
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
PARMAR AUM D., MR. AAKASH SUTHAR
1 M.Tech Student, L.J. University, Ahmedabad
2 Assistance Professor, Structural Engineering Department, L.J. University, Ahmedabad, India.
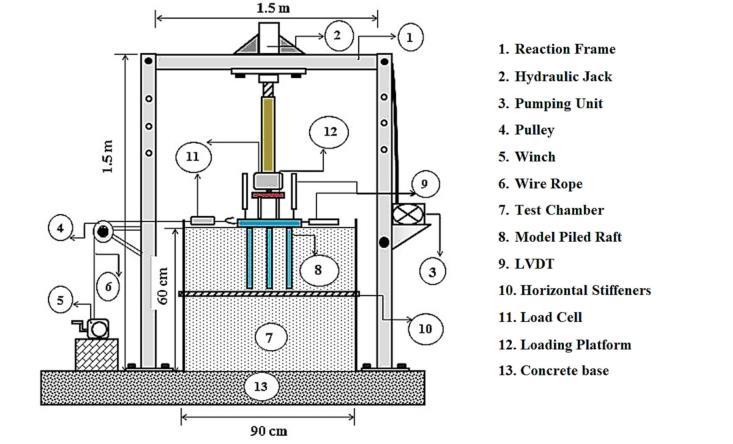
Abstract - Foundation is the integral part of structures which is taking all the structural loads and uniformly distributing to the underlying soil. Pile raft foundation is commonly used for heavy loading structure. In this paper I have reviewed few research paper on raft pile foundation. Generally I have selected two kinds of paper. First one ispaper based on practical model in which they have made porotype using different materials & second type of paper is in which software based research is done. In prototype they have used hollo cylindrical pipe considered as pile and steel plate as pile raft. From all the paper which I have gone through shows conclusion that increase is pile length will increasestrengthof Pile Raft foundation and decrease the settlement of foundation. Increase in distance betweenpilewilldecreasethe settlement.
Key Words: Pileraft,loadtransferringmechanism,Plaxis3D, Settlement.
Apileraftfoundationisanadvancedtypeofdeepfoundation system that combines both piles and a raft (or mat) to supportheavystructuralloads.Thishybridsystemisusedto optimize the load-bearing capacity and settlement performance of foundations, particularly in soils with low bearingcapacityorvariablegroundconditions.
The raft acts as a shallow foundation, distributing the building load over a large area, while the piles penetrate deeper,transferringaportionoftheloadtostrongersoilor rockstrata.Theinteractionbetweentheraftandthepiles enhances the overall stiffness and reduces differential settlement, making it especially suitable for high-rise buildings,bridges,andindustrialstructures.
Pile raft foundations offer a cost-effective alternative to traditionalpile-onlysystemsbyallowingforareductionin the number and length of piles required. Their design requirescarefulconsiderationofsoil-structureinteraction, load-sharing behavior, and settlement control, often supportedbyadvancedgeotechnicalanalysisandnumerical modeling.
1.2 Objectives
Studydistributionofloadoccursinbunchofplieby analytic method and by lap testing method with referencetosettlement.
Whateffectscomeinfoundationwithincreaseindistance betweenpiles?
Understandbehaviorofpileunderdifferentloading condition.
To use the results for designing of pile raft foundation.
(1) Merin Jose, K. Divya Krishnan, P.T. Ravichandran,Behaviourofverticallyloadedpiled raft system on cohesionless soil
Thestudyfocusesonthebehaviorofapiledraftfoundation system under vertical loads on cohesionless soil. The experimental setup involved square rafts (200 mm × 200 mm)withvaryingpilelengths(180mm,200mm,250mm) and pile numbers (4 and 9). Tests were conducted under looseanddensesoilconditionsusingahydraulicjackforload applicationanddialgaugesforsettlementmeasurement.The soil'sdensitywascalibratedforloose(1.53g/cc)anddense (1.84 g/cc) states, with sand prepared as a well-graded medium. Total 14 test where conducted. The vertical load wasgivenwithahydraulicjackof700kg/cm3.
