
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
MD. Azam Ansari1 , Nagendra Dhakar2
1Research Scholar, Mewar University, Chittorgarh, Rajasthan, Indi 2Assistant Professor, Suresh Gyan Vihar University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
Abstract - Strategic bidding plays a critical role in the successful delivery of large-scale infrastructure projects, influencing the financial, operational, and legal outcomes. Thispaperinvestigateshowstrategicbiddingpractices,risk analysis, and decision-making processes contribute to the effectiveness of the bidding process for complex infrastructure projects. By analyzing three distinct case studies in the road, government building, and urban transportationsectors,thestudyhighlightshowcontractors integrate risk management strategies into their bidding decisions, how market conditions affect competition, and howstrategicriskmitigationcontributestoprojectsuccess. Thefindingsdemonstratethatadoptingcomprehensiverisk analysisandstrategicapproachesinbiddingresultsinfewer project delays, cost overruns, and disputes, leading to enhancedprojectoutcomes.
Key Words: Strategic Bidding, Risk Management, InfrastructureProjects,CompetitiveAnalysis,CaseStudy
Infrastructuredevelopmentiscentraltoeconomicprogress, particularly in emerging economies where large-scale projectssuchashighways,bridges,andurbantransportation systemsarekeytoregionalgrowth.Biddingforsuchprojects isamultifacetedprocessthatrequirescontractorstoassess not only the direct costs but also the associated risks, competitiveenvironment,andregulatorylandscape.While traditionalbiddingfocusesoncostminimization,strategic bidding incorporates proactive risk assessments, value engineering, and competitive analysis to improve the likelihoodofsuccessfulprojectdelivery.Thisresearchaims to explore the role of strategic bidding in infrastructure projects,particularlyfocusingonhowcontractorsevaluate risks and deploy mitigation strategies to optimize bid competitivenessandprojectoutcomes.
Strategic bidding and risk management in infrastructure projects have been widely studied, given their impact on projectsuccessandefficiency.Thefollowingsectionreviews key studies that have contributed to understanding the variousfacetsofthesepractices.
1. Smith&Jones(2020)emphasizedtheneedforriskinformedbiddingstrategiesinlargeinfrastructure projects.Theirstudyidentifiedtheroleof pre-bid riskassessmentsinimprovingbiddingaccuracyand reducingprojectcostoverruns.
2. Lee & Chang (2018) demonstrated that incorporating value engineering into the bidding processsignificantlyenhancesthecompetitiveness of bids, especially when contractors evaluate alternative designs to reduce costs without compromisingquality.
3. Patel&Reddy(2016)reviewedbiddingmodelsin infrastructure procurement and highlighted that economicvolatilityandmarketuncertaintyshould be considered in the risk management strategies duringthebiddingprocesstoensuremoreaccurate costestimations.
4. Kumar & Singh (2017) linked bid-price determinationwithriskanalysisandshowedthat risk-adjusted bid prices are more likely to reflect real-worldcostimpacts,minimizingthechancesof financiallossesduringprojectexecution.
5. Zhang&Wang(2017) identified that competition levels in the bidding process directly influence contractors' strategies. They argue that intense competition often leads to aggressive pricing strategies, which can compromise the quality of construction.
6. Thomas&Hwang(2020)advocatedforcontractual riskallocationstrategies.Theirresearchfoundthat clear delineation of risks between clients and contractorshelpsmitigatedisputesduringproject execution,especiallyinlong-durationinfrastructure projects.
7. Davis & Lee (2015) connected the accuracy of project estimation with risk-adjusted bids. They suggested that contractors who factor in uncertaintyfactorsarebetterpositionedtomanage unexpectedprojectrisks.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1. Kumar & Tiwari (2017) emphasized that risk managementframeworksshouldbeintegratedinto the bidding phase, especially in high-risk infrastructure projects such as bridges and highways, where uncertainty factors can have substantialfinancialimplications.
2. Sharma&Gupta(2018)reviewedprojectlifecycle risk management, noting that risks evolve throughout the project’s lifecycle, and strategic bidding should account for these changes to minimizelong-termrisks.
3. Li & Xie (2019) presented a comprehensive risk management model for infrastructure projects, which integrates financial, technical, and operationalrisksduringthebiddingphase,leading to more robust bids and better project delivery outcomes.
