
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dipkumar
Santoshkumar Trivedi1 , Arpit Rajnibhai Joshi2 , Krunalkumar Govindbhai Patel3
1Lecturer, K. D. Polytechnic Patan, Gujarat, India
2Lecturer, K. D. Polytechnic Patan, Gujarat, India
3Junior Engineer, UGVCL, Gujarat, India
Abstract Main purpose of this paper is to check the stability of Multi machine power system with the help of Energy Preserving Function (Energy Based Direct Method).In this method first step is to compute TotalEnergygainedbythe system during the Fault and by comparing this energy with Critical Energy CCT (Critical Clearing Time) can be estimated. Total Energy can be summarized as sum of Kinetic and Potential Energy during the fault. The Critical Energy can be Find out with the help of Closest Unstable Equilibrium Point method (C-UEP). For this analysis Considered Test System is Standard WSCC (Western System Coordinating Council) 3 machine 9 Bus System.
Index Terms Transient Stability, Critical Clearing Time (CCT), Energy Function, Critical Energy, Closest Unstable Equilibrium Point Method (C-UEP).
I. Introduction
Differentformsofinstabilityhaveemergedoverthe last century. Power System Stability is a complex problem thathaschallengedpowersystemengineersformanyyears. Powersystemstabilityproblemsaresolvedwiththehelpof computationaltools,stabilitytheoriesandadvancedcontrol strategies.
The Direct Methods determines stability without solvingthesystemofdifferentialequations.Basicapproach developedin[3,5]ispractical,enoughaccurateandapplyto practical power system for better planning and operation. Directmethodswithoutthesolutionofdifferentialequations can be used to determine the transient stability analysisof powersystem.ThismethodistheLyapunov’sdirectmethod (secondmethod).Theenergy-basedmethodisaspecialcase ofLyapunov’sdirectmethod.Thesetechniquesareextensions oftheequalareacriteriontopowersystemswithmorethan twogeneratorsrepresentedbytheclassicalmodel.
Theauthorsofpaper[4]proposeddirectmethodthat uses individual machine or group of machines energy function.TheEnergyfunctionofeachmachineiscomparedto a Critical Energy which can be determined by Potential Energy Boundary Surface (PEBS) method or Boundary Controlling UEP (BCU) method or Closest Unstable Equilibriumpoint.
If the individual Machine’s Energy is greater than CriticalEnergythensystemisconsideredasunstable.Based
onthisCriticalClearingTime(CCT)iscalculatedfordifferent Fault Locations. The method used for Transient Stability analysis in [5] is combination of Step by Step method with directMethods.Thismethodfirstcalculatesthepotentialand Kinetic energy of all machines in power system before and afteroccurrenceofFault.ItfinallycomparesLargestGroupof Kinetic Energy to Smallest Group of Potential energy for EvaluationofTransientstability.IfsmallestgroupofPotential EnergyisGreaterthanLargestGroupofKineticEnergythen SystemisConsiderasstable.
Transient Stability using Energy function can be analyzed with the help of Controlling UEP method which exclusivelydiscussedin[12]whereasreference[13]mainly focus on the difficulty arise in the study of Energy based methodsLikeUEP,BCU,PEBSetcandpreparecomputational algorithmsforfindingoutsolutions.
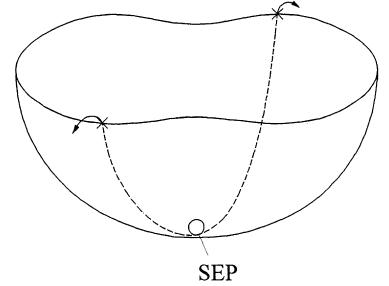
Thetransientenergyapproachcanbeunderstoodbythe example of rolling ball inside the bowl. The inside area of bowlisconsideredasstableregionandoutsideareaasthe instable.Initiallyballisatbottomthatpointisconsideredas thestableequilibriumpoint(SEP).
Whensomekineticenergyisgiventoballthenballstarts tomoveinparticulardirection.Thepointwhereballwillstop that depends on initial given kinetic energy. The surface insidethebowlrepresentsPotentialEnergysurface.Therim ofthebowlrepresentsthePotentialEnergyBoundarySurface (PEBS).ConsiderthepotentialenergyatrimisPI,andgiven kineticenergyisKI.
