How to Graphql: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Are you looking to enhance your web development skills and streamline your data-fetching process? Look no further than GraphQL! In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of GraphQL and learn how to leverage its power to build efficient and flexible APIs. Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting your coding journey, this article will provide you with the knowledge and expertise needed to master the art of GraphQL.
How to Graphql: The Basics
What is GraphQL?
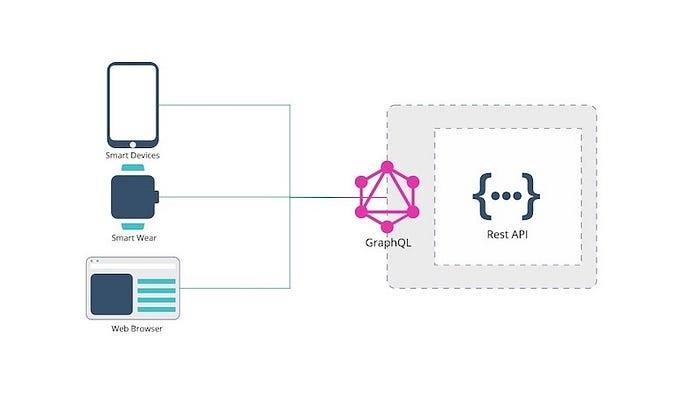
GraphQL is an open-source query language developed by Facebook that enables clients to request specific data from a server. Unlike traditional REST APIs, where clients receive a fixed set of data, GraphQL allows clients to define the structure and shape of the data they need. This flexibility empowers developers to eliminate overfetching and under-fetching of data, making applications faster and more efficient.
How Does GraphQL Work?
At its core, GraphQL revolves around the concept of a schema. A schema defines the types of data available and the relationships between them. Clients can then query this schema to request precisely what they need. The server processes the query and returns a JSON response with the requested data. This approach enables clients to reduce the number of round trips to the server, optimizing performance.
Setting Up a GraphQL Server
To start building with GraphQL, you’ll need a server that can handle GraphQL requests and resolve them to the appropriate data sources. There are several popular frameworks available for various programming languages, such as Apollo Server for JavaScript, graphql-go for Go, and many more. Choose the one that aligns with your preferred programming language and set up your server accordingly.
Defining Types and Resolvers
In GraphQL, types define the structure of your data. You can define custom types that represent specific entities in your application, such as User, Post, or Comment. Each type consists of fields that correspond to the attributes of that entity. For example, a User type might have fields like id, name, and email.
Resolvers are responsible for fetching the data for each field in a GraphQL query. They act as the bridge between the client’s request and the actual data sources. You can implement resolvers to retrieve data from databases, APIs, or any other source. By separating resolvers for each field, you can efficiently resolve data from different sources and compose complex responses.
Advanced GraphQL Techniques
Pagination with GraphQL
Pagination is a common requirement when dealing with large datasets. GraphQL provides built-in mechanisms to handle pagination efficiently. By utilizing the first, last, before, and after arguments in queries, you can fetch a specific subset of data and implement pagination in a standardized manner. This ensures that clients receive only the data they need while maintaining optimal performance.
Real-time Updates with Subscriptions
GraphQL doesn’t limit you to just fetching data; it also supports real-time updates through subscriptions. Subscriptions enable clients to subscribe to specific events or data changes and receive live updates as they occur. This feature is incredibly powerful when
building applications that require real-time data, such as chat applications, live dashboards, or collaborative tools.
Authorization and Authentication
Securing your GraphQL API is crucial to protect sensitive data and control access to resources. GraphQL provides various strategies for handling authentication and authorization. You can implement custom authentication logic within resolvers, use middleware to authenticate requests, or integrate with existing authentication providers. By properly securing your GraphQL API, you can ensure that only authorized users can access the data.
Error Handling and Validation
Effective error handling and validation are essential aspects of any robust API. GraphQL provides mechanisms to handle errors and validate incoming queries effectively. By leveraging custom error types, you can provide detailed error messages and inform clients about specific issues. Additionally, input validation ensures that the data sent by clients meets the expected criteria, preventing unexpected behaviors and ensuring data integrity.
