
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dhananjay Singh1 , Nagendra Dhakar2
1Research Scholar, Mewar University, Chittorgarh, Rajasthan, Indi 2Assistant Professor, Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
Abstract - This study investigates the enhancement of flexible pavement performance through geogrid reinforcement.Geogrids,polymer-basedmaterials,improve load distribution, reduce rutting, and enhance fatigue resistance.Theresearchcombineslaboratoryandfieldtests toevaluatethemechanicalbehaviorofgeogrid-reinforced pavements. Key findings indicate that geogrid-reinforced pavements exhibit superior performance in terms of increasedstrength,reducedrutting,andincreaseddurability comparedtonon-reinforcedpavements.Thelife-cyclecost analysis further supports the cost-effectiveness of using geogrids,withasignificantreductioninmaintenanceneeds andafavorablebenefit-costratio.Thesefindingsprovidea practicalguideforintegratinggeogridsinpavementdesign, contributing to sustainable and cost-effective road infrastructuresolutions.
Key Words: Geogrid Reinforcement, Flexible Pavement, Pavement Durability, Life Cycle Cost Analysis, Pavement Performance.
Flexible pavements are a critical component of road infrastructure due to their cost-effectiveness and adaptabilitytovarioustrafficandenvironmentalconditions. However,thesepavementsoftenfacechallengesrelatedto their durability under increasing traffic volumes, heavy loads, and extreme environmental conditions such as temperature fluctuations and moisture. Issues such as rutting,cracking,andmoisture-induceddamageoftenleadto increasedmaintenanceandrehabilitationcosts,whichcan ultimatelyaffectroadsafetyandoverallperformance.
Geogrid reinforcement, a relatively new technique, has emergedasapromisingsolutiontoaddressthesechallenges. Geogrids, which are polymeric materials with a grid-like structure,actasreinforcementlayerswithinthepavement toimproveitsstructuralcapacity.Thisreinforcementhelps in distributing loads, reducing lateral displacement of aggregates, and enhancing the bearing capacity of the pavementsystem.Geogridsalsoprovidebetterresistanceto rutting,fatiguecracking,andreducetheoverallmaintenance cost.
Despitetherecognizedbenefitsofgeogridreinforcementin flexiblepavements,thepracticeisnotyetwidelyadoptedin
pavement design, particularly in regions with varying climaticconditionsandweaksubgradesoils.Thisstudyaims toevaluatetheperformanceimprovementsassociatedwith geogrid reinforcement through comprehensive laboratory andfieldexperiments,followedbyacost-benefitanalysis.
Geogridreinforcementhasgainedsignificantattentioninthe fieldofpavementengineeringduetoitsabilitytoenhance the structural integrity of flexible pavements. Geogrids improvetheloaddistribution,reducerutting,andenhance fatigue resistance, which ultimately improves the overall performanceandlifespanofflexiblepavements.
Numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of geogrid reinforcement in pavements. Studies by Ahmed&Khan(2017),Gupta&Yadav(2018),andSharma& Das(2016)provideevidenceofimprovedruttingresistance, increasedfatiguelife,andbetterloadtransferinreinforced pavements.However,theapplicationofgeogridsisstillnot widespreadduetothelackoflong-termdata,performance validationacrossdifferentclimates,andstandardizeddesign guidelines.
S.No Author(s) &Year
Title
1 Ahmed & Khan (2017) Geogrid Reinforcement in Flexible Pavements
2 Gupta & Yadav (2018)
Effect of Geogrid on Pavement Performance
3 Sharma & Das(2016) Rutting & Durability
KeyFindings
Improved load transfer and ruttingresistance. Limited field studies.
Significant reduction in surface deformation.Lack offatiguelifedata.
Notablereduction inrutdepth,short testduration.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
4 Lee & Kim (2019) Mechanics of Reinforced Pavements
5 Patel & Joshi (2017) Urban Road Case Study
6 Ram & Soni (2018) Pavement with Geogrids
Improved stress distribution. Material variability not studied.
Performance improvedinheavy traffic zones.
Limited rural applicability.
Better structural response. No cost analysis.
Thisstudyemploysbothlaboratoryexperimentsandfield trials to evaluate the performance of geogrid-reinforced flexiblepavements.ThelaboratorytestsincludeCalifornia Bearing Ratio (CBR), wheel tracking tests, repeated load triaxial tests, and flexural fatigue tests. Field trials were conducted to measure rutting, deflection, and other key performanceindicatorsunderrealtrafficconditions.