If,
KI>PI => Ball will cross the rim =>Unstable condition. KI<PI =>Ballwillnotcrosstherim=>StableCondition.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
TransientEnergyfunctionisrepresentationoftotalenergy gainedduringfaultintermsofKineticandPotentialenergy. If fault occurs then during Fault on Period, the rotor of synchronousmachineacceleratesandacquiressomekinetic energy. Same way angular position of rotor also changed. Overall, we can say it acquires both Kinetic as well as Potential energy. Potential energy depends upon the angular position of rotor with respect to stable operatingangularpositions.
Ifsystemiscapableofabsorbingcompletelythekinetic energy then it is stable system. Same Concept can be applicableforthepowersystem.Totalenergygainedbythe systemduringthefaultiscomparedwiththeCriticalEnergy. If Total energy during fault exceeds Critical energy then system becomes unstable. With the help of this direct method we can also find out Critical Clearing Time (CCT). CriticalEnergyofthesystemcanbefoundoutwiththehelp of Closest Unstable Equilibrium Point method or BCU or PEBSmethod.
III. Proposed Direct Method
This paper represents transient stability analysis with thehelpofEnergybaseddirectmethod.HereCriticalEnergy calculated with the help of Closest Unstable Equilibrium Pointmethod.
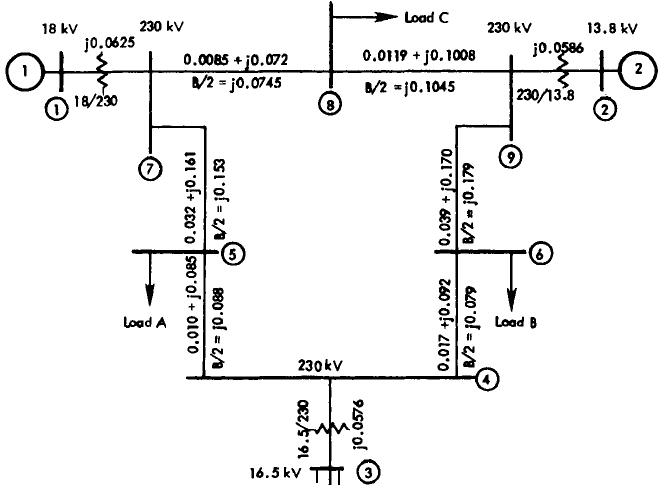
TheConsideredtestsystemfortransientstabilityanalysis wastheFamousWSCC3Machine9BusSystem[9].Machine number 3 is considered as reference machine. Load is connected at bus num 5(P=1.25pu, Q=0.5pu), 6(P=0.9pu, Q=0.3pu)and8(P=1pu,Q=0.35pu).Faultoccursatbusnum 7anditisclearedbyremovingtransmissionline(5to7).
B. Pre-Fault and Post Fault Stable Point Calculation PowerSystemDynamicsaregovernedbytheequations
NowatPrefaultandPostfaultStablePointcanbefindout by equating mechanical input (Pmi) and electrical power outputs(Pei). i.e.Pmi=Pei ,i=1,2..n
Formachine1,
Pm1=(E12*G11)+(E1E2G12cos(del1-del2)+E1E3G13cos(del1del3)+E1E2B12sin(del1-del2)+E1E3B13sin(del1))
Formachine2,
Pm2=(E22 *G22) + (E1E2G12cos(del2-del1)+E2E3G23cos(del2del3)+E1E2B12sin(del2-del1)+E2E3B23sin(del2))
These Equations can be solved using Programming as wellasSimulationModelinMATLAB.
