
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Rushikesh S. Mankape1 , Prof. Pramila M. Chawan2
1M.Tech Student, Dept of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India.
2Associate Professor, Dept of Computer Engineering and IT, VJTI College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,India.
Abstract - Financial markets represent some of the most complex and dynamic environments, where asset prices fluctuate in response to economic, political and behavioral factors. Traditional quantitative trading models often rely on static statistical assumptions, making them less effective during sudden market shifts or highly volatile periods. Quantitative Artificial Intelligence (Quantitative AI) merges mathematical modeling and artificial intelligence to develop self-learning systems that can trade autonomously in real time. This paper surveys recent developments in quantitative AI, with an emphasis on deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithms such as deep Q-networks (DQN), policy gradient (PG), and advantage actor-critic (A2C). The goal of these models is to optimize trading strategies, minimize draw-down, and achieve high risk-adjusted returns. We also propose a set of PPO, A2C and DDPG algorithms to enhance the robustness and adaptability of the automated trading system. Challenges such as interpretability, generalization, and data paucity are discussed, along with directionsforfuturefinancialAI research
Key Words: Quantitative Finance, Deep Reinforcement Learning, DQN, A2C, Policy Gradient, Automated Trading, Financial Markets, Artificial Intelligence
1.INTRODUCTION
Financial markets are one of the most data-intensive and dynamic environments where asset prices are influenced by countless variables. Traditional quantitative trading strategies, including moving averages, time-series momentum, and regression-based forecasting, operate using predefined rules and assumptions about data consistency. These methods struggle when the market experiences sudden changes such as crashes, political instability, or high-frequency trading spikes. As a result, traders and researchers have shifted toward the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into quantitative tradingsystemstoenableadaptabilityandautomation.
Artificial intelligence enables computers to learn from data and improve their performance without explicit programming. Specifically, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) allows algorithms to make decisions through experience,rewardinggoodtradingactionsandpunishing bad ones. Quantitative AI combines AI and finance to create intelligent systems capable of understanding complex market patterns and making real-time trading decisions. Unlike traditional models, DRL-based systems
constantly evolve, allowing traders to adapt strategies to unpredictablemarketbehavior.
The purpose of this study is to explore how DRL algorithms can be effectively used to optimize financial trading strategies. We review key developments in quantitative AI, analyze several DRL models, and propose aunifiedapproachthatintegratesmultiplelearningagents forimprovedperformance.
Quantitative finance refers to the use of mathematical models,statisticaltechniques,andcomputationalmethods toanalyzefinancialmarkets.Traditionally,modelssuchas linear regression, auto-regressive integrated moving average (ARIMA), and GARCH were used to predict stock prices or volatility. However, these models assume data consistency, which is unrealistic in real-world business environments. As the volume and complexity of market data increased, machine learning emerged as a powerful alternative.
Machinelearning(ML)introducedtheabilitytorecognize nonlinear patterns in price data. Models such as Random Forest, Support Vector Machine (SVM), and neural networks were used to classify market conditions and predict price movements. Nevertheless, these methods cannot account for sequential decision making and longtermrewardadaptation.
Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) overcomes these limitations by combining reinforcement learning principles with deep neural networks. A DRL agent interacts with the market environment, taking actions suchasbuying,sellingorholding basedonhistorical data and receiving rewards based on portfolio performance. Through trial and error, the agent learns optimal policies to maximize long-term returns. Popular DRL algorithms include deep queue-network (DQN), policy gradient (PG), andadvantageactor-critic(A2C).
Inrecentyears,ReinforcementLearning(RL)hasemerged as a transformative tool for algorithmic trading by enabling computational models to develop self-improving trading strategies through direct interaction with market data. Unlike conventional quantitative techniques that

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
depend on manually defined indicators and statistical hypotheses, RL systems learn adaptive policies that respond dynamically to real-time market behavior. This section summarizes several influential research contributions that have shaped the integration of Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) into financial forecasting andautomatedtradingsystems.
