
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04| Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04| Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Gokul K1 , Fathima Taskeen Z 2 , Anitha V 3
Post Graduate Student, Faculty of Architecture, Dr. M.G.R. Educational and Research Institute. Chennai, India
Asst H.O.D, Faculty of Architecture, Dr. M.G.R. Educational and Research Institute. Chennai, India
Assoc Architect, Faculty of Architecture, Dr. M.G.R. Educational and Research Institute. Chennai, India
Abstract - Resource-ConstrainedProjectScheduling(RCPS) is a pivotal aspect of project management, especially in construction and engineering domains where resources are limited. Traditional scheduling methods often struggle to efficiently handle complex constraints, leading to project delaysand costoverruns. This study introducesan integrated framework utilizing Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) to enhanceschedulingefficiencyunderresourceconstraints.PSO, inspired by the social behavior of organisms, offers a robust mechanism forexploringoptimalsolutionsincomplexsearch spaces. The proposed framework involves encoding project activities and constraints into a format suitable for PSO processing, defining a fitness function based on project duration and resource utilization, and iteratively updating particle positions to converge on optimal schedules. The framework was tested on benchmark RCPS problems, demonstrating significant improvements in project duration andresourceutilizationcomparedtotraditionalmethods.The PSO-based approach efficiently navigated the solution space, avoiding local minima and converging on high-quality solutions. Sensitivity analyses revealed the framework's robustness across various project complexities and resource availabilityscenarios.ThisintegratedPSOframeworkpresents a viable solution for optimizing project schedules under resource constraints, offering a valuable tool for project managers aiming to enhance scheduling performance.
Key Words: Particle Swarm Optimization, ResourceConstrained Project Scheduling, Optimization, Project Management, Metaheuristic Algorithms, Scheduling Efficiency, Resource Allocation, Construction Engineering.
1.INTRODUCTION
Resource-constrainedprojectscheduling(RCPS)represents acomplexproblemspacewherelimitedresourcesmustbe allocated efficiently to complete a set of tasks within specifiedtimeframes,whileadheringtovariousconstraints andobjectives.Thisintroductionembarksonanexploration of the intricacies of RCPS, delving into its significance, challenges, and the motivations driving the research presentedinthisthesis.
Atitscore,RCPSinvolvestheallocationofscarceresources, suchasmanpower,equipment,andfinances,toasetoftasks
thatcollectivelyconstituteaproject.Unlikeunconstrained scheduling scenarios, where resources are assumed to be abundant,RCPSimposesconstraintsonresourceavailability, leading to a multitude of scheduling complexities. These constraintsmayincludelimitationsonresourcequantities, availability periods, skill requirements, and inter-task dependencies. As a result, scheduling decisions must be made judiciously to balance conflicting objectives such as minimizing project duration, maximizing resource utilization,andmeetingprojectdeadlines.Thesignificanceof RCPS extends far beyond its theoretical complexities, permeating into the realms of organizational efficiency, projectsuccess,andstakeholdersatisfaction.Intoday'sfastpaced business environment, where time-to-market and cost-effectiveness are paramount, the ability to optimize project schedules becomes a strategic imperative for organizationsacrossindustries.Efficientprojectscheduling notonlyfacilitatesthetimelycompletionofprojectsbutalso enables organizations to allocate resources optimally, identifycriticalpaths,andmitigateprojectriskseffectively. Furthermore,well-executedprojectschedulescontributeto enhancedcustomersatisfaction,improvedcompetitiveness, andsustainablegrowthfororganizations.
Projectschedulingplaysacritical roleinthesuccessof any project, regardless of its size or complexity. By establishing a roadmap for project activities and resource allocation,schedulingenablesprojectmanagersto:
a. Identify critical tasks and dependencies: Scheduling helps identify the sequence of activities and their dependencies,allowingprojectmanagerstofocusoncritical tasksthatcanimpactprojectdurationandoverallsuccess.
b.Optimizeresourceallocation:Schedulingallowsforthe efficient allocation of resources such as manpower, equipment, and materials, ensuring that resources are utilizedeffectivelyandprojectcostsareminimized.
c. Manage project risks: Scheduling enables project managers to identify potential bottlenecks, conflicts, and resource shortages early on, allowing for proactive risk mitigationstrategiestobeimplemented.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04| Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
d. Monitor project progress: Scheduling provides a baseline against which project progress can be measured, allowingprojectmanagerstotrackactualprogressagainst plannedmilestonesandtakecorrectiveactionsasneeded.
The need for the study of resource-constrained project scheduling (RCPS) and the development of an integrated framework utilizing Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) arises from several key factors that underscore the importanceofaddressingthechallengesinherentinproject schedulinginresource-limitedenvironments
Theobjectivesofthestudyonresource-constrainedproject scheduling (RCPS) and the development of an integrated frameworkutilizingParticleSwarmOptimization(PSO)are multifaceted and aim to address various aspects of the complexitiesinherentinprojectschedulingunderresource limitations. These objectives are designed to guide the research process and ensure that the study contributes meaningfully to the advancement of project management methodologies.Thefirstobjectiveofthestudyistoformulate the resource-constrained project scheduling problem in a clearandcomprehensivemanner.Thestudyaimstodesign andimplementanintegratedframeworkthatcombinesPSO withestablishedschedulingalgorithmstooptimizeproject schedulesunderresourceconstraints.
Theproposedframeworkinvolvesthefollowingsteps:
Problem Encoding: Project activities, durations, dependencies,andresourcerequirementsareencoded intoaformatsuitableforPSOprocessing.
