
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Prof. H. Sheik Mohideen1, R. Kavinraj2, B. Rajeshkannan3, M. Jerome Joshua4
1Assistant Professor, Government College of Engineering, Srirangam, Tamilnadu, India 2, 3, 4 UG Student, Department of CSE, Government College of Engineering, Srirangam, Tamilnadu, India
Abstract
Sales demand forecasting accuracy represents a key necessity in modern digital commerce operations since it supportsbothoperationalexcellenceandfinancialbudgeting andcustomerserviceexcellence.Theresearchintroducesa deeplearningapproachwhichmergesConvolutionalNeural Network (CNN) with Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks and the Transformer model to advance the predictiveaccuracy.TheframeworkappliesCNNlayersto extractlocaltemporaldatapatternsafterwhichLSTMlayers model sequential relationships before the Transformer modeltracksextendedtemporaldependenciesbetweentime periods.Thisstudymakespredictionsthroughvariousretail sourceswheredifferentperiodicfluctuationsexistalongside promotionaleffects.Thehybridmodelresultsinimproved forecastaccuracybeyondstandalonemodelpartsbecauseit developsaneffectivestructureforexactdemandpredictions.
Keywords
Sales Forecasting, Demand Prediction, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Transformer Model, Hybrid Models, Retail Analytics, Data driven Forecasting, Forecasting Accuracy, Neural Network Architectures
I. Introduction
Salespredictionstandsasanessentialbusinesselementthat enables organizations to build demand forecasts and improvestockmanagementandproductiontimescalesand forecast monetary outcomes. Companies using exact forecasts mitigate the major issues created by inadequate stock levels or excessive inventory which results in sales declinesandelevatedstorageexpenses.Thecombinationof electronic commerce and online buying enables modern salesdatacollectionatfastspeedsforforecastingmodelsyet presentsnewcomplexitiestoforecastresults.
ARIMA and exponential smoothing forecasting methods needtheassumptionoflinearandstationarydatapatterns despite those patterns rarely existing in practical applications. The sales patterns are significantly nonstationarywithinherentnonlinearitiesbecauseexternal influenceslikepromotionalcampaigns,changingcustomer preferencesandcompetitivedynamicsandseasonaltrends impactthemarket.
The approach of machine learning and deep learning methodsgainedpopularitytoaddresstheissue.Operating
among them are CNNs that specialize in recognizing local dependencies and LSTM networks excel at understanding long-term dependencies along with Transformers which efficientlycaptureglobalrelationshipsusingself-attention methods.Thesystembringsdifferentmodelstogetherasone architecture to utilize their capabilities for developing precisecontext-awarepredictions.
The key contributions of this work include:
The research proposes a combined neural network structureusingCNNandLSTMandTransformerlayers which operates as a whole system for sales demand prediction.
Through ablation studies the research explains how individualcomponentsenhanceforecastingability.
The model evaluation process includes assessments under different data environments to demonstrate its universalapplicationandflexiblecharacteristics.
Researchers within the forecasting field have deeply analyzedclassicalaswellasmodernanalyticalapproaches. Thispartexaminescrucialresearchalongsidetheiracademic importance.
Theretailindustrydependsonthreefoundationalstatistical modelswhichincludeARIMAandHolt-WintersExponential Smoothing in addition to linear regression. The computationalspeedofWOEand/reciprocaltablesallows interpretation but their linear restrictions along with external variable integration limitations make them ineffectiveincomplexretailsettings. [1]
Long sequences challenge RNNs because they experience both gradient explosion and gradient vanishing problems during their specific sequence modeling operations. HTC Hoch Reiter and Schmidhuber (1997) developed LSTM which resolves the issues faced by RNN through gated memory units [4]. RNNs find their practical use in energy demand forecasting together with weather forecast modelingalongsidefinancialmarketsimulations.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ResearchhasprovenCNNstobepowerfultoolsforsequence problem-solvingthroughtheirabilitytodetectshort-term patterns.TheresearchbyBorovykhetal [2].(2017)showed thattemporalCNNseffectivelyobtainhierarchicalfeatures fromfinancialtimeseries.WeightsharingfeaturesinCNNs makes them efficient while they also minimize overfitting behavior. [9]
[7], [8], [5]
The model Transformers was developed by Vaswani et al [7].(2017)whichadoptedattentionmechanismsratherthan recurrence. Transformers have completely revolutionized sequence modeling operations. Time series forecasting obtainednewcapabilitiesthroughtheuseofInformerand Autoformer which expanded Transformer for achieving improvedlong-termpredictions[8].Modelsdesignedwith these attributes perform well when applied to parallel processingsystemsandmaintainefficiencyduringextended sequenceoperations. [7], [8], [5]
E. Hybrid
[6], [10]
Themethodologyofthisresearchinvolvesastructuredand systematic approach to building a hybrid deep learning architecture for accurate sales demand forecasting. The methodologyisdividedintofivecorephases:datacollection, preprocessing, model architecture design, training and validation,andperformanceevaluation.
