
JAYESH PRAMOD MORE 23 | Gwalior,India

19 Oct 1999 jayeshpramodmore@gmail.com [INDIA] +91-9009789347

jayesh._more Jayesh More Languages English Hindi Marathi

Hello, I’m Jayesh More, currently pursuing Bachelor of Architecture from School of planning and Architecture, New Delhi. My constant urge to learn new skills and interest in various realms of architecture universe gave me way to pursue this field. I like to travel to unexplored places to loose myself in the joy of observing. I am open for exploring and taking up new challenges. D.O.B. E-MAIL PHONE CURRICULUM VITAE
Proficient in Speaking and Writing Proficient in Speaking Mother Tongue
EDUCATION
2022
Bachelor’s of Architecture School of Planning and Architecture, New Delhi Under Top 15 in batch of 120 students
WORKSHOPS AND COURSES
2022
2018
Grade CBSE XII - 92.4%
Gwalior Gory High School, Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh School Topper | Award for Best Conduct
2016
Grade CBSE X - 9.8 CGPA
Gwalior GLory High School, Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh Gold Medalist for 5 years | SOF Gold Medalist
ACHIEVEMENTS
2022
WINNER | Solar Decathlon India
Educational Division | NetZero Energy Building 800+ Entries | Role - Design Lead
2022
2022
TOP 6 | HUDCO Trophy NASA India Low Cost Housing Design Competition 300+ Entries
Erfurt Exchange Program, Germany University of Erfurt, Germany 18 Studentes selected
2021-22
2020
Co-ordinator of SPAkriti Installation Society of SPA, New Delhi Managed the design and making of Installations
TOP 40 % | ANDC Trophy NASA India Shortlised for Bus terminal design 400+ Entries
AIR 203 | JEE Mains Paper 2 JEE Percentile - 99.92 2019
2016
EXCELLENCE AWARD | QCFI Quality Circle Forum of India HQ 49th Convention | Pune chapter
SOFTWARE SKILLS
Drafting and Modelling
Autodesk AutoCAD
Autodesk Revit
Trimble SketchUp
India Canada Research Studio Laurentian University Ontario Summer Semester joint Design Exercise
Regenerative Processes | Workshop Ar. Gaurav Shorey, Ms. Shamita Chaudhary 2022
Course on Net Zero Energy Building | SDI Self Learning Modules and Weekly Webinars for 16 Weeks 2022-21
2022
3D Print Design Method | Elective Elective course about understanding of new design methods to fully utilize the capabilities of new construction techniques
Universal Design | Elective Elective course addressing the Question - “Does One Design Fit All” 2022
2021
2020
Deducing Design Processes | Elective Elective course about understanding the Design Processses through steps of product designing
Theory of Architecture | Elective Elective course about various art movements and periods, design theories and architecture
RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
2022
Framework for Net Positive Water Management System
A case study of School of Planning and Architecture, New Delhi
2022
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj International Airport, Mumbai
A guided study tour of international airport by Ar. Lalit Jain and team, indepth understanding of operations and zoning of airport
2021
Pearl Academy, Jaipur
Documentation and analysis of college building, highlighting the connection between the vernacular and the mordern
2021
Bada Bagh Chattris, Jaisalmer
EXPERIENCE
2021-22
360
2020-22
[SCIENTIST] architects
Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh
Worked on Design Development of Residences, Commercial Complexes, Office spaces, Retail malls.
3D Visualizations, Working Drawings, Modelling, Site visits.
Freelance
Residence design, 3D visualizations, magazine design, illustrations, digital art.
Simulations Autodesk Formit Insight
Design
Presentation Google
Visualitization Enscape
Lumion
A city level study of Jaisalmer and documentation of Bada Bagh Chattris - Measured drawing Creative Suite Photoshop
Builder
Suite Figma
3D
Adobe
Indesign Premier Pro Lightroom

SELECTED WORKS BACHELOR OF ARCHITECTURE vii. MISCELLANEOUS COMIC STRIPS PHOTOGRAPHY SITY STUDY DOCUMENTATION vi. MESEAURED DRAWING BADA BAGH CHATTRIS v. WORKING DRAWING iv V vi iii New Delhi Jaisalmer, Rajasthan
i.
NET ZERO ENERGY EDUCATIONAL
TRIBHUVAN UNIVERSITY MEDICAL ACADEMIC BLOCK HUDCO LOW-COST HOUSING iii. VANSARTHIKA NASA 2022 RECREATIONAL ii. BHAKTI BHAWAN AUDITORIUM WORKING DWG 3D VISUALIZATION iv. WORK EXPERIENCE EQUILIBRIUM 23X45 RESIDENCE DATIA COMMERCIAL HG COMMERCIAL i ii Kathmandu, Nepal Kathmandu, Nepal Ahemdabad, Gujarat Gwalior, MP
TRIBHUVAN UNIVERSITY
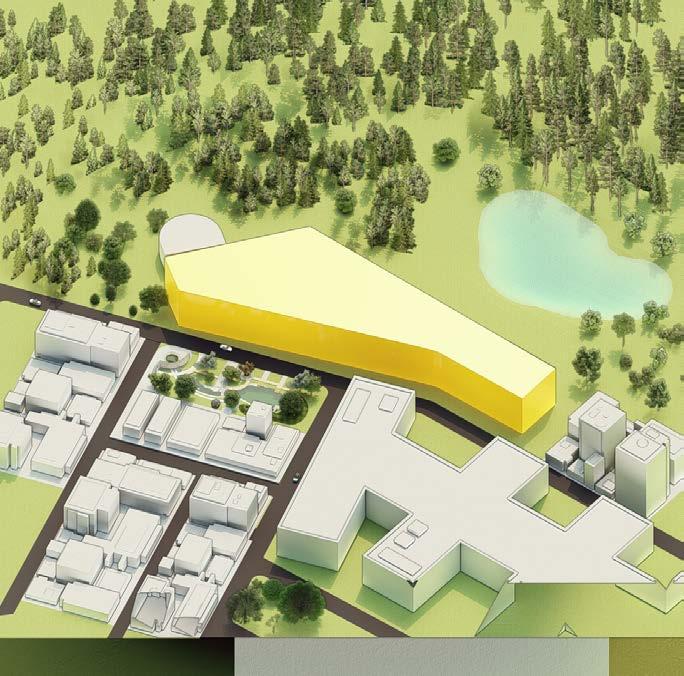
NET ZERO ENERGY AND WATER BUILDING KATHMANDU, NEPAL WINNER | Solar Decathlon India 2022


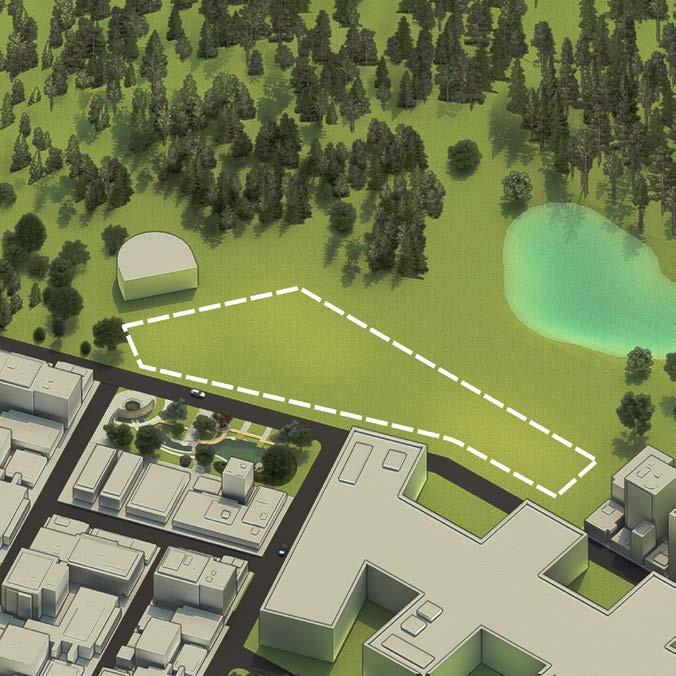
This project was a part of super speciality medical institution in Kathmandu, Nepal, that not only fosters a supportive learning atmosphere for students to share information, but also upholds environmental responsibility by becoming a net-zero energy and water building . The medical college is situated on a gradual, south-facing slope as part of a broader construction project. The area is vulnerable to monsoon flooding and earthquakes (seismic zone V). In order to provide the students with a safe environment and an overall comfortable space to be in, 10 contests were worked in detail.
The ten contest were :
Energy performance, water performance, affodability, innovation, health and well being, architectural design, engineering and operation, resilience, scalabilty and marketing, communication, solid waste management.
Status of the project : Master planning complete
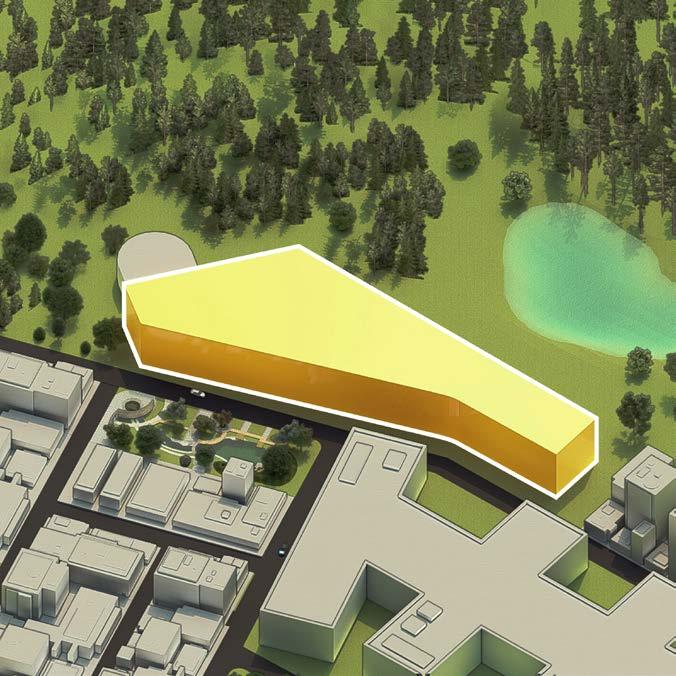
Site area : 8115 sqm
Profile of occupants : 300 Students & 80 Faculty
Hours of operation : 9 hours per day, 6 days per week
SITE CONTEXT
The site is located South West of Kathmandu city in Kirtipur District - one of the five municipalities in the valley. Tribhuvan University’s surrounding district has become a popular area for out-station students and teachers to settle and live in. The site is approximately 0.33 Km away from the ring road, which acts as the majorlink to the rest of Kirtipur.
Location
Elevation Climate Latitude
Max temp Min temp
Percipitation
Rh levels
: Kathmandu, Nepal : 1337 m : Cold : 28.3949 N, 84.1240 E : 30.5 C in summers : -1 C in winters : 362mm in monsoons and annual precipitation 1440 mm : 50 % - 90%

OBJECTIVES
Demonstration of low energy building design to achieve Net Zero Energy building
Research and practice of appropriate strategies to achieve thermal comfort.
Harness and maximize the usage of daylight. Integrate renewable energy sources as part of architectural design.

GOALS
Generate robust knowledge database for strengthening of energy efficiency
Create enhanced knowledge of construction materials and practices for energy efficient architecture.
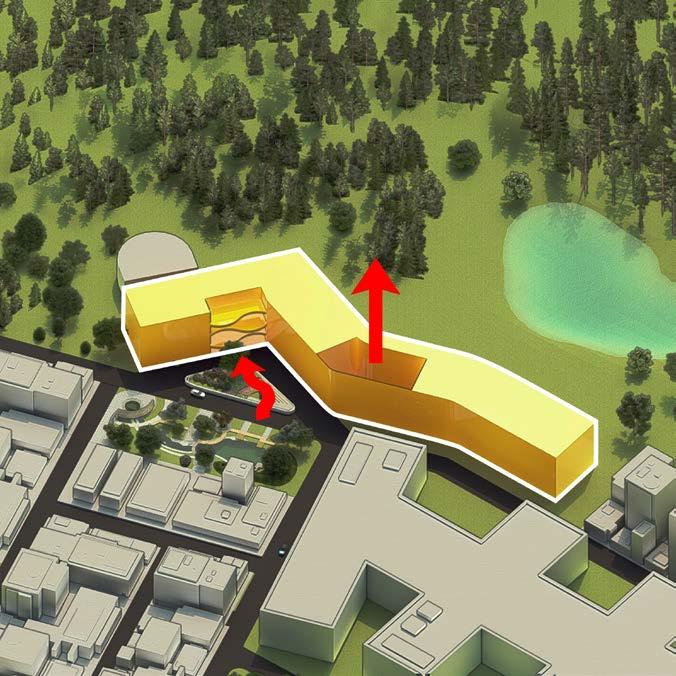
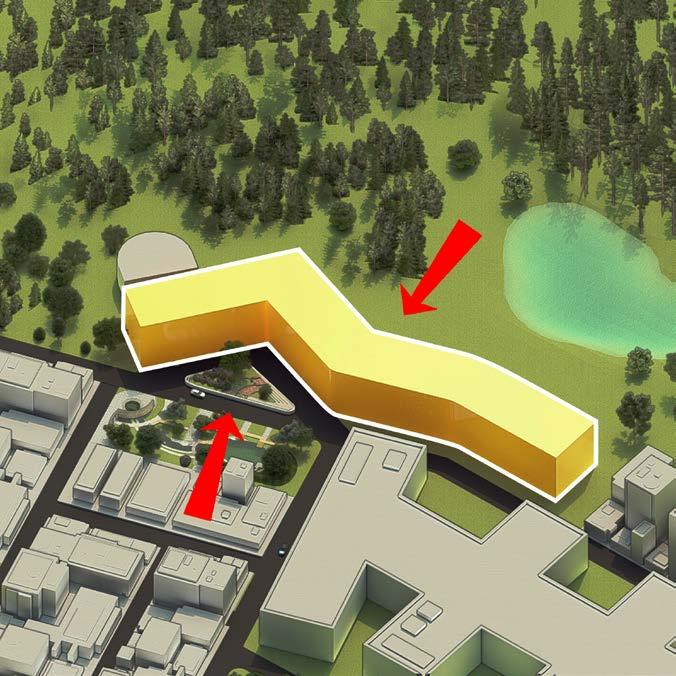
DESIGN STRATEGIES
- Building massing and orientation
- Optimized building envelope
- Optimized thermal and luminous environment
Centre for Advanced research
Case study - Net Zero
Southern side has clerestory to allow minimum south light.
CEPT CARBSE,
Cool air from southern windows enters in the building.
in Building science and energy
Zero Energy Building STACK EFFECT
It is the difference in pressure caused by the difference in elevation between two locations, conveying heated gases at zero gas flow.
The hypothesis of Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB) - a building which generates as much energy as it uses over the duration of one whole year
Warm air in the building exits from the mezzanine floor above.
Principles used in the processCross ventilation Venturi effect Buoyancy of warm air
BUILDING ENVELOP OPTIMIZATION
Windows design fenestration shading day lighting analysis
PASSIVE SYSTEM
Light shelves Courtyards Building orientation Earth berming Stack effect
ACTIVE
CARBSE, Ahemdabad
Dedicated Outdoor
Variable Refrigerant
SYSTEM Radiant cooling
Air System
Flow
Biophilia
The concept of biophilia blurs the border between indoor and outdoor living environments and aims to redefine urban lipfe by promoting health and wellbeing. It is is fundamental to develop harmonious relationships between humans and the biosphere. Unfortunately, modern people, especially children, lack direct and frequent contact with Nature and this can have negative consequences on their physical and mental health.


Proxemics Theory
The study of the various ways people understand and use space in a cultural context. Perception of the levels of intimacy of space is culturally determined. People from different cultures perceive space (and place) differently. It is the understanding of space in the holistic sense, as well as the cultural association we place upon space. It is the study of how an environment, at the interactive and interpretive level, is bestowed with meaning by people in daily life.
rendered using ‘Midjourney’
rendered using ‘Midjourney’
form development




2 2 2 3 4 7 9 5
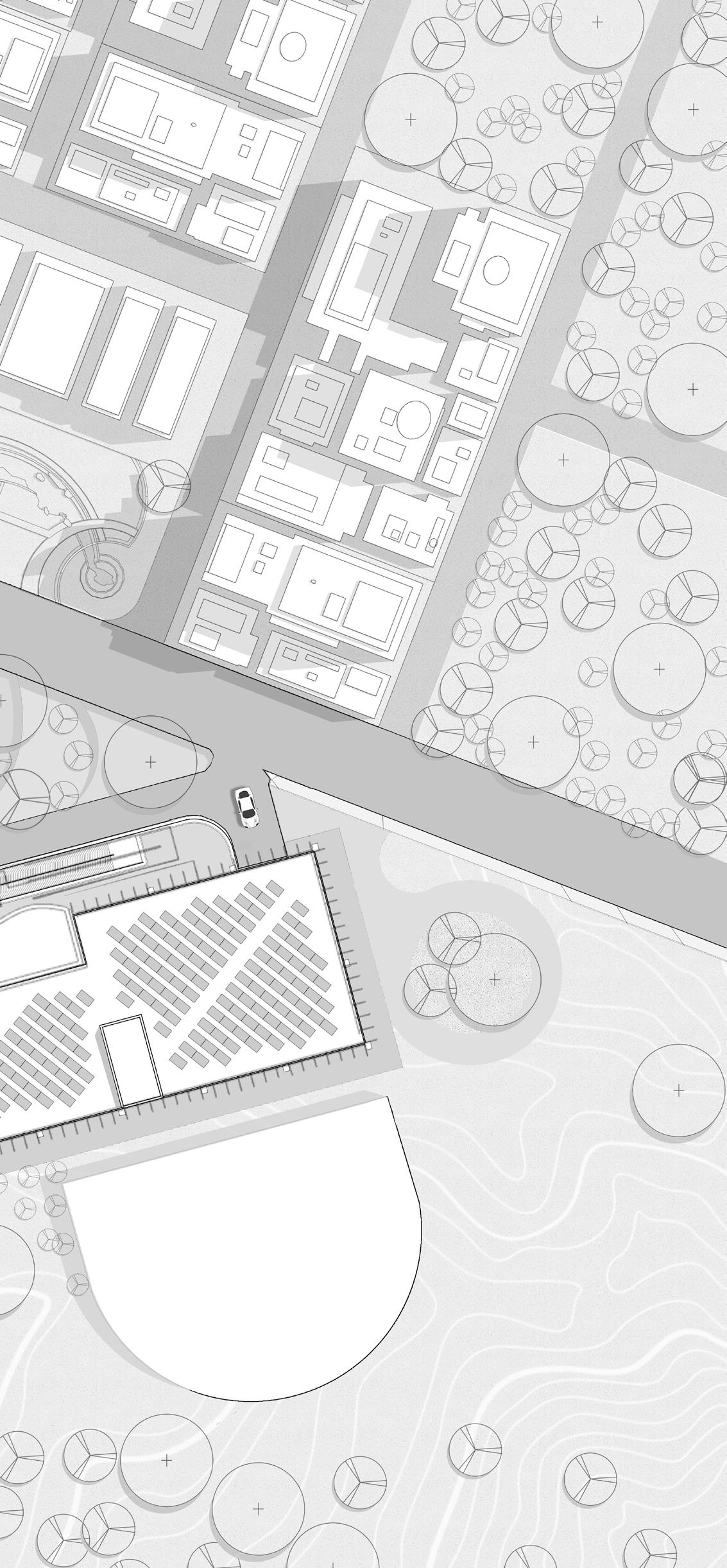

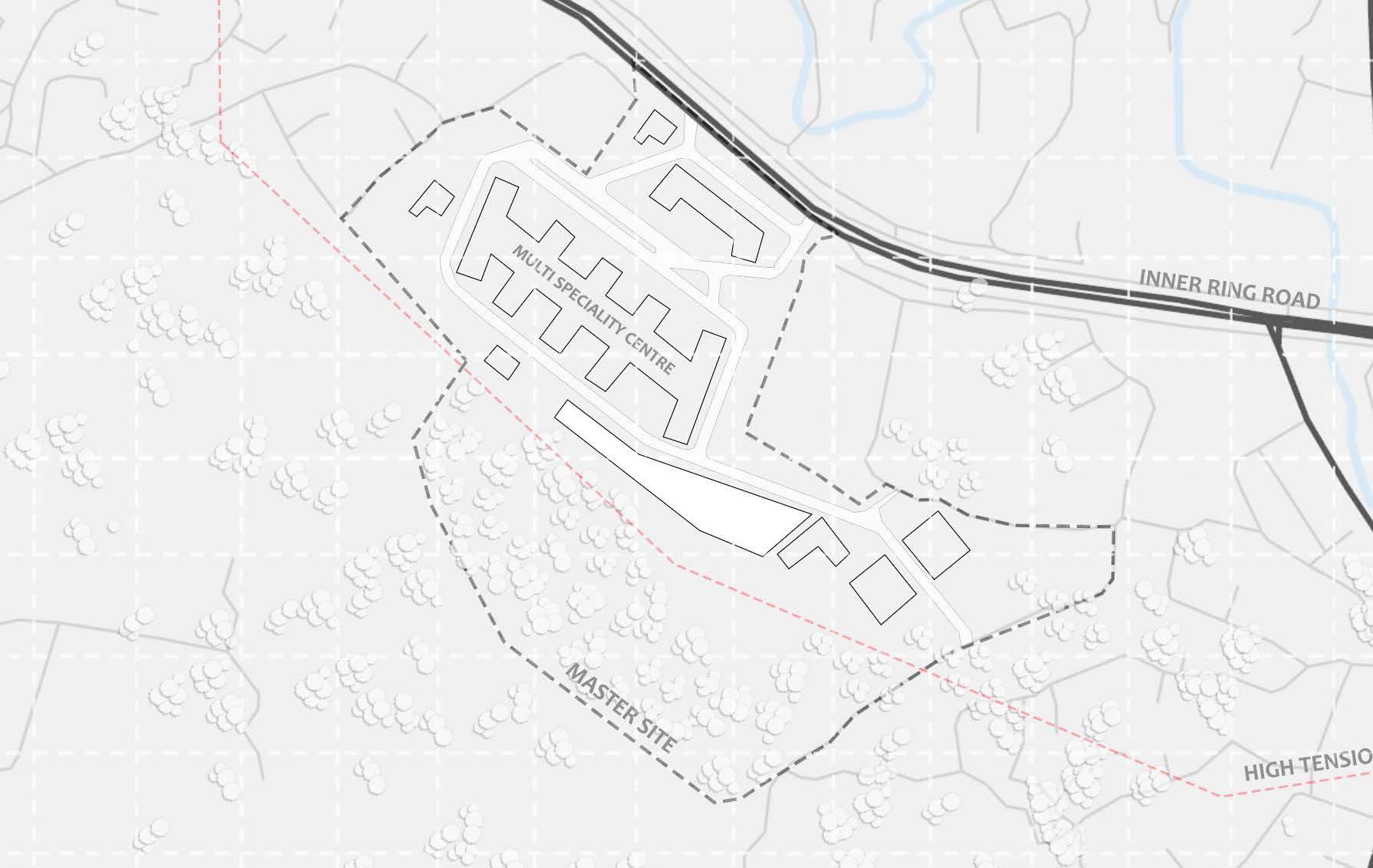
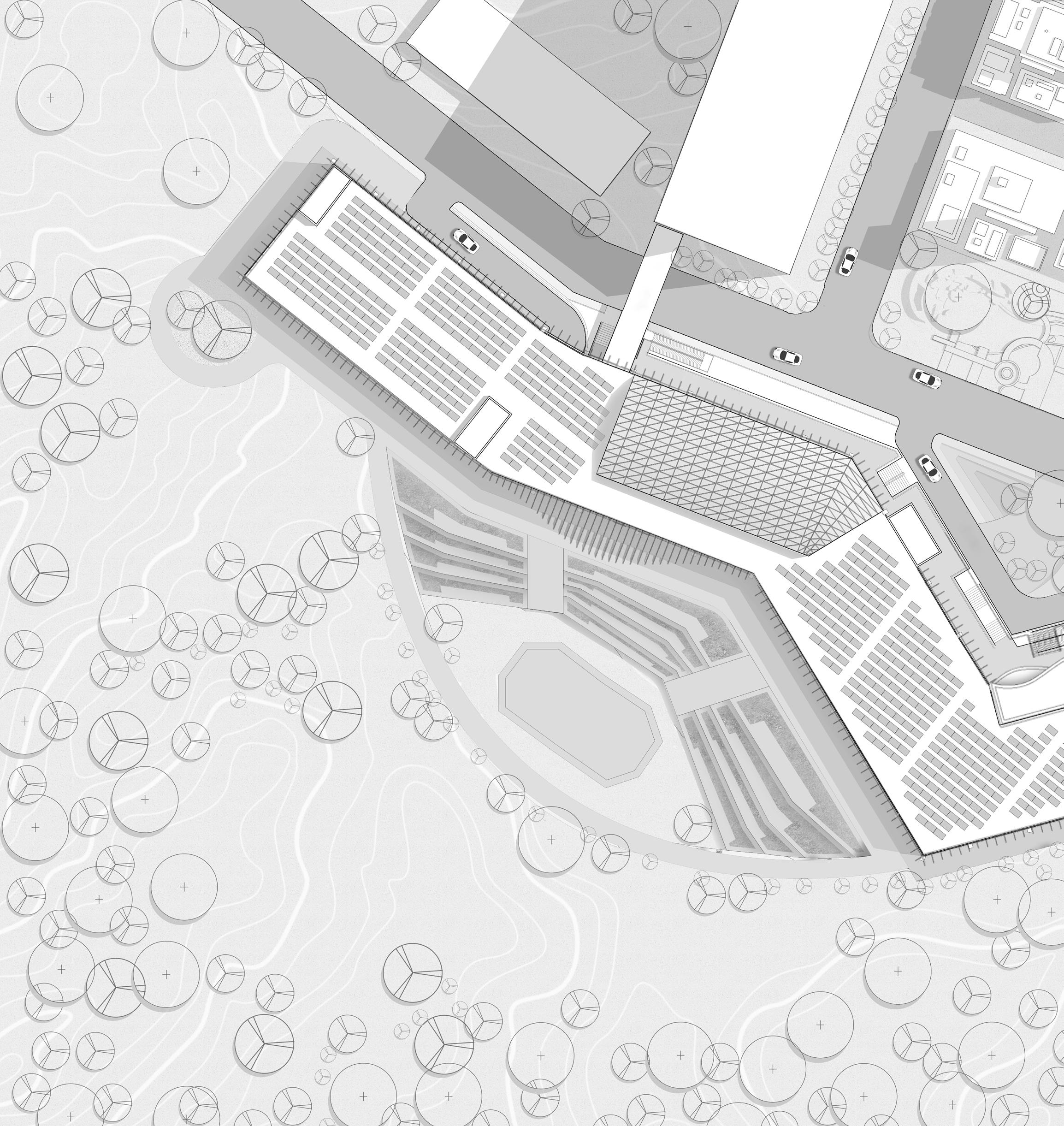
1. Drop-off 2. Entry 3. Link to hospital 4. Multi-speciality block 5. Oat 6. Auditorium 7. Recreactional Park 8. Parking entry 9. Parking exit 1 8 6 Site Plan 10 20 30 40 0
2 3 4 5 5 6 7 5 2 4 8 9 10 11 12 13 5 3 1
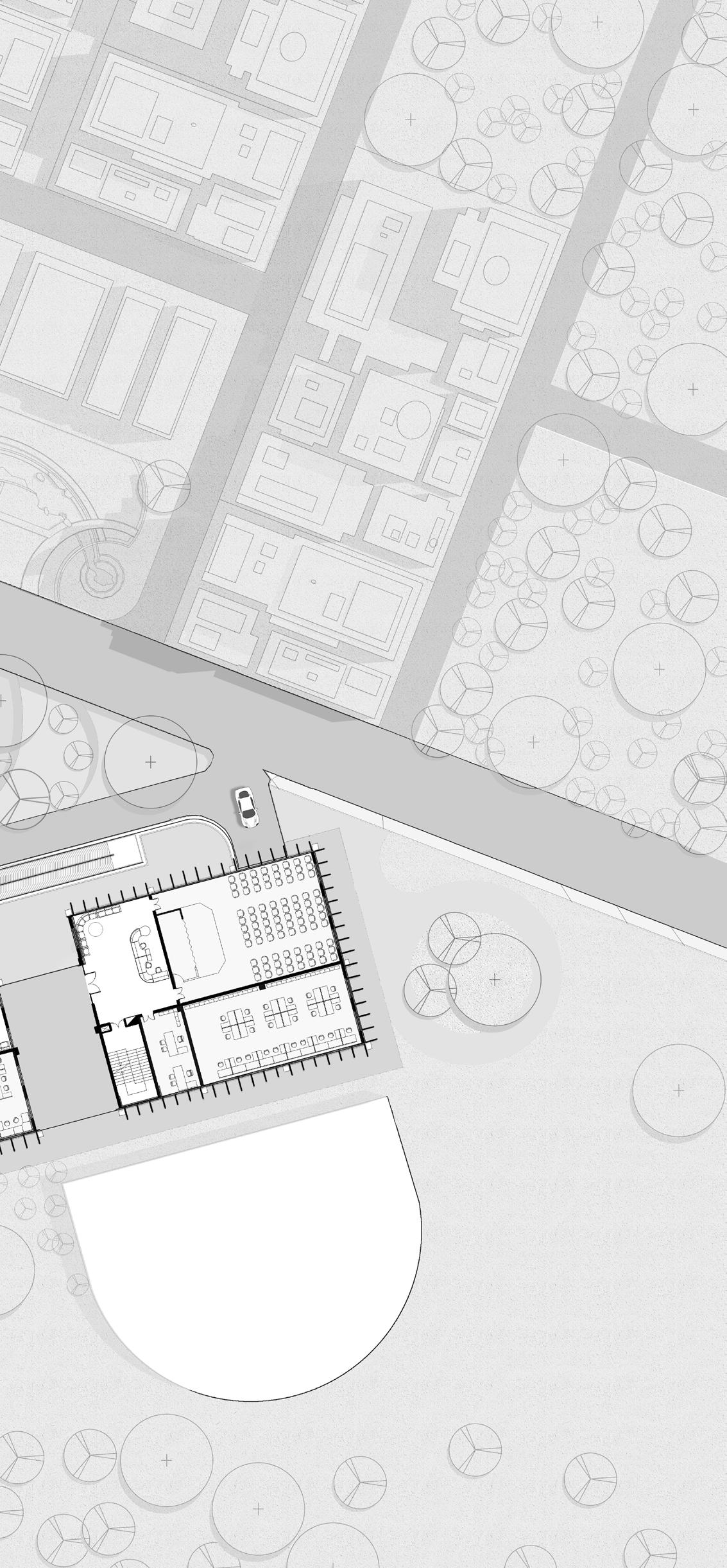

