
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 01 | Jan 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 11 Issue: 01 | Jan 2024 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
1 Research Scholar, Dept. of Computer Science and Information Science, Srinivas University Institute of Engineering & Technology, Mangalore, Karnataka, India
2 Associate Professor, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Srinivas University Institute of Engineering & Technology, Mangalore, Karnataka, India
Abstract
This research article provides a comprehensive analysis of human resources management (HRM) practices within leading software companies, with a focus on Google as a case study. The study examines various facets of HRM, including recruitment and selection strategies, compensation and benefits, employee engagement, diversity, inclusion, technology integration, challenges, and future trends. The findings elucidate Google's innovative approaches to talent acquisition, retention, development, organizational culture, and leveraging technology to drive organizational success in the competitive technology landscape. Moreover, the research highlights key challenges faced by software companies in managing human resources, such as talent acquisition, retention, organizational culture, diversity, equity, inclusion, technological advancements, digital transformation, and future trends shaping the HRM landscape. The insights derived from analysing Google's HRM practices offer valuable lessons, best practices, and recommendations for software companies aiming to optimize their human resources management strategies, foster innovation, and sustain long-term success in the global marketplace. By synthesizing empirical evidence, theoretical frameworks, and practical implications, this research contributes to the existing body of knowledge on HRM practices within the technology industry and provides a roadmap for future research, innovation, and strategic alignment in human resources management
Keywords: Human Resources Management, Software Companies, Google, Talent Acquisition, Employee Engagement, Technological Advancements
1. Introduction
In today's dynamic and competitive business environment, human resources management plays a pivotal role in driving success and sustainability, particularly in the software industry. As software companies operate in an ecosystem characterizedbyrapidtechnologicaladvancements,evolvingcustomerexpectations,andintensemarketcompetition,the abilitytoeffectivelymanage humancapital becomesincreasinglycritical.Humanresourcesmanagementextendsbeyond traditional administrative functions to encompass strategic initiatives that align talent management with organizational goals,fosterinnovation,andcreateasustainablecompetitiveadvantage.
In the context of software companies, which are often attheforefront of innovation and disruption,attracting, retaining, anddevelopingtoptalentisparamount.Thesuccessofsoftwarecompanieshingesontheirabilitytoharnessthecollective skills, expertise, and creativity of their workforce to develop cutting-edge solutions, drive growth, and maintain a competitive edge in the market. As such, human resources management in software companies is not merely about recruiting employees but entails creating a conducive work environment, fostering a culture of continuous learning and development,promotingcollaborationandinnovation,andaligningtalentstrategieswithbusinessobjectives.
Google,aleadingglobaltechnologycompany,exemplifiesthesignificanceof strategichumanresourcesmanagement indrivinginnovation,growth,andorganizationalsuccess.Foundedwithavisiontoorganizetheworld'sinformationand make it universally accessible and useful, Google has grown exponentially since its inception, diversifying its product portfolio,expandingitsglobalfootprint,andtransformingindustriesthroughitsinnovativesolutionsandservices.
Asa technologypowerhouse,Google'ssuccessisintrinsicallylinkedtoitsabilitytoattract,develop,andretain toptalent fromaroundtheworld.Withaworkforcecomprisingsomeofthebrightestmindsintechnology,engineering,design,and

business, Google's human resources management practices serve as a benchmark for excellence in the industry. By prioritizingemployeeengagement,fosteringacultureofcreativityandcollaboration,investinginemployeedevelopment, and embracing diversity and inclusion, Google has cultivated a work environment where innovation thrives, and employeesareempoweredtomakeameaningfulimpact.
ByanalyzingGoogle'shumanresourcesmanagementpractices,strategies,andinitiatives,thisresearchaimsto providea comprehensive understanding of how leading software companies manage their most valuable asset their people. Through a detailed examination of Google's recruitment, training, performance management, compensation, employee engagement,diversity,andinclusionpractices,thisstudyseekstoidentifybestpractices,challenges,andopportunitiesfor software companies to optimize their human resources management strategies and drive organizational success in an increasinglycompetitiveandcomplexbusinesslandscape.
