
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Md Zuhaib1, Mohit2, Mahesh Kumar Hans3 , Dr. Jyoti Kaushik4
1, 2, 3, 4Dept of Computer Science, Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, Delhi, India
Abstract - The healthcare industry faces challenges related to patient care, resource allocation, and technical infrastructure. To address these issues, we propose an AIbased chatbot that can analyze illnesses, provide essential information, and reduce healthcare costs. Our chatbot leverages Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to simulate conversations with users. By storing data in a database, the chatbot identifies user queries and responds appropriately. In this paper, we aim to create a fully functional chatbot that assists patients by analyzing symptoms, providing medicine information, and answeringgeneralhealthcarequestions.
Key Words: Chatbot, Healthcare, AI, NLP, Symptoms.
1.INTRODUCTION
Chatbots are transforming consumer interactions for businesses in several industries, such as finance, ecommerce, healthcare, and customer support, in the current digital age. Chatbots in customer service are skilled at answering simple questions and giving timely answers. Because of this efficiency, customer representatives can concentrate on more intricate issues. Chatbots are crucial to e-commerce because they may makeproductrecommendations,trackorderstatuses,and assistcustomers.
The emergence of chatbots has had a major impact on the healthcare industry. By providing personalized health advice and medication and appointment reminders, these automated solutions increase patient participation and reduce administrative tasks. With chatbots, patients may manage their health more actively by receiving personalized help and insightful information. Additionally, they improve operational effectiveness, which results in improvedpatientoutcomesallaround.
Chatbotsarearelativelynewtechnology,butbecauseof their capacity to engage patients more effectively and enhance healthcare results, they have swiftly established themselvesasastandardintheindustry.Therehavebeen several significant advancements in the realm of chatbot development.
In2016,theNationalHealthService(NHS)oftheUnited Kingdom introduced "Ask NHS," an AI chatbot developed by the American startup Sensley. This chatbot, which was initiallyonlyavailabletopeopleinNorthLondon.
In 2017, the British healthcare startup Babylon Health unveiled "GP at Hand," an AI-powered chatbot that providedremotepatientdiagnosisandtreatment.
In 2018, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorized "Woebot," the first AI chatbot created to provide cognitive-behavioural therapy to assist people in managing mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
In 2019, the well-known US healthcare facility Mayo Clinic introduced "Mayo Clinic First-Aid," a chatbot designed to help find emergency medical services and offeremergencyfirst-aidadvice.
The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused a spike in the use of chatbots in the healthcare industry. Chatbots were used by healthcare providers to help with remote consultations and to spread information about the virus, symptomchecks,andtestinglocations.
The year 2020 saw a surge in chatbot usage within healthcare due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Healthcare providers deployed chatbots to disseminate information aboutthevirus,symptomchecks,andtestingsites,aswell astofacilitateremoteconsultations.
Developing a healthcare chatbot comes with its own set of challenges, such as safeguarding data privacy, ensuring the accuracy and dependability of the information provided, comprehending natural language, managing intricate scenarios, keeping users engaged, considering ethicalissues,integratingwithexistinghealthcaresystems, and replicating the empathy and personal touch of human interaction.Addressingthesechallengesrequiresstringent privacy protocols, current medical knowledge, advanced natural language processing capabilities, flexible conversational interfaces, ethical AI practices, smooth integration with current systems,anda harmonious blend ofAIandhumanoversight.
MEDICHAT stands as a cutting-edge chatbot that leverages user symptoms to forecast potential health conditions and suggests subsequent actions for users.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Utilizing advanced natural language processing and machine learning techniques, MEDICHAT meticulously interpretsthesymptomsinputbyuserstoprojectpossible illnesses. Following the analysis, it provides customized advice, ranging from self-care tips and home remedies to recommendations for professional medical consultation. This innovative chatbot significantly improves service accessibility, equips users with the knowledge to make enlightened health choices, and plays a crucial role in the prompt identification and handling of health issues by offering precise, individualized advice derived from symptomevaluation.
The importance of machine learning in forecasting, recognizingpatterns,andminimizingerrorsacrossvarious sectors is underscored, highlighting AI’s expansive influence. Techniques in data mining are proposed for forecasting disease prevalence from healthcare data symptoms. Accurate forecasts are instrumental for healthcare entities to preempt medication shortages and guaranteetimelypatientcare.
