer
7. Green roof waterproofing
8. CLT roof panel
9. Glulam Rafter













Key
1. Skylight and Greenhouse roof glazing
2. Green roof
3. Cross-Laminate-Timber roof
4. Glulam beams and rafters
5. Glulam columns
Roof Technical Detail






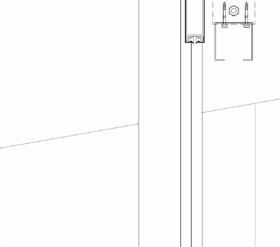













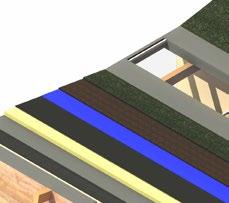










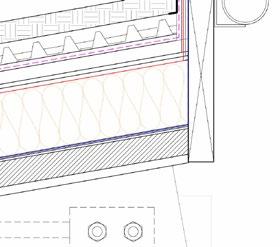










Roof composition diagram


















0 500 1000 Scale Bar (mm)
Glulam Skeleton structure
Rammed earth wall intregated with the structure
Process Modelling
Conceptualisation



Form Finding
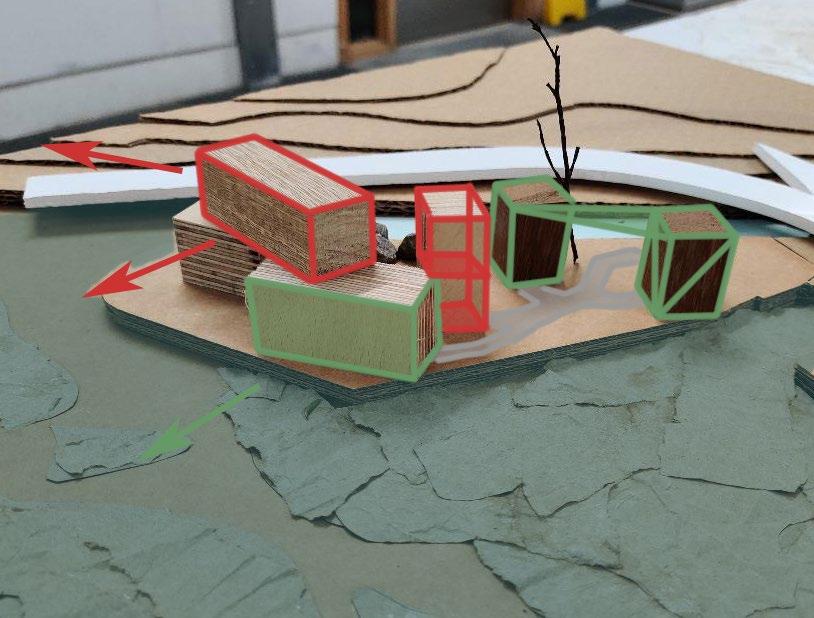



14
Exhibition space







15



16
Revit, Photoshop, Enscape

17 P.2
RIBA
Luis Mendez
Part 1 Graduate

Bristol Youth Centre
Univeristy of the West of England 2020-21
The objectives for this project were to create a building where adolescents could socialise and support each other to focus on their mental and physical well beings. The design of building was designed to help its users feel ‘like home’ and comfortable to enabe them to learn and develop trasferrable skills in a variaty of areas and a place where they could feel inspired and motivated. Moreover, the centre had to make good use of the natural light and provide well-ventilated rooms with abundant greenery.
18
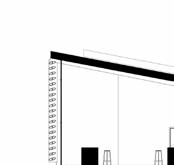
Bedminister | Bristol



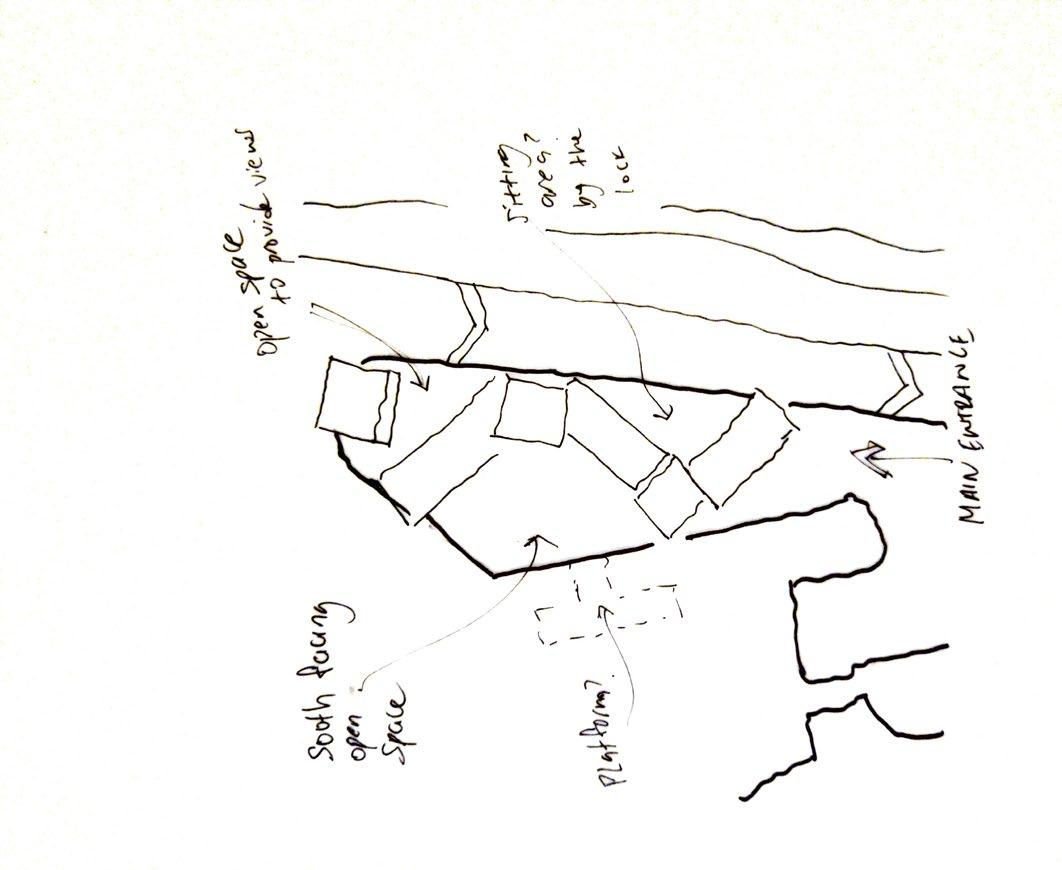
Being located at the heart of the Bedminster, the site was mostly surrounded by industrial and residential buildings. Therefore there was limited green space available around the site with the exception of some green spaces South and South East which were classified as ‘positive views’. The site, however, was very accessibile by public transport and possesed a strong character. The form of the building was influence by the environmental conditions of the site in particular that of noise. It was for this reason that the building was designed with an inverted L-shape to block the loud noise from the road.
Photogrpahic study of the site

