Key Stage 2 Curriculum Year 4

(English, Maths and Topic)

Our Vision:
To be the happiest community empowering every individual to achieve outstanding growth.
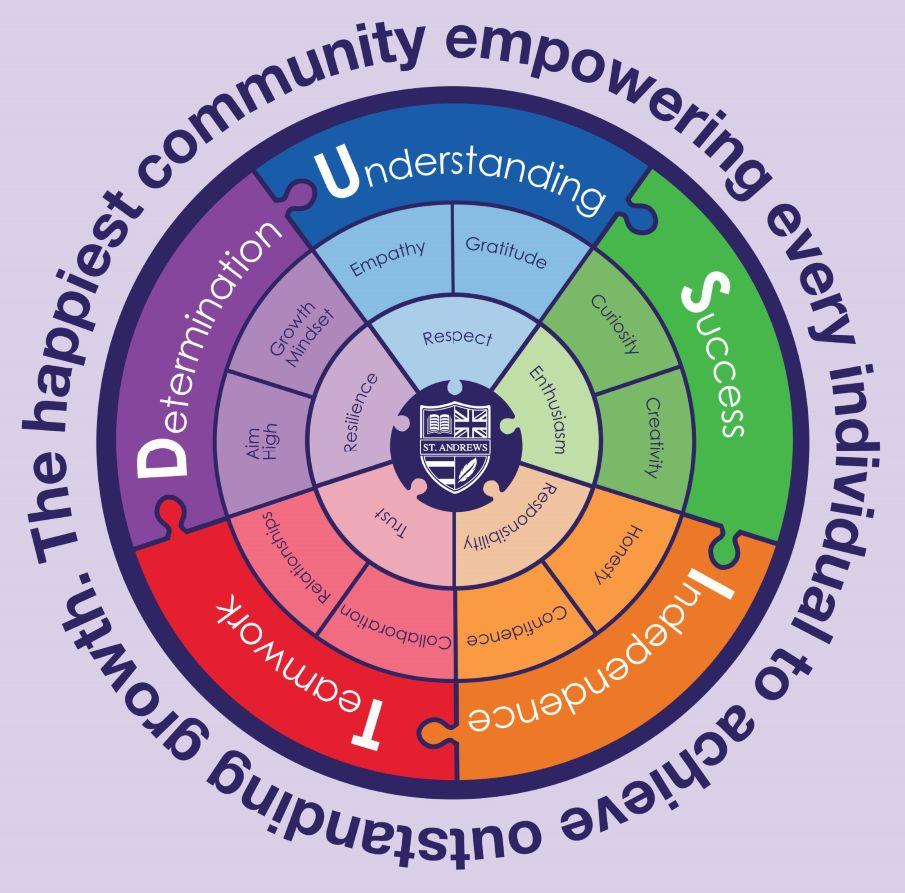
Our Values:
Aside from our academic curriculum, we are dedicated to supporting our pupils in becoming globally responsible citizens Our ‘Dusit Values’ (Determination, Understanding, Success, IndependenceandTeamwork) are central to our commitment to ‘character education’, as these aim to give our pupils an understanding of global issues, whilst encouraging and empowering them to take action and promote positive change.

An English Curriculum in an International Context

Our curriculum, (based on the British National Curriculum) encompasses a rich blend of academic skills and rigor, whilst skillfully weaving in exciting opportunities for character and outdoor education. We believe that putting a spotlight on pupil wellbeing, community projects and sustainability, gives our students all the necessary tools to embrace this rapidly changing world. Pupils are encouraged to become ‘21st century learners’, as we put a great deal of emphasis on creativity, collaboration, communication and critical thinking. We ensure that students get the chance to see the impact of their efforts come to life, through meaningful, motivating project-based learning. Our curriculum is carefully designed and regularly audited, to make sure that pupils are active learners, working on solving genuine, real problems and becoming agents of positive change.

