

Introduction to Irrigation Design and Construction
Irrigation is essential for maintaining lush landscapes and efficient water usage. This presentation will guide you through the key steps of irrigation design and construction , from assessing the site to installing and commissioning the system.

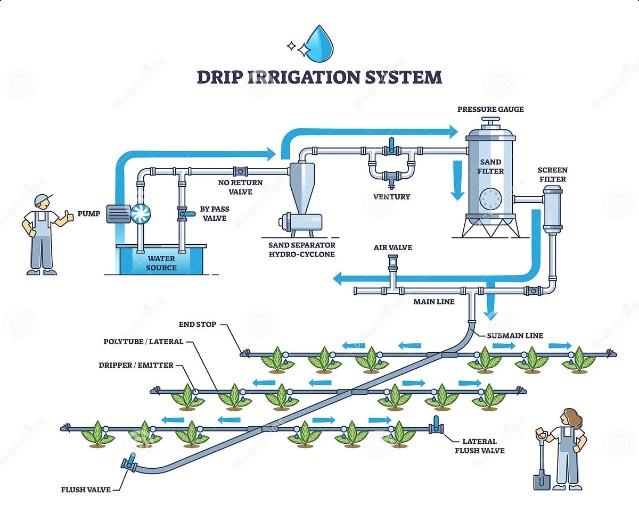
Site Assessment and Analysis

Topography
Evaluate the site's slopes, elevations, and drainage patterns to determine the optimal layout and water flow.
Soil Conditions
Analyze the soil type, infiltration rate, and nutrient content to select the right irrigation components.
Climate Factors
Consider temperature, precipitation, and wind to design a system that adapts to the local environment.
Irrigation System Components

Water Source
Determine the water supply, whether it's a well, municipal line, or other source.

Control Valves
Integrate valves to manage water flow and pressure throughout the system.

Sprinkler Heads
Select the appropriate sprinkler types and placement to achieve uniform coverage.

Control System
Utilize a programmable controller to automate irrigation schedules and monitor performance.

Hydraulic Calculations and Design
Water Demand
Determine the total water flow rate and pressure requirements based on the landscape area and plant needs.
2 Pipe Friction Loss
Calculate the pressure drop due to friction in the pipes to ensure adequate water delivery.
3 Pump Sizing
Select the appropriate pump capacity and type to meet the system's hydraulic demands.


Pipe Sizing and Layout
Pipe Material
Polyethylene, PVC, Copper
Pipe Diameter 1/2" to 4" based on flow rates
Layout Configuration Main, lateral, and distribution pipes
Trenching Depth 12-24 inches below grade

Sprinkler Head Selection and Placement

Rotor Sprinklers
Ideal for large, open areas with maximum coverage and uniform water distribution.
Spray Sprinklers
Suitable for smaller, more enclosed spaces with a focused water pattern.
Drip Emitters
Efficient for watering specific plants or landscaping features with precise application.
Spacing and Overlap
Carefully position sprinklers to achieve the desired coverage and avoid dry spots.
Irrigation Control Systems



Automatic Timers
Program schedules for efficient, hands-off watering based on site requirements.
Sensors
Integrate soil moisture, rain, and flow sensors to optimize water usage.
WiFi Connectivity
Remote monitoring and adjustments allow for convenient system management.



Installation and Commissioning
Site Preparation
Excavate trenches, install pipes, and set up sprinkler heads and valves.
2 Pressure Testing
Verify the system's integrity and identify any leaks or issues.
System Programming
Configure the control system for optimal watering schedules and performance.
4 Final Inspection
Ensure the entire irrigation system is functioning correctly before commissioning. 1 3








