
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Mrs. Namratha B S, Rajesh S
Assistant Professor, Dept. of CSE, JIT, Bangalore, Karnataka Undergraduate, Dept. of CSE, JIT, Bangalore, Karnataka
Abstract - This paper introduces an advanced deep learning-basedhealthcareframeworkaimedattransforming diseaseprediction,diagnosis,andtreatment. Byintegrating multi-modaldatasourceincludingmedicalimaging,electronic health records (EHRs), genomics, and real-time data from wearabledevices theframeworkutilizescutting-edgedeep learning models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs),Long Short-TermMemory Networks (LSTMs),and DeepBeliefNetworks(DBNs)toprocessandanalyzecomplex and heterogeneous healthcare data. This system provides accuratediseasepredictions,facilitatesearlydetection,and enables personalized treatment recommendations, improvingpatientoutcomes.Keyfeaturesincludereal-time healthmonitoringforchronicdiseasemanagement,adaptive learningfromnewpatientdata,andmulti-modaldatafusion to ensure holistic care delivery. To address privacy and securityconcerns,theframeworkemploysfederatedlearning and blockchain technologies, enabling secure data sharing andmodelupdateswhilepreservingpatientconfidentiality. Moreover, the system integrates seamlessly with telemedicine platforms to expand healthcare accessibility, especially for remote or underserved areas, and supports clinicaldecision-makinginreal-time.Futureadvancements will focus on enhancing scalability for global health monitoring,expandingprecisionmedicinecapabilities,and employingexplainableAI(XAI)to improveinterpretability for healthcare providers. This framework represents a significant leap forward in healthcare innovation, with the potentialtooptimizetreatmentstrategies,reducecosts,and enhancethequalityandaccessibilityofcareworldwide.
Key Words: Key Words: electronic health records (EHRs), privacy and data security, chronic disease management, adaptive learning, explainable AI (XAI), precision medicine, IoMT (Internet of Medical Things)
The healthcare industry is experiencing a major transformation, thanks to rapid progress in artificial intelligence especiallydeeplearning.Thesetechnologies are changing how we approach patient care by making it possible to analyze large, complex, and varied types of medicaldata.Asaresult,we’reseeingbigimprovementsin diagnosticaccuracy,personalizedtreatmentoptions,andthe abilitytodetectdiseasesearlierthaneverbefore.
Healthcaredataisgeneratedfromdiversesourcessuchas medicalimaging(e.g.,MRI,CTscans),EHRs,genomics,and wearable devices. These varied data streams hold vital health insights but differ in structure, making integration difficult. Traditional systems have struggled with this complexity,whereasdeeplearningoffersarobustsolution. Architectures such as CNNs, LSTMs, and DBNs have demonstratedhighperformanceacrossmodalities:CNNsin imaging diagnostics, LSTMs for temporal EHR data, and DBNsforgenomicsandfeatureextraction.
However,unifyingthesedisparatedatatypesintoacoherent systemremainsachallenge.Thispaperproposesahybrid deeplearningframeworkdesignedtointegratemulti-modal dataforreal-timehealthmonitoring,diseaseprediction,and personalizedcare.ThearchitecturecombinesCNNs,LSTMs, Autoencoders,andDBNstoprocessandanalyzehealthcare datastreamseffectively.
To address key implementation challenges, the system incorporatestheInternetofMedicalThings(IoMT)forrealtime data acquisition, federated learning for privacypreservingdecentralizedtraining,andblockchainforsecure, transparentdatahandling. Thesetechnologiescollectively addressconcernsofdataheterogeneity,security,andsystem scalability.
Beyondanalytics,theframeworksupportscliniciansthrough real-time insights, facilitating early interventions and aligningwithtrendsinprecisionmedicine,telemedicine,and global health surveillance. This paper further explores methodologies for data integration, hybrid model development, and ethical considerations such as privacy, fairness,andtransparency.
In doing so, it presents a forward-looking perspective on how deep learning can reshape healthcare systems to be moreintelligent,responsive,andpatient-centered.
