International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Nirmal Chodavadiya1 , Darshil Kanpariya2 , Kapu Chodavadiya3
1Dept. of Textile Engineering, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, India 2Dept of Civil Engineering, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, India 3Bachelor of Business Administration, Saurashtra University, Amreli, India ***
Abstract - For many years, the industrial world has benefitedgreatlyfromtheuseofautomation.Highdegrees ofrepeatabilityandaccuracyinproductiontoolsaswellas high levels of consistency and precision in work items have been required. Only for production in high volumes can economic justification be demonstrated. We need robotics-based adaptive manipulation systems to accomplishthis.Roboticsisnolongeranichesubject;itis now a global one! As a result, the use of robotics in both theindustrialsectorandthetextileindustryhasproduced notableadvantages.Roboticsinthetextileindustryisused to reduce labor-intensive procedures that need a lot of human work. Robotics and automation are frequently synonymsinthetextilebusinesstoday.
Key Words: - Robotics, Automation, Textile Industry
In the world request, survival in the competition of vesture assiduity depends on the advanced technology, robotization and robotics, which are used from the designing to product process and product transportation of the assiduity. There's no mistrustfulness that robotization can increase product effectiveness, reduce the number of faults and reduce the overall cost of product. The global demand for quality apparel, low product costs and competitive advantage can be achieved through robotization relinquishment. In numerous developing countries, budget constraints help garment manufacturers from espousing advanced technology. But forthevestureassiduitytosurviveintherequest,itneeds tobesuitabletoproducefurtherindefectibleproductsina lower time and at a lower cost. Operation of robotics and robotization in the cloth assiduity had begun over two centuries alone when John Kay’s constructed the flying shuttle. The flying shuttle machine not only enabled an increase in product but also brought down the number of people needed to operate the weaving impend, from two toone.Thegeographicaldistributionintheclothassiduity has seen a dramatic shift in the once 50 times. Textile manufacturers have moved a proportion of their cloth product installations from homemade to robotization. In recent times, the operation of robotics has increased, coupled with the fleetly rising stipend in Asia, has seen some manufacturers made interested in the robotics product- grounded business model. It’s clear that cloth manufacturersareshiftingprecedence’storobotizationto
increase productivity and boost effectiveness. To achieve this,clothassiduityneedstoborrowroboticsrobotization, manipulation systems need to some artificial intelligence (AI). Robotization and robotics are two nearly analogous technologies. Principally, robotics is a form of artificial robotization. This composition will describe a wide range of robotization in cloth process by using robots which is eventually adding both introductory demand of cloth assiduity both productivity and effectiveness. Areas of robotics and robotization in Textile Industry There are several areas of robotization in the product of cloth accoutrements including the yarn and fabric manufacturing process. In this composition I'll try to concentrate on the operation of robotics and robotization in the cloth fabric manufacture process and garments product. These include Robotics in running of bales in blowroom,Roboticsinregistering,Roboticsinthesplicing in bus- corners, Robotics in cleaning of cloth assiduity, Robotics infabricrunning, FabricInspection,CAD&CAM, Fabric Spreading & Cutting, Sewing, Pressing, Material Handling & Radio frequency Identification (RFID) in robotization.
1.1
Samples of the bales are transferred to a grading laboratory for observation. After it has been entered, corroborate the quality of the payload incontinently. Also passing, each overload is moved by the conveyor to a lading station. Where it’ll be picked up by a robot and broughttothestorehouse.All thebalesinblowroomwill bestoredaimlesslyinracks andpositionofoverloadwith applicability overload number, weight, and fiber characteristics. When overload is being named for processing, it’ll be removed from the storehouse by a robot on a “first in, first out” base. Robotics in Carding Robot could be programmed to pick up cams from each card, place them on to a truck and transport them to a product area for drawing frame for conventional operation. This can give excellent cross blending and it’ll beaneasymatterforadrivertoclearthebarrelsfromthe touchintoadelineationframe.RoboticsinTheSplicingin Auto-CornersandOtherWindersEachtimethere’llbean endbreakorbobbinchange.Thisjoinstheyarnendswith a splice that’s nearly analogous to the yarn. The strength andextensionvaluesofthesplicedjointarenearlyalways similar,whichisrelatively90,withthoseoftheyarnitself. Rearmost automatic splicer arm is an act kind of robot. It
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
offers indeed better opening of the yarn ends and a more favorableimbricationinsplicingzone.
The products folding and quilting can be carried out by robots.Theycantakethegarment,foldit,andpackitduly. Itcanbeanautomaticorsemi-automaticsystem.
Theproductofnonwovenand3Dstructuresfordefensive apparels by using robotics is under development by the experimenters. Particularly, the combination of robotics andasmall-scalemeltblowingunitisalsopossible.