The function of Intelligent Decision Support Systems (IDSS) in monitoring healthcare, particularly concerning cardiac diseases, is examined. Findings suggest that IDSS markedly augments decision-making processes in ambiguous medical situations, thereby substantially enhancingbothmonitoringandtreatmentmeasures.
Furthermore,theapplicationofIndependentComponent Analysis (ICA) and an HDFS-based algorithm is employed to reduce the complexity of large-scale patient data sets. This approach involves the elimination of non-essential data, leading to reductions in both storage needs and computational demands, all while achieving greater precisionthanthatofPrincipalComponentAnalysis(PCA).
This research delves into the diverse array of conversational agents utilized in chronic disease management, scrutinizing their foundational communication technologies, performance evaluation metrics,andartificialintelligencemethodologies.However, the review does not thoroughly address the ethical implications and potential hazards that may arise from deployingchatbotsinthementalhealthsector.
The study underscores the imperative for flexibility in embracing the burgeoning realm of chatbots and artificial intelligence infrastructures. Nevertheless, the relatively modest size of the study's sample curtails the broader applicability of its conclusions, signaling the necessity for furtherinvestigationwithamorevariedcohort.
An inquiry employing diaries and interviews was conducted to discern public attitudes towards chatbots possessing distinct personas, particularly in the context of health information seekers. The focus of this study is predominantlyonuserperceptions,withanotableabsence
of concrete metrics to gauge the effect of chatbot interventionsonthewelfareoftheelderly.
Aconcisehistoricalexaminationispresented,chronicling theprogressionanddesigncharacteristicsofchatbots.Yet, this overview falls short of adequately discussing the privacyandsecurityissuesthatcouldemergefromchatbot interactionsinthemanagementofconfidentialhealthdata.
Theambitionofanotherstudywastodissectthecurrent applications, challenges, and literature gaps concerning conversational agents in healthcare. The brevity of the study period, however, means that the enduring consequences of chatbot-mediated medication reminders remainuncharted.
One chatbot demonstrated proficiency in evaluating the presence and intensity of depression and anxiety symptoms, including the potential for suicidal thoughts. However, the study did not incorporate the viewpoints of healthcare practitioners, which could shed light on the practicality and assimilation of chatbot technologies in primarycareenvironments.
The aim of a different study was to appraise the data collectioncapabilitiesofextantchatbotsymptomcheckers. A notable deficiency of this study is the absence of a comparative assessment with human medical professionals, which hampers the ability to ascertain the trueprecisionanddependabilityofthesechatbots.
An article offering a viewpoint sought to succinctly summarize research on the utilization of chatbots to encourage physical activity and a nutritious diet. The study'sconcentrationisprimarilyonuserinvolvementand contentment,yetitdoesnotcomprehensivelyevaluatethe influence of chatbot interventions on modifications in healthbehaviors.
An examination was undertaken to understand how conversational agents are perceived in terms of their trustworthiness. This studyis confined to qualitative data, lacking quantitative analysis that could provide deeper insight into the efficacy of chatbot interventions amidst mentalhealthemergencies.
Lastly, the systematic review method employed in one articleadherestothePRISMAchecklistprotocol.However, this review does not extensively delve into the obstacles andconstraintslinkedwiththeintegrationofchatbotswith anarrayofhealthmonitoringdevicesandtechnologies.
3.1 Proposed approach
In the realm of healthcare, the advent of artificial intelligence has paved the way for innovative tools like

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Chatbots, which promise to revolutionize patient support by offering continuous, personalized assistance. The healthcare sector’s current infrastructure often falls short in meeting the immediate needs of patients, leading to prolonged wait times and escalating expenses. To address these issues, the development of a healthcare Chatbot namedMEDICHATisproposed.ThisChatbotisengineered to leverage the decision tree algorithm, renowned for its clarity and versatility in handling diverse data types, to engagewithpatientseffectively.
MEDICHAT is envisioned as a digital assistant that operatesaroundtheclock,providingmedicalguidanceand support. It is designed to analyze patient queries, considering their symptoms, medical background, and personal preferences, to furnish responses that are both customized and immediate. The goal of MEDICHAT is to alleviate the strain on healthcare resources, enhance patient health outcomes, and streamline the collection of healthcaredata.