Deep learning has rapidly advanced healthcare innovation over the past decade, influencing diagnostics, treatment planning,andpatientmonitoring.Thissectionoutlinesmajor developments, focusing on data integration, model architectures, privacy-preserving methods, and real-time monitoring.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Medical imaging is a leading area of deep learning application,withCNNsdemonstratingstrongperformancein detectingpatternswithinMRI,CT,andX-rayimages.Esteva et al. (2017) achieved dermatologist-level accuracy in classifying skin cancer, while Rajpurkar et al. (2018) developedaCNNthatsurpassedradiologistsindiagnosing pneumoniafromchestX-rays.
CNNs have also been applied to advanced modalities for detectingAlzheimer'sandbraintumors(Shbiroetal.,2020), aswellasheartdiseasesviaechocardiogramsandcoronary scans(Jiangetal.,2017),significantlyenhancingdiagnostic accuracyandclinicalworkflows.
(EHRs)containlongitudinaldataidealforRecurrentNeural Networks(RNNs),particularly (LSTM)networks.Choietal. (2016) used LSTMs to predict patient readmissions with higher accuracy than traditional models. LSTMs have also beenusedtoforecastdiseaseprogression,suchasdiabetic complications(Zhaoetal.,2018).
Hybrid models that combine structured and unstructured EHR data demographics, lab results, and clinical notes haveproveneffective.Forinstance,Ribeiroetal.(2019)used attention-based LSTMs to model cardiovascular disease progression,demonstratingtheabilitytoextractactionable insightsfromcomplexEHRs.
Genomic data integration has advanced personalized medicine. DBNsandConvolutionalAutoencodershavebeen usedtoidentifydiseasebiomarkersandmutations(Zhouet al., 2019). Cireşan et al. (2013) applied deep learning to predictcancerrisk,whileAlipanahietal.(2015)usedgene expressiondatatodiscovertherapeutictargets.Combining genomic data with imaging and EHRs enables tailored, effectivetreatmentplans.
Wearabledevices,includingsmartwatchesandbiosensors, offercontinuoushealthtracking(heartrate,glucose,activity levels).DeeplearningmodelslikethosebyZhouetal.(2020) havedetectedarrhythmiasusingECGdatafromwearables. Other systems track movement anomalies to identify conditions such as Parkinson’s disease or sleep apnea (Barreto et al., 2018), enabling early intervention and personalizedrecommendations.
2.5 Federated Learning and Privacy Preservation
ProtectingpatientprivacyisamajorchallengeinAI-driven healthcare.FederatedlearningaddressesthisbytrainingAI modelsdirectlyonlocaldevices suchashospitalserversor
smartphones so sensitive data never leaves its source. ResearchbyMcMahanetal.(2017)andHardetal.(2018) supports its effectiveness for medical imaging and health records. To enhance security and trust, blockchain can be usedtocreatetransparent,tamper-prooflogsofdataaccess andusage(Dinhetal.,2018).Together,thesetechnologies helpkeeppatientdataprivate,secure,andethicallyhandled.
Challengesremaininaccessinglarge,high-qualitydatasets duetodata fragmentation.The"black-box" natureofdeep modelslimitscliniciantrust.Futureresearchmustfocuson XAItoimprovetransparencyandinterpretability(Ribeiroet al.,2016).
Integrating diverse data genomics, wearables, and environmentalvariables willbeessentialtobuildingrobust modelsthatcapturethefullspectrumofhumanhealth.
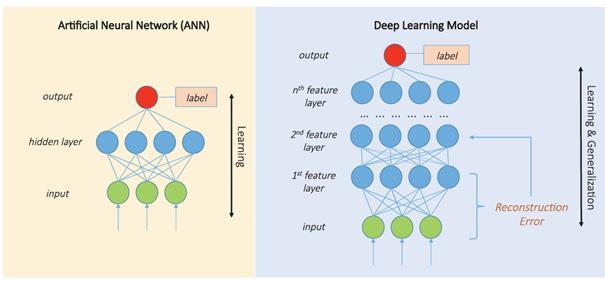
The application of deep learning technologies has transformedhealthcare,enablingsignificantadvancementsin diagnostics,patientcare,andtreatmentpersonalization.Deep learning extends traditional Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)byincorporatingmultiplehiddenlayers,forminga hierarchical structure that allows models to extract, learn, andgeneralizefromdatamoreeffectively.Thismulti-layered approachhasbeenpivotalinaddressingsomeofhealthcare's mostcomplexchallenges,includingmedicalimaginganalysis
EHRprocessing,andgenomicdatainterpretation.