The evolution of human resource management (HRM) within the software industry has been characterized by transformative shifts, reflecting the dynamic nature of technology, market demands, and organizational structures. Initially, HRM in the software sector was primarily focused on administrative tasks, compliance, and personnel management.However,astheindustrymaturedandtechnologybecameincreasinglyintegraltobusinessoperations,HRM evolved to encompass strategic initiatives aligned with organizational objectives. This transformation witnessed a shift towards talent acquisition, development, retention, and organizational culture, emphasizing the importance of human capital in driving innovation, growth, and competitive advantage. Furthermore, globalization, digitalization, and the emergenceofagilemethodologiesnecessitatedadaptiveHRMpractices,fosteringflexibility,collaboration,andcontinuous learningwithinsoftwarecompanies.
• Historical Perspective: Trace the evolution of human resource management practices within the software industry,highlightingkeymilestones,shifts,andtrendsovertheyears.
• Transformational Changes: Discuss how technological advancements, globalization, and market dynamics have influenced HR practices in software companies. Mention the transition from traditional HR practices to more strategicandinnovativeapproaches.
Software companies encounter a myriad of challenges in managing human resources, stemming from the industry's competitive landscape, talent shortages, technological advancements, and evolving workforce expectations. Talent acquisition remains a primary challenge, as companies compete for skilled professionals with specialized expertise in emerging technologies, programming languages, and domain-specific knowledge. Additionally, employee retention poses challenges, given the high demand for tech talent, competitive job market, and evolving career aspirations of millennials andGenZprofessionals.Furthermore,skill developmentandupskillinginitiativesarecrucial,consideringthe rapidpace of technological change, obsolescence of skills, and the need to foster a culture of continuous learning and innovation. Moreover, maintaining a cohesive organizational culture, promoting diversity and inclusion, ensuring regulatory compliance,andnavigatinggeopoliticalcomplexitiesfurthercompoundHRMchallengesforsoftwarecompaniesoperating indiversemarketsandregions.
• Talent Acquisition: Address challenges related to attracting top talent, competition for skilled professionals, and theneedforspecializedskillsintherapidlyevolvingtechlandscape.
• Employee Retention: Discuss retention challenges, including high turnover rates, competition from other tech firms,andtheimportanceofcreatingacompellingworkculture.
• Skill Development: Highlight the challenges associated with continuous learning, upskilling, and reskilling employeestomeetthechangingdemandsoftheindustry.
• Organizational Culture: Explore the significance of fostering a collaborative, innovative, and inclusive work environment.Addresschallengesrelatedtomaintainingcultureamidgrowth,diversification,andglobalexpansion.

• Regulatory Compliance:Mentionchallengesrelatedto compliancewithlaborlaws,data privacyregulations,and industrystandardsacrossdifferentregionsandmarkets.
Effective HR management (HRM) serves as a cornerstone for software companies striving to achieve sustainable growth, innovation, and organizational success. Strategic alignment of HRM practices with business objectives facilitates the development of a cohesive workforce, fosters a culture of collaboration and innovation, and enables companies to adapt to evolving market dynamics effectively. Furthermore, effective HRM practices contribute to enhancing employee engagement, satisfaction, and retention, thereby reducing turnover costs, promoting knowledge sharing, and preserving organizational knowledge. Moreover, prioritizing employee well-being, fostering a supportive work environment, and promoting work-life balance enhance productivity, creativity, and employee morale, driving organizational performance andcompetitiveness.Additionally,proactivetalentmanagement,leadershipdevelopment,andsuccessionplanningenable softwarecompaniestocultivatefutureleaders,buildorganizationalresilience,andcapitalizeonemergingopportunitiesin theglobalmarketplace.
• Strategic Alignment:EmphasizetheroleofHR inaligningtalentmanagementstrategies withorganizational goals, objectives,andlong-termvision.
• Competitive Advantage: Discuss how effective HR practices contribute to creating a competitive advantage, fosteringinnovation,anddrivingbusinesssuccessinthesoftwareindustry.
• Employee Well-being: Highlight the importance of prioritizing employee well-being, work-life balance, mental health, and creating a supportive work environment to enhance productivity, engagement, and satisfaction.
Google's recruitment strategies represent a paradigm shift in talent acquisition, emphasizing innovation, inclusivity, and cultural fit. Leveraging its brand reputation and global presence, Google strategically engages with universities, institutes,and industry eventsworldwide tocultivate relationships with emerging talent.Campus recruitment remainsa cornerstone of Google's talent acquisition strategy, offering internships, co-op programs, and leadership development opportunitiestonurturerelationshipswithtopstudentsandearly-careerprofessionals.Furthermore,Googleincentivizes employee referrals, recognizing the value of internal networks in identifying qualified candidates who align with the company's values, culture, and skill requirements. Moreover, Google's direct application process, coupled with its online recruitment portals and platforms, facilitates seamless interactions with potential candidates, enabling the company to access a diverse talent pool and address specific hiring needs across various functions, roles, and regions. By adopting a

multifaceted approach to recruitment, Google ensures a steady influx of talent, fostering a diverse, skilled, and engaged workforcecapableofdrivinginnovationandsustainingcompetitiveadvantageinthefast-pacedtechnologylandscape.
