
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Prabhakar1 , Ruthik H M2 , Sagar A3, Rajesh K4, Rakesh D5
1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, CMR University, Bengaluru. 2345 UG Student, Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering, CMR University, Bengaluru.
Abstract - The improper disposal of medical waste continues to pose severe threats to both public health and environmental sustainability, particularly in densely operated healthcare facilities. Traditional waste collection systems often struggle with inefficiencies such as delayed pickups, overflowing bins, and lack of accountability, all of which can lead to hazardous outcomes. In response to these challenges, this project proposes an intelligent, IoT-based waste management system tailored specifically for hospitals and medical centres. By deploying sensors that continuously monitor bin fill levels, the system generates automated alerts when predefined thresholds are reached. Integrated GPS functionality allows real-time location tracking of bins, aiding in efficient waste collection logistics. A centralized platform manages status updates and role-based notifications, enabling hospital staff and waste handlers to stay coordinated and informed throughout the disposal cycle.
This technology-driven approach promotes a cleaner, safer, and more sustainable medical environment by automating routine tasks and improving operational responsiveness.
Key Words: Medical Waste Management, Automated Monitoring, Real-Time Alerts, Route Optimization, Web Application, Digital Waste Tracking, Role-Based Access, HealthcareSafety
Medicalwastemanagementremainsacriticalchallengein modern healthcare systems due to the hazardous and potentially infectious nature of the waste produced in hospitals,clinics,laboratories,andothermedicalfacilities. This waste often includes contaminated materials such as used syringes, bandages, bodily fluids, pharmaceuticals, andchemicalsubstancesthatrequirespecialhandlingand timelydisposal.
Improper or delayed disposal of such waste can lead to severe consequences, including the spread of infectious diseases,injurytohealthcareworkersandwastehandlers, and long-term environmental pollution. According to the World Health Organization, nearly 15% of healthcare waste is considered hazardous [1]. Sharma highlight that fixed-schedule waste collection often fails to match actual usage patterns, leading to inefficiencies and risks. As healthcareinfrastructurecontinuesto modernize, there is a growing need for smarter, automated systems that can addressthesegaps[3].
As healthcare systems continue to evolve in an era of digital transformation, there is a growing need for smart, responsive solutions that can automate key aspects of medical waste handling. Enhancing the ability to monitor, report, and manage waste more accurately and efficiently is essential to promoting safer healthcare environments, reducing environmental impact, and improving overall wastemanagementprocesses.
The project aims to enhance medical waste management by enabling real-time monitoring of waste levels and ensuring timely collection. It eliminates the reliance on manual checks or fixed schedules, thereby reducing the risk of overflow, contamination, and operational inefficienciesinhealthcarefacilities.
The system also promotes role-based access, enabling communication between hospital staff and collectors. It streamlines logistics by providing optimized routes and centralized status updates through a web platform. The use of scalable, open-source technologies ensures adaptabilityandaffordability,makingthesolutionsuitable forvarioushealthcareenvironments.
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies intowastemanagementsystemshasemergedasakeyarea ofresearchinresponsetothegrowingchallengesposedby urbanization and increasing waste volumes. Researchers have emphasized the need for intelligent systems that can automatewastedetection,sorting,andcollectiontoreduce humaninterventionandimproveoperationalefficiency.
According to Al Mamun et al. [1], IoT-based waste systems can significantly enhance waste segregation and collection by utilizing sensor nodes, microcontrollers, and wirelesscommunicationmodulestomonitorbinstatusand transmit real-time data to central servers. This allows for timely interventions, optimized route planning, and efficientresourceusage.
Zhang and colleagues [2] proposed a cloud-based smart waste monitoring system that leverages sensor data to identify bin fill levels and environmental parameters such as temperature and gas emissions. Their research highlights the role of cloud computing in facilitating scalable and remote monitoring solutions. Similarly, studiesbyFoliantoetal.[3]demonstratedthepotentialof

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
integrating RFIDand GSM technologies toautomate waste bintrackingandreportinginurbanenvironments.
Furthermore, Sharma and Gupta [4] explored the environmental benefits of real-time waste management systems and emphasized their impact on reducing carbon emissions and minimizing waste handling delays. These studies collectively underline the potential of IoT and smart technologies in revolutionizing traditional waste management practices, offering scalable, sustainable, and intelligentsolutionsformodernurbanecosystems.