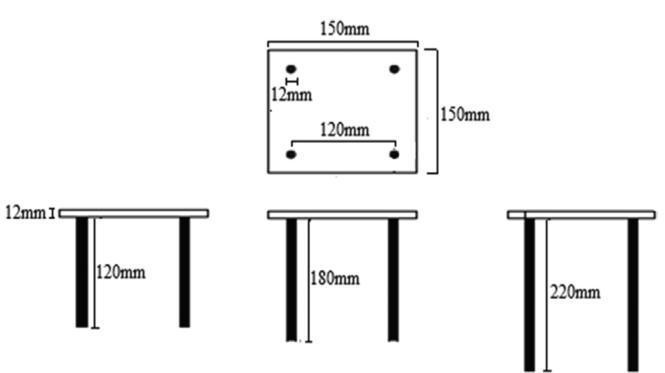
1: Pileraftmodelofsquareraftofsize200mm width4numbersofpiles.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
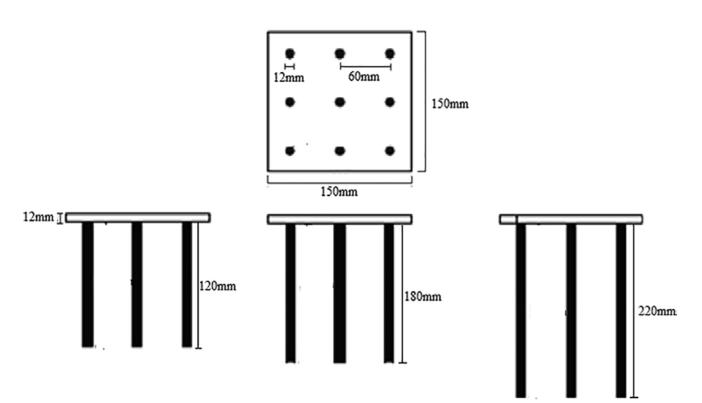
Figure 2: Pileraftmodelofsquareraftofsize200mm width9numbersofpiles
Figurebellowsindicatestheloadsettlementgraphof200_ 200mmraftwith180mm(short),200mm(medium)and 250mm(long)pilesinlooseanddensestateofsoilwith4 numbersofpiles.
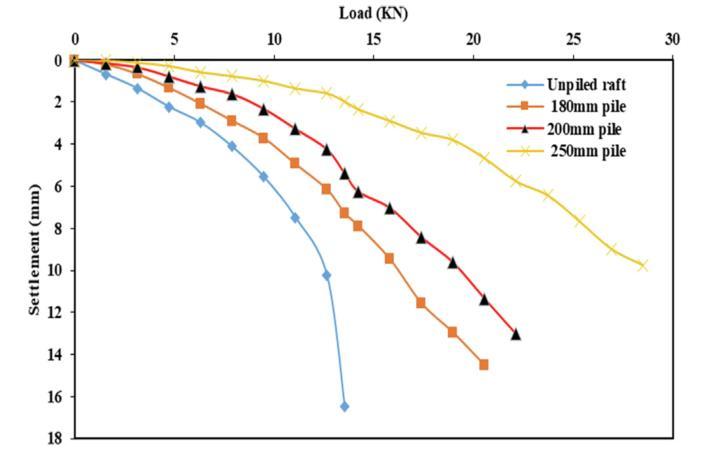
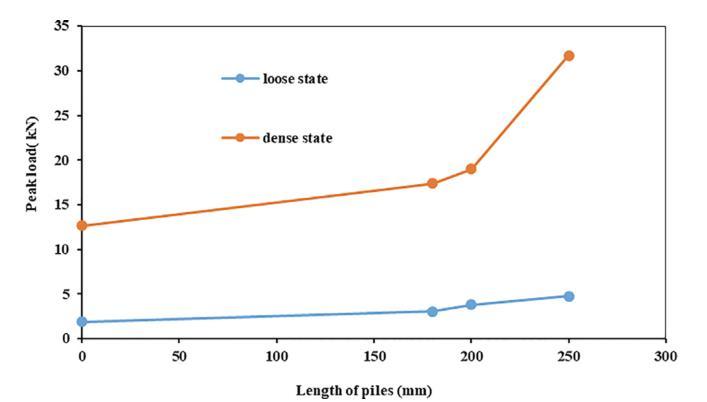
Figure 4: LoadVsSettlementwithrespecttoloosesoil anddensersoil
(2) Plaban Deb & Sujit Kumar Pal, Nonlinear analysis of lateral load sharing response of piled raft subjected to combined V-L loading.
