









Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder that causes severe damage to the lungs, digestive system, and other organs in the body It results from mutations in the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) gene, which is responsible for producing the CFTR protein.

The CFTR protein is a complex chloride channel and regulatory protein found in all exocrine tissues Disrupted transport of chloride and other ions, such as sodium and bicarbonate, leads to thick, viscous secretions in the lungs, pancreas, liver, intestines, and reproductive tract as well as increased salt content in sweat gland secretions
The signs and symptoms of CF can be divided into four categories:

SINO-PULMONARY MANIFESTATIONS
Chronic cough, sputum production, persistent infections, chest tightness, airway obstruction (wheezing) and sinus drainage.

GASTROINTESTINAL MANIFESTATIONS
Abdominal pain, steatorrhea, bowel obstruction, chronic liver disease, pancreatitis and pancreatic insufficiency
NUTRITIONAL PROBLEMS
Fat-soluble vitamin deficiency (vitamins A, D, E, K), chronic metabolic alkalosis, hypoproteinemia and failure to grow in height and weight.
MALE UROGENITAL ABNORMALITIES
Azoospermia and congenital bilateral absence of vas deferens.

Include but are not limited to:

Malnutrition
Diabetes and Pancreatitis
Renal or hepatic failure
Both of the below criteria should be met to diagnose CF:
One criteria from the below
Clinical symptoms consistent with CF in at least one organ system (e g , chronic pulmonary disease, chronic sinusitis, characteristic gastrointestinal and nutritional abnormalities, salt loss syndromes, obstructive azoospermia)



A positive newborn screen
Having a sibling with CF
In addition to another critera from the below nasal epithelium.
Any of the below evidence of CFTR dysfunction: Elevated sweat chloride ≥60mmol/L Presence of two mutations in the CFTR gene, one from each parental allele
Abnormal NPD which measures abnormalities in ion transport across the
Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome
heart failure
Bronchiectasis, pneumothorax, hemoptysis, infections
Cancers of the digestive tract
Urinary incontinence
Infertility
Mental health problems such as depression and anxiety

Intervention
Indication / Timing Comments
CFTR Modulators
Most patients, depending on genotype and age.
The CFTR modulator and strength of recommendation depend on the genotype.
Inhaled DNase
2.5 mg daily or twice daily
Inhaled Hypertonic Saline
Airway Clearance Physiotherapy (Chest Physiotherapy)
Vaccinations
Palivizumab
Infection Control Measures
Inhaled Beta-2 Adrenergic Receptor Agonist
Short acting: Albuterol
Long acting: Salmeterol
Recommended for most children and adults with CF.

DNase generally given once daily and hypertonic saline twice daily Administer a shortacting bronchodilator before each treatment.
Use inhaled DNase for all children 2 years and older regardless of symptoms. Use hypertonic saline for all children 2 years and older. Regimen should be individualized.
All patients who produce sputum, twice daily.

All patients should receive:
Annual influenza vaccine
Pneumococcal vaccine, with PCV13 and PPSV23, depending on age and prior immunization status
All other routine childhood vaccines COVID-19 vaccines
More evidence required.
Contact precautions, physical separation of patients, hand hygiene, use of masks by patients.
All patients, before each dose of inhaled antibiotics, DNase, hypertonic saline, or airway clearance therapy session
As a rescue medication for acute symptoms, in patients with signs or symptoms of airway hyperresponsiveness.
High-dose Ibuprofen (Maximum 3200mg/day)
Inhaled Glucocorticoids
Indication / Timing Comments
In children 6 to 17 years with good lung function (FEV1 >60%)

In clinical practice, this is not commonly used in the United States.
Patients with definite signs and symptoms of asthma.

