Guide 2023-24











“The Interna�onal Baccalaureate® aims to develop inquiring, knowledgeable and caring young people who help to create a be�er and more peaceful world through intercultural understanding and respect. [Our] programmes encourage students across the world to become ac�ve, compassionate and lifelong learners who understand that other people, with their differences, can also be right ”
The IB Diploma Programme (IB DP) at ISP is purpose built for our high school students. It allows them to use big ideas and real-world contexts to develop the skills, knowledge and a�tudes that are vital for future success in both academic programmes and as global ci�zens
To meet the needs of our interna�onal community, ISP DP provides a balanced educa�on, which facilitates geographic and cultural mobility and promotes the concepts of responsibility and interna�onal understanding


High-quality learning is a social and experien�al prac�ce. It sparks students’ curiosity and s�mulates their natural crea�vity. It inspires them to strive for excellence, and to take ownership of their own inquiry and research. It shapes the learner and the learning community, nurturing growth and new understanding.
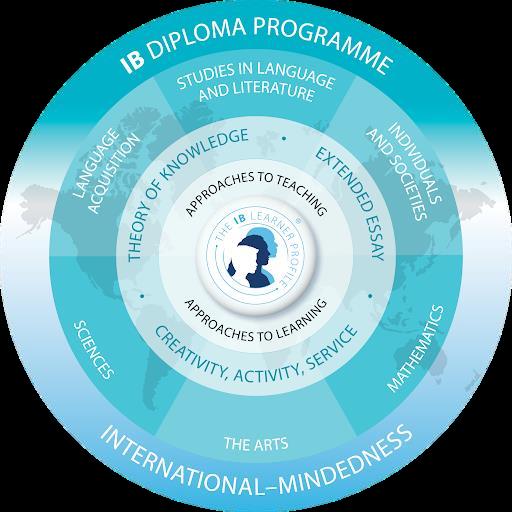
The Interna�onal Baccalaureate Diploma Programme (IB DP) was established in Geneva in 1968 to provide an interna�onal, and interna�onally recognised, university-entrance qualifica�on for students studying outside of their home country. The IB’s goal is to provide students with the values and opportuni�es that will enable them to develop sound judgments, make wise choices and respect others in the global community. The IB Programme equips students with the skills and a�tudes necessary for success in higher educa�on and employment; it has the strengths of a tradi�onal liberal arts curriculum, but with three important addi�onal features, shown at the centre of the curriculum model (below)

Today, the IB DP has expanded so that more than half the students op�ng for it come from state or na�onal systems rather than from interna�onal schools As the IB DP has grown, so too has its reputa�on for excellence; the IB DP is now recognised in almost every country in the world as a one of the pre-eminent pre-university qualifica�ons

The IB learner profile are ten personal a�ributes valued by IB World Schools We believe these a�ributes help our students become responsible members of local, na�onal and global communi�es The learner profile is what enables ISP to reach its mission, Educa�ng for Complexity The a�ributes of the learner profile permeate teaching and learning and provide a framework for our values.





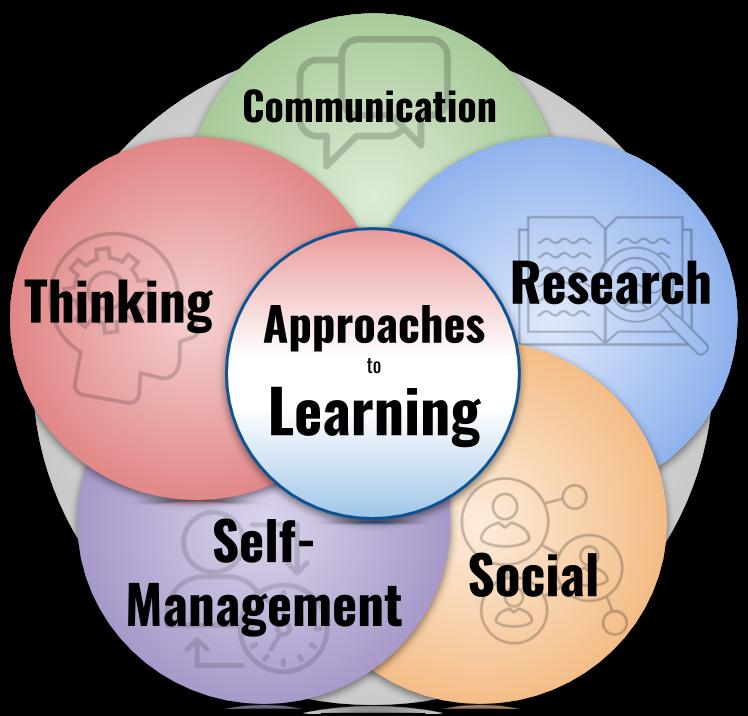
It is widely known that the development of transdisciplinary skills is just as important as learning in specific subjects The transdisciplinary skills that empower students to be successful in school, educa�on and beyond, are known as Approaches to Learning (ATLs) There are five broad categories of skills, which can be broken down into ten more specific categories of ATL skills Throughout the DP, students will learn and prac�se different strategies for developing and applying these skills
The IB Diploma Programme (DP) at ISP builds on our IB Middle Years Programme (IB MYP), a broad yet demanding course of study in Grades 6-10 and our IB Primary Years Programme (IB PYP) from Early Learners to Grade 5 The DP is a two-year interna�onal curriculum, Grades 11 and 12, that allows students to fulfil the requirements for university entrance of their na�onal or state educa�on systems. Interna�onally mobile students are able to transfer into the IB Diploma Programme from other IB World Schools, as well as from other school systems.
To be eligible for the IB Diploma Programme, ISP students should have successfully completed the IB Middle Years Programme, which includes Personal Project and ISP’s service requirements In order to ensure access to an IB Diploma Higher Level course, a student must have studied the subject in Grade 10 and gained at least an end-of-year level 5 or equivalent In order to ensure access to an IB Diploma standard level course, a student must have gained at least an end-of-year MYP level 4 (or equivalent) in the last year that he/she studied the subject Please note that if a subject is not offered in Grade 9 and 10, such as Economics, a student should have gained a suitable grade in another subject from the same group.


External applicants are assessed individually There are no universal, formal entry requirements; however, in order to have access to instruc�on and to the course materials, it is a pre-requisite that a student has competent English skills speaking, listening, reading and wri�ng. If a student does not have sufficient English skills, then we may require that they take a summer English language course before enrolling in the DP.
All the courses at DP are IB courses that last 2 years Students should start the process of choosing their personal programme by consul�ng the list of subjects offered by ISP When making course selec�ons, students should also consider their future educa�on and career plans and their personal strengths in individual subjects Students should become familiar with the specific requirements of the universi�es in the countries to which they intend to apply as different universi�es in different countries have different entrance requirements It is very important that students are aware that specific subjects or combina�ons of subjects could be required (or excluded) by the country or university of choice. Informa�on about universi�es around the world is available from ISP’s university counsellors.
It is strongly recommended that students spend as much �me as possible discussing their op�ons with as many people as possible, including parents and teachers. Decisions made at this stage in a student’s educa�on could affect the rest of their lives, so it is vital that choices are made only a�er full research and consulta�on.
To be eligible for the IB Diploma, each student is required to follow six IB courses, with one subject taken from each group in the curriculum model:
● Group 1: Language A (literature and/or language and literature)
● Group 2: Language B (language acquisi�on) or possibly second Language A
● Group 3: Individuals and Socie�es
● Group 4: Experimental Sciences
● Group 5: Mathema�cs
● Group 6: Arts OR one subject from groups 1-4
Further, all IB Diploma students must choose:
● three courses at higher level (HL); and,
● three courses at standard level (SL).
In addi�on, all IB Diploma students must complete:
● a course in the Theory of Knowledge (TOK);
● a 4,000-word Extended Essay in a subject of their choice; and,
● the Crea�vity, Ac�vity, Service (CAS) programme.
All IB courses, HL and SL, are graded on the IB 7-point scale:


