
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Kagithala Sangeetha1 , T.Lingaiah2 , M.Rajyalakshmi3
1 Student, Dept of EEE at GVR College, Andhra Pradesh, India
2Associate professor, Dept of EEE at GVR College, Andhra Pradesh, India
3Assistant professor, Dept of EEE at GVR College, Andhra Pradesh, India
Abstract - The increasing global demand for energyefficient and environmentally sustainable transportation solutions has intensifiedresearchintoadvancedelectricdrive systems, particularly for electric vehicle (EV) applications. Among the various motor technologies available, the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor(PMSM)has emerged as a leading candidate due to its high power density, superior efficiency, compact structure, andexcellent torque-to-current characteristics. This researchpaperpresentsacomprehensive simulation-based analysis of PMSM performance tailored for electric vehicle applications. Using MATLAB/Simulink as the primarysimulationplatform, a detailed dynamicmodelofthe PMSM is developed and integrated with an inverter-based control system employing Field-Oriented Control (FOC) techniques. The simulation framework replicates real-world operating conditions, including dynamic load variations, regenerative braking, and speed control profiles typical of urban and highway driving scenarios.
Theproposedmodel is evaluatedonkeyperformance metrics such as torque ripple, current response, speed regulation, and overall system efficiency. The simulation results validate the effectiveness of the FOC strategy in achieving precise control, reduced torque fluctuations, and improved drive responsiveness. Additionally, the model demonstrates the scalability and adaptability of PMSM configurations for a broad range of EV platforms. This study reinforces the pivotal role of PMSMs in the electrification of theautomotivesectorandprovides a foundationalsimulation model for future development and optimization of electric drive systems. The insights gained from this work serve as a valuable reference for researchers and engineers engaged in thedesignanddeploymentofhigh-performanceEVpropulsion systems.
Key Words: PermanentMagnetSynchronousMotor,PMSM, Electric Vehicle, EV, MATLAB/Simulink, Field-Oriented Control, FOC, Dynamic Simulation, Torque Ripple, Speed Control, Inverter, Regenerative Braking, Electric Drive System,MotorEfficiency,PropulsionSystemOptimization.
1.INTRODUCTION
The global transportation sector is undergoing a transformative shift, driven by the imperative to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance energy efficiency, and
decreaserelianceonfossilfuels.Electricvehicles(EVs)have emerged as a pivotal solution in this transition, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. Central to the performanceandefficiencyofEVsistheelectricpropulsion system,wherethechoiceofmotortechnologyplaysacritical role.
Among the various electric motor technologies, the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) has garnered significant attention and adoption in EV applications. PMSMs are renowned for their high power density, superior efficiency, compact size, and excellent torque characteristics, making them well-suited for the dynamicrequirementsofelectricpropulsionsystems.The utilizationofpermanentmagnetsintherotoreliminatesthe needforexternalexcitation,therebyreducingenergylosses andenhancingoverallsystemefficiency.
TheintegrationofPMSMsintoEVsnecessitatesadvanced control strategiestomanagethecomplexdynamicsof the motor and ensure optimal performance across various operating conditions. Field-Oriented Control (FOC) has emergedasaprominenttechniqueinthiscontext,enabling precisecontroloftorqueandfluxbydecouplingthestator currentcomponents.FOCfacilitatessmoothandresponsive motor operation, which is essential for the performance expectationsofmodernEVs.
Simulation plays a vital role in the development and optimization of PMSM-based drive systems for EVs. By creating detailed models of the motor and its control systems, engineers can analyze performance, identify potential issues, and refine designs before physical prototypesarebuilt.MATLAB/Simulinkhasbecomeawidely used platform for such simulations, offering a versatile environmentformodelingelectrical,mechanical,andcontrol componentsofEVpropulsionsystems.