Traditionalwastemanagementsystemsreliedheavilyon manual labour and fixed schedules, often resulting in inefficient collection and environmental risks. Over the years,growingurbanpopulationsandwastevolumeshave pushed researchers to explore automated solutions. This shift has laid the foundation for integrating intelligent technologiesinwastemonitoringandcontrolsystems.
1.2 Role of Smart Technologies in Waste Monitoring
Smart waste management systems utilize embedded technologies such as microcontrollers, real-time sensors, and wireless modules to detect bin status. These components collect data and transmit it to centralized platforms, reducing human intervention. This real-time visibilityenhancesresponsiveness,preventsoverflow,and ensures timely waste disposal in healthcare and urban contexts.
Cloudcomputingplaysacrucialroleinenablingscalable and remote waste monitoring. Collected sensor data is stored and analysed on cloud platforms to generate actionable insights. Data analytics helps optimize collection schedules, predict waste trends, and automate alerts, contributing to more efficient and informed waste managementdecisions.
ResearchshowsthatIoT-enabledwastesystemsreduce the frequency of waste overflow and minimize health hazards. Automated systems lower operational costs by optimizing vehicle routes and reducing energy usage. Additionally, such systems support sustainability by encouraging responsible waste disposal and limiting environmental exposure to harmful or infectious materials.
Various smart waste solutions have been developed globally, each with distinct technologies and
implementationmodels.SomeuseGSM-basedalerts,while others leverage GPS and cloud platforms. Comparative studieshighlight benefitssuchasimproved efficiencyand drawbackslikemaintenancecomplexity, offeringvaluable insightsforfuturesystemenhancementsandscalability.
Although extensive research has been conducted on the application of smart technologies in municipal waste management, there is a noticeable lack of focus on the uniquechallengesassociatedwithmedicalwastedisposal. Mostexistingsystemsaregeneralizedand do notaccount forthehazardousandtime-sensitivenatureofbiomedical waste. Additionally, many models rely solely on sensorbased monitoring without offering seamless integration into hospital workflows or role-based access control for differentuserssuchascollectorsandmedicalstaff.
There is also limited exploration of real-time communication and dynamic route optimization tailored for healthcare environments. Furthermore, cost-effective open-source solutions that ensure both scalability and security are not sufficiently addressed in current literature. These gaps underline the need for a more specialized and efficient smart waste management framework that specifically caters to the sensitive requirementsofhealthcarefacilities.
The System Design and Architecture is built around a modular structure that incorporates real-time data collection, communication, and processing. The system comprises several key components: IoT sensors, microcontrollers, communication modules, and a cloudbased application for data visualization and management. Thesecomponentswork in tandemtoensurethe efficient collection, monitoring, and reporting of waste bin fill levels,aswellasthetimelynotificationofwastecollectors andhealthcarestaff.
Thearchitectureofthesystemisdesignedtobescalable, modular, and easy to deploy in healthcare facilities. The corecomponentsinclude:
IoT Sensors: Waste level sensors (ultrasonic, infrared,loadcells)monitorthefilllevelsinmedical waste bins, while environmental sensors (temperature, humidity, gas, and air quality) track hazardous conditions in the surroundings. These sensorsaremountedinsidethebinsorsurrounding areastogatherreal-timedata.
Microcontrollers: The data from sensors is processed using microcontrollers such as the Arduino Uno/Mega or ESP32/ESP8266. These

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
microcontrollers serve as the central unit for data processing, decision-making, and communication between the sensors and cloud-based infrastructure.
Communication Modules: To enable real-time communication and notifications, communication modules such as WiFi (ESP8266/ESP32), GSM (SIM800L), and LoRa are used. These modules facilitate data transmission to the central server or cloud-basedapplicationforprocessingandstorage.
CloudPlatformandWebApplication:Theprocessed data is transmitted to a cloud platform where it is stored and analysed. A real-time web application provides users (waste collectors, healthcare staff) with a dashboard for monitoring waste levels, receiving notifications, and tracking collection logistics.
Data Collection: The system continuously collects data from the waste level and environmental sensors. The data is relayed to the microcontroller forinitialprocessing.
Processing and Communication: The microcontrolleranalysesthesensor data and,upon detecting a critical waste level or hazardous condition, triggers the communication module to send notifications via SMS, email, or push notificationtorelevantpersonnel.
Real-time Updates: The waste collectors can access the system’s dashboard, which displays real-time data on waste bin fill levels, collection status, and environmental conditions. The dashboard also provides route optimization recommendations for waste collection based on the bin's location and fill level.