7 Consistent and thorough understanding of the required knowledge and skills and the ability to apply them accurately in a wide variety of situa�ons. The student consistently demonstrates originality, insight, and cri�cal thinking The student produces work of high quality.
6 Consistent and thorough understanding of the required knowledge and skills and the ability to apply them in a wide variety of situa�ons. The student consistently demonstrates originality, insight, and cri�cal thinking
5 Thorough understanding of the required knowledge and skills and the ability to apply them in a variety of situa�ons The student occasionally demonstrates originality, insight, and cri�cal thinking.
4 General understanding of the required knowledge and skills and the ability to apply them effec�vely in normal situa�ons There is occasional evidence of cri�cal thinking
3 Limited achievement against most of the objec�ves or clear difficul�es in some areas. The student demonstrates a limited understanding of the required knowledge and skills and is only able to apply them fully to normal situa�ons with support.
2 Very limited achievement in terms of the objec�ves The student has difficulty in understanding the required knowledge and skills and is unable to apply them fully to normal situa�ons, even with support
1 Minimal achievement in terms of the objec�ves.
If a student fulfils the gradua�on requirements set out by the school (see below), they will be awarded an ISP High School Diploma. This is the equivalent of an American High School Diploma, but may also have equivalency in other countries. The condi�ons for the award of the ISP High School Diploma are determined by the school and are not con�ngent on any external examina�ons.
The requirements for the ISP High School Diploma are as follows:
● par�cipa�on in six courses during grades 11 and 12 (other than TOK);
● an average score of 18 points across all six courses over the two years;
● sa�sfactory par�cipa�on in the Service component of CAS to those required for IB Diploma candidates (note: Crea�vity and Ac�vity are op�onal); and,
● minimum 90% a�endance in each course over the two years.
The requirements for the ISP High School Honours Diploma are as follows:
● par�cipa�on in six courses, each from a different subject group, during grades 11 and 12 (other than TOK);
● an average score of 21 points across all six courses over the two years;
● no score lower than a 2 in any course in grade 12;
● sa�sfactory par�cipa�on in the Service component of CAS to those required for IB Diploma candidates (note: Crea�vity and Ac�vity are op�onal); and,
● minimum 90% a�endance in each course over the two years
The majority of our students will take examina�ons validated by the Interna�onal Baccalaureate. There are many subjects available at ISP; we offer an unusually generous and wide variety of courses. An IB Course Cer�ficate will be awarded externally, by the IB, for any IB examina�on taken. IB Course Cer�ficates are typically used in conjunc�on with an ISP High School Diploma to earn advanced standing credit and are o�en a requirement in addi�on to the High School Diploma for university applica�ons University Counsellors will help with iden�fying courses and their requirements The award of IB Course Cer�ficates is independent of the ISP High School Diploma




A student will be eligible for the award of the IB Diploma if they meet the criteria outlined by the IB (below) This will include taking external examina�ons, plus comple�ng the core requirements: Theory of Knowledge (TOK), Crea�vity, Ac�vity, Service (CAS) and the Extended Essay (EE) The award of the IB Diploma is independent of the ISP High School Diploma
Each year, the large majority of our students take the IB Diploma, and the pass rate at ISP has been significantly higher than the average rate worldwide. However, students are not obliged to take the IB Diploma. Some students may feel that their needs are not best met by the IB Diploma, and may choose to organise their programme in a different way. It may be that the IB Diploma is not required either by a student’s university of choice or in the country where the student would like to study. A student may choose fewer than three higher level subjects, or all six subjects at standard level, or even select a combina�on of subjects that does not meet the requirements for the IB Diploma.
To be a successful IB Diploma student, it is necessary to be punctual both to classes and to school, to have an excellent a�endance record and to complete work on �me and to an appropriate standard In all courses, students must complete mandatory coursework assignments; typically, this coursework amounts to 25% of the final grade for each course, although in some cases it may be higher or lower The key to doing this work to an acceptable standard is organisa�on, and the importance of keeping to internal deadlines cannot be stressed enough
There is a maximum of seven points available for each of the six subject courses; in addi�on, there are three points available for the combina�on of TOK and the Extended Essay This makes a maximum total of 45 points A minimum of three courses must be at higher level In general, in order to receive the IB Diploma, a student will have to score at least a 4 in each subject, or 24 points or more in total. The full criteria for passing the IB DP are set out below and students need to be aware that a score of 24 points will not always guarantee a pass.
The IB Diploma will be awarded to a candidate whose total score is 24, 25, 26 or 27 points, provided all the following requirements have been met:
● numeric grades have been awarded in all six subjects registered for the IB Diploma;
● all CAS requirements have been met;
● grades A (highest) to D (lowest without failing) have been awarded for both Theory of Knowledge and an Extended Essay;
● there is no grade 1 in any subject;
● there are no more than two grade 2s (higher or standard level);
● overall, there are no more than three grades of 3 or below (higher or standard level);
● at least 12 points have been gained on higher level subjects (candidates who register for four higher level subjects must gain at least 16 points at higher level);
● at least nine points have been gained on standard level subjects (candidates who register for two standard level subjects must gain at least six points at standard level); and,
● the final award commi�ee has not judged the candidate to be guilty of malprac�ce.
To be promoted from Grade 11 to Grade 12 at the end of the first year of the IB Diploma Programme, a student must meet the requirements of the ISP High School Diploma; this includes mee�ng the required a�endance in each course
The IB Diploma is a rigorous and demanding programme that provides students with a first-class prepara�on for their future a�er ISP. Students follow a course of study with a global reputa�on for academic excellence, and universi�es throughout the world recognise the IB Diploma as an entrance qualifica�on to higher educa�on degree courses. In some countries, such as the United States and Canada, the IB Diploma qualifies students for advanced placement or academic credits; furthermore, students with the IB Diploma are accepted at a higher rate at selec�ve US universi�es than those with other qualifica�ons In general, European universi�es prefer the IB Diploma for entrance over IB cer�ficates or the High School Diploma Universi�es may require standardised tests (SAT, ACT), if a student only has the High School Diploma or the High School Diploma with IB cer�ficates
ISP has a strong record in placing its graduates in universi�es around the world We employ four counsellors: one for English-speaking universi�es (North America and the UK), one for European universi�es, one for Korean universi�es and one for Japanese universi�es


Theory of Knowledge is a course focused on the ques�on, “How do we know?” Students are taught to seek out knowledge through cri�cal thinking and analysis of real world situa�ons. By the end of the course, students should be proficient in formula�ng arguments and analysing knowledge claims. The central features of the Theory of Knowledge course in grade 11 are 35 exhibi�on prompts which guide students’ thinking, while 6 essay ques�ons play a similar role in grade 12
Students are officially assessed for their IB Diploma, based solely on two pieces of work:


● Grade 12: The TOK essay on a prescribed �tle (1,200–1,600 words) – this is supervised by a teacher in the school, and then graded externally by an IB examiner.
● Grade 11: The TOK Exhibi�on and wri�en ra�onale – this is supervised and assessed by teachers in the school These grades are then moderated by the IB through samples
The final TOK grade and the final Extended Essay grade are entered into the Diploma points matrix (see below) to award a possible maximum of 3 extra points, which are added to a student’s Diploma score. Candidates not submi�ng sa�sfactory work (level E) for either task will fail the Diploma. For more informa�on, please see the TOK Student Handbook on ManageBac.
The Extended Essay is an in-depth study of a specific topic within a subject. Its purpose is to provide a student with an opportunity to engage in independent academic research. Emphasis is placed on the process of engaging in personal research, on the communica�on of ideas and informa�on in a logical and coherent manner and on the overall presenta�on of the Extended Essay in compliance with IB guidelines Students are required to devote 40 hours to the essay At ISP the process usually commences in January of Grade 11 and is completed by November of Grade 12 The Extended Essay is limited to 4,000 words and should include an introduc�on, methodology, conclusion and bibliography, along with the necessary analysis
In choosing a subject, an essen�al considera�on should be the personal interests of the student The subject should offer the opportunity for in-depth research but should also be limited in scope It should present the candidate with the opportunity to collect or generate informa�on and/or data for analysis and evalua�on. The subject a student chooses for their extended essay will be one of their higher levels, however, they will be expected to go beyond the syllabus when undertaking their research.
The Extended Essay is externally examined. Marks are awarded against a set of published criteria. The final Extended Essay grade and the final TOK grade are entered into the Diploma points matrix (see below) to award a possible maximum of three extra points, which are added to a student’s Diploma score. Candidates not submi�ng sa�sfactory work in either the EE or TOK will fail the Diploma.
For more informa�on, please see the Extended Essay Student Handbook on ManageBac.

The three elements of the Diploma Programme core (TOK, CAS and the Extended Essay) were introduced by the original curriculum designers of the Diploma Programme as a way to educate the whole person.
CAS experiences are an important source of personal knowledge, providing students with the opportunity to gain awareness of the world in a range of diverse and challenging situa�ons. Shared knowledge extends the idea from how individuals construct knowledge to how communi�es construct knowledge In CAS, students might draw on TOK discussions that deepen understanding of different communi�es and cultures In both CAS and TOK, students reflect on beliefs and assump�ons, leading to more though�ul, responsible and purposeful lives
In the CAS programme, students must:
● engage in cri�cal reflec�on, analyse their own thinking, effort and performance;
● learn how to set challenging goals and develop the commitment and perseverance to achieve them;
● develop self-awareness and a sense of iden�ty;
● consider a CAS project that fosters interna�onal-mindedness – reflects an issue of global significance, but is explored from a local perspec�ve;
● develop individual and shared responsibility, and effec�ve teamwork and collabora�on;
● demonstrate a�ributes of the IB learner profile in real and prac�cal ways;


