
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Shourya Gupta1 , Kirat Kaur Kalsi2
1,2Diploma in Computer Engineering, Thakur Polytechnic, Thakur Complex, Kandivali East - 400101
Abstract - The delivery of medical services has been completely transformed by the incorporation of robotics into healthcare systems, which has improved patient outcomes, efficiency, and precision. Robots may now undertake a wide range of duties, from patient interface and logistics to surgery and diagnostics, thanks to the development of smart technologies. This analysis examines how robots arechanging the healthcare industry and emphasizes how important they are to helping doctors, lowering human error, and enhancing hospital operations. Additionally, it looks at many kinds of healthcare robots, including assistive, surgical, service, and rehabilitation robots, with a focus on their practical uses. The study also addresses the ethical issues, technical difficulties, and potential applications of robotic systems in developing a more intelligent and adaptable healthcare setting
Key Words: Smart Healthcare,Robotics,SurgicalRobots, Service Robots, Healthcare Automation, Artificial Intelligence, Patient Assistance
1.INTRODUCTION

Fig 2: RoboticsinHealthcare
WeareintheFourthIndustrialRevolutioninpresent,inthis revolutionalltheindustrieswillbloomandwillbefilledwith robotsandreducemanpowerintheindustries.Robotsare physically embodied systems capable of sensing and respondingtotheworldthroughphysicalinteraction.They canvaryintheiraestheticappearance,sensingcapabilities anddegreeofautonomy.[1]Roboticsisavastfieldwhichhas many different types. In this research paper we will be explainingabouthowroboticscanhelpinhealthcare.Since theCOVID-19pandemic,themedicalandhealthcareindustry has got many new technologies to assist doctors in unprecedentedcircumstances.[2]Therewasahugegapinthe
doctorsrequiredanddoctorsavailablesotherewererobots whichwereintroducedtofillupthegap.
The Czech word robota, which means serf or laborer, is where the word "robot" originates. Joseph Capek first publishedthesciencefictionnovelRobotin1917.Hewrotea short story known as “Opilec” in this story he described automats.Thissciencefictiongotanewcharacteroranew topic on which writers could express their greatest imaginationwithtechnology.Later,between1938and1942, Isaac Asimov, who is widely recognized for popularizing robots, wrote a collection of short stories. These short storiesgotreallypopularwitheveryone.Thetransitionfrom sciencefrictiontorealityhappened in1958whenGeneral Motorscreated“Unimate”whichhelpedintheautomobile industry.Thiswasfirstusedin1961ontheassemblyline. The original purpose of Unimate, a hydraulic manipulator armwithrepetitivejobcapabilities,wastoremoveandstack hotmetalcomponentsfromacastingprocess.Laterin1985, theProgrammableUniversalMachineforAssembly200 the first robot platform was utilized to do neurosurgical biopsies. The Robodoc Surgical System, an image-guided deviceusedforprosthetichipreplacement,wascreatedin 1992.Afterthistherewereadvancementsinthehealthcare robotics very frequently, this helped to automate the healthcareindustrytoacertainextent.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The Robot Industries Association (RIA) has defined an industrial robot as "a reprogrammable multi-functional manipulator designed to move material, parts, tools or specializeddevices,throughvariableprogrammedmotions fortheperformanceofavarietyoftasks." Themostcommon typesofmanipulatorsmaybemodeledasanopenkinematic chainofrigidbodiescalledlinks,interconnectedbyjoints.[4] Industrial robots are programmable devices used in industrialandmanufacturingsettingstocarryoutactivities thatcallforaccuracy,consistency,andspeed.Theyperform tasksincludingwelding,assembling,materialhandling,and inspection and are usually made with multi-jointed arms. They are crucial for boosting output and guaranteeing product quality because of their capacity to operate diligentlyandprecisely.Modernindustrialrobotscanadapt tocomplexjobswithlittleassistancefromhumansbecause todevelopmentsinAIandsensortechnologies.
ServiceRobotsarenonindustrialrobots,innon-industrial settingsincludinghomes,workplaces,hospitals,andpublic areas,servicerobotsaremadetohelppeoplebycarryingout duties. They are designed for entertainment, support, or convenience and engage with people more directly than industrial robots. Robotic vacuum cleaners, customer support bots, and hospital delivery robots are typical examples. In order to explore settings and communicate successfully, these robots frequently integrate sensors, artificialintelligence,andnaturallanguageprocessing.This improvesaccessibility,comfort,andefficiencyinday-to-day living.
Advanced robotic systems created especially to support medicalprocedures,diagnosis,treatment,andpatientcare are known as medical robots. These robots improve accuracy, lower the possibility of human error, and frequently make minimally invasive operations possible, whichspeedsuprecovery.ThedaVinciSurgicalSystemis oneofthemostwell-knowninstancesofaroboticsurgical system that enables surgeons to carry out intricate procedureswithmoreprecisionandcontrol.Othervarieties includeroboticassistantsthatassistwithhospitallogistics bymovingsuppliesanddrugs,diagnostic robotsthathelp withimagingandtesting,andrehabilitationrobotsthathelp withphysicaltherapyandpatientmobility.Medicalrobots arebecomingessential in enhancingtheeffectivenessand caliberofpatientcareashealthcarecontinuestoincorporate technology
Militaryrobotsarecreatedfordefenseandwar-relateduses, includinglogisticsassistance,bombdisposal,surveillance, reconnaissance,andevencombatoperations.Theserobots lowerhumanriskandimproveoperationalefficiencysince theyaredesignedtoworkinhazardousorhostileconditions. Theyfrequentlyincorporatecutting-edgetechnologieslike remote control systems, GPS navigation, and infrared imaging. Military robots continue to develop as tactical instrumentsincontemporarydefenseandcombatsystems, despiteongoingethicalconcerns.
Humanoid robots are designed to resemble and mimic human appearance and behavior. They can communicate withhumansmorenaturallybecausetheyfrequentlyhavea head, body, arms, and occasionally facial expressions or vocalizations.Theserobotsarefrequentlyemployedinfields wherehuman-likecontactisadvantageous,suchasresearch, education, healthcare, and customer service. Their developmententailsasophisticatedfusionofbiomechanics, robotics,andartificialintelligence,withthegoalofachieving not only functioning but also human social and emotional interaction.

