





jon@jjstudioarchitecture.co.uk
www.jjstudioarchitecture.co.uk
www.facebook.com/jjstudioarchitecture
www.instagram.com/jjstudioarchitecture/
/www.linkedin.com/company/jon-james-studio-architecture







jon@jjstudioarchitecture.co.uk
www.jjstudioarchitecture.co.uk
www.facebook.com/jjstudioarchitecture
www.instagram.com/jjstudioarchitecture/
/www.linkedin.com/company/jon-james-studio-architecture
Piecing together the jigsaw puzzle to deliver affordable living to our communities.


PREFACE
CREATING HOMES, NOT HOUSING identifies the issues facing affordable housing in the UK, distils 5 principles of good design, and champions context as the golden thread which must run through the design process.
To combat the housing crisis, teams across the UK are working hard to shape a positive built environment. We have been fortunate to work with some inspirational clients and consultants. This has given us the opportunity to see, and learn, how this can be achieved through collaboration.
The document highlights how critical interdisciplinary collaboration is to successfully build quality homes and quality places. The publication aims to be an accessible guide withpracticalresourcestosupportanycontributortotheresidentialbuiltenvironment.
Pg. 04 Setting The Scene
02.
Pg. 05 Who must affordable housing deliver for?
Pg. 06 The Toolkit
Pg. 11 Innovation + Cost Pg. 07 Sustainability + Site Pg. 09 Compliance Pg. 08 Placemaking + Engagement Pg. 10 Quality + Scalability
Pg. 12 Plan
Pg. 13 Section
Pg. 14 Construction Detail
Pg. 15 Visualisation
Pg. 16 Relevant publications
Pg. 17 References
The UK's housing shortage is driven by a combination of factors: slow construction rates, high demand, and rising house prices. In the 2021-2026 Programme for Government, The Welsh government has commited to build 20,000 new low carbon social homes for rent within the next government term. In the first two years, 5,775 homes were delivered towards the target.¹
In England, the “new housing supply is currently lower than the Government’s ambitionof
300,000 new homes per year. Around 233,000 new homesweresuppliedin 2021/22.”²

In 2024, buying a house in the UK has become increasingly unaffordable. Wage growth has not kept pace with these rising property and fuel prices, leading to an affordability gap. This gap is still increasing, for example the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero have found that the fuel poverty gap has increased by 20% from 2022-2023 in England³
The latest figures in Wales suggest the proportion of the country in fuel poverty is relatively stable at 14%.4
As a result, there is a need for access to affordable housing, both rented and owned.
“In 2022-23, 3.5 million households (14%) in England lived in a home that failed to meet the Decent Homes Standard, 2.1millionhouseholds(9%) lived in a home with at least one Category 1 hazard, and 1.0 million households (4%) lived in a homewithdamp.”5
It is clear that a proportion of the existing housing stock is below desired well-being standards and without long term durability.
Over the last decade, UK housing developments have been frequently criticised for their bland and poor design. According to a 2020 audit by Place Alliance and UCL, 75% of new developments in England were deemed "mediocre" or "poor".6 The audit highlighted that these developments often lack character and fail to integrate well with their surroundings, especially in less affluent areas.6
The scientific consensus is that the planet is facing climate breakdown due to global warming, leading to weather extremes and risk to energy, food and the environment.
The UK has pledged to reach Net Zero by 2050.7 Wales has pledged to reach this milestone by 2025.8 According to The National Housing Federation, The construction industry accounts for 25% of the nation’s emissions9 This highlights the scale of the challenge facing the sector to de-carbonise, and the potential to address current global warming trends.
According to the Climate Change Committee, “the directburningoffossilfuels to heat space and water in homes accounted for 13% of the UK’s emissions.”10 Furthermore, The Green Building Council states that for the UK as a whole to meet net zero by 2050, there must be a complete elimination of these emissions from housing.11


ADDRESS FUEL POVERTY
SUSTAINABILITY + SITE
INNOVATION + COST
PLACEMAKING + ENGAGEMENT
PRINCIPLES
QUALITY + SCALABILITY
COMPLIANCE
AIMS
DESIGN RESILIENT AND DESIRABLE

PROMOTE HEALTH AND WELL
OPPORTUNITIES/CONSTRAINTS OF SITE
Identifying value in topography, trees, sight lines, heritage