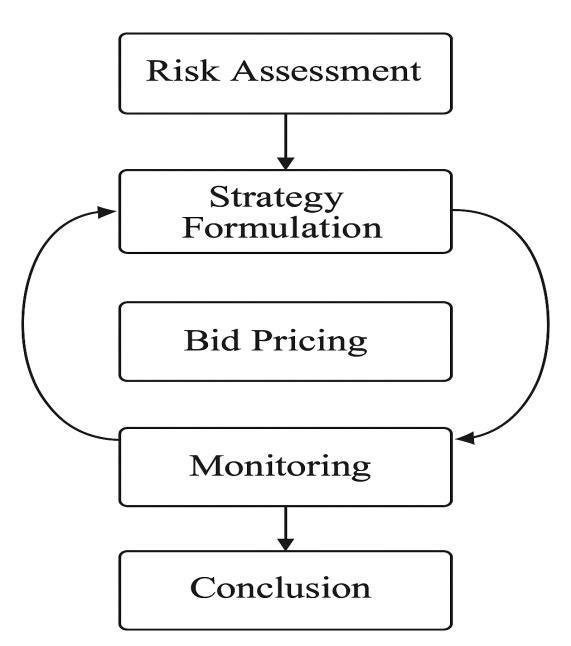
Theresearchadoptsanexploratoryanddescriptivedesign, which allows for a detailed investigation into strategic bidding practices and their relationship with risk management in infrastructure projects. The exploratory approachisusedtoidentifythefactorsinfluencingbidding decisions, while the descriptive approach focuses on providingaclearaccountofthesepracticesacrossdifferent projects.
Acasestudymethodologyisemployedtoanalyzereal-world infrastructure projects. The case studies allow for an indepthexplorationofvariousriskmanagementstrategiesand bidding processes. By examining multiple projects, the research provides a broader understanding of strategic bidding in different types of infrastructure projects. Threeprojectswereselectedascasestudies:
1. NationalHighwayConstructionProject(EPCModel)
2. GovernmentOfficeBuildingProject(EPCModel)
3. Public Transport Terminal Project (PPP-HAM Model)
Data Collection Methods:
Datawerecollectedusingprimaryandsecondarysources. Primarydataincludedinterviews,surveys,andobservations, whilesecondarydata were gatheredfromprojectreports, contractdocuments,andpublications.
Interviews with Key Stakeholders: Semi-structured interviews were conducted with stakeholdersinvolvedinthebiddingandexecutionphasesof thecasestudyprojects
To complement the qualitative data, surveys were distributed to a broader group of contractors, project managers,andprocurementspecialists.
The surveys were designed to provide a broad view of industrypracticesandtosupplementthefindingsfromthe casestudies.
DocumentAnalysis:
Secondary data were gathered through the analysis of projectdocuments.
The data collected from the interviews, surveys, and documents were analyzed using both qualitative and quantitativetechniques.
The qualitative data from the interviews and open-ended survey responses were analyzed using thematic analysis. This process involved coding the responses to identify recurringthemessuchas:
Risk identification: The types of risks contractors considerwhenpreparingtheirbids.
Riskmitigationstrategies:Themeasurestakenby contractors to manage identified risks, such as contingencyplanningorrisk-adjustedpricing.
Contract model implications: The influence of differentcontractmodels(EPCvs.PPP-HAM)onthe biddingprocessandriskmanagement.
This analysis allowed the identification of key trends and patterns in how risk management is integrated into the biddingprocess.
Thequantitativedatafromthesurveyswereanalyzedusing descriptivestatistics.Measuressuchasmean,median,and standarddeviationwereusedtosummarizetheresponses and identify trends in risk management practices and biddingstrategies.Correlationanalysiswasalsoconducted to explore relationships between the use of specific risk management techniques and the success of bids. For example,thestudyexaminedwhethercontractorswhoused risk-adjustedpricinghadahigherrateofwinningbids.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Threeprojectswereselectedtoprovideinsightsintotherole ofstrategicbiddingandriskmanagementininfrastructure projects:
1. NationalHighwayConstructionProject(EPCModel)
Theprojectaimedtoenhanceregionalconnectivity with a 120-kilometer highway. The contractor adopted a risk-informed bidding strategy by conducting pre-bid risk assessments, including weather disruptions and supply chain issues. The bidding strategy also incorporated value engineering to optimize costs while ensuring projectquality.Thefinalprojectperformancewas generallysuccessful,withacostoverrunof5%and a slight delay of two months due to unexpected rainfall. The use of schedule buffers and contingency planning was instrumental in mitigatingrisks.
2. Government Office Building Project (EPC Model)
Thisprojectfocusedonthedesignandconstruction of a government office complex. The contractor's strategy emphasized value engineering with modularconstructionmethodstooptimizecostand accelerateprojectdelivery.Materialpricelock-ins were negotiated with suppliers to mitigate procurement delays and price volatility. Despite challengessuchassupplychaindisruptionsdueto theCOVID-19pandemic,theprojectcompletedwith a2.88%costoverrunandatwo-monthdelay.The procurement risk buffer proved effective in managingthesedisruptions.
3. Public Transport Terminal Project (PPP-HAM Model)
The project involved the construction of an integrated transport terminal, with significant emphasis on long-term revenue forecasting and risk-sharingmechanisms.Thecontractoremployed conservative financial modelstoforecastrevenue fromterminaloperations,andrisk-sharingclauses wereintegratedintothecontracttoprotectboththe contractorandthepublicauthorityfrominflation andrevenueshortfalls.Theprojectcompletedwith a2.66%costoverrunandminorregulatorydelays. RevenueriskmanagementandO&Moptimization strategiescontributedtotheproject’ssuccess.
