

Dragan Vjestica 20.09.2012.



Dragan Vjestica 20.09.2012.

o Company Carlsberg
o Standard Reports
o Accounting Principles
o Production overview
o Standard COGS – Elements
o Standard COGS - Budget Costing


-Founded 1847. in Copenhagen, Denmark by J.C. Jacobsen
-Name: by son of founder “Carl” and “berg”
-Have production in 45 countries
-“Pivara Celarevo” founded by Lazar Dundjerski in 1892.
-After II world war becomes government property
-From 1975. till 1980. bigger investments
-Cooperation with company
-In September 2003. majority of shares buys company Carlsberg Breweries A/S
-Started high investments in all parts of the business but mainly in production

-Be a part of the




Product Costing is method of calculating costs of goods sold per product unit based on allocation of total production expenses.
Product Costing gives the possibility to understand product profitability
Standard Costs of Goods Sold (COGS) is budgeted production costs per unit product multiplied by actual volume. Standard COGS is reference for further analyze of COS.
Cost of Sales (COS) is actual costs of producing and purchasing goods or services. It is usually presented in the form:


•A standard cost per SKU must be developed once a year as part of the budget process
• Product cost standards should only be changed once a year

•Approved budget assumptions are used for product costing
• E.g. purchasing prices, line efficiencies, manning, std. losses
•Product cost are recorded as standard costs in actual booking
• Production variances to this standard are recorded (material variances, usage variances labour, machine variances capacity variances and support variances)
•Cost of Sales in Profit & Loss statement is related to sales volume, except for variances which are related to production volume
2. Full cost Principle
• Product costs include cost of support functions (IPO) The five Accounting Principles

• Full cost means that
•All production expenses are allocated to each single unit produced
•The products absorb all budgeted production expenses
3. Indirect Production overhead (IPO)
• Product costs are used for inventory valuation
The five Accounting Principles

4. Practical capacity
• Depreciation costs reflect capacity costs
• Capacity is by definition 8760 hours (24x365)
• Products are only charged for the capacity they actually use, including planned stops and changeover.
• Cost of idle capacity is not absorbed by products
5. Capitalization of returnable bottles & crates
• Returnable bottles and crates (B&C) are considered fixed assets and depreciated over useful lifetime.








PRODUCT RELATED COST PROCESS RELATED COST

RAW MATERIALS
(BOM & COST CENTER)
PACKAGING MATERIALS
(BOM & COST CENTER)
UTILITIES
(VARIABLE & FIXED COSTS)
CONSUMABLES
(VARIABLE COSTS)
LABOUR (VARIABLE & FIXED COSTS)
MAINTENANCE MACHINE
(VARIABLE & FIXED COSTS)
COST OF PRODUCT
COSTS)
COSTS)
Example: Bill of Material for Lav 05L
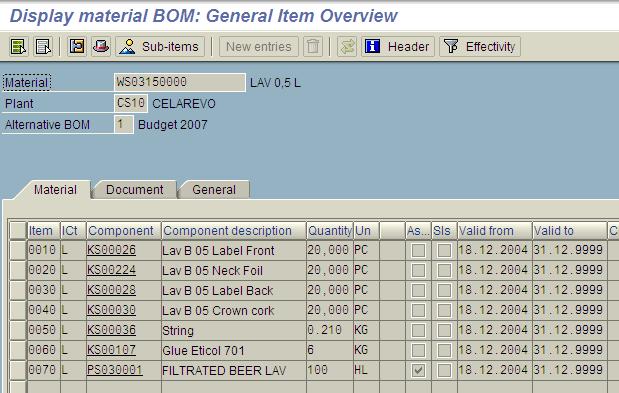