Google harnesses the power of data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) to revolutionize its recruitment processes, enhance decision-making, and optimize outcomes. By leveraging predictive analytics, Google analyzes vast datasets, recruitment trends, and historical data to forecast hiring needs, identify talent gaps, and develop targeted recruitment strategies. Additionally, Google employs AI-driven tools, chatbots, and automation technologies to streamline candidate sourcing, screening, and selection processes, reducing administrative burdens, minimizing biases, andacceleratingtime-to-hire.Furthermore,Google'scommitmenttomitigatingunconsciousbiasinrecruitmentisevident through its data-driven approach, which focuses on objective assessments, standardized evaluations, and structured interviewstoensurefairness,consistency,andtransparencythroughouttherecruitmentlifecycle.Byintegratingadvanced technologiesanddata analyticsintoitsrecruitment processes,Googleexemplifiesbestpracticesinleveraginginnovation to attract, assess, and onboard top talent effectively, thereby maintaining its competitive edge and industry leadership position.
Google's assessment techniques and interview processes reflect its commitment to identifying candidates who align with its values, competencies, and cultural principles. Emphasizing behavioral interviews, Google utilizes structured questioningtechniques,situationaljudgmenttests,androle-specificassessmentstoevaluatecandidates'problem-solving abilities,collaborationskills,andculturalfit.Additionally,Google'stechnicalassessments,codingchallenges,anddomainspecific evaluations enable recruiters and hiring managers to assess candidates' technical proficiency, expertise, and suitability for specific roles within the organization. Moreover, Google prioritizes cultural fit, ethical considerations, and alignmentwithitsorganizationalvaluesduringtheinterviewprocess,fosteringaninclusive,collaborative,andsupportive work environment. By adopting a comprehensive, data-driven, and objective approach to candidate evaluation, Google ensures alignment with its strategic objectives, fosters a culture of excellence, and cultivates a diverse, high-performing workforcecapableofdrivinginnovation,growth,andorganizationalsuccessinthecompetitivetechnologylandscape.
By examining Google's recruitment and selection strategies in detail, you can gain insights into how leading software companies leverage innovation, technology, and best practices to attract, assess, and onboard top talent. Analyzing Google'smultifacetedapproachtotalentacquisition,data-drivendecision-making,andcandidateevaluationwillprovidea comprehensive understanding of its recruitment strategies and practices, setting the stage for exploring other aspects of humanresourcemanagementwithintheorganization.
• Campus Recruitment: Discuss Google's approach to campus recruitment, partnerships with universities, internshipprograms,andstrategiestoattracttopgraduatesfromleadinginstitutionsglobally.
• Employee Referrals: Highlight the significance of employee referrals in Google's recruitment process, incentives forreferrals,andtheroleofinternalnetworksinidentifyingpotentialcandidates.
• Direct Applications:ExploreGoogle'sonlineapplicationprocess,recruitmentportals,andplatformsusedtosource candidatesdirectlyfromthemarket.
• Global Talent Acquisition: Discuss Google's strategies for attracting international talent, managing global recruitmentprocesses,andleveragingdiversetalentpoolsfromdifferentregions.