NowforSolvingabovetwoequationsinmatlabModelwe getanswers:
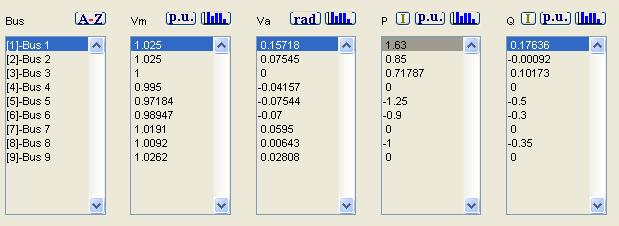
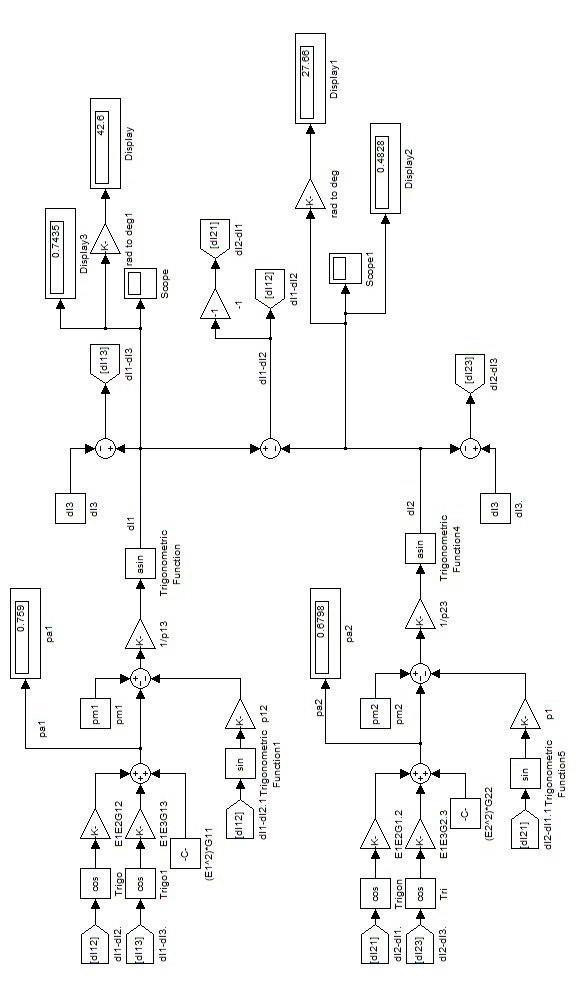
PrefaultStablepoint: del1=0.3116 del2=0.1949
PostfaultStablepoint: del1=0.7435 del2=0.4828
The MATLAB models for Pre fault Stable Point CalculationsandPostfaultStablePointCalculationaregiven inFig4&5.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
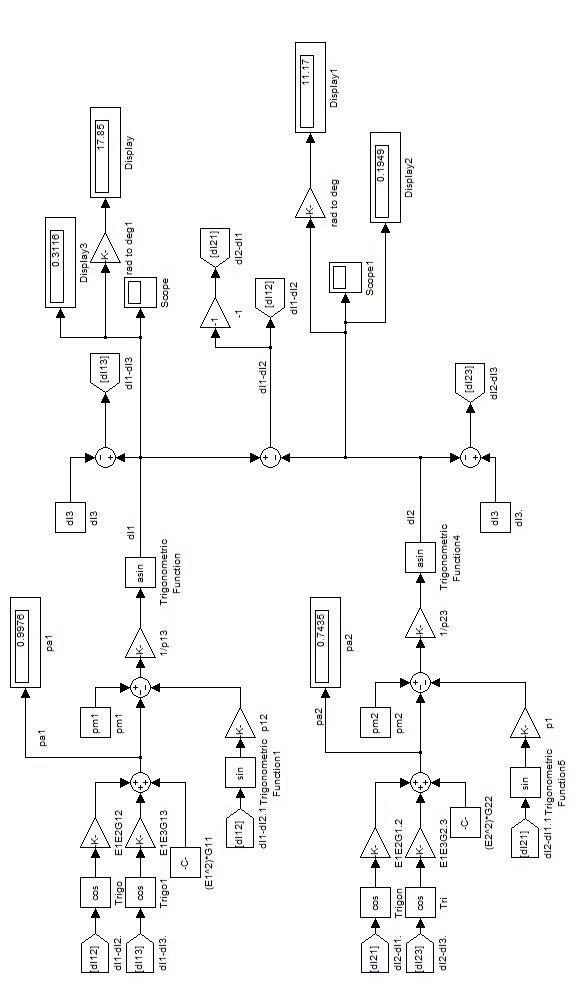
StablePointMATLABModel
C. Identification of Closest Unstable Equilibrium Point
TotalenergyDuringFault(Es)iscalculatedby
Total EnergyduringFaultisidentifiedasa SumofKinetic andPotential Energyofthe system.NowClosestUnstable Equilibrium Point (C-UEP) can be identified with partial Derivative of Potential Energy and then find closest
equilibrium point from Post fault Stable point for that we plot