MAXIMISE FREE PASSIVE GAINS
South facing glazing + shading, thermal mass
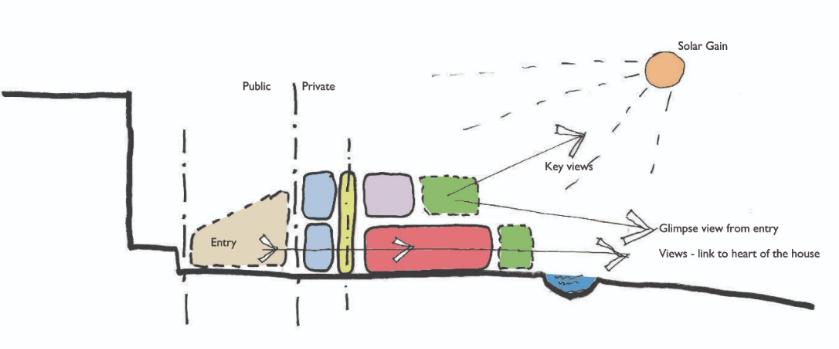
Minimise long term energy losses with thermally efficient envelope





Build with local timber, straw and other low carbon materials and evidence via environmental product declarations.


Reduce energy bills, fossil fuel consumption and flooding


Scientifically proven to promote quality12




COMMUNITY INVOLVEMENT




Regulatory compliance is a legal requirement. This is a non-exhaustive list, care should be taken to ensure compliance with all regulatory requirements.






To achieve the aims set out in this toolkit, best practice, not just regulatory minimums, need to be the benchmark.






The rigour of certification promotes higher quality work throughout the design and build process. Certification also evidences the commitments and values of the housing provider to the wider world.





• Robust materials which are long life and low in embodied carbon.
• Local character
• Meets best practice area set out in statutory requirements
• Optimised but homely layout
• Minimised maintenance
• Locally sourced sustainable materials
• Energy efficiency - Lowering energy bills
• Buildings integrated to landscape,active travel and Highway design
• Modular layouts creating‘kit of parts’ increases buildablity
• Standardised library of house types
• Follow placemaking principles
• House type library flexible to context
• Construction system adaptable to local styles/techniques
• Palette of quality materialsscalar savings.
• Clear visual identity / character












While innovation has a cost, It is clear that the price gap is reducing. For example, a report for the CCC by Currie & Brown and AECOM states that thecostupliftforPH canbebetween4-20%.15
Housing providers should prioritise longterm returns. Innovation’s long term value is key, because system based efficiency produces accelerated delivery, reduced waste, and lowers maintenance costs.


Europe excels in MMC due to investment in prefabrication techniques, streamlined supply chains, and regulatory aid. Key manufacturers state “serial modular construction is a decisive factor in the fight against the housing shortage”.16
Due to the scale of house building, and how disjointed and antiquated the UK system is, the affordable housing sector has the potential to maximise the value and cost savings associated with MMC.17