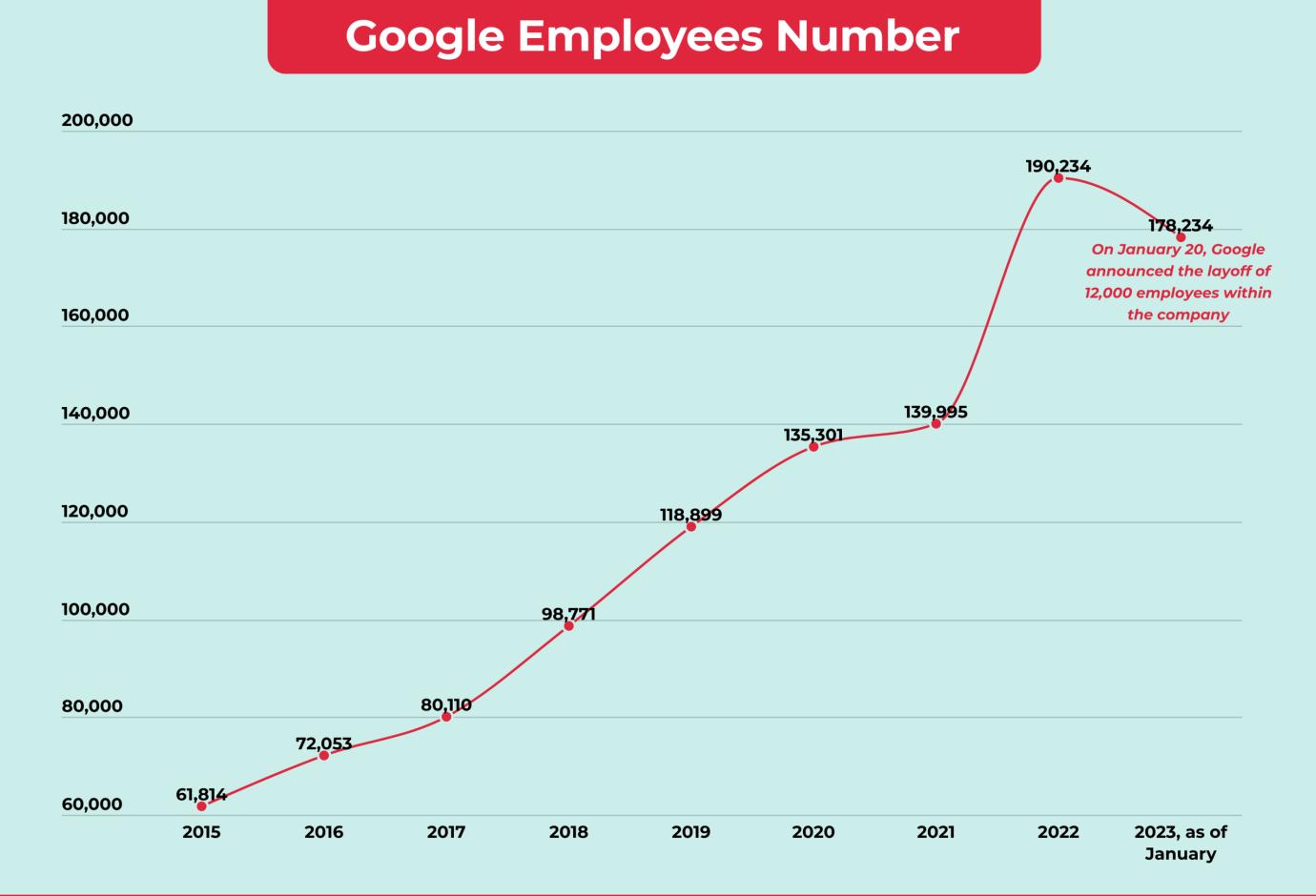
3.4 Use of Data Analytics and AI in Recruitment Processes:
• Predictive Analytics: Highlight how Google utilizes data analytics, machine learning, and predictive modeling to analyzerecruitmenttrends,forecasthiringneeds,andoptimizerecruitmentstrategies.
• AI-Driven Tools: Discuss the use of AI-driven tools, chatbots, and automation technologies in screening resumes, conductinginitialassessments,andstreamliningtherecruitmentprocess.
• Bias Mitigation:AddressGoogle'seffortstomitigateunconsciousbiasinrecruitment,promotediversity,andensure fairandequitablehiringpracticesusingAIanddata-drivenapproaches.
3.5 Assessment Techniques and Interview Processes:
• Behavioral Interviews: Explore Google's use of behavioral interviews, situational judgment tests, and competency-basedassessmentstoevaluatecandidates'skills,experience,andculturalfit.
• Technical Assessments: Discuss Google's approach to conducting technical assessments, coding challenges, and evaluatingcandidates'technicalproficiencyforspecificroles.