19

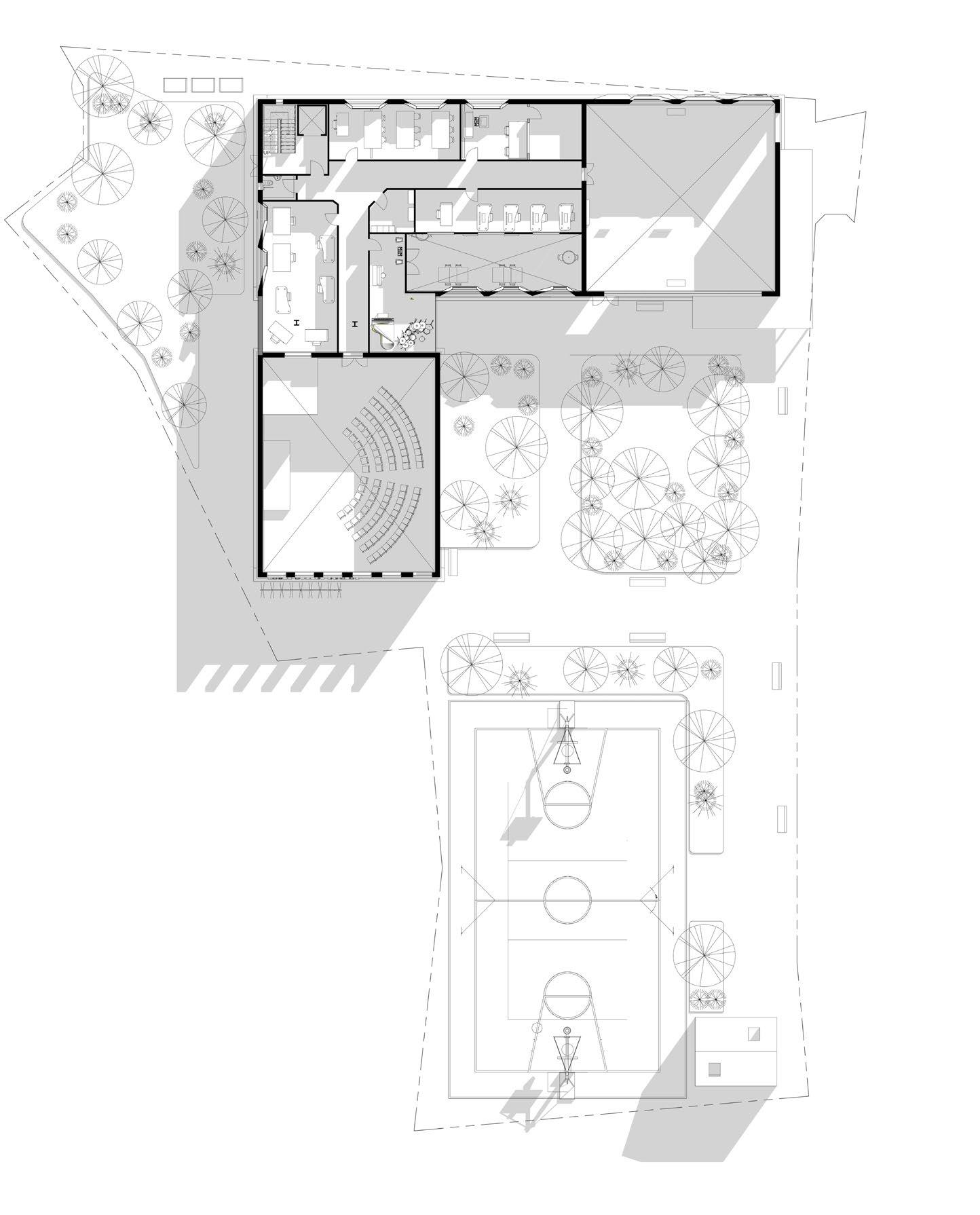
20 Ground Floor N
South Elevation

21 First
Floor
2.
3.
1.
Multimedia room
Storage
Seminar
4.
Music room
5.
Recording studio 6. Studio/making 7. Lift 8. Stairs 9. Toilet
1 3 5 4 8 7 6 2 9 10 9 12
10.Central green space 11. Main entrance 12. East entrance

Structural strategy and Materiality
Concrete beam
Concrete floor slab
Concrete columns
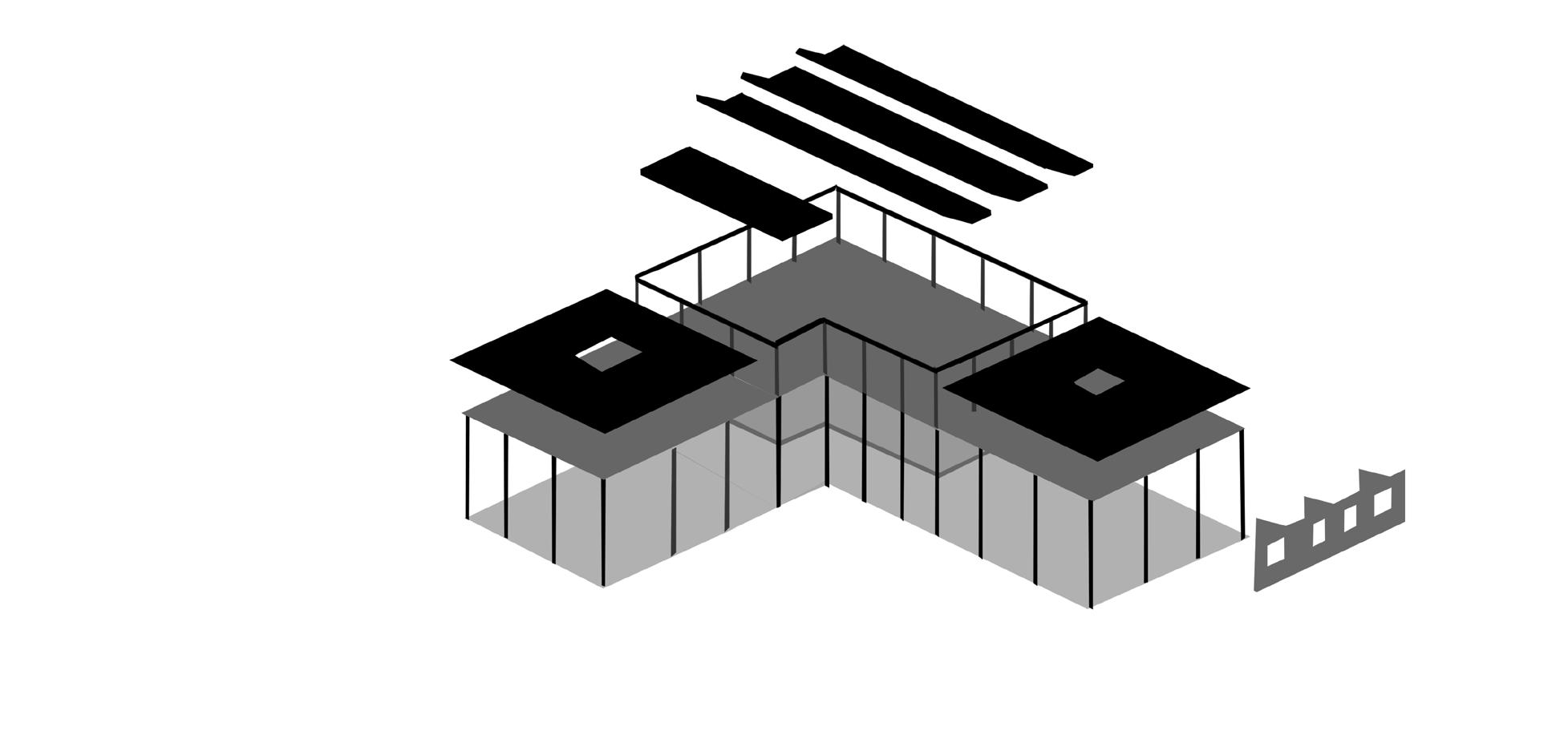
Standing seam metal roof and sawtooth roof structure