Theresearchadoptsasystematicapproachthroughwhicha hybriddeeplearningstructurewillbeconstructedtoachieve accurate sales demand forecasting. A creative process consistsoffiveprimarysteps:dataprocurement,datacleanup, model creation design and model training, validation testingandmodelperformancemeasurementassessment.
To achieve accurate forecasting one must first obtain reliable information that is suitable for the task. The authoracquiredinformationfromvariousdatasources torepresentmultiplesalescontextsinthestudy.
Historical Sales Data: Toachieveaccurateforecasting onemustfirstobtainreliableinformationthatissuitable for the task. The author acquired information from various data sources to represent multiple sales contextsinthestudy.
Promotional and Marketing Events: Customers can obtain information on discount rates alongside campaignannouncementsandspecialsalespromotions.
Temporal Features: The dataset contains multiple time-relatedvariablesfeaturingdate,dayoftheweek, month, quarter as well as weekend and holiday indicators.
External Influencers: The demand for tortellini is directly affected by weather conditions (including temperature and rainfall) and by regional events and macroeconomic indicators that track employment statisticsandinflationrates.
Calendar Data: The weather patterns involving both temperatureandrainfallalongwithregionaleventsand macroeconomicfactorsincludingemploymentrateand inflationneedexamination.
The datasets were pulled from multiple sources including OpenWeatherMap API calls and Python scripts that performedSQLdatabasequeriesanddatascrapingthrough requestingdataandpandasaswellassqlalchemylibraries.
1. Deep learning models demand meticulous data preprocessing since they are sensitive to input qualitythereforeresearchersconductedextensive preprocessing to make the data ready for use in modeltraining.
2.Data Cleaning:
Interpolation methods and forward fill help addressmissingvalueswithinthedata.
ThestatisticalproceduresZ-scoreandIQRcan beutilizedtoremoveoutliersfromthedataset.
The system detects incorrect entries through regexrulestogetherwithvalidationprotocolsto makenecessarycorrections.
Feature Engineering:
Themodeldesignutilizeslag-basedfeaturesto identifyrecentmarketpatterns.
Coding day of week features into calendar cyclescanbeachievedthroughtheuseofsine andcosinemathematicalfunctions.
Flagging special days (holidays, events) with binaryindicators.
1. Calculatingrollingaveragesanddifferences(e.g.,7daymovingaverage)tosmoothenvolatiledata.
2. Normalization and Scaling:
The Min-Max and Z-score normalization techniqueswereusedonsalesvaluesdepending ontheirdistributionpatterns.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
ThecategoricalfeaturesincludingstoreIDsand product types received encoding through embeddinglayerswithone-hotrepresentation.
3.Sequence Framing:
The data received fixed-length input-output sequenceprocessingthroughslidingwindows.
A 30-day period input serves to forecast daily salesforthefollowingsevendays.
C. Hybrid Model Architecture
Thehybridmodelarchitecturecombinesthebestelements fromCNNsalongwithLSTMsandTransformers.Thesystem merges all attention patterns from local trends and longterm dependencies together with global features into one processingstream. [7], [8], [5] [9]
1. CNN Module: [9]
Applies 1D convolutions to the time-series input.
Extractsshort-termpatternsandlocalfeatures.
Bydecreasing noise the model simultaneously improvessignalquality.
LSTM Module:
This part of the model functions by processing CNN results to analyze both nearby and distal time dependencies. [9]
The model retains sequence information because it learnsrecurringtrendsandseasonalities.
Information flow in this model functions through the gateswhichincludeforget,inputandoutputelements.
2.Transformer Module: [7], [8], [5]
The module applies self-attention mechanics with multipleheadsthatfocusonspecifictimeunits.