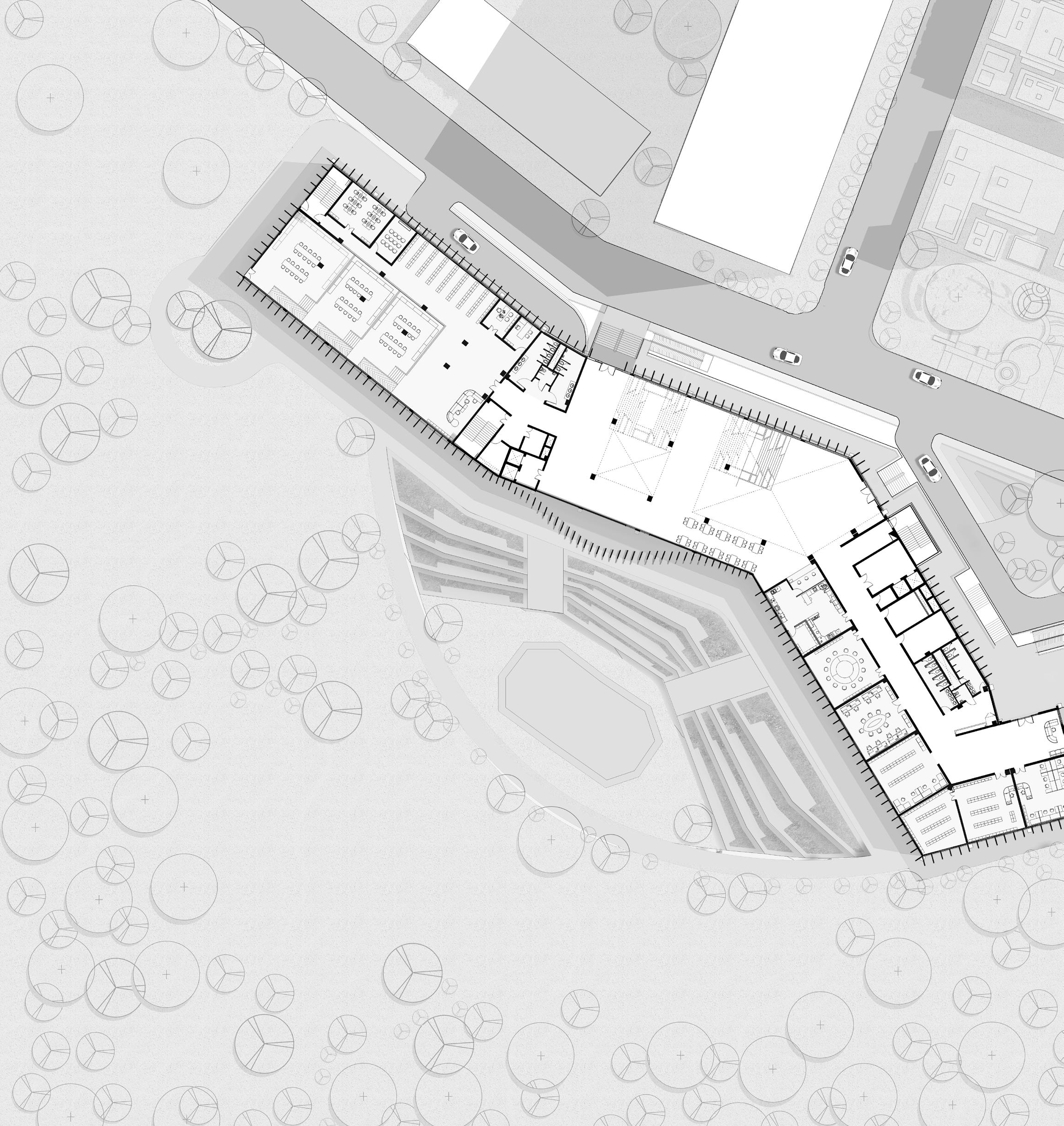
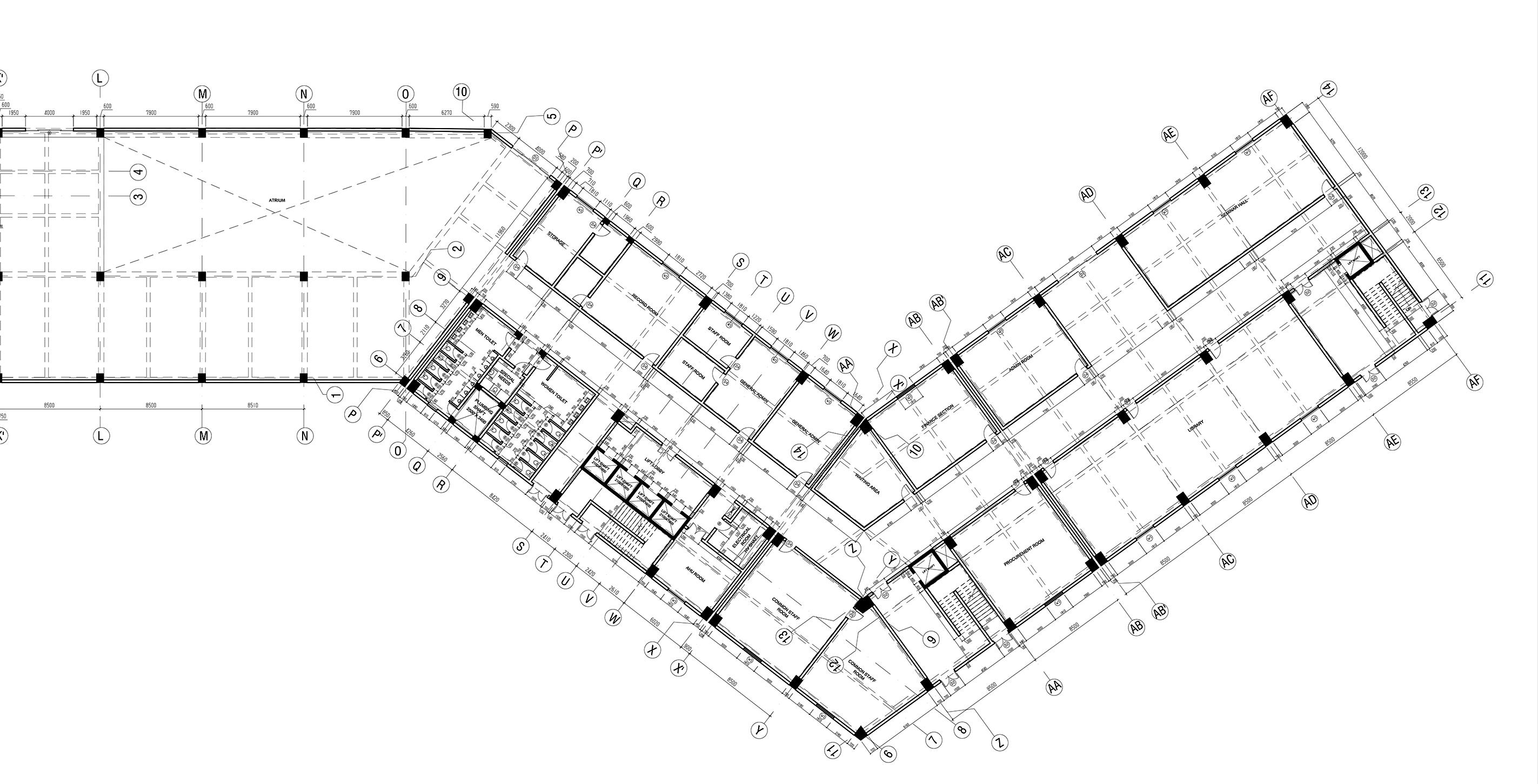
1. Library 2. Staircase 3. Restroom 4. Lift Lobby 5. Entry & Exit 6. Atrium 7. Cafeteria 8. Conference Room 9. Planning & Evaluation room 10. Procurement Section 11. Medical Record Room 12. Finance Section 13. Reception 14. Seminar Hall 15. General Admin 16. Social And Welfare Section 5 13 2 16 15 14 Ground Floor Plan 10 20 30 40 0
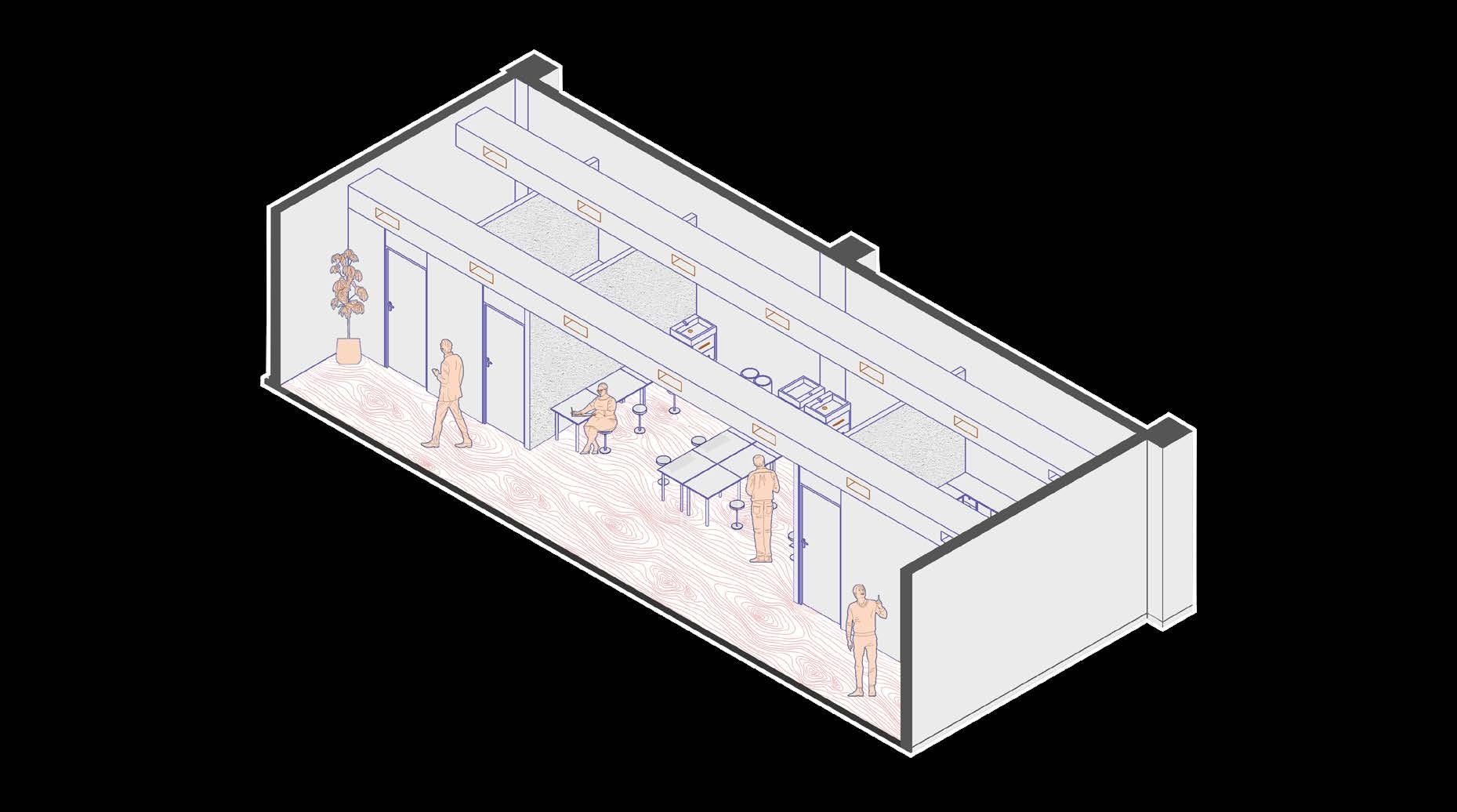
axonometric view of laboratory
axonometric view of library
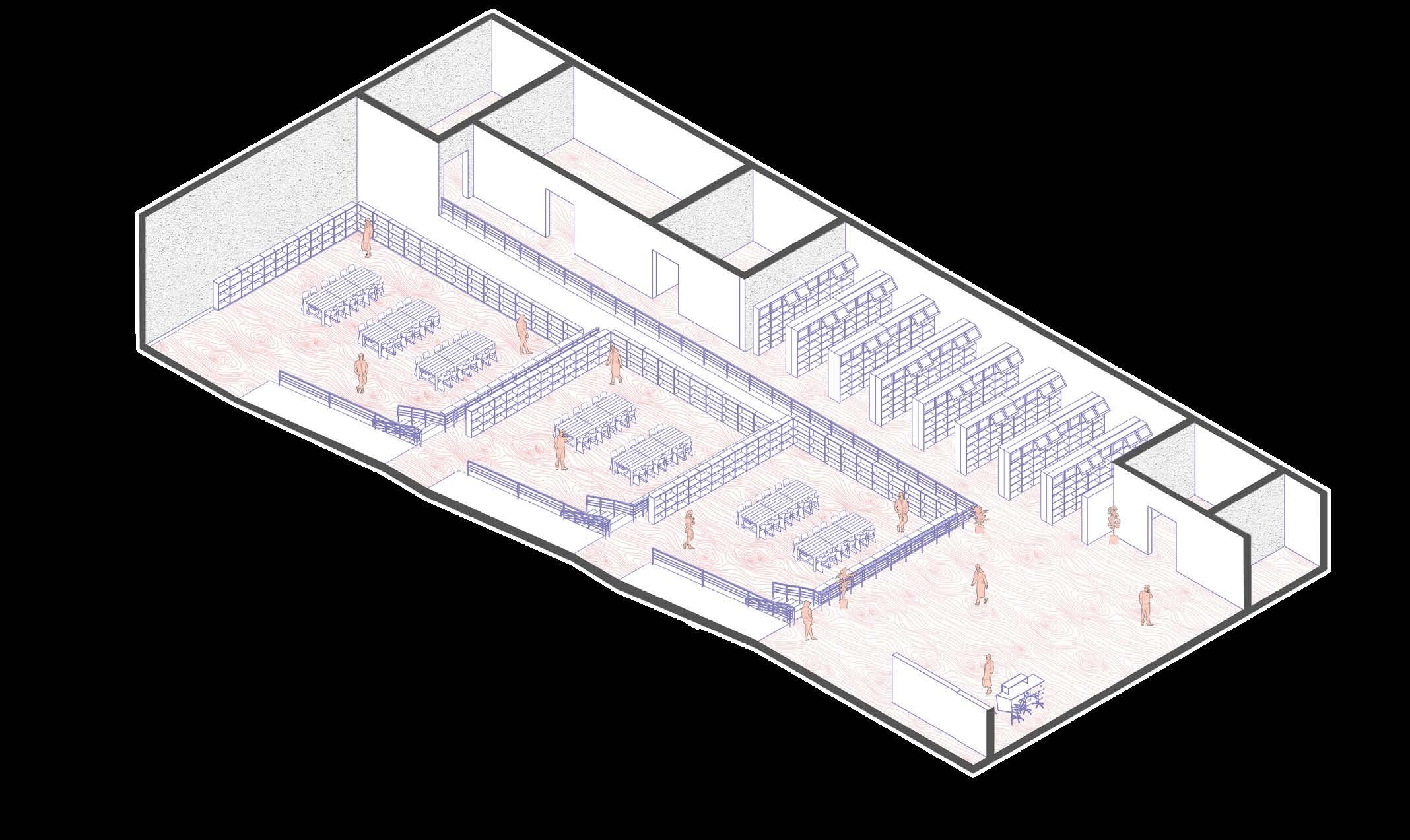

Stepped library view
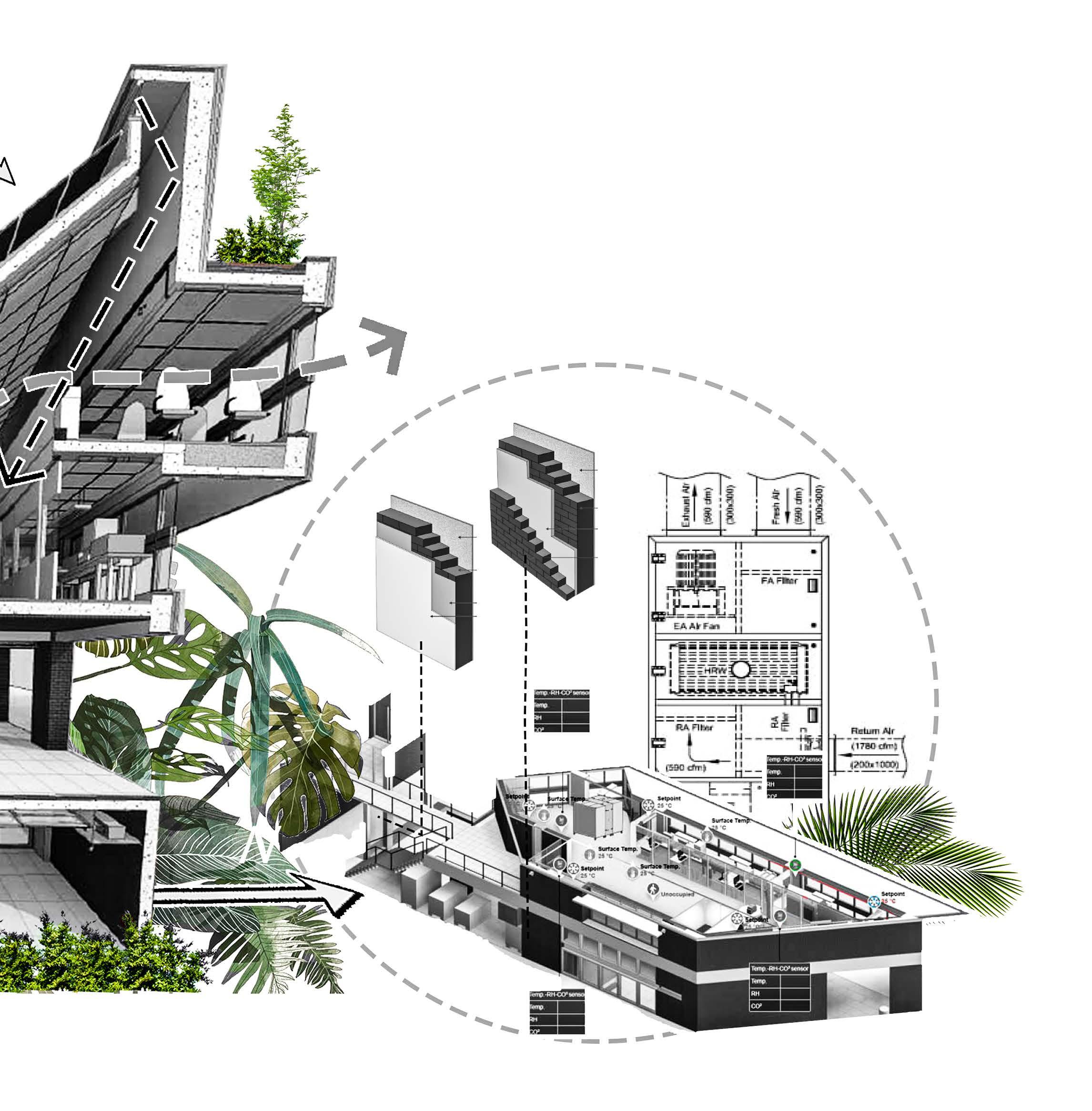
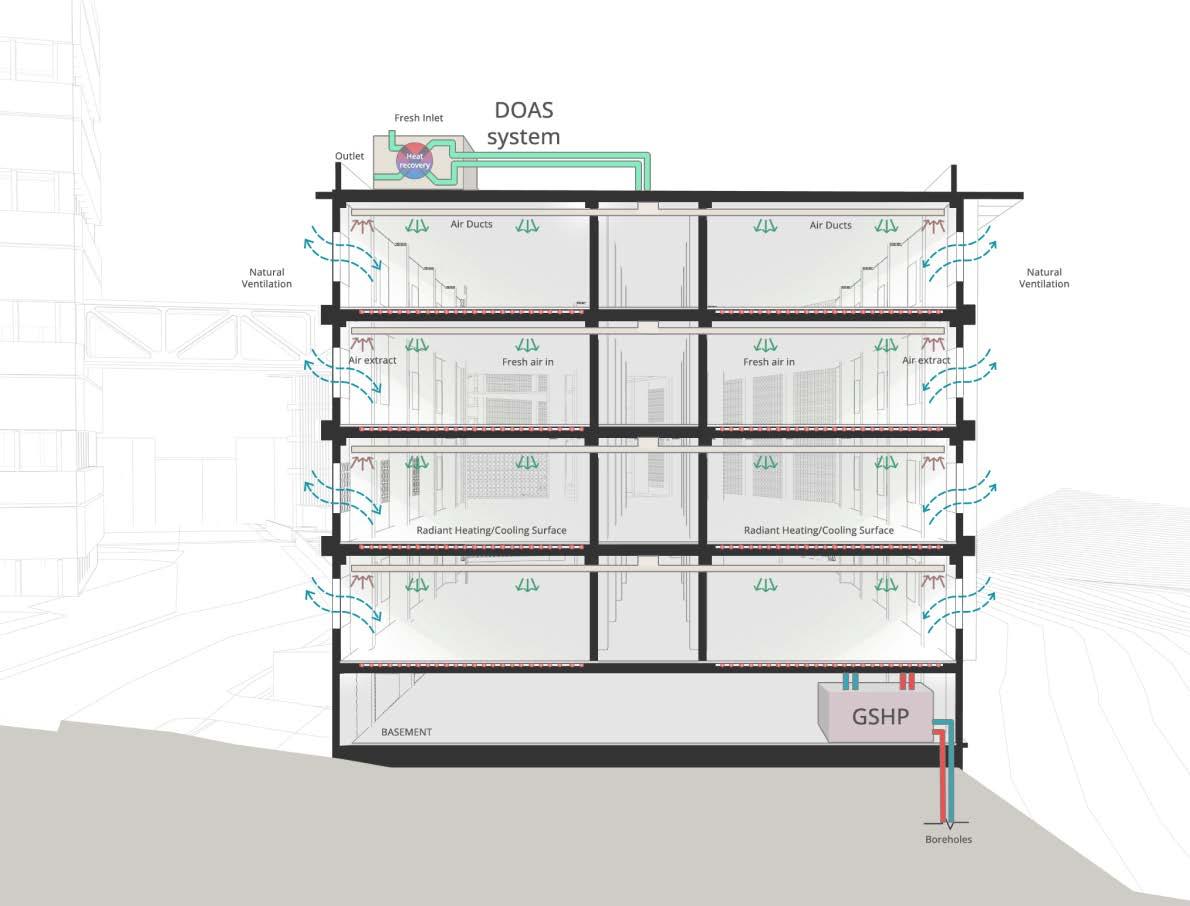
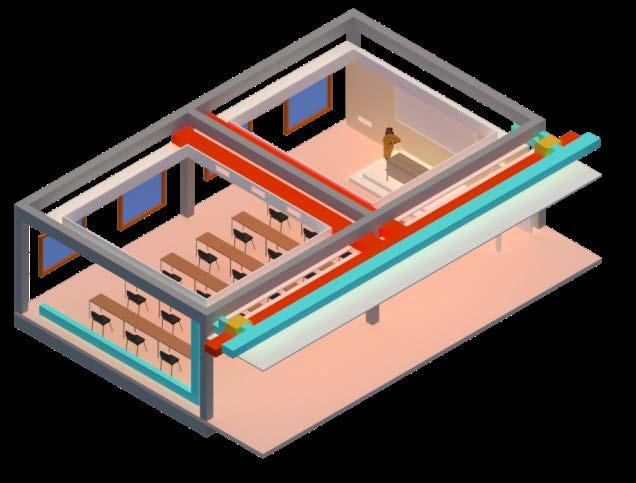
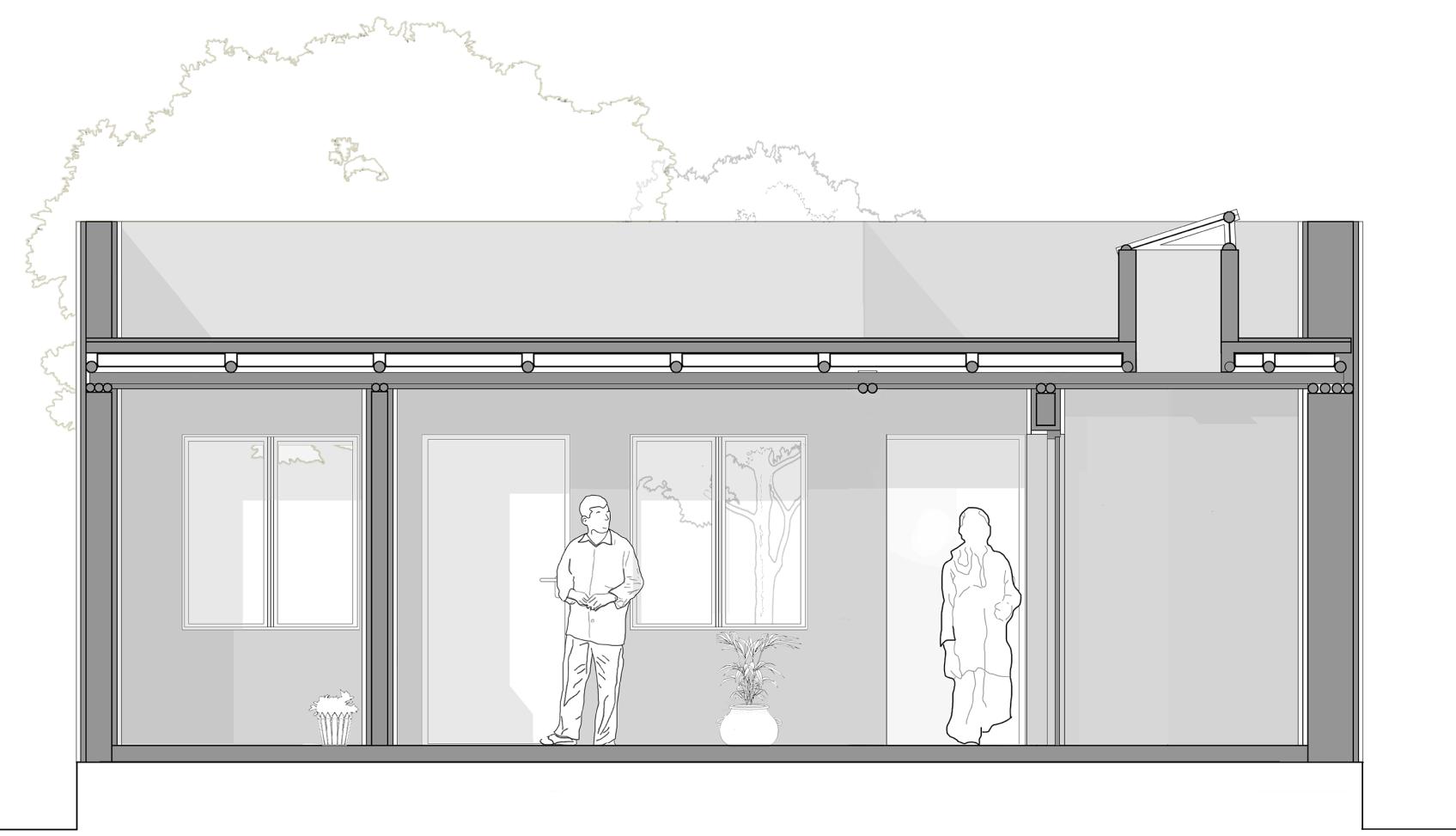
HVAC SYSTEM
The proposed system for institutional building is a combination of a Ground Source Heat Pump along with a Dedicated Outdoor Air System. While the ground source heat pump takes care of the latent heat load, the DOAS takes care of the sensible heat load. Two systems have been deployed for the institute, where they work parallelly instead of letting one system take on a load of Kathmandu’s col d and humid climate.
SETBACK & SETPOINT TEMP : OPERATING SCHEDULE :
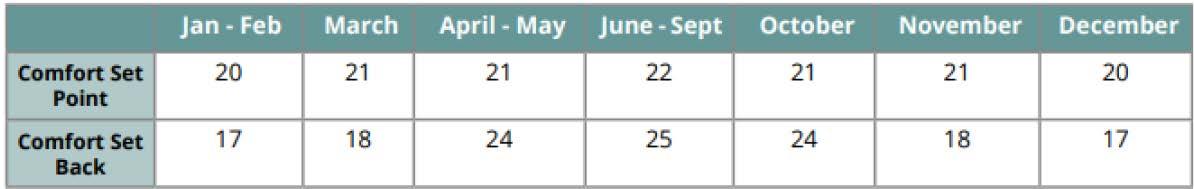
Comfort setpoint and setback temperatures have been set according to Comfort Temperatures Analysis according to ASHRAE 2019. This helps in decreasing the overall loads on the system.
The system is operated an hour prior to the starting of the university, with the temperature set back to ease the load on the system to directly condition the space and help achieve comfort.
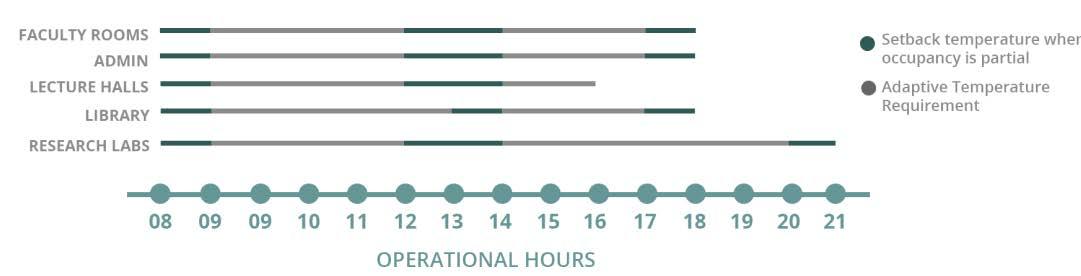
TEMPERATURES ACHIEVED :