● develop skills, a�tudes and disposi�ons through a variety of individual and group experiences;
● allocate sufficient �me to the CAS programme (weekly basis, 18-month journey); and,
● reflect on CAS experiences and provide evidence in CAS por�olios of achieving the 7 learning outcomes
CAS complements a challenging academic programme in a holis�c way, providing opportuni�es for self-determina�on, collabora�on, accomplishment and enjoyment A meaningful CAS programme is a journey of discovery of self and others Each individual student has a different star�ng point and different needs and goals
For more informa�on, please see the CAS Student Handbook on ManageBac
Occasionally, the grades students receive in their final examina�ons do not meet their expecta�ons. In such cases a student might ask for their externally assessed work to be remarked. The IB refers to such a request as ‘Enquiry upon results’ (EUR). Before proceeding the school will request wri�en confirma�on from the student, or parent, that they wish the examined component for a subject to be remarked. It is important to recognise that the remark may raise or lower the final grade. The cost of a remark is 150 euros which covers both the IB and school’s administra�on fee Another route is to retake the examina�on(s) in the November or May session Retakes will not result in the lowering of the final grade, as the highest grade stands The cost of a retake is 300 euros which covers both the IB and school’s administra�on fee A student may only retake the subject’s external component three �mes


Language A: Language and Literature (HL and SL)
The language A: Language and Literature course aims at studying the complex and dynamic nature of language and exploring both its prac�cal and aesthe�c dimensions. The course will explore the crucial role language plays in communica�on – reflec�ng experience and shaping the world – and the roles of individuals themselves as producers of language. Throughout the course, students will explore the various ways in which language choices, text types, literary forms and contextual elements all affect meaning Through close analysis of various text types and literary forms, students will consider their own interpreta�ons, as well as the cri�cal perspec�ves of others, to explore how such posi�ons are shaped by cultural belief systems and to nego�ate meanings for texts
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● engage with a range of texts, in a variety of media and forms, from different periods, styles and cultures;
● develop skills in listening, speaking, reading, wri�ng, viewing, presen�ng and performing;
● develop skills in interpreta�on, analysis and evalua�on; and,


● develop sensi�vity to the formal and aesthe�c quali�es of texts and an apprecia�on of how they contribute to diverse responses and open up mul�ple meanings
External assessment
Paper 1: Guided textual analysis (2 hours 15 minutes) (35%)
The paper consists of two non-literary passages, from two different text types, each accompanied by a ques�on. Students write an analysis of each of the passages.
Paper 2: Compara�ve essay (1 hour 45 minutes) (25%)
The paper consists of four general ques�ons. In response to one ques�on students write a compara�ve essay based on two literary works studied in the course
HL essay (20%)
Students submit an essay on one non-literary body of work, or a literary work studied during the course (20 marks) The essay must be 1,200-1,500 words in length 16
Paper 1: Guided textual analysis (1 hour 15 minutes) (35%)
The paper consists of two non-literary passages, from two different text types, each accompanied by a ques�on. Students choose one passage and write an analysis of it.
Paper 2: Compara�ve essay (1 hour 45 minutes)(35%)
The paper consists of four general ques�ons. In response to one ques�on students write a compara�ve essay based on two literary works studied in the course
Supported by an extract from both one non-literary body of work and one from a literary work, students will offer a prepared response of 10 minutes, followed by 5 minutes of ques�ons by the teacher, to the following prompt:
Examine the ways in which the global issue of your choice is presented through the content and form of one of the works and one of the bodies of work that you have studied.
Supported by an extract from one non-literary body of work and one from a literary work, students will offer a prepared response of 10 minutes, followed by 5 minutes of ques�ons by the teacher, to the following prompt: Examine the ways in which the global issue of your choice is presented through the content and form of one of the works and one of the bodies of work that you have studied.
The Language A: Literature aims at exploring the various manifesta�ons of literature as a par�cularly powerful mode of wri�ng across cultures and throughout history The course aims at developing an understanding of factors that contribute to the produc�on and recep�on of literature the crea�vity of writers and readers, the nature of their interac�on with their respec�ve contexts and with literary tradi�on, the ways in which language can give rise to meaning and/or effect and the performa�ve and transforma�ve poten�al of literary crea�on and response Through close analysis of a range of literary texts in a number of literary forms and from different �mes and places, students will consider their own interpreta�ons, as well as the cri�cal perspec�ves of others, to explore how such posi�ons are shaped by cultural belief systems and to nego�ate meanings for texts.
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● engage with a range of texts, in a variety of media and forms, from different periods, styles and cultures;
● develop skills in listening, speaking, reading, wri�ng, viewing, presen�ng and performing;
● develop skills in interpreta�on, analysis and evalua�on;


● develop sensi�vity to the formal and aesthe�c quali�es of texts and an apprecia�on of how they contribute to diverse responses and open up mul�ple meanings;
● develop an understanding of rela�onships between texts and a variety of perspec�ves, cultural contexts, and local and global issues, and an apprecia�on of how they contribute to diverse responses and open up mul�ple meanings;
● develop an understanding of the rela�onships between studies in language and literature and other disciplines;
● communicate and collaborate in a confident and crea�ve way; and,
● foster a lifelong interest in and enjoyment of language and literature. 17
External assessment Paper 1: Guided literary analysis (2 hours 15 minutes) (35%)
The paper consists of two literary passages, from two different literary forms, each accompanied by a ques�on. Students write an analysis of each of the passages.
Paper 2 Compara�ve essay (1 hour 45 minutes) (25%)
The paper consists of four general ques�ons. In response to one ques�on, students write a compara�ve essay based on two works studied in the course
Higher level (HL) essay (20%)
Students submit an essay on one work studied during the course
The essay must be 1,200–1,500 words in length
Internal assessment IIndividual oral (15 minutes) (20%)


Supported by an extract from one work wri�en originally in the language studied and one from a work studied in transla�on, students will offer a prepared response of 10 minutes, followed by 5 minutes of ques�ons by the teacher, to the following prompt: Examine the ways in which the global issue of your choice is presented through the content and form of two of the works that you have studied.
Paper 1: Guided literary analysis (1 hour 15 minutes) (35%)
The paper consists of two passages from two different literary forms, each accompanied by a ques�on. Students choose one passage and write an analysis of it.
Paper 2 Compara�ve essay (1 hour 45 minutes) (35%)
The paper consists of four general ques�ons. In response to one ques�on, students write a compara�ve essay based on two works studied in the course
Individual oral (15 minutes) (30%)
Supported by an extract from one work wri�en originally in the language studied and one from a work studied in transla�on, students will offer a prepared response of 10 minutes, followed by 5 minutes of ques�ons by the teacher, to the following prompt: Examine the ways in which the global issue of your choice is presented through the content and form of two of the works that you have studied.


Language B is designed for students with some previous experience of the target language. Students further develop their ability to communicate through the study of language, themes and texts. There are five prescribed themes: iden��es, experiences, human ingenuity, social organisa�on and sharing the planet. Offered at SL only, Language ab ini�o is a language acquisi�on course designed for students with no previous experience in – or very li�le exposure to – the target language Both Language B SL and HL students learn to communicate in the target language in familiar and unfamiliar contexts The dis�nc�on between Language B SL and HL can be seen in the level of competency the student is expected to develop in recep�ve, produc�ve and interac�ve skills At HL the study of two literary works originally wri�en in the target language is required and students are expected to extend the range and complexity of the language they use and understand in order to communicate
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● develop interna�onal-mindedness through the study of languages, cultures, and ideas and issues of global significance;
● enable students to communicate in the language they have studied in a range of contexts and for a variety of purposes;
● encourage, through the study of texts and through social interac�on, an awareness and apprecia�on of a variety of perspec�ves of people from diverse cultures;
● develop students’ understanding of the rela�onship between the languages and cultures with which they are familiar;
● develop students’ awareness of the importance of language in rela�on to other areas of knowledge;
● provide students, through language learning and the process of inquiry, with opportuni�es for intellectual engagement and the development of cri�cal- and crea�ve-thinking skills;
● provide students with a basis for further study, work and leisure through the use of an addi�onal language; and,
● foster curiosity, crea�vity and a lifelong enjoyment of language learning
External assessment Paper 1 (1 hour 30 minutes) (25%) Produc�ve skills wri�ng (30 marks)
One wri�ng task of 450–600 words from a choice of three, each from a different theme, choosing a text type from among those listed in the examina�on instruc�ons.
Paper 2 (2 hours)
Recep�ve skills separate sec�ons for listening and reading (50%)
Listening comprehension (1 hour) (25 marks) (25%)
Reading comprehension (1 hour)(25%)
Comprehension exercises on three audio passages and three wri�en texts, drawn from all five themes.
Paper 1 (1 hour 15 minutes) (25%) Produc�ve skills wri�ng (30 marks)
One wri�ng task of 250–400 words from a choice of three, each from a different theme, choosing a text type from among those listed in the examina�on instruc�ons.
Paper 2 (1 hour 45 minutes)
Recep�ve skills separate sec�ons for listening and reading (50%)


Listening comprehension (45 minutes) (25%)
Reading comprehension (1 hour)(25%)
Comprehension exercises on three audio passages and three wri�en texts, drawn from all five themes.
Internal assessment
Individual oral assessment (25%)
A conversa�on with the teacher, based on a visual s�mulus, followed by discussion based on an addi�onal theme.
Individual oral assessment (25%)
A conversa�on with the teacher, based on a visual s�mulus, followed by discussion based on an addi�onal theme.


