
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Dr.
G Tej Varma1, S. Lalitha Jyothi1 , K. Sravani2 , V. Anusha3 , K. Vasavi4
1Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, Sri Vasavi Engineering College(A), Pedatadepalli, Tadepalligudem534101
1-4CST, Sri Vasavi Engineering College(A), Pedatadepalli, Tadepalligudem-534101 ***
Abstract - By facilitating risk-based screening and intelligentpassengerassessment,automateddecision-making isrevolutionizingairportsecurity.Makingsurethat decisions are made impartially is a major challenge in automated security screening. respecting privacy laws like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). By integrating bias detectionmechanisms,thissystem ensuresthatallpassengers aretreatedfairlybyidentifyingandmitigatingdiscriminatory patterns in security checks. It also makes behavioral analysis and baggage tracking possible, which enhances security monitoring and anomaly detection. The project improves security measures while preserving passenger rights, data privacy,andoperationalefficiencybyfusingAI-driveninsights with decision-making. This strategy guarantees a more intelligent,impartial,anddependableairportsecuritysystem for contemporary air travel. This system's frontend is implemented using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, while the backend is developed usingJava Servlets andJSP, withMySQL as the database. This technology stack ensures a seamless, scalable, and secure system for effective airport security screening.
Key Words: (Automated Security Screening, Risk-Based Screening, Bias Detection, GDPR, Behavioural Analysis, AirportSecurity,AIinSurveillance
Intelligentpassengerassessmentandrisk-basedscreening aretwowaysthatautomateddecision-makingischanging airportsecurity.Ensuringimpartialdecisionswhileabiding by privacy laws is a major challenge in this system. SuchastheGeneralDataProtectionRegulation(GDPR).To solvethis,thesystemincorporatesbiasdetectiontoolsthat spot and lessen discriminatory trends in security checks, guaranteeing that every traveler is treated fairly. Additionally, it facilitates behavioral analysis and luggage tracking, which enhances anomaly detection and general security monitoring. This method improves operational efficiency, protects passenger rights, and strengthens securitybyfusingAI-driveninsightswithdecision-making procedures.Inairportsecurity,risk-basedsecurity(RBS)isa developing idea that aims to strike a balance between passenger convenience and safety. Long lines and X-ray scansareexamplesoftraditionalproceduresthatcanirritate passengers, but RBS concentrates on targeted examination of particular people, in line with behavior analysisinitiativessuchasthosefromtheU.S.Departmentof
Homeland Security, the European Commission's H2020 FLYSEC project, and IATA/ACI's Smart Security. RBS improves security effectiveness, but it also brings up privacyandethicalissues,includingpossibleracial,gender, andreligiousdiscrimination.IfRBSisappliedunfairly,itmay result in financial losses, legal issues, and a decline in passengerconfidence.RBSneedstobeseenasimpartialand fair to be accepted. With a focus on privacy issues considering GDPR regulations, this article explores the ethicalramificationsofautomatedsecuritydecisionmaking. Itexamineshowmachinelearningcanbeusedinsecurity and suggests an expert system to identify possible biases. RBSisnotnew,butithaschangedwithdevelopmentsinAI andmachinelearning,whichallowsecurityexpertstomore precisely identify threats and analyze large data sets. Notwithstanding its benefits, RBS still needs to address importantissueslikedataprivacyandtransparency.Tokeep thepublic'strust,securitydecisionsneedtobetransparent and well-supported. Additionally, RBS needs to be continuouslyassessedtoremainimpartialandeffective.This includes regular updates to machine learning models and cooperation between governments, airlines, and privacy advocates. In the end, RBS has the power to transform airport security by improving its intelligence and effectiveness. Its success hinges on its ethical application, openness, and continuous improvement, guaranteeing a smootherandsaferjourneyfortravelerseverywhere.
