
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Srijita Bhattacharyya1, Abhijit Majumder2, Ipsita Pal2, Pratik Halder1, Satrajit Das1 , Hiranmoy Samanta2
1Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Gargi Memorial Institute of Technology, Kolkata-700144, India
2Department of Mechanical Engineering, Gargi Memorial Institute of Technology, Kolkata-700144, India
Abstract - A lot of people are excited about artificial intelligence's(AI)potentialtopromotesustainabilitybecause it has transformed several industries, including healthcare, transportation,agriculture,energy,andmedia.Analysingthe two sustainability of AI in and of itself as well as its applications for advancing sustainability, this article scrutinises the rapidly changing field of AI sustainability. An impartial viewpoint on the economic, social, and environmental aspects is offered by the study's methodical classification of the body of current literature. Significantly, since 2019, the area has matured, as seen by an increase in publications and empirical studies, with a growing focus on holistic approaches that are in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations. Problems still exist even with AI's bright future in addressing difficult problemslikeclimatechangeandenvironmentaldegradation. These include the unpredictability of human behavioural responses, the over-reliance on historical data in machine learning models, the increased dangers associated with cybersecurity, and the negative effects of AI applications. Subsequent investigations must to incorporate multilevel perspectives, systems dynamics methodologies, design thinking, psychological and sociological factors, and evaluations of economic values. In the end, our work emphasises the necessity for creative AI solutions that lower the energy and natural resource intensity of human activity while also enabling efficient environmental regulation and preventing long-term risks to sustainability.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, AI Sustainability, Resource Management, Multilevel Analysis, Machine LearningChallenges.
Significantprogresshasbeenachievedinartificial intelligence(AI)overthepastfewdecades.AIhasthepowerto drasticallyalteranumberofsectorsandindustriesandbring about unanticipated change. AI systems have resulted in significant improvements being applied in a number of sectors, including the media, healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and energy. Though enthusiasm about AI is broad, there is a noteworthy caution that stems from concerns about potential
negativeimpactsaswellasevidenceofAI'sefficacy.For example,trainingastate-of-the-artmodel,particularlyone for natural language processing (NLP), demands a large amountofcomputationalpower,imposingalargeamountof energyalongwithrelatedcoststotheenvironmentandthe economy. Inaddition,newmoralandsocietalissuesforthe economyandsocietywerebroughtforthbythedevelopment ofAI.Theseissuesincludeworriesaboutthespreadoffake news,stagnantactualpayforworkers,andsocietalinjustice broughtonbyAIsystemsthatdiscriminate.Becauseofthis, scientistsarebecomingmoreandmoreinterestedinstudying howtheyaffect sustainability. Understanding AI's impacts and revolutionary potential, particularly with regard to sustainability,necessitates a critical analysisofthesubject [1].
This paper presents case studies from multiple sectors where AI has been applied in order to give a thorough analysis of AI's role in sustainability. These instances will show both the achievements and difficulties faced in demonstrating the valuable uses of AI in advancing sustainability.Theywillactaspracticalillustrationstohelp comprehend the intricate connection between AI advancementanditseffectsonsociety,theenvironment,and the economy. This study aims to investigate AI's double contributiontosustainability:evaluatingAI'ssustainabilityas aconceptanditspotentialusesforpromotingsustainability. The study systematically divides the corpus of existing literature by providing an unbiased opinion on financial, social,andenvironmentalissues.Itseekstoaddressethical and societal issues while analysing AI's transformational potential. It will also stress the significance of striking a balance between environmental responsibility and innovationandoffersuggestionsforfutureresearchavenues [2][20].
Theexponentialgrowthofartificialintelligence(AI)inthe lastfewdecadeshasbeenwell-documented,demonstrating AI'sdisruptivepotentialinanumberofindustries,including media, healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and energy. Several studies demonstrate how AI may spur innovation efficiency,resultinginnotableadvancements

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
inseveralsectors(Russell&Norvig,2020;Goodfellowetal., 2016).Buttheresearchalsoshowsthattherearegrowing worriesaboutthefinancialandenvironmentalconsequences of training sophisticated AI models, especially those for naturallanguageprocessing(NLP)(Strubelletal.,2019).