Language ab ini�o students develop their recep�ve, produc�ve and interac�ve skills while learning to communicate in the target language in familiar and unfamiliar contexts Students develop the ability to communicate through the study of language, themes and texts There are five prescribed themes: iden��es, experiences, human ingenuity, social organisa�on and sharing the planet While the themes are common to both Language ab ini�o and Language B, the Language ab ini�o syllabus addi�onally prescribes four topics for each of the five themes, for a total of 20 topics that must be addressed over the two years of the course.
Standard Level
External assessment
Paper 1 (1 hour) (25%)
Produc�ve skills wri�ng
Two wri�en tasks of 70–150 words each from a choice of three tasks, choosing a text type for each task from among those listed in the examina�on instruc�ons.
Paper 2 (1 hour 45 minutes)
Recep�ve skills separate sec�ons for listening and reading (50%)
Listening comprehension (45 minutes) (25%)
Reading comprehension (1 hour) (25%)
Comprehension exercises on three audio passages and three wri�en texts, drawn from all five themes.
Internal assessment
Individual oral assessment (25%)
A conversa�on with the teacher, based on a visual s�mulus and at least one addi�onal course theme.
Economics is an exci�ng, dynamic subject that allows students to develop an understanding of the complexi�es and interdependence of economic ac�vi�es in a rapidly changing world. At the heart of economic theory is the problem of scarcity. Owing to scarcity, choices have to be made. The economics course, at both SL and HL, uses economic theories, models and key concepts to examine the ways in which these choices are made: at the level of producers and consumers in individual markets (microeconomics); at the level of the government and the na�onal economy (macroeconomics); and at an interna�onal level, where countries are becoming increasingly interdependent (the global economy) The DP economics course allows students to explore these models, theories and key concepts, and apply them, using empirical data, through the examina�on of six real-world issues Through their own inquiry, students will be able to appreciate both the values and limita�ons of economic models in explaining real-world economic behaviour and outcomes. By focusing on the six real-world issues through the nine key concepts (scarcity, choice, efficiency, equity, economic wellbeing, sustainability, change, interdependence and interven�on), students of the economics course will develop the knowledge, skills, values and a�tudes that will encourage them to act responsibly as global ci�zens.
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● develop a cri�cal understanding of a range of economic theories, models, ideas and tools in the areas of microeconomics, macroeconomics and the global economy;
● apply economic theories, models, ideas and tools, and analyse economic data to understand and engage with real-world economic issues and problems facing individuals and socie�es; and,
● develop a conceptual understanding of individuals’ and socie�es’ economic choices, interac�ons, challenges and consequences of economic decision-making.
External assessment
Higher Level Standard Level
Paper 1 (1 hour and 15 minutes)(20%)
An extended response paper
Syllabus content including HL extension material


Paper 2 (1 hour and 45 minutes)(30%)
A data response paper
Syllabus content excluding HL extension material Includes some quan�ta�ve ques�ons
Paper 3 (1 hour and 45 minutes)(30%)
A policy paper
Syllabus content including HL extension material Includes both quan�ta�ve and
Paper 1 (1 hour and 15 minutes)(30%)
An extended response paper
Syllabus content (excluding HL extension material)
Paper 2 (1 hour and 45 minutes)(40%)
A data response paper
Syllabus content (excluding HL extension material) Includes some quan�ta�ve ques�ons
Internal assessment
qualita�ve ques�ons.
Internal assessment (20 teaching hours)(20%)
This component is internally assessed by the teacher and externally moderated by the IB at the end of the course.
Students produce a por�olio of three commentaries, based on different units of the syllabus (excluding the introductory unit) and on published extracts from the news media Each of the three commentaries should use a different key concept as a lens through which to analyse the published extracts
Maximum 800 words for each commentary
Internal assessment (20 teaching hours)(30%)


This component is internally assessed by the teacher and externally moderated by the IB at the end of the course.
Students produce a por�olio of three commentaries, based on different units of the syllabus (excluding the introductory unit) and on published extracts from the news media Each of the three commentaries should use a different key concept as a lens through which to analyse the published extracts
Maximum 800 words for each commentary
Geography is a dynamic subject firmly grounded in the real world, and focuses on the interac�ons between individuals, socie�es and physical processes in both �me and space. It seeks to iden�fy trends and pa�erns in these interac�ons It also inves�gates the way in which people adapt and respond to change, and evaluates actual and possible management strategies associated with such change Geography describes and helps to explain the similari�es and differences between different places, on a variety of scales and from different perspec�ves Geography as a subject is dis�nc�ve in its spa�al dimension and occupies a middle ground between social or human sciences and natural sciences The course integrates physical, environmental and human geography, and students acquire elements of both socio-economic and scien�fic methodologies Geography takes advantage of its posi�on to examine relevant concepts and ideas from a wide variety of disciplines, helping students develop life skills and have an apprecia�on of, and a respect for, alterna�ve approaches, viewpoints and ideas. Students at both SL and HL are presented with a common core and op�onal geographic themes. HL students also study the HL core extension. Although the skills and ac�vity of studying geography are common to all students, HL students are required to acquire a further body of knowledge, to demonstrate cri�cal evalua�on and to further synthesise the concepts.
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● develop an understanding of the dynamic interrela�onships between people, places, spaces and the environment at different scales;
● develop a cri�cal awareness and consider complexity thinking in the context of the nexus of geographic issues, including:
o acquiring an in-depth understanding of how geographic issues, or wicked problems, have been shaped by powerful human and physical processes;
o synthesising diverse geographic knowledge in order to form viewpoints about how these issues could be resolved; and,
● understand and evaluate the need for planning and sustainable development through the management of resources at varying scales.
Paper 1 (1 hour 30 minutes)(35%)
Geographic themes three op�ons
External assessment Paper 1 (2 hours 15 minutes)(35%)
Structured and extended response ques�ons.
Paper 2 (1 hour 15 minutes)(25%)
Geographic perspec�ves global change
Structured and extended response ques�ons.
Paper 3 (1 hour)(20%)
Geographic perspec�ves global interac�ons.
Extended response ques�ons.
Geographic themes two op�ons
Structured and extended response ques�ons.
Paper 2 (1 hour 15 minutes) (40%)
Geographic perspec�ves global change
Structured and extended response ques�ons.
Internal assessment
Internal assessment (20 hours)(20%) This component is internally assessed by the teacher and externally moderated by the IB at the end of the course.


Fieldwork (20 hours)
Fieldwork, leading to one wri�en report based on a fieldwork ques�on, informa�on collec�on and analysis with evalua�on
Internal assessment (20 hours) (25%)
This component is internally assessed by the teacher and externally moderated by the IB at the end of the course.
Fieldwork (20 hours)
Fieldwork, leading to one wri�en report based on a fieldwork ques�on, informa�on collec�on and analysis with evalua�on
The DP History course is a world history course based on a compara�ve and mul�-perspec�ve approach to history It involves the study of a variety of types of history, including poli�cal, economic, social and cultural, and provides a balance of structure and flexibility. The course emphasises the importance of encouraging students to think historically and to develop historical skills as well as gaining factual knowledge. It puts a premium on developing the skills of cri�cal thinking and on developing an understanding of mul�ple interpreta�ons of history. In this way, the course involves a challenging and demanding cri�cal explora�on of the past. Teachers explicitly teach thinking and research skills such as comprehension, text analysis, transfer and use of primary sources There are six key concepts that have par�cular prominence throughout the DP history course: change, con�nuity, causa�on, consequence, significance and perspec�ves
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● develop an understanding of, and con�nuing interest in, the past;
● encourage students to engage with mul�ple perspec�ves and to appreciate the complex nature of historical concepts, issues, events and developments;
● promote interna�onal-mindedness through the study of history from more than one region of the world;


● develop an understanding of history as a discipline and to develop historical consciousness including a sense of chronology and context, and an understanding of different historical perspec�ves;
● develop key historical skills, including engaging effec�vely with sources; and,
● increase students’ understanding of themselves and of contemporary society by encouraging reflec�on on the past.
External assessment
Higher Level Standard Level
Paper 1 (1 hour)(20%)
Source-based paper based on the five prescribed subjects. Choose one prescribed subject from a choice of five. Answer four structured ques�ons
Paper 2 (1 hour 30 minutes) (25%)
Essay paper based on the 12 world history topics
Paper 3 (2 hours 30 minutes) (35%)
Separate papers for each of the four regional op�ons. For the selected region, answer three essay ques�ons
Paper 1 (1 hour) (30%)
Source-based paper based on the five prescribed subjects. Choose one prescribed subject from a choice of five. Answer four structured ques�ons
Paper 2 (1 hour 30 minutes) (45%)
Essay paper based on the 12 world history topics
Internal assessment
Internal assessment (20 hours)(20%)
This component is internally assessed by the teacher and externally moderated by the IB at the end of the course
Historical inves�ga�on
Students are required to complete a historical inves�ga�on into a topic of their choice
Internal assessment (20 hours) (25%)
This component is internally assessed by the teacher and externally moderated by the IB at the end of the course
Historical inves�ga�on
Students are required to complete a historical inves�ga�on into a topic of their choice
Biology is the study of life. The vast diversity of species makes biology both an endless source of fascina�on and a considerable challenge. Biologists a�empt to understand the living world at all levels from the micro to the macro using many different approaches and techniques. Biology is s�ll a young science and great progress is expected in the 21st century. This progress is important at a �me of growing pressure on the human popula�on and the environment By studying biology in the DP students should become aware of how scien�sts work and communicate with each other While the scien�fic method may take on a wide variety of forms, it is the emphasis on a prac�cal approach through experimental work that characterises the sciences Teachers provide students with opportuni�es to design inves�ga�ons, collect data, develop manipula�ve skills, analyse results, collaborate with peers and evaluate and communicate their findings
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● appreciate scien�fic study and crea�vity within a global context through s�mula�ng and challenging opportuni�es;
● acquire and apply a body of knowledge, methods and techniques that characterise science and technology;