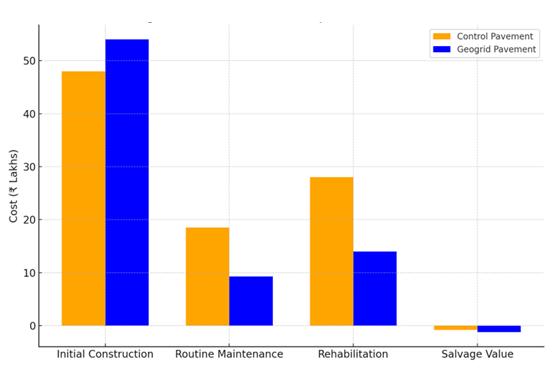
Themethodologyalsoincorporateslife-cyclecostanalysis (LCCA)todeterminethecost-effectivenessofusinggeogrids inpavementconstruction,accountingforinitialconstruction costs,routinemaintenance,andrehabilitationcostsovera 20-yearperiod.
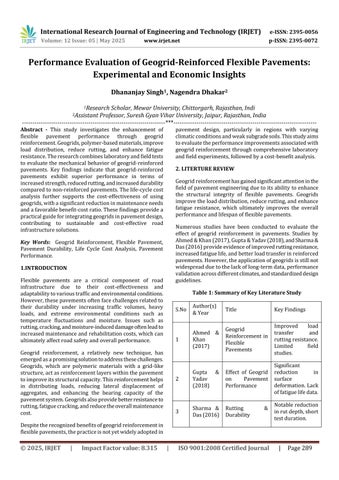
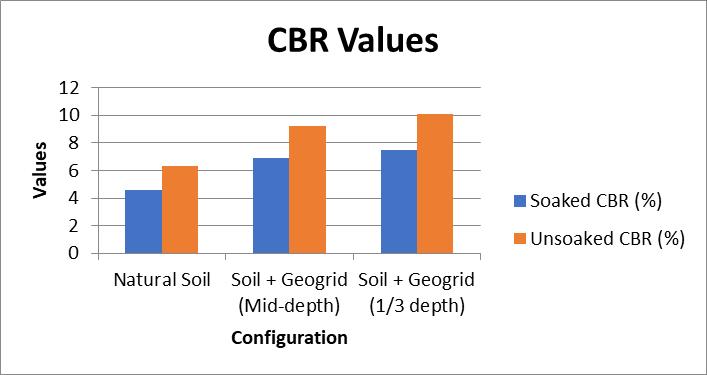
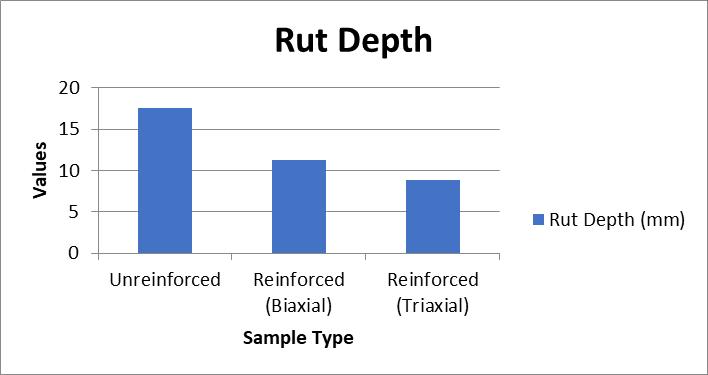
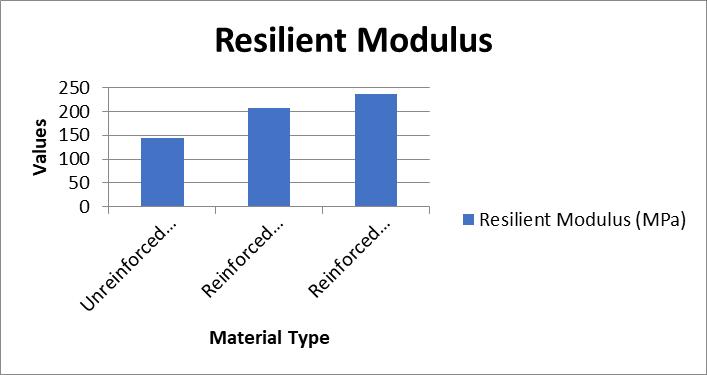
The laboratory results show that geogrid reinforcement leads to a significant increase in the CBR values, resilient modulus,andfatiguelifeofthepavements.Inparticular,the inclusion of geogrids reduced rutting by up to 40%, increasedthefatiguelifeby82%,andimprovedtheoverall structuralintegrityofthepavement.