SUSTAINABILITY + SITE CONTEXT
PLACEMAKING + ENGAGEMENT
COMPLIANCE QUALITY + SCALABILITY
INNOVATION + COST
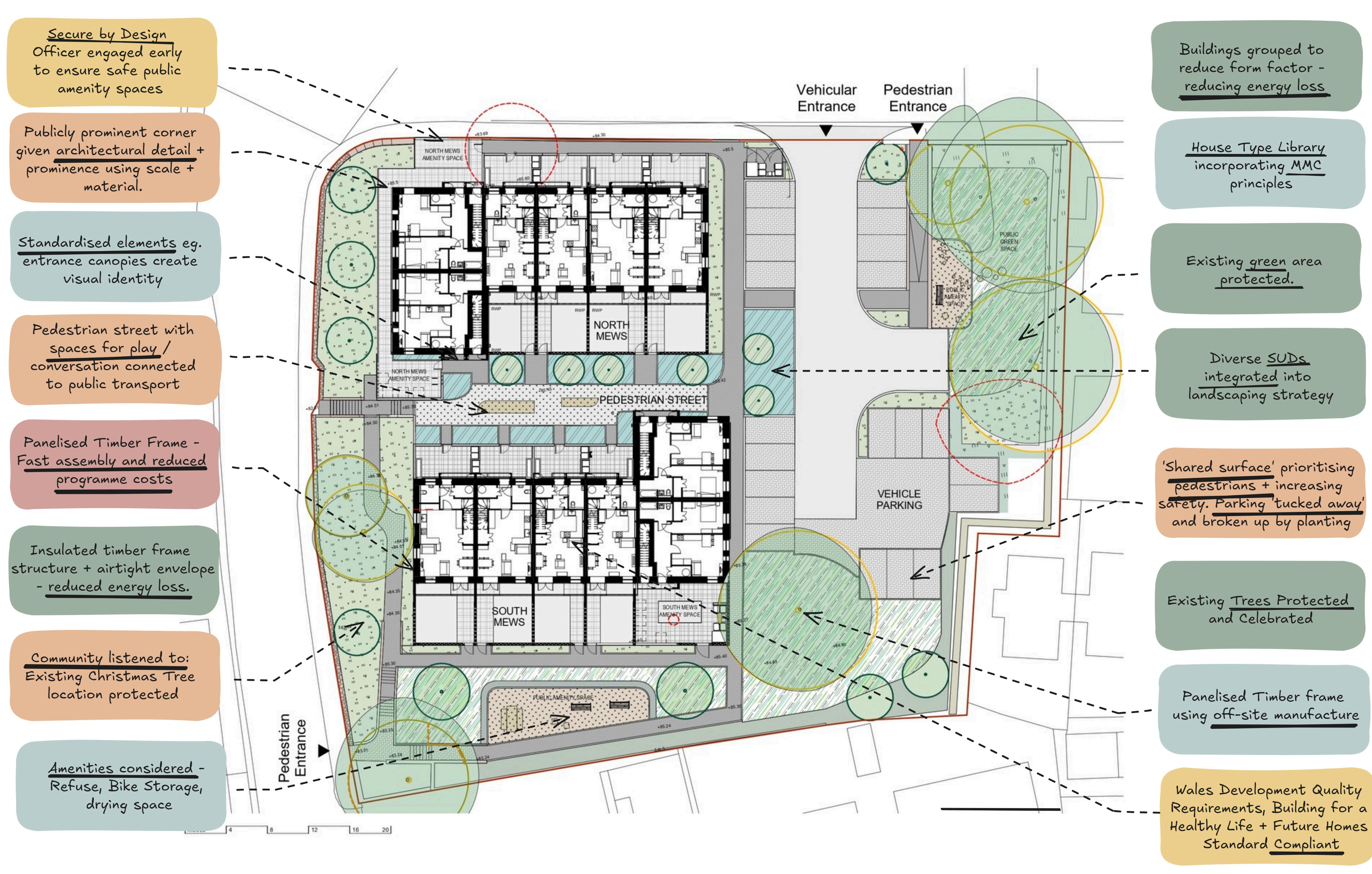

