
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
p-ISSN:2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
p-ISSN:2395-0072
Keerthi
A Kumbar1
Dept. of ECE
ATMECE
Mysuru, India
Pushpa M J2
Specialist
Accenture
Bangalore
Dr. Prakash Kuravatti3
Professor, Dept. of ECE
Rajeev Institute of Technology, Hassan, India
Abstract - The paper presents the design and modeling of a microstrip patch antenna for 5G applications using the High-Frequency Structure Simulator - HFSS. The introduction of 5G and the ongoing advancement of mobile communication systems are elevating demand for high-performance antennas that operates efficiently at high frequencies. Its small size, ease of manufacturing, and versatility in the form of device integration, a patch antennas are selected. Resonance frequency, BW and radiation pattern features are optimized to satisfy the demanding specifications of 5G systems, including low latency and high data throughput. The intended frequency range is 10 GHz. Simulation tests indicate that the antenna's broad bandwidth, low return loss, and good impedance matching make it suitable for high-frequency 5G applications. The findings additionally illustrate the antenna's directional radiation pattern, which is essential for beamforming and MIMO technologies in 5G networks.
Index Terms - Circularly polarized (CP), MPA (Microstrip Patch Antenna), HFSS, MIMO.
In a rapidly developing technology, wireless communication is essential to contemporary communication. In order to provide high-speed internet, particularly in remote places, satellites of different types like GPS communication and remote sensing are essential. A thorough study of the circularly polarized (CP) antennas is mentioned in the publication [1], at Ku band with microstrip feedline using structured slots. The significance of creating low-profile, straightforward antennas that can function well at millimeter-wave frequencies and that overcomes the drawbacks of current technologies. Trends in antenna design are changing to accommodate growing demands for compactness and performance. First proposed in 1953, microstrip antennas gained popularity as PCB technology and advances in wireless communications have placed significant demandsonantennadesigntechnology.Furthermore,mobilephonestobecomewidelyutilizedinmodernlife,increasingthe concernsabouttheirpotentiallyharmfulradiation[2].
The ground, substrate, and patch layers make up microstrip patch antennas. Aperture coupling, proximity coupling, microstripline,andcoaxial feedingaresomeofthefeedingtechniques. Severalacademicsarecurrentlystudyingthevarious planar antenna types and moreover numerous geometrical shapes of monopole antennas, including triangular, pentagonal, hexagonal, elliptical, ring/split ring, annular ring, circular disc, modified English alphabet and dipole antenna configurations likebow-tieantennas,arefoundthroughathoroughproductionofthereviewprocess[2].
A microstrip antenna has natural limitations: narrow bandwidth, low gain, low efficiency, and high power constraint. Thestandardmicrostripantenna'slimited BWwhichisthemostseverelimitationssinceitlimitsusersfromusingtheentire Ku-band spectrum [1–3]. In earlier research, they devised various methods to get around the BW and gain restrictions, is summarized as follows: (i) used an aperture in the patch antenna to change the dielectric constant, decreasing the quality factor and expanding the bandwidth; (ii) employing partial substrate removal in multiple layer dielectric substrates to improve the gain and bandwidth, respectively, (iii) Using probe feeds or microstrip feed lines to manipulate slots on microstrip patches, the KU-band was separated into two or more resonances, promoting polarization variety and stable radiation performance and (iv) slotting the ground and stacking microstrip antennas, which greatly increased gain and bandwidth. However, when included into an array system, it raised the cost and complexity of the design [3]. Condensed search revealed that all of the previously mentioned methods, in addition to utilizing expensive materials and intricate designs,wereunabletocovertheentirecommercialsharedKu-bandspectrum(10.95-14.5GHz)thathasbeendesignatedby theFederalCommunicationsCommission(FCC)andInternationalTelecommunicationUnion(ITU)[3]

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
p-ISSN:2395-0072
Multi-antenna systems such as MIMO are susceptible to mutual coupling effects, which can seriously reduce system performancebyincreasingunwantednear-fieldelectromagneticcouplingandsochangingthesystem'sradiationpattern.The couplingstrengthbetweentwopatchantennasplacedclosetooneanother reliesonthepositionofoneantennawithrespect totheother[4].Theprimaryobjectiveistoenhancetheatributesofantennas,suchasgain,radiationpatterns,andbandwidth. The approach is crucial to meeting the high-speed, low-latency communication needs of 5G networks. Modifying the substrate'sparameterinamethodicalmannerhelpstoincreasethebandwidth[5].Microstripantennasarecurrentlyessential partsofcontemporarymobilecommunicationsystemsbecauseoftheirintrinsicbenefits,whichincludetheirlowcost,easeof usage, lightweight design, and variety of shapes. Therefore, the main purpose of this work is to build and optimize a patch antennathatfunctionsbetterat28GHzfor5Gwirelessapplications.Theemploymentofsophisticatedsubstratematerialsand simulationtechniquesismeanttoincreasea numberof antenna performancecharacteristics,includinggain, bandwidth,and radiationpatterns.