Lately, operation of robotics in cleaning of cloth assiduity hasbeenstartedwithamobilerobot.ArobotnamedMRP Nomad 200 can clean and polish of bottom shells in cloth assiduity.
Fabric handling tasks bear colorful tools and detectors in clothassiduity.Toaccommodatethesetasks,ATIArtificial robotization Gamma30/1 00 FIT detector is mounted at the robot arm. A tool changer is also mounted on the FT detector.Thecustom-erectedtoolrackprovidesspacefor a standard curvaceous gripper and other special end effectorsforfabricmanipulationintheclothassiduity.
RoboticsSimulatorinFabricHandlingTherobotsimulator allows running the robot control programs in simulation mode,withoutpenetratingtackle.
This is veritably effective for remedying robot programs without the threat of damaging the robot during fabric running. The driver can fluently navigate by using the mouse,opting,anddefiningcustomshoes
Fabric In automotive assiduity, realistic manipulation processes involve commerce of fabric corridor with other objects similar as work shells, robot manipulators, and other fabrics. That’s why the capability to model contact hadbeenenforced.
Ray slices are helpful to fabric slice. Among the colorful typescuttingtechnologiescomputer-controlledspotlights cutting system are suitable formulate-ply slice of heavy cloth accoutrements. It has been most extensively espousedtoincreasethemassproductinclothassiduity.
Preliminarily fabric examinations were performed in a homemade process, so numerous times blights could not be directly linked. The use of automated outfits helps to enhance the effectiveness of the fabric examination process. Fabric examination has proven to be one of the most delicate of all cloth processes to automate. Colorful fashion like Statistical Approach, Spectral Approach and Model grounded Approachcanbe espousedforautomatic fabric examination. In all these styles, the fabric image is manipulated by a software or modeling tool to prize information about the inflexibility of the fabric disfigurement. The linked blights are automatically linked on the fabric, if the quantities of blights in a fabric lot exceedacertainlimit,they'rerejected.
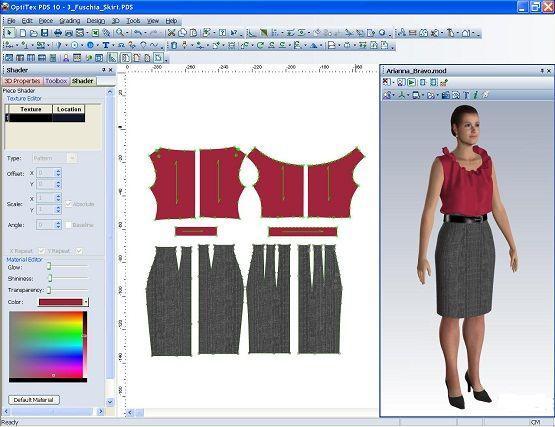
Fabric design was traditionally done by hand. To spend a lot of time and capture the design on paper. However, modern clothing factories create clothes using computeraided design (CAD) and manufacturing (CAM). Computer programmerscalledCADareusedtocreate3Ddesignsfor clothing, and CAD also transmits that data to CAM. Based on that data, CAM oversees and controls the production process.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Numeroustimesago,fabricspreadingwasdonemanually; workers spread the fabric by hand. It also needed more than one worker to complete the work. Also came the robotic machine, where one could operate the machine and get the job done. At present fabric spreading can be donewiththehelpofcompletelyautomaticmachines.This invention is very amazing and can be helpful in every textileindustry.Really,automationinFabricisimperative and has a high capability to produce massive amount of productionwithinafewtimes.Moreover,faultsmightalso belessenedwiththehelpofAutomation.
Most of the garment manufacturing process, particularly the sewing process, is still carried out by skilled employees in nations like Vietnam, Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos. Manufacturers haven't made much headway in acquiring Sewing Robots or automatic sewing machines, whichhashelpedkeeptheirinvestmentmodest.However, manufacturers who haven't made the investment in cutting-edge equipment face fierce rivalry to keep labor costs down. Artificial robots that can handle fabric during sewing conditions, where labour is not required, are now being built in preparation for the robotization of the sewing process. These autonomous devices form confluence in a manner like that of conventional sewing machines. Different sorts of sewing hurts, such as double chain, double cinch, and over cinch aches, can be created bysewingmachine

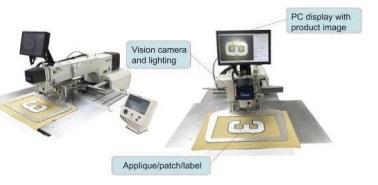
Prior to today, this operation was also carried out manually, however automatic fabric cutting machines are nowinuse.Asaresult,cuttingthefabricmoredirectlyand easily than before is conceivable. According to the pattern'sdesignforthegarment,itisnowsaveddirectlyin the computer's memory without being printed on marker paper. Following that instruction, the cutting machine instantlyandautomaticallycutsnumerouslayersoffabric together. In a similar manner, rays are used to perform thisslice.Whencomparedtomanuallyordriver-operated devices, the usage of automatic slice machines has decreasedboththenumberofworkersandtheamountof time.