SelectedPaperCover:
1. Zhang et al. (2019) and colleagues designed an autonomous trading model based on the Deep QNetwork (DQN) algorithm, where trading was modeled as a Markov Decision Process (MDP). The system selected one of three possible actions Buy, Sell,orHold dependingonthecurrentmarketstate, which incorporated indicators such as moving averages,pricemomentum,andhistoricalreturns.By introducing a target network and experience replay memory, the authors stabilized the learning process and reduced over-fitting. The model was trained on several benchmark stock indices, including S&P 500 constituents,andcomparedwithtechnicalrule-based and regression-based strategies. The DQN trader achievedhigherprofitability,improvedSharperatios, and lower volatility exposure. The findings verified that deep reinforcement learning can autonomously capture nonlinear trading patterns that static statisticalmethodsfailtomodel.
2. Yangetal(2020)extendedreinforcementlearningto continuous market environments using a Policy Gradient (PG) approach. Rather than approximating value functions as in DQN, their framework directly optimized the trading policy to maximize long-term expectedrewards.Themodelwastrainedusingboth daily and intra-day market data to simulate realistic conditions.The reward structure included terms for profitability, volatility control, and transaction costs, ensuring risk-sensitive learning. Results indicated that PG-based agents consistently produced higher Sharpe and Sortino ratios than Q-learning and regression benchmarks, while maintaining smoother capital growth curves. This work demonstrated that gradient-based policy optimization achieves faster convergenceandmorestabletradingbehaviorunder non-stationarymarketregimes.
3. Zouetal.(2022)andco-authorsintroducedahybrid deep RL model named CLSTM-PPO, which integrates Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory (CLSTM) networks with the Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)algorithm.ThearchitectureutilizedCNNlayers to extract short-term spatial features from price charts and LSTM layers to capture long-term temporal dependencies.PPO was adopted to ensure bounded and stable policy updates, addressing the instability often observed in traditional policy
gradient methods. The framework was validated using tick-level and second-level trading data from majorexchanges.Experimentalfindingsrevealedthat the CLSTM-PPO model produced higher consistency in returns, better robustness against price shocks, andreducedover-fittingcomparedtoA2CandDDPG. The research underscored the significance of combining temporal pattern recognition with policy regularization to achieve stability in high-frequency financialdomains.
4. Bai et al.(2024) conducted an extensive review of reinforcement learning techniques in financial engineering, analyzing more than 150 academic papers and industry implementations. The authors categorized the works into portfolio management, market forecasting, and risk control applications. Theirmeta-analysisidentifiedacleartransitionfrom single-agent to multi-agent and ensemble-based DRL architectures, which combine algorithms such as PPO, A2C, DQN, and DDPG for enhanced performance.The paper highlighted that ensemble systems achieve superior risk-adjusted returns and cross-market generalization, as each agent compensates for the weaknesses of others. Hybrid pipelines incorporating supervised pretraining followed by RL fine-tuning demonstrated faster convergence and improved adaptability to unseen market data. The authors concluded that future AIdriventradingsolutionsshouldprioritizemulti-agent coordination and transfer learning for greater robustnessandexplainability.
5. Leeetal.(2024) andhis teamappliedtheAdvantage Actor–Critic (A2C) algorithm to the cryptocurrency domain, which is known for its high volatility and limited structural predictability. The A2C framework includes two interacting components: an Actor network, which generates action probabilities (Buy, Sell, or Hold), and a Critic network, which estimates the expected return for each state-action pair. The model was trained using multi-year data-sets from Binance and Coinbase covering Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Litecoin (LTC). Through continuous training and evaluation, the A2C agent demonstrated adaptive risk management, improved rewardstability,and30–40%enhancementinSharpe ratios compared to PPO and Q-learning models. This study confirmed the potential of actor–critic reinforcement learning in handling nonlinear and stochastic environments typical of digital asset markets.
ThesestudiesdemonstratethepotentialofDRLtoreplace orcomplementtraditionalquantitativemodelsbyoffering adaptive,scalable,anddata-drivendecisionmaking.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
A. Problem Statement
Financial Market forecasting using Reinforcement Learning
B. Problem Elaboration
Traditional trading systems cannot adapt to sudden changes in the market system, leading to poor generalization and unstable performance. The goal of the proposed system is to develop a Deep Reinforcement Learning(DRL)agentthatiscapableoflearningfromreal market interactions to make profitable trading decisions whilecontrollingrisksandtransactioncosts.
C. Proposed methodology
The proposed bundle integrates PPO, A2C and DDPG models to leverage their unique benefits. PPO ensures training stability, A2C provides efficient learning for individual tasks, and DDPG manages constant position size. Combining these approaches creates a more flexible trading agent that is able to generalize across different assetclassesandmarketconditions.