The model understands how earlier points within the timescaleaffectpresentdemandlevels.
Incorporates positional encoding to retain temporal ordering.
D. Output Layer:
DenselayerswithReLUandsigmoidactivations.
Thelastlayergeneratespredictedsalesvaluesthat correspondtotheforecastperiod.
Hybridarchitecturetrainingdemandedprecisemanagement beforereachingoptimumperformancewhileminimzingthe riskofoverfitting.
The Mean Squared Error (MSE) proved to be the optimallossfunctionforreasonsofhighsensitivity tosubstantialerrorsduringtraining.
Optimizer: Adam optimizer with adaptive learning ratescheduling.
The model includes dropout layers containing 2030%forregularizingoverfittingandL2weightdecay asanotherwaytoreduceoverfitting.
The model operated using batch sizes that varied from 32 to 128 based on the available system memory.
Asidefromepochsthetraininglasted50–100epochs with an early stopping mechanism triggered by validationlossperformance.
The algorithm used grid search combined with Bayesian optimization to determine the best parametersbetweenkernelsizesandlearningrates andattentionheadsandhiddenunits.
For data segregation purposes we applied timeawaresplitmethodologythatsplittheinformation intotraining(70%),–(15%),andtest(15%)parts.
CNN-LSTMModel:Combinesconvolutionallayersto extract spatial patterns followed by LSTM for temporalmodeling. [9]
TransformerModel:Adeeplearningmodelutilizing only Transformer encoders with attention mechanisms. [7], [8], [5]
The following step in my presentation covers System Architecture.ShouldIproceedtothatsectionnow?
The designed system architecture presents a productionready modular pipeline which uses hybrid CNN-LSTMTransformermodeltoautomatesalesforecastingthrougha scalable architecture. The system development targeted threemainoperationalaspectsincludingquickperformance andcustomizabledesignforflexibleintegrationandusein practicalbusinessneeds. [7], [8], [5] [9]
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
System Architecture Diagram
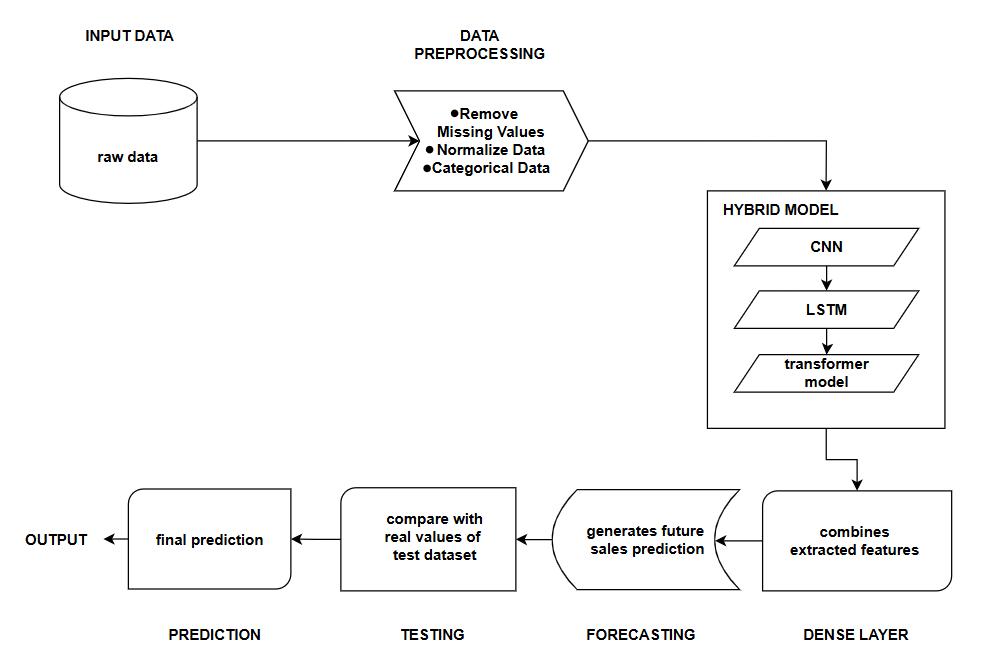
A. Overview
The system architecture functions through five connected layersthathandledifferentstagesoftheforecastingprocess.