Contour graph and mesh grid Plots identified Closest Unstable Equilibrium Point (CUEP) From Graphs is (1.55,1.45) which is also known as Critical Point. The PotentialEnergyatCUEPpointisknownasCriticalEnergy (Ecr
NowTotalEnergyduringfaultiscomparedwithCritical EnergysowecanfindoutCriticalClearingTime(CCT).we gotnearly0.17secCCTtime.Itmeansiffaultmustbecleared maximum up to CCT time then we can say that system is stableotherwiseitsunstable.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
I. Results
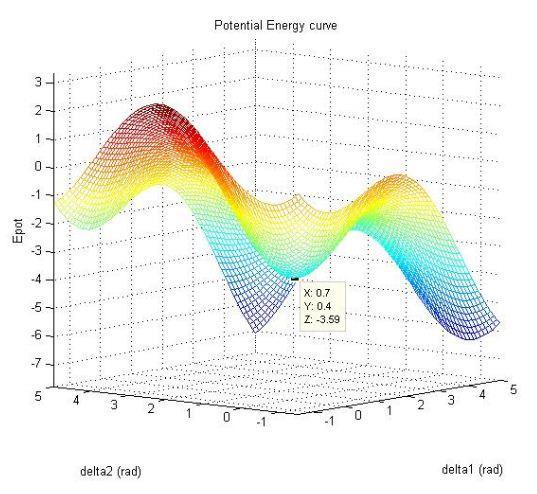
PotentialEnergyCurve
Post Fault Stable Point
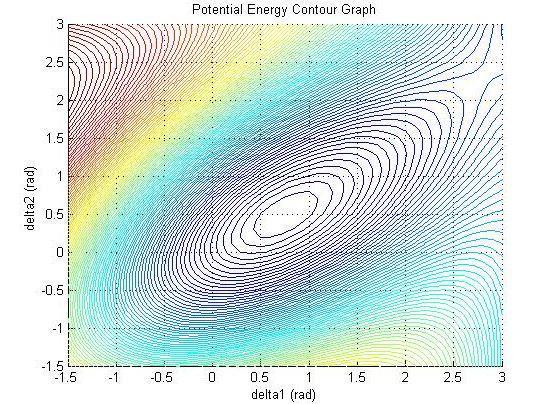
PotentialEnergyContourCurve
(1.55, 1.45)
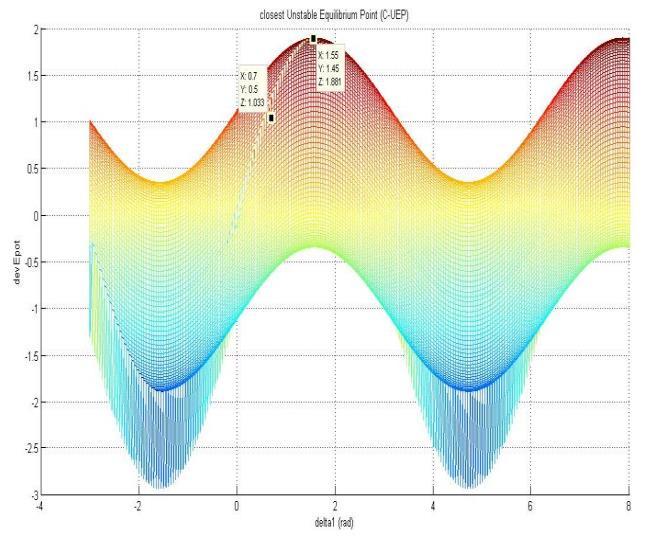
Fig.8.DerivativeofPotentialEnergyVsdelta1
(1.55, 1.6)
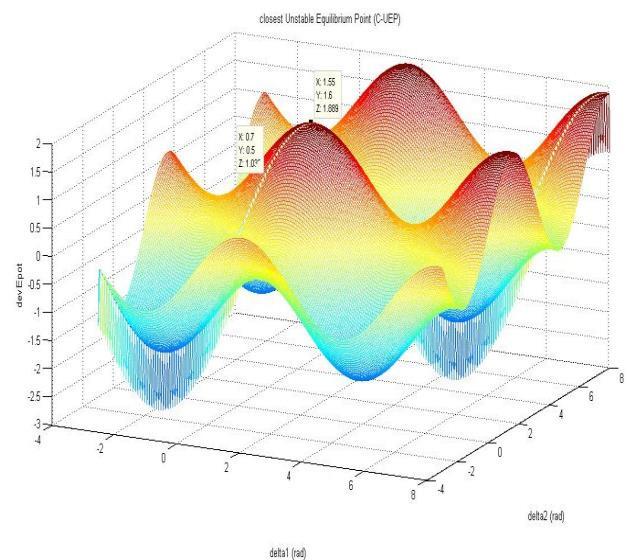
Fig.9.DerivativeofPotentialEnergyVsdelta2

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
CUEP from Post Fault Stable Point
(1.55, 1.45)
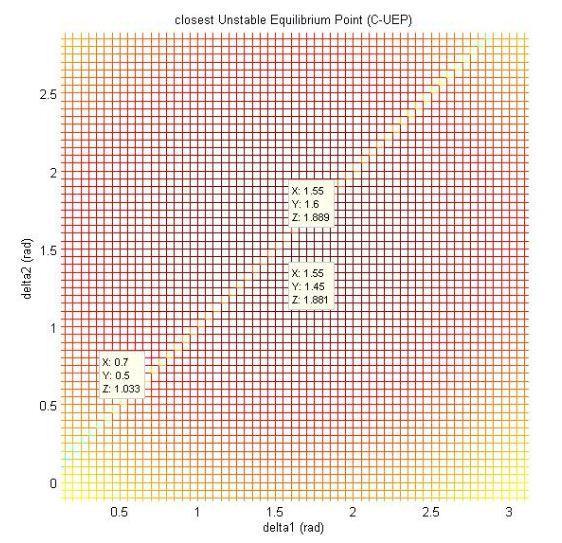
Post Fault stable Point.