Apart from the technical difficulties, the ethical and sociologicalconsequencesofartificialintelligencehavecome under closer examination. Modern research routinely addresses topics like the persistence of social biases, the spread of fake news,andthestagnationofreal wagesasa resultofautomation(O'Neil,2016;Benderetal.,2021).These difficulties highlight how crucial it is to evaluate AI's total influenceonsustainability,takingintoaccountitseffectson thesocial,economic,andenvironmentalspheres.
ThedualroleofAIinsustainability itspotentialtohelp accomplishtheSustainableDevelopmentGoals(SDGs)andits own inherent sustainability challenges has come into attentioninrecentresearch(Vinuesaetal.,2020).Thisdual viewpointdrawsattentiontothenecessityofawell-rounded strategy that incorporates moral considerations, environmental stewardship, and creative potential. The existing research highlights the need for thorough and multifaceted examinations of AI's function in improving sustainability by looking at case studies and actual data (Floridietal.,2018).
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) could be significantlyaidedbyartificialintelligence.Thefollowingare somewaysAIcansupporttheSDGs:
Poverty and Hunger: AIcanaidinreducingpovertyand hunger by enhancing resource allocation, forecasting crop yields,andoptimisingagriculturaloperations[8].
Healthcare: AI can improve healthcare systems by facilitating remote monitoring, personalised treatment regimens, and early disease diagnosis, which will improve patientaccessandoutcomes.
Education: AI can help everyone have access to highquality education in remote locations, customise learning experiences for students, and create chances for lifelong learning.
Gender equality: artificial intelligence can assist in recognising and resolving biases in hiring procedures, encouragingworkplacediversity,andguaranteeingthatboth gendershaveequalchances[4].
Cleanenergy: Artificialintelligence(AI)canhelppromote sustainable energy practices by streamlining the implementationofsourcesofrenewableenergy,enhancing gridmanagement,andoptimisingenergyuse.
Climateaction:ArtificialIntelligence(AI)canassistwith climate change adaptation and mitigation by analysing climatic data, forecasting natural disasters, and providing ideasforreducingenvironmentalimpacts[19].
Solutions based on artificial intelligence (AI) are beingusedmoreandmoretotackleavarietyofissuesand helpmanysectorsreachtheSustainableDevelopmentGoals (SDGs). The following are some instances of AI-based solutions that are enhancing the results of sustainable development:
Climate Modelling: AI uses data on the climate to forecastfuturetrends,assistingscientistsandpoliticiansin creatingmitigationplans.
Reducing Carbon Footprint: AI integrates renewable energysourcesandmaximisesenergyutilisationinbuildings andindustries[6].
Precisionfarming:Byexaminingsoil,meteorological,and crop health data, artificial intelligence (AI) tools offer accurate suggestions on fertilisation, irrigation, and pest management. Supply Chain Optimisation: In agricultural supply chains,artificial intelligence (AI) forecasts demand, cuts waste, andimproveslogistics.
Animals Monitoring: To help with conservation, AIpoweredcamerasanddronestrackpoachingactivitiesand keepaneyeonanimals.Theydothisbyanalysingimagesand sounds.
Habitat Mapping: AI maps and tracks changes in ecosystems through satellite imagery, assisting in the preservationandrestorationofhabitats.
Energy Forecasting: AI forecasts renewable energy generation,enhancinggridefficiencyandintegration.
AI-enhanced energy storage management ensures a steadysupplyofelectricityfromsporadicrenewablesources [7][9].
AI is used in health data analysis to forecast illness outbreaksandcreatepreventativemeasures.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
AI-poweredsystemsandgadgetsfacilitateremotehealth monitoring and diagnosis, hence enhancing healthcare accessibilitythroughtelemedicine[10].