Roboticsinhealthcareandmedicineisnotanewconcept.It has been helping people worldwide way beyond than expectationforover30years.Today,robotscanbefound assistinginanumberofmedicalareas:

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
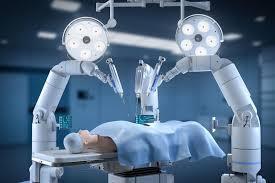
The pioneers of robotics in healthcare is a surgical robot. Whenyoursurgeonperformsanoperationusingarobotic equipment,itisknownasroboticsurgery Theroboticarms usingthecontrollersandaviewingscreenaredesigned to workassurgeonshencethename.Thousandsofpatientsare undergoing less invasive surgery and fewer surgical blunders thanks to the da Vinci Surgical System, a multiarmedwonderbot.Asurgicalrobotisanaiddeviceusedto perform surgical procedures. Often, a human surgeon operatesmechanicalarmsfromacontrolcenterduringthese maneuvers,whicharealsoknownasroboticproceduresor robot-assistedsurgery.

Fig
Enhance productivity and efficiency of work is the key importance of Pharmacy robots. These robots take input from the customer and the head of the robot moves 180 degrees,scanstherequireddrug/medicine.Thentherobotic handspickthemedicine,andfinallyitreachestothecounter through the conveyor belt. In an industry with limited
resources, the pharmacy saves a lot of money by hiring employees that would not otherwise be accessible. McKessonROBOT-Rxisoneexample.Itisaroboticdevice designedtoprocessmedicationsautomatically.Itautomates the selection, return, restocking, storage, and crediting of medications.AstheMcKessonwebsitestates,morethan1/3 ofallhospitalsinNorthAmericausetheirroboticsystem.So itisquitewidespread.[13]

Industrialrobotsaremachinesbuilttocompleteautomated manufacturing tasksin warehouses or factories, such as product assembly, material handling and more.[13] An industrial robot is one that has been created to automate labor-intensivemanufacturingoperations,includingthose needed by an assembly line that moves continuously. Becausetheyarebig,heavyrobots,theyarepositioned in specific areas of an industrial facility, and every other workerdutyandprocedurecentersonthem.