KS2 Year 4 Timings

In Key Stage 2, pupils study the majority of their lessons with their class teacher There are also a range of specialist lessons (highlighted below) which are delivered by our specialist teaching team.
There are 30 periods of 50 minutes (or equivalent) a week. Children in Key Stage 2 study the following:
English 5 periods a week Maths 5 periods a week Guided Reading 20 minutes daily Project-based learning 4 periods a week Thai language & Cultural studies 3 periods a week World Languages (Mandarin/French/German/Extra Thai) 2 periods a week Science 2 periods a week PSHE (Personal/Social/Health education) 1 period a week Computing 1 period a week Art 1 period a week Spelling 1 period a week Library 1 period a week Music 1 period a week PE (Physical Education) 1 period a week Swimming 1 period a week
In English, we adapt the National Curriculum for England to suit our international context From Years 1-6, we focus on teaching the four main areas of English: reading, writing, speaking and listening.


At Dusit, we recognise that the skill of reading is required to access all areas of the curriculum, therefore a passion and love for reading is something we strive to instil in all our pupils We use carefully selected, high-quality texts to plan and deliver our lessons. This helps to expand our children’s vocabulary and deepen their understanding of the mechanics of the English language. Our chosen texts provide an excellent scaffold for all children to access, encouraging them to view themselves as aspiring authors.
English is often also embedded in our project-based learning, as this approach creates many opportunities for our children to write for a purpose, using an engaging and challenging stimulus.
English
➤ Year 4 English Progression of Skills
Writing:
● Produce thoughtful and considered writing (uses simple explanation, opinion, justification and deduction)
● Use a range of styles and genres confidently and independently
● Organise ideas appropriately for both purpose and reader
● Develop ideas in creative and interesting ways

● Select interesting strategies to move a piece of writing forward
● Write in a lively and coherent style
● Select from a range of known ambitious/adventurous vocabulary for a purpose, with some words being particularly well chosen
● Use links to show time and cause
● Use more sophisticated connectives
● Use paragraphs, although they may not always be accurate
● Use or attempt grammatically complex structures
● Use a wide range of punctuation mainly accurately; full stop and capital letters, question mark, exclamation mark, comma, apostrophe, inverted comma
● Open sentences in a wide range of ways for interest and impact
● Use nouns, pronouns and tenses accurately and consistently throughout Advise assertively, although not confrontationally, in factual writing
● Spell unfamiliar regular polysyllabic words accurately and most of the Year 4 High Frequency words and the Year 4 words in the National Curriculum.
PunctuationandGrammar:
Sentence:
● Use long sentences to enhance description or information
● Use short sentences to move events on quickly
● Start with a simile
● Use simple / embellished simple sentences securely
● Use compound sentences (coordination) using coordinating conjunction and / or / but / so / for / nor / yet (coordinating conjunctions) securely
● Develop complex sentences: (subordination)
● Main and subordinate clauses with range of subordinating conjunctions
● Use ‘ed’ clauses as starters Use expanded -‘ing’ clauses as starters
● Drop in –‘ing’ clause
● Use sentences of 3 for action
● Use repetition to persuade
● Use dialogue - verb + adverb Make appropriate choices of pronoun or noun within a sentence to avoid ambiguity and repetition.
Word:
● Use prepositions at underneath since towards beneath beyond conditionalscould, should, would

● Use comparative and superlative adjectives
● Use proper nouns refers to a particular person or thing
● Recognise the grammatical difference between plural and possessive –s
● Use standard English forms for verb inflections instead of local spoken forms (e g we were instead of we was, or I did instead of I done)
Punctuation:
● Use commas to mark clauses and to mark off fronted adverbials
● Use full punctuation for direct speech: each new speaker on a new line
● Use commas between direct speech and reporting clause
● Use apostrophes to mark singular and plural possession.
Reading:
● Prepare poems and play scripts to read aloud and to perform, showing understanding through intonation, tone, volume and action
● Recognise some different forms of poetry
● Check that the text makes sense to them, discussing their understanding and explaining the meaning of words in context
● Ask questions to improve their understanding of a text
● Identify main ideas drawn from more than one paragraph and summarising these.
● Draw inferences such as inferring characters’ feelings, thoughts and motives from their actions.
● Justify inferences with evidence.
● Predict what might happen from details stated and implied.
● Discuss words and phrases that capture the reader’s interest and imagination Identify how language, structure, and presentation contribute to meaning.
● Participate in discussion about both books that are read to them and those they can read for themselves, taking turns and listening to what others say
● Retrieve and record information from non fiction
SpeakingandListening:
(Thesestatementsapplytoallyears. Thecontentshouldbetaughtatalevelappropriatetotheageofthechildren. Children shouldbuildontheorallanguageskillsthathavebeentaughtinprecedingyears)
● Listen and respond appropriately to adults and their peers