ENERGY SAVING :
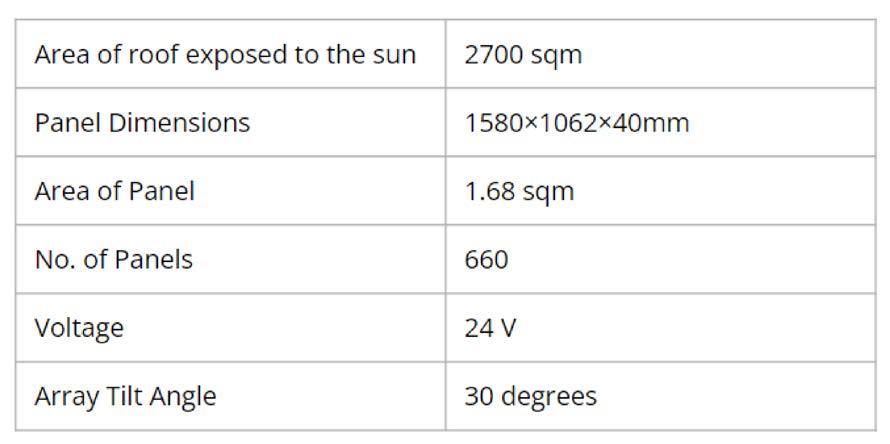
Through multiple iterations and simulations, after incorporating passive strategies, enhancing the building envelope and incorporating our proposed HVAC System, a reduction of 68% in heating loads and 84% in cooling loads of the building.
Indoor Temperatures achieved using simulation
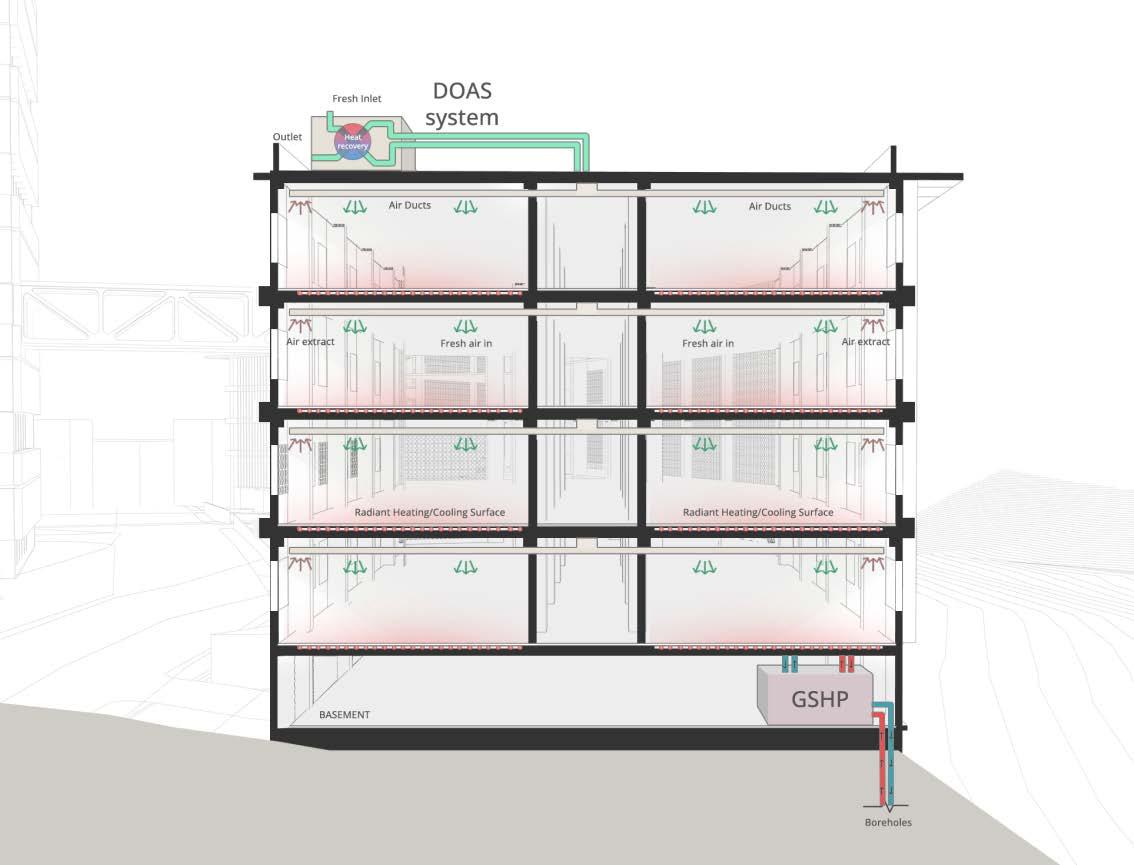 Sections showing working of HVAC during different months
Sections showing working of HVAC during different months
HEALTH AND WELLBEING MEASURES
INDOOR AIR QUALITY :




Created a green barrier using native plant species on the North-Eastern facade. This physical barrier cuts down the sun in summers and provides PM filtration as well. Plants with dehumidification and producing oxygen properties were planted throughout the atrium. These help in keeping CO2 levels below 1000 ppm (as per ASHRAE standards).
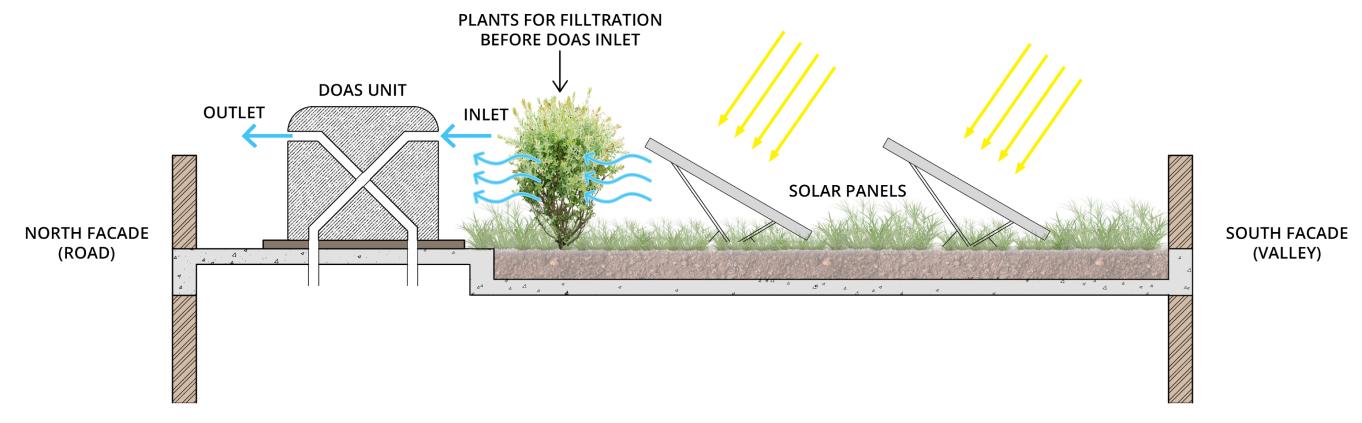 ROOF GARDEN FOR FILTERATION :
ROOF GARDEN FOR FILTERATION :
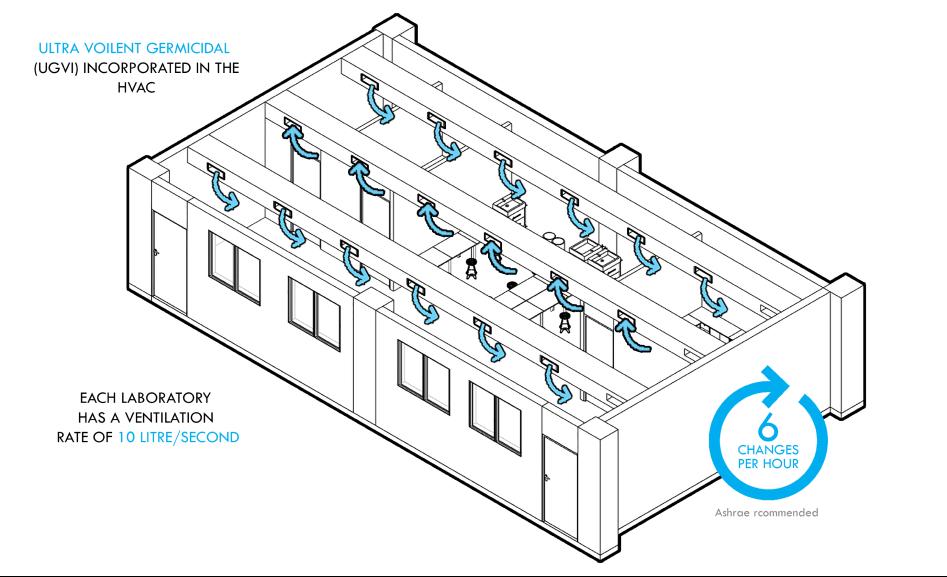
The DOAS unit placed on top of the roof takes in fresh air directly after it goes through a terrace garden surrounding the unit. The vegetation chosen black pine and golden dhupi are native and are known to assist in the deposition and removal of particulate pollutants as the air passes through the leaves The system has been laid out in a way to provide suitable air pressure, velocity and temperatures in the spaces. For the same, the fresh air supply ducts have been placed in the lower end of the walls and the exhausts have been placed on the ceiling level. Furthermore, media filters have been placed in the ducts as they are good for filtering out bacteria and fungus.
HVAC DUCTING & FILTERS :
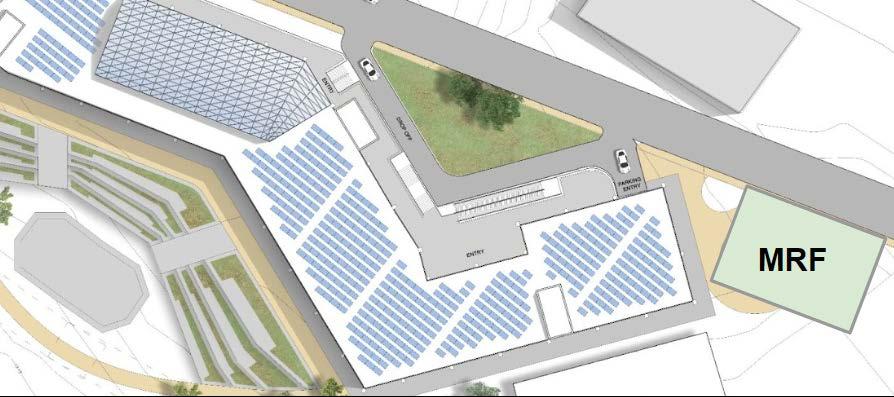
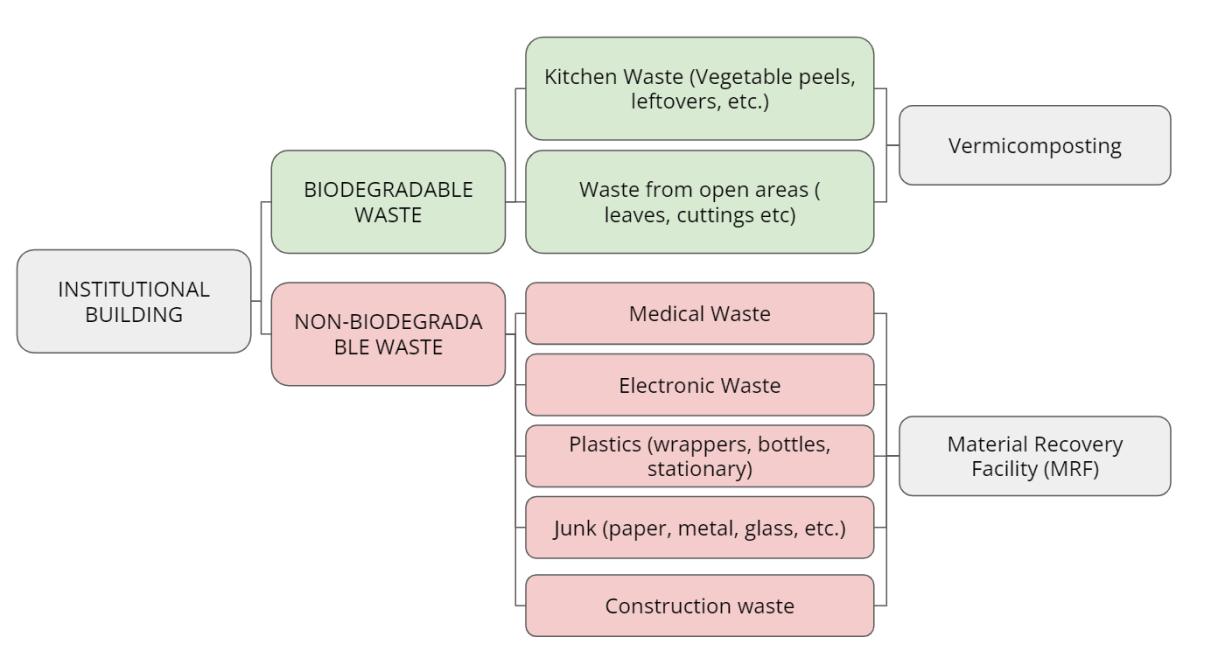
SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT
Setting up a Material Recovery Facility (MRF) onsite which is used to segregate the waste and create clean waste from the mixed waste. This clean waste is used to earn profit by selling it to the respective buyers and consumers.
The recyclable materials are sold to the recyclers and some industries, whereas the non-recyclables are sold to specific industries interested in buying this clean waste.
 Roof Schematic
Ducting Schematic
Roof Schematic
Ducting Schematic
ENERGY PERFORMANCE
DAYLIGHTING ANALYSIS
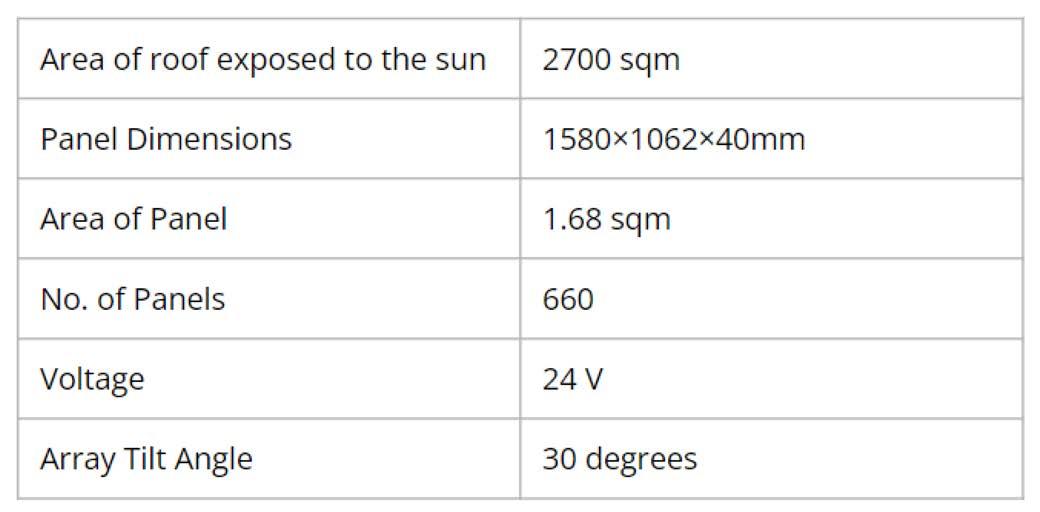
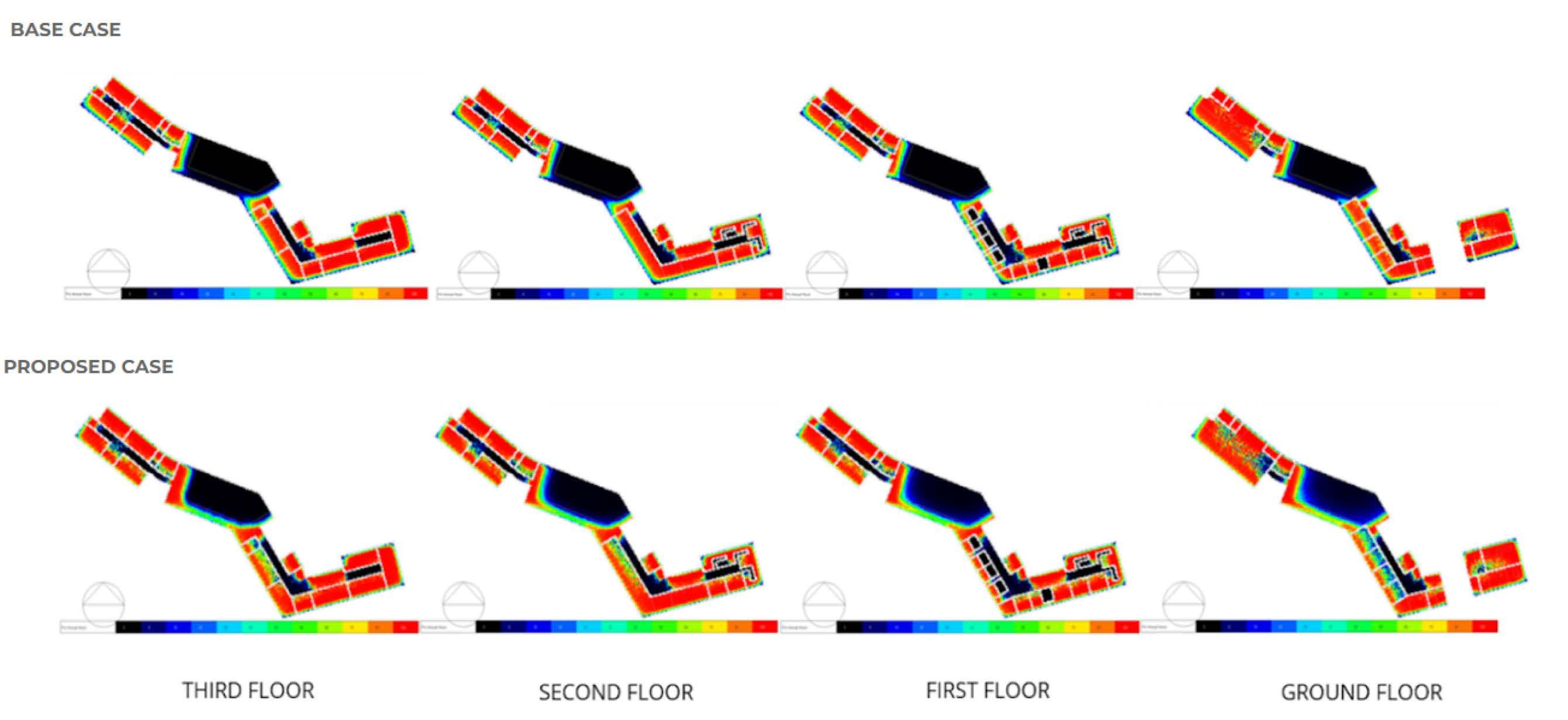
:

In terms of daylighting, For the Base case the window-wall ratio as 40% was considered, windows have no shading and have single 6mm glass panes. Also, there are no shading devices installed for the atrium skylight. For the proposed case, shading device were used which were designed using shadin g mask.

Simulations done on Design Builder
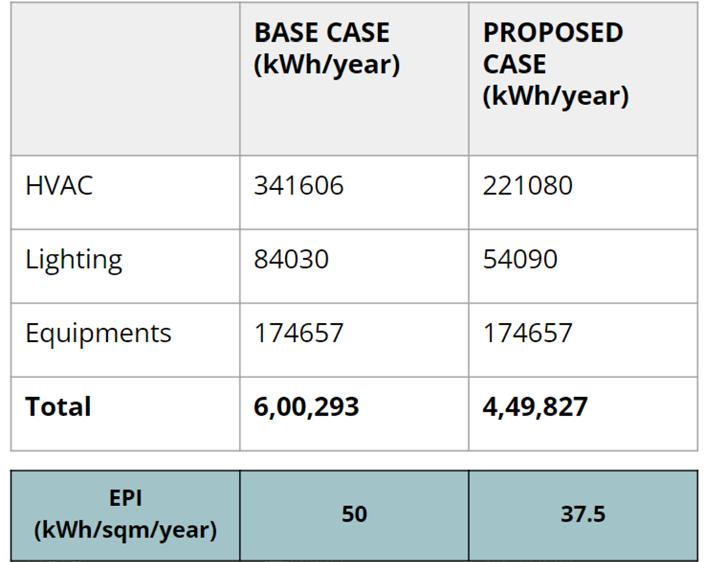
PERFORMANCE INDEX : ENERGY GENERATION :
Energy efficient measures were taken to reduce the electrical consumption. After all the simulations a final energy consumption comparison between the base case and the proposed case was done. Overall there was a 25% decrease in energy consumption.
REQUIREMENT
GENERATION
37.5 kWh/sqm/year 38.4 kWh/sqm/year
Net Zero energy status of the building = 38.4 - 37.5 = 0.9 kWh/sqm/year (Net Zero Achieved)
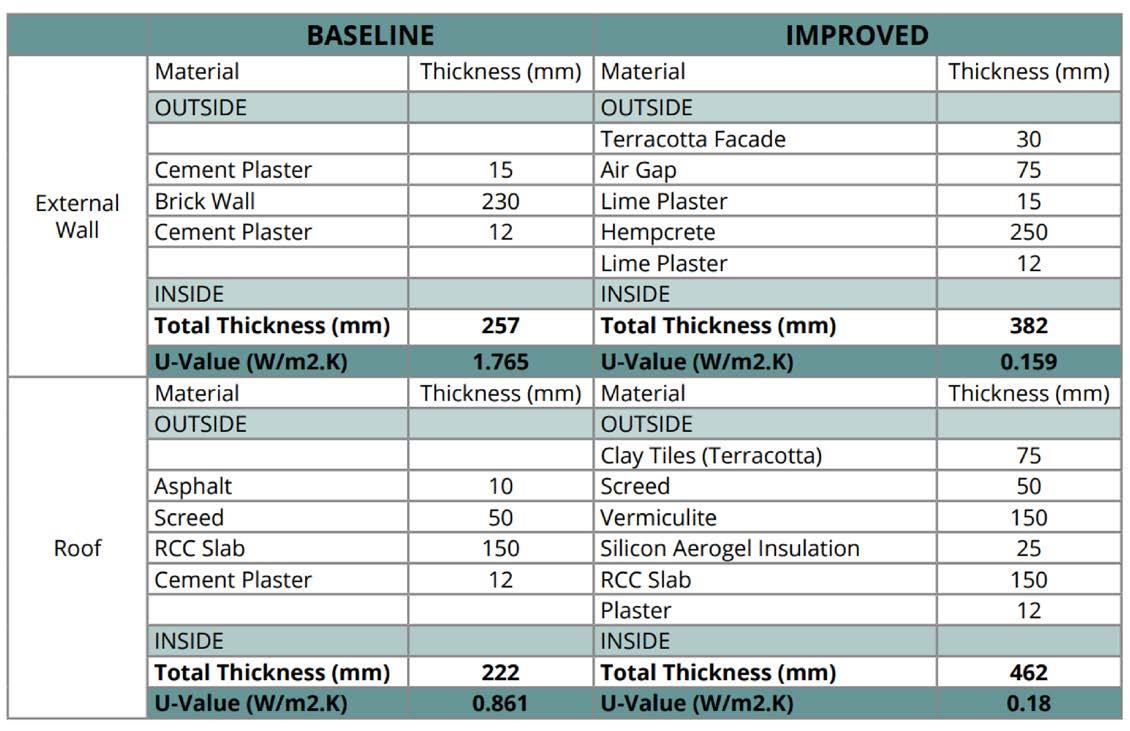
BUILDING ENVELOPE
EXTERNAL WALL SECTION :
Cement Concrete Coping (100 x 350)
Brick Wall (230)
Brick Flooring (50)
Cement Screed (1:3:6, 50)
Cement Concrete Fillet (1:2:4, 75x75)
Vermiculite mixed with Cement (4:1, 150)
Silicon Aerogel Waterproo ng Layer
Light-shelf (750)
Wooden Window Frame
RCC Cill (100 x 350)
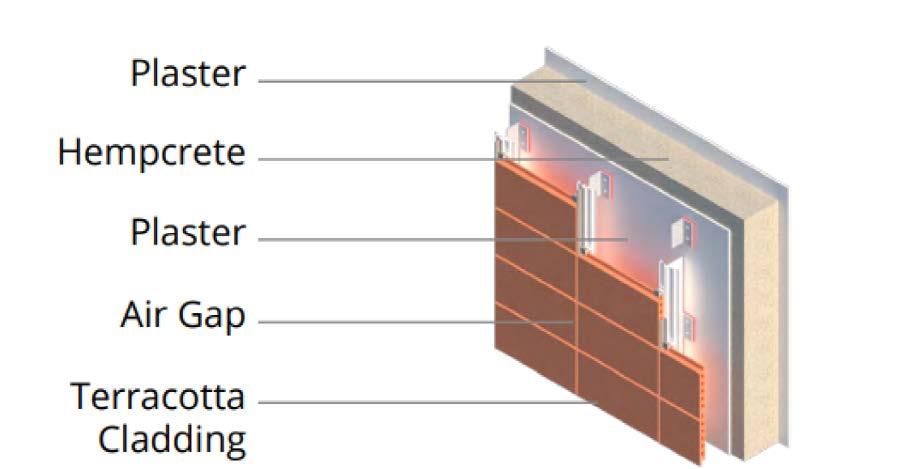
Terracota Cladding (25)
SS Framing (75)
External Cement Plaster (15)
RCC Slab (150)
RCC Beam (750)
RCC Lintel (100 x 350)
Vertical Louvre (175)
SS Framing (50 x 25)
RCC Cill (100 x 350)
Hempcrete Wall (250)
Internal Cement Plaster (12)
RCC Beam (Elevation)


Flooring (40)
PCC Sub- Floor (60)
Radiant Heating & Cooling Piping (25)
Skirting (125 x 15)
Transom (67 x 130)
Mullion (130)
Double Glazed Unit (6+12+6)
Vertical Louvre (175)
SS Framing (50)
Ceiling Plaster (6)
Concrete Block (50 x 100)
Plinth Protection (1500)
RCC Retaining Wall (230)
Brick Wall (115)
Tremix Flooring (100)
PCC (250)
Sand (450)
RCC Foundation (600)
PCC Gola (75 x 75)
Stone Waterproo ng (25)
PCC (1:4:8, 75)
Nepal has a humid climate for 50% of the year and heavy rainfall during the monsoon months, thus a terracotta ventilated facade system was used. Due to terracotta’s high water absorption capacity it draws moisture away from the structure and protects the hempcrete wall while also preventing rise in humidity indoors.
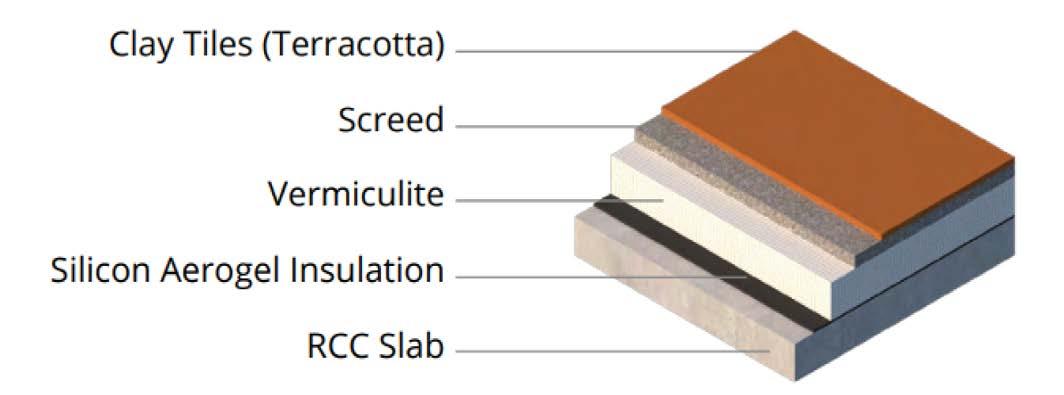
Isometric of Roof Assembly
Isometric of Wall Assembly
FACADE AND ROOF TREATMENT :
For the wall and roof assembly of the building, ECBC Guidelines were refered to maximise the building’s efficiency.
WATER PERFORMANCE
The goal to develop a net zero water building was achieved thanks to the abundant rainfall in Kathmandu, Nepal. Water for domestic use was collected from the roof surfaces & hardscapes. After an analysis of the drainage & contours, an artificial pond storing harvested rainwater all ye ar round was proposed.
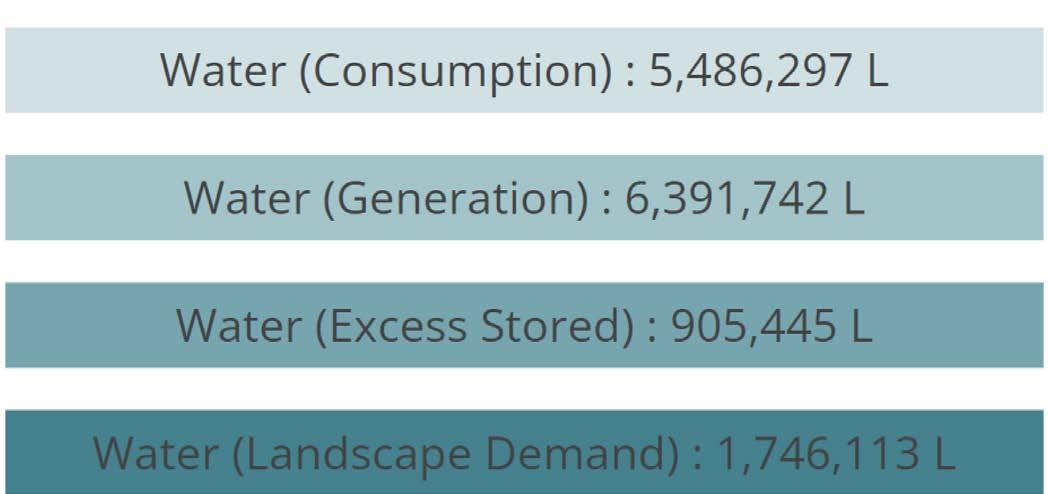
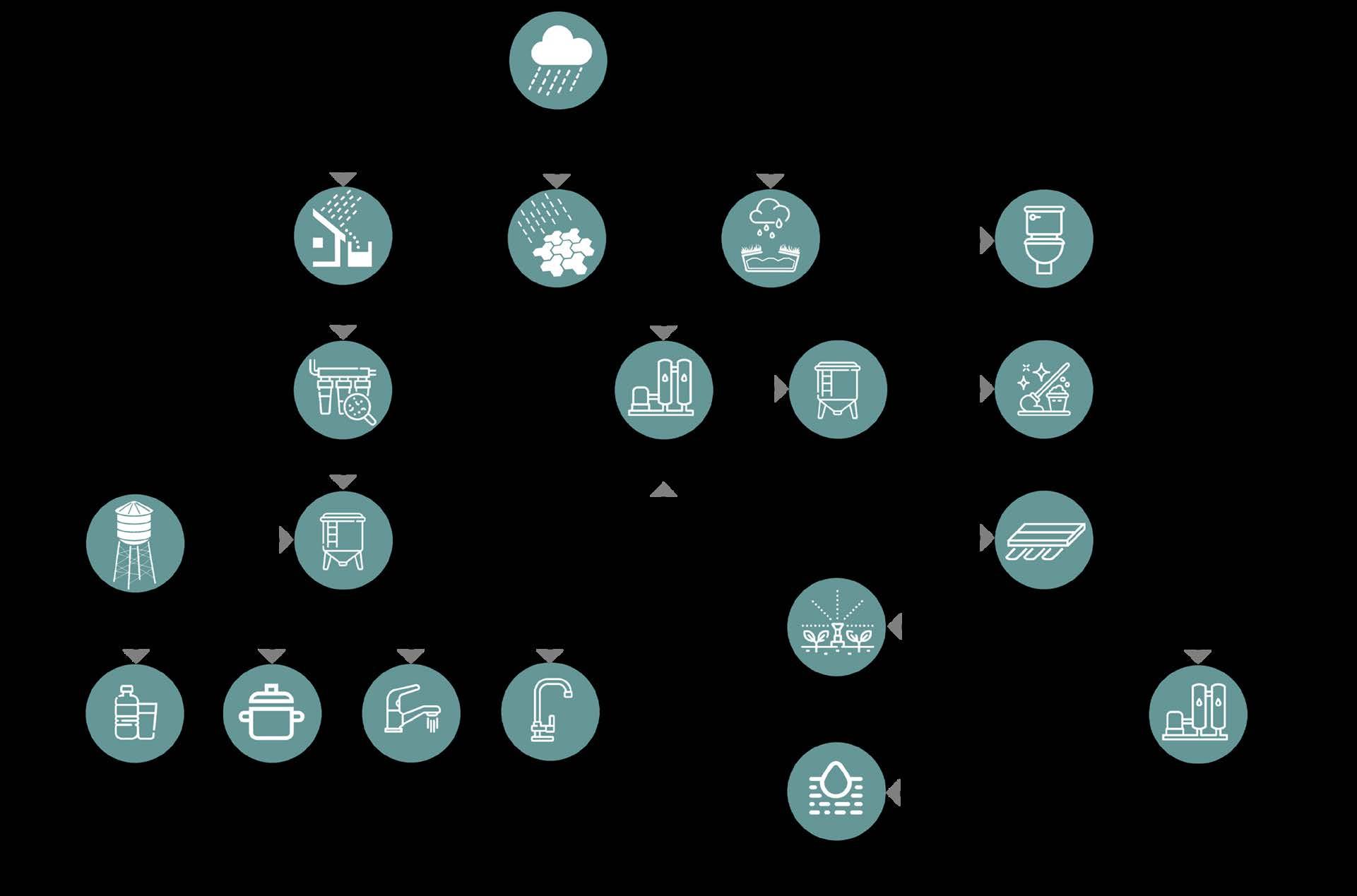