Asdepictedintheaccompanyingimage,thetransitionfrom ANNs to deep learning architectures underscores their growingcapacitytohandlediverseandcomplexmedicaldata sources.WhileANNsaretypicallycomposedofthreelayers andinvolveasingletransformationtowardthefinaloutput, deeplearningarchitecturesutilizemultiplelayersofneural networks. These layers are optimized through layer-wise unsupervised pre-training, enabling the extraction of deep structuresfromrawinputsandcreatinghigher-levelfeatures that significantly improve predictions. This hierarchical learning structure has become foundational in modern healthcareapplications.
CNNsandRecurrentNeuralNetworks(RNNs)haveplayeda pivotalroleinadvancingdeeplearningapplicationswithin healthcare. CNNs, known for their exceptional ability to extract spatial features from medical images, have transformed diagnostic imaging. They have been instrumental in detecting tumors, segmenting lesions, diagnosing diabetic retinopathy, and predicting neurodegenerativediseasesusingMRIscans.Byidentifying intricate patterns in visual data, CNNs enhance diagnostic

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
precision,providingclinicianswithreliabledecision-making supportwhileminimizinghumanerrors.
Ontheotherhand,RNNs,specificallydesignedforsequential dataprocessing,arehighlyeffectiveinanalyzinglongitudinal (EHRs). These models excel in tasks such as predicting disease progression, forecasting patient outcomes, and recommendingtreatments,whereunderstandingtemporal dependenciesiscrucial.Byleveraginghistoricalmedicaldata, RNNs generate accurate predictions of patient health trajectories,enablingthedevelopmentofmorepersonalized, data-drivenhealthcaresolutions.
Theintegrationofdeeplearningwithbigdataanalyticsand the IoMT has led to substantial progress in smart health monitoring systems. IoMT-powered wearable devices continuously capture real-time physiological and activity data, enabling early detection of chronic illnesses and facilitatingpredictivediagnostics.Tofurtherenhancesystem performance, Deep Ensemble Learning (DEL) frameworks combine multiple models, including Convolutional Neural Networks CNNs, LSTMs, and DBNs, thereby improving predictiveaccuracy.
To optimize these monitoring systems, researchers have implementedhybridoptimizationstrategiessuchasHybrid Dingo Coyote Optimization (HDCO). These approaches enhance feature selection and refine model efficiency, makinghealthtrackingsolutionsmorepreciseandreliable. These advancements have revolutionized real-time health monitoring, enabling proactive interventions and significantlyimprovingpatientcareandhealthcaresystem efficiency.
Despite these advancements, challenges persist. The high dimensionality, heterogeneity, and sparsity of biomedical datasets present significant obstacles, as integrating and training models on such complex data is computationally intensive. Furthermore, the "black-box" nature of deep learningmodelscontinuestohindertheirclinicaladoption,as cliniciansrequireinterpretabilityandtransparencytotrust AI-generatedrecommendations.
To address these issues, research efforts are increasingly focused on XAI techniques, which aim to improve model interpretability without sacrificing performance. Additionally, the development of more scalable and computationally efficient architectures will be crucial to overcomingtheconstraintsposedbybigdatainhealthcare.
The accompanying image highlights the evolution of deep learning architectures from traditional ANNs to sophisticated multi-layered systems. These architectures demonstrate how hierarchical learning allows models to extract meaningful insights from raw, unstructured data, ultimately enhancing diagnostic accuracy, treatment personalization,andreal-timehealth monitoring.
Deep learning holds significant potential in fields like personalizedmedicine,predictivediagnostics,andeffective disease management. However, fully harnessing its capabilities will depend on continuous improvements in modelarchitecture,computationalmethodologies,andthe responsibleintegrationofAIwithinhealthcare.
The proposed deep learning-based healthcare system integrates diverse data sources through a hybrid architecturedesignedtoprocessandanalyzecomplex,multimodal healthcare data. This section outlines the key components of the methodology, as illustrated in the accompanyingdiagram.
