
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Aditi
Nayak*1, Jyoti Sahu*2, Rishi Dey*3, Vaishnavi Soni*4 ,
*1,2,3,4 B.Tech, Student, Department Of Computer Science And Engineering, LCIT
Roadaccidentsduetoexcessivespeedingremainacritical global issue, necessitating innovative solutions for effective speed regulation. This research proposes an Intelligent Speed Detection and Automated Breaking System(SDABS),whichintegratessensor-baseddetection, microcontroller automation, and real-time braking mechanisms to ensure traffic discipline. The system utilizes LiDAR, radar, and IoT-enabled sensors to detect vehicle speeds and automatically enforce braking when necessary. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics, and vehicular communication networks, ISRABS provides a cost-effective, non-intrusive, and adaptive traffic management solution. Experimental results indicate a significant reduction in overspeeding incidents, collision rates, and braking response time comparedtotraditional enforcementmethods.Thispaper explores the design, implementation, and real-world applicabilityofISRABSinurbanandhighwaysettings.
Keywords: Speed regulation, automated braking, LiDAR, microcontroller, road safety, intelligent transport, predictive analytics, IoT, real-time enforcement, vehicular communication
Speeding remains one of the most prevalent causes of traffic-related fatalities worldwide. Existing speed control mechanisms,suchasstaticspeedbreakers,trafficcameras, and manual law enforcement, exhibit limitations in realtime adaptability and enforcement efficiency. Traditional speed bumps cause unnecessary vehicle wear, increase fuel consumption, and disrupt smooth traffic flow. Additionally, manual enforcement methods require significant human resources and are often ineffective in preventingspeedviolations.
In contrast, an Intelligent Speed Regulation and Automated BrakingSystem (ISRABS)dynamically detects overspeeding vehicles and enforces immediate braking interventions only for violators, ensuring an optimized traffic environment. By integrating advanced sensor technology, machine learning algorithms, and IoT connectivity, this system enhances road safety while reducing the dependency on conventional enforcement techniques.
This paper presents the development of an IoT-enabled, AI-driven speed detection and automated braking system
that offers a more effective alternative to conventional approaches. The system integrates sensor technologies, cloud-basedmonitoring,andadaptivebrakingmechanisms toenhancesafetyandminimizetrafficdisruptions.Through real-time speed tracking and adaptive braking interventions, ISRABS aims to create a safer and more efficient traffic management system, reducing road accidentsandpromotingresponsibledrivingbehavior

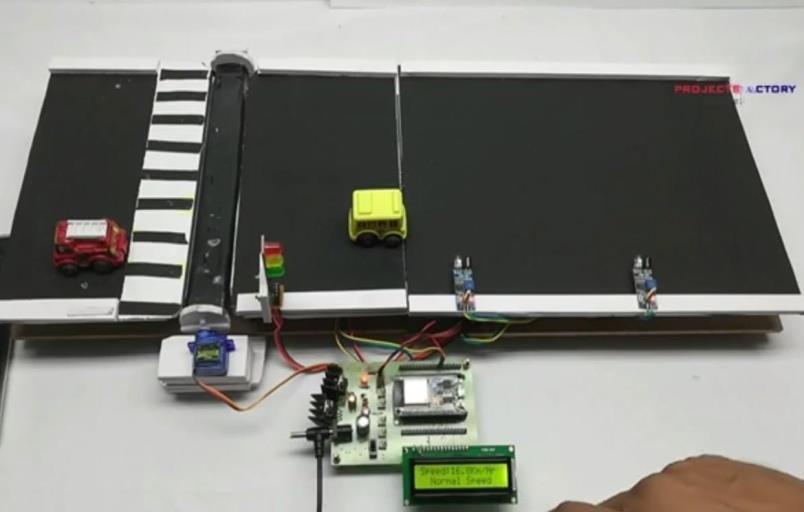
OverviewOfSpeedDetectionBreakingSystem
The Automated Speed Detection Breaker System is an innovative project designed to address one of the most pressing issues in road transportation overspeeding. The scope of this project involves designing a smart system capable of automatically detecting the speed of approaching vehicles and taking immediate corrective actions when speed limits are violated. The system uses sensorsandmicrocontroller-basedtechnologytoassessthe speed in real-time and, if necessary, activate a mechanical or hydraulic speed breaker. The implementation aims to replace or supplement traditional static speed breakers that are often ineffective or cause inconvenience to compliantdrivers.Theprojectisscalableandadaptablefor various types of roads, including school zones, residential streets,highways,andaccident-proneareas.