1. DataIngestionLayer
2. PreprocessingandFeatureEngineeringLayer
3. ModelProcessingLayer
4. ForecastDeliveryLayer
5. MonitoringandEvaluationLayer
Each component interacts with others through a defined interface,ensuringmodularityandmaintainability.
B. Layer 1: Thefirstlayersecuresrawdatathroughmultiple acquisitionsourcesbeforeitssystemloadforprocessing
Sources:
ThesystemobtainsFlatfiles(CSV,Excel)andotherinternal salessystemdatathroughthislayer.
Tools Used:
ThesystemusesPythonscriptswhichintegratepandas, sqlalchemy and requests packages for operational functionality.
ThesystemusescronjobstogetherwithApacheAirflow schedulingtoperformautomateddataloading.
Features:
Real-timeandbatchdataingestionmodes.
Logginganderrorhandlingmechanisms.
C. Layer 2: Preprocessing and Feature Engineering All data cleans up into an optimal format before it becomes model-ready.
Functions:
The layer focuses on two functions: data cleaning and missingvaluetreatment.
Thedataprocessinginvolvestimeseriesnormalization alongwithdataencodingtogetherwithtransformation steps.
The process includes moving averages as well as lag features and seasonality indicators and trend componentsasextractablefeatures.
Tools:
Python(NumPy,pandas,scikit-learn).
The system uses Redis and PostgreSQL intermediate storageorimplementsin-memoryRediscaching.
D. Layer 3: ModelProcessingLayer
The core system engine operates through the implementation of the hybrid CNN-LSTM-Transformer model. [7], [8], [5] [9]
Model Structure:
CNNBlock:Capturesshort-termfeatures.[9]
LSTMBlock:Learnssequentialdependencies.
Transformer Block: Applies self-attention for global dependencies. [7], [8], [5]
Frameworks Used:
The model building and training process uses TensorFlowincombinationwithKerasasdevelopment frameworks.
GPUaccelerationviaCUDAforfastercomputation.
Functionality:
The model receives historical data input that needs trainingthenvalidationalongwithtestingprocedures.
The program saves model versions as checkpoints throughHDF5orSavedModelformats.
ThesystemusesKerasTunertogetherwithOptunafor automatedhyperparametertuning.
E. Layer 4: ForecastDeliveryLayer
Thedeliverylayertransmitsmodelsoutputthrough RESTAPIsforutilizationbydownstreambusiness applications.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Visualization:
Interactiveanalysisfeaturesaredeveloped through Dash or Streamlit dashboard implementation.
Graphsshowinghistoricalsales,forecasts, predictionintervals,andmodelaccuracy.
Integrations:
ExporttoExcel,emailalerts,orintegration withERPsystems(e.g.,SAP).
F. Layer 5: MonitoringandEvaluationLayer
Thesystemtracksdistributionchangesindatawhichleads toautomaticretrainingneedsassessments.
Model Drift Detection:
The system tracks distribution changes in data which leadstoautomaticretrainingneedsassessments.
Alerts when forecast accuracy deteriorates beyond a threshold.
Performance Monitoring:
Logsmetricslikelatency,accuracy
Real-time analytics using tools like Grafana or Prometheus.
Error Handling:
Built-infallbackmechanismsandnotificationsystemsin caseofmodelordatafailure.
G. Deployment and Scalability
Dockerservesasanimplementationtoolthatallows developers to create containers for installing applications uniformly throughout multiple deploymentplatforms.
The system requires CI/CD Pipelines that use Jenkins or GitHub Actions for automated deployment.
Thesystemrunsasacloud-basedsolutiononcloud platformsthatincludeAWS(EC2,S3,Lambda),GCP andAzure.
H. Security and Data Privacy
The system uses HTTPS encryption for transit operations together with AES-256 encryption for dataprotectionwhendataremainsatrest.
Usertypesreceiveaccesscontrolpermissionsbased ontheirrolesthroughoutthesystem.
Compliance with GDPR and other regional data protectionlaws.
The hybrid forecasting model leverages the strengths of three advanced deep learning algorithms: Convolutional NeuralNetworks(CNN),LongShort-TermMemory(LSTM) networks, and Transformer architectures. The algorithms operateindependentlytoextractuniquecharacteristicsof thetime-seriessalesdatathatincludelocalpatternstogether with long-term dependencies and global attention representation. The next part delivers an extensive description about the algorithms' contributions to the completemodelstructurealongwithdetaileddescriptionsof theirtechnologicalimplementations. [2] [7], [8], [5] [9]
A. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) [2] [9]
1. Role in the Hybrid Model:
Time-seriesforecastingalgorithmsuseCNNstoanalyzethe inputsequencesfordetectingshort-termpatternstogether withlocaldatafeatures.TheCNNlayersachievethisthrough 1D filters by recognizing both established patterns and sudden value shifts while detecting anomalies across the datawhichhelptounderstandshort-termbusinessevents.