Metamaterials as materials which are designed to have properties not found in natural materials, enhance antenna performance. Split ring resonators (SRRs) are one type of metamaterial that generates magnetic responses. Metamaterial antennas have several uses, such as wireless communication and GPS. High-frequency antennas need to have their designs altered because of problems like heat emission. Reflectors reroute electromagnetic waves to enhance antenna performance. Antennas can be classified as either omnidirectional or directional based on their intended purpose and gain is the primary attentionofradiatedpowerinacertaindirection.
5G technology has expanded the demand for fast wireless connection, affordability and ease of use, for which microstrip patch antennas, or MPAs, are preferred. Microstrip patch antennas find widespread use in everything from medicinalequipmenttocommunicationsystems.Itiscomposedofconductingmaterialsandhasaradiatingpatch.Thepatch and feed lines is photo etched onto a substrate with a ground plate [6]. The design process for MPAs for 5G applications utilizes HFSS for accurate simulations. The block diagram is illustrated in fig 1 where MPAs consist of a metallic patch on dielectricsubstrateandgroundplanebelow Suchantennassupportshigh-frequencybandsandbroadbandcharacteristics.
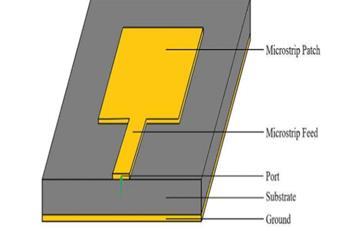
The role of millimeter waves in enabling high-speed mobile networks, particularly for applications like Vehicle-toeverything (V2X) communication to attain high gain and wide bandwidth while preserving compactness, it highlights the necessityofefficientantennadesign[7].Compactsizeandhighergainareessentialfordeviceslikesmartphonesandrouters. MPAscanbeadaptedformassiveMIMOsystems,enhancingnetworkcapacity.Challengesincludeachievingwiderbandwidth and high impedance matching. The design process in HFSS allows for accurate modeling of electromagnetic behavior. HFSS ensuresthatMPAsmeetperformancecriteriaforhigh-speedcommunication.TheMPAsfor5Ghasobtainedstrongattention duetohigh-frequencyrequirements.VariousstudieshaveexploredMPAdesignandoptimizationusingHFSS.
Themotivationisthatthe5Gtechnologyenablesfasterdatatransferandhigherconnectivityforvariousapplications andMPAsareessentialfor5Gsystemsforthecompactsizeandefficientperformance.
Due to the developments, the need for high-frequency, wideband, and tiny antennas appropriate for 5G applications, thebroad area ofMPAs hasattracted theattention.Researchershavefocusedonimprovingtheseantennasto encounterthe strictrequirementsofrecentwirelesscommunicationsystems.Several researcheshavebuilt,simulated,andoptimizedMPAs

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
usingtheHigh-FrequencyStructureSimulator(HFSS).Duetoitstrackrecordofaccuratelysimulatingandevaluatingantenna performance, HFSS is a tool of choice in this field of study [1]. The authors point out that a major drawback for real-world applications is that the majority of single-fed antennas that operate at millimeter-wave frequencies do not offer a broad AR angularbeamwidth.