The external finishes of the building were choosen to provide a unique exterior facing wall, giving a sculptural appearance to the centre. Coquina-sand concrete was the material implemented as it is a ligthweight concrete and low in carbon (its easily compressed and provides long-term durability). Timber wood panels were chosen for the external cladding of the west side of the building. Timber flooring used for the second and third floors as they add a welcoming and warm ambience to the space.
22
Exposed concrete wall
Conquina-Sand concrete
Timber cladding
Polished concrete flooring
Timber flooring

Environmental Strategy





The main environmental strategy of the building focuses on the saw-tooth roof structure. The 45 degree inclination of the roof towards the sun allows natural light to easily enter the building helping the rooms at the far back be illuminated by the midday sun during summer. Furthemore, the building benefits from cross ventilation in the multi-purpose hall thanks to the wall and window vents placed on the south and west facade of the building. A similar ventilation also happens on the third floor through the saw-tooth roof. This ventilation system will help to remove hot and cold temperatures from interior rooms
23
Rain-water Harvesting Cross-ventilation Saw-tooth roof Super insulation

1. - Precast Concrete pavers
- Waterproof membrane
- 150mm Insulation
- Vapour Control layer
- Leveling screed
- Concrete deck
- Timber battens
- Plasterboard Ceiling
2. - 175mm facing concrete wall
- 50mm Air gap
- Waterproof Membrane
- 150mm wall insulation
- Vapour control layer
- Inner Block work
- Timber battens
- Plasterboard
3. - Polished concrete finish
- Screed
- Vapour Control layer
- Thermal floor insulation
- Additional insulation
- Waterproof membrane
- Leveling Screed
- Hardcore gravel
4. - 60mm Concrete blocks
- 30mm Sand Bedding
- Open graded crushed rock
- Compacted earth
Scale 1:20 1:20 Section