Selectivesecurityscreeningandrisk-basedapproacheshave beenwidelyexploredtoenhanceefficiencyandfairnessin airport security. Tamara Stotz [1] examined public perceptionregardingrisk-basedandrandomizedscreenings, highlighting concerns over fairness, discrimination, and privacy while advocating for AI-driven bias detection. Similarly, Z. Zhang [3] analyzed risk-based passenger differentiation techniques to optimize security checks, reducinginconvenienceforlow-riskindividuals.K.Michalski etal.[6]Decision-supportsystems,biometricadvancements, and optimization techniques have played a crucial role in improvingairportsecurityoperations.G.Scozzaroetal.[2] introduced a simulation-optimization-based system to efficiently allocate security resources, reducing wait times while maintaining security standards. J. Skorupski and P. Uchroński [4] applied data-driven queuing simulations to enhance cargo screening, ensuring both security and operationalefficiency.A.Knoletal.[7]usedcognitiveagent

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
models to analyze checkpoint performance, providing insights into decision-making and workload management. Meanwhile,A.K.Jainetal.[5]exploredtheroleofbiometric technologies like facial recognition, iris scanning, and fingerprinting in automating passenger identification and improving verification accuracy. These innovations collectively enhance security measures while streamlining airportoperations.Thesocialandhumanaspectsofairport securityscreeningremaincriticalconsiderations.A.Carretal. [8]examinedsocialjusticeconcerns,highlightingbiasesin security procedures that disproportionately affect certain groupsandproposingstrategiestomitigatediscrimination.C. Lumetal.[9]
3.EXISTING
Concerns about ethics and privacy are intensifying as automated information processing and profiling become essential components of more effective, risk-based, and intelligent security. These worries are represented in the changing legal and regulatory frameworks designed to guarantee equitable and open security procedures. In airports we face particular difficulties when putting advanced security and surveillance systems in place to improve safety while adhering to legal and ethical requirements. To keep an eye on the equity of intelligent manual surveillance systems in airports and other vital infrastructures,asolutionhasbeendeveloped.Thesystem incorporates algorithms that analyze high-level data and data from dispersed sensors to deduce suspicious activity and evaluate the reliability of visitors. However, unfair conclusions may result from biases in algorithms or data sources. A bias detection system that makes use of a structuredrepresentationoflegalregulationsissuggestedas a solution to this problem. The system guarantees more impartialandobjectivesecurityevaluationsbycontrasting theseruleswithassociationrulesobtainedfrominputand outputdatasets.
Byevaluatingoperationalandtechnologicalopportunities, the suggested system investigates the possibilities of automatedsecuritydecisionmaking.Toensurecompliance with the most recent General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR),itassessesrisksandramificationsusingthemost recentprivacyandethicalframeworks.Thesystemseeksto improve security measures while upholding transparency and safeguarding individual rights by adhering to these rules.Thesystemoffersanexpertmechanismthatcanassess fairnessinsecuritydecisions,withaparticularfocusondata processing and the risks that come with it. This system identifies deviations that could result in human rights violationsordiscrimination.Thesystemminimizesbiasand fosters a more equitable security environment by consistentlycomparingsecuritydecisionstostructuredlegal regulations,ensuringthatfairnessandethicalconsiderations aremaintained.
5.EXPERIMENTAL
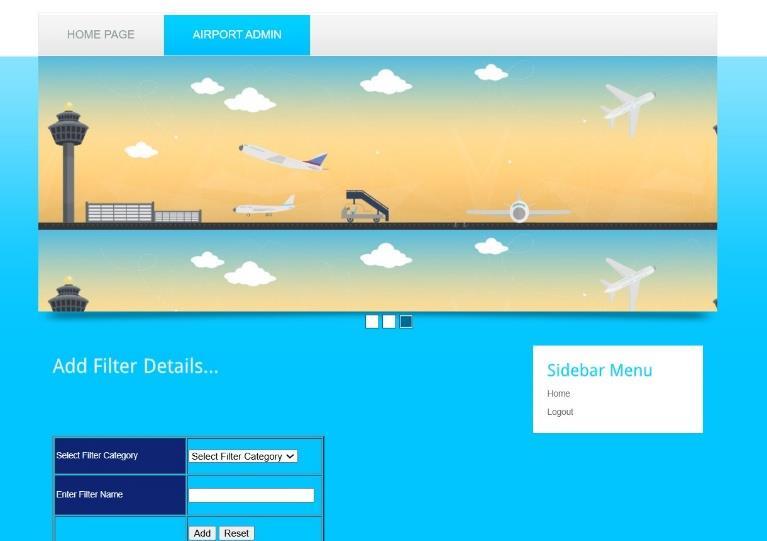
5.1.RiskAssessmentDashboard
This dashboard introduces a new filter based on negative emotionstoenhancetheassessmentofpassengerrisklevels. Itenablessecuritypersonneltoidentifypotentialconcerns moreeffectivelyusingreal-timevisualindicators.