● Ask relevant questions to extend their understanding and knowledge
● Ask relevant strategies to build their vocabulary.
● Articulate and justify answers, arguments and opinions.
● Give well-structured descriptions, explanations and narratives for different purposes, including for expressing feelings.
● Maintain attention and participate actively in collaborative conversations, staying on topic and initiating and responding to comments.
● Use spoken language to develop understanding through speculating, hypothesising, imagining and exploring ideas
● Speak audibly and fluently with an increasing command of Standard English Participate in discussions, presentations, performances, role play/improvisations and debates
● Gain, maintain and monitor the interest of the listener(s)
● Consider and evaluate different viewpoints, attending to and building on the contributions of others.
● Select and use appropriate registers for effective communication.
Maths
At Dusit, we aim to provide a depth of learning that enables all children to develop a full conceptual understanding of Maths, rather than to merely memorise abstract solutions.

We follow the English National Curriculum, but have adapted it to the needs of our children, providing greater opportunities for mastery We understand that children have different abilities, but instead of driving the more able forward, with a fleeting abstract knowledge, we encourage them to look deeper. We provide a variety of challenges labelled as ‘tricky, trickierandtrickiest ’ , in order to make sure that each child is working at an appropriate level of challenge. Our teachers strive to create investigators, always seeking to extend their understanding
We want our pupils to enjoy the experience of acquiring new number concepts, and realise that It is not about how quickly they get there, but the depth of understanding they experience along the way.

➤ Year 4 Maths Progression of Skills
Numberandplacevalue:
● Count in multiples of 6, 7, 9, 25 and 1000
● Find 1000 more or less than a given number
● Count backwards through zero to include negative numbers

● Recognise the place value of each digit in a four-digit number (thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones)
● Order and compare numbers beyond 1000
● Identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations Round any number to the nearest 10, 100 or 1000
● Solve number and practical problems that involve all of the above and with increasingly large positive numbers
● Read Roman numerals to 100 (I to C) and know that over time, the numeral system
Addition, Subtraction, MultiplicationandDivision:
● Add and subtract numbers with up to 4 digits using the formal written methods of Columnar addition and subtraction where appropriate
● Estimate and use inverse operations to check answers to a calculation
● Solve addition and subtraction two-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why.
MultiplicationandDivision:
● Recall multiplication and division facts for multiplication tables up to 12 × 12
● Use place value, known and derived facts to multiply and divide mentally, including: multiplying by 0 and 1; dividing by 1; multiplying together three numbers
● Recognise and use factor pairs and commutativity in mental calculations
● Multiply two-digit and three-digit numbers by a one-digit number using formal written layout
● Solve problems involving multiplying and adding, including using the distributive law to multiply two digit numbers by one digit, integer scaling problems and harder
● Correspondence problems such as n objects are connected to m objects.
Fractions:
● Recognise and show, using diagrams, families of common equivalent fractions
● Count up and down in hundredths; recognise that hundredths arise when dividing an object by one hundred and dividing tenths by ten

● Solve problems involving increasingly harder fractions to calculate quantities, and fractions to divide quantities, including non-unit fractions where the answer is a whole number
● Add and subtract fractions with the same denominator
● Recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths or hundredths Recognise and write decimal equivalents ¼, ½, and ¾.
● Find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as ones, tenths and hundredths
● Round decimals with one decimal place to the nearest whole number
● Compare numbers with the same number of decimal places up to two decimal places
● Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to two decimal places
Measurement:
● Convert between different units of measure [for example, kilometre to metre; hour to minute]
● Measure and calculate the perimeter of a rectilinear figure (including squares) in centimetres and metres
● Find the area of rectilinear shapes by counting squares
● Estimate, compare and calculate different measures, including money in pounds and pence
● Read, write and convert time between analogue and digital 12- and 24-hour clocks
● Solve problems involving converting from hours to minutes; minutes to seconds; years to months; weeks to days
Geometry:
● Compare and classify geometric shapes, including quadrilaterals and triangles, based on their properties and sizes
● Identify acute and obtuse angles and compare and order angles up to two right angles by size
● Identify lines of symmetry in 2-D shapes presented in different orientations
● Complete a simple symmetric figure with respect to a specific line of symmetry
● Know angles are measured in degrees: estimate and compare acute, obtuse and reflex angles.
PositionandDirection:
● Describe positions on a 2-D grid as coordinates in the first quadrant
● Describe movements between positions as translations of a given unit to the left/right and up/down