Data Visualization: The cloud-based web application presents data in an easy-to-understand formatwithinteractivevisualizationsandreal-time alerts, ensuring swiftaction byhealthcare staffand wastemanagementteams.
Thesystemisdesignedwithflexibilityinmind,enabling it to be easily adapted for deployment in various healthcare environments. Its modular design allows the addition of more sensors, microcontrollers, or communication modules to cover larger areas or adapt to specificfacilityneeds.Thesystemcanbescaledfromsmall clinics to large hospitals, ensuring widespread applicabilityinmedicalwastemanagement.
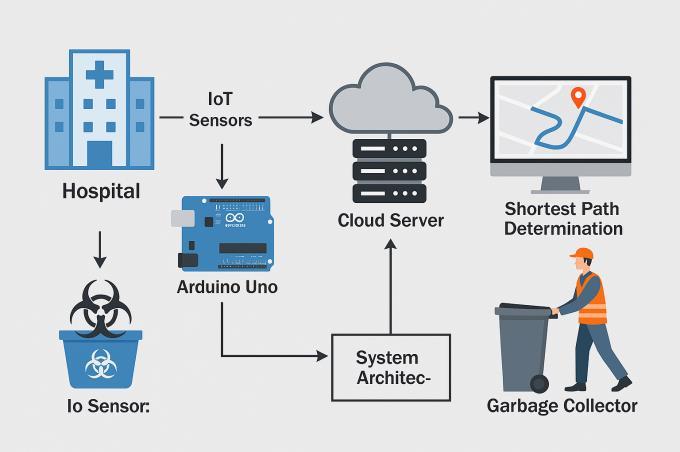
The integration of the various hardware and software componentswithinthemedicalwastemanagementsystem ensures seamless communication and real-time data flow. This integration enables automatic updates and alerts to relevant personnel, reducing manual intervention. Compatibility between modules such as communication devices (WiFi, GSM) and the central controller ensures stable operation across multiple locations. The user interface enhances decision-making accuracy for waste collection.
The system is designed with scalability in mind, allowing for easy expansion across larger healthcare networks. New bins can be integrated with minimal configuration flexible hardware architecture. The use of cloud-baseddatastorageandprocessingenableshighdata volume management without performance degradation AdditionalfeaturessuchaspredictiveanalyticsorAI-based optimizationinthefuture.Thus,thesystemsupportslongterm adaptability and broader implementation in diverse healthcareenvironments.
The implementation phase transforms the theoretical systemarchitectureintoa workingsolution bycombining hardware components, firmware, communication protocols, and user interfaces. Each subsystem is methodicallydevelopedandtestedtoensurereliablerealtime monitoring, data transmission, and user engagement through web-based platforms. The following subsections highlightmajorareasofimplementation.
Various sensors are strategically embedded within the medical waste bins to collect diverse environmental and operational data.Ultrasonic sensorsmeasurethefilllevel, infrared sensors serve as backups, load cells determine bin weight, and gas/air quality sensors detect hazardous conditions.Thesesensorsarevitalformaintainingsystem accuracyandresponsiveness.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Microcontrollers such as the Arduino Uno/Mega and ESP32/ESP8266 are responsible for gathering data from sensorsandmanagingbasic processing.These devicesact as intermediaries, collecting sensor data and transmitting it to the web platform or server. They also support multiple interfaces, enabling compatibility with various sensorsandcommunicationmodules.
3.3
Reliable communication is established using GSM modules (SIM800L), WiFi modules (ESP8266/ESP32), LoRa for long-distance coverage, and Bluetooth for localized configuration. These modules ensure that realtime data from the sensors reaches the central system or cloud storage securely, facilitating prompt actions based onsystemconditionsandthresholds.
3.4
Thehardwarecomponents arepoweredusingregulated 5V/12V sources, rechargeable Li-ion batteries (18650), and optionally, solar panels for sustainable outdoor installations.Abatterymanagementsystemensuressafety and longevity, while voltage regulators and power monitoring circuits safeguard the electronics from overvoltage,under-voltage,orshort-circuitissues.
3.5
Acustomwebapplicationisconfiguredtodisplaysensor data in real time, notify staff when bins are full, and provide historical insights. The interface supports user authentication, location mapping, and dashboard visualizations. This improves the system’s usability and helps administrators manage waste collection proactively andefficiently.
After assembly, the system undergoes comprehensive testinginsimulatedandreal-worldenvironments.Testing parameters include sensor accuracy, communication latency, and fault tolerance. Successful validation ensures that the system is robust, scalable, and ready for deployment in healthcare facilities with minimal failure rates.