● develop an ability to analyse, evaluate and synthesise scien�fic informa�on;
● develop a cri�cal awareness of the need for, and the value of, effec�ve collabora�on and communica�on during scien�fic ac�vi�es;
● develop experimental and inves�ga�ve scien�fic skills including the use of current technologies;
● develop and apply 21st century communica�on skills in the study of science;
● become cri�cally aware, as global ci�zens, of the ethical implica�ons of using science and technology;
● develop an apprecia�on of the possibili�es and limita�ons of science and technology; and,
● develop an understanding of the rela�onships between scien�fic disciplines and their influence on other areas of knowledge.
External assessment
Higher Level Standard Level
Paper 1 (2 hours) (36%)
Paper 1A Mul�ple-choice ques�ons
Paper 1B Data-based ques�ons (four ques�ons that are syllabus related, addressing all themes)
Paper 2 (2 hour and 30 minutes)(44%)
Sec�on A Data-based and short answer ques�ons
Sec�on B Extended-response ques�ons
Paper 1 (1 hour and 30 minutes) (36%)
Paper 1A Mul�ple-choice ques�ons
Paper 1B Data-based ques�ons (four ques�ons that are syllabus related, addressing all themes)
Paper 2 (1 hour and 30 minutes)(44%)
Sec�on A Data-based and short answer ques�ons
Sec�on B Extended-response ques�ons
Internal assessment Internal assessment (10 hours) (20%)
The internal assessment consists of one task: the scien�fic inves�ga�on
Internal assessment (10 hours) (20%)
The internal assessment consists of one task: the scien�fic inves�ga�on
Chemistry is an experimental science that combines academic study with the acquisi�on of prac�cal and inves�ga�onal skills. Chemical principles underpin both the physical environment in which we live and all biological systems. Chemistry is o�en a prerequisite for many other courses in higher educa�on, such as medicine, biological science and environmental science Both theory and prac�cal work should be undertaken by all students as they complement one another naturally, both in school and in the wider scien�fic community This course allows students to develop a wide range of prac�cal skills and to increase facility in the use of mathema�cs It also allows students to develop interpersonal and informa�on technology skills By studying chemistry, students should become aware of how scien�sts work and communicate with each other While the scien�fic method may take on a wide variety of forms, it is the emphasis on a prac�cal approach through experimental work that characterises the subject. Teachers provide students with opportuni�es to develop manipula�ve skills, design inves�ga�ons, collect data, analyse results and evaluate and communicate their findings.
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● appreciate scien�fic study and crea�vity within a global context through s�mula�ng and challenging opportuni�es;
● acquire and apply a body of knowledge, methods and techniques that characterise science and technology;


● develop an ability to analyse, evaluate and synthesise scien�fic informa�on;
● develop a cri�cal awareness of the need for, and the value of, effec�ve collabora�on and communica�on during scien�fic ac�vi�es;
● develop experimental and inves�ga�ve scien�fic skills including the use of current technologies;
● develop and apply 21st century communica�on skills in the study of science;
● become cri�cally aware, as global ci�zens, of the ethical implica�ons of using science and technology;
● develop an apprecia�on of the possibili�es and limita�ons of science and technology; and,
● develop an understanding of the rela�onships between scien�fic disciplines and their influence on other areas of knowledge.
External assessment
Higher Level
Paper 1 (2 hours) (36%)
Paper 1A
Mul�ple-choice ques�ons
Paper 1B Data-based ques�ons
Standard Level
Paper 1 (1 hour and 30 minutes) (36%)
Paper 1A
Paper 1B
Mul�ple-choice ques�ons
Data-based ques�ons
Paper 2 (2 hour and 30 minutes)(44%)
Short-answer and extended-response ques�ons
Internal assessment Internal assessment (10 hours) (20%)
The internal assessment consists of one task: the scien�fic inves�ga�on.
Paper 2 (1 hour and 30 minutes)(44%)
Short-answer and extended-response ques�ons
Internal assessment (10 hours) (20%)
The internal assessment consists of one task: the scien�fic inves�ga�on.
The Design Technology course aims to develop interna�onally-minded people whose enhanced understanding of design and the technological world can facilitate our shared guardianship of the planet and create a be�er world Inquiry and problem-solving are at the heart This course requires the use of the design cycle, which provides the methodology used to structure the inquiry and analysis of problems, the development of feasible solu�ons, and the tes�ng and evalua�on of the solu�on defined as a model, prototype, product or system that students have developed independently. DP Design Technology enables students to develop cri�cal thinking and design skills, which they can apply in a prac�cal context. While designing may take various forms, it will involve the selec�ve applica�on of knowledge within an ethical framework.
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● build a sense of curiosity as they acquire the skills necessary for independent and lifelong learning and ac�on through inquiry into the technological world around them;
● explore concepts, ideas and issues with personal, local and global significance to acquire in-depth knowledge and understanding of design and technology;
● apply thinking skills cri�cally and crea�vely to iden�fy and resolve complex social and technological problems through reasoned ethical decision-making;


● understand and express ideas confidently and crea�vely using a variety of communica�on techniques through collabora�on with others;
● demonstrate a propensity to act with integrity and honesty, and take responsibility for their own ac�ons in designing technological solu�ons to problems;
● develop an understanding and apprecia�on of cultures in terms of global technological development, seeking and evalua�ng a range of perspec�ves;
● show a willingness to approach unfamiliar situa�ons in an informed manner and explore new roles, ideas and strategies to confidently ar�culate and defend proposals;
● develop an understanding of the contribu�on of design and technology to the promo�on of intellectual, physical and emo�onal balance;
● build empathy, compassion and respect for the needs and feelings of others in order to make a posi�ve difference to the lives of others and to the environment; and,
● increase skills that enable reflec�on on the impacts of design and technology on society and the environment.
External assessment
Higher Level
Paper 1 (1 hours) (20%)
Mul�ple-choice ques�ons
Paper 2 1 hour minutes)(20%)
Sec�on A: one data-based ques�on and several short-answer ques�ons on the core material
Sec�on B: one extended-response ques�on on the core materials.
Paper 3 (1 hour)(20%)
Sec�on A: two structured ques�ons on the HL extension material
Sec�on B: one structured ques�on on the HL extension material based on a case study
Internal assessment Internal assessment (60 hours) (40%)
The internal assessment consists of one task: Individual design project


Standard Level
Paper 1 (45 minutes) (30%)
Mul�ple-choice ques�ons
Paper 2 (1 hour and 30 minutes)(30%)
Sec�on A: one data-based ques�on and several short-answer ques�ons on the core material
Sec�on B: one extended-response ques�on on the core materials
Internal assessment (40 hours) (40%)
The internal assessment consists of one task: Individual design project
Environmental Systems and Socie�es (ESS) is an interdisciplinary course that can fulfil either the Individuals and Socie�es or the Sciences requirement; it enables students to sa�sfy the requirements of both subject groups simultaneously while studying one course ESS is firmly grounded in scien�fic explora�on of environmental systems in their structure and func�on, and in the explora�on of cultural, economic, ethical, poli�cal and social interac�ons of socie�es with the environment. As a result of studying ESS, students will become equipped with the ability to recognise and evaluate the impact of our complex system of socie�es on the natural world. The interdisciplinary nature requires a broad skill set from students, including the ability to perform research and inves�ga�ons, par�cipa�on in philosophical discussion and problem-solving. The course requires a systems approach to environmental understanding and promotes holis�c thinking about environmental issues Teachers explicitly teach thinking and research skills such as comprehension, text analysis, knowledge transfer and use of primary sources They encourage students to develop solu�ons at the personal, community and global levels
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● acquire the knowledge and understandings of environmental systems and issues;
● apply the knowledge, methodologies and skills to analyse environmental systems and issues at a variety of scales;
● appreciate the dynamic interconnectedness between environmental systems and socie�es;
● value the combina�on of personal, local and global perspec�ves in making informed decisions and taking responsible ac�ons on environmental issues;
● be cri�cally aware that resources are finite, that these could be inequitably distributed and exploited, and that management of these inequi�es is the key to sustainability;
● develop awareness of the diversity of environmental value systems;
● develop cri�cal awareness that environmental problems are caused and solved by decisions made by individuals and socie�es that are based on different areas of knowledge;
● engage with the controversies that surround a variety of environmental issues; and,
● create innova�ve solu�ons to environmental issues by engaging ac�vely in local and global contexts.
External assessment
Standard Level
Paper 1 (1 hour) (25%)
Students will be provided with a range of data in a variety of forms rela�ng to a specific, previously unseen case study.
Ques�ons will be based on the analysis and evalua�on of the data in the case study. Paper 2 (2 hours)(50%)
Short-answer and structured essays
Internal assessment 10 hours (25%)
Internal assessment (individual inves�ga�on)