The harvested rainwater is stored on campus for daily potable use. The grey water generated is recycled for use in cooling & irrigation. Black water is treated & then used for irrigation.
For on-site wastewater treatment, we used DEWAT Systems and Constructed Wetlands as a cost effective, natural and sustainable treatment system for wastewater.
WATER CYCLE DIAGRAM :
Water system proposed for design
AFFORDABILITY : Cost Breakdown, Life Cycle Cost and Savings
BASELINE COST BREAKDOWN :
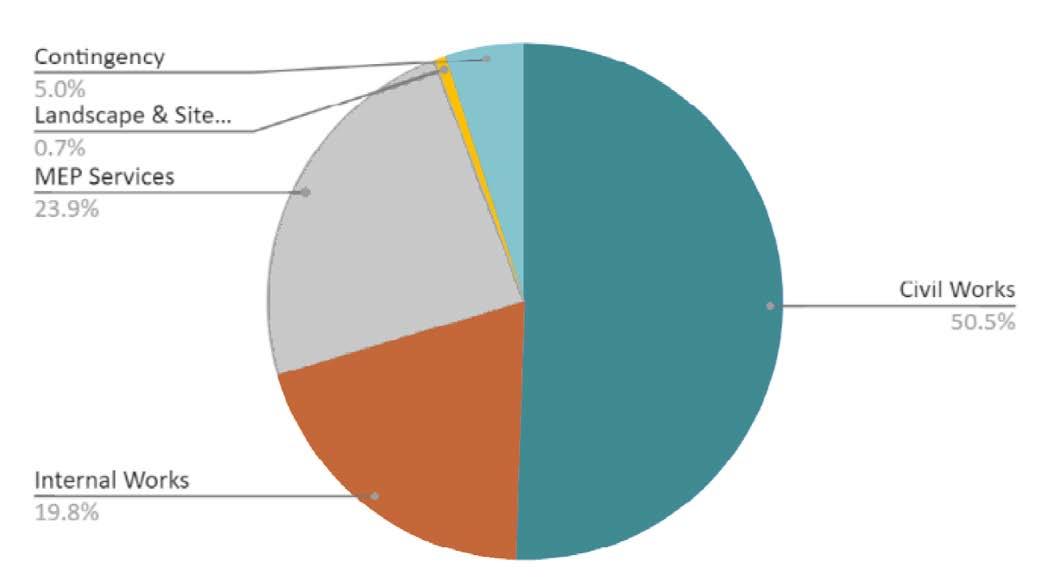
PROPOSED COST BREAKDOWN :
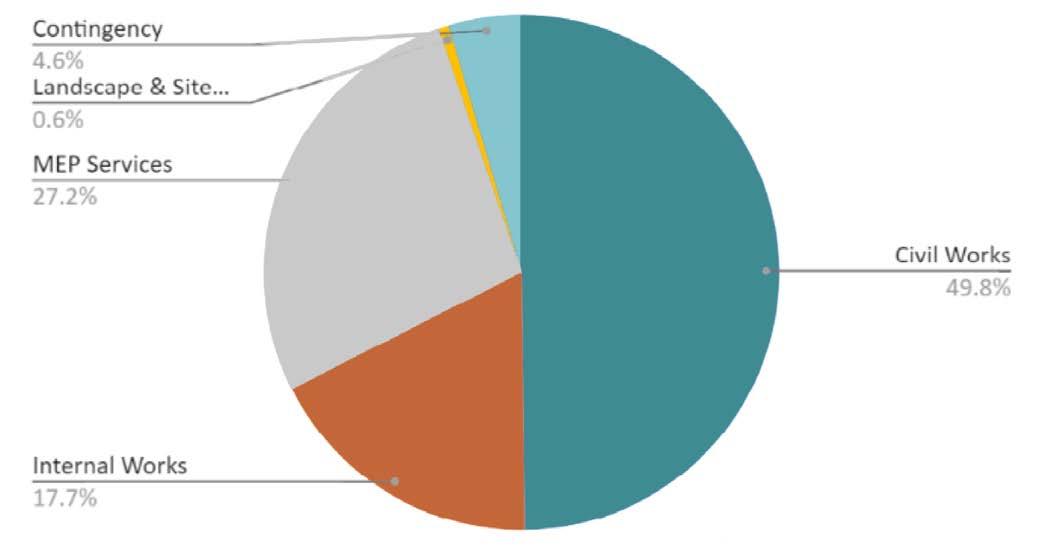
Total cost - 469.91 million NPR. (294.56 INR)
Cost per Sqm - 28917.6 NPR (17,961 INR)
OPEX- 99 million NPR (62.05 million INR)
Total cost - 513.42 million NPR (321.84 INR)
Cost per Sqm - 31,594.6 NPR (19,624 INR)
OPEX- 49 million NPR (30.7 million INR)
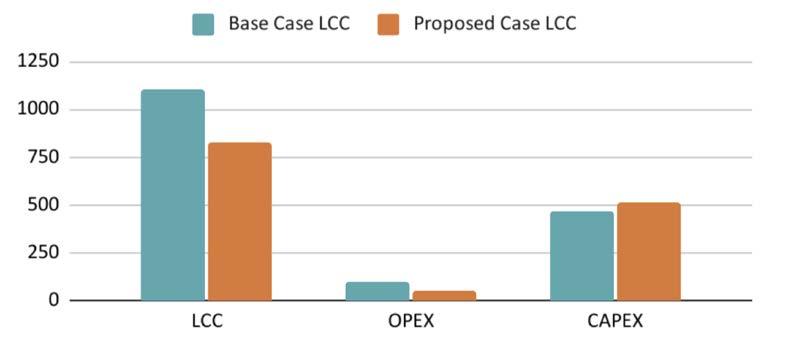
• Proposed design is 9.3% more expensive than the base case.
• Life cycle cost decreased by 25% i.e. from 1101 million (Basecase) to 826 million (Proposed).
• Operational cost is reduced to almost half, from 99 Million NPR to 49 Million NPR.
RESILIENCE
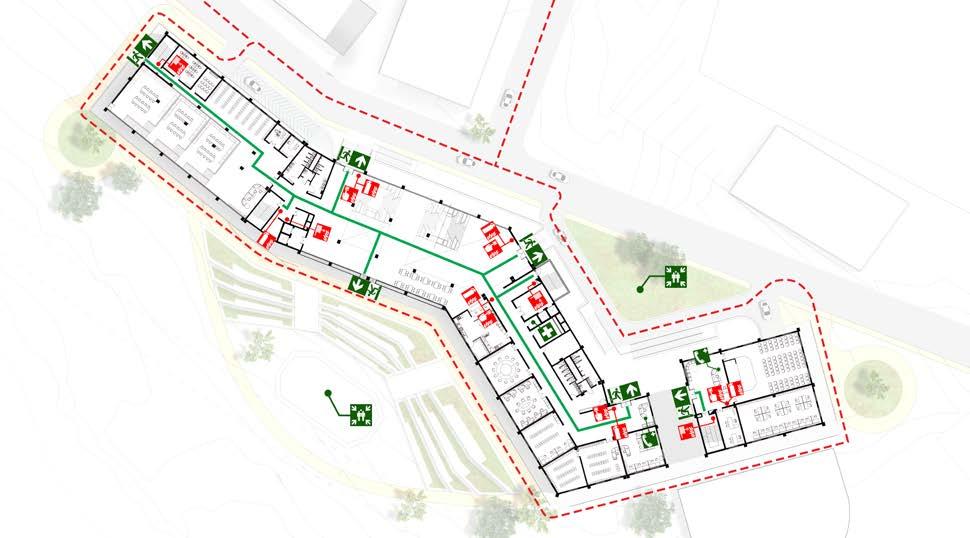
FIRE RESILIENCE : PUBLIC HAZARD :
Our building is designed in accordance with the fire safety norms of the Nepal NBC 107 : 1994. All the staircases are compliant to fire safety.
Indoor air recirculation shall be prevented or reduced to the greatest extent practicable. One of the initiatives we took to achieve this in ourinterior areas was to install a DOAS (Dedicated Outdoor Air System).
Fire Safety Plan
Indoor Air Circulation : Labs
BHAKTI BHAWAN
AUDITORIUM BLOCK, TRIBHUVAN UNIVERSITY KATHMANDU, NEPAL


BHAWAN UNIVERSITY
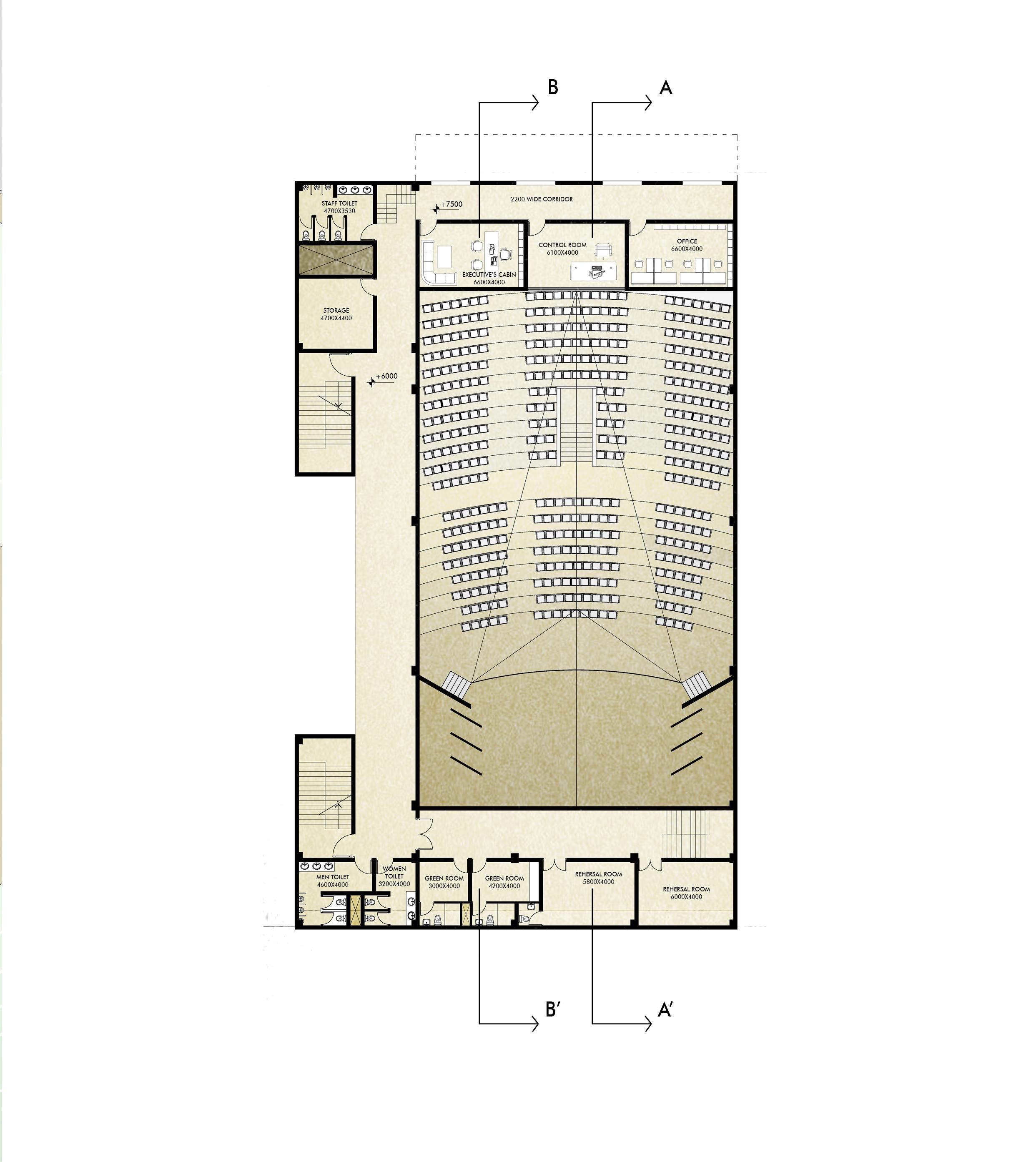
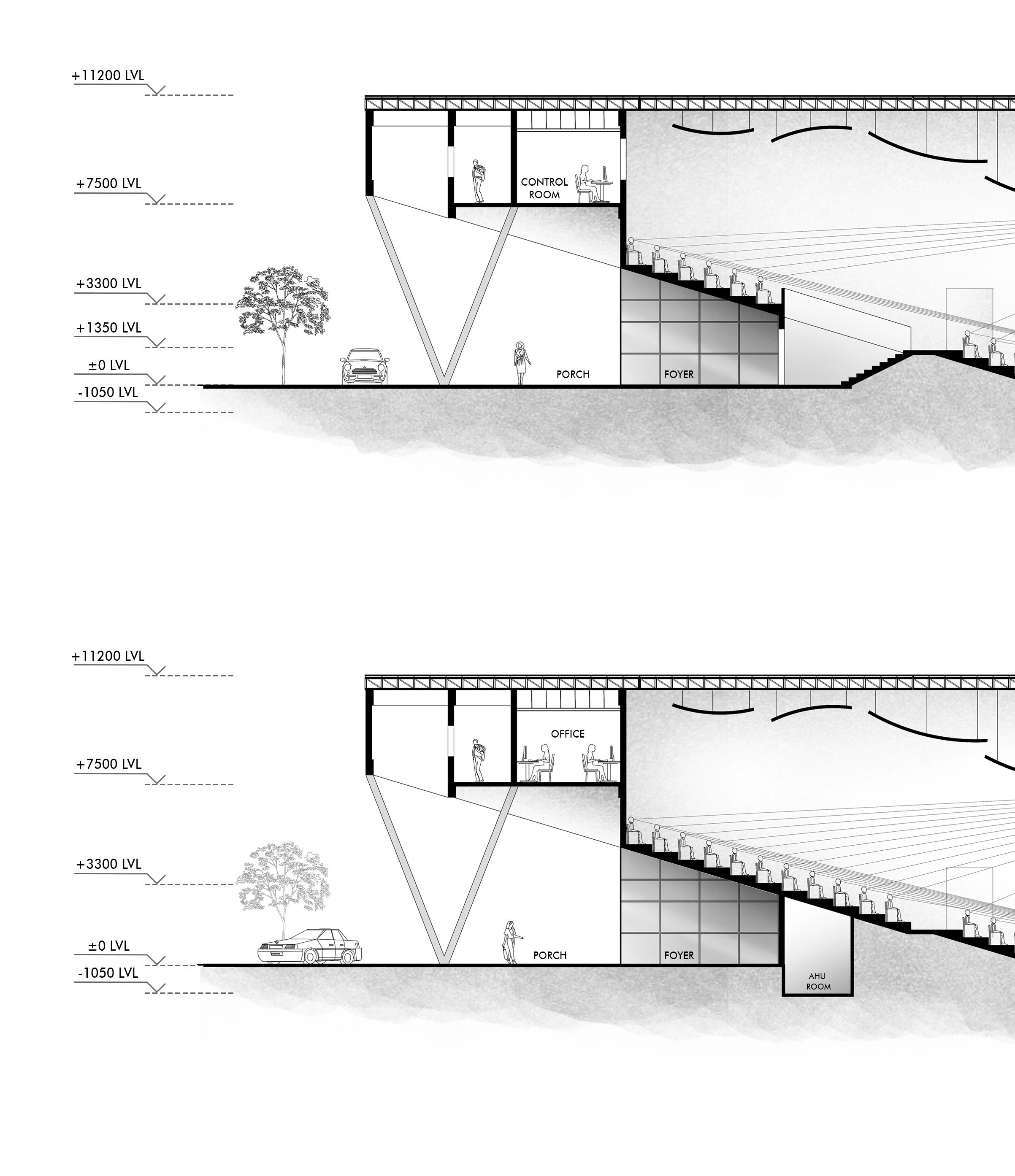
The project is a part of Tribhuvan University Medical expansion project. Brief was to build an auditorium with a capacity of 500 people . The auditorium block is next to the academic block. Little Theatre Group (LTG) Auditorium, New Delhi was visited as primary case study. Site AreaBuilt-Up Area2400 sqm 1600 sqm
Area Programme -
Foyer / Exhibit area Hall Stage Green rooms VIP lounges Prop storage Rehersal room Washrooms AHU
: 92.4 sqm : 480 sqm : 167.5 sqm : 57.6 sqm : 23.2 sqm : 24 sqm : 47.2 sqm : 97 sqm : 13.4 sqm
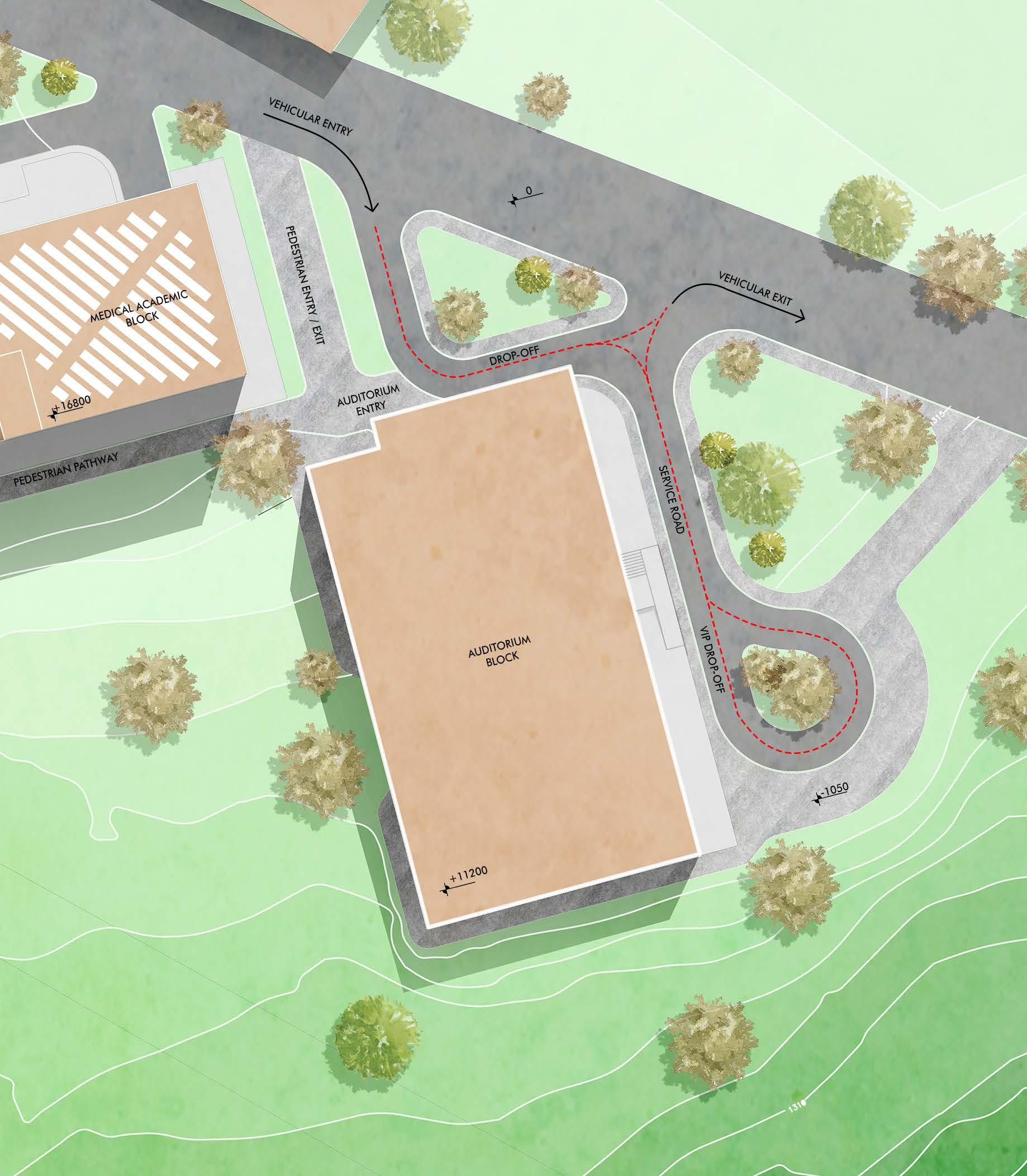

Site Plan 10 20 30 40 0
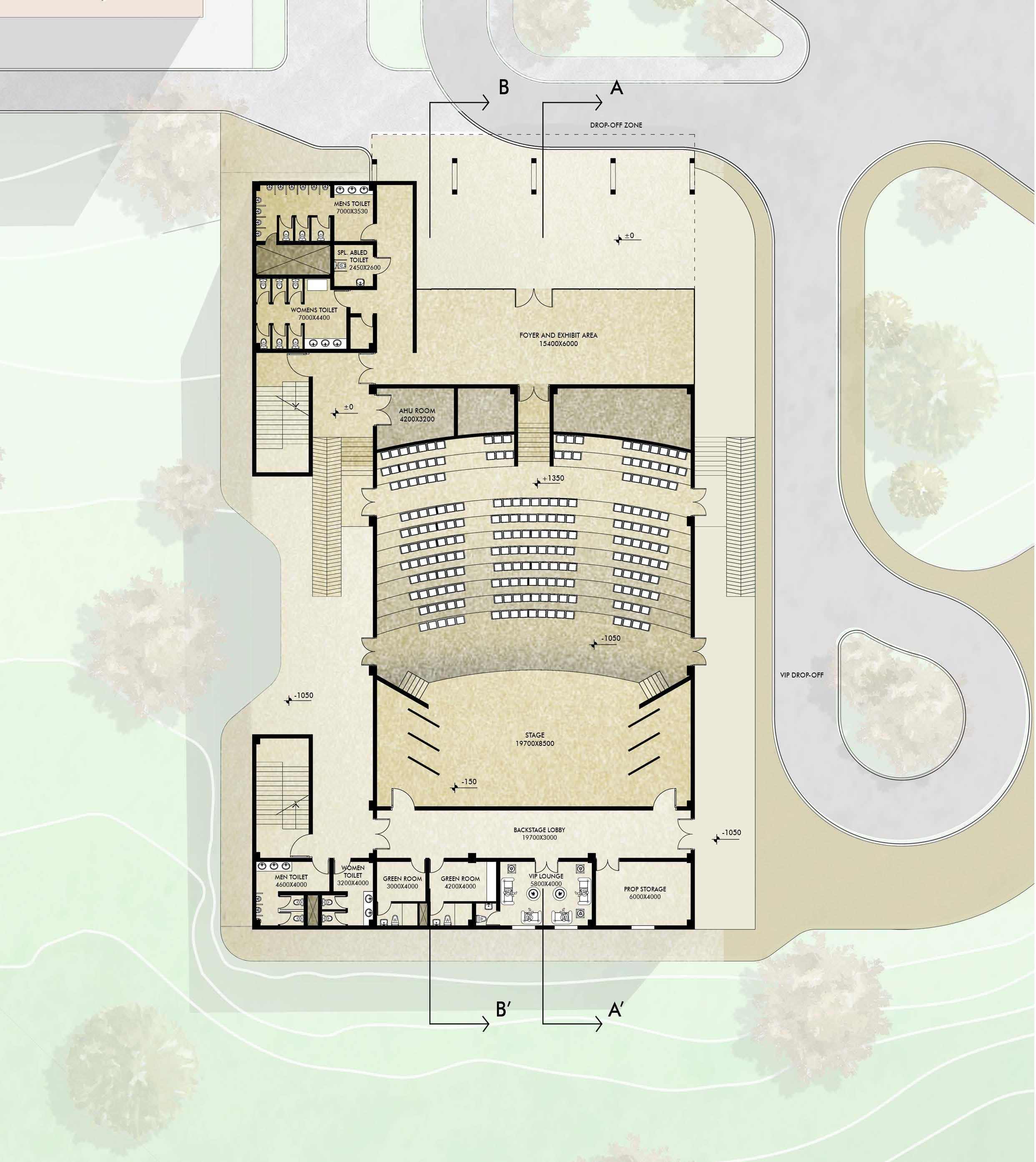


Lower Floor Plan 10 5 0


Upper Floor Plan 10 5 0
5 10 0
5 10 0
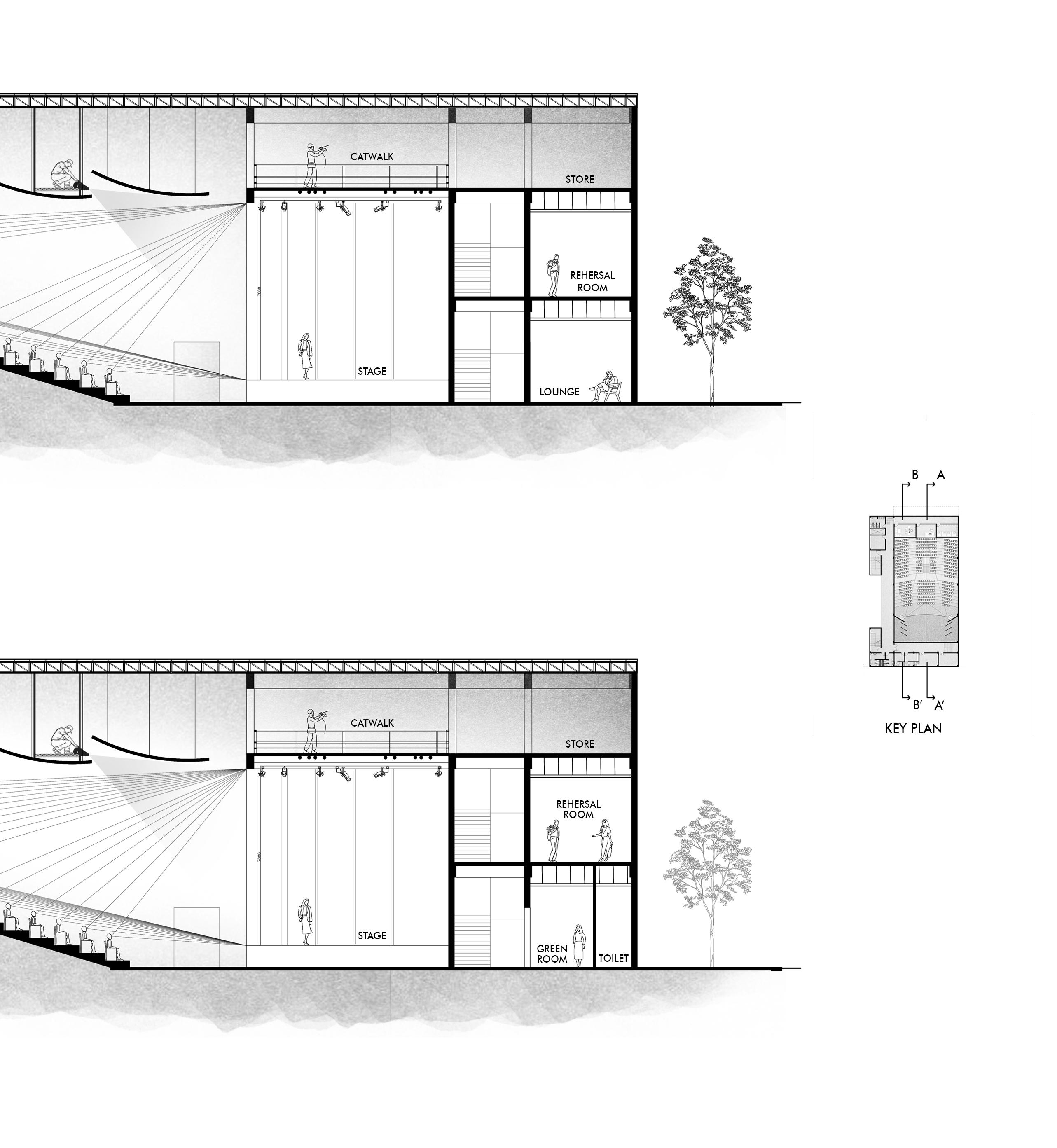
Section AA’
Section BB’