2. Key Concepts:
1D Convolution Operation: Appliesfiltersacrosstemporalsequences:
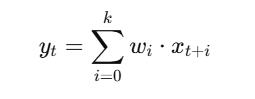
Thefunctionusesthreecomponents-thecurrentsequence elements are represented by xx while ww stands for the filtersandkkrepresentsthesizeofthekernel.
ActivationFunctions: ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) functions as the primaryactivationoperationfortheintroductionof non-linearcharacteristics
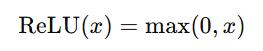
Pooling:
Max pooling or average pooling reduces the dimensionalityandfocusesonprominentfeatures.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
3. Advantages:
High computational efficiency due to shared weights.
Localrepetitivepatternsinsequencesaredetected verywellbythisapproach.
Throughitsmechanismsitfunctionseffectivelyasa signalsmootherandcleanser.
ThesecondcomponentisLongShort-TermMemory Networks(LSTM).
1. Role in the Hybrid Model:
LSTMsareincludedwithinthepipelinestructuretoanalyze both temporary and long-range sequential relationships betweenelements.TheCNN-derivedlocalfeaturespassinto LSTMlayerstotracktheirtemporalevolutionwhichextracts information about seasonality along with periodic trends andtime-basedcorrelations. [9]
2. Core Mechanics:
LSTMsoperatewithamemorycellwhoseoperationdepends onthreegatemechanisms.
Forget Gate:
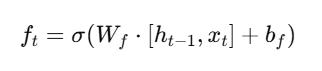
Input Gate:
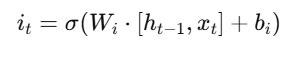
Output Gate:
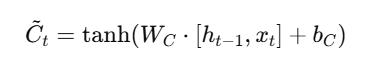
ThecombinationofgatesenablestheLSTMtodetermineits memory course and updates along with output decisions throughoutchronologicalstages.
3. Benefits:
The method successfully counters the usual gradient vanishing problem in convolutional networks.
Suitable for long sequences with temporal dependencies.
Themodelperformsadaptablesequencemodeling onsequencesofdifferentdurationlengths.
1. Role in the Hybrid Model:
The transformer layer operates as the top architecture componenttoexploreextendeddependenciesbetweeninput and contextual elements.The Transformer architecture enables self-attention processing which lets the model determinerelevancebetweentimestepsnomatterwhere theystandinthesequence. [7], [8], [5]
2. Attention Mechanism:
TheTransformerimplementsmulti-headscaleddot-product attentioninitsoperation. [7], [8], [5]
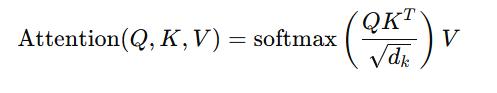
Inputcontainsthreematricesrepresentedthrough QQ,KKalongwithVVwhichderivefromtheinput data.
The key vector scaling dimension dkd_k is used duringthisprocesstonormalizethevalues.
3. Positional Encoding:
Thetransformerarchitecturerequirespositionalencoding because it lacks recurrent connections to monitor the sequenceorder.
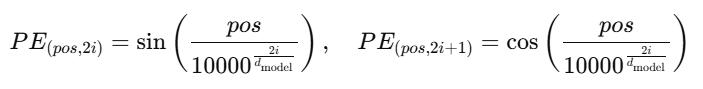
4. Advantages:
Transformersoperateefficientlybecausethey modelworldwiderelationshippatterns. [7], [8], [5]
The parallel processing capability during training outperforms LSTM and occurs at a fasterspeed.
Superiorscalabilitytolongsequences.
D. Combined Advantages in the Hybrid Model
Theintegratedsystemofthesethreealgorithmsproduces thefollowingbenefitsthroughitsimplementation:
CNNforefficientlocalpatterndetection,[9]
LSTMforstrongtemporalmemoryretention,
Transformer for holistic sequence-level understanding. [7], [8], [5]

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Themulti-perspectivemodelstructureprovidesathorough modeling capability that exceeds the modeling ability of singlemodelsbyitself.