Physics is the most fundamental of the experimental sciences, as it seeks to explain the universe itself, from the very smallest par�cles to the vast distances between galaxies Despite the exci�ng and extraordinary development of ideas throughout the history of physics, observa�ons remain essen�al to the very core of the subject Models are developed to try to understand observa�ons, and these themselves can become theories that a�empt to explain the observa�ons. Besides helping us be�er understand the natural world, physics gives us the ability to alter our environments. This raises the issue of the impact of physics on society, the moral and ethical dilemmas, and the social, economic and environmental implica�ons of the work of physicists. By studying physics, students should become aware of how scien�sts work and communicate with each other While the scien�fic method may take on a wide variety of forms, it is the emphasis on a prac�cal approach through experimental work that characterises the subject Teachers provide students with opportuni�es to develop manipula�ve skills, design inves�ga�ons, collect data, analyse results and evaluate and communicate their findings
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● appreciate scien�fic study and crea�vity within a global context through s�mula�ng and challenging opportuni�es;
● acquire and apply a body of knowledge, methods and techniques that characterise science and technology;


● develop an ability to analyse, evaluate and synthesise scien�fic informa�on;
● develop a cri�cal awareness of the need for, and the value of, effec�ve collabora�on and communica�on during scien�fic ac�vi�es;
● develop experimental and inves�ga�ve scien�fic skills including the use of current technologies;
● develop and apply 21st century communica�on skills in the study of science;
● become cri�cally aware, as global ci�zens, of the ethical implica�ons of using science and technology;
● develop an apprecia�on of the possibili�es and limita�ons of science and technology; and,
● develop an understanding of the rela�onships between scien�fic disciplines and their influence on other areas of knowledge
External assessment
Higher Level
Paper 1 (2 hours) (36%)
Paper 1A Mul�ple-choice ques�ons
Paper 1B Data-based ques�ons
Paper 2 (2 hour and 30 minutes)(44%)
Short-answer and extended-response ques�ons
Standard Level
Paper 1 (1 hour and 30 minutes) (36%)
Paper 1A Mul�ple-choice ques�ons
Paper 1B Data-based ques�ons
Paper 2 (1 hour and 30 minutes)(44%)
Short-answer and extended-response ques�ons


Internal assessment
Internal assessment (10 hours) (20%)
The internal assessment consists of one task: the scien�fic inves�ga�on
Internal assessment (10 hours) (20%)
The internal assessment consists of one task: the scien�fic inves�ga�on
The Mathema�cs: Analysis and Approaches course recognises the need for analy�cal exper�se in a world where innova�on is increasingly dependent on a deep understanding of mathema�cs. The focus is on developing important mathema�cal concepts in a comprehensible, coherent and rigorous way, achieved by a carefully balanced approach. Students are encouraged to apply their mathema�cal knowledge to solve abstract problems as well as those set in a variety of meaningful contexts Mathema�cs: Analysis and Approaches has a strong emphasis on the ability to construct, communicate and jus�fy correct mathema�cal arguments Students should expect to develop insight into mathema�cal form and structure, and should be intellectually equipped to appreciate the links between concepts in different topic areas Students are also encouraged to develop the skills needed to con�nue their mathema�cal growth in other learning environments The internally assessed explora�on allows students to develop independence in mathema�cal learning Throughout the course students are encouraged to take a considered approach to various mathema�cal ac�vi�es and to explore different mathema�cal ideas.
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● develop a curiosity and enjoyment of mathema�cs, and appreciate its elegance and power;
● develop an understanding of the concepts, principles and nature of mathema�cs;
● communicate mathema�cs clearly, concisely and confidently in a variety of contexts;
● develop logical and crea�ve thinking, and pa�ence and persistence in problem solving;
● employ and refine their powers of abstrac�on and generalisa�on;
● apply and transfer skills to alterna�ve situa�ons;
● appreciate the moral, social and ethical ques�ons arising from mathema�cs;
● appreciate the universality of mathema�cs and its mul�cultural, interna�onal and historical perspec�ves;
● appreciate the contribu�on of mathema�cs to other disciplines;
● develop the ability to reflect cri�cally upon their own work and the work of others; and,
● independently and collabora�vely extend their understanding of mathema�cs
External assessment
Higher Level
Paper 1 (120 minutes)(30%)
No technology allowed
Sec�on A
Compulsory short-response ques�ons based on the syllabus
Sec�on B
Compulsory extended-response ques�ons based on the syllabus
Standard Level
Paper 1 (90 minutes)(40%)
No technology allowed
Sec�on A
Compulsory short-response ques�ons based on the syllabus
Sec�on B
Compulsory extended-response ques�ons based on the syllabus


Internal assessment
Paper 2 (120 minutes)(30%)
Technology required
Sec�on A
Compulsory short-response ques�ons based on the syllabus
Sec�on B
Compulsory extended-response ques�ons based on the syllabus.
Paper 3 (60 minutes)(20%)
Technology required
Two compulsory extended response problem-solving ques�ons
Mathema�cal explora�on (20%)
Internal assessment in mathema�cs is an individual explora�on This is a piece of wri�en work that involves inves�ga�ng an area of mathema�cs
Paper 2 (90 minutes)(40%)
Technology required
Sec�on A
Compulsory short-response ques�ons based on the syllabus
Sec�on B
Compulsory extended-response ques�ons based on the syllabus


Mathema�cal explora�on (20%)
Internal assessment in mathema�cs is an individual explora�on This is a piece of wri�en work that involves inves�ga�ng an area of mathema�cs
The Mathema�cs: Applica�ons and Interpreta�on course recognises the increasing role that mathema�cs and technology play in a diverse range of fields in a data-rich world. As such, it emphasises the meaning of mathema�cs in context by focusing on topics that are o�en used as applica�ons or in mathema�cal modelling. To give this understanding a firm base, this course includes topics that are tradi�onally part of a pre-university mathema�cs course such as calculus and sta�s�cs Students are encouraged to solve real-world problems, construct and communicate this mathema�cally and interpret the conclusions or generalisa�ons Students should expect to develop strong technology skills, and will be intellectually equipped to appreciate the links between the theore�cal and the prac�cal concepts in mathema�cs All external assessments involve the use of technology Students are also encouraged to develop the skills needed to con�nue their mathema�cal growth in other learning environments The internally assessed explora�on allows students to develop independence in mathema�cal learning Throughout the course students are encouraged to take a considered approach to various mathema�cal ac�vi�es and to explore different mathema�cal ideas.
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● develop a curiosity and enjoyment of mathema�cs, and appreciate its elegance and power;
● develop an understanding of the concepts, principles and nature of mathema�cs;
● communicate mathema�cs clearly, concisely and confidently in a variety of contexts;
● develop logical and crea�ve thinking, and pa�ence and persistence in problem solving;
● employ and refine their powers of abstrac�on and generalisa�on;
● apply and transfer skills to alterna�ve situa�ons;
● appreciate the moral, social and ethical ques�ons arising from mathema�cs;
● appreciate the universality of mathema�cs and its mul�cultural, interna�onal and historical perspec�ves;
● appreciate the contribu�on of mathema�cs to other disciplines;
● develop the ability to reflect cri�cally upon their own work and the work of others; and,
● independently and collabora�vely extend their understanding of mathema�cs
Standard Level
External assessment Paper 1 (90 minutes) (40%)
Technology required
Compulsory short-response ques�ons based on the syllabus
Paper 2 (90 minutes) (40%)
Technology required
Compulsory extended-response ques�ons based on the syllabus


Internal assessment Mathema�cal explora�on (20%)
Internal assessment in mathema�cs is an individual explora�on This is a piece of wri�en work that involves inves�ga�ng an area of mathema�cs
The Film course aims to develop students as proficient interpreters and makers of film texts. Through the study and analysis of film texts and prac�cal exercises in film produc�on, students develop cri�cal abili�es and apprecia�on of ar�s�c, cultural, historical and global perspec�ves in film. They examine concepts, theories, prac�ces and ideas from mul�ple perspec�ves, challenging their own views to understand and value those of others Students are challenged to acquire and develop cri�cal thinking, reflec�ve analysis and the imagina�ve synthesis through prac�cal engagement in the art, cra� and study of film Students experiment with film and mul�media technology, acquiring the skills and crea�ve competencies required to successfully communicate through the language of the medium They develop an ar�s�c voice and learn how to express personal perspec�ves through film The course emphasises the importance of working collabora�vely, interna�onal and intercultural dynamics and an apprecia�on of the development of film across �me and culture. The film syllabus allows for greater breadth and depth in teaching and learning at HL through an addi�onal assessment task, requiring HL students to reflect on the core syllabus areas to formulate their own inten�ons for a completed film. They work collabora�vely as a core produc�on team in order to effec�vely communicate on screen.
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● explore the various contexts of film and make links to, and between, films, filmmakers and filmmaking techniques (inquiry);
● acquire and apply skills as discerning interpreters of film and as creators of film, working both individually and collabora�vely (ac�on); and,
● develop evalua�ve and cri�cal perspec�ves on their own film work and the work of others (reflec�on).
External assessment
Textual analysis (20%)
Students at SL and HL demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of how meaning is constructed in film They do this through a wri�en analysis of a prescribed film text based on a chosen extract (las�ng no more than five minutes) from that film Students consider the cultural context of the film and a variety of film elements
Students submit the following:
A textual analysis (1,750 words maximum) and a list of all sources used.