At the foundation of the system is the integration of heterogeneoushealthcaredata includingmedicalimaging, EHRs,genomicdata,andwearabledeviceoutputs.Eachdata typeundergoesspecificpreprocessingtoensureconsistency andusability:
Medical Imaging: MRI, CT, and X-ray images are normalized and augmented to address variations in resolutionandenhancemodelrobustness.
EHRs: Sequential data is processed using feature extraction, missing value handling, and temporal alignment to preserve relationships between patient events.
Genomic Data:Gene expressionand sequencingdata are standardized and normalized to reduce dimensionalityandmaintainanalyticalconsistency.
Wearable Devices:Physiologicalmetricssuchasheart rateandbloodpressurearefilteredtoremovenoiseand ensurecleaninputsforreal-timeanalysis.
This preprocessing ensures that all data sources are harmonizedforeffectiveintegrationandanalysiswithinthe system.
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Tomanagediversedatatypes,thesystememploysahybrid deep learning architecture composed of the following elements:
CNNs: Convolutional Neural Networks are used to analyzemedicalimages,extractingspatialfeaturesfor tasks like tumor detection and cardiovascular diagnostics.
LSTMs:LongShort-TermMemorynetworks,aformof RNN, handle sequential data in EHRs, enabling predictions of disease progression and treatment outcomes.
Autoencoders: These are used for feature extraction and dimensionality reduction, especially for genomic and imaging data, helping improve model generalization.
Deep Ensemble Learning (DEL): An ensemble of CNNs,LSTMs,andDBNsisusedtoenhancepredictive accuracy and robustness across tasks such as classification,regression,andanomalydetection.
Thishybridframeworkeffectivelyaddressesdatacomplexity and heterogeneity, supporting accurate, reliable, and personalizedhealthcareanalytics.
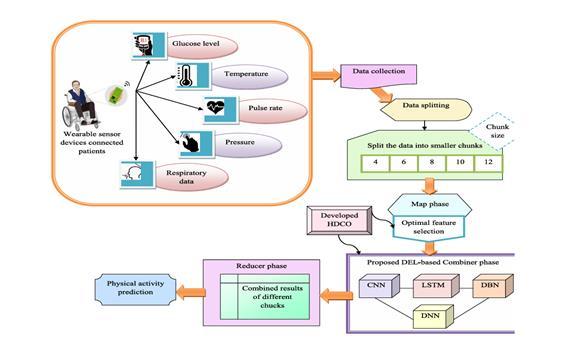
Fig2-Thesystemarchitectureofdevelopedbig data-based healthmonitoringsystem
4.3
An essential capability of the system is its integration of diversehealthcaredata suchasmedical images,genomic sequences, EHRs, and wearable sensor outputs into a unifiedmodel.Thisfusionenablesaholisticviewofpatient healthby:
Correlating information across modalities to enhance diagnosticinsights.
Improvingpredictionaccuracythroughcomplementary data.
Delivering personalized, context-aware treatment recommendations.
Toovercomethelimitationsofsmallorimbalancedmedical datasets,thesystemincorporatestransferlearning.Models pre-trainedonlargedatasets(e.g.,ImageNet)arefine-tuned on domain-specific healthcare data. This approach acceleratestraining,reducesdatadependency,andenhances performanceinspecializedapplications.
The framework supportscontinuous health trackingusing data from IoMT devices such as ECG monitors and smartwatches.Real-timeanalysisenablesthesystemto:
Identify abnormal patterns and forecast critical events likecardiacorrespiratorydistress.
Deliver personalized alerts and lifestyle recommendations.
Offer timely,actionable feedback tobothcliniciansand patients.
4.6
Giventhesensitivityofhealthcaredata,thesystememploys privacy-preservingstrategies:
FederatedLearningensuresdataremainsonlocaldevices whilesharingonlymodelupdates,aligningwithHIPAA andGDPRrequirements.
Blockchain technology maintains secure, tamper-proof logsofdiagnoses,treatments,andsysteminteractions, promotingdataintegrityandtransparency.
Toreducelatencyandensureefficientreal-timeprocessing, edgecomputingisimplemented.Processingdatalocallyon wearablesormobiledevicesminimizesdependenceoncloud infrastructure critical for remote or bandwidth-limited environments.