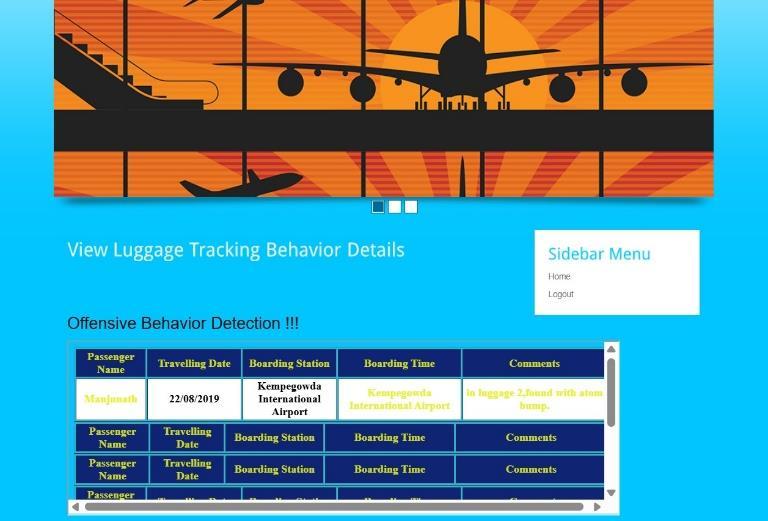
5.2.LuggageBehaviorTracking
Thisoutputdisplaysluggagetrackinglinkedwithpassenger behavior.Itmonitorshowpassengershandletheirbaggage and flags suspicious patterns, helping identify potential securityrisks.

Research
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
5.3.AdminDashboard
This image shows the admin dashboard, which provides accesstoallcorefunctionalities.Itallowstheadministrator to manage users, monitor system activity, track security alerts, and control system settings from a centralized interface.
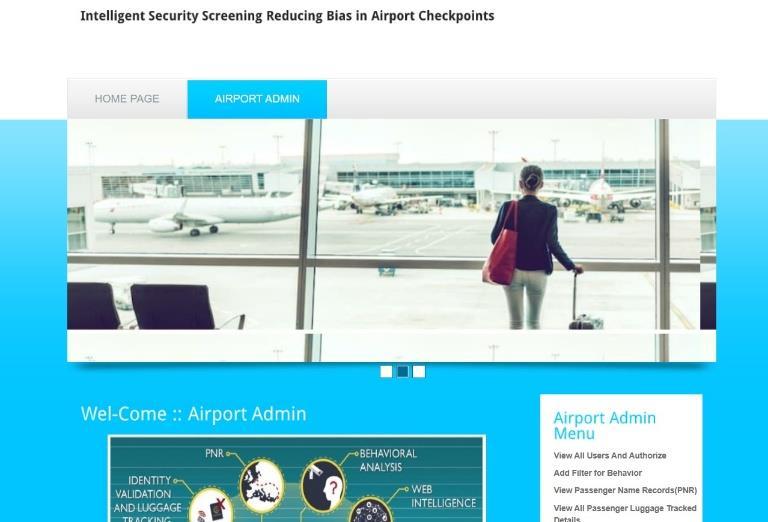
5.4.HomePage
Thisisthehomepageofthesystem,providinganoverview ofthewebsite’spurposeandfeatures.Itincludesasection foradminlogin,allowingauthorizedpersonneltoaccessthe securebackenddashboard.
Byincorporatingethicalnormsandlegalrequirementsinto thescreeningprocedure,theIntelligentSecurityScreening system aims to combat biases at airport security checkpoints. By reducing the possibility of discriminatory results through manual oversight and rule-based assessments, itguarantees fairness. Thesystempreserves the efficacy of security measures while giving privacy compliance and ethical standards top priority. Future advancements in the system will concentrate on streamlining the screening processes, enhancing transparency, and utilizing real-world data for ongoing optimization. In the end, the system is a workable and effective way to improve passenger trust and operational efficiencywhiledevelopingamoreequitableanddependable airport security management procedure. Improved Bias Detection:Toguaranteemoreequitabledecision-makingand reduce biases in security screening, the system will incorporate legal requirements. To guarantee more equitable decision-making and reduce biases in security screening, the Intelligent Security Screening System will keep developing by incorporating legal requirements. Simulation models will be created to produce realistic datasets to improve data accuracy. This will decrease the possibility of discriminatory patterns and increase the dependabilityofscreeningresults.Additionally,thesystem will be deployed in the real world at several airport checkpoints, allowing for ongoing data collection, monitoring, and screening procedure improvement. This continuousimprovementwillguaranteeamorereliableand efficientairportsecuritymanagementsystembyimproving securityefficiency,equity,andtransparency.
WearegratefultoDr.GTejVarmaM.Tech.,Ph.D.Assistant ProfessorDepartmentofComputerScienceandEngineering, forallofherhelpandassistanceduringthecreationofthis project.Hermeticulouscritiquesinsightfulobservations,and

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
continuousencouragementhavebeencrucialinhelpingto shapeandbringourresearchtocompletion.Inadditionto helpingourprojectsucceed,hercommitmenttocreatingan atmosphere of academic rigor and creative thinking has givenusaloveforlifelonglearninganddiscovery.Wedeeply appreciate her for her perseverance, awareness, and dedication, which have served as the cornerstones of our path.