LOW
COST
HUDCO 2022
COST HOUSING DESIGN COMPETITON AHEMDABAD, GUJARAT

Ahmedabad was founded in 1411 by Sultan Ahmed, to serve as the capital of the Gujarat Sultanate. The city is now the hub of industrial, trade, and commerce activities in Western India. Ahmedabad has a segmented development pattern due to a high concentration of textile mills in the eastern part and rental housing for industrial workers in the form of Chawls – single-room housing units with common water and sanitation facilities – that were built in the proximity of the textile mills in the East. The migrant labour and other low-income families had to find shelter in the slums that emerged as a response to the demand for low-income housing. Thus, there was a huge increase in the number of chawls from 1990 to 2001. Ahmedabad is one of the few cities in India that has a pro-poor policy for the provision of water and sanitation to slums. Making Ahmedabad a slum-free city was a goal in the City Development Plan (CDP) prepared in 2006. Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation’s ‘Slum Free City Action Plan’ is a part of its overall strategy that comes under the Rajiv Awas Yojana.
The main focus of this scheme is in:
• Bringing existing slums within the formal system and enabling them to avail of a similar level of basic amenities as the rest of the town/ city.
• Redressing the failures of the formal system that underlie the creation of slums.
• Tackling the shortages of urban land and housing that keep shelter out of reach of the urban poor and compelte them to resort to extralegal solutions in a bid to retain their sources of livelihood and employment.
Many private companies provided low-cost rental units to migrant industrial workers.
No new Chawls were built. Low-income families had to find shelter in the slums
Many new slums also came up in Ahmedabad due to the Urban Land Ceiling Act
The presence of mills led to widespread encroachment, leading to a sudden increase of the number of slums






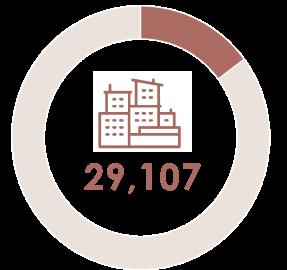
The growth rate declined at a negative rate of 0.3%, with 19,355 households living in 67 pockets by 2012.
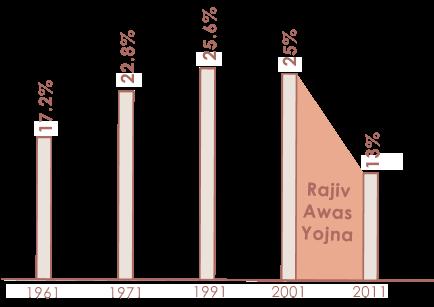
Change in the Percentage of Slum Housing over the Years
The city is expected to grow at a moderate rate and stabilize by the year 2035 with a population of 11 million. The plan for a city without slums will have to take cognizance of this projected growth and ensure that new slums do not occur in the future.
 Urban land and ceiling act
Rajeev Awas Yojana 1976 2009
THE TIMLINE : SLUMS IN AHEMDABAD
Total Slum Settlements in Ahmedabad
Urban land and ceiling act
Rajeev Awas Yojana 1976 2009
THE TIMLINE : SLUMS IN AHEMDABAD
Total Slum Settlements in Ahmedabad
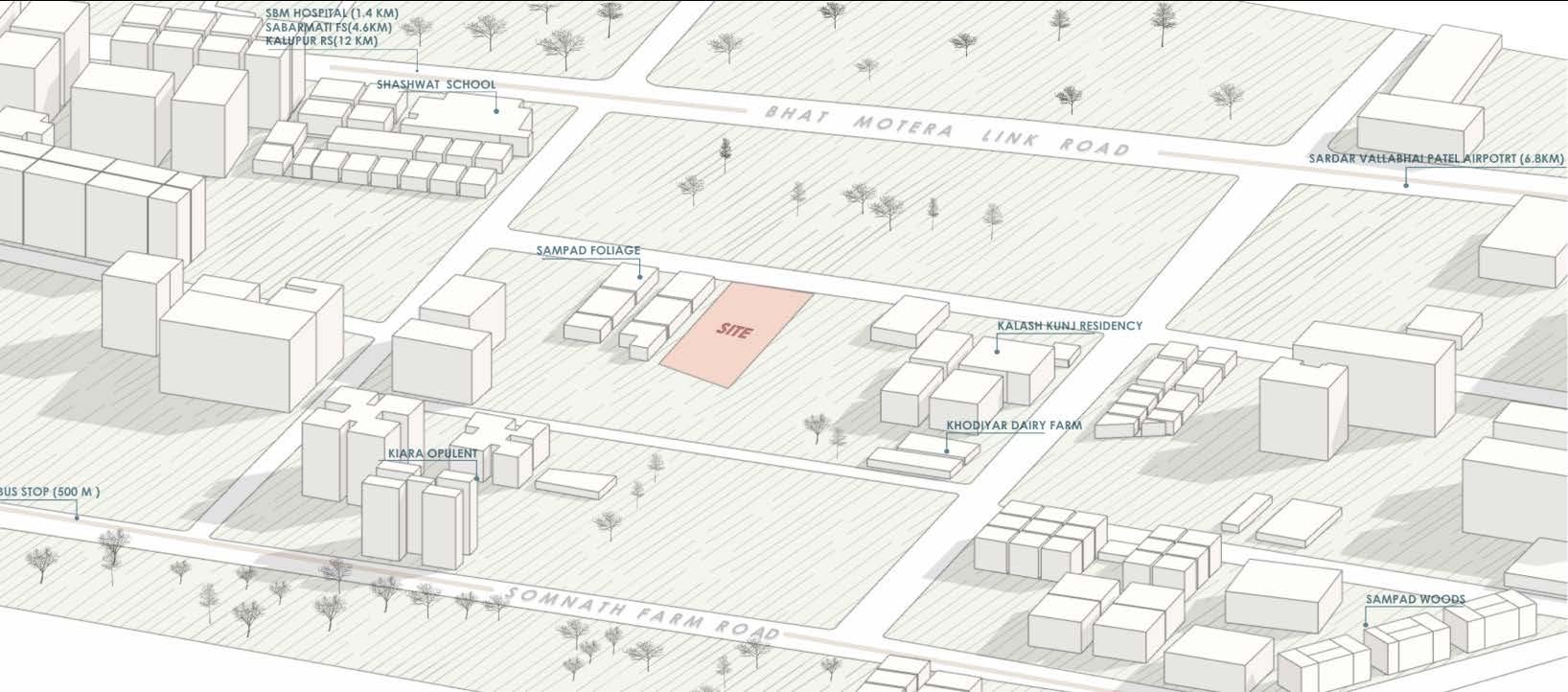
SITE STUDY
A Glance at Hot and Dry Region in India
SITE CONTEXT




RAINFALL (LOWEST)
Arid- 350mm per year
Semi arid- 500mm per year

HUMIDITY
Low 10-15% DURATION
April - June TEMPERATURE
Around 30 -32 C
SKY CONDITION
Cloudless skies, high solar radiation, (clausing glare)
INTERNAL COURTYARD
Cross ventilation and Thermal buffer.
STRATEGIES



RADIATION BARRIER



Canopies, Chajjas,and long verandahs etc. on the west side
EXTERNAL WALLS

Walls are thick and hollow for insulation
VEGETATION

For purification of air and increasing humidity in and around

ROOFS
Applying light and ahining paints to reflect solar radiation.
SUSTAINABLE MATERIAL
SMALL WINDOW OPENINGS
Small and minimal to reduce heat gain
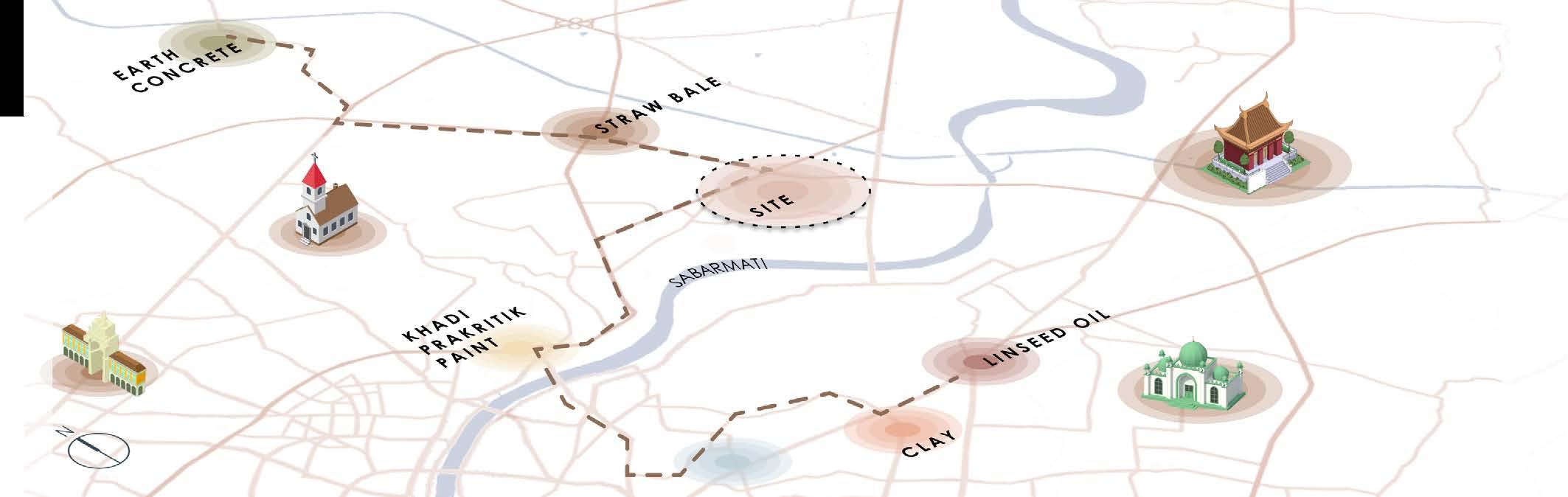
CLAY
BAMBOO EARTH CONCRETE
STRAW BALE KHADI PAINT LINSEED OIL


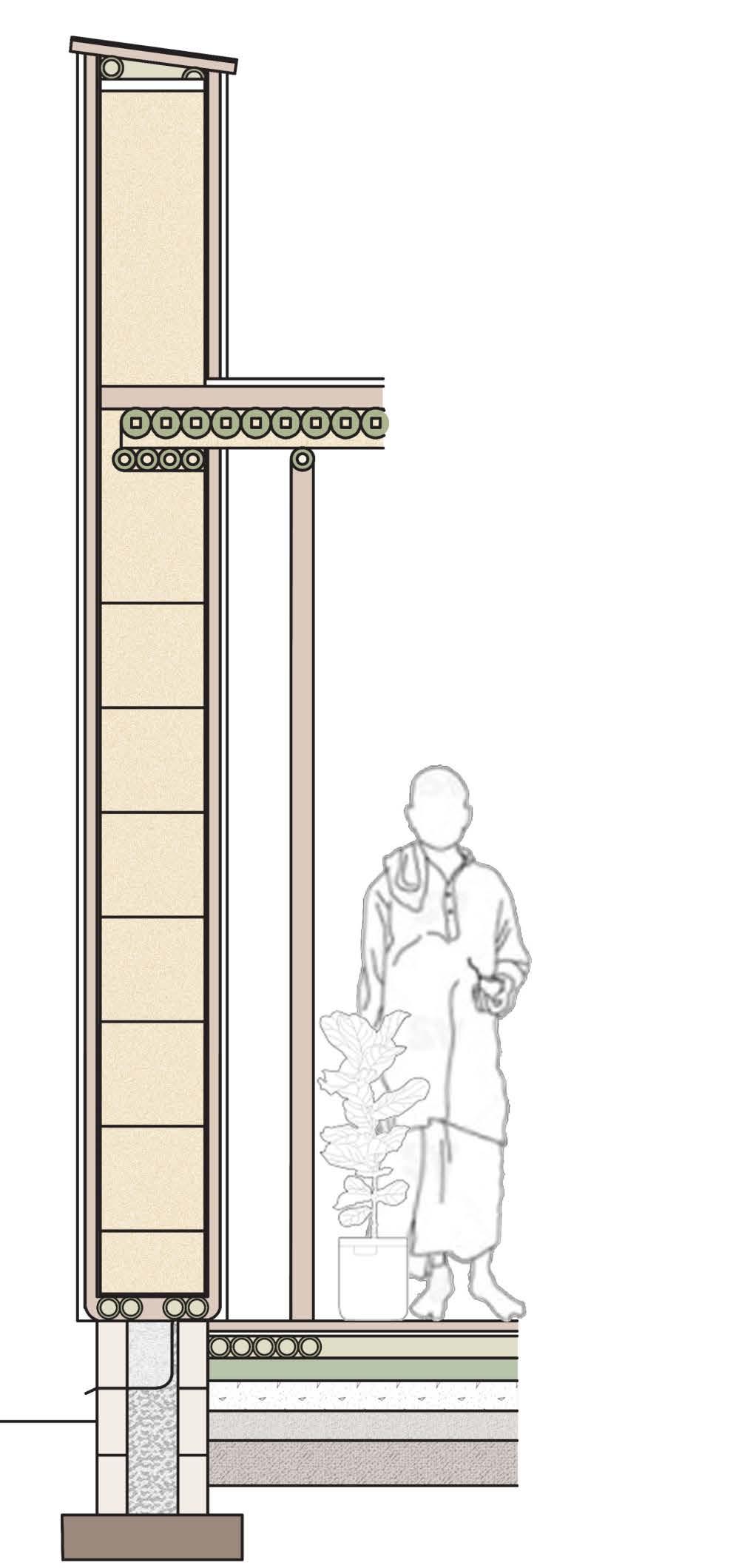
300 MM THK. STRAWBALE 40 MM THK. CLAY PLASTER 0.5 MM POLYPROPYLENE MESH 125X35 TIMBER PANEL 125 MM THK. CLAY INFILL WALL 12MM THK LIME PLASTER 75 MM DIA. BAMBOO FRAMING
DETAIL A
24 MM THK. PLYWOOD
50X75 WINDOW FRAME 350X380 HARDWOOD 24 MM THK. PLYWOOD 50 MM THK. TIMBER PANEL 75 MM DIA. BAMBOO FRAMING PLAN
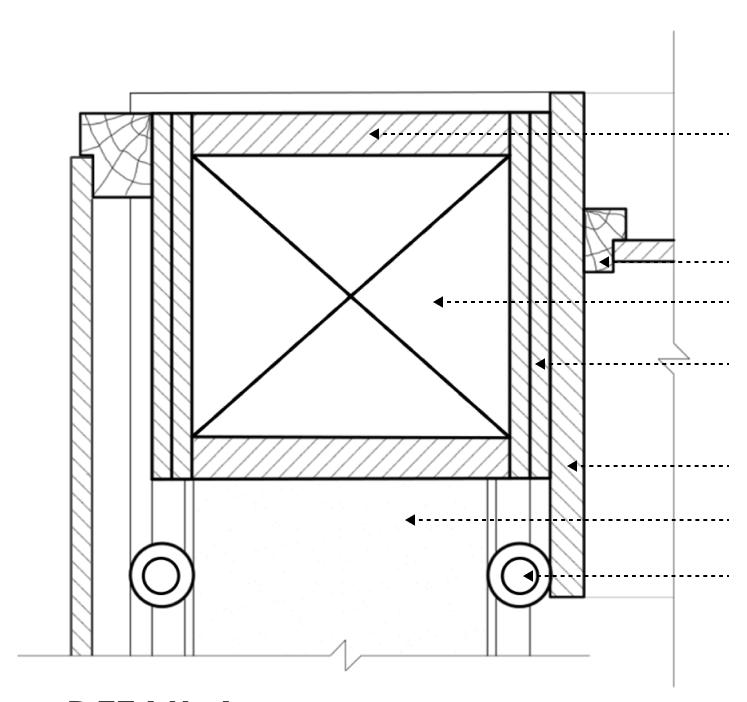
DETAIL B
125X35 TIMBER PANEL 12 MM THK. LIME PLASTER 125 MM THK CLAY INFILL WALL
50 MM THK. TIMBER PANEL 330X300 HARDWOOD 85X100 DOOR FRAME 24 MM THK. PLYWOOD
DETAIL C
85X100 DOOR PANEL 125X35 TIMBER PANEL 125X35 HARDWOOD 125 MM THK. CLAY INFILL
12 MM THK. LIME PLASTER
25MM THK. DOOR SHUTTER
DETAIL D
PLAN
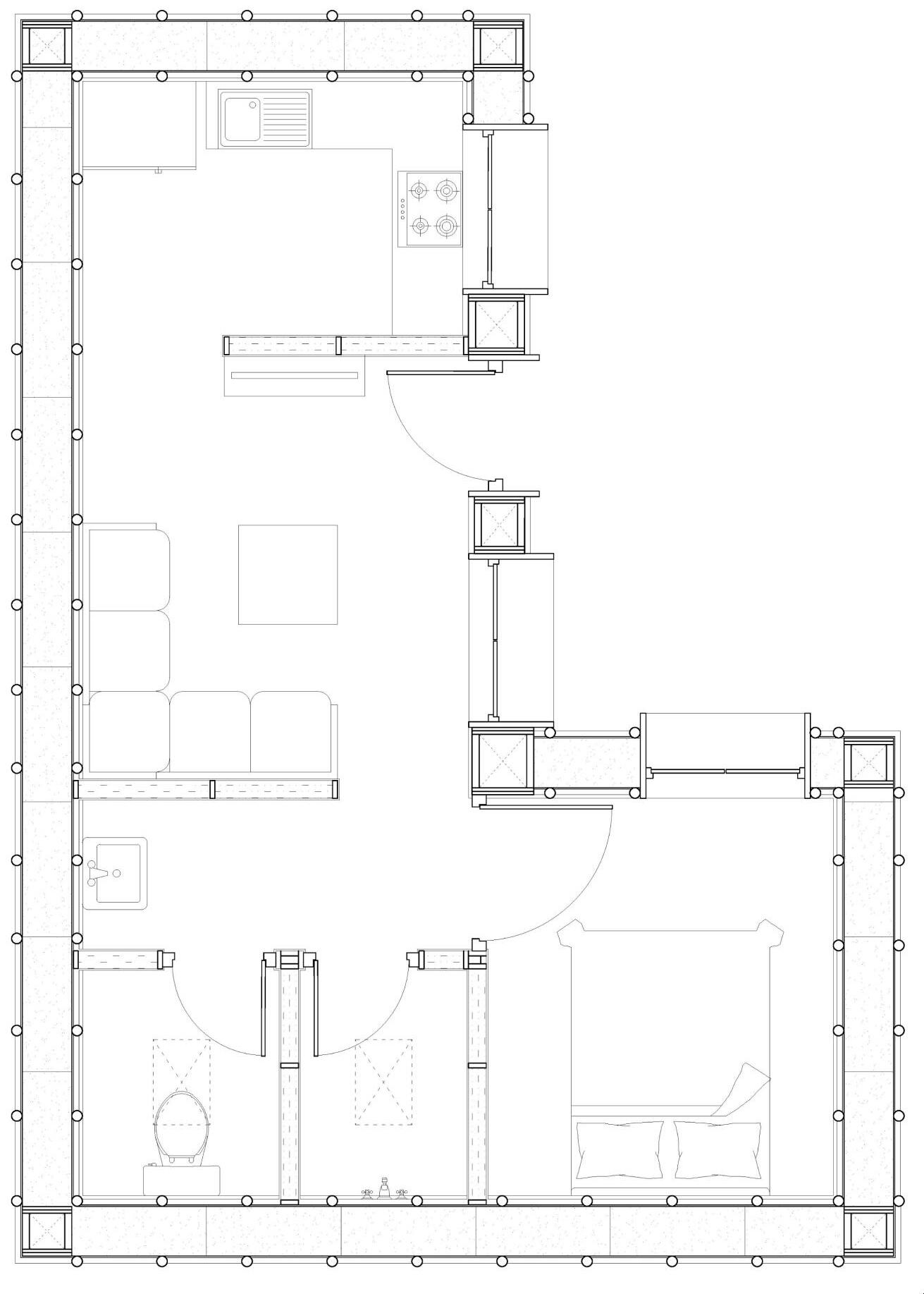
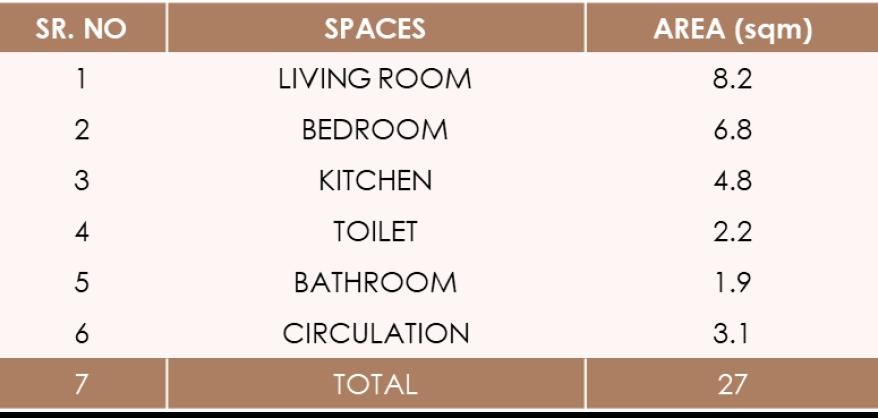
AREA PROGRAMME
DETAIL C A DETAIL B DETAIL A DETAIL D A’ B’ B
KITCHEN TOILET LIVING BATHROOM BATHROOM BEDROOM SECTION AA’ SECTION BB’
BEDROOM
BATHROOM
TOILET
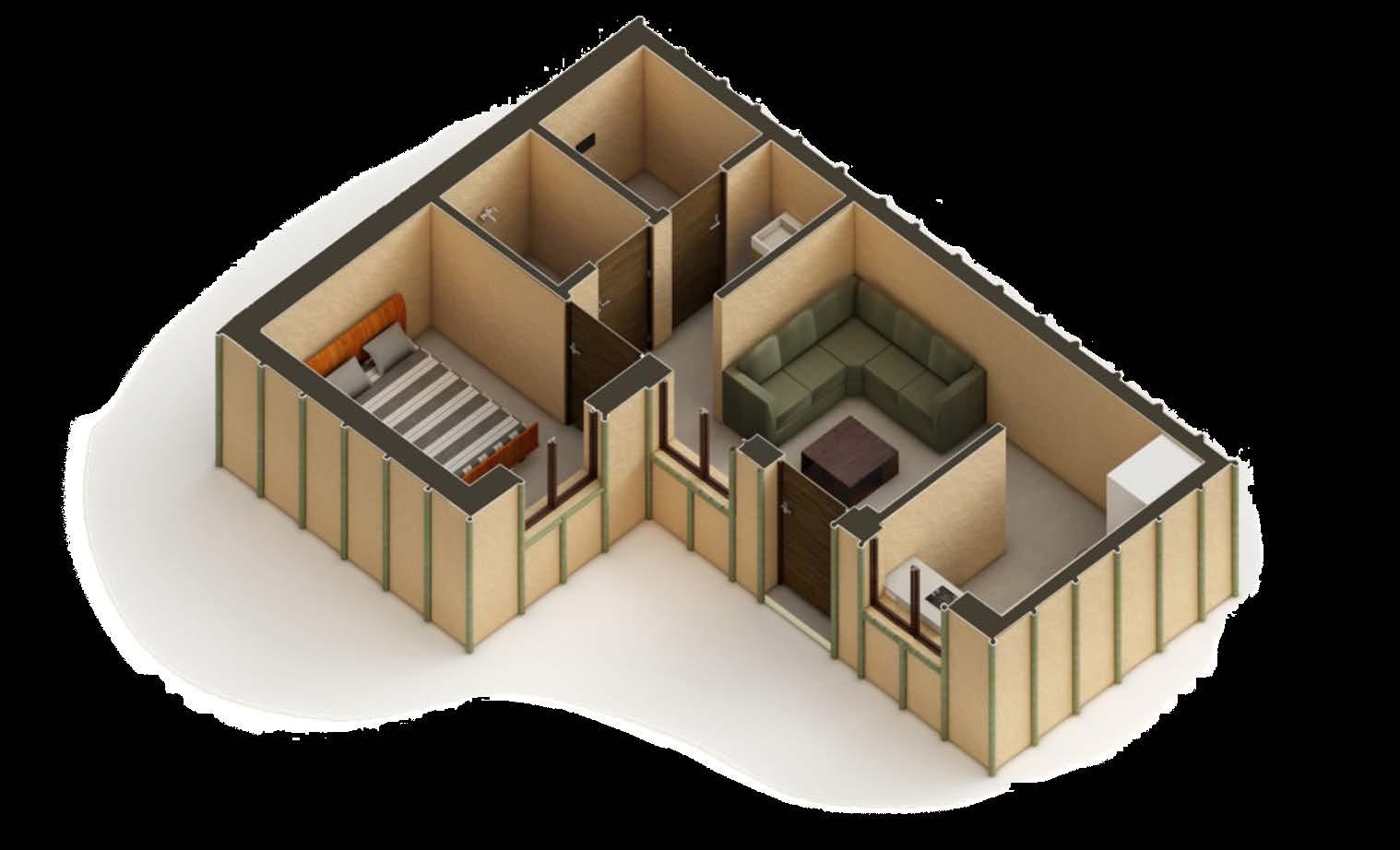
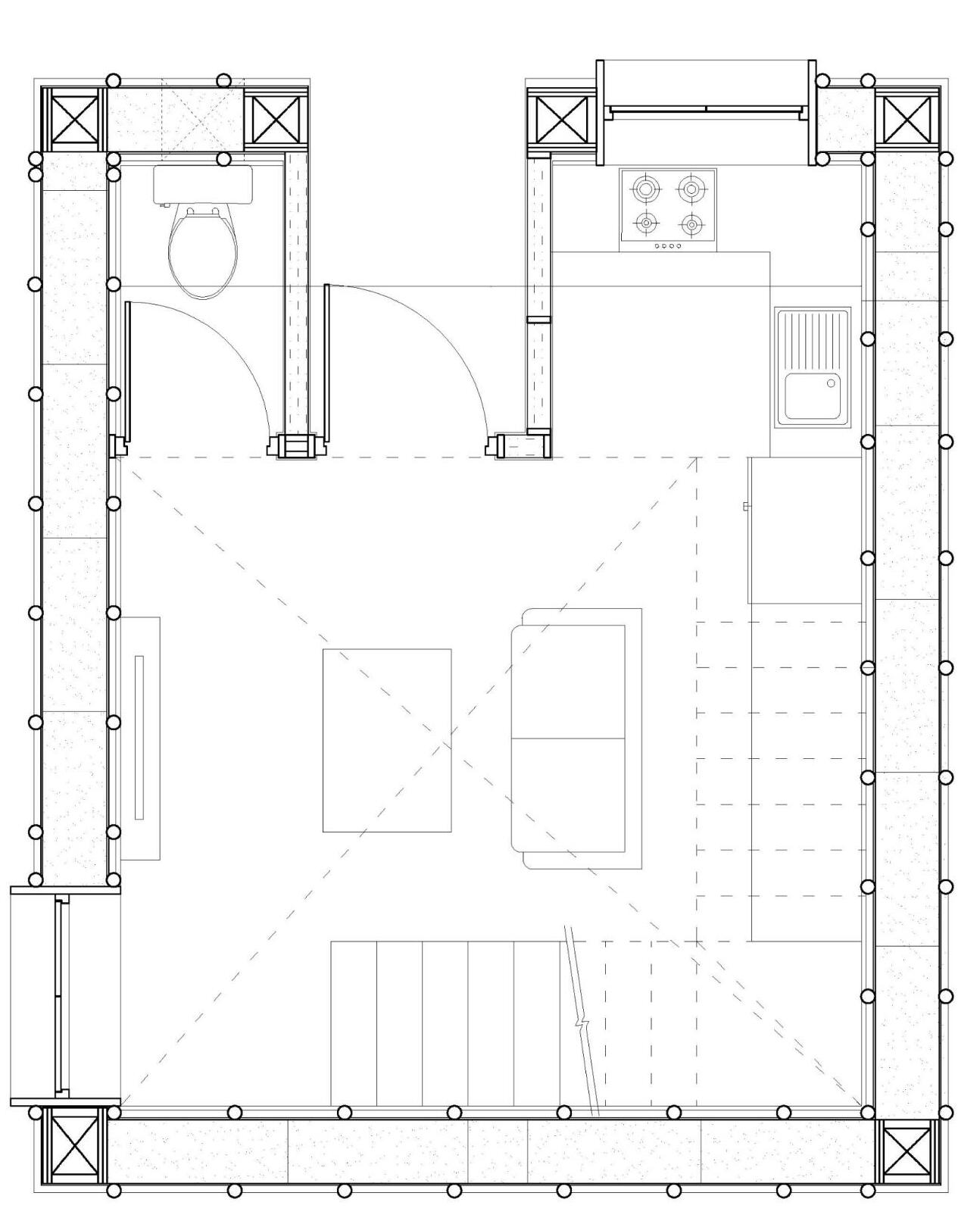
LIVING ROOM ISOMETRIC PLAN