Key Section

25
1:5 Junction


26
Revit, Photoshop, Enscape
27 P.3
RIBA
Luis Mendez
Part 1 Graduate

Social Housing Project
Univeristy of the West of England 2020-21
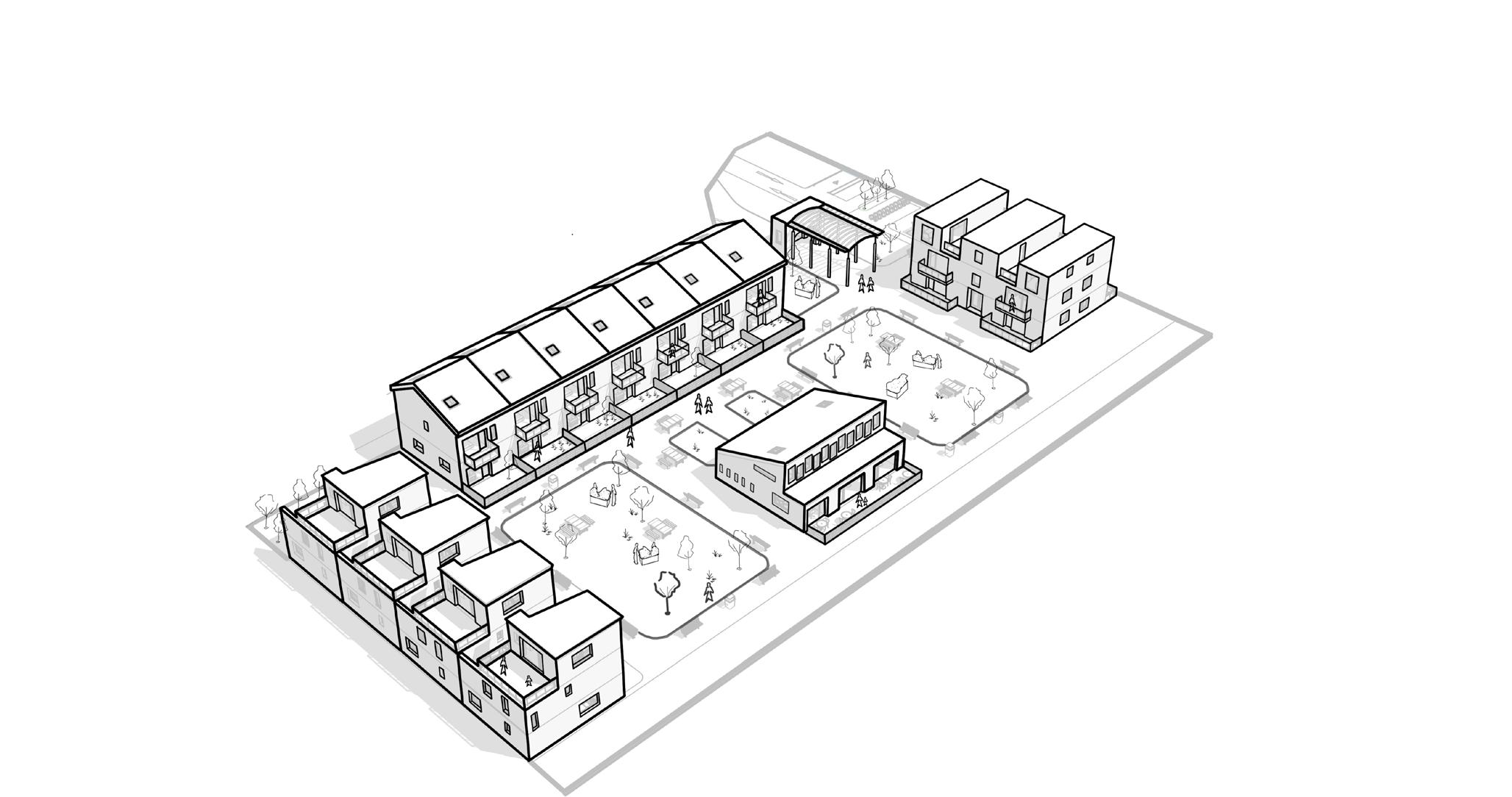
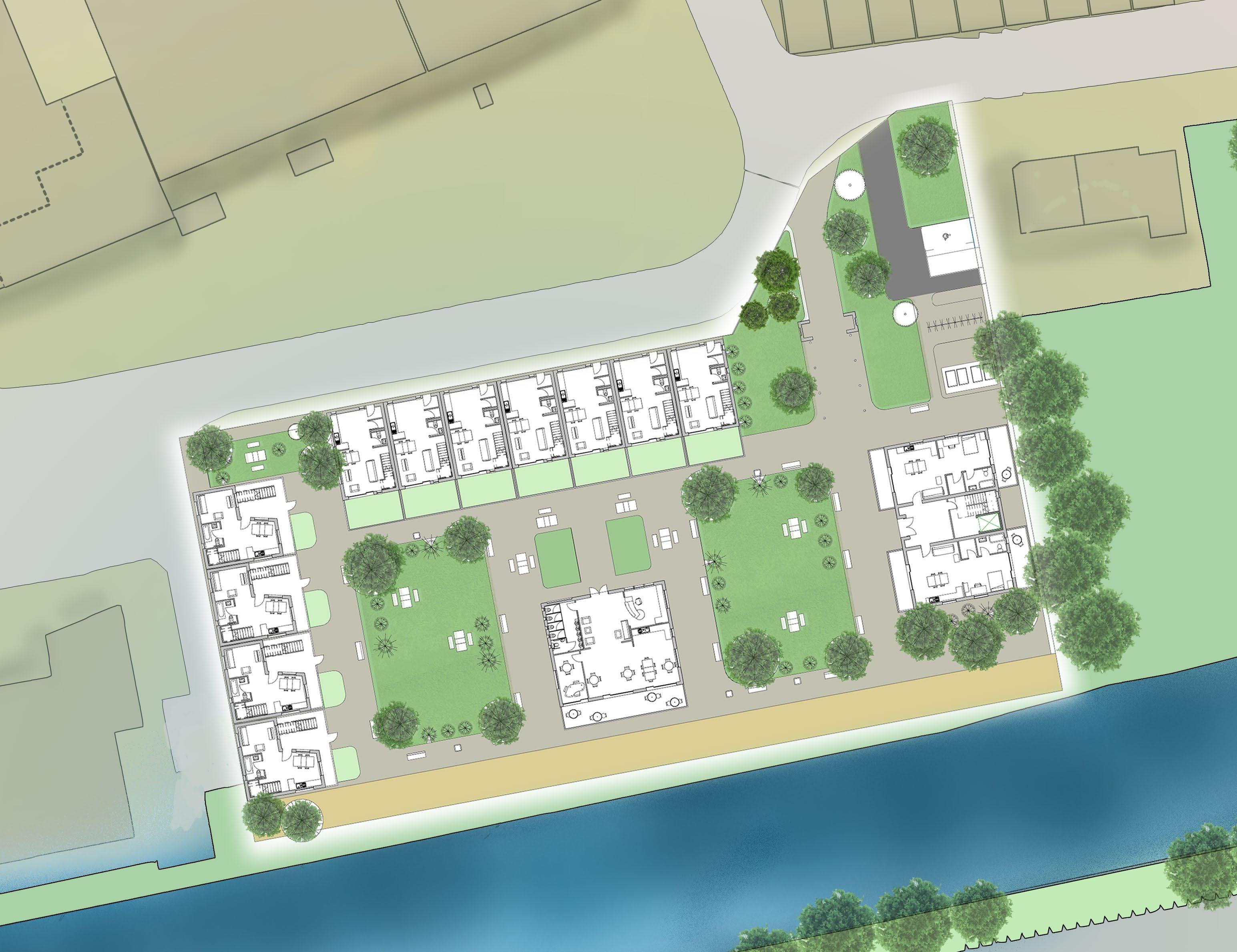
This social housing project is based in the popular area of Barton Hill, Bristol. The main aims for this project were to challenge the traditional ways of living, playing and working through providing different sustainbale housing solutions. The project was designed in a way that space efficiency and social mobility would be significanlty increased as well as reduce alienation between its users for a intergenerational living space. This was done by creating 3 compacted unit blocks with main communal facilities at the centre of the livable space.
28
Barton Hill | Bristol

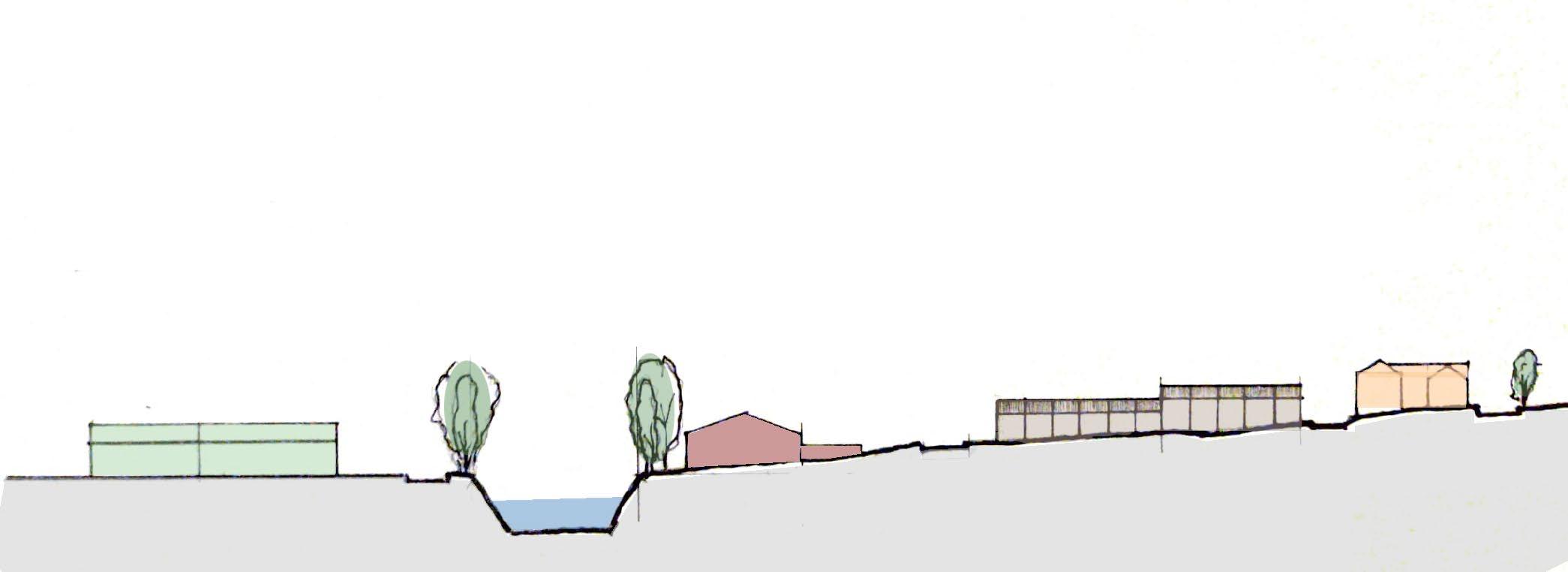
The surrounding architecture of the Barton hill varied from Victorian terrace housing to contemporary family housing. To respect this similar pattern, I took the typical Victorian streets as inspiration and implemented into the project by creating a row of houses on the north of the site. This was one of the first design decisions that was present through out the project as it was very important to minimise the noise coming from the road as well as to provide a more pleasent visual experience to the occupants.
Precedents