Students at HL carry out research into a chosen area of film focus, iden�fying and comparing two films from within
Students at SL and HL demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of how meaning is constructed in film They do this through a wri�en analysis of a prescribed film text based on a chosen extract (las�ng no more than five minutes) from that film Students consider the cultural context of the film and a variety of film elements
Students submit the following:
A textual analysis (1,750 words maximum) and a list of all sources used.
Students at SL carry out research into a chosen area of film focus, iden�fying and comparing two films from within
Internal assessment
that area and presen�ng their discoveries as a recorded mul�media compara�ve study.
Students submit the following:
A recorded mul�media compara�ve study (10 minutes maximum)
A list of all sources used
Collabora�ve film project (35%) Bringing together all they have encountered during the film course, students at HL work collabora�vely in a core produc�on team to plan and create an original completed film
Students submit the following:
A completed film (7 minutes maximum).
A project report (2,000 words maximum) and a list of all sources used
Film por�olio (25%)
Students at HL undertake a variety of film-making exercises in three film produc�on roles, led by clearly defined filmmaker inten�ons They acquire and develop prac�cal skills and techniques through par�cipa�on in film exercises, experiments and the crea�on of at least one completed film
Students submit the following:
Por�olio pages (9 pages maximum: 3 pages maximum per film produc�on role) and a list of all sources used.
A film reel (9 minutes maximum: 3 minutes maximum per film produc�on role, including one completed film)
that area and presen�ng their discoveries as a recorded mul�media compara�ve study.
Students submit the following:
A recorded mul�media compara�ve study (10 minutes maximum)
A list of all sources used


Film por�olio (40%)
Students at SL undertake a variety of film-making exercises in three film produc�on roles, led by clearly defined filmmaker inten�ons They acquire and develop prac�cal skills and techniques through par�cipa�on in film exercises, experiments and the crea�on of at least one completed film
Students submit the following:
Por�olio pages (9 pages maximum: 3 pages maximum per film produc�on role) and a list of all sources used.
A film reel (9 minutes maximum: 3 minutes maximum per film produc�on role, including one completed film)
The Diploma Programme Music course has been designed to prepare the 21st century music student for a world in which global musical cultures and industries are rapidly changing The course is grounded in the knowledge, skills and processes associated with the study of music and offers a strengthened approach to student crea�vity through prac�cal, informed and purposeful explora�ons of diverse musical forms, prac�ces and contexts. The course also ensures a holis�c approach to learning, with the roles of performer, creator and researcher afforded equal importance in all course components. The course seeks to be inclusive of students with wide-ranging personal and cultural musical backgrounds. In place of prescribed musical content, students and teachers have the agency to personalise unique approaches to musical forms, genres and pieces. The explora�on of diverse musical material is focused through the lenses of four areas of inquiry: music for sociocultural and poli�cal expression; music for listening and performance; music for drama�c impact, movement and entertainment; and, music technology in the digital age
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● explore a range of musical contexts and make links to, and between, different musical prac�ces, conven�ons and forms of expression;
● acquire, develop and experiment with musical competencies through a range of musical prac�ces, conven�ons and forms of expression, both individually and in collabora�on with others; and,


● evaluate and develop cri�cal perspec�ves on their own music and the work of others
External assessment
Presen�ng music (30%)
Students submit a collec�on of works demonstra�ng engagement with diverse musical material from four areas of inquiry
The submission contains: Presen�ng as a researcher programme notes (maximum 600 words)
Presen�ng as a creator composi�on and/or improvisa�on (maximum 6 minutes)
Presen�ng as a performersolo and/or ensemble (maximum 12 minutes) excerpts, where applicable (maximum 2 minutes)
Exploring music in context (20%)
Students select samples of their work for a por�olio submission (maximum 2,400 words).
Presen�ng music (40%)
Students submit a collec�on of works demonstra�ng engagement with diverse musical material from four areas of inquiry
The submission contains:
Presen�ng as a researcher programme notes (maximum 600 words)
Presen�ng as a creator composi�on and/or improvisa�on (maximum 6 minutes)
Presen�ng as a performer solo and/or ensemble (maximum 12 minutes) excerpts, where applicable (maximum 2 minutes)
Exploring music in context (30%)
Students select samples of their work for a por�olio submission (maximum 2,400 words).
Internal assessment
Students submit:
wri�en work demonstra�ng engagement with, and understanding of, diverse musical material
prac�cal exercises: crea�ng: one crea�ng exercise (score maximum 32 bars and/or audio 1 minute as appropriate to style) performing: one performed adapta�on of music from a local or global context for the student’s own instrument (maximum 2 minutes)
suppor�ng audio material (not assessed).
Experimen�ng with music (20%)
Students submit an experimenta�on report with evidence of their musical processes in crea�ng and performing in two areas of inquiry in a local and/or global context. The report provides a ra�onale and commentary for each process
Students submit:
a wri�en experimenta�on report that supports the experimenta�on (maximum 1,500 words)
prac�cal musical evidence of the experimenta�on process three related excerpts of crea�ng (total maximum 5 minutes) three related excerpts of performing (total maximum 5 minutes)
The contemporary music-maker (30%)
Students submit a con�nuous mul�media presenta�on documen�ng their real-life project Students submit mul�media presenta�on (maximum 15 minutes), evidencing:
a the project proposal
b the process and evalua�on
c the realised project, or curated selec�ons of it.
Students submit:
wri�en work demonstra�ng engagement with, and understanding of, diverse musical material
prac�cal exercises: crea�ng: one crea�ng exercise (score maximum 32 bars and/or audio 1 minute as appropriate to style) performing: one performed adapta�on of music from a local or global context for the student’s own instrument (maximum 2 minutes)
suppor�ng audio material (not assessed).
Experimen�ng with music (30%)
Students submit an experimenta�on report with evidence of their musical processes in crea�ng and performing in two areas of inquiry in a local and/or global context. The report provides a ra�onale and commentary for each process
Students submit:
a wri�en experimenta�on report that supports the experimenta�on (maximum 1,500 words)

prac�cal musical evidence of the experimenta�on process three related excerpts of crea�ng (total maximum 5 minutes) three related excerpts of performing (total maximum 5 minutes)

Theatre is a prac�cal subject that encourages discovery through experimenta�on, risk-taking and the presenta�on of ideas The course is mul�faceted and gives students the opportunity to ac�vely engage in theatre as creators, designers, directors and performers It emphasises working both individually and collabora�vely as part of an ensemble The teacher’s role is to create opportuni�es that allow students to explore, learn, discover and collaborate to become autonomous, informed and skilled theatre-makers. Students learn to apply research and theory to inform and to contextualise their work. Through researching, crea�ng, preparing, presen�ng and cri�cally reflec�ng on theatre, they gain a richer understanding of themselves, their community and the world. Students experience the course from contras�ng ar�s�c and cultural perspec�ves. They learn about theatre from around the world, the importance of making theatre with integrity, and the impact that theatre can have on the world It enables them to discover and engage with different forms of theatre across �me, place and culture, promo�ng interna�onal mindedness and an apprecia�on of the diversity of theatre
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● explore theatre in a variety of contexts and understand how these contexts inform prac�ce;
● understand and engage in the processes of transforming ideas into ac�on;
● develop and apply theatre produc�on, presenta�on and performance skills, working both independently and collabora�vely; and,
● understand and appreciate the rela�onship between theory and prac�ce
External assessment Research presenta�on (20%)
Students at SL and HL plan, deliver and video record an individual research presenta�on (15 minutes maximum) in which they provide evidence of their academic and prac�cal explora�on and learning of a world theatre tradi�on they have not previously studied.
Each student submits the following
A video recording of the student’s research presenta�on (15 minutes maximum)
A list of all sources cited and any addi�onal resources used by the student during the presenta�on.
Collabora�ve project (25%)