Servicerobotsinhealthcareareincreasinglyusedtosupport hospitalstaffandimprovepatient care.Thishelpstorelieve thestressforhumanstrengthandbyhandlingtheroutine

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
tasks. This robot performed a number of tasks, including making gestures, taking blood pressure and body temperature,administeringmedication,planningmeals,and directingthesurroundings.Datawasgatheredforadditional observation.Inthehealthcareindustry,servicerobotsare beingutilizedmoreandmoretoassisthospitalemployees andenhancepatientcare.Humanstrengthislessstressedas a result of this. Service robots are mostly used to help medicalprofessionalsbyperformingroutinelogisticaltasks and, when finished, producing a report. Prepare patient rooms, keep track of supplies, replenish medical supply cabinets, and carry bed linens to and from laundromats, among other tasks. Data is gathered for additional monitoring from the many services this robot offered, including blood pressure and body temperature checks, medication administration, meal planning, and environmentalguidance.
Exclusive Patient Care: AI and physically aided technologieshavecometogethertocreatesocially helpful robots, or SARs. Because SARs may communicate with patients in a number of ways that elicit emotional responses, they are emotionally intelligent devices that result in superior patient care. The healthcare system's prudentuseofrobotsguaranteessuperiorpatient care, flawless medical procedures, and a safe environment for both patients and medical staff. When autonomous robots are used in healthcare, the likelihood of human error and carelessness is minimal
Organized Operational Tasks: Automatedmobile robots(AMRs)ensurethatmoreaccuratemethods are employed, reduce the physical strain on healthcare professionals, and regularize routine chores.Theserobotscanhandlestaffingshortages, maintain records, and place orders on schedule. Theyguaranteetheavailabilityofmedicationsand other supplies as needed. Automated robots can swiftlycleanandsanitizeroomsandpreparethem for incoming patients, freeing up medical staff to handle other crucial patient-related tasks. With artificial intelligence, robots can effectively diagnoseavarietyofillnesses
Drug Discovery: Thetopicofdrugdiscoveryisone of the main areas where AI application can be beneficial.Conventionalmethodstakeanaverageof 2.6billiondollarsand14yearstobringanewdrug to market, while artificial intelligence (AI) can do the same in less time. Clinical trials of recently developedmedicationsusingAIhavebeenshownto
becompletedinaveryshortamountoftime.AIis also capable of identifying both cardiotoxic and non-cardiotoxic anticancer medications. Additionally,itcanbeusedasamediumtofindnew antibioticsandcanidentifylikelyantibioticsfroma listofthousandsofcompounds.
Protected Working Conditions: In order to protectmedicalpersonnelfrompathogenexposure and thereby stop the spread of infections, automatedmobilerobots,orAMRs,areutilizedina variety of healthcare facilities. These include providingpatientsinhospitalswithfoodandwater, collecting data and information about them, and distributing medical supplies and linen. Thus, duringthecurrentCOVID-19outbreak,theserobots wereheavilyutilized.
Privacy & Data Protection: Mostofthetime,the study of robotics and the application of robots in healthcareleadtosignificantchallengesaroundthe collection of data, its storage, who actually has access to it, who owns it, what happens to it, and othermatters.
High Initial Cost: Ingeneral,implementingrobotic systems in healthcare necessitates a large investmentinequipment,training,andupkeep.For manymedicalfacilities,especiallysmallerones,this expensemightbeamajordeterrent.
Technical Glitches & Dependence: Robotic systems, like any technology, are prone to malfunctions or technical issues that could jeopardizepatientsafetyandconfidence.Theytruly believed that an over-reliance on robots might potentially result in a reduction in the abilities of essentiallyhumanspecialists.
In the healthcare sectorRobots are transforming surgery, speeding up cleaning and supply delivery, and allowing medicalstafftofocusonpatientcareandinteraction,robots have evolved drastically with time and the advancements haveprovenitsimportance.Thesearmedtechnologieswere first deployed in in the 1980s to assist surgery in the healthcareindustry.Now,AIanddataanalyticsiswidening thescopeofrobotstoo.AIisusedtounderstandthescenario moreeffectivelyasearliertherobotscouldonlydothetasks programmed.Personalizationandbetterassistancecanbe achieved through AI. In order to assist medical staff and improve patient care, robots are now utilized in clinical settings as well as operating rooms. Doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals can thus devote more time to