6. Google DeepMind AI Cuts 40% of Google Data Centre Cooling Expenses
GOOGLEhasdevelopedartificialintelligencethatreduces the quantity of energy required to run its data centres.An astounding40%lessenergywasneededtocoolthecentres because to machine learning technology created by the company's AI research division, DeepMind. It was able to increase the effectiveness of its own centres, which run YouTube,Gmail,GoogleSearch,andallofGoogle'sservices, byimplementingmachinelearning.Onabroaderscale,the algorithmsandtechniquesemployedmightalsobeappliedto minimisewasteintheelectricitygridortoairconditioning systems in major manufacturing plants. In relation to the amountofserveractivitythatwaspredicted,theDeepMind teamgatheredafive-yearperiodofdataobtainedfromdata centresanddevelopedapredictionmodelfortheamountof energy the centre would require. Data on temperatures, power consumption, pump speeds, and other topics were suppliedtoeachneuralnetwork.Themachinelearningwas "trained"andretainedmoreexamplesoftheoperationsof thecentresthroughtheuseof the enormous data sets than a human could [11][12].
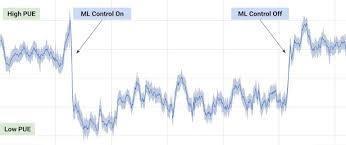
Figure2: GoogleDeepMindAICuts40%ofGoogle Data Centre Cooling Expenses
6.1.1 Algorithmsused
Google DeepMind uses cutting edge methods for data centreenergyoptimisation,mostlybasedonreinforcement learning (RL). Below is a summary of the DeepMind algorithmsandtheunderlyingequationsforeach[13]:
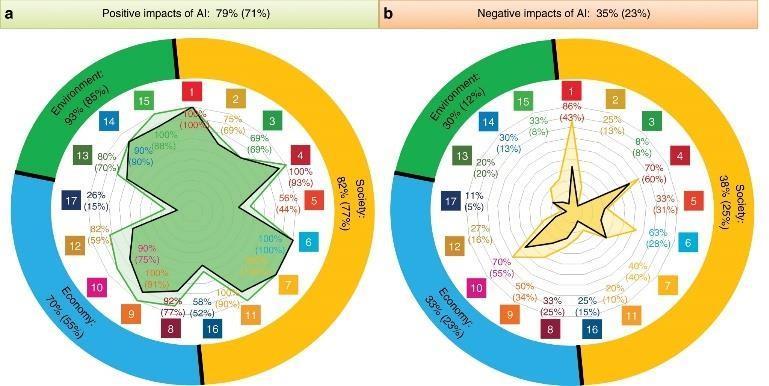
Figure1:AnoverviewofAI'seffects,bothgoodandbad, on the many SDGs (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-14108y)
7. DRL, or deep reinforcement learning:
DeepMindoptimisesdatacentreenergyconsumptionvia DRL. Learning an optimal policy by interaction with the environment in this example, the data centre infrastructure isthefundamentalprincipleofDRL.Typical algorithmsthatareemployedareasfollows:
a. Q-Learning:Q-LearningisafundamentalRL algorithm that learns an optimal actionselection policy for an agent in a Markov decision process (MDP). The Q-value represents the expected cumulative future rewardfortakingaction a instate s
Q(s,a)←Q(s,a)+α[
Q(s′,a′) Q(s,a)]
Q(s,a): Q-value for action a and state s α: Rate of learning.r: Thebenefitreceivedafteractinginacertainstate. γ: The factor of discount.a′: The action in state s′ that maximises the Q-value. s′: Thestatethatfollowsactionaninstate s.
b. Deep Q-Networks (DQN): DQN extends QLearning by using a deep neural network to approximatetheQ-function Q(s,a;θ)where θ are theparametersofthenetwork.
θ←θ +α[ r+ γ maxa′ Q(s′,a′;θ−)−Q(s,a;θ)]∇θ
Q(s,a;θ)
θ−:Parametersofthetargetnetwork(usedto stabilizelearning).
c. DeepDeterministicPolicyGradient(DDPG):DDPG isusedforcontinuousactionspacesandinvolves learning a deterministic policy μ(s;θμ) that maximizestheexpectedcumulativereward.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
R:Regularizationterm.