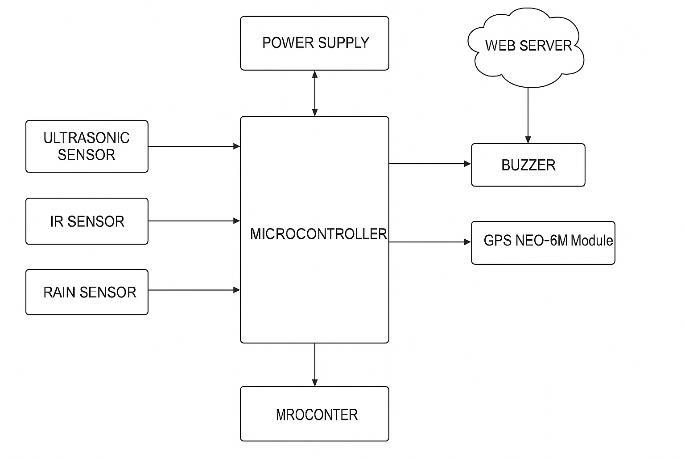
3.7 Bolck Diagram Components
Power Supply: Provides the necessary electrical energy to all hardware components, ensuring stable operation of the microcontroller, sensors, and communication modules under various environmentalconditions.
Ultrasonic Sensor: Measures the distance from the top of the bin to the waste level using sound waves, helpingdeterminehowfullthebinisinrealtime
IR Sensor: Detects the presence or motion of objects using infrared light, serving as a backup sensor for wasteleveldetectionandensuring accuratereadings eveninlowvisibility.
Microcontroller: Acts as the brain of the system, processing data from all sensors, triggering alerts, andmanagingcommunicationbetweenthehardware andcloud/webinterfaces.
GPS NEO-6M Module: Tracks and sends the exact geographic location of the waste bin, enabling authorities to locate, monitor, and schedule pickups efficiently.
Buzzer: Emits sound notifications in case of critical bin status, such as being full or detecting hazardous waste, improving system responsiveness and public awareness.
WebServer:Collectsanddisplaysreal-timedatafrom the microcontroller, allowing remote users to monitor waste bin conditions and receive notificationsthroughaninternet-connectedinterface.
The smart medical waste management system was tested in a simulated hospital environment. The sensors

International Research Journal of
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net
accurately detected the fill levels of medical waste bins usingultrasonicandloadcelltechnology.Oncethresholds were reached, the system successfully triggered real-time alerts via email and dashboard notifications, allowing authorized personnel to take timely action. The GPS moduleefficientlytrackedbinlocations,andupdateswere reflected instantly on the web interface, improving transparencyandcoordinationamonghospitalstaff.
Additionally, the integration of environmental sensors such as temperature, gas, and air quality detectors provided insights into the waste bin surroundings. This data not only helped monitor safety but also contributed to early detection of potential hazards. The role-based access control ensured that only designated individuals could modify the system status, maintaining operational security. Overall, the system enhanced efficiency, minimized risks, and showcased strong potential for scalabilityacrossvarioushealthcareinstitutions.
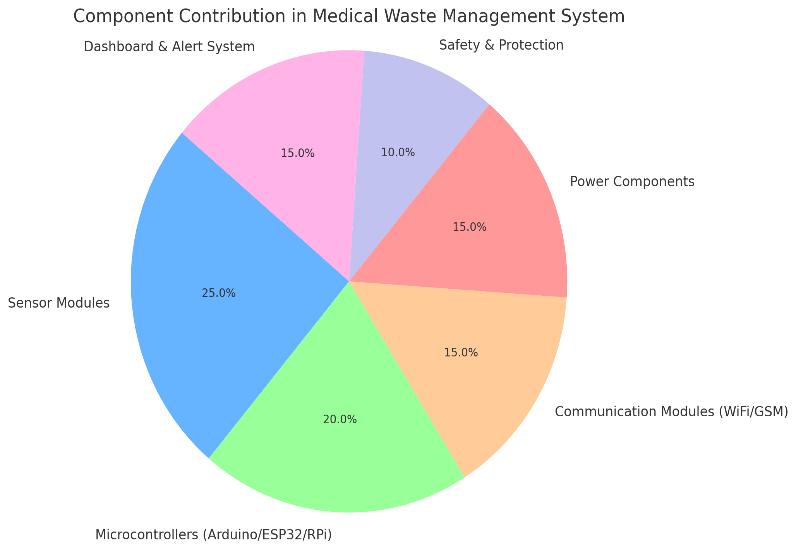
The above Chart represents the distribution of medical wastebinstatusesacrossthehospitalfacilityduringatrial period. A significant percentage of bins triggered alerts due to high fill levels or hazardous gas detection, demonstrating the system’s efficiency in identifying potential risks in real-time. This graphical insight helps stakeholders understand waste accumulation trends and take immediate action, ensuring a cleaner and safer hospitalenvironment.Additionally,thedatareinforcesthe importance of deploying intelligent sensors and centralized monitoring to streamline waste handling and reducemanualoversight.