Site Elevation

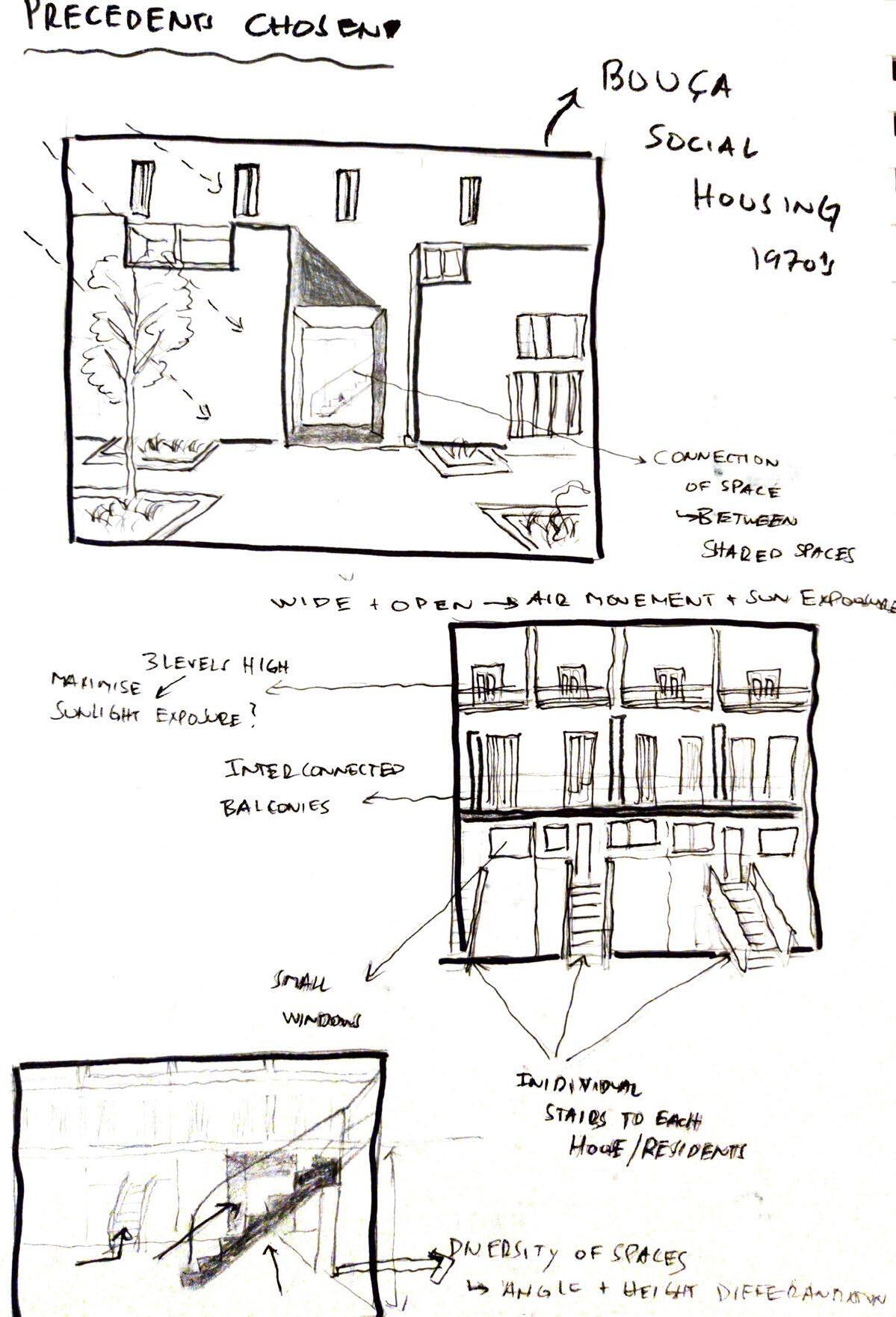

 Alvaro Siza Bouca Social Hosing
Peter Barber Architects Brick Terrace housing
Alvaro Siza Bouca Social Hosing
Peter Barber Architects Brick Terrace housing
Site Terraced housing Canal Terraced housing Glendare street
The flat roof provides extensive space to install PV solar panels.
The three large openings allow to have terraces that extends from one side of the building to the other, helping to ventilate interior spaces.

Terraces and Balconies provide essential outdoors space for both dissable people and elders without needing to leave the building.