The Sewbot is a commercial robot used in the clothing industryformanipulatingandgrabbingfabric.Therehave beenseveral testrunsemployingrobotstosewtheentire garment. Sewbot, a robot created by Zornow that can automatically handle fabric components during sewing, is one such example. Zornow created the "Sewbo" robot in 2015,whichcansewaT-shirtfrombeginningtoend.This accomplishment represented a significant step toward obtaining complete outfit automation at 100%. It is possible to programme the robot for a particular size and look. The robot must be reprogrammed if the clothing's sizeorstylechanges.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
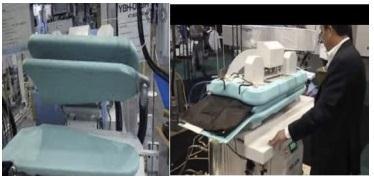
LOWRY SewBot is constructed by Atlanta grounded companyofUSA‘Softwarerobotization”,it’saspecialtype of robot that's designed for the vesture assiduity. These SewBots are erected using the advanced artificial4.0 revolution technology similar as computer vision or advanced robotics, which can analyze and manipulate the fabriclikemortal.SewBotscanperformmultiplegarments manufacturing tasks similar as Fabric Cutting, sewing, Awaking,labeling,examinationetc thisentireworkshopis controlledwithjustonetouchpanel.
Sewsbecauseitcanresultinhigh-qualityclothing.Philipp MollGmbH&Co.developed3DSewingTechnology,which could generate 3D Confluence automatically. A 3D sewing robotic arm was also developed in China, and it can quickly cut the garments and stitch the fabric pieces together using pre-programmed designs. The entire operationtakesjustafewblinkstocomplete.Thestitching of automobile interiors is currently done with 3D robotic arms. Clothing (trousers, coats, and shirts), auto seat covers, and airbag textiles can all be produced using 3D sewing technology. With the aid of this 3D technology, better-quality, more functional sewing goods can be produced.Theuseof3Dstitchingtechnologysignificantly boostsproductivityandlowerslabourexpenses.
One of the crucial stages to improve the product's appearance before it is delivered to the consumer is pressing. Any creases in the garment are removed throughout the pressing process to ensure that it looks good when the consumer purchases it. Finding and keepingskilledstaffforurgentoperationsisneveraneasy task.
Robotizationandroboticsarenowextensivelyusedinthe cloth sector. In the cloth assiduity, significant robotics improvements are formerly being made. Still, the sectors that produce fabrics don't use mass produce. There are frequently smaller studies on robots and robotization in cloth manufacturing. As a result, the use of robots in the cloth sector has not swerved significantly from standard running, assembly, welding, slice, and other processes. As a result,ourclothmanufacturermustmakethenecessary investments and take the necessary conduct to further probetheuseofroboticsintheclothassiduity.
We now understand that robotics and automation are essential for boosting production and prosperity in the textile and clothing sector, as was covered above. The sooner robotics and automation are introduced into the textile and garment industries, the more benefits are available to us. Therefore, the textile and garment industries cannot compare robotics and automation to remaininthecurrentcutthroatmarket.
1. https://www.textileblog.com/application-ofrobotics-in-textile-industry/
2. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1023/A:102 6194432448
3. https://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journa l/paperinfo?journalid=220&doi=10.11648/j.ijmea .20130101.13
4. https://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journa l/paperinfo?journalid=220&doi=10.11648/j.ijmea .20130101.13
5. https://www.academia.edu/49639357/Robotics_ and_Automation_in_Textile_Industry
6. https://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/journa l/paperinfo?journalid=220&paperId=6001724


When operators reach a certain level of proficiency, they move on to other industries in search of higher pay. As a result, this industry is lacking skilled people. By implementing automation strategies in the critical sector, these issues can be resolved. Presently being sold commercially are several cutting-edge technologies like pressing robots, jacket finishers, shirt finishers, and shirt pressers.
Mr. Nirmal A. Chodavadiya

StudentofTextileEngineering, ThemaharajaSayajirao University,Baroda.
Mr. Darshil Kanpariya
StudentofCivilEngineering, ThemaharajaSayajirao University,Baroda.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page44