4.8Evaluation
The system’s performance is assessed through both quantitative metrics (accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, MSE)andqualitativeclinicalvalidation.Thisdualevaluation ensures:
Broadapplicabilityacrossvariedpatientpopulations.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Practicalrelevanceinclinicalenvironments.
Alignmentwithethicalandregulatorystandards.
Building upon existing advancements in deep learning technologies, this proposed work intro-duces a transformative and secure healthcare system. It aims to addressthechallengesofmulti-modaldataintegration,realtimemonitoring,privacy,andmodelinterpretability,thereby enhancingthescalability,accuracy,andusabilityofAI-driven healthcare systems. The methodology incorporates innovativeapproachestoimproveclinicaldecision-making, patient outcomes, and healthcare accessibility. Key componentsoftheproposedsystemareoutlinedbelow,with eachelementsupportedbyinsightsfromreferencedstudies.
5.1
Theproposedsystemintegratesanenrichedsetofhealthcare datamodalities,includingmedicalimaging,(EHRs),genomic data,andreal-timedatafromwearabledev-ices.Inaddition, it incorporates psychosocial and environmental data to provideacomprehensiveunderstandingofindividualhealth profiles.
WearableDevices:Leveragingdatafromsmartwatches, fitness trackers, and biosensors, the system captures real-time metrics such as heart rate, activity patterns, sleepquality,andbloodpressure.Thiscontinuousdata collectionenhancespersonalizedhealthmonitoringand earlydetectionofanomalies,aligningwithadvancements in IoMTtechnologies.
Multi-Modal Data Fusion: The integration of diverse data sources within a unified framework improves diagnostic accuracy and actionable insights. By correlatingimagingbiomarkers,genomicvariations,and longitudinal EHR data, the system delivers holistic assessmentsofpatienthealth.
The system employs an adaptive learning framework, enabling models to evolve dynamically as new data is collected.
Reinforcement Learning and Transfer Learning: Reinforcement learning optimizes the system’s predictivecapabilities,whiletransferlearningleverages pre-trainedmodelstoenhanceperformancewithlimited healthcare-specificdata
Real-Time Updates: By continuously learning from patient interactions and new health data, the system ensuresthatpredictionsandrecommendationsremain accurateandrelevantovertime.
The system focuses on real-time health monitoring for chronicdiseasemanagementandearlyintervention.
Predictive Analytics with LSTMs: Recurrent Neural Networks(RNNs),specifically LSTMs,analyzereal-time data from wearable devices and EHRs to predict the onsetofconditionssuchasdiabetes,hypertension,and cardiovasculardiseases.
Proactive Interventions: By detectinganomaliesand predictinghealthrisks,thesystemprovidesearlyalerts and recommendations, significantly improving patient outcomesthroughtimelyaction.
Privacypreservationisacorefocusoftheproposedsystem, achievedthroughfederatedlearninganddecentralizeddata processing.
Decentralized Training:Modelsaretrainedlocallyon personal devices or hospital systems, with only aggregated updates shared across networks. This approachensuresthatsensitivepatientdataneverleaves itsoriginalenvironment,addressingprivacyconcerns
Compliance with Privacy Standards: The system adheres to global regulations, including GDPR and HIPAA,ensuringsecureandethicalhandlingofpatient information.
Toaddressthe"black-box"natureofdeeplearningmodels, theproposedsystemintegrates XAItechniques:
Human-Understandable Insights:Visualizationtools andinterpretablemodelsprovideclearexplanationsfor predictions, enabling clinicians to understand the reasoning behind AI-driven diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
Enhanced Trust: By demonstrating transparency in decision-making, XAI fosters trust among healthcare providers,improvingadoptioninclinicalsettings.
Edge computing enhances the system’s efficiency and responsiveness, particularly in remote or resource-limited environments.
Local Processing: Dataisprocesseddirectlyondevices such as smartphones and wearable health devices, reducingrelianceoncloud-basedservers

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Low-Latency Insights: This approach ensures immediate feedback to patients and healthcare providers,makingitinvaluableforemergencyscenarios andcontinuousmonitoring.
5.7 Hybrid Optimization and Feature Selection Techniques
Theproposedworkemployshybridoptimizationtechniques toimprovemodelperformanceandefficiency.