Antennas that can function across a broad frequency range while being small and effective are in high demand as mobile technology advances. The various antenna modeling’s investigated results a new trend that includes planar patch antennas, which are well-liked because of their simple construction and simplicity of integration. The iterative character of antennamodelingisfurtherunderscoredtheutilizationofparametricanalysisduringthesimulationphase[2].Formonopole antennas, researchers have looked into a variety of geometrical shapes, including triangular, pentagonal, and hexagonal designs, which have demonstrated encouraging performance outcomes. 79% Ku-band utilization has been gained by a small patchantennapropsedforsatellitecommunication.Withitsinternalresonatorandrectangularpatch,itoptimizesdimensions for a wide operating band of 2.8 GHz (11.2 to 14.0 GHz). The antenna demonstrates an average gain of 4.65 dB and a total efficiency of 65%. With modification of the antenna's effective electric length, the inner resonator greatly improves performance. CST Microwave Studio simulations confirm the design's efficacy and appropriateness for contemporary communicationapplications[3].
Inordertohandlethelargedataratesandlowlatencyneededby5Gnetworks,researchhashighlightedthenecessity ofwidebandandhigh-gain designs. Triangular,pentagonal,andhexagonal designs are oneamong thegeometrical monopole antennaformsandtheircombinationsaremostlikelystudiedinanattempttoenhanceperformance[2].Theadvancementof antenna technology has been greatly aided by the discovery of Metamaterials, especially structures like SSR- Split Ring Resonators.Bymanipulatingelectromagneticcharacteristics,thesematerialscanincreasethebandwidthandgainofantennas thatoperateathigherfrequencies[3].Evenwithimprovements,MPAsstillfacedifficultiesinobtainingbroadbandwidthand effective impedance matching. To get over these restrictions and improve antenna performance overall, researchers have lookedintoavarietyoffeedingstrategiesandstructuralchanges[4].TheliteratureemphasizeshowimportantMPAsarefora number of uses, such as industrial automation, healthcare, and mobile communication. MPAs are a good option for 5G technologybecauseoftheirversatility w.r.t deviceintegration[5].Thepurposeofthecurrentresearchistofurther optimize MPA design for 5G applications, with an emphasis on performance, efficiency, and compactness at millimeter-wave frequencies. As per the literature, in order to satisfy the changing needs of wireless communication systems, antenna design innovation will need to continue The structuring and enhancement of a MPA for 5G applications operating at 28 GHz is the main attraction of the paper [5]. It improves radiation patterns, gain, and bandwidth by using Rogers RT/duroid 5880 substrate material. In order to maximize bandwidth - which is crucial for high-speed, low-latency communication in 5G networks substrate height is optimized from 0.1 mm to 0.6 mm using sophisticated simulation tools like HFSS and CST in conjunction with artificial intelligence techniques. 5G networks will be created between 2020 and 2030; at current time, researchers are mostly focused on 5G wireless communication for smartphones. The millimeter wave spectrum is highly attractive for 5G mobile applications because of its massive capacity availability [6]. The importance of MPAs in 5G technologiesisunderscoredbythisliteraturereview,thatpointoutsthefield'sachievementsandongoingdifficulties.
Along with affordability, small size, and ease of integration into devices, microstrip patch antennas are crucial for 5G communication.However,antennaarraysonhigh-performancesubstratesmightassisttheminovercomingobstacleslikelow gain and constrained bandwidth. The study is on a 32-element patch antenna array intended for the 26 GHz band, with the goal of maximizing gain and efficiency while improving directivity through patch spacing optimization. The feeding network architectureiscrucialforensuringeffectiveperformancein5Gapplicationsandachievingexcellentimpedancematchingover theoperationalfrequencyband[7].Research focusesonwidebandandhigh-gaindesignsfor5Gapplications.Dual-frequency feedingwasconsideredinastudytomodelawidebandrectangularpatchantenna.EBGstructuresandmetamaterialimprove gain and bandwidth for millimeter-wave applications. In the 5G network, compact MPAs are essential for mobile devices. Slotted patch designs reduces the size of the antenna without compromising its functionality. Effective communication is ensured through performance tests at mmWave frequencies. Beamforming techniques enhance coverage and throughput in microstrip patch arrays. HFSS has advanced the design of wideband, multi-band, and high-gain antennas. Optimization algorithmsandadvancedfeedingtechniquesimproveantennaperformance.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
