
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Chiranjeevi T.S 1 , Dr. Annapoorna T. L 2 , Dr. LEELA B.N 3
1st Semester, MTech PDM Department of Mechanical Engineering, 1sth semester students, Sri Siddhartha Institute of Technology, Tumkur – 572105
2&3 Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sri Siddhartha Institute of Technology, Tumkur –572105
Abstract - The purpose of this project is to develop a stairclimbing robot which can able to perform process of climbing and landing by improving the combination of rocker Bogi mechanism. The combination of two different mechanism makes more efficient in carrying load, reduce friction on ground or climbing and cannot get the backward force due to gravitational force.
In our project, the robot is equipped with Tri-Star wheels which enable us to carry load up and down the stairs. It also eases the movement of robot in irregular surfaces like holes, bumps, etc.
A stair climbing robot is a specialized robotic system designedtonavigateandtraversestaircases,overcomingthe challenges posed by changes in elevation and varying terrains. Unlike traditional wheeled robots, which may struggle with stairs and uneven surfaces, stair climbing robots are equipped with mechanisms that allow them to ascendanddescendstepsefficiently.
Thedesignofstairclimbingrobotscanvary,anddifferent modelsmayusewheels,tracks,oruniqueconfigurationslike a star wheel design to achieve stability and mobility on stairs. The primary goal of these robots is to extend the reach of robotic systems into environments with complex geometries, making them versatile tools in industries ranging from emergency response to logistics and exploration
Todeveloptheintelligentautomated stair-climbingrobot which can carry heavy load on the stair. 2. To develop the more efficiency climbing and lending performancebyusingtheprocessofwirelesscontrolsystem 3.Tocreateastairclimbingrobotthatcancarryapayload upanddownastandardflightofstairs,whilemaintaining wirelesscontrol.
Theinabilitytoclimbcoarsewalls,frictionalresistanceand abrasionofsuckers,andpoorobstacle-surmountingability
are some of the technical problems faced by traditional robotswhichusevacuumsuckers.Anewnegativepressure adsorption mechanism is used in the design of the robot. Thismechanismgeneratesandmaintainsnegativepressure and adsorption force by using the air’s rotational inertia effect;therefore,thestructureincorporatingthismechanism iscalledtheelectricallyactivatedrotational-flowadsorption unit. The most important characteristic of the adsorption unitisthatitcanfunctionwithoutbeingincontactwiththe wall,whichfundamentallysolvesthesetechnicalproblems associatedwithtraditionalclimbingrobots.Forimproving therobotsloadabilityandobstaclesurmountingability,it has been designed a square shaped rotational-flow absorptionunit andsoftskirt structure.Thesehavebeen testedintheactualwallandresultsshowsthattherobotcan movestably.Somerobotshavebeendesignedfortraversing through stairs and obstacles by researchers such as quadrupedandhexapodrobots.Althoughtheserobotscan traverse stairs and obstacles, but they usually don’t have smoothmanoeuvringonflatsurfacesduetotheirmotionon legs[1].Ontheothersidewheeledandleg-wheeledrobots havebeenintroducedthattheycanclimbonlyonestair[6].
Iftherobotsclimb,declinethroughaslopedpath,therobot switchestostar-wheelsmotion.Thestar-wheelscanrotate freelyaroundtheiraxes.Oneofthewheelsofthestar-wheel getfixedononestairasabaseandtherotation ofthestarwheels effects in stair climbing. It allows the robot adapts itselfwithrespecttopathcurvatureandpreventstheshocks ofchangesofpathslope.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

Also,itenablesalltheeightwheelstohavefirmcontactwith thegroundandensurethatthewheelsandgroundareintact atallthestagesoftraversingperiod.Itshouldbenotedthat the material of wheels and stairs are Rubber. So, we can attach the robot to the wheel chair which carries the movementdisabledpersontomovethrough stairswithout help of anyone in the home or in any other places where elevator facilities are not available. This makes them to movearoundupstairsanddownstairwithoutseekinghelp fromothers