We also extend our appreciation to Dr.D.Jaya Kumari and Dr.G.V.N.S.R.RatnaKara Rao for cooperation and encouragement.
Lastly,weacknowledgetheunwaveringsupportofourstaff of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering playedacrucialroleinfacilitatingourprojectwork,andwe thankthemfortheircontributions.
[1] T.Stotz,"ThePerceptionandAcceptabilityofSelective Security Checks at Airports," doctoral thesis, ETH Zurich,2021.10.3929/ethz-b-000507787istheDOI.
[2] G. Scozzaro at al., "Simulation-Optimization-Based DecisionSupportSystemforManagingAirportSecurity Resources,"inAdvancesinSimulation:Proceedingsof the 2023 EUROSIM Congress, A. Biedenkapp, J. P. Chaves, and P. M. Pardalos, Eds., Cham, Switzerland: Springer,2023,pp.111–118.DOI:10.1007/978-3-03168438-8_11. P. Gupta and S. Sharma, "Digital Menu SystemsinHospitality:AComparativeAnalysis,"IEEE International Conference on Information Systems, 2019,pp.245-252.
[3] Z. Zhang, “Research on Risk-based Passenger DifferentiationTechniquesAppliedtoAviationSecurity Screening,” Journal of Electronics and Information Science, vol. 9, no. 1, 2024. DOI: 10.23977/jeis.2024.090103.G.Brown,"Integrationof MicrocontrollersinRestaurantManagementSystems," IEEETransactionsonControlSystemsTechnology,vol. 9,no.2,pp.123-135,2016.
[4] J.SkorupskiandP.Uchroński,"Data-DrivenAnalysisof theAirportCargoScreeningProcess,"inProceedingsof the 33rd European Safety and Reliability Conference (ESREL 2023), M. Brito, T. Aven, and P. Baraldi, Eds., London,UK:CRCPress/Balkema,2023,pp.3448–3454. DOI:10.3850/978-981-18-8071-1_P507-cd.R.Zhang,X. Liu,andY.Huang,"SmartTechnologiesinRestaurant Management:ASurvey,"IEEETransactionsonSystems, Man,andCybernetics:Systems,vol.19,no.5,pp.12031215,2019.
[5] A. K .Jain et al., "Enhancing Airport Security through AdvancedBiometrics,"ProceedingsoftheIEEE,vol.91,
no. 12, pp. 1686–1698, Dec. 2003. DOI: 10.1109/JPROC.2003.819038
[6] K. Michalski et al “The Implementation of Selective PassengerScreeningSystemsBasedonData Analysis andBehavioralProfilingintheSmartAviationSecurity Management – Conditions, Consequences and Controversies,” Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 1145–1155, Jun. 2020. DOI: 10.9770/jssi.2020.9.4(2)
[7] A. Knol et al., “Analyzing airport security checkpoint performanceusingcognitiveagentmodels,”Journalof AirTransportManagement,vol.75,pp.39–50,2019. DOI:10.1016/j.jairtraman.2018.11.003.
[8] A. Carr et al., “Airport operations and security screening:Anexaminationofsocialjustice,”Journalof Air Transport Management, vol. 85, p. 101814, 2020. DOI:10.1016/j.jairtraman.2020.101814.
[9] C.Lumetal.,Discretionandfairnessinairportsecurity screening,"SecurityJournal,vol.28,pp.352–373,2015. DOI:10.1057/sj.2012.51.
[10] J.M.Wolfeetal.,“Prevalenceeffectsinnewlytrained airportcheckpointscreeners:Trainedobserversmiss raretargets,too,”JournalofVision,vol.13,no.3,Dec. 2013.DOI:10.1167/13.3.33.
[11] B. Hasisi and D. Weisburd, "Going Beyond Ascribed Identities: The Importance of Procedural Justice in AirportSecurityScreeninginIsrael,"Negotiationand Conflict Management Research, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 185208,2011.DOI:10.1111/j.1540-5893.2011.00459.x.
[12] P. Madhavan and J. R. Brown, "How (Un)biased Are Airport Security Screening Procedures?" Current ResearchinPsychology,vol.1,no.2,pp.71-74,2010. DOI:10.3844/crpsp.2010.71.74.
[13] T. Stotz et al., "Increasing the Deterrence of Airport Security Checks by Managing Expectations Through Communication,"SecurityJournal,vol.34,pp.223-240, 2021.DOI:10.1007/s12198-021-00240-8.
[14] S.L.Gabbidonetal.,"TheInfluenceofRace/Ethnicity on the Perceived Prevalence and Support for Racial Profiling at Airports," Criminal Justice Policy Review, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 31-45, 2010. DOI: 10.1177/0887403409332569.