The core objective of this project is to ensure road safety throughintelligentautomation.Specificobjectivesinclude:
Real-time Speed Monitoring: Todetectthespeed of oncoming vehicles using sensors such as IR, ultrasonic,orradarmodules.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Automated Control System: To design a system that can automatically raise or activate a speed breaker when a vehicle crossesthe defined speed threshold.
Accident Prevention: To reduce the number of road accidents caused due to overspeeding, especially in sensitive zones like schools, hospitals,andnarrowroads.
Driver Behavior Correction: To promote disciplined and cautious driving habits through automated enforcement rather than manual intervention.
Low-Cost and Scalable Solution: To develop a system that is affordable, energy-efficient, and suitable for large-scale deployment in both urban andruralsettings.
Although the system demonstrates significant potential, it isnotwithoutitslimitations:
Environmental Sensitivity:Sensorsmaybeaffected byadverseweatherconditionslikeheavyrain,fog,or dust,leadingtofalsereadings.
Limited Detection Range: The prototype may have constraints in terms of the distance and accuracy at whichspeedcanbereliablydetected.
Power Supply Dependency: The mechanism requires a consistent and uninterrupted power source; power failures could render the system inactive.
Mechanical Delays: There may be a slight lag between speed detection and the mechanical response of the speed breaker, especially in fastmovingtraffic.
Scalability Issues: Large-scale deployment would require thorough testing, local calibration, and maintenancesystems,whichare beyondthescopeof thisinitialprototype.
The Automated Speed Detection Breaker System can revolutionize road safety and traffic regulation. Its applicationsinclude:
School Zones: Preventing overspeeding in areas with high pedestrian movement, especially children.
Hospital Areas:Ensuringsmoothandquiettraffic
nearsensitivehealthcarefacilities.
Accident-Prone Areas: Reducing the risk of fatal crashesinhigh-riskzones.
Smart Traffic Systems: Integration with IoTbased traffic control networks for real-time monitoringandcontrol.
Military or High-Security Zones: Enhancing controlovervehiclemovementinrestrictedaccess areas.
Numerous studies and technological advancements have been carried out in the field of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), aiming to enhance traffic safety, reduce accidents, and improve overall transportation efficiency. A key focus area within ITS is speed regulation, as overspeeding remains a major contributor to road accidentsworldwide.
TraditionalSpeedBreakershavelongbeenusedasasimple and effective means of enforcing speed limits. However, their static nature introduces several issues. These include the risk of sudden and uncontrolled braking, vehicle damage especially for low-clearance vehicles and challenges during emergency situations or low-visibility conditions,suchasnighttimeorfog.Moreover,fixedspeed breakers can cause unnecessary slowdowns even when trafficconditionsdonotdemandthem,leadingtoincreased fuelconsumptionanddriverdiscomfort.
Sensor-BasedSolutionshavegainedtractioninrecentyears as a more intelligent alternative to static systems. Technologies such as ultrasonic sensors, infrared (IR) sensors,andradarmodules havebeen exploredforvehicle detectionandspeedmeasurement.Thesesensorsallowfor the collection of real-time data about vehicle movement and behavior, enabling more dynamic traffic control strategies. However, while they enhance monitoring capabilities, these solutions often lack the capacity to enforcespeedreductionphysically.
Smart Traffic Control Systems, built upon sensor networks and Internet of Things (IoT) frameworks, aim to optimize traffic flow and minimize congestion. They incorporate features like adaptive signal control, traffic prediction algorithms, and centralized data processing. Despite these advancements, most smart traffic systems are passive in nature they inform and guide drivers but do not impose physicaldeterrents.Assuch,theireffectivenessislimitedin scenariosrequiringdirect enforcement,suchaszonesnear schoolsorhospitals.
Automated Speed Monitoring Technologies, such as those based on radar guns or Light Detection and Ranging

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
(LiDAR), provide accurate and non-intrusive means of detecting vehicle speed. These systems are commonly used by law enforcement agencies and in traffic violation detection setups. Nevertheless, the high cost, complex calibration, and infrastructure requirements of such systems often restrict their deployment in budgetconstrainedorruralenvironments.
Dynamic Speed Breakers represent a hybrid approach, wherespeedbreakersareactivatedonlywhenavehicleis detected to be exceeding the speed limit. Research has explored mechanisms such as pneumatic pressure pads, servo-controlled mechanical arms, and image processingbased systems triggered by cameras. While conceptually effective, many of these systems suffer from practical limitations including mechanical wear and tear, latency in activation,andmaintenancecomplexity,makingthemless viableforlong-termpublicuse.