To analyze the behavior of piled raft foundations under vertical loads and combined vertical-lateral (V-L) loading. Theresearchfocusesonload-bearingcapacity,settlement reduction, and the effects of pile length, spacing, and soil properties.

Experimental Setup:Raftdimensions:250mm×250mm, thickness:10mm.Piles:300mmlength,20mmdiameter. Sub-soilmaterials:Siltyclay(upperlayer)andsand(lower layer). Soil preparation ensured uniform density (70% relativedensityforsand).Forevaluating thelateralloadstransferredfromtherafti.e.,thelateralload sustainedbythepilehead,shearstraingaugeswerepasted near the pile head perpendicular to the direction of the application of lateral load at 10 mm below the raft base. Total2testwhereperformfordifferentarangment1)3x3 (Total 9 pile) and 2) 2 x 2 (Total 4 pile). S/d ration consideredare3,4and5.t/Lratioconsideredare0.5,1and 1.5. And total 18 test where performed for 1 loading condtion.Theyhadtotal5loadingcondition.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
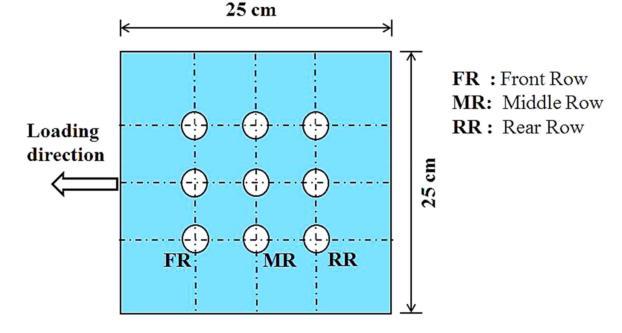
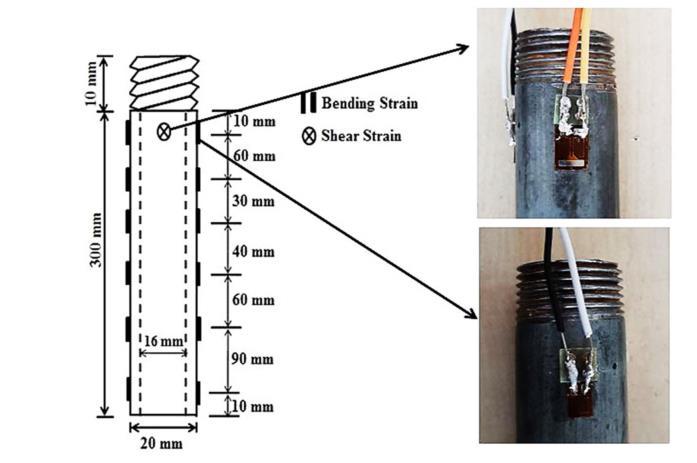
Figure 8: Detailsofmodelpiledraftinstrumentedpile
(3) Biya Degefu Teji and Argaw Asha Ashango, Performance Optimization of Piled Raft Foundations in Layered Soil under Uniform Vertical Loading Using Plaxis 3D.
Thestudyfocusesonoptimizingthe performanceofpiled raft foundations (PRFs) in layered soils under uniform verticalloadingusingfiniteelementmodelling(Plaxis3D). Parameters such as raft thickness, pile length, spacing, diameter, and number are evaluated to understand their impactonsettlementandloaddistribution.