(0.7, 0.5)
Fig.10.ClosestUnstableEquilibriumPoint
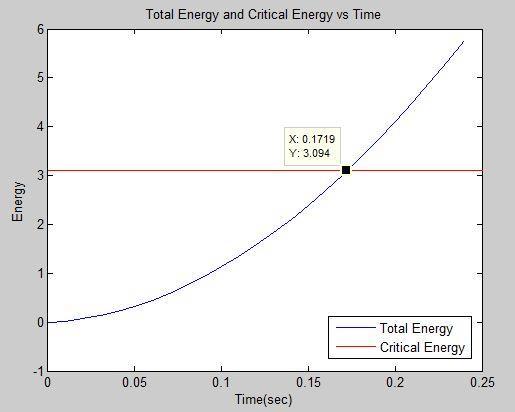
Fig.11.ComparisonbetweenCriticalEnergyandTotal Energy
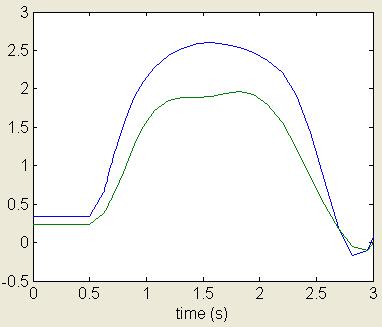
Fig.12.DeltaVsTime(TimeDomainMethod)at0.142 sec
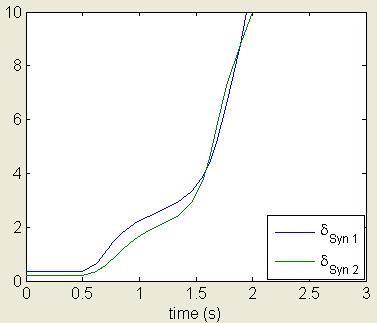
Fig.13.DeltaVsTime(TDM)at0.15sec. (OutofSynchronism-Unstable)
IV Conclusion
Thispaperpresentsthetransientstabilityanalysisfor powersystemwiththehelpofEnergybaseddirectmethod. TotalEnergyduringfaultiscomparedwithCriticalEnergy and the Critical Clearing Time (CCT) obtained using this directmethodwasnearly0.17second.HereCriticalEnergy found by Closest Unstable Equilibrium Point (C-UEP) method.TheseResultsverifiedwiththehelpofTimeDomain method and CCT obtained using this method is 0.142 sec. whichisinacceptablelimits.
References
[1] H.K.Khalil,nonlinearsystems,3 rd edition,Prenticehall, NJ,USA,2002.
[2] J.J.ESlottine,WeipingLi“AppliedNonlinear Control” Englewoodcliffs,NJ,USA,Printicehall,1991.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[3] T.Athay,Rpodmore,Svirmani “Apracticalmethodfor the Direct Analysis of Transient Stability,” IEEE TransactiononPowersystemapparatusandsystems, vol.PAS-98,no-2,pp573-584,March1979.
[4] Michel, A. fouad,V. vittal,” Power System Transient Stability using Individual machine energy functions,” IEEE Transactions on circuits and Systems, volume 30,no5,Pp266-276,May1983.
[5] H.H.AlMarhoon,I.Leevongwat,ParvizRastgoufard“A PracticalMethodforPowersystemsTransientStability andSecurityanalysis,”IEEE-2012.
[6] MarianAnghel,FedericoMilano,Antonis Papachristodolou“AlgorithmicConstructionof