SUSTAINABILITY + SITE CONTEXT
PLACEMAKING + ENGAGEMENT
COMPLIANCE QUALITY + SCALABILITY
INNOVATION + COST
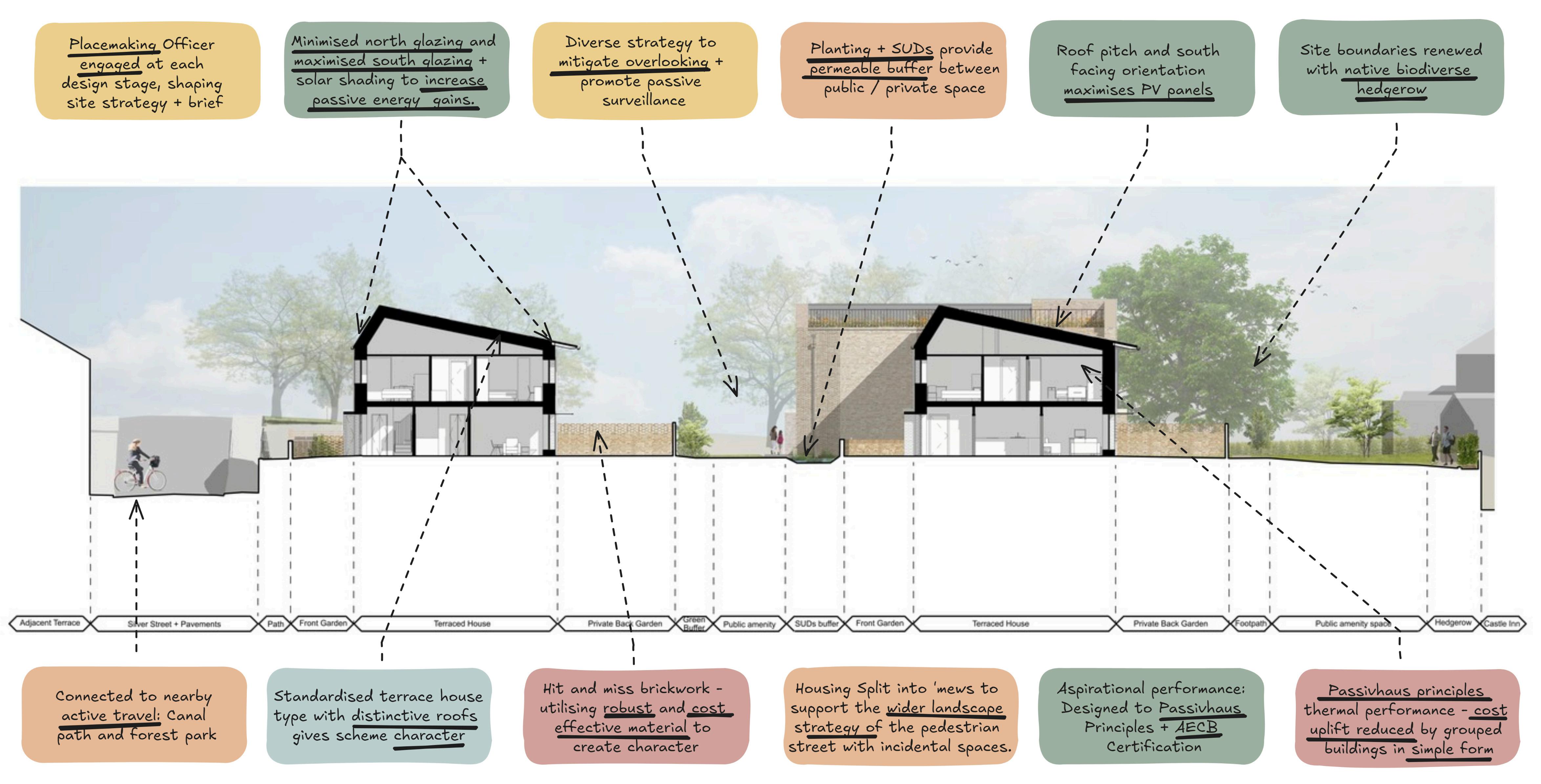

SUSTAINABILITY + SITE CONTEXT
PLACEMAKING + ENGAGEMENT
COMPLIANCE QUALITY + SCALABILITY


INNOVATION + COST
SUSTAINABILITY + SITE CONTEXT
PLACEMAKING + ENGAGEMENT
COMPLIANCE QUALITY + SCALABILITY
INNOVATION + COST


+ SITE CONTEXT
Passivhaus Social Housing:Maximising benefits,minimising costs / PassivHaus Trust
The Construction Material Pyramid / CINARK
Net Zero Carbon Toolkit
Lifetime Homes Design Guide / Habinteg
Wheelchair Housing Design Guide / Habinteg
Welsh Development Quality Requirements / Welsh Govt.
Welsh Housing Quality Standards / Welsh Govt.
Planning PolicyWales Ed.12 / Welsh Govt.
Nationally Described Space Standards / UK Govt.
Building for a Healthy Life / UK Govt.
Future Homes Standard / UK Govt.
QUALITY + SCALABILITY
MMC Definition Summary / Greater London Authority