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
directlycaringforpatients.Socialrobotsarebeingusedby anincreasingnumberofhealthcareorganizationstoengage with patients and guests in long-term healthcare settings. These robots can guide patients and visitors in a medical facility,promotecognitiveengagement,boostpatientmood, andencouragepatientstoadheretotreatmentplans.
Robotics in healthcare is no longer just a glimpse into the future it's becoming a powerful part of our present. From helping surgeons perform complex procedures with unmatchedprecisiontosupportingpatientsduringrecovery, robotsareplayingagrowingroleinimprovinghowcareis delivered.Thesetechnologiesarenotjustaboutmachines; they’re about making healthcare safer, faster, and more accessibleforeveryone.Ofcourse,therearestillhurdlesto cross like affordability, proper training, and ethical questions.However,thefutureisbrightaslongasengineers, physicians,andresearcherscontinuetoinnovateandwork together. As robotics develops further, it could lead to a more patient-centered, efficient, and compassionate approachtohealthcareinwhichtechnologyenhancesrather thanreplacesthehumantouch.
[1] Silvera-Tawil,David.(2024).RoboticsinHealthcare:A Survey.SNComputerScience.5.10.1007/s42979-02302551-0.
[2] Morgan AA, Abdi J, Syed MAQ, Kohen GE, Barlow P, Vizcaychipi MP. Robots in Healthcare: a Scoping Review. Curr Robot Rep. 2022;3(4):271-280. doi: 10.1007/s43154-022-00095-4. Epub 2022 Oct 22. PMID:36311256;PMCID:PMC9589563.
[3] Cresswell K, Cunningham-Burley S, Sheikh A, Health Care Robotics: Qualitative Exploration of Key Challengesand FutureDirections, JMedInternet Res 2018;20(7):e10410,DOI:10.2196/10410
[4] Golnazarian,Wanek&Hall,Ernest.(2002).Intelligent IndustrialRobots.10.1201/9780203908587.ch6.5.
[5] HocksteinNG,GourinCG,FaustRA,TerrisDJ.Ahistory of robots: from science fiction to surgical robotics. J Robot Surg. 2007;1(2):113-8. doi: 10.1007/s11701007-0021-2. Epub 2007 Mar 17. PMID: 25484946; PMCID:PMC4247417.
[6] Morrell ALG, Morrell-Junior AC, Morrell AG, Mendes JMF,TustumiF,DE-Oliveira-E-SilvaLG,MorrellA.The history of robotic surgery and its evolution: when illusion becomes reality. Rev Col Bras Cir. 2021 Jan 13;48:e20202798. doi: 10.1590/0100-6991e20202798.PMID:33470371;PMCID:PMC10683436.
[7] Lee I. Service Robots: A Systematic Literature Review.Electronics.2021;10(21):2658.
[8] Saeedvand S, Jafari M, Aghdasi HS, Baltes J. A comprehensive survey on humanoid robot development.TheKnowledgeEngineeringReview. 2019;34:e20.doi:10.1017/S0269888919000158
[9] M.Glavan,M.ČerničIstenič,R.Cvejić,andM.Pintar, ‘Urban Gardening: From Cost Avoidance to Profit Making ExamplefromLjubljana,Slovenia’,Urban Agriculture. InTech, Jun. 15, 2016. doi: 10.5772/62301.
[10] Guang-Zhong Yang et al. Medical robotics Regulatory, ethical, and legal considerations for increasing levels of autonomy.Sci. Robot.2,eaam8638(2017).DOI:10.1126/scirobotics. aam8638
[11] Deo, Niyati, and Ashish Anjankar. “Artificial Intelligence With Robotics in Healthcare: A Narrative Review of Its Viability in India.” Cureus vol. 15,5 e39416. 23 May. 2023, doi:10.7759/cureus.39416
[12] BerndCarstenStahl,MarkCoeckelbergh,Ethicsof healthcarerobotics:Towardsresponsibleresearch andinnovation,RoboticsandAutonomousSystems, Volume86,2016,Pages152-161,ISSN0921-8890,
[13] M. Vij,“Roboticsinhealthcarearchitecture,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol.,vol. 4,no. 7,pp. 693–697,Jul. 2017.
[14] V. Darokar,T. Ghatge,M. Wakchaure,V. Pande,and A. K. Mahindrakar, “The role of robots in smart health care system: A review,” Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol.,vol. 8,no. 8,pp. 3973–3979,Aug. 2021.