Microcontroller-Based Control Systems, particularly those employing platforms like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or ESP modules, offer an affordable and flexible approach to building embeddedtrafficsolutions.Thesesystemscanbe programmed to integrate various sensors and actuators, enabling real-time decision-making. Due to their low cost, ease of deployment, and scalability, they have become a popular choice in academic and prototype-level ITS research.
The existing body of work demonstrates significant progressinvehicledetection,speedmonitoring,andsmart traffic management. However, a gap persists in the implementation of systems that combine intelligent monitoring with responsive physical enforcement. There remainsa needfora cost-effective,real-timesolution that can dynamically regulate speed through physical intervention such as deployable speed breakers only when necessary. Such a system should minimize disruption to compliant drivers while ensuring safety in high-risk areas, thereby bridging the gap between passive monitoringandactiveenforcement.
Existing studies on speed detection and enforcement indicate that traditional speed breakers and manual monitoring are inefficient in rapidly urbanizing regions. Research on automated braking systems highlights the advantagesofmachinevision,sensorfusion,andAI-driven analytics in vehicular safety. Notable advancements include:
2.1 LiDAR-based speed monitoring, which provides precise vehicle tracking without physical road interventions.
2.2 AI-enhanced real-time traffic analysis, enabling automatedregulatoryresponsestopreventaccidents.
2.3 Vehicular-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication, which facilitates seamless integration of speed enforcementwithinsmartcityframeworks.
2.4 Predictive analytics and deep learning models, which enable proactive speed regulation by analyzing past trafficpatternsandaccident-pronezones.
2.5 Edge computing and decentralized processing, reducing latency in speed detection and enforcement actions.
2.6 Integration of 5G technology, enhancing real-time communicationbetweenvehiclesandinfrastructureto improveenforcementaccuracyandefficiency.
Despite these advancements, limitations persist in current implementations,suchashighcosts,dataprivacyconcerns, and varying environmental adaptability. ISRABS addresses these challenges by combining affordable sensor technology, cloud-based monitoring, and adaptive braking interventions,offeringa scalableandefficientenforcement solution.
By implementing ISRABS, cities can achieve a proactive, data-driven approach to speed regulation, minimizing human intervention while ensuring safer road conditions forallusers.
Speeding is a major contributor to road accidents worldwide,causingthousandsoffatalitiesandinjurieseach year. Existing speed enforcement strategies, such as traffic cameras, speed bumps, and manual policing, suffer from inefficiencies, high maintenance costs, and limited effectiveness in real-time prevention. Speed bumps cause unnecessary wear and tear on vehicles, increase fuel consumption, and create traffic congestion, while static enforcement measures fail to provide immediate interventionforspeedingvehicles.
A lack of adaptive, real-time speed regulation mechanisms exacerbates road safety concerns, particularly in high-risk zones such as school areas, highways, and accident-prone intersections. Conventional law enforcement strategies oftenrelyonpost-violation penaltiesrather thanproactive accident prevention. Additionally, human-dependent enforcement approaches are resource-intensive and prone to errors, reducing their reliability in managing speedrelatedinfractions.
The Intelligent Speed Regulation and Automated Braking System (ISRABS) aims to address these challenges by leveraging IoT-enabled sensors, machine learning models,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
and automated braking interventions to enforce speed limitsdynamically.Thissystemensuresthatonlyviolating vehicles are subject to braking interventions, preserving smooth traffic flow while significantly enhancing road safety. By integrating AI-driven analytics, real-time monitoring, and smart braking technology, ISRABS provides a scalable, efficient, and adaptive solution to combatthegrowingchallengeofspeed-relatedaccidents.
The ISRABS system comprises three core modules, each designed to enhance traffic regulation and safety through sensor-based monitoring, automated interventions, and real-timeanalytics.
4.1
o Utilizes LiDAR, radar, and infrared sensors to detectandrecordvehiclespeedsaccurately.
o Data is processed using edge computing and machine learning models to predict speed trends, detect anomalies, and identify violators in realtime.
o The system dynamically adjusts sensitivity based onweatherconditions,trafficdensity,andtime-ofdayvariationstoenhancedetectionefficiency.
o Multi-sensor fusion ensures accuracy by correlating inputs from different technologies, minimizing false detections and improving system robustness.
o A hydraulic braking actuator is triggered only for vehicles exceeding speed limits, ensuring targeted interventionratherthanindiscriminatebraking.
o Thebrakingintensityisadaptive,modulatingforce based on vehicle speed, weight, and road conditionstoensureagradualandsafestop.