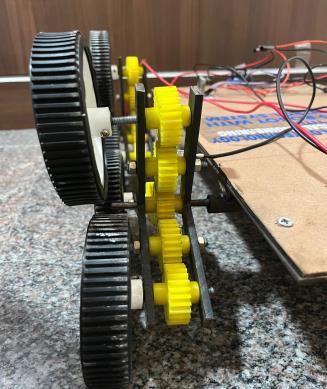
To design a tri star wheel-based robot, Wheels are mounted on motor shaft. Robot is powered with 4 gearedmotorsmountedonframe.All3wheelsonstar wheelisgearedtomainmotortoachieve.
1. MotionMechanism:Employingareliablemotionsystem, suchastrackedorleggedmechanisms,tonavigatestairs effectively.
2. PowerSource:Providingasuitablepowersource,often rechargeable batteries, to ensure sustained operation duringclimbing.
3. MaterialandDesign:Choosinglightweightyetdurable materialsfortherobot’sconstructionanddesigningitto balancestabilityandagility.
4. TestingandOptimization:Iterativelytestingtheroboton variousstaircases,bycombiningtheseelements,astairclimbingrobotcannavigatestairssafely.
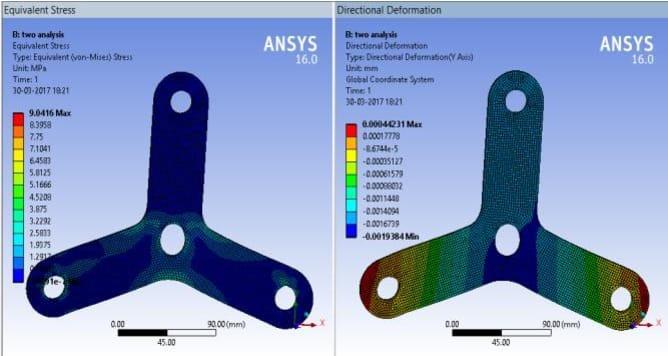
Fig 4: 3Dmodeloftri-squarewithanalysis
Thisdesigninvolvesarrangingthreewheelsinatriangular pattern. This configuration allows the robot to "roll" over obstacles, including stairs, by sequentially engaging each wheel.
Simplifiedmechanicscomparedtoleggedrobots.
Abilitytotraversebothflatsurfacesandstairs.
Canprovidegoodstabilityincertainstairclimbing situations.
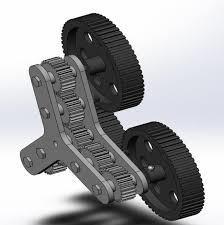
Fig 5: 3DCADmodelofgearsandwheelassembled
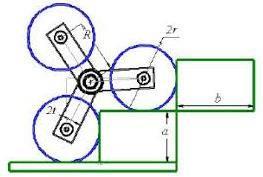
DerivingtheStar-Wheelparametersdependsontheposition ofStar-Wheelonstairswhereitdependsontwoparameters, thedistancebetweentheedgeofwheelonlowerstairandthe faceofnextstair(L1),andthedistancebetweentheedgeof wheel on topper stair and the face of next stair (L2). By comparingtheseparameters,threestatesmayoccurL1<L2. After each stair climbing, L2 becomes greater and after severalclimbingitwillbeequalorgreaterthanb(L2>=b).In the design of Star-Wheel, five parameters are important whicharetheheightofstairs(a),widthofstairs(b),radiusof regular wheels (r), radius of Star-Wheel, the distance

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
betweenthecenterofStar-Wheelandthecenterofitswheels (R)andthethicknessofholdersthatfixwheelsonitsplaceon Star-Wheels(2t).ForthecalculationofradiusofStar-Wheels (R)withrespecttothestairsize(a,b),thisequationisused: 3() a2 b2 R +=(1),whereaandbaretheheightandwidthof stairs. The minimum value of the radius of regular wheels (rmin) to prevent the collision of the holders to the stairs whereRistheradiusofStar-Wheelsandtisthehalfofthe thicknessofholders.
The Tri-Star isanovelwheeldesignoriginallybyRobertand JohnForsyth,assignorstoLockheedin1967inwhichthree wheelsarearrangedinanuprighttrianglewithtwoonthe groundandoneabovethem.Ifeitherofthewheelsincontact withthegroundgetsstuck,thewholesystemrotatesover theobstruction.

Advantages
• Thecontrolsystemissimpleandtherobotiscontrolled remotely.
• Mechanism is simple comparing to other available designsanditiseasytoassembleanddisassemblewhen necessary.
• UseofCastermidasthematerialforgearsmakesthem lightandnolubricationisrequiredduringmovement.
• Usingthewormgearboxmakesrobot‘stravelsafe.Ifby any chance voltage is cut off or batteries ran out of chargetherobotwillstayinitsposition.
Spurgearsorstraight-cutgearsarethesimplesttypeofgear. It consists of a cylinder or disk with the teeth projecting radially,andalthoughtheyarenotstraight-sidedinformof theedgeofeach tooth is straight and aligned parallel to the axis of rotation. These gears can be meshed together correctlyonlyiftheyarefittedtoparallelshafts.