J:Cumulativereward. ρ:Statedistribution. θμ: Policyparameters.
θQ:Q-functionparameters[14].
PlantVillage Nuru usesAI toassist farmers in Kenya in identifying crop illnesses. Farmers may instantly identify diseasesandreceivetreatmentadvicebysnappingpicturesof theircropsandsubmittingthemtoasmartphoneapp.The region'sfoodsecurityandfarmerlivelihoodshaveimproved asaresultofthistechnology'snotablereductionincroploss andincreaseinyields[15][16].
7.1.1
PlantVillage Nuru uses machine learning techniques specifically designed for picture classification and disease detectiontoassistfarmersindiagnosingcropdiseasesand pests using artificial intelligence. These general sorts of algorithmsand theirconceptual frameworks thatcouldbe usedarelistedbelow,whilespecificimplementationdetails maydifferandtheprecisealgorithmsusedbyPlantVillage Nuruareproprietary:
a. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Application: Image classification and segmentation of crop diseases and pests. Equation (High-level Concept):
y=σ(Wx+b)
x: Inputimagedata.W: Weightmatrix. b: Biasvector.
σ: Activationfunction(e.g.,ReLU,Sigmoid).
y: Output (classification probabilities for different diseases/pests).
b. TransferLerning:
Application: Leveraging pre-trained CNN models (e.g.,trained on ImageNet)andfinetuningthemonspecificcropdiseasedatasets.
Equation(concept):
θ fine-tuned = arg minθ ℒ(fθ (xi), yi) + λR(θ) θ: Modelparameters.
xi:Inputimage. yi:Truelabel.fθ:CNNmodel.
ℒ:Lossfunction(e.g.,cross-entropy).
λ:Regularizationparameter[17].
c. EnsembleMethods:
Application: Combining multiple models (ensemble)forimprovedaccuracyindisease andpestdetection.
Equation(Concept):
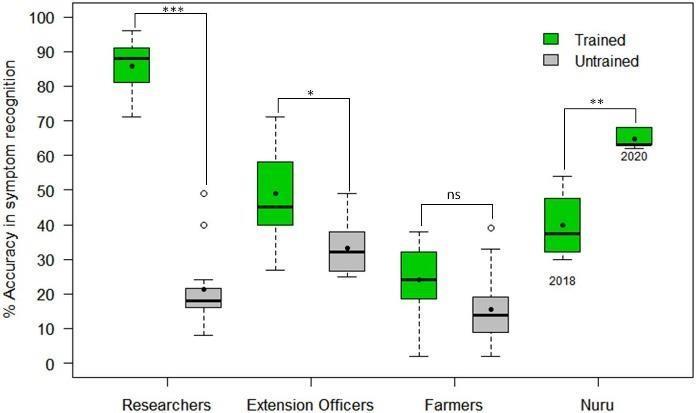
Figure 3: Accuracy in identifying signs of CMD, CBSD, and CGM damage by researchers, farmers, agricultural extension agents, and Plant Village Nuru is compared.
Application: Increasing the diversity of the training datasetbyapplyingtransformationstoinputimages.
Equation(Concept):
x′=augment(x)
x′:Augmentedimage.
augment:Augmentationfunction(e.g., rotation,flipping,scaling)[18].
TheefficacyofAIislimitedinmanydevelopingnations because high-quality, diversified datasets are essential for building correct AI models. Ensuring that AI technology reaches remote and impoverished populations is a major challenge because advanced AI solutions require powerful computationalinfrastructure,whichisfrequentlyabsentin less developed places. Furthermore, if AI systems are not effectively controlled, they might reinforce preexisting prejudices and inequalities. For this reason, it is crucial to guarantee accountability, transparency, and justice in AI applications to prevent societal gaps from getting worse. Moreover, the energy-intensive nature of training and

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
implementing AI models especially deep learning algorithms may counteract the intended environmental advantages[3].