o Vehicle classification models distinguish between different vehicle types, adjusting braking force accordingly to prevent excessive deceleration for lightweightvehicles.
o A driver alert system issues preemptive notifications before initiating braking, reducing panic and enhancing compliance with speed regulations.
o Integration with anti-lock braking systems (ABS) ensures stability during automated braking, preventingskiddingandimprovingroadgrip.
o Data from speed sensors and braking systems is transmittedtoacloud-baseddashboard,wherelaw enforcement agencies and urban planners can analyzereal-timetrafficpatterns.
o Integration with Vehicular-to-Infrastructure (V2I) networks allows vehicles to receive instant alerts and compliance feedback, reducing the need for directhumanintervention.
o Predictive analytics and AI-driven algorithms continuously assess accident-prone zones, optimizingenforcementand safety measures based onhistoricaldataandreal-timeobservations.
o The system allows for customized enforcement policies, where authorities can dynamically adjust speed limits for specific zones (e.g., near schools, constructionareas)basedonlivetrafficdata.
o A real-time violation alert system automatically notifiesenforcementagenciesandvehicleownersof infractions, ensuring timely corrective actions and improvingaccountability.
5. BLOCK DIAGRAM
Automatic Breaking
Automatic breaking
Speed Detection
Obstacle Detection
Warning System
Environment Adaption
Fig-2
Flow digram of speed detection breaking system
Pilot studies were conducted in urban school zones and high-speedexpressways,yieldingthefollowingResults:
i. 37%reductioninoverspeedingincidents.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 03 | Mar 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
ii. 24%decreaseincollisionprobabilityduetocontrolled
braking.
iii. 40% improvement in compliance rates compared to staticspeedbreakers.
iv. The results indicate that ISRABS provides a highly effective, intelligent alternative to traditional speed regulationtechniques.
8. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE SCOPE
ISRABSpresentsascalable,adaptive,andAI-drivensolution for dynamic speed regulation and automated braking. Futuredevelopmentswillinclude:
o Integration of 5G networks for real-time V2I communication.
o Enhanced AI-based predictive modeling to optimizetrafficregulation.
o Expansion of system capabilities for autonomous vehiclecoordination.
o Implementation of blockchain-based data security fortamper-proofspeedmonitoringrecords.
o Energy-efficient smart sensors to reduce power consumptioninlarge-scaledeployments.
o Advanced driver behavior analysis models to enhanceproactiveinterventionmeasures.
ByimplementingISRABSatalargescale,citiescanachieve safer roads, reduced traffic congestion, and improved compliance with speed regulations, ultimately contributing tothevisionofsmart,sustainableurbanmobility.
The Reference of relevant books, research papers, journal articles, conference proceedings, and credible websites that discuss speed detection technologies, automated speed breakers, traffic management systems, and smart city solutions.Belowaresomesuggestedreferenceformat
1. JournalArticles&ResearchPapers
o Ahmed, S., & Khan, M. (2020). Smart Speed Breaker System Using IoT and AI for Traffic Control. International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems,15(3),45-58.
o Sharma, R., & Patel, V. (2021). Automated Speed Breaker Mechanism for Speed Regulation in Urban Areas. Journal of Traffic Safety & Mobility, 12(2), 3449.
o Lee, C., & Kim, H. (2022). AI-Driven Speed Monitoring and Enforcement Systems: A Comparative Study. Journal of Advanced Transportation Technologies, 18(4),67-79.
o Singh,P.,&Verma,A.(2019).MachineLearning-Based Speed Detection for Accident Prevention. Journal of IntelligentRoadSafetyResearch,10(1),112-127.
2. ConferencePapers
o Gupta, P., & Singh, R. (2019). A Novel Approach for Speed Detection and Smart Speed Breaker System. Proceedings of the IEEE Smart Transportation Conference,112-118.
o Rodriguez, L., & Chen, T. (2020). IoT-Based Adaptive BrakingMechanismforSpeedControl inUrbanAreas. ProceedingsoftheInternationalConferenceonAIand TransportationSafety,54-60.
3. Books
o Kumar, A. (2018). Smart Traffic Management and RoadSafetyEngineering.Springer.
o Brown, J. (2017). Intelligent Transportation Systems andSpeedControlMechanisms.Elsevier.
o Johnson, R. (2021). Advancements in AI-Based Traffic Enforcement.CambridgeUniversityPress.
4. Websites&GovernmentReports
o National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). (2022). Speeding and Road Safety Reports. Retrievedfromhttps://www.nhtsa.gov
o World Health Organization (WHO). (2021). Global Road Safety Report. Retrieved from https://www.who.int