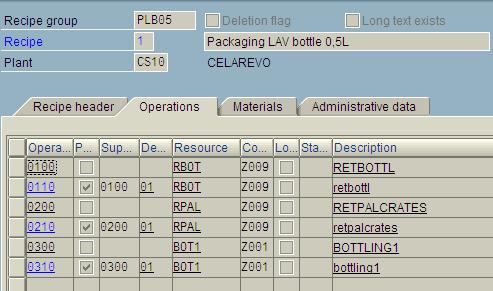

Connecting production resources with materials from BOM :
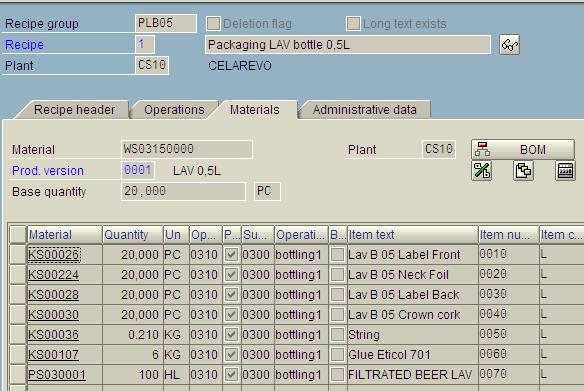
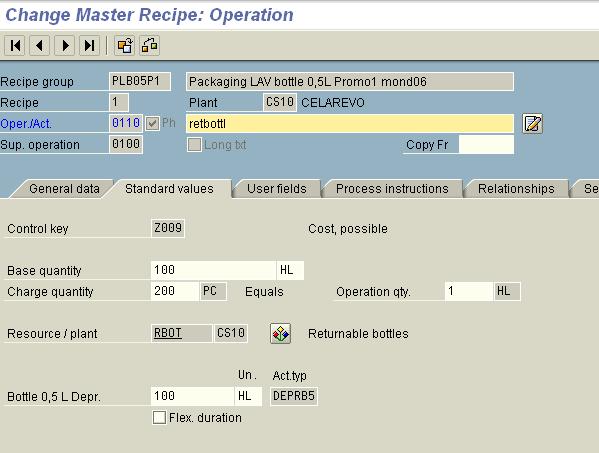

