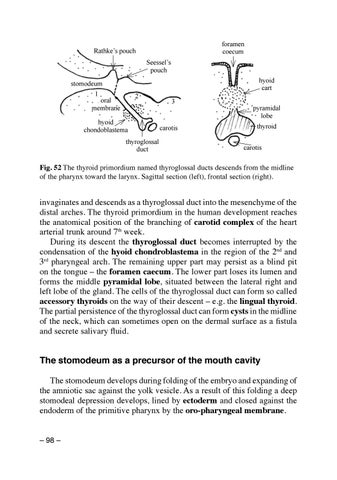
foramen coecum
Rathke’s pouch Seessel’s pouch stomodeum 1 oral membrane
2
hyoid chondoblastema thyroglossal duct
hyoid cart 3
carotis
pyramidal lobe thyroid carotis
Fig. 52 The thyroid primordium named thyroglossal ducts descends from the midline of the pharynx toward the larynx. Sagittal section (left), frontal section (right).
invaginates and descends as a thyroglossal duct into the mesenchyme of the distal arches. The thyroid primordium in the human development reaches the anatomical position of the branching of carotid complex of the heart arterial trunk around 7th week. During its descent the thyroglossal duct becomes interrupted by the condensation of the hyoid chondroblastema in the region of the 2nd and 3rd pharyngeal arch. The remaining upper part may persist as a blind pit on the tongue – the foramen caecum. The lower part loses its lumen and forms the middle pyramidal lobe, situated between the lateral right and left lobe of the gland. The cells of the thyroglossal duct can form so called accessory thyroids on the way of their descent – e.g. the lingual thyroid. The partial persistence of the thyroglossal duct can form cysts in the midline of the neck, which can sometimes open on the dermal surface as a fistula and secrete salivary fluid.
The stomodeum as a precursor of the mouth cavity The stomodeum develops during folding of the embryo and expanding of the amniotic sac against the yolk vesicle. As a result of this folding a deep stomodeal depression develops, lined by ectoderm and closed against the endoderm of the primitive pharynx by the oro-pharyngeal membrane. – 98 –
Ukázka elektronické knihy, UID: KOS257538