Creating novel approaches to data collecting, including crowdsourcing and IoT integration, can improve the availability and quality of data, increasing AI's efficacy. ResearchonedgecomputingandlightweightAImodelscan increasetheviabilityandaccessibility ofAIapplications in low-resourceenvironments.Astrongethicalcodeandother frameworksforAIdevelopmentandusewillassistcombat prejudiceandguaranteethatAIsolutionsareinclusiveand egalitarian. AI in conjunction with other disciplines, like public health, agriculture, and environmental science, can providecomprehensiveanswerstochallengingsustainability issues. Strong legal and regulatory frameworks are also requiredtoensurethattechnologybreakthroughsareinline withlargersocietalobjectivesandtodirecttheresponsible applicationofAIinsustainabledevelopment[5].
AI has great potential to advance sustainability in a numberoffields,includingenergymanagement,healthcare, and agriculture. The revolutionary potential of AI in accomplishingtheSustainableDevelopmentGoals(SDGs)as wellasthethreatsitposestosustainabilityitselfhaveboth beenexamined
��
in this study. It is clear from case studies and an analysis of
��(��):Ensembleprediction.
T:Numberofmodelsintheensemble.
Ft(x):Predictionofmodel t
d. DataAugmentation:
recentresearchthatartificialintelligence(AI)may greatly improve resource efficiency, streamline operations,andlessenenvironmentaleffects.Buttheuse ofAIalsobringsupmoral questionsaboutthingslike algorithmicbiasandtheamountofenergyrequiredfor modeltraining.Amultidisciplinarystrategy
that incorporates moral considerations, strong legal frameworks,andcutting-edgetechnicalsolutionsisneeded toaddresstheseissues.ProjectssuchasGoogle'sDeepMind, whichaimstolowerdatacentreenergyuse,showhow,when usedcarefully,AImayhaveasignificantpositiveimpactonthe environment.
Lookingahead,maximisingAI'spotentialforsustainable development will require promoting cooperation between
academics,decision-makers,andstakeholders.Transparency, inclusivity, and environmental stewardship are key components that can help us direct AI progress towards buildingamoreresilientandequitablefuture.
In summary, although artificial intelligence (AI) brings advantagesanddisadvantages,itsappropriateuseprovidesa meansofaccomplishingsustainabledevelopmentgoalsona worldwidescale.RealisingAI'sfullpotentialasacatalystfor positivechangeinthegoalofasustainableandprosperous society will require ongoing study and deliberate deployment.
[1] Liang, Guangqi, Yi Liang, Dongxiao Niu, and Musarat Shaheen. "Balancing sustainability and innovation: The role of artificial intelligence in shapingminingpracticesforsustainablemining development." Resources Policy 90 (2024): 104793.
[2] Kulkov,I.,Kulkova,J.,Rohrbeck,R.,Menvielle,L., Kaartemo, V. and Makkonen, H., 2023. Artificial intelligence‐driven sustainable development: Examining organizational, technical, and processingapproachestoachieving global goals. Sustainable Development
[3] Nishant, Rohit, Mike Kennedy, and Jacqueline Corbett."Artificialintelligenceforsustainability: Challenges,opportunities,andaresearchagenda." InternationalJournalofInformationManagement 53(2020):102104.
[4] Pigola, A., da Costa, P.R., Carvalho, L.C., Silva, L.F.D., Kniess, C.T. and Maccari, E.A., 2021. Artificial intelligence-driven digital technologies to the implementation of the sustainabledevelopmentgoals:Aperspective from Brazil and Portugal. Sustainability, 13(24),p.13669.
[5] Abulibdeh,A.,Zaidan,E.andAbulibdeh,R.,2024. Navigatingtheconfluenceofartificialintelligence andeducationforsustainabledevelopmentinthe eraofindustry4.0:Challenges,opportunities,and ethicaldimensions. JournalofCleanerProduction, p.140527.