Thecoremissionofthisinitiativeistoforgeahealthcare Chatbot that stands as a beacon of medical support for patients.Itisnotjustaprogram;it’sanAI companionthat converseswithpatientsandhealthcareprofessionalsalike, offering solutions that are tailored to individual needs. By harnessingthedecisiontreealgorithm’spower,MEDICHAT aims to transform the landscape of patient care, making it more accessible, efficient, and responsive to the unique demandsofeachpatient.
Toenhancethepatientexperiencewithinthehealthcare domain, the following steps are proposed for the creation ofasophisticatedChatbotinterface:
1. Crafting an Intuitive Chatbot Interface**: The design focus will be on an intuitive interface for the Chatbot, enablingpatientstocommunicatetheirhealthconcernsin everyday language. This approachable design will facilitate a seamless interaction, encouraging users to share their symptoms without the constraints of medical jargon.
2.IncorporatingAdvancedNaturalLanguageProcessing (NLP):Byintegratingcutting-edgeNLPmethodologies,the Chatbotwillbeadeptatdecipheringtheintricaciesofuser input.Thisincludesrecognizingthesubtletiesandcontext behind the symptoms described, ensuring a nuanced understandingofpatientcommunication.
3. Developing a Predictive Machine Learning Framework: A robust ML architecture will be established, drawing upon extensive symptom datasets and medical insights. This framework will be calibrated to identify potential health conditions with remarkable precision, therebysupportinginformedhealthcaredecisions.
Theseinitiativesaim tobridgethegapbetweenpatients and healthcare access, providing a reliable and efficient avenueformedicalconsultationandsupport.
Flow Diagram
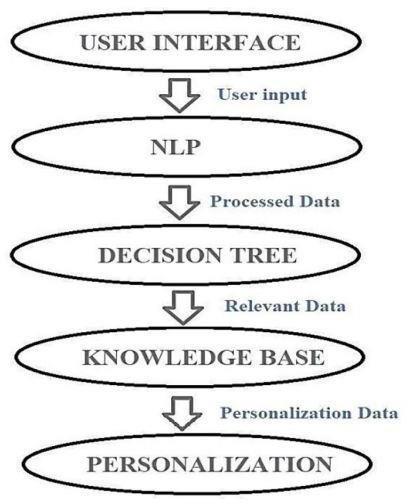
Figure 1. FlowChart.
Inthehealthcarechatbot system, the UserInterface module is the initial point of contact, capturing and forwarding user inputs to the Natural Language Processing (NLP) module. This module is adept at interpreting the input and transforming it into structured data, which is then conveyed to the DecisionTreemodule.
Utilizing the Classification and Regression Tree (CART) algorithm, the Decision Tree module evaluates the data and formulates suitable responses. It may also engage with the Knowledge Baseandaccessthepersistenthealthcaredata.
Moreover,thepersonalizationmoduleleveragesthe DecisionTree'soutputalongwithindividual datato tailor the responses more closely to the user's preferences.
The decision-making process is intricate, consideringthedecisiontree'sarchitecture,thepreset hyper-parameters, and the extensive knowledge base to ascertain the most fitting and precise responseforeachinquiryposedbytheuser.
This diagram offers a bird's-eye view of the interplay among the various modules User Interface, NLP, Decision Tree, Knowledge Base, and Personalization culminatinginthechatbot'sability to deliver responses that are both accurate and customizedtotheuser'sneeds.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Architecture
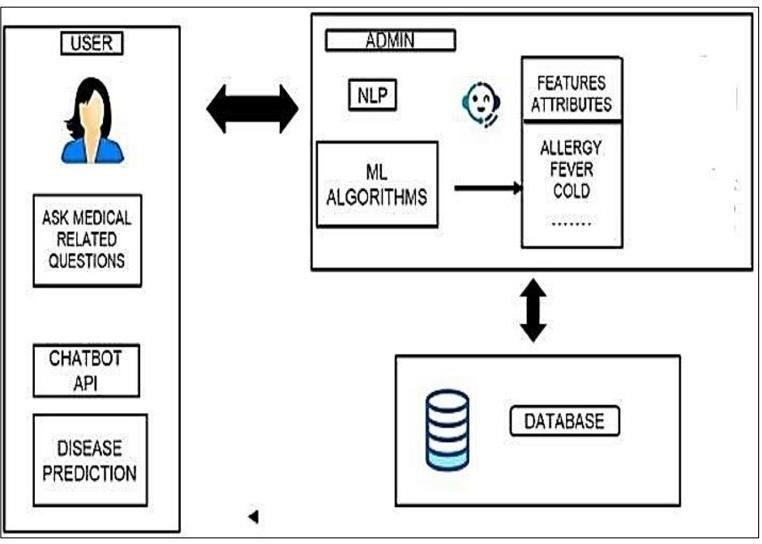
TheMEDICHAThealthcareChatbot'sstructureiscrafted to ensure fluid interaction and astute decision-making capabilities. It adopts a client-server framework, with the client embodying the user interface or the Chatbot application, and the server accommodating the backend mechanisms that process inputs and craft responses. Belowarethepivotalelementsofthisarchitecture:
Client-Side: This facet of the architecture denotes the user interface, which serves as the conduit for userinteractionswiththeChatbot.