Hybrid Dingo Coyote Optimization (HDCO): This advancedtechniquerefinesfeatureselection,ensuring thesystemfocusesonthemostrelevantdataattributes. Byreducingdimensionalityandcomputationaloverhead, HDCOenhancesthemodel’saccuracyandscalability.
5.8 Clinical Validation and User Feedback Integration
To ensure real-world applicability, the system undergoes rigorousclinicalvalidationandincorporatesfeedbackfrom users:
Expert Evaluation: Clinical trials assess the system’s effectiveness in improving diagnostic accuracy and patientoutcomes.
User-Centric Design: Feedback from health care professionalsandpatientsinformsiterativerefinements, ensuring the system remains intuitive, reliable, and practicalfordiverseclinicalworkflows.
5.9 Global Health Applications
Thesystemisdesignedtoaddressglobalhealthchallenges, enablingpublichealthmonitoringandprecisionmedicineat scale:
Disease Surveillance: By integrating global health databases, the system predicts and tracks emerging disease trends, contributing to early containment and resourceallocation.
Cultural Adaptability: Supportformultiplelanguages and regional health contexts ensures accessibility in underserved regions, enhancing healthcare equity worldwide.
Deeplearningcontinuestoreshapehealthcare,offeringvast potential for more precise diagnostics, personalized treatments, and improved healthcare delivery. While the proposed system lays a strong foundation, future advancementswillfocusonseveralkeyareas:
6.1 Broader Data Integration
Expanding beyond current modalities, future systems will incorporate microbiome data, environmental inputs, and
social determinants of health like socioeconomic status. Additionally, real-time mental health indicators such as moodandbehavioraldatafromwearables willhelpbuilda morecompletepictureofpatientwellness,supportingmore accurateandpersonalizedcare.
The next phase of precision medicine will involve tighter integrationofgenomics,biomarkers,anddynamictreatment protocols.Combiningmulti-omicsdatawithpatientfeedback loops will enable adaptive, highly individualized therapies andimproveddiseasemanagementstrategies.
6.3
Real-timedecisionsupporttoolswillevolvetobetterdetect bothchronicandacuteconditions.Bycontinuouslyanalyzing patientdata,thesesystemscanflagearlywarningsignsand guide clinicians with timely, evidence-based recommendations especiallycrucialincriticalcaresettings.
6.4
XAI will be vital to building trust. Future tools will offer interactive, interpretable visualizations, helping clinicians understand how AI arrives at its conclusions based on genetics,lifestyle,andenvironment.Thistransparencywill supportclinicaladoption.
6.5
Federatedlearningwill continuetoevolvetosupportdata privacy,regulatorycompliance,andcollaborativeresearch. Futureimprovementswillreducecommunicationoverhead and enable efficient, decentralized model training across institutionswithoutsharingrawdata.
EnsuringfairnessinAI-drivenhealthcarewillrequirediverse, representative datasets. Future systems will include bias monitoringandcorrectionmechanismstoreducedisparities andensureequitableoutcomesacrosspopulationsofvarying gender,ethnicity,andsocioeconomicbackgrounds.
6.7
Advancedwearableslikecontinuousglucosemonitorsand blood pressure sensors will provide real-time health data. Futuresystemswillusethisinputtorecommendimmediate interventions suchasmedicationadjustments reducing relianceonin-personvisits.
6.8
OngoingengagementwithclinicianswillensureAIsystems remain aligned with practical workflows and ethical standards.Medicalfeedbackwillguiderefinement,makingAI outputsmoreactionableinreal-worldhealthcaresettings.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Future versions will be tailored for global deployment, particularly in underserved regions. Low-cost sensors and multilingual, culturally adaptive interfaces will support diseasemonitoringandpublichealtheffortsatscale.
Seamlessintegrationwithtelemedicineplatformswillallow remoteconsultationsandcontinuousmonitoring.Real-time data shared through these systems will enable timely interventions, expanding healthcare access in rural and remotecommunities.
Thenewdeeplearninghealthcaresystemrepresentsabig step forward in modern medical care. By combining many types of data from medical scans and health records to genes,wearables,surroundings,andmentalfactors ithelps delivermorepersonal,exact,andquickhealthcare.Thismix allowsdoctorstomakesmartchoicessuitedtoeachpatient's healthstory.