Thestudyperformedtestsonthreeseparatedatasets.
Electronicssales
Grocerysales
Fashionretail
Metrics:
MAE:MeanAbsoluteError
RMSE:RootMeanSquaredError
MAPE:MeanAbsolutePercentageError
BaselineComparisons
(ours) 13.1 18.9 8.6%
The hybrid model delivers superior performance than standardbaselinesonallmeasurementparametersforevery datasetevaluated.
Compare With Forecast VS True Sales
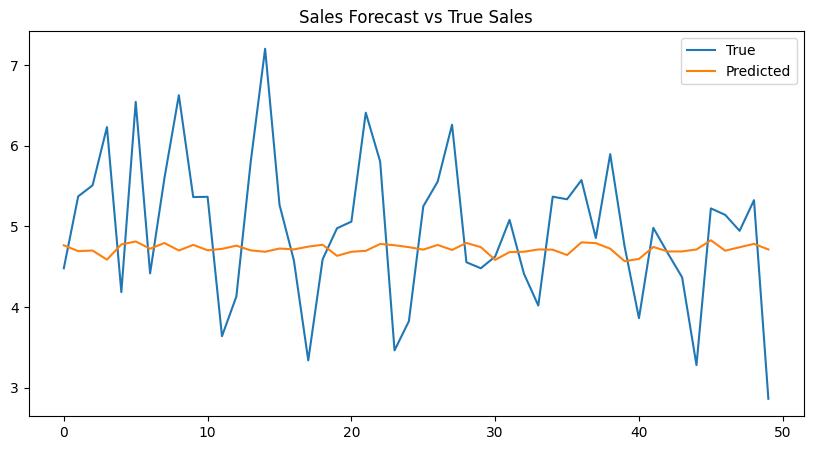
Researchfindingsdemonstratethatallindividualelements withinthehybridmodelleadtoitsenhancedperformance capability. Each part of CNN identifies patterns from structured data while LSTM understands the sequential orderingofinformationandTransformerfollowspatterns throughouttheentiresequence.Noiseinterferenceaswellas missingdataandexternaleventsdonotaffectthecombined
model's performance. The implementation of this model facestwomainproblemswhicharecomputationalexpense and multiple required hyperparameter adjustments. The modeldemonstratesgoodgeneralizationperformancewhile working across different product categories as well as markettypes.Futureworkmayexplore: [7], [8], [5] [9]
Themodelcanbenefitfromanaddedexplainability featurethroughattentionvisualizationmechanisms.
Implementingtransferlearningacrossdomains.
Real-timedeploymentinproductionsystems.
This research provides a strong foundation for demand forecasting using deep learning and opens avenues for further exploration in multi-source data integration and adaptivemodeling.
Bai,Y[1].,Chen,Z.,Xie,J[9].,&Li,C.(2016).Daily reservoir inflow forecasting using multiscale deep feature learning with hybrid models. Journal of Hydrology,532,193–206.
Borovykh,A[2].,Bohte,S.,&Oosterlee,C.W.(2017). Conditional time series forecasting with convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.04691.
Chevalier, G [3]. (2023). LSTM Image. Wikimedia Commons.
Hochreiter, S [4]., & Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long Short-TermMemory.NeuralComputation.
Li,S.,Jin,X[5].,Xuan,Y.,etal.(2019).Enhancingthe Locality and Breaking the Memory Bottleneck of TransformeronTimeSeriesForecasting.NeurIPS. [7],[8],[5]
Liu,B.,etal[6].(2021).AHybridCNN-LSTMModel forTime-SeriesForecasting. IEEETransactionson NeuralNetworks.[9]
Vaswani, A [7]., et al. (2017). Attention is All You Need.NeurIPS.
Wu,H[8].,etal.(2020).Autoformer:Decomposition TransformerswithAuto-CorrelationforLong-Term SeriesForecasting.NeurIPS.[7],[8],[5]
Xie, X [9]., et al. (2020). CNN for time-series forecasting:Areview.JournalofMachineLearning.
Zhou,Y[10].,etal.(2022).SalesDemandForecasting with Hybrid LSTM and Transformer Models. International Journal of Forecasting. [7],[8],[5] Model