• Cultural Fit: Highlight the importance of assessing candidates' alignment with Google's values, mission, and organizationalcultureduringtheinterviewprocess
4. Compensation, Benefits, and Employee Engagement:
4.1 Compensation and Benefits at Google:
Google's compensation and benefits strategies are designed to attract, retain, and motivate top talent while aligning with the company's culture, values, and business objectives. Recognizing the importance of competitive compensation packages in the tech industry, Google offers a comprehensive compensation structure that includes competitive base salaries, performance-based bonuses, and stock options. Moreover, Google's benefits offerings extend beyond traditional

perks, encompassing healthcare, retirement plans, wellness programs, and work-life balance initiatives tailored to meet employees' diverse needs and preferences. Additionally, Google's emphasis on equity ownership, profit-sharing opportunities, and long-term incentives aligns employees' interests with organizational success, fostering a sense of ownership,commitment,andalignmentwiththecompany'sstrategicgoals.Byprioritizingfair,transparent,andmarketdrivencompensationpractices,Googledemonstratesitscommitmenttorewardingexcellence,promotinginternalequity, andcreatingasupportive,rewarding,andinclusiveworkenvironmentthatempowersemployeestothrive,innovate,and contributetothecompany'ssuccess.
Employee engagement and retention remain paramount for Google, given the competitive nature of the technology industry and the company's focus on fostering a collaborative, innovative, and inclusive work environment. Google's employeeengagementstrategiesencompassaholisticapproachtotalentmanagement,encompassingcareerdevelopment opportunities, continuous learning and growth, recognition programs, and feedback mechanisms designed to empower employees, enhance job satisfaction, and cultivate a sense of belonging and purpose within the organization. Moreover, Google'semphasisonfosteringacultureoftransparency,opencommunication,andinclusivityenablesemployeestovoice their opinions, contribute to decision-making processes, and collaborate cross-functionally to drive innovation and business results. Furthermore, Google's commitment to employee well-being, work-life balance, and mental health initiatives underscores its dedication to supporting employees' holistic well-being, resilience, and long-term success. By prioritizing employee engagement, recognition, and retention, Google fosters a culture of excellence, innovation, and collaboration that enables the company to attract, develop, and retain top talent, drive organizational performance, and maintainitsleadershippositioninthecompetitivetechnologylandscape.
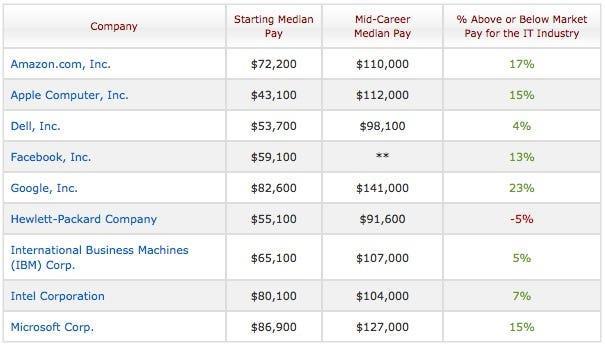
DataSource:
https://www.businessinsider.com/google-really-is-the-best-tech-company-to-work-for-2011-16?IR=T
Google's integration of technology within its human resources management (HRM) practices exemplifies the company's commitment to innovation, efficiency, and data-driven decision-making. Leveraging advanced HR software tools, cloud-based platforms, and analytics solutions, Google automates routine HR tasks, streamlines processes, and enhancescollaborationacrosstheorganization.Furthermore,Google'suseofartificialintelligence(AI),machinelearning (ML), and predictive analytics facilitates talent acquisition, performance management, learning and development, and employeeengagementinitiatives.Byharnessingthepoweroftechnology,GoogleempowersHRprofessionalstofocuson strategicinitiatives,talentdevelopment,andorganizationalculturewhileleveragingdata-driveninsightstooptimizeHRM practices,drivecontinuousimprovement,andsupportbusinessobjectives.

Google's adoption of HR software tools and platforms underscores its commitment to enhancing operational efficiency, employee experience, and organizational effectiveness. Google utilizes integrated HRM systems, talent management platforms, and employee self-service portals to streamline recruitment, onboarding, training, performance management, and succession planning processes. Additionally, Google's use of advanced analytics, dashboards, and reporting tools enables HR professionals to analyze workforce trends, monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), and make informed decisions to drive organizational success. Furthermore, Google's emphasis on user-friendly interfaces, mobile accessibility, and personalized experiences enhances employee engagement, productivity, and satisfaction while promoting transparency, collaboration, and communication across the organization. Google optimizes HRM processes, fostersacultureofcontinuousimprovement,andenhancestheemployeeexperience,therebymaintainingitscompetitive edgeandindustryleadershippositioninthedynamictechnologylandscape.