Thesystemshinesinitsabilitytochangeandkeeplearning, whichhelpsinhandlinglong-termhealthissueslikediabetes and high blood pressure. Live data from wearable gadgets helpstoactfastandcutsdownonhealthcaresystemstress. Plus,itspowertopredictthingsmeansitcanspotearlysigns of sudden health problems like strokes or heart troubles, whichhelpsstopcomplicationsandkeepspeopleoutofthe hospital.
InthecomingyearsnewdevelopmentswillmakeAImore see-throughwithXAIhelpingdoctorstograspandrelyonAIbasedfindings.Securespread-outdatausewillgetaboost fromfederatedlearning,whichwillkeeppatientinfosafeand opendoorsforteamresearch.Asthesystemgrows,itwillfit with tailored medicine mixing genetic, lifestyle, and surroundingsdatatogiveverypersonaltreatments.
Tackling issues like bias, privacy, and understanding how modelsworkwillbekeytomakesureweusethesesystems and.Gettingmorepeopleinless-servedareastousethistech -throughcheapersensorsandlinkingupwithonlinedoctor visits-willhelpmorefolksaroundtheworldgethealthcare. Intheend,thissetupcouldcausearevolutioninhowwetake careofpatientsbymakingitmoreforward-thinkingopento all,andbasedonrealinfo.
[1] R. Miotto, F. Wang, S. Wang, X. Jiang, and J. T. Dudley, "Deeplearningforhealthcare:Review,opportunitiesand challenges,"BriefingsinBioinformatics,vol.19,no.6,pp. 1236–1246, Nov. 2018. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx044. Available:
https://academic.oup.com/bib/article/19/6/1236/3800 524.
[2] M.H.Abidi,U.Umer,S.H.Mian,andA.Al-Ahm,"BigData Based Smart Health Monitoring System: Using Deep EnsembleLearning,"IEEEAccess,vol.11,pp.114880–114903,Oct.2023.doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3325323.
[3] S.Wang,L.Fu,J.Yao,andY.Li,"Theapplicationofdeep learninginbiomedicalinformatics,"inProceedingsofthe 1stInternationalConferenceonRoboticsandIntelligent Systems(ICRIS),2018.doi:10.1109/1CRlS.2018.00104.
[4] C. Cao et al., "Deep Learning and Its Applications in Biomedicine," Genomics,Proteomics&Bioinformatics, Mar.2018.
[5] R. J. Williams and D. Zipser, "A learning algorithm for continually running fully recurrent neural networks," Neuralcomputation,vol.l,no.2,pp.270-280,1989.
[6] J. Schmidhuber and S. Hochreiter, "Long short-term memory,"NeuralComput,vol.9,no.8,pp.1735-1780, 1997.
[7] Y. Jia et al., "Caffe: Convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding," in Proceedings of the 22nd ACM internationalconferenceonMultimedia,2014,pp.675 678.
[8] Lyman GH, Moses HL. Biomarker tests for molecularly targeted therapies the key to unlocking precision medicine.NEnglJMed2016;375:4–6.
[9] Collins FS, Varmus H. A new initiative on precision medicine.NEnglJMed2015;372:793-5.
[10]D. Zhang, D. Zhu, and T. Zhao, ‘‘Big data monitoring of sportshealthbasedonmicrocomputerprocessingand BPneuralnetwork,’’MicroprocessorsMicrosyst.,vol.82, Apr. 2021, Art. no. 103939, doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2021.103939.
[11] W.Zhu,G.Ni,Y.Cao,andH.Wang,‘‘Researchonarolling bearing health monitoring algorithm oriented to industrialbigdata,’’Measurement,vol.185,Nov.2021, Art. no. 110044, doi: 10.1016/j. measurement.2021.110044.
[12] M.H.Abidi,H.Alkhalefah,andM.K.Mohammed,‘Mutated leadersine cosine algorithm for secure smart IoTblockchain of Industry 4.0,’ Comput., Mater. Continua, vol. 73, no. 3, pp. 5367–5383, 2022, doi: 10.32604/cmc.2022.030018.