[6] Ryan,Mark,JosephinaAntoniou,LaurenceBrooks, Tilimbe Jiya, Kevin Macnish, and Bernd Stahl. "The ethical balance of using smart information systems for promoting the United Nations’ Sustainabl Development Goals." Sustainability 12,no.12(2020):4826.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 05 | May 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[7] Ikromjonovich, B.I., 2023. Sustainable Development in TheDigital Economy: Balancing GrowthandEnvironmentalConcerns. Al- Farg’oniy avlodlari, 1(3),pp.42-50.
[8] HaiYen,TranThi,Wing-KeungWong,Mohammed HasanAliAl-Abyadh,IskandarMuda,FelixJulcaGuerrero,SanilS.Hishan,and Md Monirul Islam. "The impact of ecological innovation and corporatesocialresponsibilitiesonthesustainable development: Moderating role of environmental ethics." Economic research- Ekonomska istraživanja 36,no.3(2023).
[9] Singh, H. L., Khaturia, S., & Chahar, M. (2021). EnergyEfficiency.In IntroductiontoAITechniques for Renewable Energy System (pp.185-200).CRC Press.
[10] Sayed, A., Himeur, Y., Bensaali, F. and Amira, A., 2022. Artificial intelligence with iot for energy efficiency in buildings. In Emerging Real-World Applications of Internet of Things (pp. 233-252). CRCPress.
[11] Olatunde, T.M., Okwandu, A.C., Akande, D.O. and Sikhakhane, Z.Q., 2024. Reviewing the role of artificial intelligence in energy efficiency optimization. Engineering Science & Technology Journal, 5(4),pp.1243-1256.
[12] Isaev,EvgeniiAnatol'evich,VasiliiVyacheslavovich Kornilov,andAnatoliiAlekseevichGrigor'ev."Data centerefficiencymodel:Anewapproachandthe roleofArtificialIntelligence." Математическая биология и биоинформатика 18, no. 1 (2023): 215-227.
[13] Hodson,H.,2019.DeepMindandGoogle:thebattle to control artificial intelligence. The Economist, ISSN,pp.0013-0613.
[14] Kelechi, Anabi Hilary, Mohammed H. Alsharif, OkpeJonahBameyi,PaulJoanEzra,IorshaseKator Joseph,Aaron-AnthonyAtayero,ZongWooGeem, and Junhee Hong. "Artificial intelligence: An energyefficiencytoolforenhanced high performance computing." Symmetry 12, no. 6 (2020):1029.
[15] Mrisho,Latifa,NeemaMbilinyi,MathiasNdalahwa, Amanda Ramcharan, Annalyse Kehs, Peter McCloskey, Harun Murithi, David Hughes, and James Legg. "Evaluation of the accuracy of a smartphone-based artificial intelligence system, PlantVillage Nuru, in diagnosing of the viral diseasesofcassava." BioRxiv (2020):2020-01.
[16] Coletta, A., Bartolini, N., Maselli, G., Kehs, A., McCloskey, P. and Hughes, D.P., 2020. Optimal deployment in crowdsensing for plant disease diagnosisindevelopingcountries. IEEEInternetof Things Journal, 9(9),pp.6359-6373.Mrisho,L.M., Mbilinyi, N. A., Ndalahwa, M., Ramcharan, A. M., Kehs,A.K.,McCloskey,P.C..&Legg,J.P.(2020). Accuracy of a smartphone-based object detection model, PlantVillage Nuru, in identifying the foliar symptoms of the viral diseasesofcassava–CMDandCBSD. Frontiers in plant science, 11,590889.
[17] Musa,A.,Hamada,M.,Aliyu,F.M.andHassan, M., 2021, December. An intelligent plant dissease detection system for smart hydroponic using convolutionalneuralnetwork.In 2021 IEEE 14th international symposium on embedded multicore/many-core systems-on-chip (MCSoC) (pp.345-351).IEEE.
[18] Visvizi, A., 2022. Artificial intelligence (AI) and sustainabledevelopmentgoals(SDGs):exploring the impact of AI on politics and society. Sustainability, 14(3),p.1730.
[19] Goralski, M. A., & Tan, T. K. (2020). Artificial intelligence and sustainable development. The International Journal of Management Education, 18(1),100330.
2025, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 8.315 | ISO 9001:2008