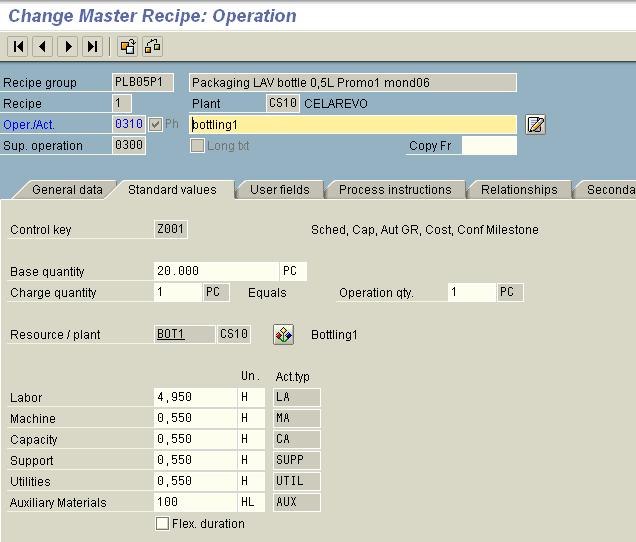


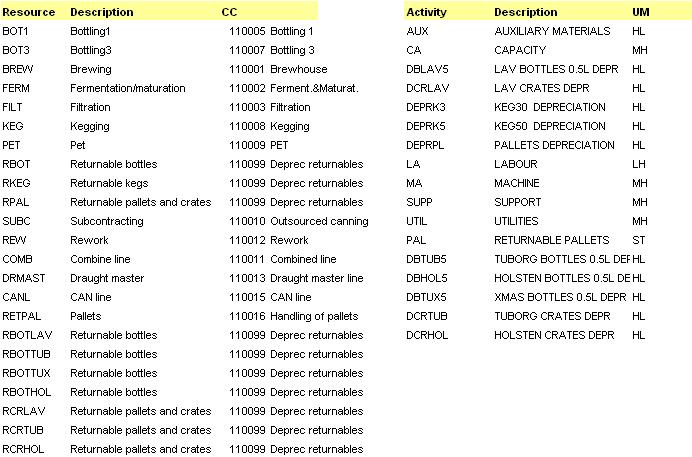

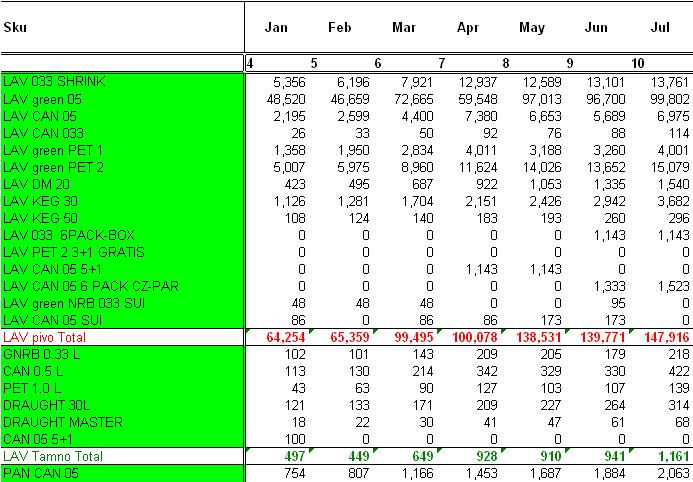

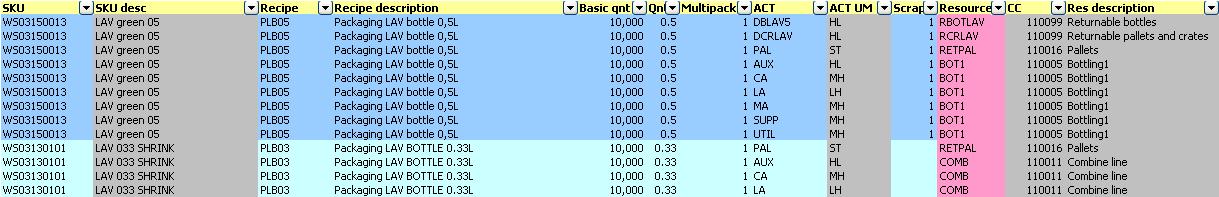
Example: Quantities of activities
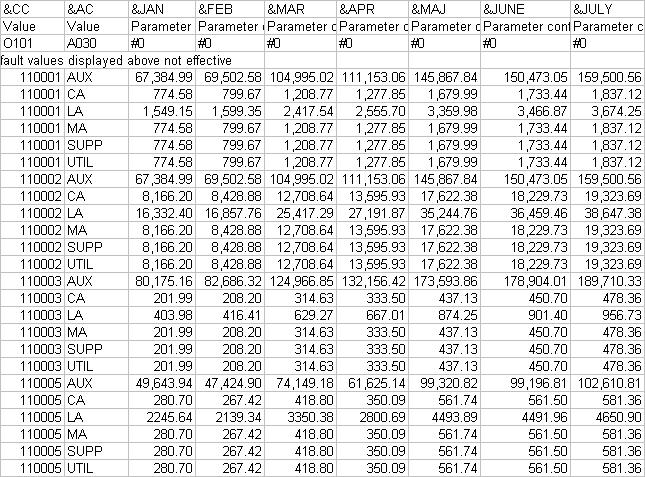

Cost allocation cycles

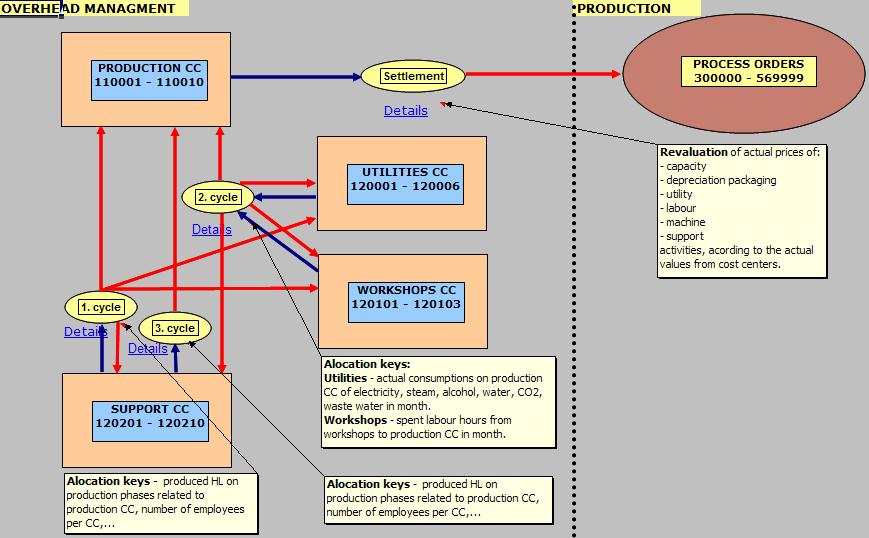


Product costing:
1. Prices of MATERIALS
– Raw materials
– Packaging materials
– TG (trading good)
2. BOM
– SFP (semi finished products)
– FP (finished products)
3. MASTER RECIEPE
– Resursi
– Sati rada
4. CC BUDGET
– Fiksni troškovi
– Varijabilni troškovi (Output, Qnt, KP06_VAR)
5. ALLOCATION KEYS
– Utillities (Output, Qnt(fix,var))
– Mechanical workshop (Output, Qnt(fix,var))
– Electrical workshop (Output, Qnt(fix,var))
6. CAPACITY
6. a) Enter Statistical Key Figure FTE
7. ALLOCATIONS
8. PC RUN