p-ISSN:2395-0072
Themethodologyincludeskeystepssuchasdesign,simulationandoptimizationensuringthattheantennameetsthe performance requirements essential for 5G communications, including wider bandwidth and highest gain [1]. To simulate the antenna is to produce extremely precise solutions for complicated electromagnetic problems which are essential for analyzingtheantenna'sperformance theHFSSusestheFiniteElementMethod(FEM)[2].Optimizingcrucialcharacteristics includingradiationpattern,bandwidth,andresonancefrequencyisthe oneofthemainintentionofthedesignprocess.The strictrequirementsof5Gnetworks,whichcallforlowlatencyandhugedatathroughput,requirethese optimizations[3].A complicatedstructure composedoftwodielectricsubstratesandthreemetal layersis engaged intothe mentionedantenna design. This multi-layered strategy focuses to improve the performance of antenna by achieving a directional radiation patternandhigh-axialratio(AR)bandwidth,bothofwhichare requiredforefficientbeamformingin5Gnetworks[4]. The design now includes a rectangular feed line as an excitation input. Because it guarantees that electromagnetic power from the feed line is correctly coupled to the patch, this design is critical to the operating efficiency of the antenna [5]. The simulation results are analyzed to evaluate key performance characteristics such radiation patterns, bandwidth, gain, and return loss. A number of features are essential for assessing an antenna's feasibility for high-frequency 5G applications [6]. The strategies include a methodical design approach that focuses on parameter optimization, employs a multi-layered antennastructure,andusesHFSSforsimulationinordertoacquiretherequirementsof5Gtechnology.
TheprimarygoalofthetargetedapproachistodevelopandsimulateMPAsfor5Gapplications.Itseekstosatisfyhigh gain and broad bandwidth performance requirements. The precision of HFSS, a specialized tool for electromagnetic simulation,iswellknown.Figure2displaystheproposedantenna'sschematic.Theratioofintensityinacertaindirectionto isotropicradiationisknownasgain.ThemismatchbetweenanantennaanditsfeedlineisshownbyVSWR.Itsvaluebelow2 is considered acceptable for maximum antenna application. Bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies an antenna can effectivelytransmitorreceive.Efficiencyistheratioofradiatedpowertotheinputpowersuppliedtotheantenna.
The S11 parameter characterizes impedance matching and reflection properties of antennas. HFSS provides direct calculations for radiation efficiency in antenna designs. Specific substrate materials and dimensions are considered for antenna design. The design process involves systematic steps in HFSS for MPA simulation. Simulation results for the S11 parameter are analyzed for performance evaluation. 3D polar plots show the antenna's radiation and gain patterns. For reliableconnectivity,5GbasestationsmakeextensiveuseofMPAs.Wearablehealthmonitorsandmedical gadgetswith5G capabilitiesaremadepossiblebyMPAs.MPAshelpindustrialautomationsystemsmonitorandcontrolinrealtime.Flexible MPAsareusedinwearableelectronicsforavarietyofpurposes.
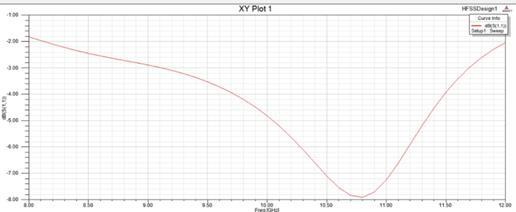
The design and simulation outcomes of a MPA customized for 5G applications using the High-Frequency Structure Simulator (HFSS) are presented in this work. For 5G communication networks, the antenna's performance in the 10 GHz frequencyrangeiscrucial.Thesimulationresultsfocusthattheantennawithgoodimpedancematchingandminimalreturns loss,bothofwhichareessentialforefficientsignaltransmission.Theantenna,inparticular,hasalowreturnloss, becauseof whichmostofthepowerisradiatedratherthanreflected.GraphoftheS11parameterwhichindicatestheantenna'sreturn loss,areshowninfigure3below.TheresultsofthisinvestigationindicatethattheS11parameter'sminimumpointisfound

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
atroughly10.8GHz,withintheintendedfrequencyrangeof10.5to11GHz.Inorderfor5Gapplicationstoworkproperly,it isrequiredthattheantennahastobetunedfortherequiredoperatingfrequency.