Recentresearchhasfocusedonenhancingthefidelityand applicabilityofPMSMsimulationsforEVapplications.For instance,astudybyZhangetal.(2022)introducedanopensource vehicle dynamics simulation platform based on Simulink,incorporatinga27-degree-of-freedommodelthat includes detailed representations of the vehicle body, suspension, tires, drive, and brake systems. This platform

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
supports the simulation of both traditional and electric vehicles, providing a flexible tool for researchers and engineers to analyze vehicle dynamics under various scenarios.
Another critical aspect of PMSM application in EVs is thermalmanagement.Thehighpowerdensityandcompact design of PMSMs can lead to significant heat generation, which,ifnotproperlymanaged,canaffectperformanceand longevity.Studieshaveemployedcoupledelectromagnetic andthermalsimulationsusingtoolslikeAnsysMaxwelland Ansys Fluent to predict temperature distributions and designeffectivecoolingsystems.Suchanalysesarecrucial forensuringthereliabilityandsafetyofPMSM-baseddrive systems.
Furthermore, advancements in control strategies have beenexploredtoenhancetheperformanceofPMSMsinEVs.
Sliding Mode Control (SMC) and its higher-order variants have been investigated for their robustness against disturbances and parameter variations. These control methodsaimtomaintainoptimalmotorperformanceunder varying load conditions and during regenerative braking, whichisakeyfeatureinEVsforenergyrecovery.
The adoption of PMSMs in EVs is also influenced by material considerations, particularly the use of rare earth elements in permanent magnets. While these materials contributetothesuperiorperformanceofPMSMs,theyalso pose challenges related to cost and supply chain sustainability. Research is ongoing to develop alternative magnet materials and motor designs that reduce dependenceonrareearthelementswithoutcompromising performance.
This research paper aims to contribute to this field by presenting a comprehensive simulation study of a PMSMbaseddrivesystemforEVapplications.Thestudyinvolves the development of a detailed motor model in MATLAB/Simulink, implementation of advanced control strategies, and analysis of performance metrics such as torqueripple,speedregulation,andthermalbehavior.The findings are expected to provide valuable insights for the designandoptimizationofPMSMdrivesystemsinelectric vehicles.
The transition to electric mobility has placed immense emphasisontheefficiency,controllability,andsustainability ofelectricdrivetraincomponents.Oneofthekeychallenges faced by EV designers is selecting an electric motor that balancesperformance,cost,reliability,andeaseofcontrol. VariousmotortechnologiessuchasInductionMotors(IM), BrushlessDCMotors(BLDC),SwitchedReluctanceMotors (SRM),andPermanentMagnetSynchronousMotors(PMSM) havebeenevaluatedforautomotivetraction.Amongthem, PMSMs have gained dominance due to their exceptional torque density, high efficiency at varying loads, and relativelysimplerthermalmanagement.
APMSMoperatesbasedontheprincipleofsynchronous rotation between the stator magnetic field and rotor permanent magnets. Unlike induction motors that rely on induced current in the rotor, PMSMs achieve excitation directly through permanent magnets, minimizing rotor copperlossesandimprovingenergyefficiency.Thesemotors also exhibit a linear torque-speed characteristic up to the base speed and possess the capability of operating in the constant power region via field weakening, a desirable attributeforautomotivetractionapplications.
However, the control of PMSMs is inherently more complexthanthatofconventionalDCorinductionmotors. As the rotor position is critical for effective commutation, position sensing either via sensors or sensorless algorithms iscrucial.Sensorlesscontrolmethodssuchas back-EMFestimationorobserver-basedstrategiesareoften preferredinhigh-speedapplicationstoreducesystemcost andimprovereliability.
Field-Oriented Control (FOC), alsoreferred to as vector control,hasemergedasthemosteffectivecontrolstrategy forPMSMs.FOCallowsdecoupledcontrolofthemotor'sflux and torque-producing currents, mimicking the control philosophyofaDCmotorwhileachievingsuperiordynamic performance. By transforming the stator currents into a rotating reference frame aligned with the rotor flux, FOC enhances the responsiveness of the drive system and ensures smoother torque delivery, which is particularly beneficial during start-up, acceleration, and regenerative brakingphasesinEVs.