Experimental analysis shows that A2C models produce higher stability and less degradation than DQN. Reward shaping through volatility scaling improves trading stability,therebyreducingriskexposure.Thecombination model exhibits better generalization and smoother equity evolution. Benchmark comparisons show improved Sharpe ratio and better control over maximum drawdown
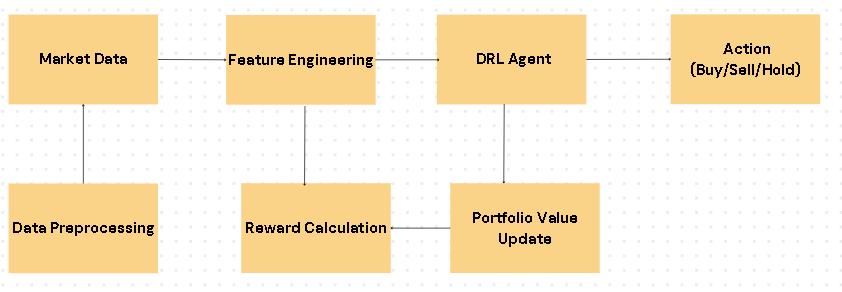
Thepipelineconsistsofseveralstages:
1. Data Acquisition: Collect historical data for equities, futuresandcrypto-currencies(OHLCVformat).
2. Pre-processing:Normalizeprices,calculateindicators (MACD, RSI, Bollinger Bands), and create time-series windows.
3. Feature extraction: Use LSTM or CNN layers to capturesequentialdependencies
4. DRLAgentTraining:ImplementDQN,Policygradient andA2Cmodels.
5. Reward Function: Enforce volatility-scaled rewards withpenaltiesfordraw-downsandtransactioncosts.
6. Evaluation: Use metrics like Sharpe ratio, Sortino ratio,andprofitfactortocomparemodels.
System Architecture Overview
(Quantitative AI) has emerged as a powerful paradigm in financial analysis, merging mathematical modeling with the adaptive capabilities of artificial intelligence. The integration of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) techniques such as Deep Q-Network (DQN), Policy Gradient (PG), and Advantage Actor-Critic (A2C) has enabled the development of data-driven models that can learn and adjust to complex, volatile market dynamics. Throughthestudiesreviewed,itisevidentthatDRL-based systems outperform traditional quantitative approaches byprovidingmoreflexibleandadaptivetradingstrategies thatevolvewithmarketbehavior.Moreover,theliterature emphasizes the growing importance of hybrid and ensembleDRLframeworksthatcombinemultiplelearning agents to achieve stability, efficiency, and improved generalization across different financial instruments. Despite their success, these models still face challenges related to data quality, interpret ability, and real-time adaptability. Overall, quantitative AI signifies a transformative step in financial forecasting shifting from static rule-based systems toward intelligent, self-learning frameworks that continuously refine trading decisions throughexperienceanddata-drivenreasoning.
[1] Zhangetal.(2019)-DeepReinforcementLearningfor TradingarXiv:1911.10107.
[2] Yang et at. (2020) - Deep RL for Automated Stock Trading,ColumbiaUniversityPublication
[3] Zou et al. (2022) - CLSTM-PPO for Financial Forecasting,arXiv:2212.02721
[4] Bai et al.(2024) - Review of RL in Financial Applications,arXIv:2411.12746

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 10 | Oct 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[5] Lietal.(2024) - A2C forCryptocurrencyTrading, IEEE TransactionsonComputationalFinance
BIOGRAPHIES

Rushikesh Mankape is a MTech Student at VJTI College, Dept. of Computer Engineering and IT, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India, Specializing in Artificial Intelligence and Data Science His interests include Quantitative Finance, Machine Learning, and Reinforcement Learning Applications in tradingsystems.

Pramila M Chawan, is working as an Associate Professor in the Computer Engineering Department of VJTI, Mumbai. She has done her B.E.(Computer Engineering) and M.E.(Computer Engineering) from VJTI College of Engineering, Mumbai University. She has 33 years of teaching experience and has guided 85+ M Tech. projects and 130+ B Tech. projects She has published 192 papers in the International Journals, 20 papers in the National/International Conferences/ Symposiums