● Plot specified points and draw sides to complete a given polygon.
Statistics:
● Interpret and present discrete and continuous data using appropriate graphical methods, including bar charts and time graphs.
● Solve comparison, sum and difference problems using information presented in bar charts, pictograms, tables and other graphs.
Topic
At Dusit, we believe in a creative curriculum where the skills below are interwoven between subjects Each term children's learning will be framed by a theme or topic and they will then get to apply the skills below through cross curricular activities where the child is at the centre of their own learning journey.
➤ Year 4 Topic - Progression of Skills
Identify key features and events of the time studied.
Place a variety of events from the period of time I am studying on a timeline
Use vocabulary appropriate for the time period and date particular events within that period.
Use evidence to reconstruct life in the time studied.
Compare and contrast one aspect of a life to the same aspect in another person
Suggest reasons for, and results of, the main events and changes from the past.
Identify physical and human features of an area and understand the difference.
Compare the features of an area and understand that a place can have both similar and differing characteristics.
Use a variety of resources (extend to include aerial photographs and satellite images) as sources of information.
Identify significant features and environments on aerial photographs and recognise the same area on a map
Collect and record information with some aid.

Analyse a variety of evidence and draw simple conclusions.
Begin to understand how a change might affect the lives of people differently
Respect that people are different and develop tolerance for other people's views and beliefs.
Recognise that there are reasons why people in the past acted as they did
Plan for and undertake unstructured but supervised exploration of local areas and natural places followed by reflection and observations.
Move safely outdoors in non controlled environments through pre-planning and hazard identification
Skills Coverage - History Skills Coverage – Geography Environmental Education Coverage
Offer a reasonable explanation for events studied
Begin to understand that effects from one event can have an effect on future events
Communicate knowledge and understanding through; discussion, ICT, drama.

Use a variety of sources from different media to find evidence about a period of time.
Choose relevant material to present a picture of one aspect of life in time past.
Begin to understand the usefulness of some sources.
Recall and select historical information
Identify settlements and look for reasons people may have decided to settle there (defense, water, resources, food).
Use and understand some geographical vocabulary (latitude, longitude, equator, tropic of cancer, tropic of capricorn)
Locate countries and capital cities using a globe or atlas
Draw maps from aerial photographs or satellite images using a simple key and symbols.
Begin to use an 8-point compass when discussing direction verbally.
Use letter/number coordinates confidently to locate features on a map.
Make a simple scale drawing of an area.
Use a variety of information to respond to geographical questions (point, evidence).
Begin to take on leadership roles during an outdoor experience and learn that the decision of a group may not be the same as their own.
Analyse the human impact of a local environment and ways to minimise this
Identify how some changes impact on the environment and how to teach others about this
Plan for and/or participate in long term clean-up and conservation activities and begin to monitor the impact they have.
Show respect for flora and fauna by caring for or cultivating a living thing themselves
Identify basic elements of ecosystems in a local environment (flower, tree, grass, bird, insects) using age appropriate scientific vocabulary. Overall, begin to develop an understanding of responsibility for their world and start to think of ways to make things better
Parent Involvement


In addition to the exciting events that take place throughout the year to enrich our curriculum such as International Week, Book Week, Science Week and many more, parents will also be invited into school regularly to see what the children have been learning, to hear presentations and celebrate their child’s work
We will also be holding half-termly #keepingupwiththekids workshops for parents so that they can be kept up to speed on how they can best support their child’s learning journey Parents are also encouraged to volunteer and read with students in the library during the week.