Google'scommitmenttodata-drivendecision-makinginHRunderscoresitsstrategicapproachtotalentmanagement, organizationaldevelopment,andbusinesssuccess.Bycollecting,analyzing,andinterpretingworkforcedata,Googlegains actionable insights into employee performance, engagement, retention, and organizational effectiveness. Moreover, Google's use of predictive analytics, workforce planning tools, and scenario modeling enables HR professionals to anticipate future talent needs, identify potential risks, and develop proactive strategies to address evolving business requirements.Additionally,Google'semphasisondiversityanalytics,payequityanalysis,andinclusionmetricsreflectsits commitment to fostering a diverse, equitable, and inclusive workplace culture. By leveraging data-driven insights to inform HRM practices, Google aligns talent management strategies with business objectives, drives organizational performance, and cultivates a high-performing workforce capable of navigating challenges, capitalizing on opportunities, andsustaininglong-termsuccessinthecompetitivetechnologylandscape.
One of the foremost challenges that software companies like Google face in human resources management is talent acquisition and retention. In an increasingly competitive landscape, attracting top-tier talent with specialized skills in emerging technologies remains a significant hurdle. The rapid pace of technological advancements necessitates a continuous focusonupskillingandreskillinginitiatives toensurethatemployeespossesstherequisiteexpertisetodrive innovation and maintain a competitive edge. Moreover, retaining top talent requires creating an organizational culture thatfostersgrowth,recognizescontributions,andalignswithemployees'careeraspirations,values,andwork-lifebalance preferences.Additionally,competitionfromothertechcompanies,changingdemographics,evolvingjobmarketdynamics, and the rise of remote work models further complicate talent acquisition and retention efforts, requiring strategic workforce planning, employer branding, and employee engagement initiatives to mitigate turnover risks and sustain organizationalperformance.
Maintainingacohesiveorganizationalculture,fosteringcollaboration,andpromotingdiversity,equity,andinclusion (DEI) present ongoing challenges for software companies operating in diverse markets and regions. Ensuring alignment withGoogle'svalues,mission,andidentityamidgrowth,diversification,andglobalexpansionrequiresproactiveeffortsto preserve cultural cohesion, promote cross-cultural understanding, and address cultural differences. Furthermore, fostering an inclusive work environment that values diversity, promotes equal opportunities, and celebrates individual differences is essential for attracting, retaining, and developing a diverse workforce capable of driving innovation, creativity, and organizational success. Addressing unconscious bias, promoting cultural competence, and implementing DEI initiatives that resonate with employees, stakeholders, and customers' diverse needs and preferences will be critical forfosteringaninclusive,collaborative,andhigh-performingorganizationalculture.
The advent of technological advancements, digital transformation, and automation technologies is reshaping human resources management practices, workforce dynamics, and organizational structures within the technology industry. Embracing artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), data analytics, and predictive modeling tools enables HR

professionals to optimize talent acquisition, performance management, employee engagement, and decision-making processes.However,integratingtechnologyintoHRMpracticesnecessitatesaddressingchallengesrelatedtodataprivacy, cybersecurity, ethical considerations, and the human-machine interface. Moreover, navigating the transition to remote workmodels,virtualcollaborationtools,digitalonboardingprocesses,andflexibleworkarrangementsrequiresadapting HRM practices, policies, and strategies to meet employees' evolving needs, preferences, and expectations while maintainingorganizationalculture,collaboration,andcommunication.
Lookingahead,several futuretrendsare poisedtoshapethelandscapeofhuman resourcesmanagement withinthe technology industry, reflecting evolving workforce dynamics, technological advancements, global market trends, and societal expectations. Emphasizing employee well-being, mental health, work-life balance, and fostering supportive, inclusive, and collaborative work environments will be critical for attracting, retaining, and developing top talent. Additionally, embracing diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB) initiatives, promoting cultural competence, addressing systemic inequalities, and creating equitable opportunities for all employees will be paramount for fostering innovation, collaboration, and organizational performance in the competitive and dynamic technology landscape. Therefore, adopting a forward-thinking, adaptive, and strategic approach to human resources management will enable softwarecompaniestonavigatechallenges,capitalizeonopportunities,andsustainlong-termsuccessinarapidlyevolving andinterconnectedglobalmarketplace.
In conclusion, Google's human resources management (HRM) practices serve as a benchmark for excellence, innovation, andstrategicalignmentwithorganizationalobjectiveswithinthecompetitiveanddynamictechnologylandscape.Through a comprehensive analysis of Google's recruitment, training, performance management, compensation, employee engagement, diversity, inclusion, and technology adoption strategies, this research elucidates how leading software companies optimize human resources management to foster a culture of collaboration, innovation, and employee engagement. Google's commitment to leveraging technology, data-driven decision-making, continuous improvement, and fosteringadiverse,inclusive,andhigh-performingworkforceunderscoresitsleadershipinhumanresourcesmanagement, organizationaldevelopment,andbusinesssuccess.