Field performance data further supports these findings, showing reduced rut depths and lower deflection measurements for geogrid-reinforced pavements. The regressionanalysisindicatesastrongcorrelationbetween resilientmodulusandrutdepth,confirmingtheeffectiveness of geogrids in improving the load-bearing capacity of pavements.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Figure 4.4: Resilient Modulus
Alinearregressionwasperformedtoanalyzetheeffectof geogridreinforcementonrutdepthasafunctionofresilient modulus:
RegressionEquation:RutDepth=24.81-0.068×Resilient Modulus
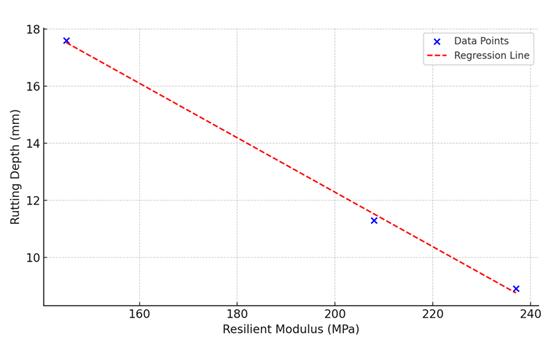
R² Value: 0.91 indicating a strong negative correlation betweenresilientmodulusandrutdepth.
An ANOVA was conducted to evaluate the statistical significanceofgeogridinclusiononfatiguelife.Thegroups were:
Group1:ControlSpecimens
Group2:ReinforcedSpecimens
The p-value < 0.05 confirms significant improvement in fatiguelifeduetogeogridreinforcement.
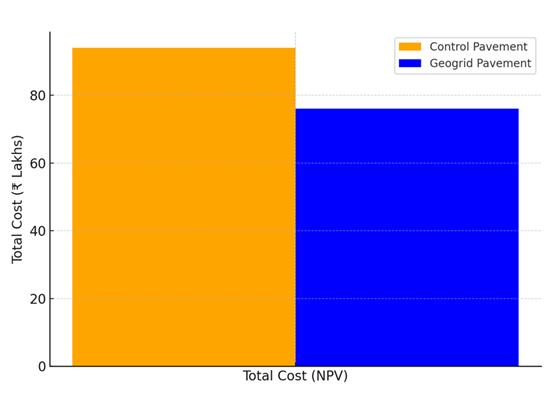
Figure 4.10: Cost Comparison over 20-Year Design Life
5. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Thestudyconcludesthatgeogridreinforcementsignificantly improves the mechanical and structural performance of flexible pavements. Key benefits include reduced rutting, enhancedfatigueresistance,andlongerpavementlife.
Fromaneconomicperspective,theuseofgeogridsleadsto substantial long-term savings, with reduced maintenance and rehabilitation costs. Based on these findings, it is recommendedthatgeogridreinforcementbeincorporated into pavement designs, especially for roads with weak subgradesandhightrafficvolumes.
Future research should focus on long-term field studies across varying climates and the optimization of geogrid placement and type for different pavement conditions. Further studies are also recommended to investigate the environmental impacts of geogrid use, such as reduced carbonfootprint.
[1] Ahmed, S., & Khan, M. (2017). Geogrid reinforcement in flexible pavements: A review. International Journal of Road Engineering, 12(2), 56–64.
[2] Gupta, R., & Yadav, A. (2018). Effect of geogrid reinforcementonpavementperformance.Journalof GeotechnicalEngineering,19(4),102–108.
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page291

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[3] Sharma,R.,&Das,S.(2016).Impactofgeogridon pavement rutting and durability. Journal of Civil Engineering,21(1),77–85.
[4] Lee, J., & Kim, P. (2019). Mechanics of geogrid reinforced pavements. Construction Materials and Technology Journal,18(3),44–50.
[5] Patel, D., & Joshi, S. (2017).Comparativestudyof geogridreinforcedpavementsinurbanareas. Urban Infrastructure Journal,25(2),32–40.
[6] Ram, K., & Soni, R. (2018).Performanceanalysisof pavementswithgeogridreinforcement. Journal of Pavement Engineering,14(3),99–105.
[7] Thomas, M., & Kumar, R. (2020). Geogrids in pavement design: State of the art. Journal of Transportation Engineering,29(1),120–128.
[8] Hossain, M., & Islam, R. (2016).Enhancementof flexible pavement performance with geogrid reinforcement. Journal of Road and Pavement Engineering,12(4),72–79.
[9] Singh, A., & Reddy, K. (2019).Soilreinforcement with geogrids for pavement design. Geotechnical Engineering Journal,17(2),58–64.
[10] Jha, P., & Bansal, H. (2020). Effectiveness of geogridsinpavementdesignforhightrafficloads. Traffic Engineering and Control Journal,16(3),40–47.