ACUTE EXACERBATIONS
Not recommended in severe lung function abnormalities
Requires pharmacokinetic studies to ensure proper dosing and monitoring for adverse effects (gastrointestinal bleeding, renal impairment).
Concerns about adverse effects especially on growth.
The most common pathogen is Pseudomonas aeruginosa, but others may be involved as well. Antimicrobial therapy is selected based on both the pathogen and susceptibility results.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Penicillin: Piperacillin/Tazobactam
Cephalosporins: Ceftazidime, Cefepime
Carbapenems: Imipenem/Cilastatin, Meropenem
Fluoroquinolones: Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin

Aminoglycosides: Gentamicin, Tobramycin, Amikacin
Aztreonam
CHRONIC SUPPRESSIVE ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY
CF patients are at a constant risk of infection even after receiving treatment for acute infections Options for chronic suppressive therapy include:
Inhaled Tobramycin or inhaled Aztreonam

Chronic oral antibiotic therapy (e.g., with Azithromycin)
Staphylococcus aureus

Nafcillin, oxacillin or cephalosporins
If Methicillin-resistant (MRSA): Linezolid, Vancomycin
Spina bifida is a congenital neural tube defect that affects the spine and spinal cord. It is a rare condition with a prevalence of 0.7 cases per 1,000 live births in the United States, with similar rates reported globally. In Lebanon, the incidence rate is lower, with an estimated 0.2 cases per 1,000 live births.
There are three main types of Spina Bifida:

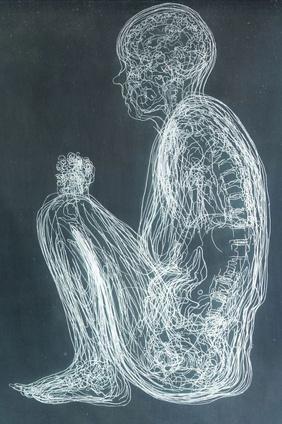
Spina bifida occulta is the mildest form. It occurs when the spinal column is not fully closed but the spinal cord and nerves are normal.
Meningocele occurs when when the spinal membrane pushes out through an opening in the spine, but the spinal cord and nerves are not affected
Myelomeningocele is the most severe form and can lead to paralysis of the legs and the bladder as well as bowel control problems and learning disabilities. It occurs when the spinal cord and nerves push out through an opening in the spine.
Difficulty walking
Bladder and bowel control problems
Lower back pain
Muscle weakness

Difficulty with fine motor skills
In severe cases, it can cause hydrocephalus, which can lead to intellectual disability, developmental delays, and other neurological problems.
Can be made through prenatal
Ultrasonography

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Amniocentesis
In order to prevent spina bifida, pregnant women should take 400 to 800 micrograms of folic acid daily before conception and during the first trimester of pregnancy. This has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of neural tube defects, including spina bifida.


Typically the first line treatment modality for patients with myelomeningocele


The goal of surgery is to repair the spinal cord and close the opening in the spine to prevent further damage to the spinal cord and prevent infection.
Helps improve mobility and prevent muscle wasting
Physical therapists can also help individuals develop strength, coordination, and balance.
Can help individuals with spina bifida improve their daily living skills, such as dressing and grooming.
Occupational therapists can also help these individuals find adaptive equipment to make daily tasks easier
Pain relievers: Including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and naproxen.
Muscle relaxants: Baclofen and tizanidine are commonly used to manage muscle spasms and improve mobility These medications work by blocking nerve impulses that cause muscle spasms.
Anticonvulsants: Gabapentin and pregabalin can be used to manage neuropathic pain, as well as prevent seizures. They work by stabilizing the electrical activity in the brain to prevent seizures
Medications for bladder control: Oxybutynin, tolterodine, and solifenacin are commonly used to manage bladder dysfunction. They work by blocking the action of acetylcholine, which is a neurotransmitter that causes bladder contractions.
Antidepressants: Duloxetine and amitriptyline are commonly used to manage neuropathic pain and depression
Antibiotics: May be used to treat infections, a common complication in individuals with spina bifida due to impaired mobility and bladder dysfunction.
Antispasmodics: Dantrolene is a muscle relaxant that can be used to manage spasticity. It works by decreasing the release of calcium from muscle cells, leading to relaxation of muscle fibers
In recent years, research has explored the use of botulinum toxin type A (Botox) in the treatment of spasticity in individuals with spina bifida Botox is injected directly into the affected muscles and temporarily blo release of acetylcholine

S i c k l e C e l l S i c k l e C e l l D i s e a s e D i s e a s e
Anemia is a common effect of Sickle Cell Disease, but it can be treated.

Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. In patients with SCD, the hemoglobin is abnormal, which causes red blood cells to become hard and sticky and look like a Cshaped farm tool called a “sickle.” The sickle cells die early, which causes a constant shortage of red blood cells.

Types
HbSS: People who have this form of SCD inherit two genes, one from each parent, that code for hemoglobin “S.” Hemoglobin S is the abnormal form of hemoglobin that causes the red cells to become rigid, and sickle-shaped This is commonly called sickle cell anemia and is usually the most severe form of the disease.
HbSC: People who have this form of SCD inherit a hemoglobin “S” gene from one parent and a gene for a different type of abnormal hemoglobin called “C” from the other parent. This is usually a milder form of SCD.
HbS beta thalassemia: People who have this form of SCD inherit a hemoglobin “S” gene from one parent and a gene for beta thalassemia, another type of hemoglobin abnormality, from the other parent There are two types of beta thalassemia: “ zero ” (HbS beta0) and “plus” (HbS beta+). Those with HbS beta0-thalassemia usually have a severe form of SCD. People with HbS beta+-thalassemia tend to have a milder form of SCD
Causes
SCD is a genetic condition that is present at birth It is inherited when a child receives two genes, one from each parent, that code for abnormal hemoglobin.
Diagnosis
SCD is diagnosed with a simple blood test.
It can also be diagnosed while the baby is in the womb using tests such as chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis to can check for chromosomal or genetic abnormalities
People with sickle cell trait can be found most heavily in areas of the world that have malaria. In fact, the sickle cell trait can protect a person from becoming infected with malaria!


Complications
Stroke
Acute chest syndrome
Pulmonary hypertension
Organ damage
Splenic sequestration
Blindness
Leg ulcers.
Gallstones
Priapism.
Deep vein thrombosis.
Pregnancy complications.
Signs & Symptoms Treatment
Episodes of pain
To prevent some of the complications, patients should Swelling

Drink plenty of water
Avoid getting too hot or cold. Avoid high altitudes. Avoid places or situations with low oxygen levels.
Hydroxyurea (Droxia, Hydrea, Siklos): It may help patients with SCD ages 2 years and older
Hydroxyurea is an antimetabolite used to treat sickle cell anemia crisis.
L-glutamine Oral Powder (Endari): It may help people with SCD ages 5 years and older. Endari works to increase the amount of free glutamine circulating in the blood.
Crizanlizumab (Adakveo): It may help people with SCD ages 16 years and older.
Voxelotor (Oxbryta): It may help people with SCD ages 4 years and older. It is used to prevent the painful and sometimes lethal vaso-occlusive crises associated with SCD


















































 Rita Murr, P3 Writer & Editor
Cyrine Dhainy, P3 Writer
Elena Chalhoub, P2 Writer
Mabelle Rechdan, P2 Writer & Designer
Nour Chidiac, P3 Chairperson Designer & Editor
Amanda Rose Khater, P4 Secretary Writer & Editor
Rita Murr, P3 Writer & Editor
Cyrine Dhainy, P3 Writer
Elena Chalhoub, P2 Writer
Mabelle Rechdan, P2 Writer & Designer
Nour Chidiac, P3 Chairperson Designer & Editor
Amanda Rose Khater, P4 Secretary Writer & Editor





 Nour Adra, P2 Writer
Sarah El Ali, P2 Writer
Thea Maria Nader, P2 Writer
Maria Fadel, P1 Writer
Mahmoud Nassrallah, P2 Writer & Editor
Marc Anlian, P2 Writer
Nour Adra, P2 Writer
Sarah El Ali, P2 Writer
Thea Maria Nader, P2 Writer
Maria Fadel, P1 Writer
Mahmoud Nassrallah, P2 Writer & Editor
Marc Anlian, P2 Writer
 Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia Gravis
