1 minute read
project 1.4 - experience deviance
r e t a i l a c t i v i t y i n r u r a l a r e a s impacts on food distribution food prices
Climate Change A N D T H E Food System
Advertisement
rising temperatures heat waves exports (imports) impacts on trade impacts on food security threats f rural oumigration debt food yields job loses food prices farm incomes disruptions to food processing and retail

Drought Flooding Cyclones
threats to local s e c u r i t y inflation c h a n g e d h o m e purchasing patterns regional political instability
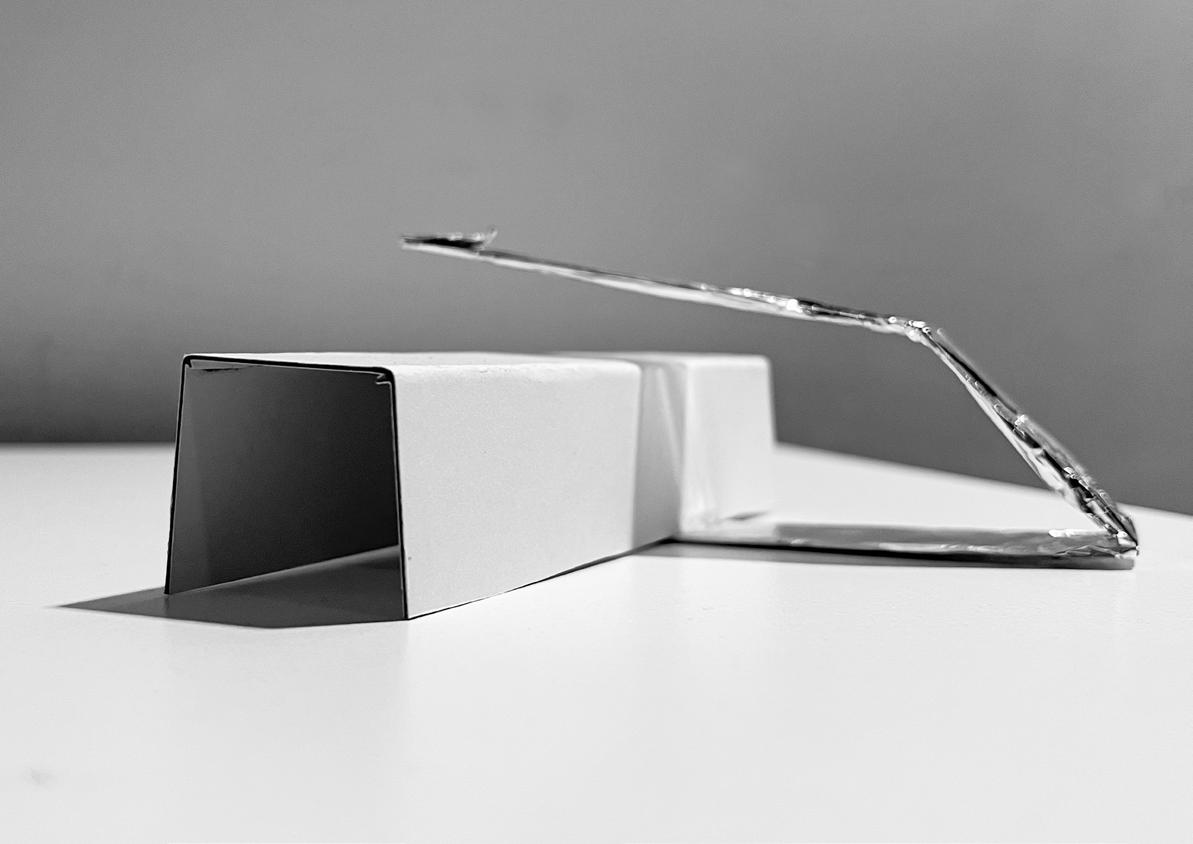
Why Hydroponics?
Climate change brings unpredictable weather patterns, including droughts, floods, and extreme temperatures, which can negatively impact traditional agriculture. Hydroponic systems, being indoor and controlled, are less susceptible to weather fluctuations and climate risks. Crops can be grown consistently throughout the year, independent of external climate conditions, ensuring a more reliable food supply. They minimize the use of chemical fertilizers, herbicides, and pesticides, as the closed-loop system reduces nutrient and water runoff. This decreases the potential for soil and water pollution, protecting ecosystems and human health. Additionally, hydroponics uses less land, reducing the need for excessive land clearing and soil degradation.
By implementing hydroponics in our design we understand that cities now are with limited agricultural capabilities, and encourage hydroponics so communities can have access to fresh, nutritious produce grown locally. This reduces the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation of food and supports local economies.
Grow