The insights gained from examining Google's HRM practices, challenges, future trends, and strategic alignment offer valuablelessons,bestpractices,andrecommendationsforsoftwarecompaniesstrivingtoenhancetheirhumanresources management practices, leverage technology, and drive organizational success. As software companies navigate talent acquisition, retention, development, organizational culture, and global expansion, adopting a strategic, data-driven, and employee-centric approach to human resources management becomes paramount. By incorporating Google's innovative strategies, initiatives, and practices into their HRM frameworks, software companies can optimize talent management, foster a culture of excellence, innovation, and collaboration, and capitalize on emerging opportunities in the competitive globalmarketplace.
Looking ahead, the future of human resources management in the technology industry will be shaped by evolving workforce trends, technological advancements, global market dynamics, and societal expectations. As remote work, flexible arrangements, digital transformation, diversity, equity, inclusion, and lifelong learning become integral components of HRM practices, software companies must adapt, innovate, and continually evolve to meet the changing needs, preferences, and aspirations of their employees, stakeholders, and customers. Moreover, investing in employee well-being,mentalhealth,work-lifebalance,andcreatingsupportive,inclusive,andcollaborativeworkenvironmentswill be critical for attracting, retaining, and developing top talent, fostering innovation, and driving organizational performance, sustainability, and success in the competitive and dynamic technology landscape. Therefore, embracing a forward-thinking, adaptive, and strategic approach to human resources management will enable software companies to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and sustain long-term success in a rapidly evolving and increasingly interconnectedglobalmarketplace.

References:
1. Armstrong, M. (2014). Armstrong's Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice. Kogan Page. https://euczelnia.uek.krakow.pl/pluginfile.php/604792/mod_folder/content/0/Armstrongs%20Handbook%20of%2 0Human%20Resource%20Management%20Practice_1.pdf?forcedownload=1
2. Cascio,W.F.(2018).ManagingHumanResources:Productivity,QualityofWorkLife,Profits.McGraw-HillEducation.
3. Boxall,P.,&Purcell,J.(2016).StrategyandHumanResourceManagement.PalgraveMacmillan. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/37149236_Strategy_and_Human_Resource_Management
4. Becker, B., Huselid, M., & Ulrich, D. (2001). The HR Scorecard: Linking People, Strategy, and Performance. Harvard BusinessReviewPress.
5. Davenport, T. H. (2017). Human Capital: What It Is and Why People Invest It. Jossey-Bass.https://www.wiley.com/enus/Human+Capital%3A+What+It+Is+and+Why+People+Invest+It-9780470436813
6.Stone,R.J.(2019).HumanResourceManagement.Wiley.
7.Rothwell,W.J.,&Kazanas,H.C.(2017).MasteringtheInstructionalDesignProcess:ASystematic Approach.JohnWiley &Sons.
8. Pfeffer, J. (2018). Dying for a Paycheck: How Modern Management Harms Employee Health and Company Performance andWhatWeCanDoAboutIt.HarperBusiness.
9.Cascio,W.F.,&Boudreau,J.W.(2016).TheOxfordHandbookofEvidence-BasedManagement.OxfordUniversityPress. https://global.oup.com/academic/product/the-oxford-handbook-of-evidence-based-management-9780199763986
10.Boudreau,J.W.,&Jesuthasan,R.(2015).TransformativeHR:HowGreatCompaniesUseEvidence-Based ChangeforSustainableAdvantage.JohnWiley&Sons.
11.Stone,D.L.,&Deadrick,D.L.(2015).Challengesandopportunitiesaffectingthefutureofhumanresourcemanagement. HumanResourceManagementReview,25(2),139-145.
12. Allen, D. G., Bryant, P. C., & Vardaman, J. M. (2010). Retaining Talent: Replacing Misconceptions with Evidence-Based Strategies.AcademyofManagementPerspectives,24(2),48-64.
13. Lawler, E. E. (2019). Reinventing talent management: Principles and practices for the new world of work. BerrettKoehler Publishers. https://ceo.usc.edu/2017/10/11/reinventing-talent-management-principles-practices-newworld-work/
14.Cascio,W.F.,&Aguinis,H.(2005).AppliedPsychologyinHumanResourceManagement(6thed.).Pearson.