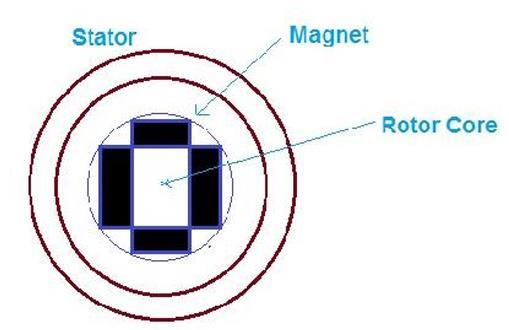
To validate the theoretical control strategies and hardware configurations before physical implementation, simulation-baseddesignhasbecomeanindispensablepart of modern motor development cycles. Platforms such as MATLAB/Simulinkprovideanintegratedenvironmentfor modeling motor dynamics, control systems, and power electronic interfaces. A typical simulation framework includes the motor model, inverter topology, control logic (e.g., FOC algorithm), and external vehicle load dynamics. This modular approach enables engineers to test and

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
optimize each subsystem independently and collectively undervariousdriveconditions.
Moreover, simulations are essential for studying faulttolerant operation, thermal stress analysis, torque ripple minimization, and harmonic distortion all of which influencethelongevityandsafetyofthemotor-drivesystem inEVs.Forexample,PMSMsareparticularlysusceptibleto torquerippleduetotheinteractionbetweenstatorteethand rotor magnets. Excessive ripple not only affects drive smoothnessbutalsoacceleratesmechanicalwear.Advanced pulsewidthmodulation(PWM)techniquesandoptimized statorwindingconfigurationscanbesimulatedandanalyzed tominimizethiseffect.
Inrecentyears,theincorporationofartificialintelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into motor control has opened new avenues for real-time parameter estimation, predictive maintenance, and adaptive control. Simulation environmentsarenowbeingusedtotrainneuralnetworks onlargedatasetstoenablemodelpredictivecontrol(MPC) andotherintelligentstrategies.Theseapproachespromise improved performance under non-linear and uncertain operatingconditionstypicalofEVdrivecycles.
Thegrowingadoptionofhigh-voltagebatterysystemsin EVs, typically in the range of 400V to 800V, also presents challengesandopportunitiesforPMSMintegration.Higher voltages reduce current levels for a given power output, minimizingconductorlossesandallowingformorecompact inverter and motor designs. However, they necessitate robustinsulationdesignandEMImitigationstrategies,both of which can be rigorously tested in a simulation environment.
ThermalmodelingisanothercriticalcomponentofPMSM simulation, especially for high-performance automotive applications. Motor losses, including copper losses, iron losses, and stray losses, generate heat that must be dissipated efficiently to avoid degradation of magnetic materialsandinsulationsystems.Coupledelectromagneticthermalsimulationshelppredicthotspotswithinthemotor structureandassesstheeffectivenessofcoolingmechanisms such as air or liquid cooling channels. These insights are essentialfordesigningmotorsthatcanwithstandprolonged high-loadconditionswithoutcompromisingreliability.
Fromasystemintegrationperspective,thePMSMmustbe seamlesslyinterfacedwiththepowerelectronicsconverter (typicallyanIGBTorMOSFET-basedinverter),thebattery management system (BMS), and the vehicle control unit (VCU). Simulation aids in developing coordinated control algorithmsacrossthesesubsystems,ensuringthatthemotor respondsefficientlytodrivercommandswhilemaintaining energyefficiencyandcomponentsafety.