This intelligent medical waste management system can be further enhanced with advanced analytics and predictive algorithms to forecast bin fill levels and optimize collection routes. Integrating AI and machine learning can enable pattern recognition for waste generation, helping hospitals plan resources more effectively. Additionally, expanding the system's compatibility with mobile applications and healthcare
2395-0072
information systems will promote wider adoption. Solarpowered units, blockchain for traceability, and multilingual interfaces are other innovations that can contribute to global scalability, environmental sustainability, and enhanced user accessibility in diverse healthcareenvironments.
Table 1
Thetableprovidesaconcisesnapshotofreal-timewaste bin data across different hospital zones, including fill levels,gaspresence,temperature,andcorrespondingalert statuses. For instance, the ICU bin is nearly full at 90%, with high gas detection and elevated temperature, triggering an emergency alert. In contrast, the General Ward shows moderate fill levels at 60% with no gas detection,requiringonlybasicmonitoring.
The Operation Theatre presents a critical 95% fill and medium gas levels, warranting a high-priority alert. This clear, organized format allows hospital staff to efficiently identify and respond to urgent waste management needs, promoting hygiene, safety, and streamlined operations withinthemedicalenvironment.
The system has wide applications across hospitals, clinics, diagnostic labs, and pharmaceutical industries, ensuring hygienic and efficient waste disposal. It can also be implemented in dental and veterinary centers and integrated into smart city frameworks, promoting realtime waste monitoring, sustainability, and enhanced publichealthandsafetystandards.
[1] Al Mamun M A, Hannan M A, Hussain A, Basri H, "Integrated sensing systems and algorithms for solid wastebinstatemanagementautomation," Sensors,vol.14, no.6,pp.10379–10395,2014.
[2] Zhang D, Cao Q, Zhou L, "Cloud-based waste management with real-time monitoring," International Journal of Cloud Computing, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 120–135, 2016.
[3] Folianto F, Low Y S, Yeoh W, "Smartbin: Smart waste managementsystem," IEEE TENCON,pp.1–4,2015.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[4] Sharma R, Gupta A, "Real-time medical waste monitoring for sustainability," Journal of Environmental Management,vol.18,no.4,pp.101–110,2020.
[5]WorldHealthOrganization,"Health-carewaste,"WHO, 2018.
[6] Adebayo P. V., "Smart waste bin monitoring using IoT for sustainable biomedical waste management," Environmental Science and Pollution Research, vol. 30, pp. 1–15,2023.
[7] Paul L., Mohalder R. D., Alam K. M., "An IoT Based Smart Waste Management System for the Municipality or City Corporations," arXiv preprint, arXiv:2411.09710, 2024.
[8]GhahramaniM.,ZhouM.,MolterA.,Pilla F.,"IoT-based Route Recommendation for an Intelligent Waste Management System," arXiv preprint, arXiv:2201.00180, 2022.
[9]LamK.N.,HuynhN.H.,NgocN.B.,NhuT.T.H.,ThaoN. T., Hao P. H., Kiet V. V., Huynh B. X., Kalita J., "Using Artificial Intelligence and IoT for Constructing a Smart TrashBin," arXiv preprint,arXiv:2208.07247,2022.
[10] White G., Cabrera C., Palade A., Li F., Clarke S., "WasteNet: Waste Classification at the Edge for Smart Bins," arXiv preprint,arXiv:2006.05873,2020.
[11]AdebayoP.V.,"SmartwastebinmonitoringusingIoT for sustainable biomedical waste management," ResearchGate,2023.
[12] "Smart waste bin monitoring using IoT for sustainablebiomedicalwastemanagement," Leeds Beckett University,2023.
[13] "Smart Waste Management System using IOT," ResearchGate,2020.
[14] "IoT based biomedical waste classification, quantificationandmanagement," ResearchGate,2018.
[15] "Intelligent waste management system using deep learningwithIoT," ScienceDirect,2020.