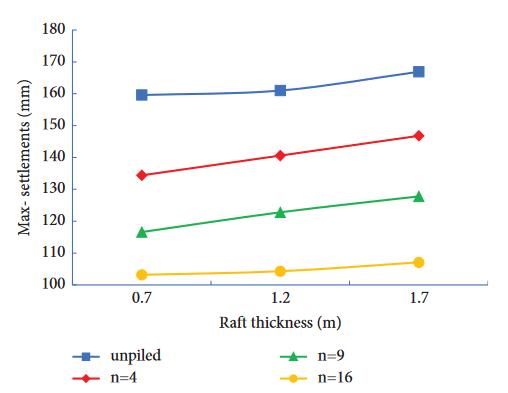
In this study’s author has consider rectangular raft, dimensionsarekeptinsuchawaythatL/B(Lengthtowidth ratio)is1.5.Widthofraft/pilecapisconsideredas10m.To this length became 15m because of L/B ratio. Author has considertothicknessas1)0.7m,2)1.2mand3)1.7m.This dataofthicknesswidthandlengthisconsideredformSafe 20andEtabs.Inmodelling3typeofpiledia.areconsidered asmentionedbelow1)0.6m,2)0.8mand3)1mandtothis theyhaveconsideredspacingof3D, 4Dand 5D.Length of pileisconsideredas15m,12and9mindifferentcases.It’s beentestedinformof4piles(2x2),9piles(3x3)and16 piles(4x4).
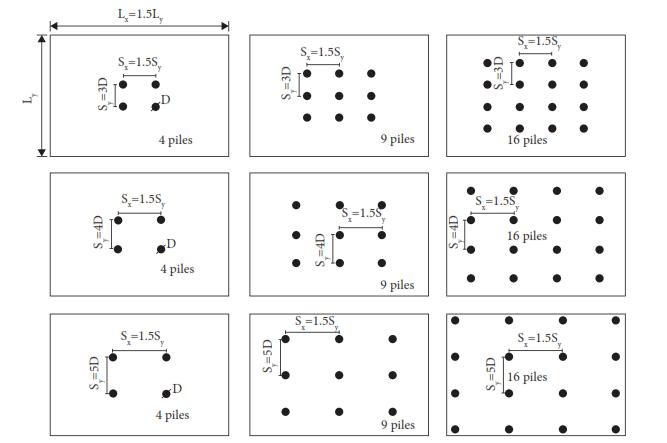
Effect of Raft Thickness: - The effect of raft thickness on settlementwasinvestigatedthroughvaryingraftthicknesses
(0.7 m, 1.2 m, and 1.7 m), fixed pile length (9 m), pile diameterandspacing(0.8mand3timesofpilediameter), and applied loading. Maximum settlement increased with increasedraftthicknessforbothpiledandunpiledcasesdue to the increased self-weight of the raft. Piled rafts experienced lower maximum settlement compared to unpiledones,thankstosharedloadsbetweenpilesandraft, and increased stiffness. Te number of piles also affected settlement values, with more piles providing better load distribution. Differential settlements tended to Decrease with increasing raft thickness for both piled and unpiled rafts due to their increased rigidity and even load distribution.However,therelationshipbetweendiferential settlementandthenumberofpilesiscomplex,withvalues decreasing from 4 to 9 piles, but increasing from 9 to 16 piles, attributing to uneven load distribution among edge and centre piles. Optimal piled raft performance requires carefulconsiderationofpilearrangementandraft
Thickness

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
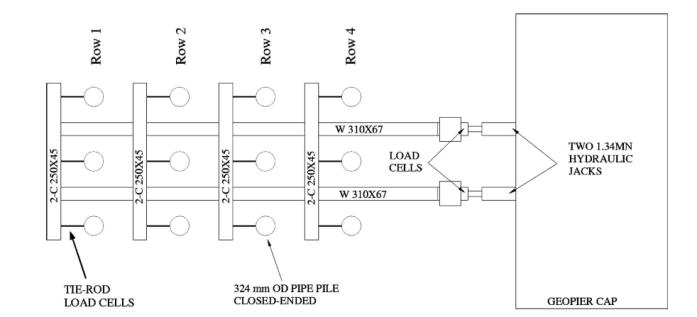
(4) Kyle M. Rollins, Ryan J. Olsen, Jeffery J. Egbert, Derek H. Jensen, Kimball G. Olsen and Brian H. Garrett, Pile Spacing Effects on Lateral Pile Group Behavior: Load Tests
Thestudyfocusesongroupinteractioneffectsasafunction of pile spacing. Full-scale cyclic lateral load tests were conductedonpilegroupsinstiffclay.Pilespacing'stested: 3.3,4.4,and5.65pilediameters(D).Uptofiverowsofpiles wereincludedinthetests.Thistestwasperformonsingle pileandingroupofpile.Testpilewere324mmindia.Steel pipes(having9mmthickness)forsinglepile.Theloadwhere appliedat0.38mabovethegroundsurface. 15loadcycles weretypicallyappliedtosimulatethecyclicloadingtypical of a M7.5 earthquake Seed et al. 1975 and to evaluate the changeinlateralresistanceduetocyclicloading.Forgroup ofpiletotal3separategroupswherecreatedwithdifferent spacing.Pilewheredriveninsoilusinghydraulichammer eachblowtransferenergyof7to27KNm.loadwasapplied usingtwohydraulicjackof1.34MNcapacity.Averagelateral loadoneachpilewas180KNmingroupofpileandinsingle piletestitwas300KNm.