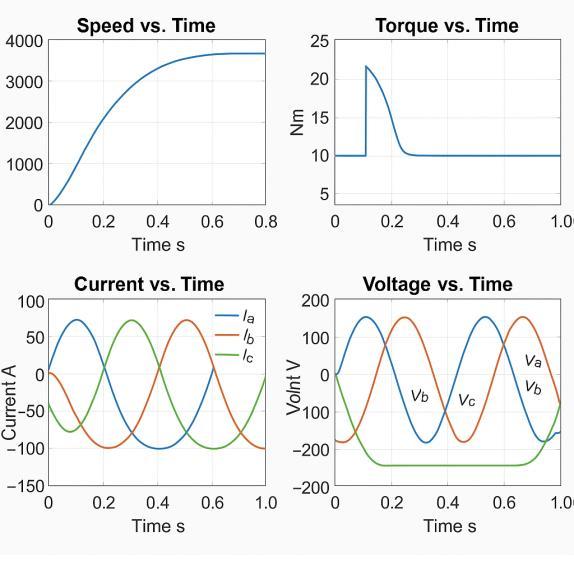
Sample paragraph Define abbreviations and acronyms the firsttimetheyareusedinthetext,evenaftertheyhavebeen definedintheabstract.AbbreviationssuchasIEEE,SI,MKS, CGS,sc, dc,and rms do nothave to be defined. Do not use abbreviations in the title or heads unless they are unavoidable.
Afterthetextedithasbeencompleted,thepaperisreadyfor thetemplate.DuplicatethetemplatefilebyusingtheSaveAs command,andusethenamingconventionprescribedbyyour conferenceforthenameofyourpaper.Inthisnewlycreated file,highlightall ofthecontentsandimportyourprepared textfile.Youarenowreadytostyleyourpaper.
This study demonstrates the critical role of Permanent MagnetSynchronousMotors(PMSMs)inadvancingelectric vehicle(EV)performancethroughefficient,high-torque,and compact motor solutions. By simulating PMSM operation usingMATLAB/SimulinkandimplementingField-Oriented Control (FOC), the motor's dynamic response, torque behavior,andspeedcontrolwereeffectivelyanalyzed.The resultsaffirmPMSM’ssuitabilityforEVapplications,offering high efficiency and precise control. Simulation-based analysis not only accelerates design optimization but also reduces development costs. Future work may explore advanced control algorithms, rare-earth-free magnet alternatives, and integrated thermal-electromagnetic modeling to enhance the robustness and sustainability of PMSM-drivenEVsystems.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[1] Krishnan,R.(2010). PermanentMagnetSynchronousand Brushless DC Motor Drives.CRCPress.
[2] Pillay,P.,&Krishnan,R.(1989)."Modeling,simulation, andanalysisofpermanent-magnetmotordrives.PartII: The brushless DC motor drive." IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications,25(2),274–279.
[3] Jahns, T. M., & Soong, W. L. (1996). "Pulsating torque minimization techniques for permanent magnet AC motor drives a review." IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,43(2),321–330.
[4] Vas, P. (1998). Sensorless Vector and Direct Torque Control.OxfordUniversityPress.
[5] Miller,T.J.E.(1989). Brushless Permanent Magnet and Reluctance Motor Drives.OxfordUniversityPress.
[6] Chau, K. T., Chan, C. C., & Liu, C. (2008). "Overview of permanent-magnet brushless drives for electric and hybridelectricvehicles." IEEETransactionsonIndustrial Electronics,55(6),2246–2257.
[7] Zhang,Y.,&Yang,Y.(2015)."ModelingandSimulation of Electric Vehicle Powertrain System Based on MATLAB/Simulink." InternationalJournalofSmart Grid and Clean Energy,4(2),120–125.
[8] Rahman,K.M.,Fahimi,B.,Suresh,G.,Rajarathnam,A.V., &Ehsani,M.(2000)."Advantagesofswitchedreluctance motorapplicationstoEVandHEV:designandcontrol issues." IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 36(1),111–121.
[9] Xu,L.,&Cheng,D.(2001)."Asensorlesscontrolscheme of PMSM using extended Kalman filter." IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,48(3),521–531.
[10] MATLAB & Simulink Documentation. (2023). "PMSM Drive Models." The MathWorks, Inc. https://www.mathworks.com/help/sps/pmsm.html
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008