+ COST
Debunking the myth that Passivhaus is costly to achieve / AECOM
PLACEMAKING + ENGAGEMENT
Place making Guide 2020 / Placemaking Wales
Manual for Streets 2 / CIHT
¹Welsh Government (2023) Affordable housing provision: April 2022 to March 2023
Available at: https://www.gov.wales/affordable-housing-provision-april-2022-march-2023-html
(Accessed: 19 September 2024)
²House of Commons Library (2023) Tackling the under-supply of housing in England
Available at: https://researchbriefings.files.parliament.uk/documents/CBP-7671/CBP-7671.pdf
(Accessed: 19 September 2024)
³Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (2024) Annual Fuel Poverty Statistics in England, 2024 (2023 data)
Available at: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/65ccecba1d939500129466a9/annual-fuel-povertystatistics-report-2024.pdf
(Accessed: 19 September 2024)
4House of Commons Library (2024) Fuel Poverty
Available at: https://researchbriefings.files.parliament.uk/documents/CBP-8730/CBP-8730.pdf
(Accessed: 19 September 2024)
5Ministry of Housing, Communities & Local Government (2024) English Housing Survey 2022 to 2023: housing quality and condition
Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/english-housing-survey-2022-to-2023-housing-qualityand-condition/english-housing-survey-2022-to-2023-housing-quality-and-condition
(Accessed 25 September 2024)
6Place Alliance / UCL (2020) A Housing Audit for England
Available At: https://indd.adobe.com/view/23366ae1-8f97-455d-896a-1a9934689cd8
(Accessed 10 September 2024)
7Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (2023) Net Zero Government Initiative - UK Roadmap to Net Zero Government Emissions
Available At: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/6569cb331104cf000dfa7352/net-zero-government-emissionsroadmap.pdf
8Welsh Government (2022) Working Together to Reach Net Zero
Available At: https://www.gov.wales/sites/default/files/publications/2022-04/working-together-to-reach-netzero-all-wales-plan-april-22-update.pdf
(Accessed 19 September 2024)
9National Housing Federation (2021) Defining net zero for social housing.
Available at: https://www.housing.org.uk/globalassets/files/climate-and-sustainability--energy-crisis/definingnet-zero-discussion-paper-2021.pdf
(Accessed: 09 September 2024)
10Climate Change Committee (2020) The Sixth Carbon Budget Available At: https://www.theccc.org.uk/publication/sixth-carbon-budget/ (Accessed 19 September 2024)
11UK Green Building Council (UKGBC). (2022) Climate change mitigation
Available at: https://ukgbc.org/climate-change-mitigation/ (Accessed: 9 September 2024)
12Passivhaus Trust (2021) Research Reports - Passivhaus Costs & Benefits
Available at: https://www.passivhaustrust.org.uk/guidance_detail.php?gId=41#Part%202:%20Benefits (Accessed: 21 October 2024)
13Ministry of Housing, Communities & Local Government (2019) Modern Methods of Construction: introducing the MMC definition framework
Available at: 11https://www.cast-consultancy.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/MMC-I-Pad-base_GOVUKFINAL_SECURE.pdf (Accessed 19 September 2024)
14Lowfield Timber Frames (2024) Gallery Available At: https://www.lowfieldtimberframes.co.uk/gallery/ (Accessed: 19 September 2024)
15Committee on Climate Change; Currie & Brown. (2019) A report for the Committee on Climate Change - The costs and benefits of tighter standards for new buildings
Available at: https://www.theccc.org.uk/publication/the-costs-and-benefits-of-tighter-standards-for-new-buildingscurrie-brown-and-aecom/ (Accessed: 19 September 2024).
16MMC Online. (2023) GERMANY: SERIAL MODULAR CONSTRUCTION
Available At: https://mmcmag.co.uk/germany-serial-modular-construction/ (Accessed 09 September 2024)
17UK Government (2019) Modern Methods of Construction inquiry
Available at: https://committees.parliament.uk/work/1939/modern-methods-of-construction-inquiry/ (Accessed: 21 October 2024).
183D CGI’s throughout the document by Studio NESH.
19RIBA (2020) RIBA Plan of Work
Available At: https://www.architecture.com/knowledge-and-resources/resources-landing-page/riba-plan-ofwork?srsltid=AfmBOoqFbot8OVOWbrOlxDj7c0BcYRKSFA7MkJpp7gAXfZ9tzZZeL6jA#available-resources (Accessed 09 September 2024)
We are proud members / signatories of the below:









Let’s Connect





jon@jjstudioarchitecture.co.uk
www.jjstudioarchitecture.co.uk
www.facebook.com/jjstudioarchitecture
www.instagram.com/jjstudioarchitecture/
/www.linkedin.com/company/jon-james-studio-architecture


© Jon James Studio Architecture Ltd.