
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Sagar Y. Kumbhar1, Omkar Patil2, Truptali
Aundhkar
3, Sakshi Shinde4, RahulChougule5
1Assistant Professor, E&TC Engineering Department, D. Y. Patil Technical Campus, Faculty Of EngineeringAnd Faculty Of Management, Talsande, Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India. 2345Student, E&TC Engineering Department, D. Y. Patil Technical Campus, Faculty Of Engineering AndFaculty Of Management, Talsande, Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India.
ABSTRACT: The escalating demand for uninterrupted power supply (UPS) solutions, coupled with the imperativeforsustainableenergysources,hasledtothe emergenceofhybridUPSsystemsintegratingrenewable energy inputs. This paper presents the design and implementation of a novel Intelligent Hybrid UPS Charging System (IHUCS) leveraging solar and wind energy. The proposed system integrates advanced power electronics and intelligent control algorithms to efficiently manage energy flow, ensuring reliable UPS operationwhilemaximizingtheutilizationof renewable resources. This research offers a promising solution for critical applications in remote or off-grid locations, contributing to the reduction of carbon footprint and dependenceonconventionalenergysources.
KEYWORDS: UPS, Renewable sources, Actuator, Microprocessor,Enginehead,Solar,Wind,Hybrid.
In today’s dynamic energy landscape, ensuring uninterrupted power supply is paramount for various sectors, ranging from critical infrastructure to everyday households.UninterruptedPowerSupply(UPS)systems serveasacruciallineofdefenceagainstpoweroutages, safeguarding operations and preventing data loss. However, the reliance on conventional UPS systems powered by non-renewable energy sources poses sustainability challenges and contributes to carbon emissions.
To address these challenges, the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind energy, into UPS systems has gained traction. This integration not only aligns with global efforts to transition towardssustainableenergysolutionsbutalso offers opportunities to enhance energy resilience and reducedependencyonfossilfuels.
SmarthybridUPScharging systemsrepresenta pioneering approach in this domain, leveraging the complementary attributes of solar and wind energy to ensure continuous and sustainable power supply. By intelligently combining these renewable energy sources with conventional UPS infrastructure, smart hybrids systems aim to optimize energy utilization, minimize
environmental impact, and enhance overall system reliability.
This research paper aims to explore the design, implementation, and performanceevaluation of a smart hybrid UPS charging system that harnesses solar and wind energy. Through a comprehensive analysis of existingliterature,simulationstudies,andreal-worldcase studies, this paper seeks to elucidate the feasibility, benefits, and challenges associated with integrating renewableenergysourcesintoUPSsystems.
This integration of solar and wind energy into UPS systems not only holds promise for reducing carbon emissions and operational costs but also contributes to building a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure. By sheddinglightonthe potential of smart hybrid UPSchargingsystems,thisresearchendeavoraims to catalyse further advancements in renewable energy integrationandpavethewaytowards a moresustainable energyfuture.
Dr. Emily Jones, Dr. Michael Smith[1] Investigated the technical feasibility and economic viability of Integrating solar panels into UPS systems, emphasizing potential energy savings andenvironmental benefits.
Dr. Wei Wang, Dr. Xiaojun Liu[2] Focused on optimization techniques for hybrid renewable energy systems in UPS configurations, aiming to maximize efficiency and reliability through advanced optimization algorithms.
Dr. Raj Patel, Dr. Priya Sharma[3] Conducted a casestudy on the practical implementationofhybridUPS systems,evaluatingperformanceandeconomicviabilityof integratingsolarandwindenergyintoUPSsetups.
Herearetheobjectivesofthisproject
1. Feasibility Assessment: Evaluate the technical feasibility of integrating solar and wind energy

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
sources into UPS systems, considering factors such as resource availability, system compatibility, and energy conversionefficiency.
2. Efficiency Analysis: Analyz ether energy conversion efficiency of the hybrid UPS system, comparingitwithtraditional UPSsystems,todetermine its effectiveness in providing reliable backup power whileminimizingenergylosses.
3. Reliability Evaluation: Evaluatethe reliability and resilience of the hybrid UPS system under different operating conditions, including varying solar and wind energy inputs, grid fluctuations, and load demands, to ensurecontinuousanduninterruptedpowersupply.
4. Cost-Effectiveness Study: Investigate the economic viability of the hybrid UPS system by analyzing its lifecycle costs,including initial investment, operation, maintenance, and potential savings in electricity bills or diesel fuel expenses compared to conventionalUPSsolutions.
5. Environmental Impact Assessment: Quantify the environmental benefits of utilizing solar and wind energy in the UPS system, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, fossil fuel consumption, and dependenceonnon-renewableresources,tohighlightits contribution to sustainability and climate mitigation efforts.
6. Optimization Strategies: Explore optimization techniques and control algorithms to enhance the performance and efficiency of the hybrid UPS system, including maximum powerpoint tracking (MPPT), energy management algorithms, and adaptive control strategies tailoredto dynamic renewable energy inputs.
7. Technological Advancements: Review recent advancementsinrenewableenergytechnologies,energy storage systems, power electronics, and smart grid integration, and assess their potential impact on the designandoperationoffuturehybridUPSsystems.
1. Centre tapped Bridge Rectifier:

A centre-tapped bridge rectifier is a typeof full wave rectifier circuit commonly used in power supply applications to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current(DC).Itconsistsoffourdiodesarrangedin a bridge configuration, with a centre-tapped transformer secondarywindingprovidingtheinputACvoltage.
2. MPPTchargecontroller:


Fig.2:MPPTChargeController
MPPT charge controllers playcrucial role in maximizing theefficiencyandperformanceofsolar PV(photovoltaic) systems by continuously tracking and extracting the maximum power from the solar panels, thereby ensuring optimalenergyharvestandbatterycharging.
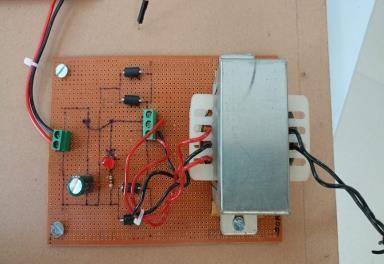
3. AutoChange OverUnit:
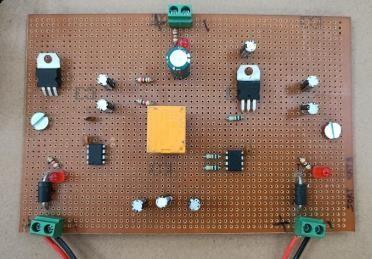

Fig.3:AutoChangeOverUnit
Anautochangeoverunitplays acrucialrole inensuringreliableanduninterrupted powersupplyto critical loads by seamlessly transitioning between multiple power sources based on real-time monitoring andintelligentdecision-makingalgorithms.
4. DC PowerSupplyMonitoring System:
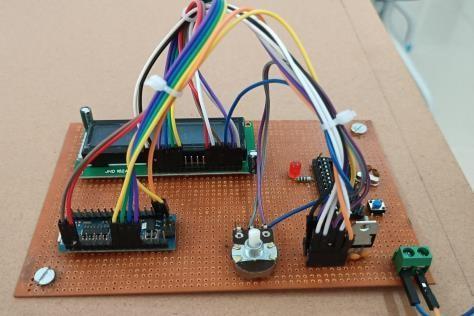

Fig.4:DCPowerSupplyMonitoringSystem

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
DC power supply monitoring system used for ensuring the reliability, efficiency, and safety of DC power supply systems by continuously monitoring key parameters, detecting faults, and providing real-time insights for proactive maintenance andmanagement.
5. BatteryBank:


Fig.5:BatteryBank
A12volt,12Ahbatterybankconsistsofoneormore12 volt batteries connected together to provide a specific voltage and capacity suitable forthis project, offering a balancebetweenvoltage,capacityandportability.
6. Compensator:


Fig.6:Compensator
A compensator for wind energy, also known as a power electronic compensator, is crucial component in wind energy conversion systems (WECS) that helps improve the stability, and reliability of the grid connectedwindturbines.
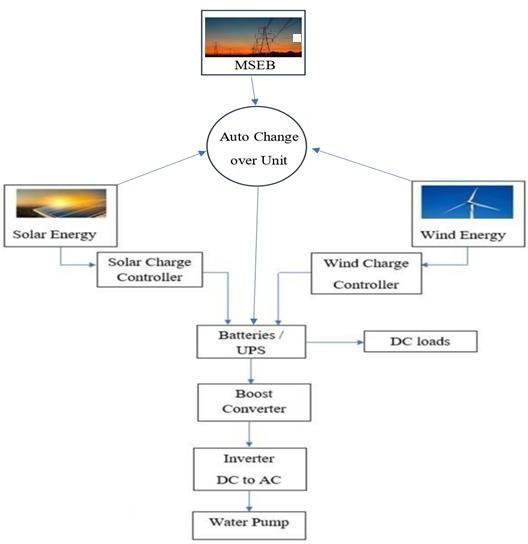
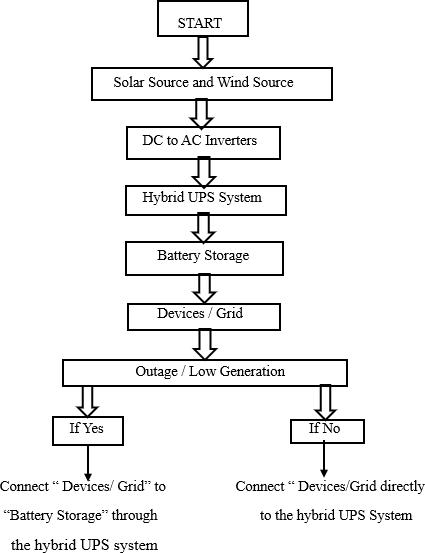
Smart hybrid UPS charging system leveraging solar and windenergyoperates byharnessing renewableresources to generate electricity while ensuring a stable power supply. Solar panels and wind turbines capture energy from the sun and wind, respectively, converting it into electricalpower.Achargecontrollerservesasthesystem’s nervecentre,efficientlymanagingthechargingofbatteries to prevent overcharging and effectively store surplus energy. Batteries act as energy reservoirs, storing excess power for use during periods of low renewable energy production or grid outages. An inverter then transforms