The Spur Gear Design Mechanical engineers working in transmissionfieldwouldoftenhavetodecideuponkindof gears for usage. A designed gear criteria conforming to AGMAstandardsshouldhavethefollowing:
1. Enough mechanical strength to withstand force transmitted
2. Enoughsurfaceresistancetoovercomepittingfailure
3. Enoughdynamicresistancetocarryfluctuatingloads
3.2
Weight
Dimensions 25x40cm
2.5Kg
Framematerial: wood.
LengthofRover -53cm
WidthofRover 25cm
HeightofRover 22cm
WheelDiameter 11cm
GearDiameter 4cm
DCmotor

International Research
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Proceedings of the 17th IAARC/CIE/IEEE/IFAC/IFR InternationalSymposiumonAutomationandRobotics inConstruction,2000.[1]
InthispaperwepresentedaPCbasedwirelessstairclimbing robot which is capable of climbing all terrains stairs in its path and which is wirelessly controlled through PC using Zigbee technology. The controlling device of the whole systemisaMICROCONTROLLERtowhichZigbeemodule;DC motors of robot are interfaced through a motor driver. Whenevertheappropriatekeysarepressedinthekeyboard of computer, the data related to those keys will be transmittedoverZigbeemoduleusingRS232cable.Thisdata willbereceivedbyZigbeemoduleatrobotandthisdataisfed asinputtothecontroller.Thecontrollingdeviceofthewhole systemisaMicrocontroller.Whenevertheuserpressesany keyfromkeyboardofthePC,thedatarelatedtothatkeyis sentthroughZigbeemoduleinterfacedtoPC.Wheneverthe appropriatekeysarepressedinthekeyboardofcomputer, thedatarelatedtothosekeyswillbetransmittedoverZigbee module.ThisdatawillbereceivedbyZigbeemoduleatrobot and this data is fed as input to the controller. The Microcontrollerchecks thedatawiththeprogramembedded initandperformsappropriateactionsontheDCmotorsof the stair climbing robot. This data will be received by the Zigbee module in the robot system and feds this to Microcontroller which judges the relevant task to the information received and acts accordingly. The Microcontrollersusedintheprojectareprogrammedusing EmbeddedClanguage.
Thisprojectaimedtodevelopamechanismforclimbingstair usingstarwheelsystemwhichitsmainideawasmakingthe wheels rolling within motion in flat surfaces while in climbingmotionthewholesystemwill roll together.Gear systemwaschosenastransmissionsystem.Thedesignand modeling of a mobile robot with Wheel-Based motion, is inspired from legs of human beings while climbing and descendingstairs. Due to itsstar wheel motion, it has the advantage of ascending, descending and traversing with flexibility toward uphill, downhill and slope surfaces. Furthermore,onflatsurfacesithassmoothandfastmotion whichisduetoitswheelsmotion.Itshowsthattherobotcan beusedforanyterrainahumancango.Itcanalsobeusedfor space researchers as a Spacecraft or war regions identificationorunknownterrains
[1]AracilR,R.Saltaren,M.Almonacid,J.M.Sabater,J.M. Azorin, (2000), Kinematic control for navigation of mobile parallel robots applied to large structures, in:
[2]Buehler M, U. Saranli, D. Papadopoulos and D. Koditschek.(2002),Dynamiclocomotionwithfourand six-legged six-legged robots, Centre for Intelligent Machines, Ambulatory Robotics Laboratory, McGill University, Buchler M., (2002) Dynamic Locomotion withOne,FourandSix-LeggedRobots,Ambulatory
[3]Robotics Laboratory (ARL), Centre for Intelligent Machines,McGillUniversity,Montreal,
[4]E. Z. Moore, D. Campbell, F. Grimminger, and M. Buehler, ReliableStairClimbingintheSimpleHexapod 'RHex', IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Vol 3, pp 2222-2227, Washington, D.C., USA, May11-15,2002
[5]Crespi A., A. Badertscher, A. Guignard and A.J. Lispeert: Amphibot I, an amphibious snakelike robot, Robotics and Autonomous Systems, vol. 50, issue 4, pages163-175,[5]
[6]DalvandM,MajidM.Moghadam,(2003)Designand modeling of a stair climber smart mobile robot, published in the 11th International Conference on AdhanomRobotics(ICAR2003),Portugal,June30-July 3,2003,
[7] Buehler, Dynamic Locomotion with One, Four and Six- Legged Robots , Invited Paper, Journal of the RoboticsSociety ofJapan,20(3),(2002)15-20
[8]E. Z. Moore, D. Campbell, F. Grimminger, and M. Buehler, ReliableStairClimbingintheSimpleHexapod 'RHex', IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Vol 3, pp 2222-2227, Washington, D.C., USA, May11-15,2002
[9]E.Z.MooreandM.Buehler,StableStairClimbingina Simple Hexapod,4thInt.Conf.onClimbingandWalking Robots, Karlsruhe,SGermany,September24-26,2001.
[10]U.Saranli,M.Buehler,andD.E.Koditschek,RHex:A Simple and Highly Mobile Hexapod Robot, Int. J. RoboticsResearch, 20(7):616-631,July2001