Server-Side: The server-side houses the core infrastructure of the healthcare Chatbot, enabling backendfunctionalities.
NLP Processing: At the heart of the server-side, the Natural Language Processing (NLP) component is integral for understanding and processing user communications.
Decision-Making:Thiscomponentistaskedwiththe critical role of dissecting user queries and formulatingfittingresponses.
Knowledge Base: Serving as a wellspring of healthcare information, the knowledge base componentisacomprehensiverepository.
Personalization: Concentrating on enhancing user experience, the personalization component adapts theChatbot'sresponsestoalignwithindividualuser profiles.
4.1 Dataset description
The "Disease Symptom Prediction Dataset" available on Kaggleisapivotalassetforthoseinthefieldofdatascience and healthcare, offering a foundation for crafting precise disease symptom prediction models. This dataset aggregatesadiversearrayofhealthrecordsandsymptoms from a broad patient base, which is instrumental in constructingresilientpredictivealgorithms.
Contained within this dataset are anonymized patient entries, each comprising a set of attributes including demographic details, medical antecedents, and reported symptoms. These attributes are meticulously selected to encapsulateessentialdatathatcouldimpacttheemergence of particular disease symptoms. As machine learning technologies continue to advance, this dataset presents a chance to train algorithms that can discern intricate patterns and correlations. Analytical techniques such as decisiontrees,randomforests,logistic regression,support vector machines (SVM), and neural networks are among thetoolsthatcanbeemployedtoexaminethisdatasetand createpredictivemodels.
ThedatasetisorganizedintofourCSVfiles:
1. Symtom_severity.csv: This file catalogues symptoms alongside their frequency within the dataset, arranged in twocolumns.
2. Symtom_Description.csv: This file pairs diseases with theirrespectivedescriptionsacrosstwocolumns.
3. Symptom_precaution.csv: This file, with five columns, lists diseases followed by four columns of corresponding precautions.
4. Dataset.csv: This extensive file features diseases and theirassociatedsymptoms,spanningnearly5000entries.
The utility of disease symptom prediction models derivedfromthisdatasetismanifoldwithinthehealthcare sector. Practitioners can harness these models to better understand the likelihood of symptom manifestation, which can lead to timely interventions and tailored treatmentstrategies.Additionally,thesemodelsareaboon forresearchersaimingtopinpointpatientsatelevatedrisk, streamline resource distribution, and enhance the efficacy of healthcare services. In essence, the Disease Symptom Prediction Dataset from Kaggle is an invaluable tool for generating models that can foresee disease symptoms, empowering researchers, and healthcare professionals to unearth novel insights into the intricate nexus of patient characteristics and symptom development, thereby refining diagnostic processes, therapeuticapproaches,and patientcareoutcomes.