Students at SL and HL collabora�vely create and perform an original piece of theatre (las�ng 7–10 minutes maximum) created from a star�ng point of their
Research presenta�on (30%)
Students at SL and HL plan, deliver and video record an individual research presenta�on (15 minutes maximum) in which they provide evidence of their academic and prac�cal explora�on and learning of a world theatre tradi�on they have not previously studied.
Each student submits the following
A video recording of the student’s research presenta�on (15 minutes maximum)
A list of all sources cited and any addi�onal resources used by the student during the presenta�on.
Collabora�ve project (40%)
Students at SL and HL collabora�vely create and perform an original piece of theatre (las�ng 7–10 minutes maximum) created from a star�ng point of their
Internal assessment
choice. The piece is presented to an audience as a fully-realised produc�on.
Each student submits the following.
A project report (a maximum of 10 pages of wri�en text and images, with wri�en text not exceeding 4,000 words) plus a list of all sources used
A video recording of the final piece (7–10 minutes maximum)
Solo theatre piece (35%)
Students at HL research a theatre theorist they have not previously studied, iden�fy an aspect(s) of theory and create and present a solo theatre piece (las�ng 4–7 minutes maximum) that demonstrates the prac�cal applica�on of this theory to a theatre piece for an audience.
Each student submits the following
A report (2,500 words maximum) plus a list of all primary and secondary sources cited
A con�nuous unedited video recording of the whole solo theatre piece (4–7 minutes maximum).
Produc�on proposal (20%)
Students at SL and HL choose a published play text they have not previously studied and formulate a vision for the design and theore�cal staging of the en�re play text for an audience. These ideas are presented in the form of a proposal.
Each student submits the following
A produc�on proposal (a maximum of 12 pages of wri�en text and images, with wri�en text not exceeding 4,000 words) plus a list of all sources used.
choice. The piece is presented to an audience as a fully-realised produc�on.
Each student submits the following.
A project report (a maximum of 10 pages of wri�en text and images, with wri�en text not exceeding 4,000 words) plus a list of all sources used
A video recording of the final piece (7–10 minutes maximum)
Produc�on proposal (30%)
Students at SL and HL choose a published play text they have not previously studied and formulate a vision for the design and theore�cal staging of the en�re play text for an audience. These ideas are presented in the form of a proposal.
Each student submits the following
A produc�on proposal (a maximum of 12 pages of wri�en text and images, with wri�en text not exceeding 4,000 words) plus a list of all sources used.


The Visual Arts course encourages students to challenge their own crea�ve and cultural expecta�ons and boundaries It is a thought-provoking course in which students develop analy�cal skills in problem solving and divergent thinking, while working towards technical proficiency and confidence as art makers In addi�on to exploring and comparing visual arts from different perspec�ves and in different contexts, students are expected to engage in, experiment with and cri�cally reflect upon a wide range of contemporary prac�ces and media. The course is designed for students who want to go on to further study of visual arts in higher educa�on as well as for those who are seeking lifelong enrichment through visual arts. The role of visual arts teachers is to ac�vely and carefully organise learning experiences for the students, direc�ng their study to enable them to reach their poten�al and sa�sfy the demands of the course Students should be empowered to become autonomous, informed and skilled visual ar�sts
The main objec�ves in this course are for students to:
● make artwork that is influenced by personal and cultural contexts;
● become informed and cri�cal observers and makers of visual culture and media; and,
● develop skills, techniques and processes in order to communicate concepts and ideas.
External assessment
Part 1: Compara�ve
Students at HL analyse and compare different artworks by different ar�sts. This independent cri�cal and contextual inves�ga�on explores artworks, objects and artefacts from differing cultural contexts
Process por�olio (40%)
Students at HL submit carefully selected materials which evidence their experimenta�on, explora�on, manipula�on and refinement of a variety of visual arts ac�vi�es during the two-year course
Internal assessment Part 3: Exhibi�on (40%)
Students at HL submit for assessment a selec�on of resolved artworks from their exhibi�on The selected pieces should show evidence of their technical accomplishment during the visual arts course and an understanding of the use of materials, ideas and prac�ces appropriate to visual communica�on • HL students submit a curatorial ra�onale that does not exceed 700 words.


Students at SL analyse and compare different artworks by different ar�sts. This independent cri�cal and contextual inves�ga�on explores artworks, objects and artefacts from differing cultural contexts
Part 2: Process por�olio (40%)
Students at SL submit carefully selected materials which evidence their experimenta�on, explora�on, manipula�on and refinement of a variety of visual arts ac�vi�es during the two year course
Part 3: Exhibi�on (40%)
Students at SL submit for assessment a selec�on of resolved artworks from their exhibi�on The selected pieces should show evidence of their technical accomplishment during the visual arts course and an understanding of the use of materials, ideas and prac�ces appropriate to visual communica�on • SL students submit a curatorial ra�onale that does not exceed 400 words.
Homework is an extension of the regular daily school work and is given in all courses The func�ons of homework are to help students prepare for classes and to develop the skills of organisa�on, �me management, independent responsibility, self-direc�on and self-discipline
Long-range assignments such as reports and projects take careful planning and organisa�on on the part of the student Parents are encouraged to assist in monitoring student progress toward the comple�on of the assignments, but should not do the students’ work for them Parents can be most helpful to their children by providing a rou�ne �me and a place that is conducive to undisturbed study Students can seek help in developing more effec�ve study skills from their teachers, counsellors, and the learning support department.
The amount of homework assigned for Grades 11 and 12 will vary between ten to twelve hours a week. The nature of the homework will change, but it can be assumed that students will always be required to be reading set texts in prepara�on for lessons and reading around all of their subjects as a ma�er of course. Ge�ng work done on �me requires careful planning, organisa�on, determina�on and self-discipline. These quali�es are important in students’ careers and in their personal lives.
To promote the habit of punctuality, while recognising that difficul�es can arise, our expecta�ons are:
● All assignments are due by the deadline set by the teacher (Diploma coursework or any other assignment) It is the class teacher’s responsibility to ensure that the due date – for wri�en work and oral presenta�ons – is clearly understood by all of the students in the class IB Diploma deadlines are placed on ManageBac


● Students who an�cipate having difficulty mee�ng a deadline must see the teacher well before the due date to discuss a possible extension. An extension may be granted if the teacher judges that there is an acceptable and legi�mate reason.
● Students with an absence for the day that an assignment was due should hand in the assignment by email or on their return
ISP is commi�ed to academic integrity and will ensure that all students in the IB Diploma Programme are aware of what this entails While we trust that all students enrolled in the school will submit work of their own that is appropriately referenced, we feel that it is necessary to give guidelines as to what this means and what the consequences will be if any work does not meet this standard
Although the following list is not exhaus�ve, academic dishonesty can, in general, take several forms:
● Plagiarism: taking work, words, ideas, pictures, informa�on or anything that has been produced by someone else and submi�ng it for assessment as one’s own.
● Copying: taking work of another student, with or without his or her knowledge and submi�ng it as one’s own
● Exam chea�ng: communica�ng with another candidate in an exam, bringing unauthorised material into an exam room or consul�ng such material during an exam in order to gain an unfair advantage;
● Duplica�on: submi�ng work that is substan�ally the same for assessment in different courses without the consent of all teachers involved
● Falsifying data: crea�ng or altering data which have not been collected in an appropriate way
● Collusion: helping another student to be academically dishonest.
ISP, in line with IB recommenda�ons and prac�ce, may submit random or selected pieces of work to external bodies for verifica�on and evalua�on of sources. Students should be able to submit electronic copies of any work to either the teacher or the relevant curriculum coordinator for such verifica�on at any �me We recommend that students keep all rough notes and dra�s that they produce in preparing work for submission to teachers or examiners in order to be able to defend themselves against charges of malprac�ce


If a teacher, or another member of staff, suspects that a student may have breached the school’s standards of academic honesty, he or she will inform the IB DP coordinator, the Department Leader, the Grade Level Leader, and Homeroom Teacher. The ma�er will be inves�gated, and the student will be informed of the concerns of the teacher, giving the student the chance to reply to the accusa�ons If it can be shown that inappropriate work has been submi�ed, the IB DP Coordinator will make a recommenda�on to the Secondary School Principal as to whether or not the case is one of academic dishonesty, or of an academic infringement Again, in line with the IB’s policy and prac�ce, the determining difference between these two possibili�es will be one of intent The Principal will decide the outcome of the case
Any student who has been found to be academically dishonest in any of the above ways, or otherwise, will have a record of this put into his or her student file, and this will be communicated to the student’s parents If the work has been submi�ed as an official piece of IB coursework, it will not be accepted; if there is �me for him or her to do so, the student will be allowed to resubmit another piece of work in its place. If there is not �me for the student to produce new work, he or she will normally not receive a grade for that course and will therefore not receive an IB Diploma. A second viola�on will result in the student being removed from that par�cular IB DP course, and being disallowed from being able to receive an IB course cer�ficate in that subject. In addi�on, the student will not receive credit towards the High School Diploma for the course. If a student submits work to the IB which is later recognised as having been produced dishonestly, the IB will not award a diploma to that student
Students should recognise that they are ul�mately responsible for their own work and that the consequences of any breaches of the standard of academic honesty will be theirs alone They should speak to teachers regularly about their work and show dra�s of it at various stages in the produc�on process They should ask teachers for advice if they are at any �me unsure of what they have done in rela�on to referencing sources
Turni�n.com
ISP currently uses “turni�n.com” as a useful tool for electronically collec�ng work that will be submi�ed to Diploma examiners. All Extended Essays and TOK essays will be submi�ed this way, and subject teachers will use it through the ManageBac pla�orm.


ISP reserves the right to use anonymised student work for educa�onal purposes When students’ work is used in this way it will only be used internally and never published externally Student has the right to retain full permission of his/her work (in accordance with the Interna�onal Baccalaureate Organisa�on) and withdraw the work at any point