30
Site plan 1:500

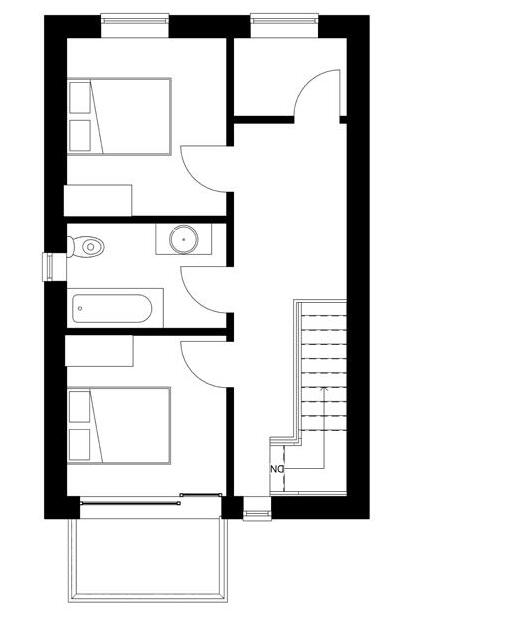
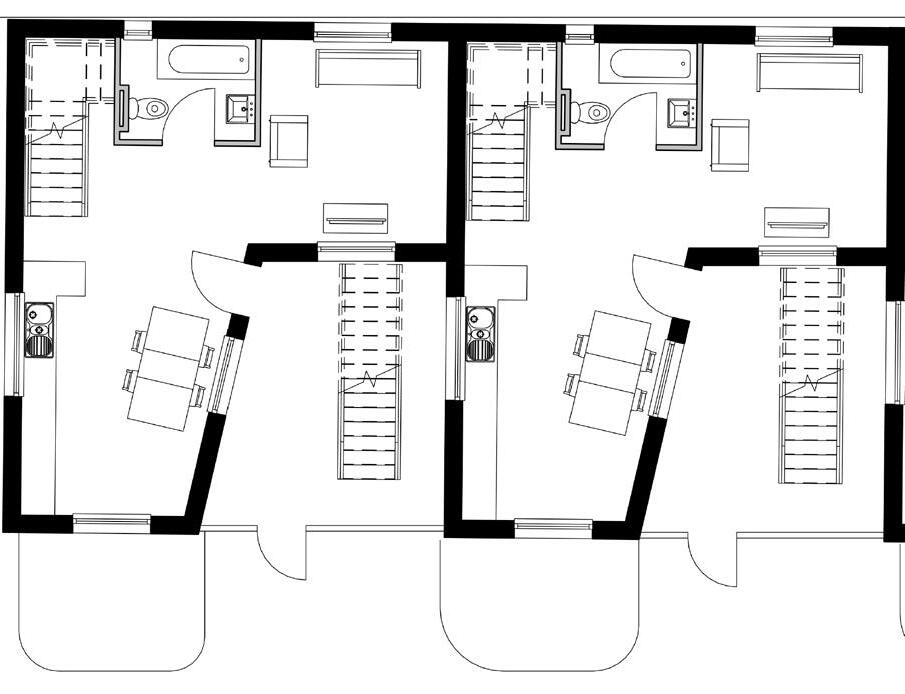
Young Professional units | 2 Beds
1 - Entry/Kitchen
2 - Living room
3 - Garden
4 - Toilet
5 - Bedroom 2
6 - Bathroom
7 - Main room
8 - Storage room
9 - Balcony
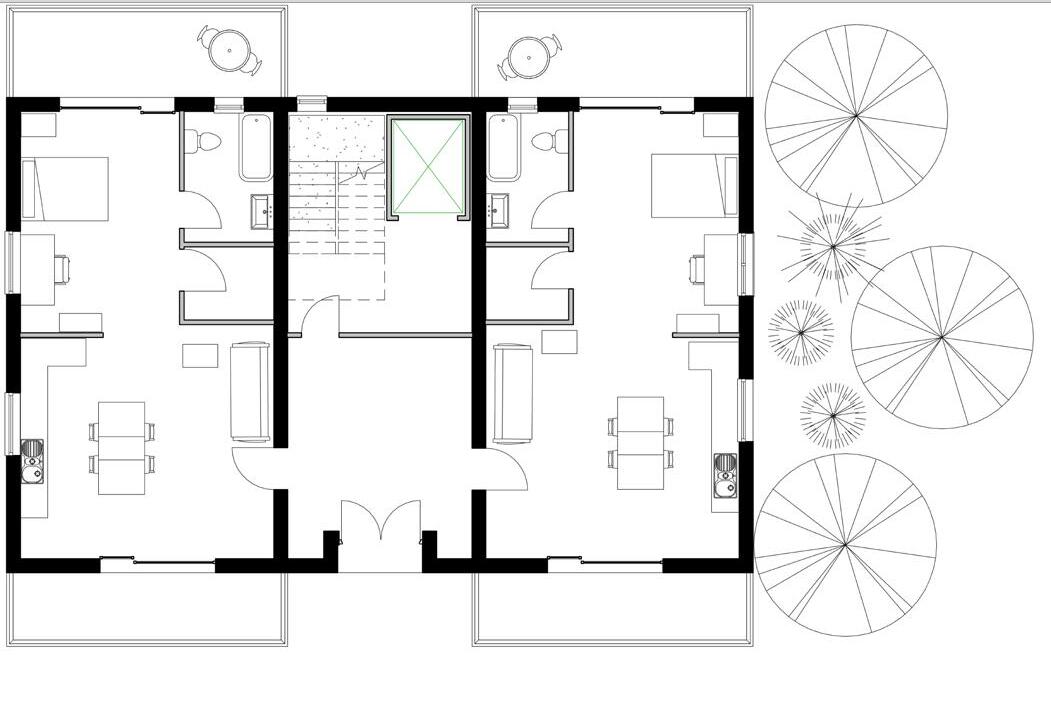
Mid-Large Families | 3 beds
1 - Dinning area
2 - Kitchen
3 - Bathroom
4 - Living room
5 - Front garden
Senior Apartments | 1 and 2 beds
1 - Living space
2 - Kitchen and Dinning area
3 - Storage space
4 - Main bedroom
5 - Bathroom
6 - Terrace/Balcony
7 - Communal lift
8 - Building entrance