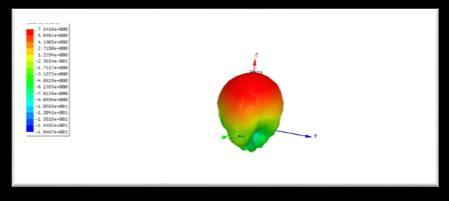
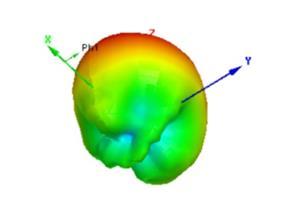
The figure 4 below presents a 3D polar plot that visualizes the gain of the MPA across different angles. This type of plot is essential for understanding the pattern of the antenna, which is crucial for its performance in applications of the 5G technologies.Theplotshowsthatthemaximumgainoftheantennaisapproximately7.45dB,whichisanimportantvaluefor ensuring effective signal transmission and reception. The gain distribution is not uniform; it shows regions of higher intensity at certain angles while exhibiting nulls or dips around the -90° and +90° directions. This uneven radiation distributionismustforapplicationsthatneeddirectionalsignaltransmission,suchasbeamformingin5Gnetworks.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net
p-ISSN:2395-0072
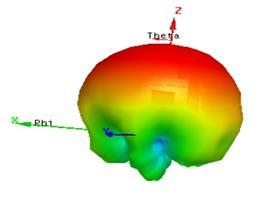
Theradiationpatterndepictedinthisfigure7belowisenvisionedtoshowacleardirectionalcharacteristic,indicating thattheantennafocusesitsenergyinspecificdirectionsratherthanradiatinguniformly.Unlikeomnidirectionalantennasthat radiateenergyequallyinalldirections,theradiationpatterninFigure7belowlikelydemonstratesamoreconcentratedbeam, which is beneficial for reducing interference and maximizing signal quality in desired directions. This characteristic aligns withthedesigngoalsofMPAs,whichareoftenoptimizedforhighestgainanddirectivity.
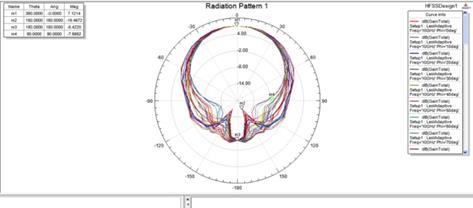
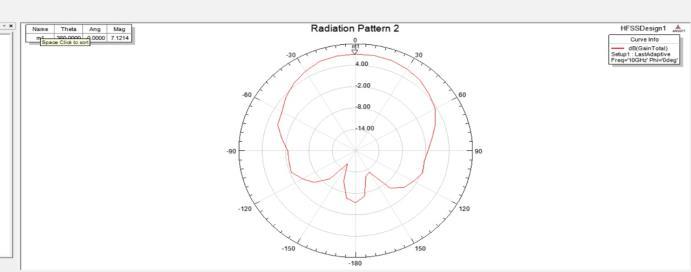
Similar to the preceding radiation pattern, Figure 8 below is meant for directed focus, suggesting that the antenna need to emit energy more effectively in specific directions. This feature is crucial for applications that expect precise signal targeting,suchasbeamformingandMIMO(MultipleInputMultipleOutput)technologiesseenin5Gnetworks.Thepresenceof nulls(areasoflowradiation)andpeaks(areasofhighradiation)inthepatterncanindicatetheeffectivenessofthe antennain specificdirections.Understandingthesecharacteristicsaidsintheantennadesign,reducinginterferenceandincreasingsignal strengthindesireddirections.Itgivesimportantinformationontheradiationparametersofthemicrostrippatchantenna.