Additional Advanced GraphQL Techniques
Caching with GraphQL
Caching is a crucial aspect of optimizing application performance. GraphQL provides built-in support for caching by utilizing a concept called “dataloading.” Dataloading allows you to fetch and cache data efficiently, avoiding redundant requests. By leveraging caching
mechanisms such as Redis or Memcached, you can store frequently accessed data and reduce the load on your server.
Federation and Microservices
As applications grow in complexity, it becomes essential to break them down into smaller, manageable services. GraphQL Federation enables you to combine multiple GraphQL services into a unified schema. This approach allows each service to maintain its own schema and handle its data while providing a single endpoint for clients to query. Federation simplifies the development and maintenance of microservices architectures.
Performance Monitoring and Analytics
To ensure your GraphQL API performs optimally, it’s crucial to monitor its performance and analyze usage patterns. Tools like Apollo Studio and GraphiQL offer insights into query execution times, resolver performance, and error tracking. By monitoring these metrics, you can identify bottlenecks, optimize slow queries, and deliver an exceptional user experience.
GraphQL in Mobile Development
GraphQL’s efficiency and flexibility make it an excellent choice for mobile app development. With GraphQL, you can precisely tailor your data requirements to minimize data transfer and optimize battery usage on mobile devices. Additionally, GraphQL’s ability to batch multiple requests into a single query reduces network overhead, making it ideal for mobile applications with limited connectivity.
Testing and Debugging GraphQL APIs
As with any software development, testing and debugging are crucial to ensuring the quality and stability of your GraphQL API. Tools like Jest, Postman, and GraphQL Playground provide a testing environment where you can write unit tests, integration tests, and perform manual testing. Additionally, GraphQL’s introspection capabilities allow you to explore the schema and execute queries interactively for debugging purposes.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we have covered various aspects of GraphQL, from the basics to advanced techniques. You now have a solid foundation to start building powerful and efficient APIs using GraphQL. Remember to define your types and resolvers, leverage advanced techniques like pagination and subscriptions, and secure your API with proper authentication and authorization. By adopting GraphQL, you can streamline your data-fetching process and build modern, scalable applications.
Keep exploring GraphQL’s ecosystem and stay up to date with the latest best practices and tooling. As you gain more experience, you’ll unlock the full potential of GraphQL and its ability to revolutionize the way you handle data in your applications. Happy coding!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does GraphQL compare to REST APIs?
A: GraphQL vs Rest, unlike REST APIs, which often suffer from over-fetching or under-fetching of data, GraphQL enables clients to request precisely the data they need. This reduces unnecessary data transfer and optimizes performance. Additionally, GraphQL provides a strongly-typed schema, making it easier to understand and explore the available data.
Q: Can I use GraphQL with existing databases?
A: Absolutely! GraphQL can be used with any data source, including existing databases. By implementing resolvers that interact with your database, you can seamlessly integrate GraphQL into your existing stack without significant changes to your data layer.
Q: Is GraphQL only for frontend development?
A: Not at all! While GraphQL is well-suited for frontend development, it can be used in various contexts. GraphQL’s flexibility makes it an excellent choice for backend APIs, microservices, and even IoT applications. Its ability to consolidate and unify data from multiple sources makes it a versatile tool for developers.
Q: Are there any performance concerns with GraphQL?
A: GraphQL’s performance largely depends on how efficiently you implement your resolvers and handle data fetching. By carefully designing your schema and optimizing resolver logic, you can ensure excellent performance. Additionally, GraphQL’s ability to batch and defer requests can further enhance performance by reducing the number of round trips to the server.
Q: Can I use GraphQL with my favorite programming language?
A: Absolutely! GraphQL is language-agnostic, meaning you can use it with any programming language. There are GraphQL implementations and libraries available for popular languages like JavaScript, Python, Ruby, Go, and many more. Choose the implementation that aligns with your preferred language and start building with GraphQL.
Q: Is GraphQL suitable for large-scale applications?
A: Yes, GraphQL is well-suited for large-scale applications. Its ability to handle complex data requirements, optimize performance, and support real-time updates makes it an excellent choice for applications of any size. Many renowned companies, including Facebook, GitHub, and Shopify, have adopted GraphQL successfully for their large-scale systems.