KITCHEN
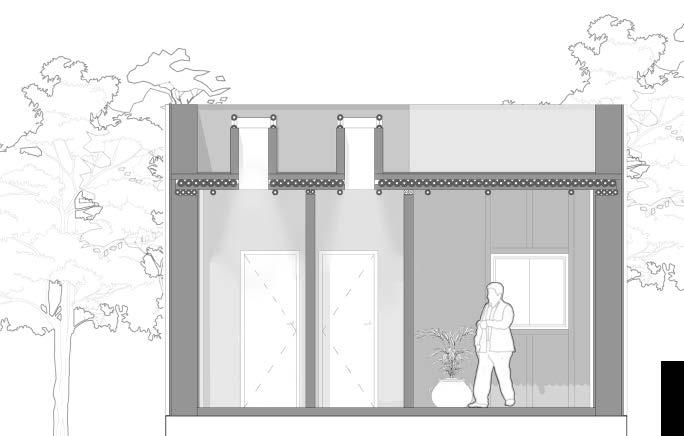
 View of living room facing the Kitchen
View of the living room facing the Entrance
View of living room facing the Kitchen
View of the living room facing the Entrance
SKYLIGHT TIMBER SLITS
MASONRY WALL
SKYLIGHT DETAIL
KHADI PRAKRITI PAINT
CLAY PLASTER (40 MM)
STRAW BALE UNITS (350X350X950)
35 MM THICK EARTHERN FLOORING
TRANSVERSE BAMBOO FLOORING
LONGITUDINAL BAMBOO FLOORING
100 MM PCC (1:3)
FINE AGGREGATE (100 MM THK)
COARSE AGGREGATE (150 MM THK)
CONCRETE BLOCK (225X100X100)
DRAINAGE GRAVEL
CONCRETE PAD
WALL SECTION
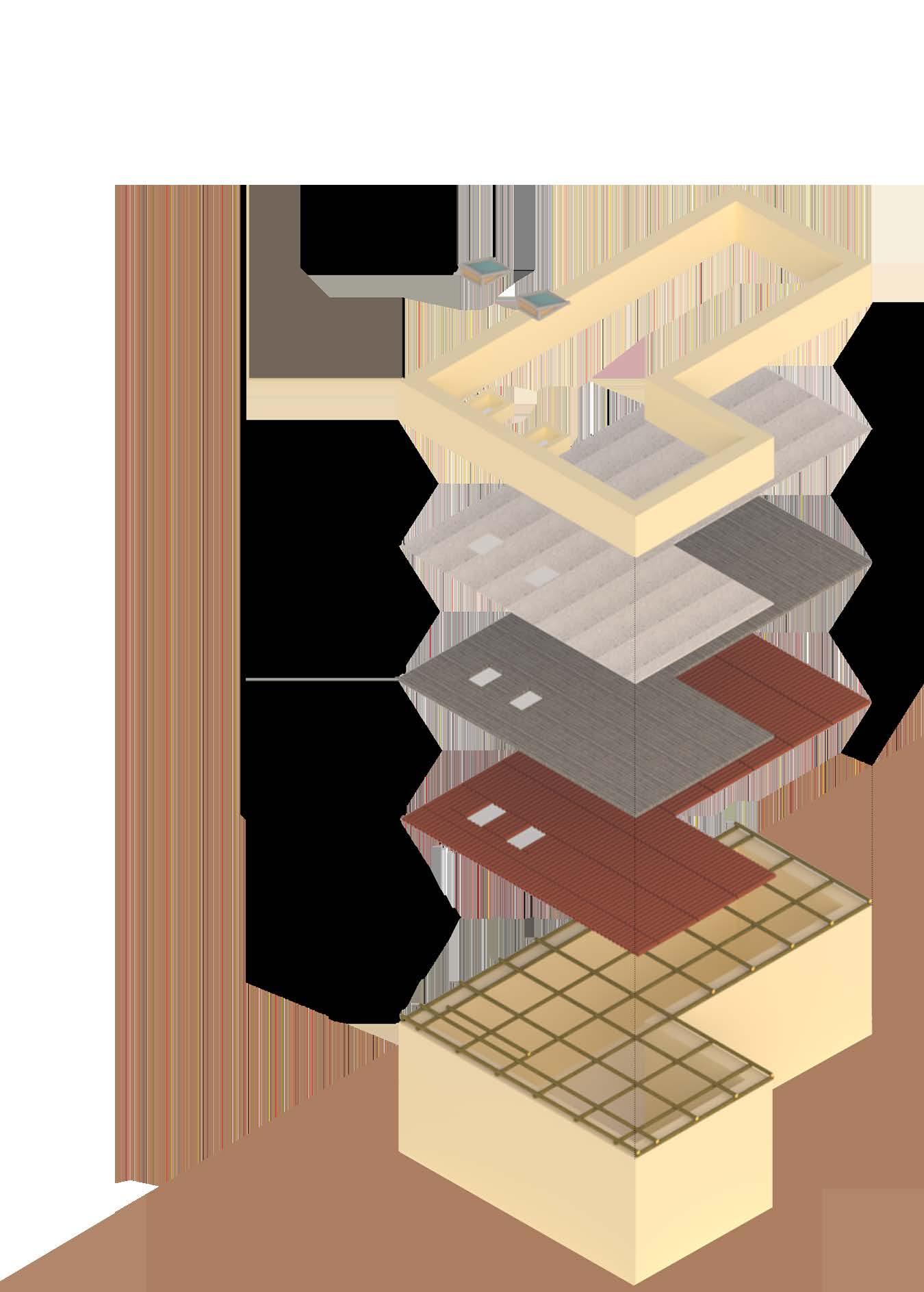
EXPLODED ROOF ASSEMBLY
PARAPET
CHINA MOSAIC FINISH
MUD CONCRETE
MUD ROLLS
SKYLIGHT BAMBOO SUPPORT FRAME


PROGRAMME
12 MM THK. LIME PLASTER
65X100 DOOR FRAME
35X125 MM TIMBER PANEL
125 MM THK. CLAY INFILL

DETAIL A
35X125 MM TIMBER PANEL
125X55 HARDWOOD
35X125 MM TIMBER PANEL




12 MM THK. LIME PLASTER
125 MM THK. CLAY INFILL
DETAIL B
DETAIL A
DETAIL B
UPPER LEVEL
PLAN -
PLAN - LOWER LEVEL AREA
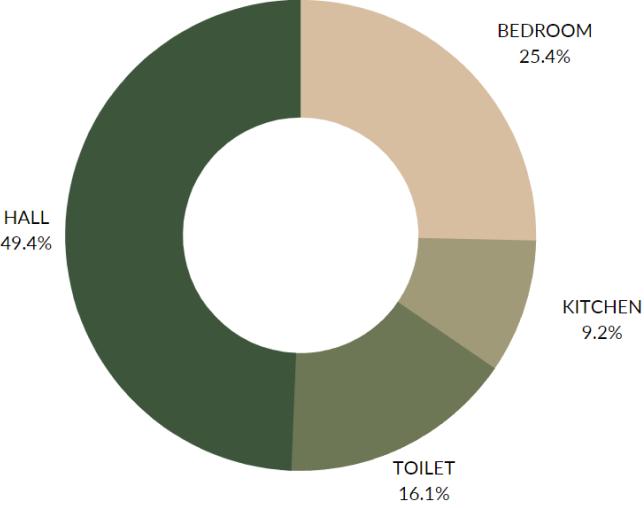
25.4 % 9.2 % 16.1 % 49.4 % HALL BEDROOM KITCHEN BATHROOM
STAIRCASE BEDROOM KITCHEN

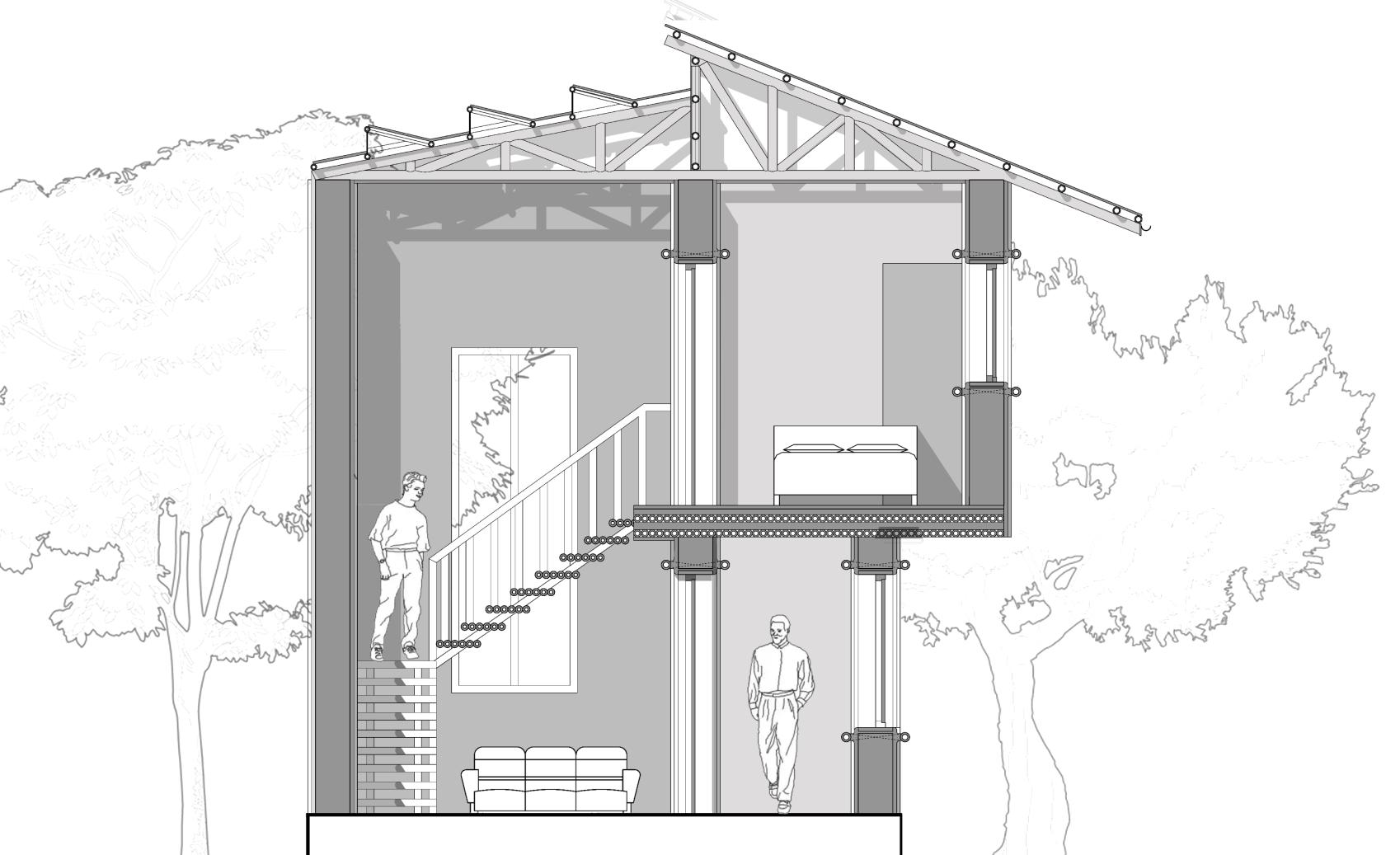
SECTION
 View from the Staircase
View of the Living Room
View from the Staircase
View of the Living Room
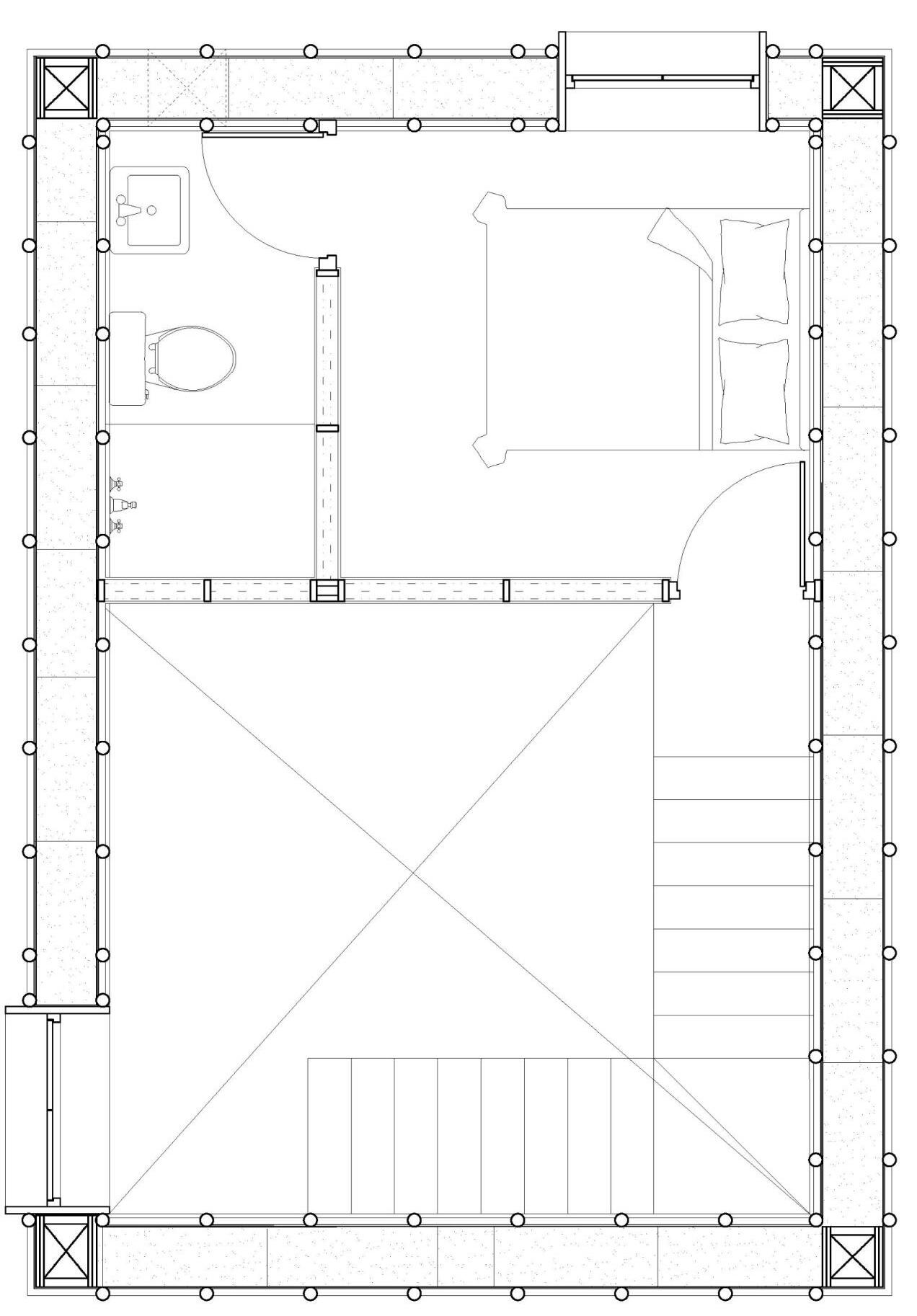
BATHROOM
TOILET
KITCHEN LIVING ROOM
ISOMETRIC PLAN
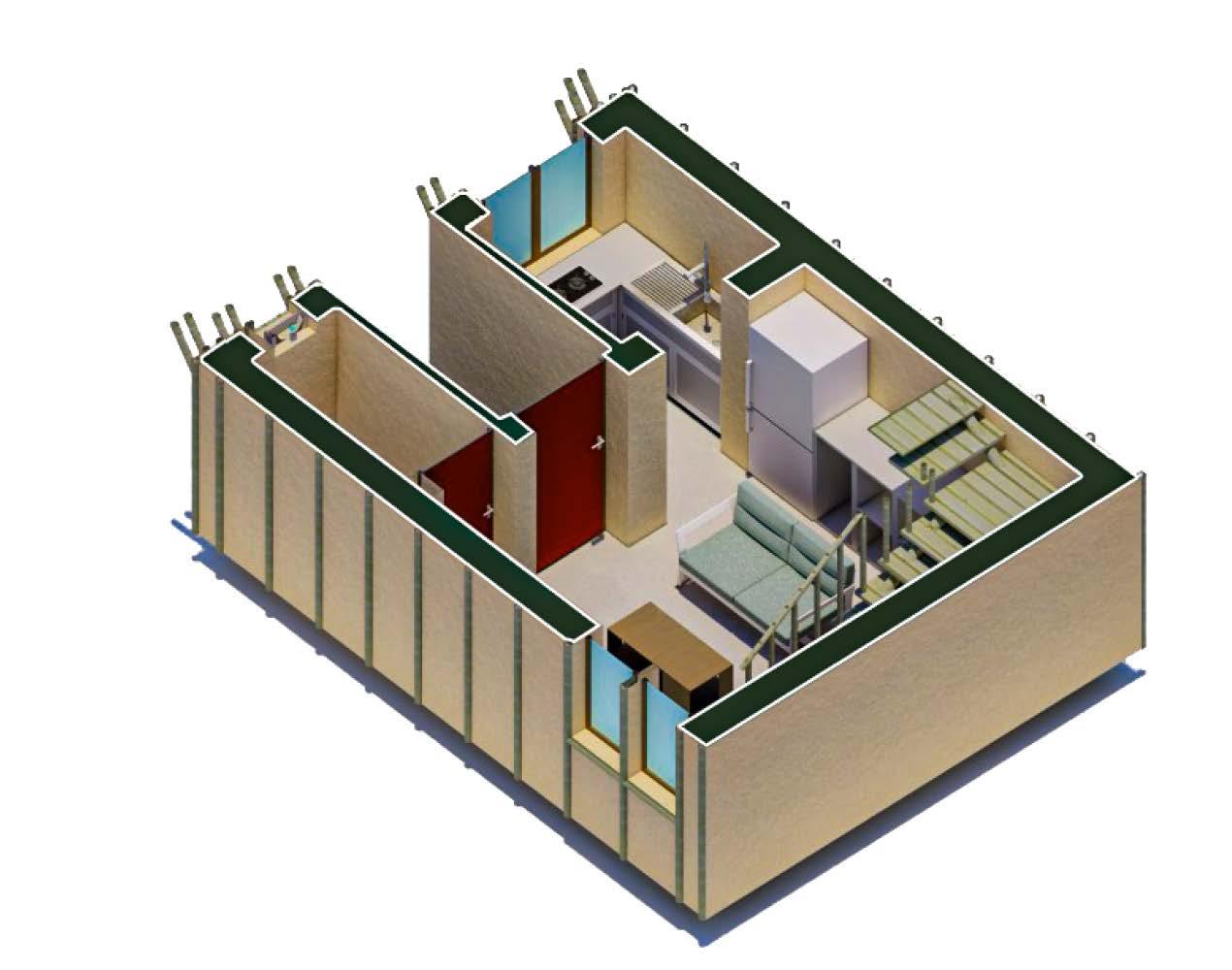
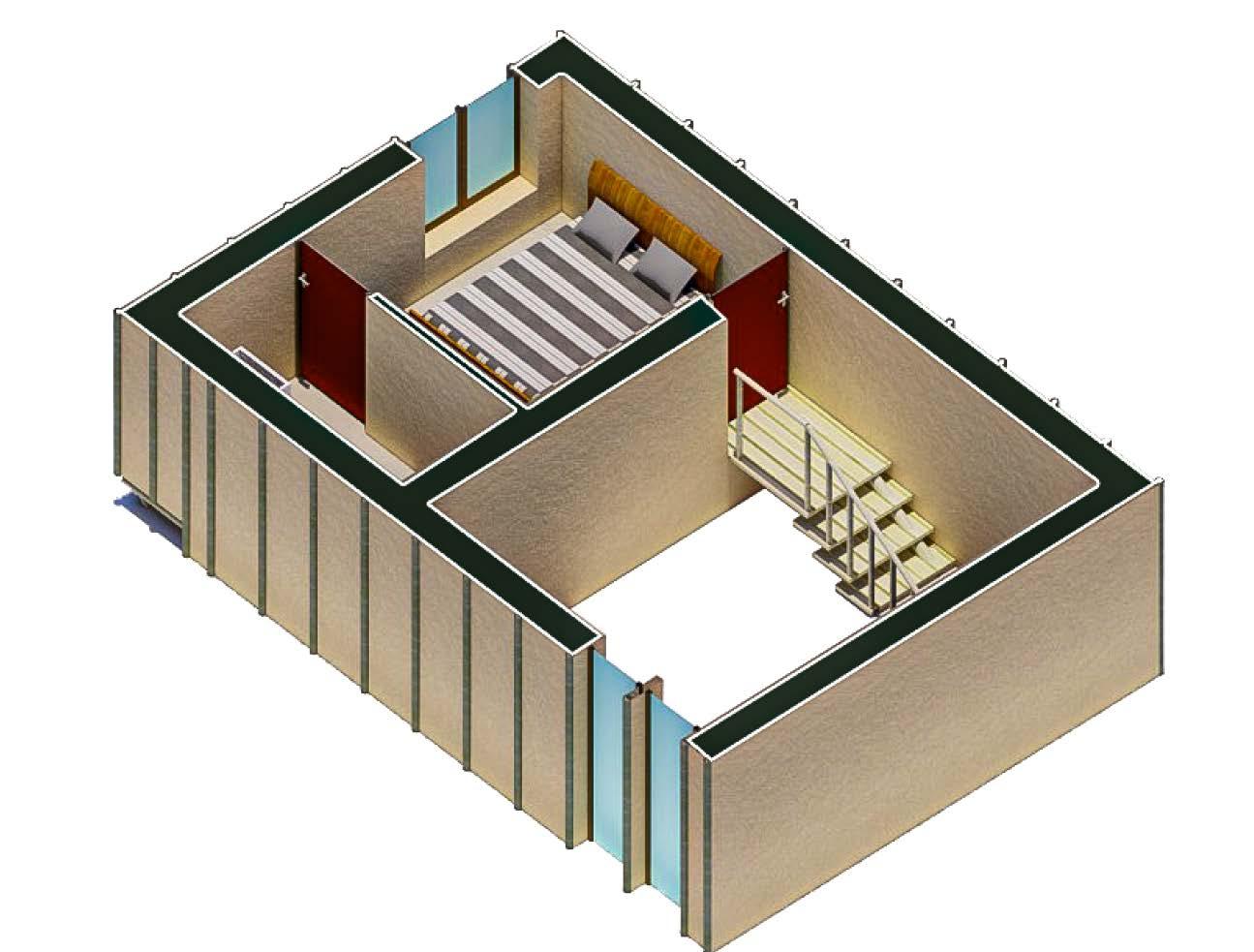
BEDROOM STAIRCASE
TRANSVERSE BAMBOO FLOORING
LAONGITUDINAL BAMBOO FLOORING
BAMBOO EDGE BEAM
KHADI PRAKRATIK PAINT
CLAY PLASTER (40 MM)
TIMBER SUTTER (40 MM)
TIMBER WINDOW FRAMES (40 MM)
STRAW BALE UNITS (350X350X950)
TRANSVERSE BAMBOO FLOORING 35 MM THICK EARTHERN FLOORING
LONGITUDINAL BAMBOO FLOORING
FINE AGGREGATE (100 MM THK) 100 MM PCC (1:3)
COARSE AGGREGATE (150 MM THK)
RAMMED EARTH
CONCRETE BLOCK (225X100X100)
DRAINAGE GRAVEL
CONCRETE PAD
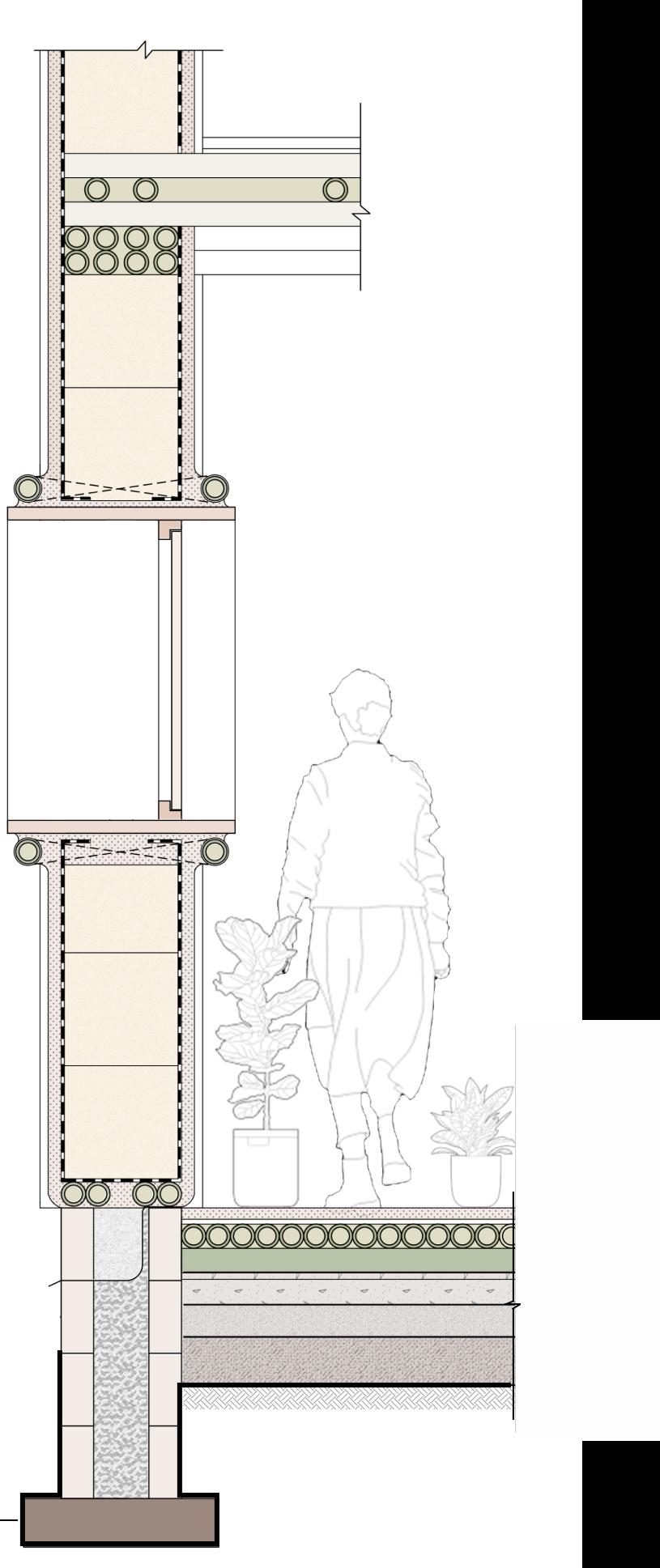
WALL SECTION
SKYLIGHTS
EXPLODED ROOF ASSEMBLY
HALF BAMBOO SHINGLES
WATERPROOFING MEMBRANE
FLAT BAMBOO SHINGLES
BAMBOO PURLINS
BAMBOO MAP CEILING FINISH
BAMBOO TRUSS
INTERNSHIP WORKS
DESIGN AND 3D VISUALIZATIONS GWALIOR, INDIA