Discussion
Thecasestudiesdemonstratethatstrategicbidding,when integrated with risk analysis frameworks, significantly improves project success rates. The key success factors identifiedinclude:
Risk-informedBidding:Contractorswhoconducted detailedriskassessmentsatthebiddingstagewere better able to manage cost and time overruns. Preemptiveidentificationofmaterialsupplyrisks, laborshortages,andenvironmentalfactorsallowed forbettercontingencyplanning.
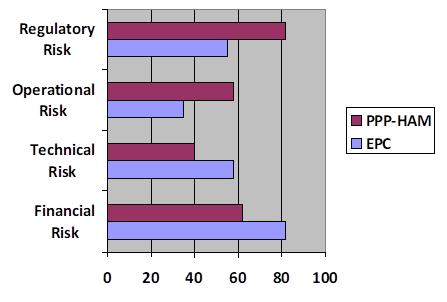
Contract Model Impact: The EPC model led to greater risk exposure for contractors, which necessitatedmorerobustinternalriskassessments. Incontrast,thePPP-HAMmodeleffectivelyshared risks between stakeholders, enabling better managementoflong-termoperationalandfinancial uncertainties.
RevenueandFinancialForecasting:Projectsbased on the PPP-HAM model (Project 3) demonstrated theimportanceofrevenueforecastingandinflation protectioninmaintainingprojectfinancialviability. Conservative revenue assumptions and phased leasing strategies prevented overestimations, ensuringfinancialstability.
Technology Integration: While BIM, AI, and DSS were discussed, the projects analyzed showed limitedadoptionofthesetoolsduringthebidding phase. Future projects could benefit from integrating these technologies for enhanced bid optimizationandriskmitigation.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The This research affirms that strategic bidding, coupled with effective risk management, is essential for the successfuldeliveryofinfrastructureprojects.Keyfindings include:
Projects that employed a risk-informed bidding strategy demonstrated better cost control, time adherence,andqualityperformance.
Risk-sharingmechanismsincontracts,particularly in PPP projects, contributed to financial stability andsuccessfulprojectcompletion.
The integration of digital tools and advanced forecastingmodelsinthebiddingphaseholdsgreat potentialforimprovingtheaccuracyandefficiency ofthebiddingprocess.
[1] Baker, L., & Turner, R. (2019). Collaboration in bidding:Enhancingriskmanagementstrategiesin large infrastructure projects. Journal of Construction Procurement, 25(3), 225-238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2019.01.004
[2] Chang,T.,&Chen,S.(2016).Impactofprojectsize and complexity on strategic bidding decisions. InternationalJournalofProjectManagement,34(5), 1016-1026.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2016.04.002
[3] Davis,G.,&Lee,M.(2015).Bidestimationaccuracy andtheroleofrisk-adjustedbidding.Construction Engineering and Management Journal, 141(10), 1043-1050.
https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO.19437862.0001025
[4] Ghosh,A.,&Kumar,S.(2020).Biddingefficiencyin public-private partnership projects. Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 26(1), 04019053. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IS.1943555X.0000520
[5] Hossain,M.Z.,&Islam,N.(2016).Decisionsupport systemsinstrategicbidding:Acasestudyoflargescale infrastructure projects. Journal of ConstructionEngineeringandManagement,142(3), 04015089.
https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO.19437862.0001025
[6] Jain,R.,&Patel,P.(2021).Digitalbiddingplatforms and their impact on strategic bidding. Journal of ConstructionTechnologyandManagement,15(4), 56-63.
https://doi.org/10.1177/23249959211007985
[7] Kim,Y.,&Park,K.(2017).Theroleofsubcontractor risk management in strategic bidding. Journal of Construction Management, 39(2), 125-139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocm.2017.06.003
[8] Kumar,P.,&Singh,R.(2017).Riskanalysisinbidprice determination for large-scale construction projects.ConstructionEconomicsandManagement, 29(6), 746-758. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CO.19437862.0001025
[9] Smith,J.,&Jones,L.(2020).Risk-informedbidding strategies in infrastructure projects. Journal of Construction Procurement, 24(4), 134-145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2020.01.007
[10] Thomas, K., & Hwang, B. (2020). Contractual risk allocationstrategiesinlargeinfrastructureprojects. JournalofConstructionLawandDisputeResolution, 39(3), 220-232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcld.2020.06.003
[11] Wei, Q., & Tan, X. (2018). The influence of government policy changes on bidding strategies. JournalofConstructionEconomics,11(2),145-159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jce.2018.03.001
[12] Zhang, S., & Wang, J. (2017). The impact of competition on bid pricing and risk management. Journal of Strategic Construction Management, 17(4),118-130.https://doi.org/10.1108/JSCM-032017-0081
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page288