The healthcare chatbot, named MEDICHAT, is designed toreceivesymptomsfromusersasinputandthenprovide apredicteddiagnosisalongwithrecommendedactions.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
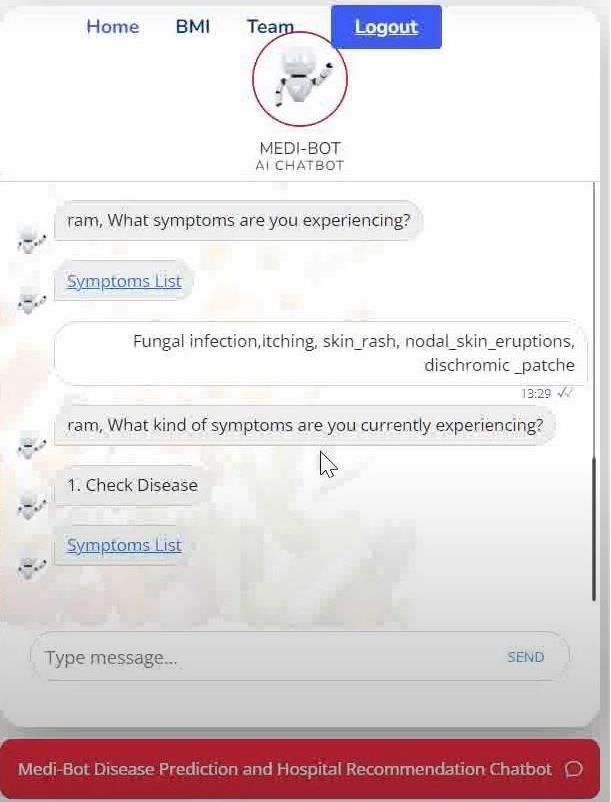
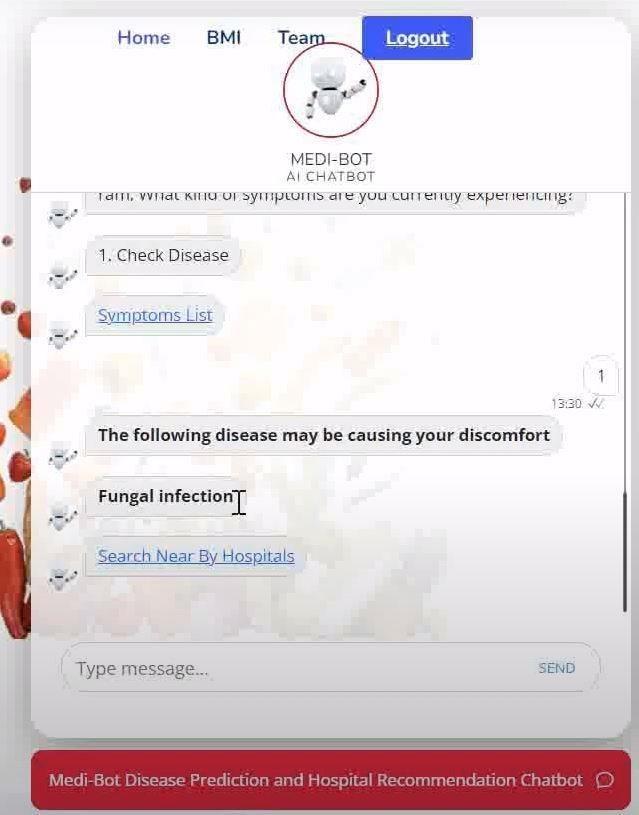
The chatbot MEDICHAT is engineered to aid individuals byevaluatingtheirreportedsymptomstoidentifypossible health conditions. Upon processing the input from users, MEDICHAToffersaconjectureontheprobableailmentand suggestscorrespondingactionstotake.
The chatbot's output encompasses two primary elements: the conjectured ailment and the action recommendations. The conjectured ailment is deduced from the user's described symptoms, utilizing a comprehensive database or an algorithm to ascertain the closest matching condition. For instance, inputting symptoms like fever, cough, and a sore throat might lead MEDICHATtosuggestthattheusercouldbesufferingfrom the'CommonCold'or'Influenza'.
Moreover, MEDICHAT provides a compilation of action recommendations tailored to the conjectured ailment, aimedathelpingtheusermanagetheconditioneffectively. These recommendations could range from general guidance to specific steps, lifestyle changes, or suggested medications. For example, if MEDICHAT surmises that the user is likely experiencing a 'Common Cold', it might recommend rest, hydration, over-the-counter remedies andmaintaininghygienetocurbthevirus'sspread.