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
the stored DC power into AC power, suitable for powering electrical loads likeappliances and devices. Optionally, if the system is grid-tied, it can interface with the main electrical grid, facilitating energy export during surplus production and grid backup during energy deficits.Monitoringsystemscontinuallyevaluate system performance by monitoring various parameters, while dynamic control algorithmsoptimize energy flow toenhanceefficiencyandreliability.Thiscomprehensive approachensuresasustainableandrobustpowersupply while reducing dependence on non-renewable energy sources.


Fig.7:HardwareofProject
IX. RESULT
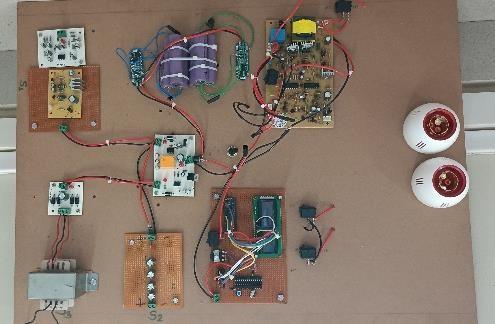

Fig.8:FinalResult
The low testing confirms the smart hybrid UPS system’sabilitytosustainpowerdelivery,showcasing itsrelianceonsolarandwindenergy integration.This underscores its effectiveness in providing uninterrupted power while minimizing reliance on conventionalsources.
Utilizing solar and wind energy reducesreliance on fossil fuels, leading to a significant decrease in greenhousegasemissionsandenvironmentalimpact.
Overtime,theoperationalcostsofasmarthybridUPS system can be lower than traditional UPS systems poweredbygridelectricityordieselgenerators.
Develop industry standards and regulationsspecific to smart hybrid UPS systems to ensure safety, interoperability,andgridcompatibility.
1. Environmental Sustainability : Utilizing solar and wind energy reduces carbon emissions and promoteseco-friendlypowergeneration.
2. Enhanced energy efficiency :Combining solar and wind energy in a hybrid system maximizes energy production and ensures reliable UPS charging.
3. Cost Effectiveness : Renewable energy sources offerpotentialsavingsonelectricitybillsandlong termeconomicbenefits.
4. Reliability : Hybrid system providescontinuous power supply, even during periods of low sunlight or wind, initially uninterrupted operationofcriticalloads.
5. Technological innovation : Smart control algorithm and remote monitoring capabilities optimize system performance and integration withexistinginfrastructure.
6. Versatile application : The hybrid UPS charging system has diverse real world applications across industries,showcasing itspracticalityandadaptability.
The Smart Hybrid UPS Charging System presents an innovative approach to integrating solar and wind energyforUPS batterycharging.Itsefficientoperation, reliability, cost savings, and environmental benefits make it a compellingsolution for various applications requiring uninterrupted power supply. Further research and development in this area can lead to advancements in renewable energy integration and power management systems, contributing to a more sustainableenergyfuture.
1. Nishant Jha, Deepak Prashar, Mamoon Rashid,Zeba Khanam, Amandeep Nagpal, Ahmed Saeed AlGhamdi, and Sultan S. Alshamran, “Energy-Efficient Hybrid Power System Model Based on Solar and Wind Energy for Integrated Grids”, 2022 Hindawi, Research Article ID 4877422
2. RashidAlBadwawi,MohammadAbusara&Tapas Mallick, “A Review of Hybrid Solar PV and Wind Energy System”, Smart Science Vol. 3,No. 3, pp. 127-138(2015)

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 04 | Apr 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
3. Bandla Pavan Babu, P.Venkatesh , T.Swetha, D.Viswa Teja, Sk.Masoor Assistant Professor “Solar powered ups”, 2018 IJCRT | Volume 6, Issue2April2018|ISSN:2320-2882
4. Simon Rohlèn, Martin Skilbred, “Strategy for designing solar powered UPS systems” in hospitals in Eastern Africa, Department of Energy and Environment CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Gothenburg, Sweden2016
5. Vignesh M, Praveen Kumar V, Santhosh Kumar G,PremKumarSandPonkumarG,“UPSSYSTEM USING SOLAR AUTO TRACKING”, JETIR April 2021,Volume8,Issue4
6. Martin J. Leahy, David Connolly & Denis N. Buckley, “Wind energy storage technologies”, The Charles Parsons Initiative, University of Limerick,Irelan