3. CONCLUSIONS
1. Pile Length and Diameter Significantly Influence Performance: Increasing pile length enhances both verticalandlateralloadcapacities,reducessettlement, andimprovesloadtransfertodeeper,stiffersoillayers. Largerpilediametersincreasebaseresistance,further reducingsettlement.
2. Soil Compaction: Densersoilconditionssubstantially increase both load capacity and stress distribution effectiveness, improving the overall stability and performanceofpile-raftfoundations.
3. Optimal Pile Spacing and Arrangement Enhance Efficiency: Increasingpilespacing(withinan optimal range of 4D–5D) improves lateral load resistance and reduces group interaction effects. Uneven load distribution can occur with higher pile counts, but properspacingmitigatesthis.
4. Raft Characteristics Affect Settlement and Load Distribution: Thickerandlargerraftsenhanceuniform load distribution and reduce differential settlement, althoughtheymayslightlyincreasetotalsettlement.
5. Cyclic Loading Reduces Peak Capacity over Time: Repeated loading leads to a measurable reduction in peak load capacity and stiffness, especially in trailing row piles, highlighting the importance of considering fatiguebehaviorindesign.
6. Load Sharing and Group Behavior Are Key to Performance: Efficientloadsharingbetweenpilesand rafts,influencedbypileconfigurationandraftrigidity, minimizesdifferentialsettlementandbendingmoments, ensuringbetterlong-termstructuralintegrity.
[1] Numericalinvestigationsofpileloaddistributioninpile groupfoundation subjected to verticalloadand large moment BUkritchon,JCFaustino,SKeawsawasvongGeomech.Eng,2016-researchgate.net
[2] Pilespacing effects on lateralpile groupbehavior:loadtests KM Rollins, RJ Olsen, JJ Egbert……of geotechnical and…, 2006ascelibrary.org
[3] Numerical analysis ofgroupeffects of a largepile groupunder lateral loading K Jones,M Sun,C LinComputersandGeotechnics,2022-Elsevier
[4] An experimental study of the interaction of vertically loadedpilegroupsinsandSHLee,CKChung-Canadian GeotechnicalJournal,2005-cdnsciencepub.com
[5] Anon-linearloadtransfermethodfordeterminingthe settlementofpilesunderverticalloadingTBoonyatee,Q VanLai-InternationalJournalofGeotechnical…,2020Taylor&Francis
[6] Pile Spacing Effects on Lateral Pile Group Behavior: Analysisuthors:KyleM.Rollins,KimballG.Olsen,Derek H.Jensen,Brian H.Garrett,Ryan J.Olsen, andJeffery J.Egbert
[7] PileSpacingEffectsonLateralPileGroupBehavior:Load TestsAuthors:Kyle M.Rollins,Ryan J.Olsen,Jeffery J.Egbert,Derek H.Jensen,Kimball G.Olsen, andBrian H.Garrett