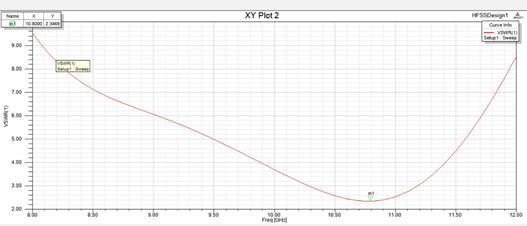
Thefigure9explainsabouttheVSWRclosetothethreshold,ithighlightsthattheantennaiswell-matchedtothefeed line,minimizingsignalreflectionsandlossestheVSWRplotindicatesavaluearound1.9,whichisclosetotheoptimalvalue of 2. This suggests that the antenna operates efficiently at the specified frequency, which is crucial for high-frequency applicationslike5G.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
TheseresultsservestovisuallysumuptheperformanceoftheMPA,showcasingitsimpedancematching,returnloss, and bandwidth characteristics These illustrations are essential for comprehending how effectively the antenna satisfies the demandingspecificationsof5Gsystems,suchasreducedlatencyandlargedatathroughput.
Combining MPA design with HFSS modeling has various advantages. HFSS provides accurate simulations for key antenna parameters. It makes it possible to optimize the antenna's materials and dimensions iteratively. Simulation saves time and money by doing away with the need for actual prototypes. It accurately models antennas in sub-6 GHz and mmWave frequencies.Theprogramalsoprovidesthoroughradiationpatternvisualizationsforoptimization.Itcombinesstructuraland thermal simulations to ensure performance and models antenna arrays for beamforming and MIMO applications. Modeling differentsubstratematerialsforoptimizationismadepossiblebyHFSS.Itsimplifiesthedesignprocesswithitseasy-to-useUI andtemplates. Satellite,radar,and wirelesscommunicationsystemsusemicrostrip patchantennasbecauseof their reduced size,lowprice,andeaseofmanufacturing.Theyprovideeffectivesignaltransmissionwithlowweightandflexibleintegration, andareusedinbiomedicalequipment,GPS,RFID,Wi-Fi,mobilephones,andaerospacesystems.
AMPAsfor5GapplicationswasstructuredandsimulatedusingHFSSsoftware,demonstratinghowmicrostripantennas'tiny size, affordability, and ease of fabrication make them perfect for next-generation wireless communication systems The simulated results verify that the antenna is effective within the targeted frequency range, which is usually in the sub-6 GHz andmillimeter-wavespectra.Keyperformanceindicatorssuchasgain,BW,efficiency,radiationcharacteristics,andreflection lossdemonstratethattheantennameetstheneedsof5Gapplications.Forthestructureandenhancementofmicrostrippatch antennas, HFSS software proves that a dependable tool by enabling comprehensive electromagnetic analysis and parameter customization. The study is on the integration of micro strip antennas into small 5G communication devices to enable connectivityandhigh-speeddatatransmission.
REFERENCES
[1] Hussam Al-Saedi, Wael M. Abdel-Wahab, Suren Gigya, Raj Mittra and Saifuddin Safavi-Naeini, “Ka-Band Antenna with HighCircularPolarizationPurityandWideARBeamwidth”.
[2] M.R.Ahsan,1,2M.HabibUllah,1,2F.Mansor,1N.Misran,1,2andT.Islam(2014)“AnalysisofaCompactWidebandSlotted AntennaforKuBandApplications”.
[3] Mohamed Ahmed Hassan Oweis Master student in Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering Arab AcademyforScience,TechnologyandMaritimeTransport(AASTMT).“ANovelKu-BandMicrostripAntenna”.
[4] MohammadAlibakhshikenari1,StudentMember,MohsenKhalily2,BalS.Virdee3ChanH.See4,5,RaedAbd-Alhameed6,7 and Ernesto Limit “Mutual Coupling Suppression Between Two Closely Placed Microstrip Patches Using EMB and gap MetamaterialFractalLoading”.
[5] Ahmed Mohamed Salem, Hanane Djellab, Mohamed Lashab, Mohamed Lashab, “Design and optimization of Microstrip Patch Antenna at 28GHz for 5G wireless applications:, 2024 6th International Conference on Pattern Analysis and IntelligentSystems(PAIS),2024IEEE.
[6] Deepak Kumar, Chanchal Anushka, Surya Deo Choudhary, Vineet Shekher,” Design and Simulation of I-Slot Microstrip PatchAntennawithDefectedGroundStructurefor5GApplications”,2018IEEE.
[7] SirineGhenjeti,RimBarrak,SoumayaHamouda,“HighGainandCompactMicrostripPatchAntennaArrayDesignfor26 GHzbroadbandWirelessSystems”,2023IEEE