1 2 3 7 6 5 9 8 4
2 4 3 1 5 4 3 2 1 7 6 5 Floor plans 7 8
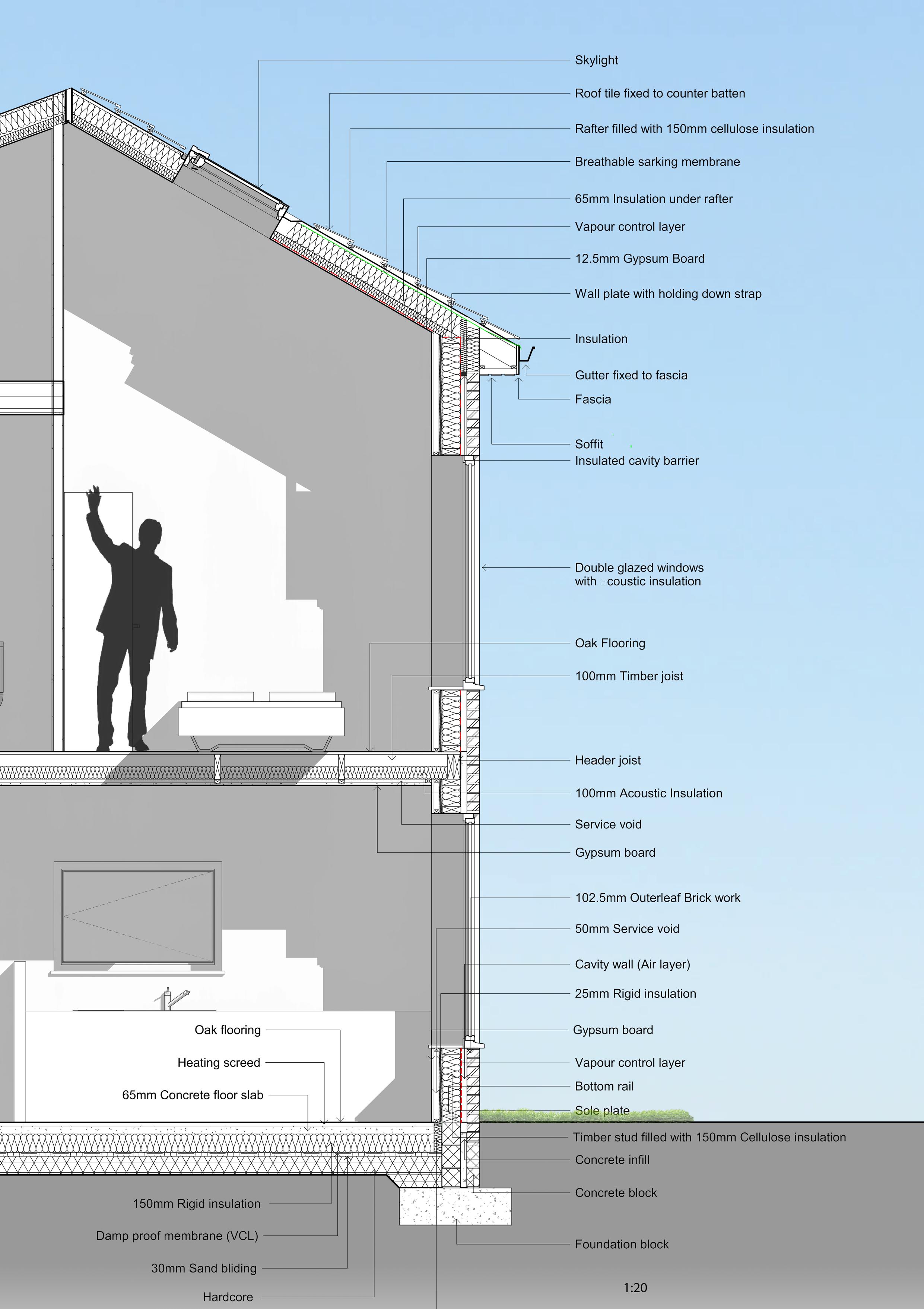
1:20 Technical
Cross-ventilation
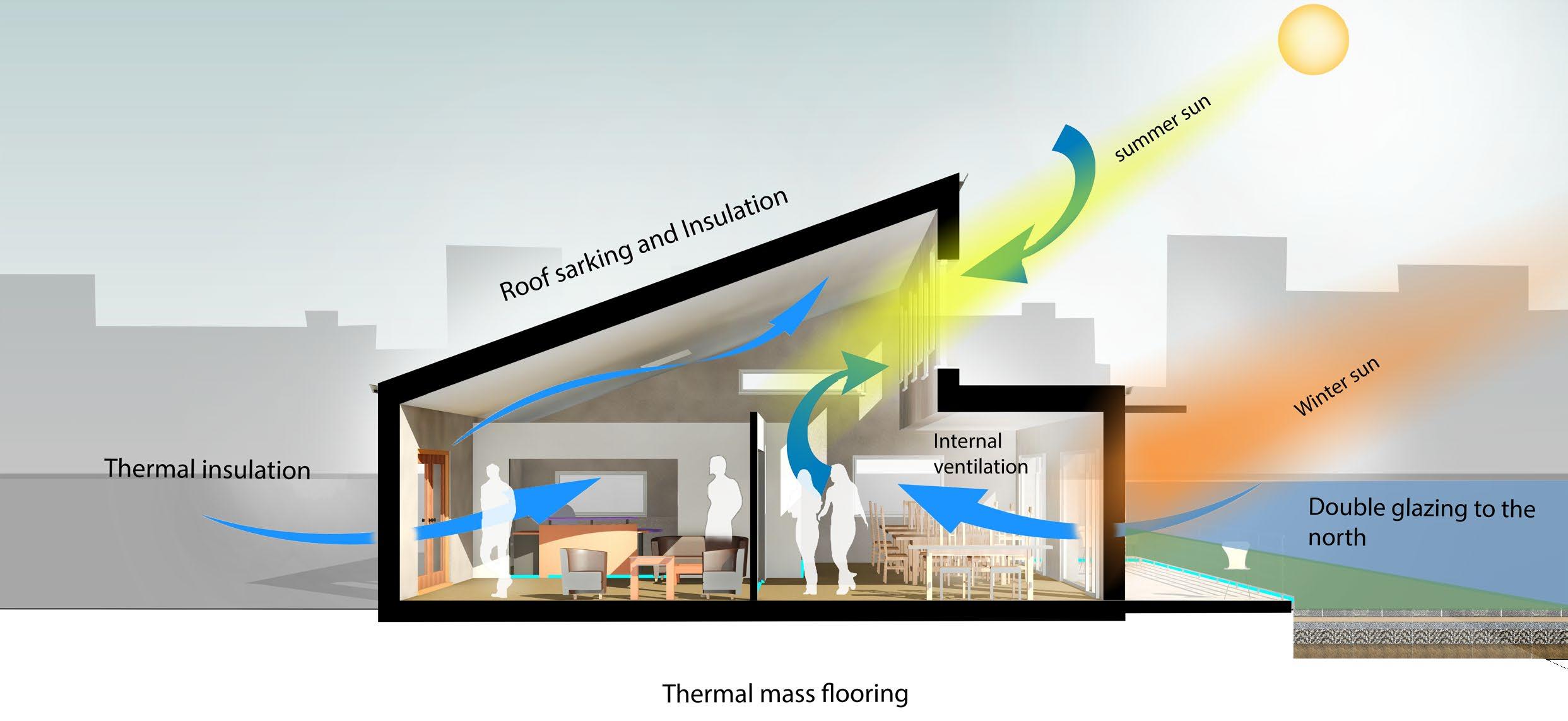

Sustainable materials
Double glazed windows
Structural Axonometric



Permeable pavement

33 Environmental strategy
Brise soleil sun shade
Clay roofing tiles
Timber stud partition walls
Timber framed wall (Primary structure)
Timber framed floor primary structure
Foundation
Outer Brick wall structure
Group Modelling