EQUILIBRIUM

GWALIOR, MADHYA PRADESH
Stage - Under-Construction
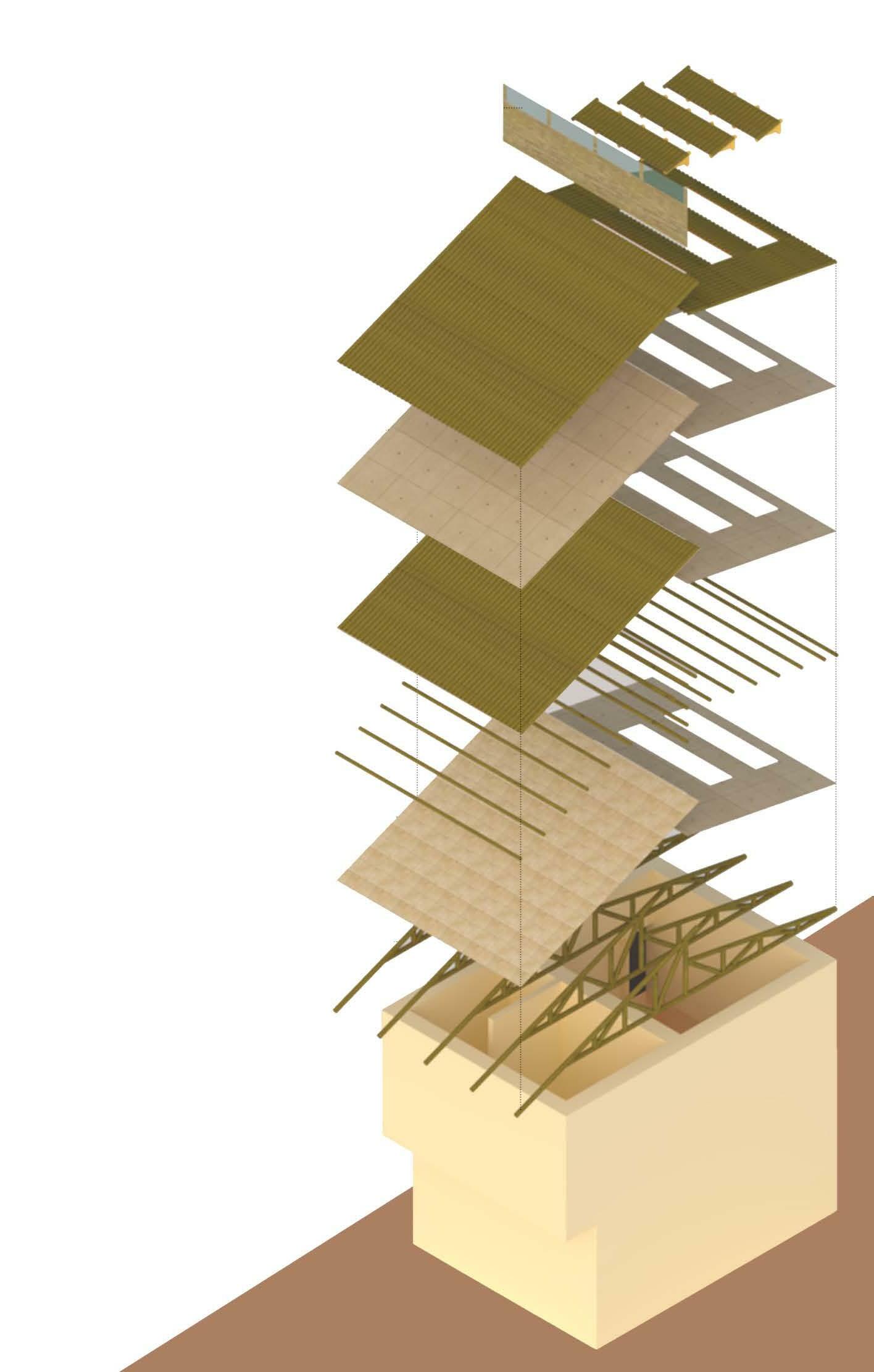
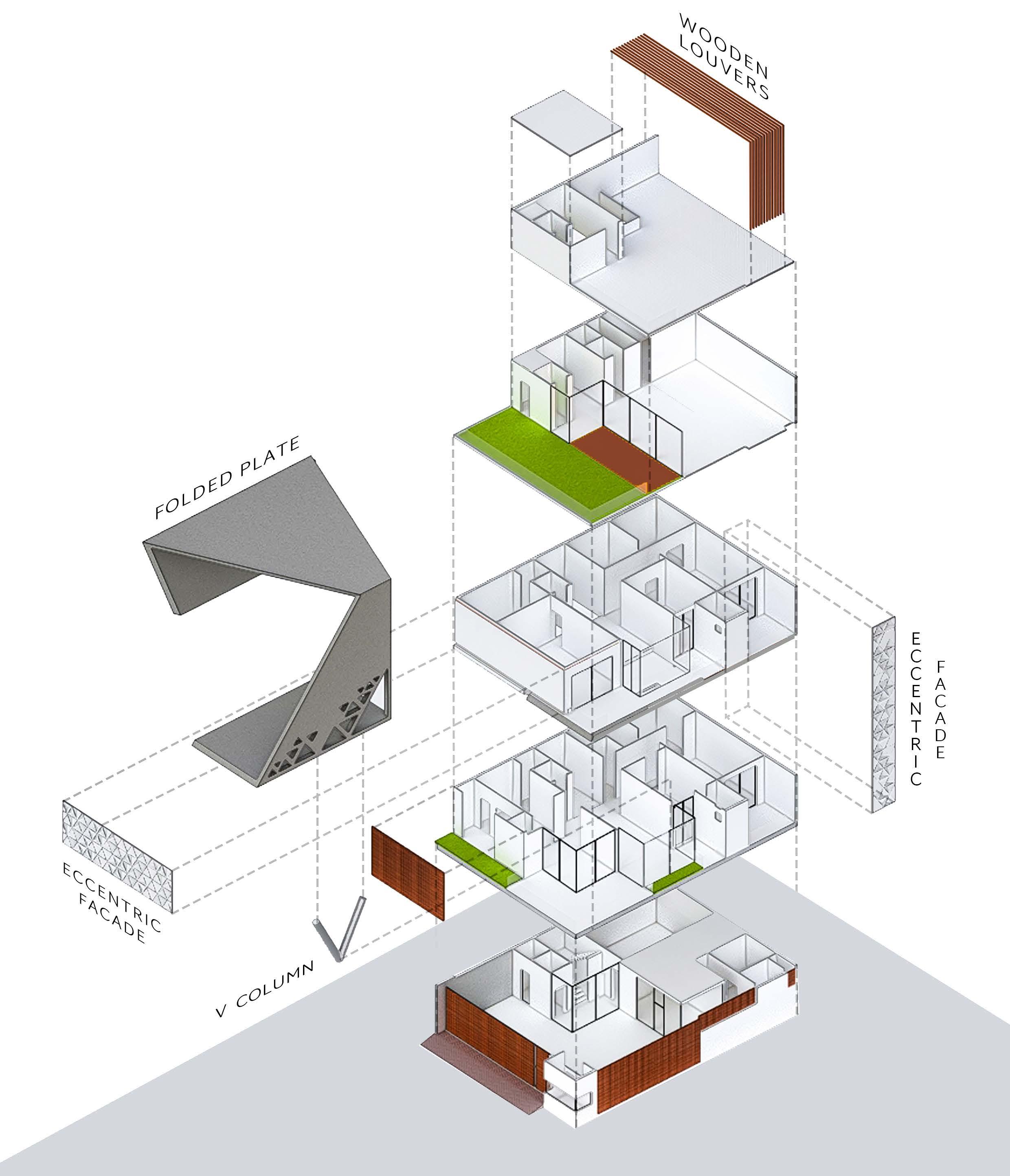
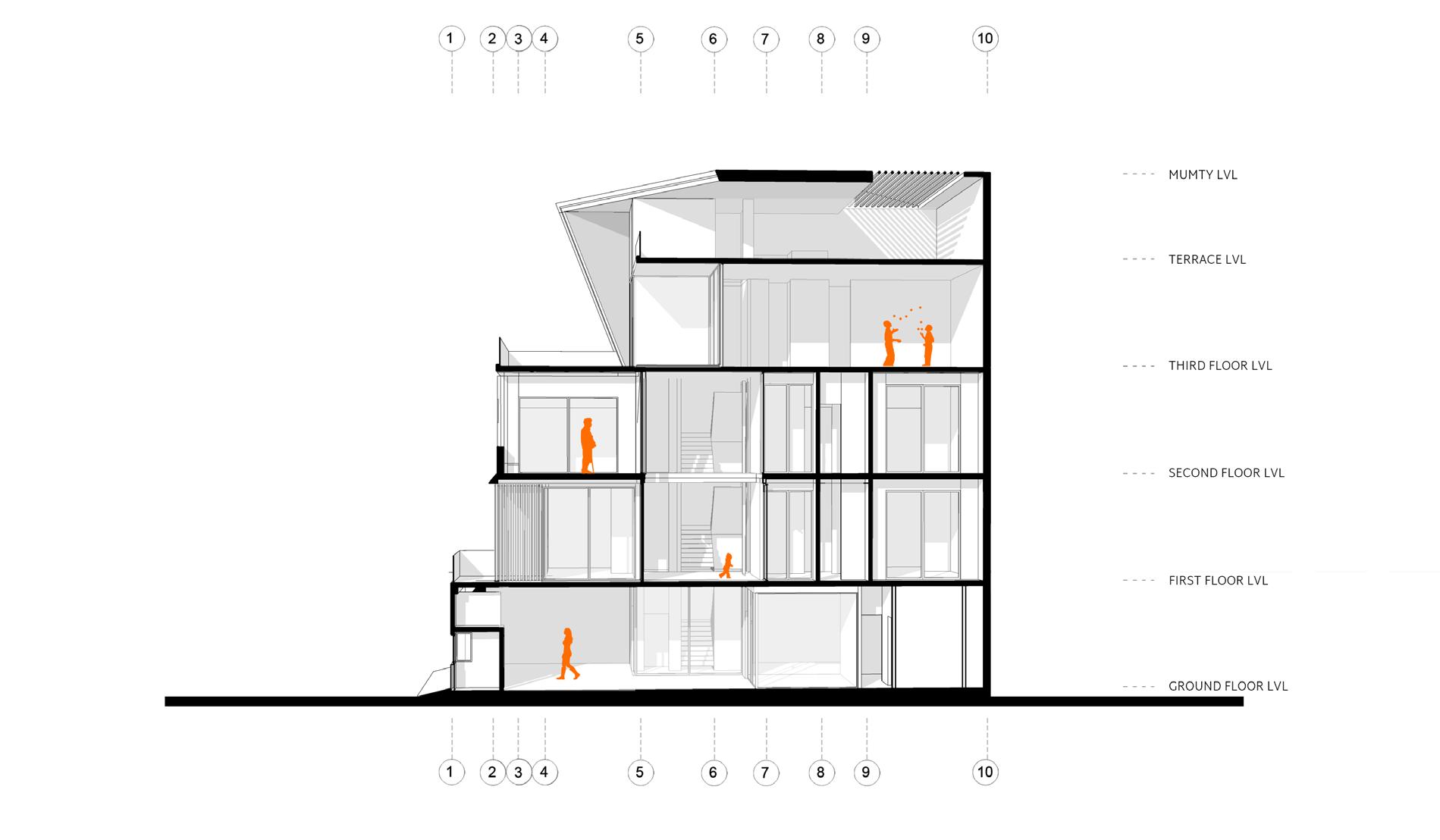
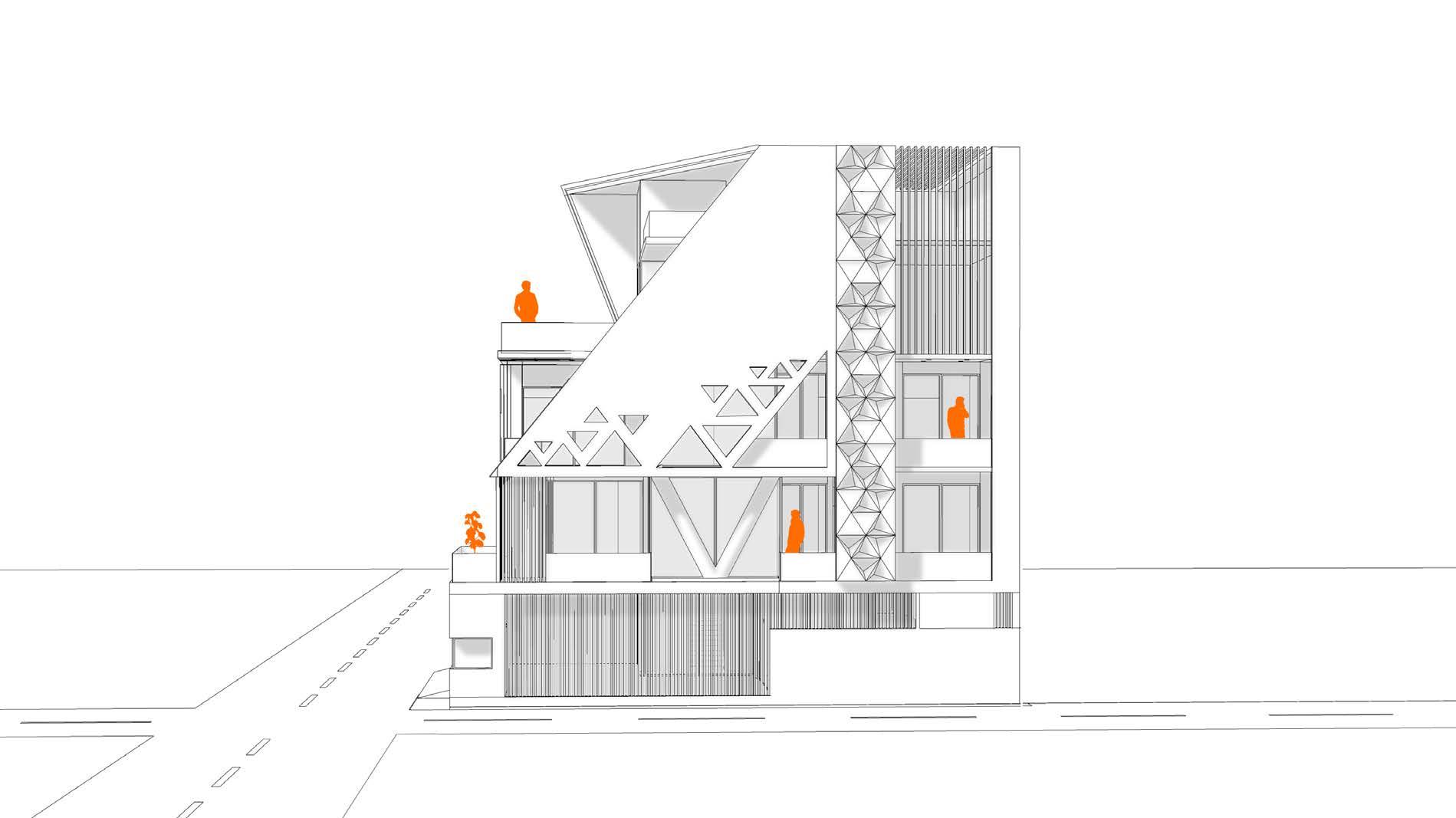
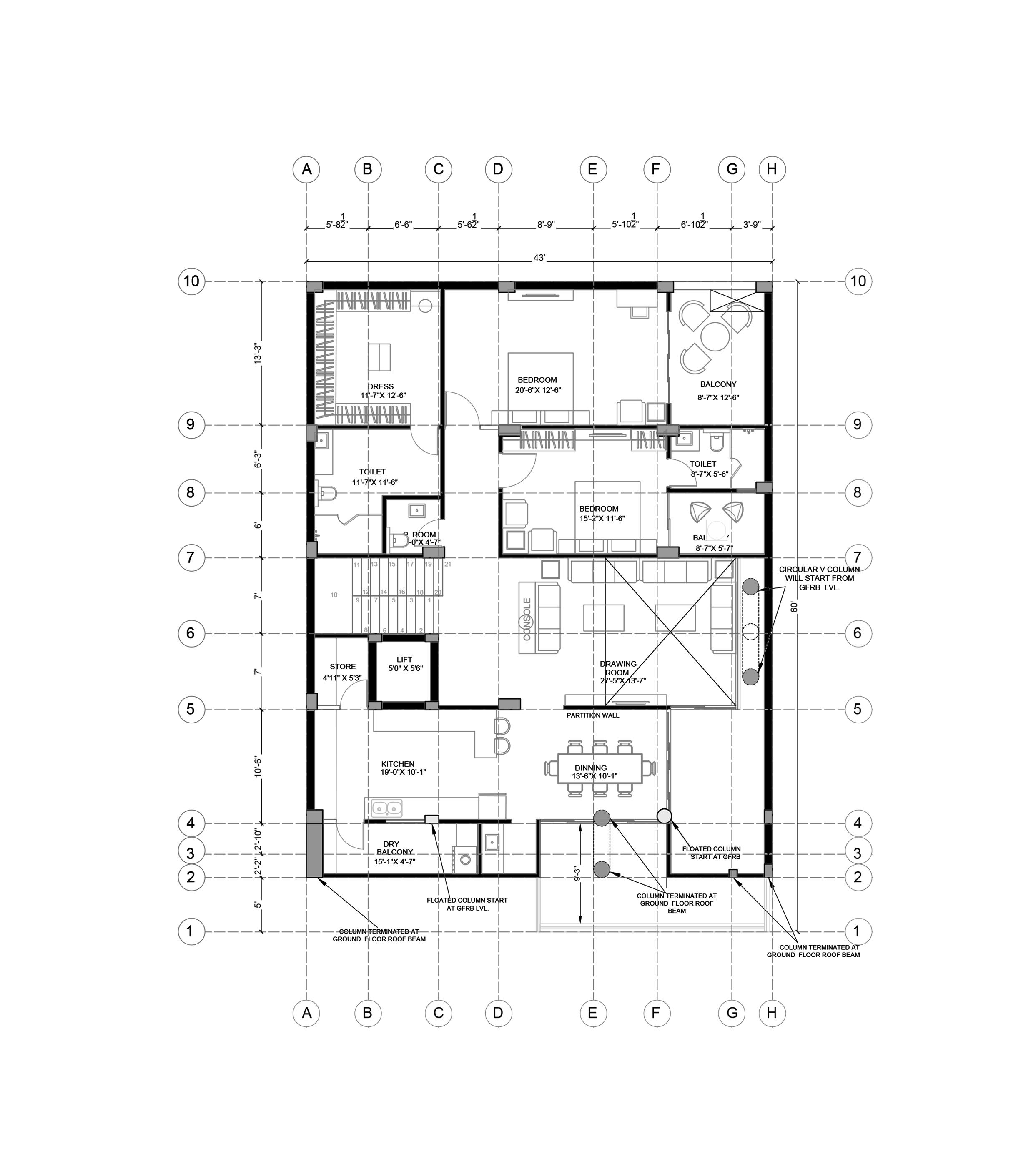
A residence for a family of four with office space on ground floor. Folded Plate is the key design element of the form design. The plate wrapps around the space inside. Site is a corner plot inside a residencial society
Site AreaBuilt Up Area2,580 sqft (240 sqm) 8,800 sqft (817 sqm)
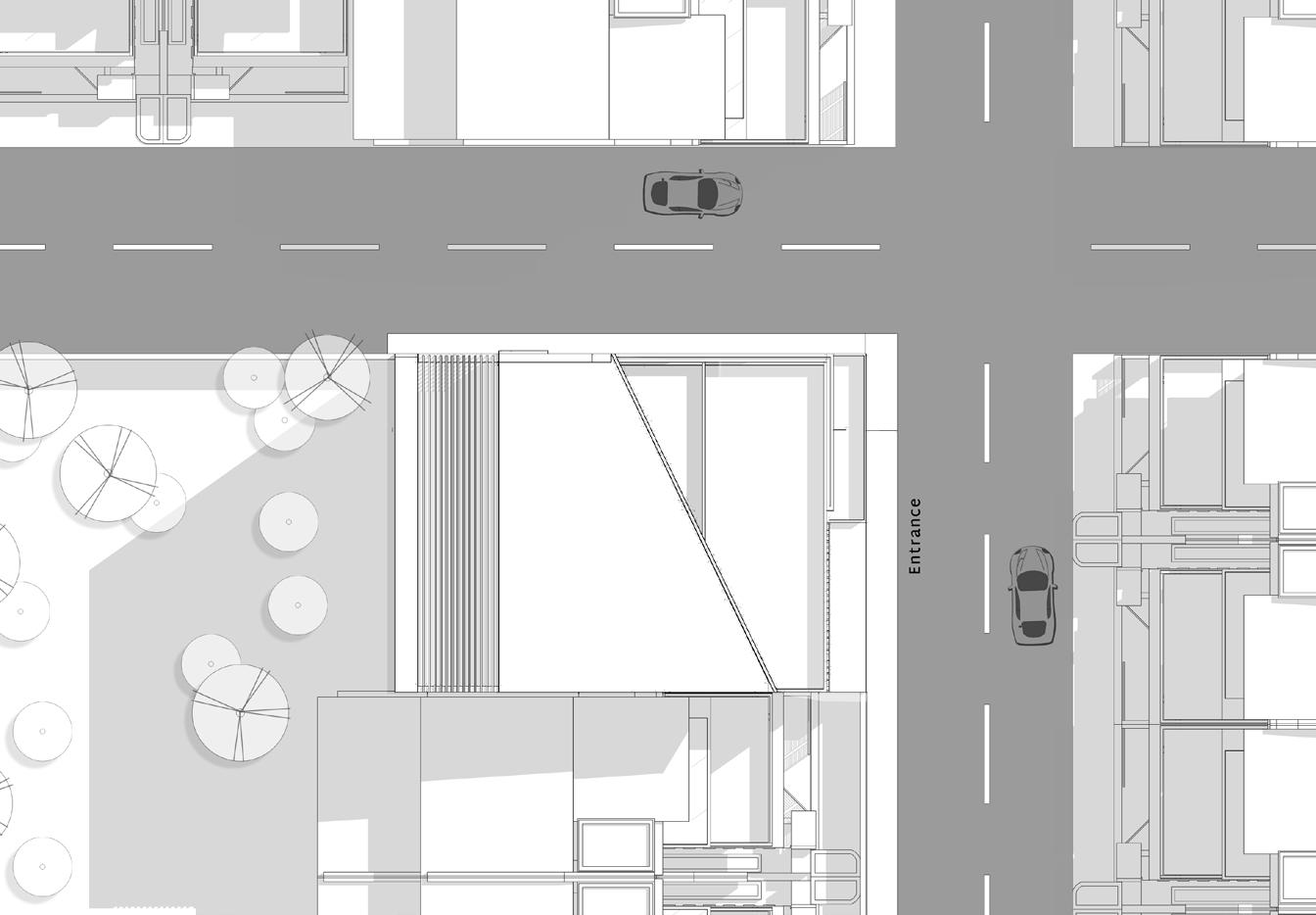
Site plan
Exploded isometric view
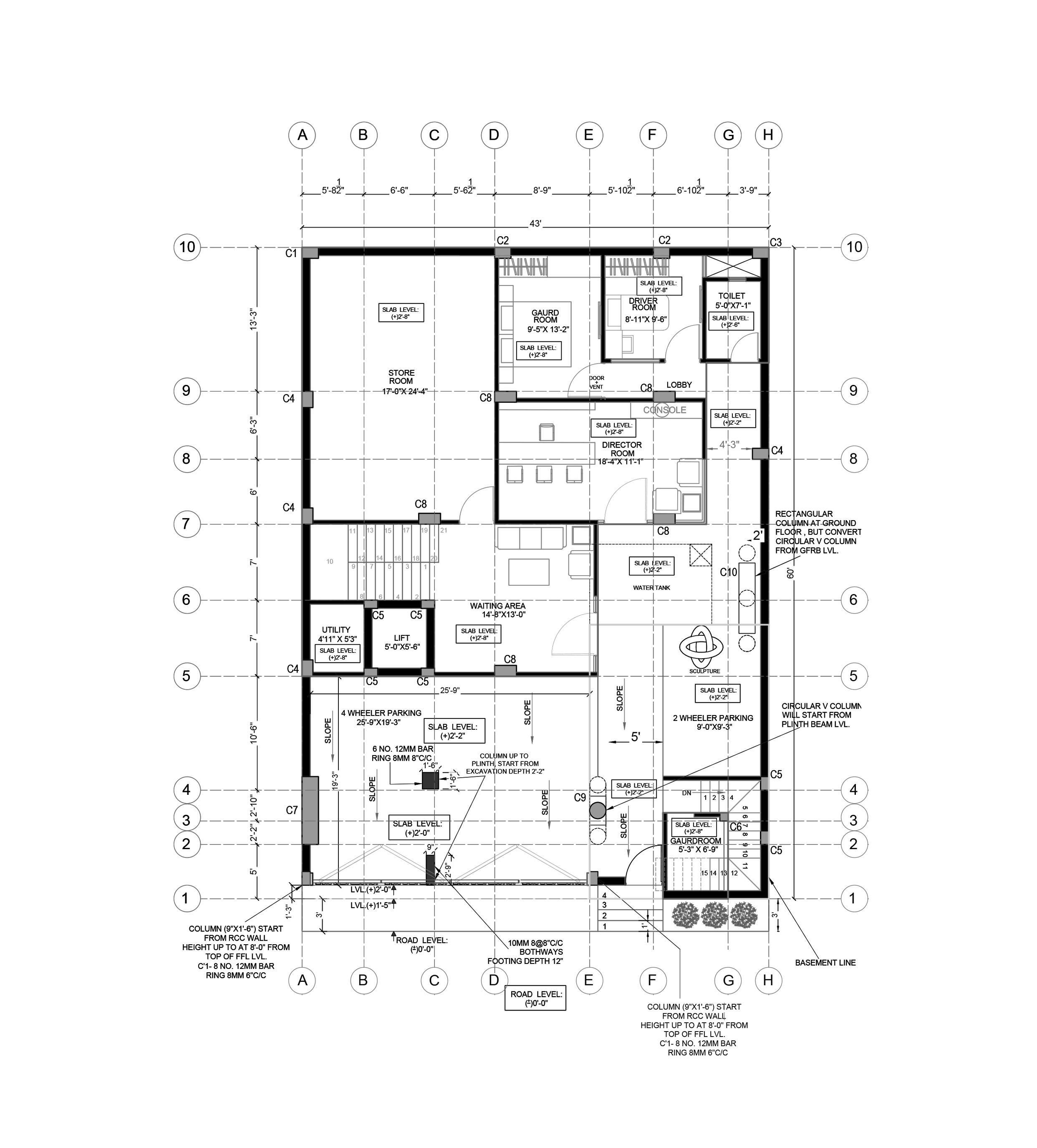
Ground Floor Plan
Elevation showcasing V column
Section through double height space
First Floor Plan
 Front elevation
Front elevation
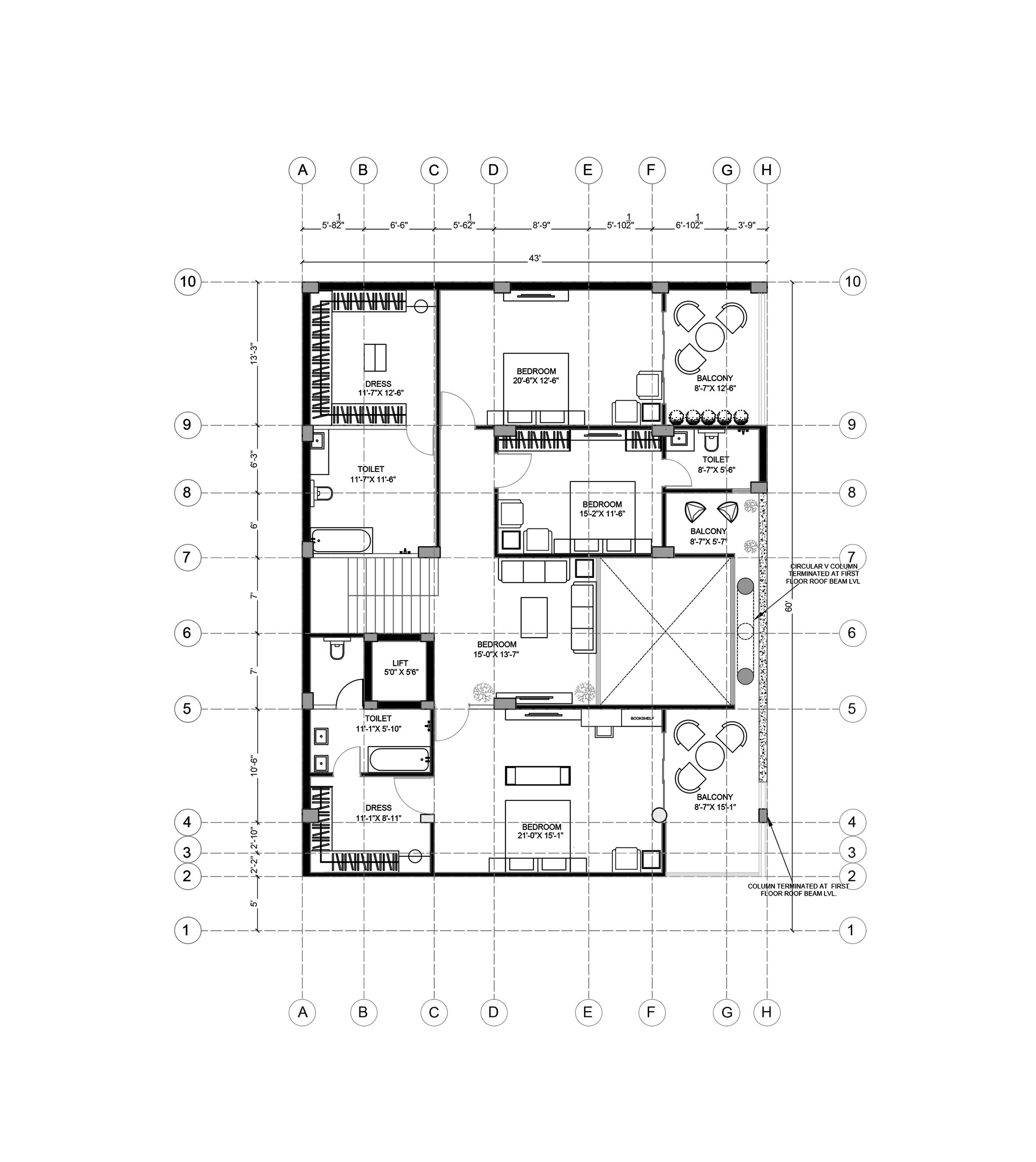
Third Floor Plan

Side elevation


23X45 RESIDENCE
GWALIOR, MADHYA PRADESH
Stage - Design Development
A small residence for a family of four. Ground floor has drawing hall, pooja room and guest room. First floor has master bedroom, kitchen and a living room. The terrace floor also has a bedroom.
Site AreaBuilt Up Area1035 sqft (96 sqm) 2480 sqft (230 sqm)
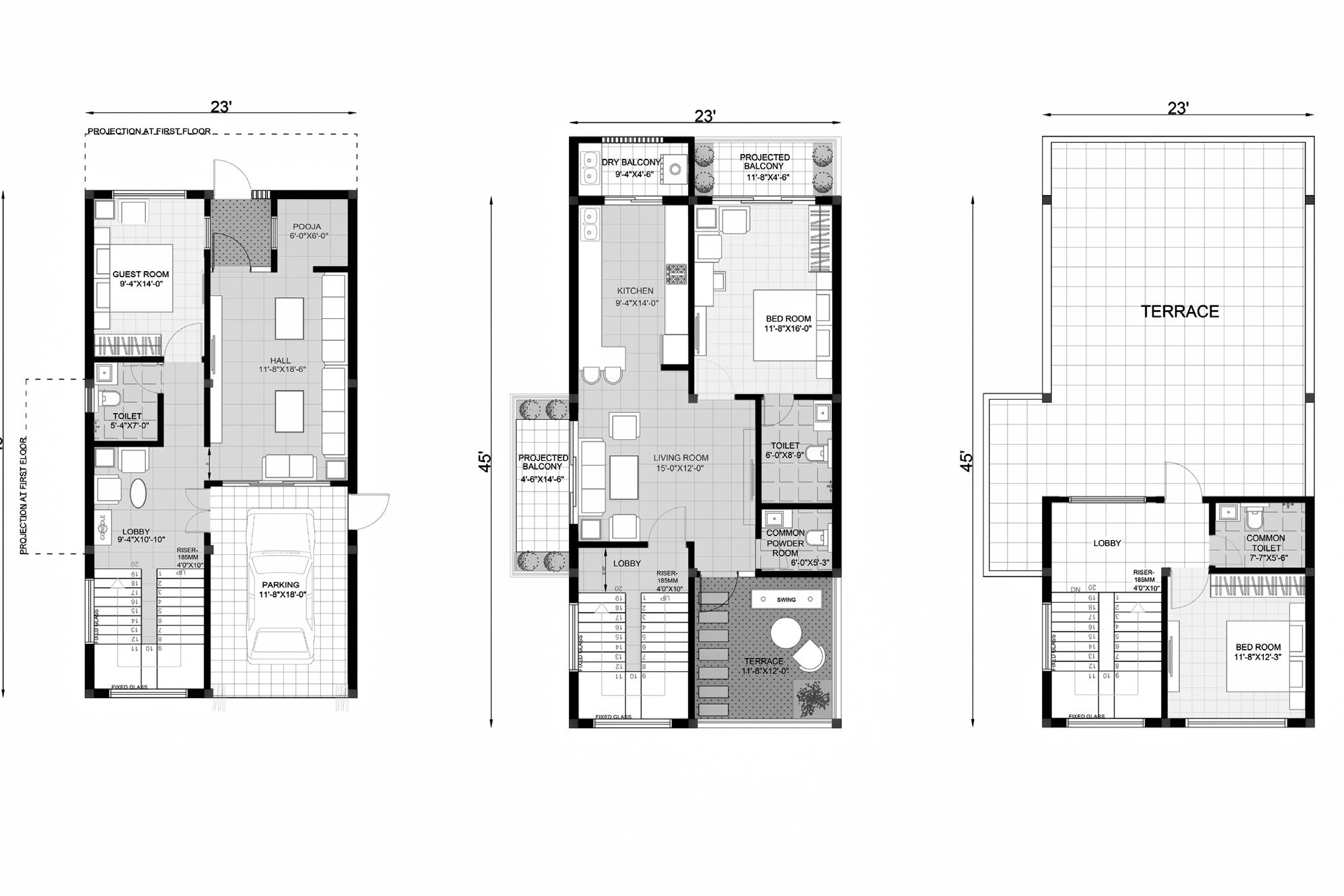
FIRST FLOOR PLAN
FLOOR PLAN TERRACE FLOOR PLAN
GROUND