It iscrucial to recognize thatMEDICHAT’s outputserves merelyasaguideandisnotareplacementforprofessional medical consultation. Users are advised to consult healthcare professionals for a precise diagnosis and tailoredtreatmentplans,consideringtheiruniquemedical historyandcurrenthealthstatus.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 05 | May 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
MEDICHAT is a cutting-edge, intuitive digital assistant crafted to support individuals in evaluating their health symptoms, forecasting possible medical conditions, and suggesting appropriate actions. Users can input their symptoms into the chatbot to gain insightful advice and guidance for a better grasp of their health status. Leveraging advanced machine learning techniques and an extensive database of medical knowledge, the chatbot scrutinizes the user's symptoms. It utilizes a decision tree approach to forecast the most likely illness corresponding tothereportedsymptoms.Thisfeatureofearlyprediction fosters prompt intervention, enhancing overall health management.
Following the prediction of an illness, MEDICHAT presents a suite of preventive recommendations and actions.Thesesuggestionsmayencompasschangesindaily habits, proposed treatments, self-care tips, and strategies for prevention. The chatbot ensures that the information regarding these recommendations is precise and current, providing users with dependable health management advice. Additionally, MEDICHAT functions as a comprehensiveeducationalplatform,furnishinguserswith in-depth knowledge about various health conditions. It underscores the significance of active health care engagement, offering advice on preventive measures, cultivating healthy routines, and promoting overall wellbeing.
[1] SK Tan and SC Chong, “Personalized Healthcare: A Comprehensive Approach for Symptom Diagnosis and Hospital Recommendations Using AI and Location Services” in Journal of Informatics and Web Engineering ,2024,pp5-8.
[2] Z. Ni and M. L. Peng, “Implementation of Chatbot Technology in Health Care: Protocol for a Bibliometric Analysis” in Proc. of the 2nd Global Conf. on Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare,Italy,2024,pp5-7.
[3] L. De Angelis and F. Baglivo, "Artificial Intelligence Chatbots for Medical Training in PublicHealth:ATooltoExplore,"in Proc. ofthe 7thAnnualConf. onInnovations inPublicHealth Education, Rome,Italy,2023,pp.4-5.
[4] G.KarunaandG.GowthamiReddy,"Helpi –An Automated Healthcare Chatbot," Proc. of the 5th Int. Conf. on Healthcare Informatics New Delhi,2023,pp.2-5.
[5] Wang X, Sanders HM, Liu Y, Seang K, Tran BX, Atanasov AG, et al. "ChatGPT: promise and
challengesfordeploymentinlow- andmiddleincome countries." in Lancet Reg Health West Pac., 2023,pp4-10.
[6] Li H, Moon JT, Purkayastha S, Celi LA, Trivedi H,GichoyaJW."Ethicsoflargelanguagemodels in medicine and medical research" in Lancet DigitHealth.2023,pp10-13.
[7] Howard A, Hope W, Gerada A. "ChatGPT and antimicrobial advice: the end of the consulting infection doctor?" in Lancet Infect Dis., 2023;23(4),pp4-6.
[8] Zheng Y, Wang L, Feng B, Zhao A, Wu Y. “Innovating healthcare: the role of ChatGPT in streamlining hospital workflow in the future.” In Ann Biomed Eng. Preprint posted online, 2023,pp5-10.
[9] Sajjad M, Saleem R. "Evolution of healthcare with ChatGPT: a word of caution." in Ann BiomedEng. ,2023,pp6-10.
[10] Cascella M, Montomoli J, Bellini V, Bignami E. "Evaluating the feasibility of ChatGPT in healthcare: an analysis of multiple clinical and research scenarios." in J Med Syst. ,2023, pp 413.
[11] Sallam M. "ChatGPT utility in healthcare education, research, and practice: systematic reviewonthepromisingperspectivesandvalid concerns."in Healthcare(Basel). 2023,pp6-7.
[12] NiZ,WuB,YangQ,YanLL,LiuC,ShawRJ."An Health intervention to improve medication adherence and health outcomes among patients with coronary heart disease: randomized controlledtrial."in J Med Internet Res.,2022,pp7.
[13] NaveenD,SatishK,DebmalyaM,NiteshP,Lim WM. "How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines." in J Bus Res., 2021,pp13-15.
[14] V. Shinde and A. Akhade, "Healthcare Chatbot System Using Artificial Intelligence," Proc. of the 3rd Int. Workshop on AI in Health, San Francisco,CA,USA,2021,pp.11-13.
[15] Feng H, Zou Z, Zhang Q, Wang L, Ouyang YQ, Chen Z, et al. "The effect of the group-based Otago exercise program on frailty among nursing home older adults with cognitive impairment"in GeriatrNurs.2021,pp9-13.