Wall-board presentation
34
The Engine Shed facade model


35
Jacobs house floor plan
Jacobs house model 1:200
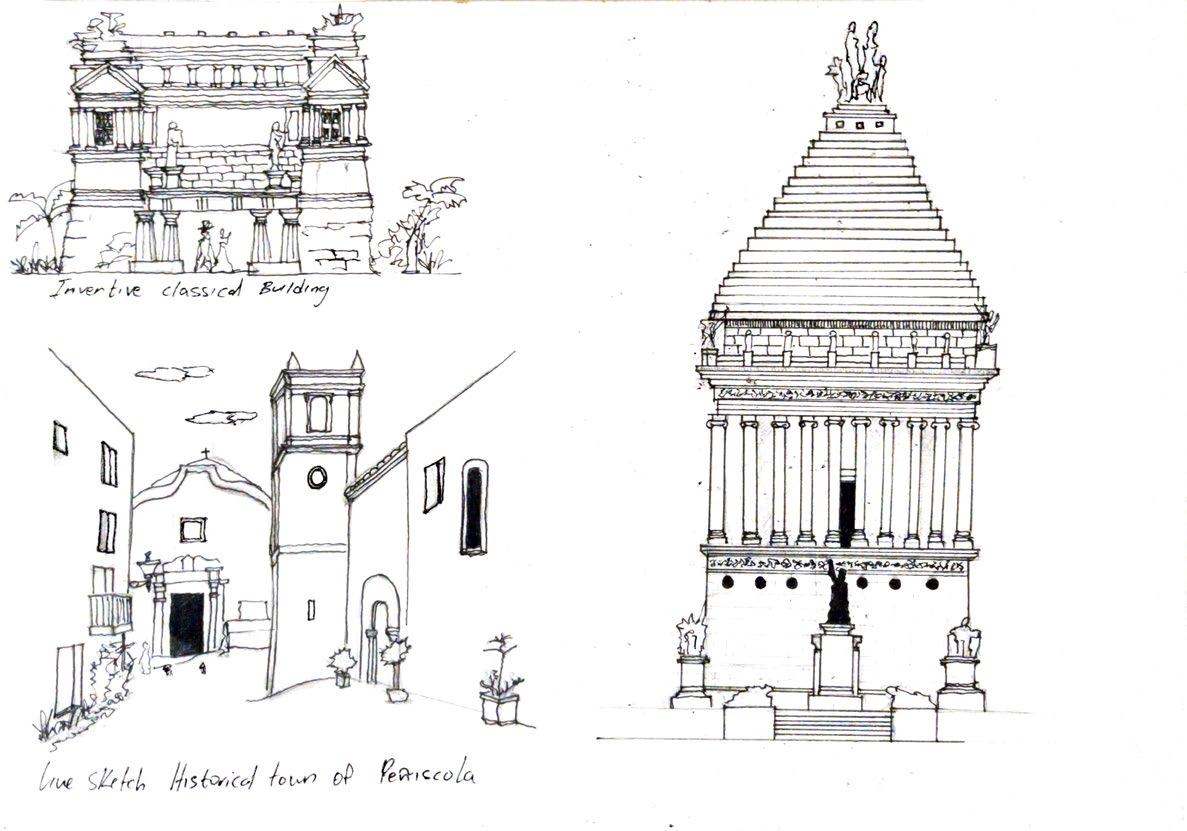
Sketches


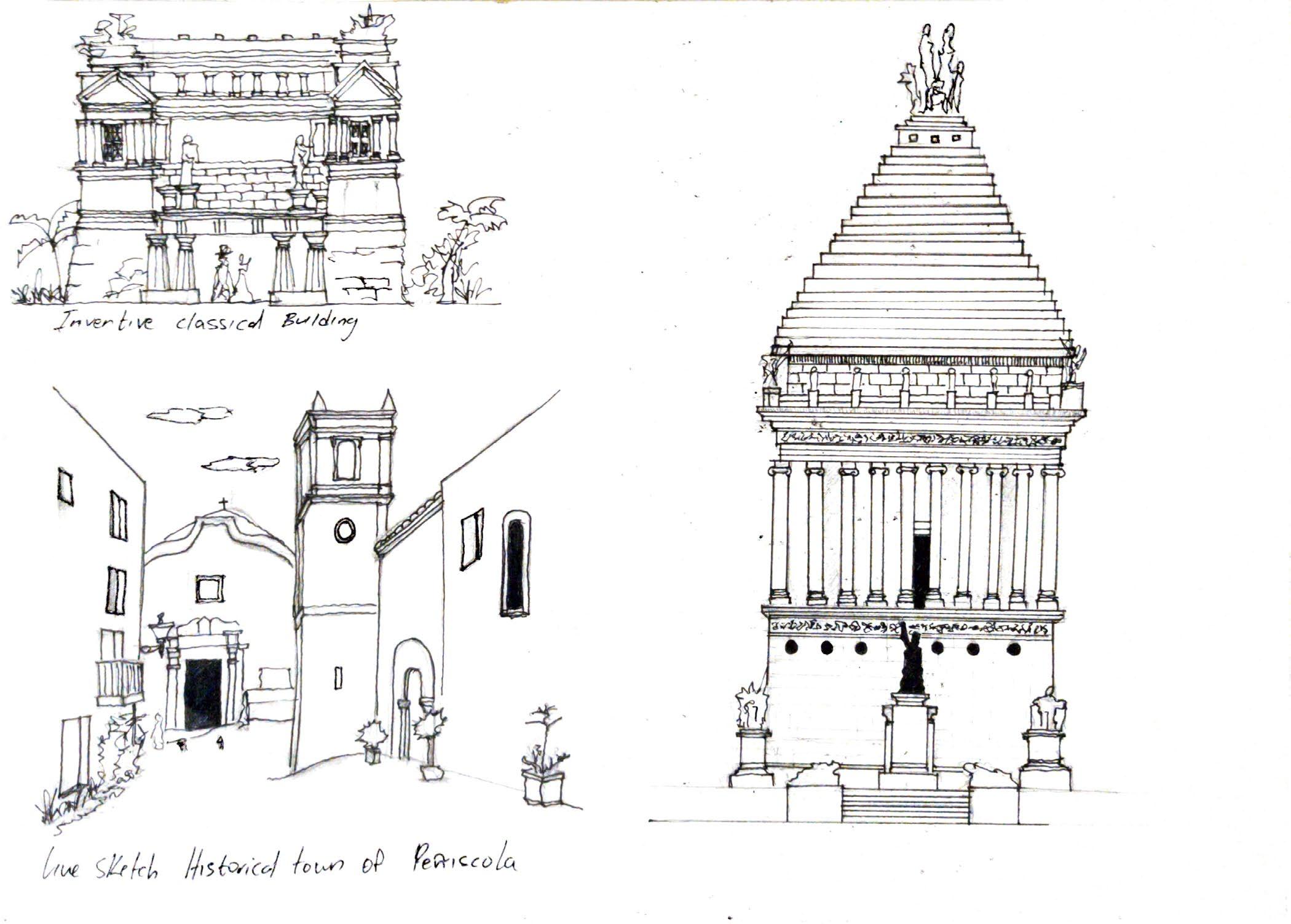
Inventive classical building


36
Sketche of St. Nicholas Market
Victorian Rooms sketch (Edited)
View from St. Nicholas Church Renaissance architecture sketch
Classical monumental building



37
Syracuse Cathedral
Acadamie Nationale de Musique
Digital Sketches



38
Bristol’s library
San Michele Arcangelo
Church of St. María of Belém


39
Renders
Domestika render exercise
House project render




40
Lisbon and Bristol Photography




41
Thank you for reading!
42
+34663480237 luismend10a@yahoo.es
Valencia,
+447403695043
Bristol, United Kingdom
Spain Linkedin: Luis Antonio Mendez





























































































































































































 Alvaro Siza Bouca Social Hosing
Peter Barber Architects Brick Terrace housing
Alvaro Siza Bouca Social Hosing
Peter Barber Architects Brick Terrace housing









