15.Delery,J.E.,&Roumpi,D.(2017).Strategichumanresourcemanagement,humancapitalandcompetitiveadvantage:is thefieldgoingincircles?HumanResourceManagementJournal,27(1),1-21.
16.Wright,P.M.,Dunford,B.B.,&Snell,S.A.(2001).Humanresourcesandtheresource-basedviewofthefirm.Journalof Management,27(6),701-721.https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/014920630102700607
17.Lawler,E.E.(2003).Treatpeopleright!Howorganizationsandindividualscanpropeleachotherintoavirtuousspiral ofsuccess.Jossey-Bass.
18. Ulrich, D., & Brockbank, W. (2005). The HR value proposition. Harvard Business Review, 83(3), 115-123. https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=1713120
19. Jackson, S. E., & Ruderman, M. (1999). Diversity in work teams: Research paradigms for a changing workplace. AmericanPsychologist,54(4),17-277.
20.Barney,J.(1991).Firmresourcesandsustainedcompetitiveadvantage.JournalofManagement,17(1),99-120.

21.Lepak,D.P.,&Snell,S.A.(1999).Thehuman resourcearchitecture:Towarda theoryofhumancapital allocationand development. Academy of Management Review, 24(1), 31-48. https://www.scirp.org/reference/ReferencesPapers?ReferenceID=1183468
22.Huselid,M.A.(1995).Theimpactofhumanresource management practiceson turnover,productivity,and corporate financialperformance.AcademyofManagementJournal,38(3),635-672.
23. Cappelli, P. (2008). Talent on Demand: Managing Talent in an Age of Uncertainty. Harvard Business Press. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311798995_Talent_on_Demand__Managing_Talent_in_an_Age_of_Uncertainty
24. Denning, S. (2018). The Age of Agile: How Smart Companies Are Transforming the Way Work Gets Done. HarperBusiness.
25. Pfeffer, J., & Sutton, R. I. (2000). The knowing-doing gap: How smart companies turn knowledge into action. Harvard BusinessPress.
26.Duhigg,C.(2016).SmarterFasterBetter:TheSecretsofBeingProductiveinLifeandBusiness.RandomHouse.
27. Pink, D. H. (2011). Drive: The Surprising Truth About What Motivates Us. Riverhead Books. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drive:_The_Surprising_Truth_About_What_Motivates_Us
28.Capelli,P.,&Tavis,A.(2018).HRgoesagile.HarvardBusinessReview,96(2),44-52.
29. Boudreau, J. W., & Ramstad, P. M. (2006). Talentship, talent segmentation, and sustainability: A new HR decision scienceparadigmforanewstrategydefinition.HumanResourceManagement,45(3),429-448.
30.Davenport,T.H.,Harris,J.,&Shapiro,J.(2010).Competingontalentanalytics.HarvardBusinessReview,88(10),52-58.
31. Lawler, E. E., & Worley, C. G. (2006). Built to Change: How to Achieve Sustained Organizational Effectiveness. JosseyBass.
https://www.wiley.com/enus/Built+to+Change%3A+How+to+Achieve+Sustained+Organizational+Effectiveness-p-9780787980610
32. Gratton, L., & Truss, C. (2003). The three-dimensional people strategy: Putting human resources policies into action. AcademyofManagementExecutive,17(3),74-86.
33. Rothwell, W. J., Prescott, R. K., & Taylor, W. C. (1998). Human resource transformation: Demonstrating strategic leadershipinthefaceoffuturetrends.HumanResourcePlanning,21(4),29-42.
34. Van Den Heuvel, S., & Bondarouk, T. (2017). The rise (and fall?) of HR analytics: A study into the future application, value,structure,systemsupport,andsystemcomplexity.InternationalJournalofHumanResourceManagement,28(2), 243-258.
35. Bock, L. (2015). Work Rules!: Insights from Inside Google That Will Transform How You Live and Lead. Twelve. https://books.google.com/books/about/Work_Rules.html?id=M6idBAAAQBAJ
36.Davenport,T.H.,Harris,J.,&Shapiro,J.(2010).Competingontalentanalytics.HarvardBusinessReview,88(10),52-58.
37.Marler,J.H.,&Boudreau,J.W.(2017).Anevidence-basedreviewofHRAnalytics.TheInternationalJournalofHuman ResourceManagement,28(1),3-26.