DATIA COMMERCIAL
DATIA DISTRICT, MADHYA PRADESH
Stage - Design Development
A commerical building coming up in Datia, MP that houses cafeteria in basement, shops and offices on ground floor, banquet hall on first floor, hotel rooms on second and third floor and swimming pool on terrace floor. The form is inspired from Datai Fort.
Site AreaBuilt Up Area550 sqm (5920 sqft) 2295 sqm (24,700 sqft)
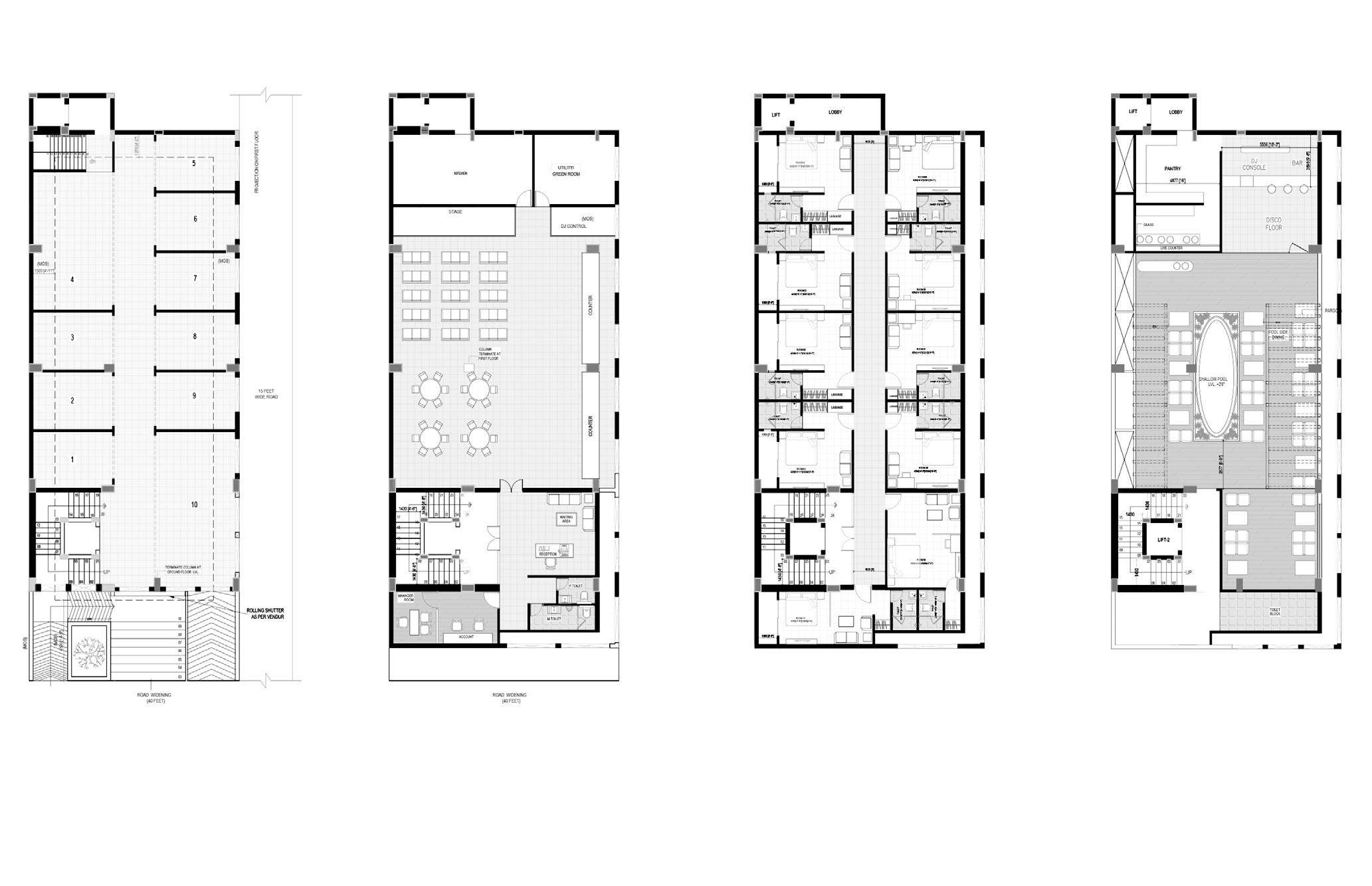 GROUND FLOOR PLAN
SECOND AND THRID FLOOR PLAN FIRST FLOOR PLAN TERRACE FLOOR PLAN
GROUND FLOOR PLAN
SECOND AND THRID FLOOR PLAN FIRST FLOOR PLAN TERRACE FLOOR PLAN



HG COMMERCIAL
GWALIOR, MADHYA PRADESH
Stage - Design Development
These two building are part of the ongoing coming HG plotted develepment project. Building facade and form were developed. More than 10 diffrent iterations were explored and analysed, finally this iteration was finalized with the client. Club House has one basement and four floors with facalities like gym area, banquet halls, indoor play zone and swimming pool. HG commercial has shops and offices.
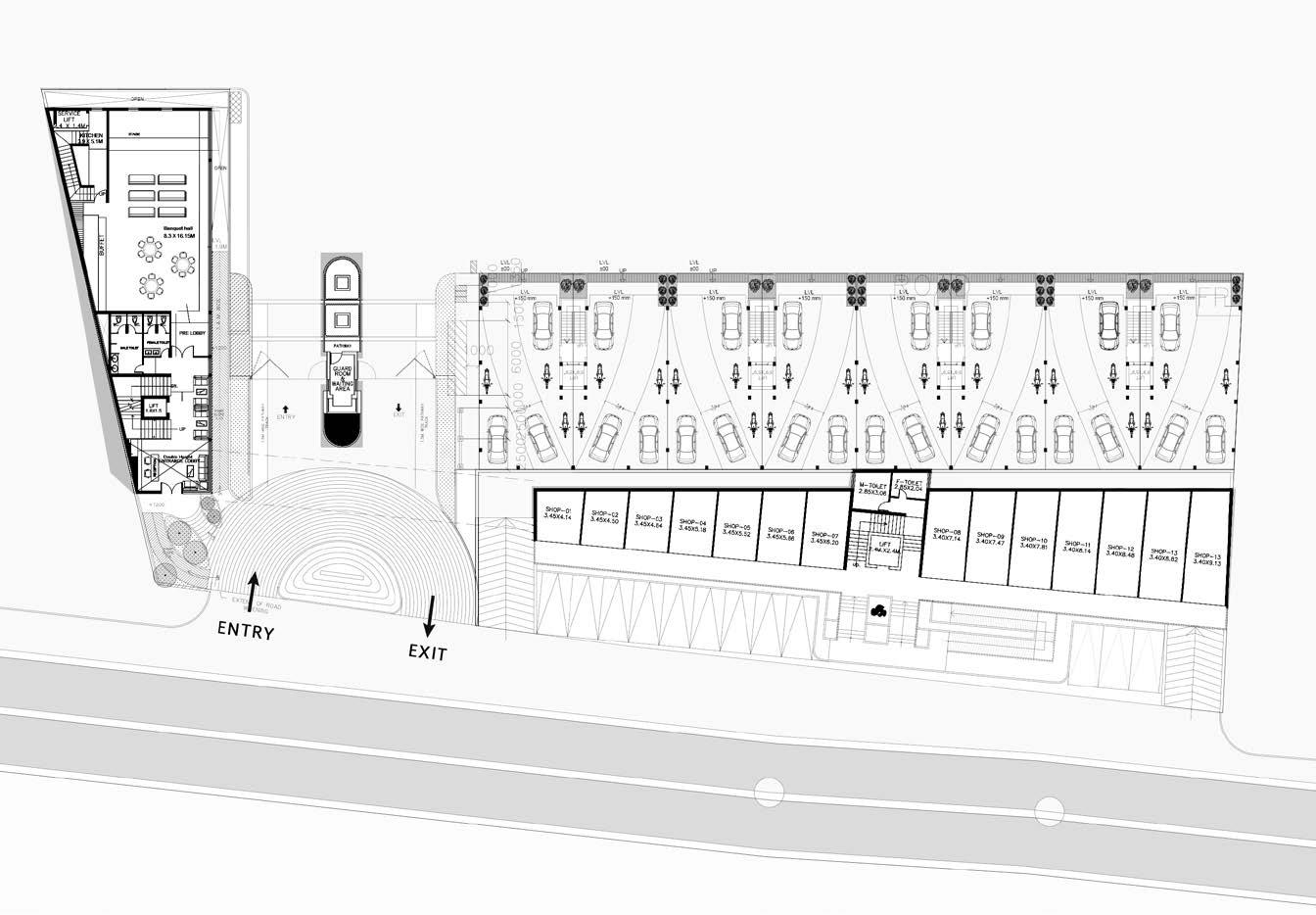
Club House built up areaHG Commercial built up area1300 sqm (14000 sqft) 2500 sqm (27000 sqft)

Site plan



WORKING DRAWINGS
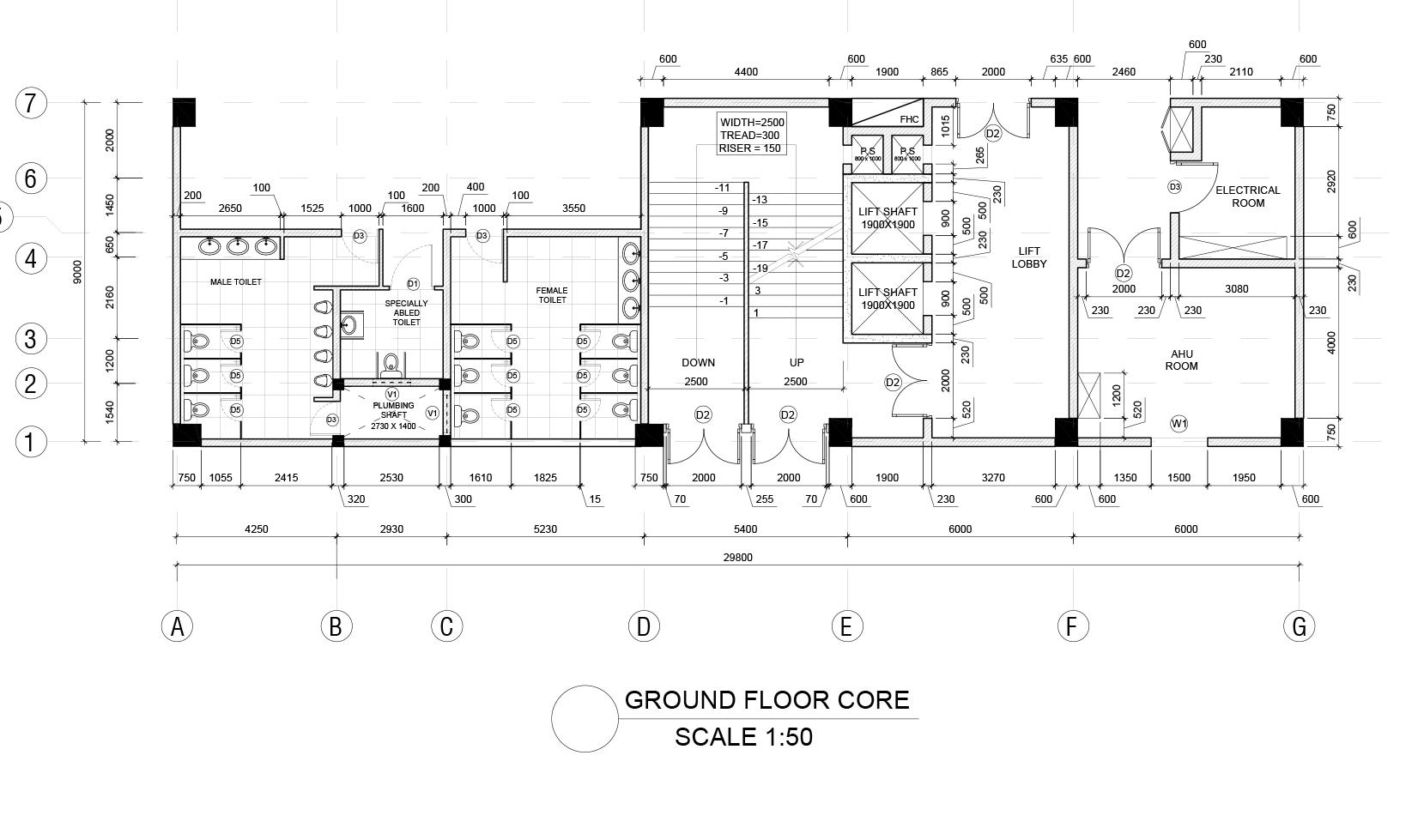
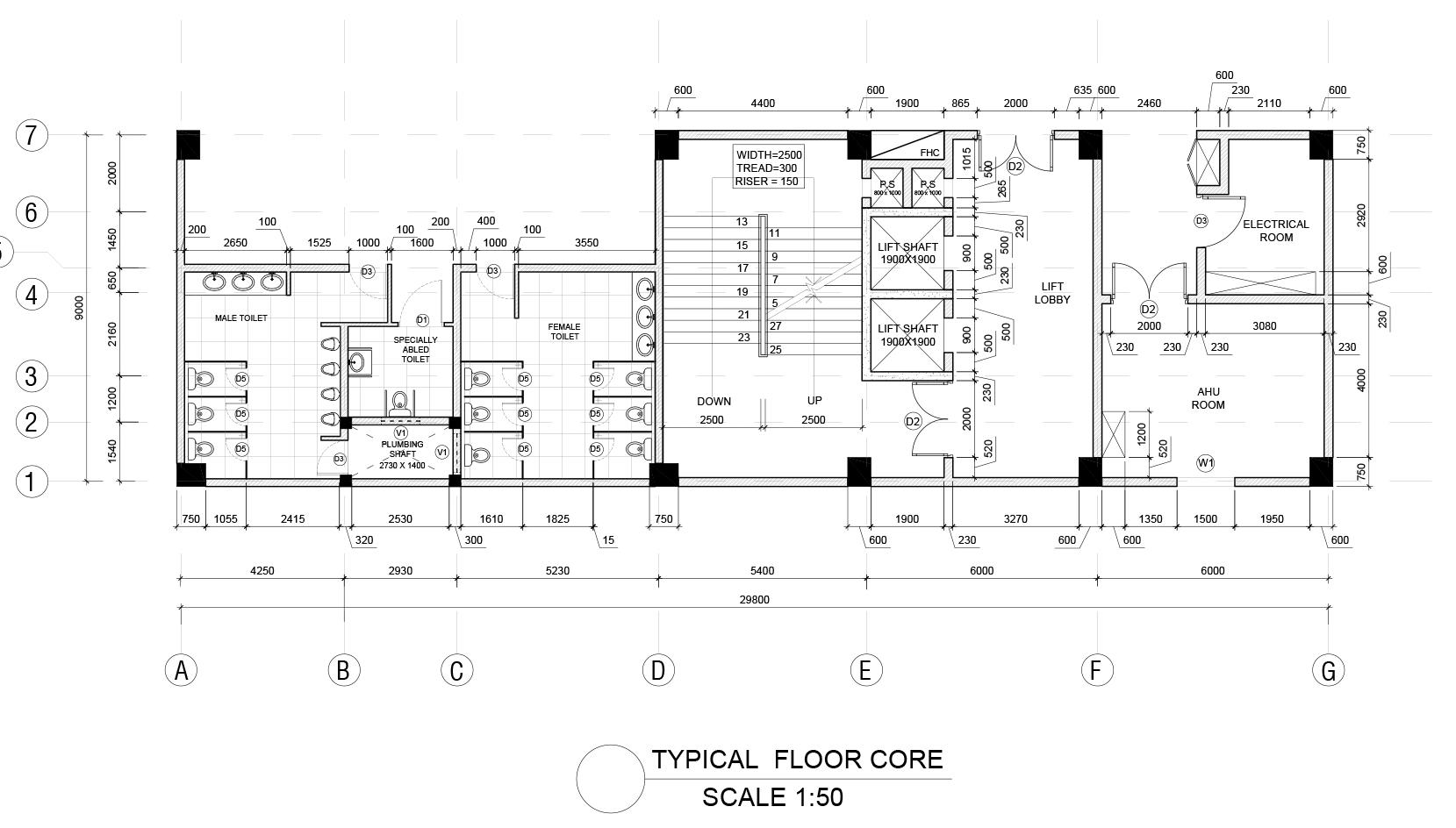
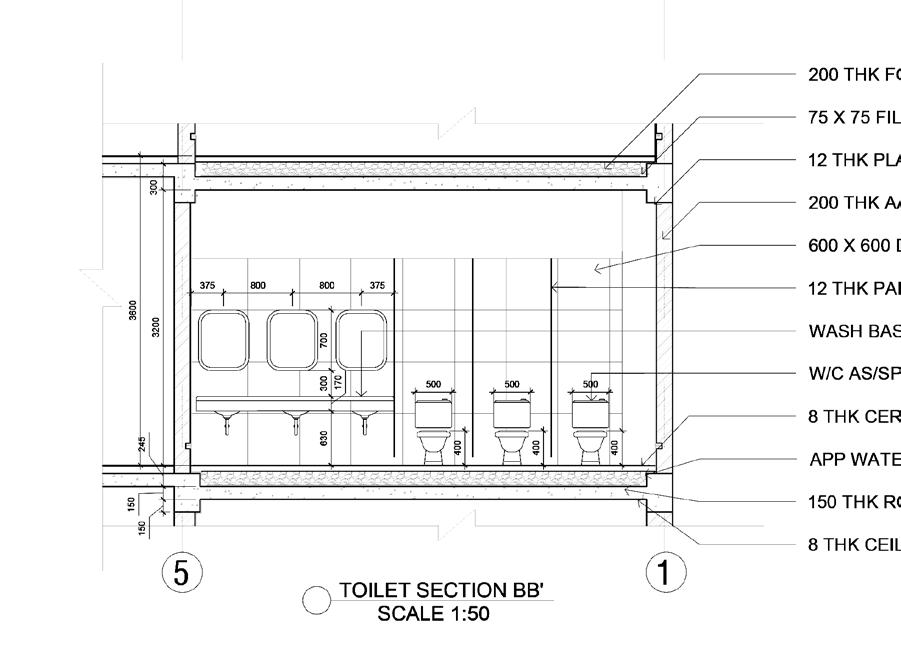
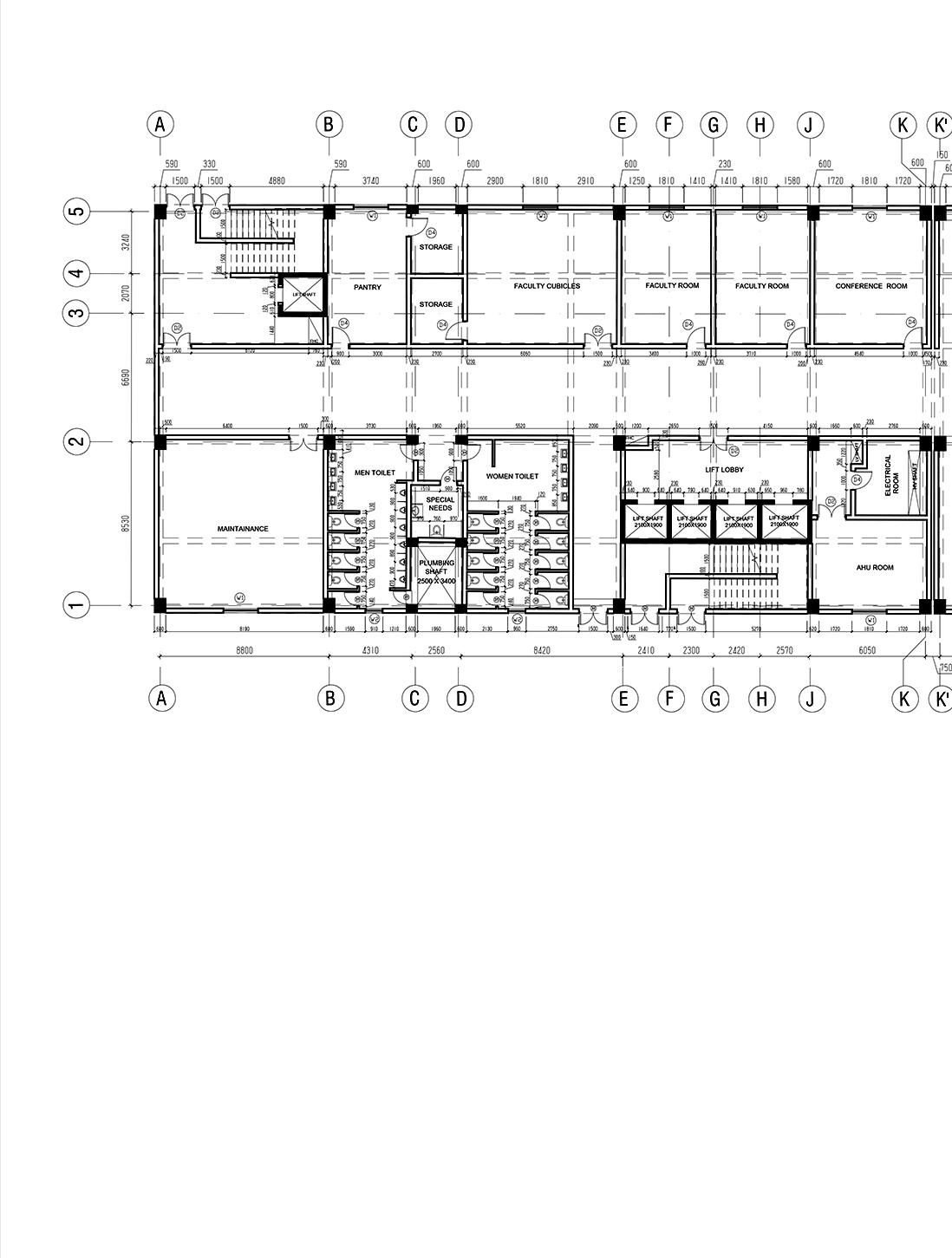
Guide - Ar. Punnet Sethi Semester - VI

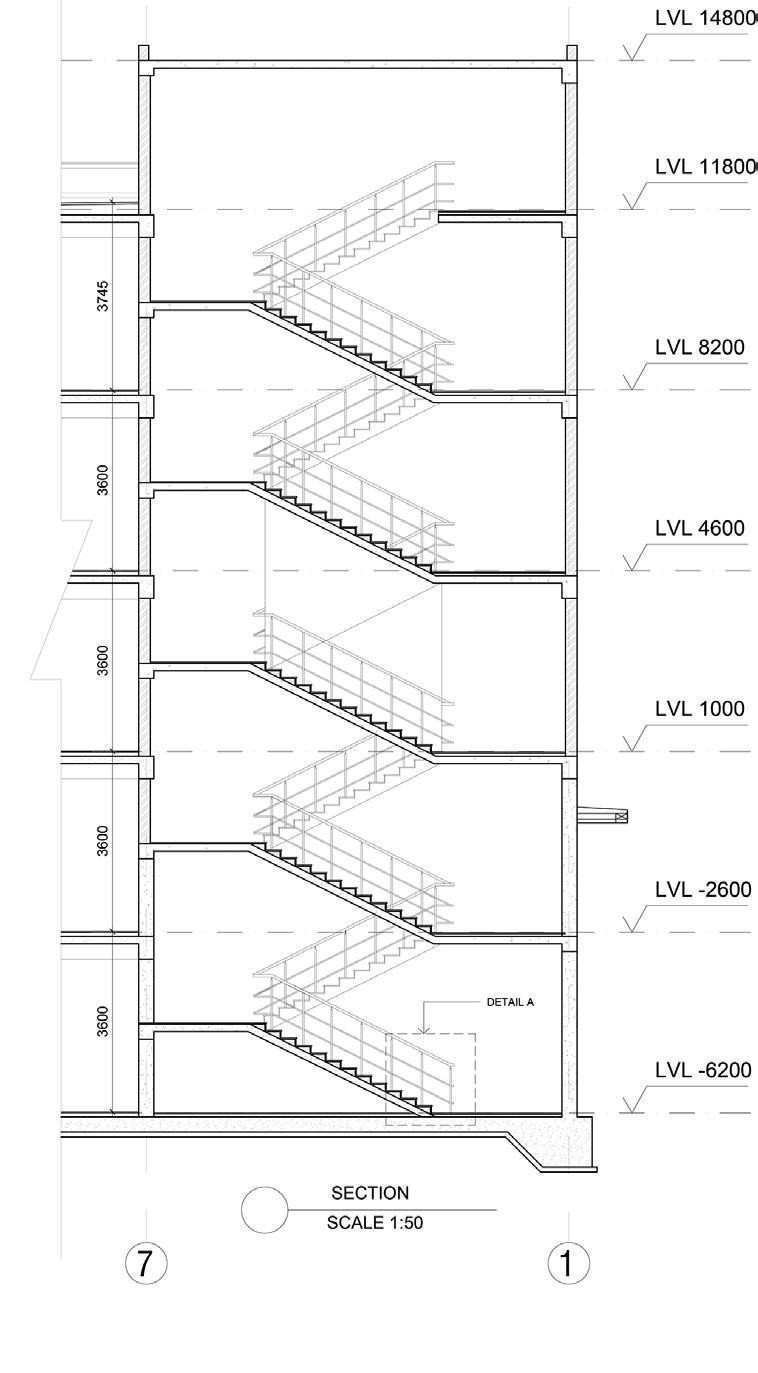


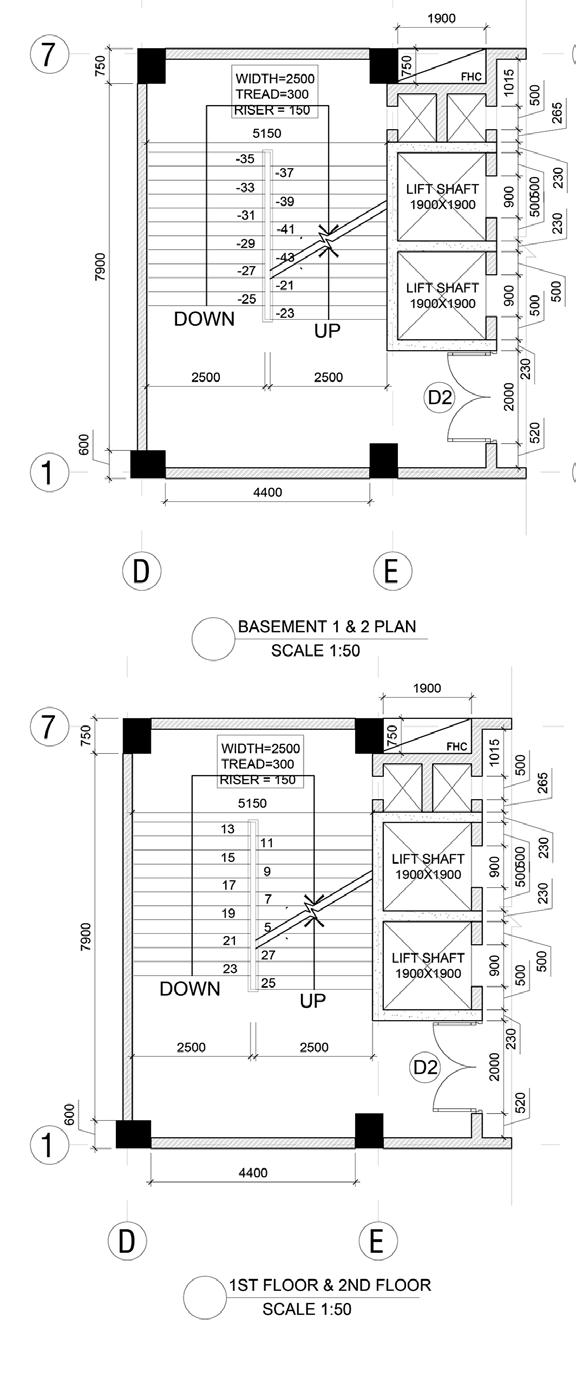
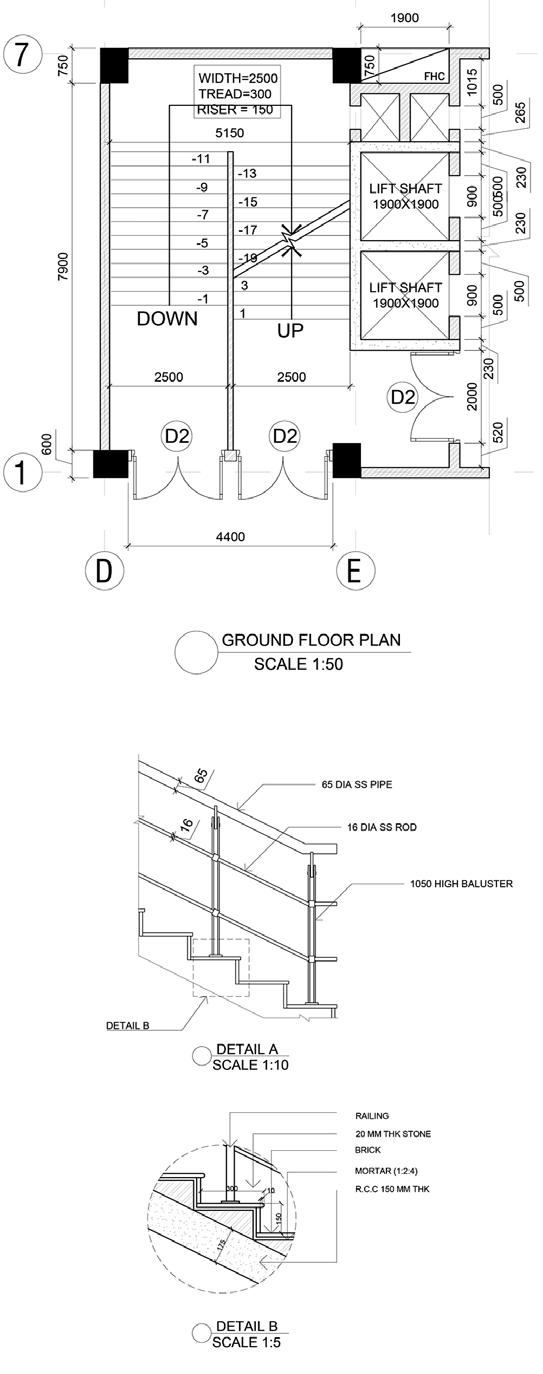
MEASURED DRAWING
BADA BAGH CHATTRIS, JAISALMER Hand rendered - Micron Pen Stippling


MISCELLANEOUS
Photography and sketching

Mumbai Airport

Mumbai Airport

Comic strip - Cube exploration
BOOKLET DESIGN

Based on Helvetica typeface





THANK YOU!



JayeshPramodMore / 9009789347 / jayeshpramodmore@gmail.com



































 Sections showing working of HVAC during different months
Sections showing working of HVAC during different months




 ROOF GARDEN FOR FILTERATION :
ROOF GARDEN FOR FILTERATION :

 Roof Schematic
Ducting Schematic
Roof Schematic
Ducting Schematic




































 Urban land and ceiling act
Rajeev Awas Yojana 1976 2009
THE TIMLINE : SLUMS IN AHEMDABAD
Total Slum Settlements in Ahmedabad
Urban land and ceiling act
Rajeev Awas Yojana 1976 2009
THE TIMLINE : SLUMS IN AHEMDABAD
Total Slum Settlements in Ahmedabad

































 View of living room facing the Kitchen
View of the living room facing the Entrance
View of living room facing the Kitchen
View of the living room facing the Entrance
















 View from the Staircase
View of the Living Room
View from the Staircase
View of the Living Room












 Front elevation
Front elevation






 GROUND FLOOR PLAN
SECOND AND THRID FLOOR PLAN FIRST FLOOR PLAN TERRACE FLOOR PLAN
GROUND FLOOR PLAN
SECOND AND THRID FLOOR PLAN FIRST FLOOR PLAN TERRACE FLOOR PLAN
