Initialization: Aswarmofparticles,eachrepresentinga potential project schedule, is initialized with random positionsandvelocities.
Fitness Evaluation: Eachparticle'sfitnessisassessed based on project duration and resource utilization efficiency.
Velocity and Position Update: Particlesupdatetheir velocities and positions based on personal and global best positions, guiding the swarm towards optimal solutions.
Iteration: The process iterates until convergence criteria are met, such as a maximum number of iterationsorasatisfactoryfitnesslevel.
AdaptingParticleSwarmOptimization(PSO)tothecontext ofResource-ConstrainedProjectScheduling(RCPS)entails integrating PSO into a framework that can effectively address the complexities of scheduling tasks with limited resources.Thisadaptationinvolvesmodifyingthetraditional PSOalgorithmtosuittherequirementsandconstraints of RCPS,suchastaskdependencies,resourceavailability,and projectobjectives.Here'sanelaborationoftheadaptationof PSOinthecontextofRCPS:

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04| Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
UnderstandingPSO: Beforedelvingintoitsadaptation,it's crucial tounderstand the basicprinciplesof PSO.PSOis a population-based optimization algorithm inspired by the social behaviour of bird flocks or fish schools. In PSO, a population of candidate solutions, called particles, moves throughasearchspacetofindtheoptimalsolutiontoagiven problem.Eachparticleadjustsitspositionbasedonitsown experience(personalbest)andthecollectiveexperienceof theswarm(globalbest).
FormulatingtheRCPSProblem: Thefirststepinadapting PSO to RCPS is formulating the problem in a way that is amenabletooptimizationusingPSO.InRCPS,theobjectiveis to optimize project schedules while considering resource constraints,taskdependencies,andprojectobjectives.This involvesdefiningthedecisionvariables(e.g.,taskstartand finishtimes,resourceallocations),constraints(e.g.,resource availability, task precedence), and the objective function (e.g., minimizing project duration, maximizing resource utilization).
Encoding Solutions for PSO: Once the RCPS problem is formulated,thenextstepistoencodetheproblemspaceinto a format that PSO can handle. This involves representing candidate solutions as particles in the PSO swarm. Each particlecorrespondstoapotentialprojectschedule,withits position representing a feasible solution in the problem space.Theparticle'spositionisupdatediterativelybasedon itsvelocity,whichisinfluencedbyitspersonalbestandthe globalbest.
Adapting PSO Operators:AdaptingPSOtoRCPSrequires modifying the standard PSO operators to incorporate domain-specific knowledge and constraints. This may involve customizing the velocity update equation, considering task dependencies and resource constraints when updating particle positions, and incorporating mechanisms to handle constrained optimization. For example, the velocity update equation may be adjusted to prioritizetaskschedulingbasedonresourceavailabilityand taskprecedence.
HandlingResourceConstraints:Resourceconstraintsarea fundamental aspect of RCPS and must be explicitly considered in the adaptation of PSO. This involves developingmechanismstoensurethatresourceallocations are feasible and do not exceed available resources. One approachistoincorporateresourceconstraintsdirectlyinto the optimization process by constraining the particle positionstofeasibleresourceallocationsateachiteration.
Problem formulation in the context of resourceconstrainedprojectscheduling(RCPS)involvesdefiningthe parameters, variables, constraints, and objectives that characterize the scheduling problem. It serves as the foundation for developing optimization models and
algorithms to generate feasible and optimal project schedules. Elaborating on problem formulation entails specifying the key components of the RCPS problem and understanding their interrelationships. Here's a detailed elaborationofproblemformulationforRCPS:
Definition of Tasks and Activities: TheRCPSproblem typicallyinvolvesasetoftasksoractivitiesthatneedtobe scheduled to complete the project. Each task has specific characteristics,includingitsduration,resourcerequirements, andprecedencerelationshipswithothertasks.Tasksmaybe represented as nodes in a project network, with directed edgesindicatingprecedencerelationshipsbetweentasks.
Resource Constraints: Resourceconstraintsrepresent limitations on the availability of resources, such as manpower, equipment, andmaterials,thatare requiredto executeprojecttasks.Eachresourcehasafinitecapacity,and tasksrequirecertainamountsofresourcestobeperformed. Resource constraints may include maximum resource capacities, resource availability over time, and resource dependencies.
Task Dependencies: Task dependencies define the sequencing requirements between tasks, specifying which tasks must be completed before others can start. Dependencies may be represented by precedence relationships,suchasfinish-to-start,start-to-start,finish-tofinish, or start-to-finish relationships. Task dependencies ensure that project activities are executed in the correct ordertomeetprojectobjectives.
The objective function in the context of resourceconstrainedprojectscheduling(RCPS)playsapivotalrolein guiding optimization algorithms, such as Particle Swarm Optimization(PSO),togeneratefeasibleandoptimalproject schedules.Itquantifiestheperformanceofagivenschedule based on project objectives and constraints, providing a metric that optimization algorithms seek to minimize or maximize. Elaborating on the objective function involves defining its components, considering various project objectives,andaddressingthecomplexitiesofRCPS.Here's anin-depthelaborationoftheobjectivefunctionforRCPS:
TheobjectivefunctioninRCPStypicallycomprisesmultiple components that capture different aspects of project performance.Thesecomponentsmayinclude:
Project Duration: Minimizing project duration is a commonobjectiveinRCPS,asithelpsensuretimelyproject completion and reduces associated costs. The objective functionmaypenalizescheduledeviationsfromtheminimum project duration, encouraging optimization algorithms to prioritizeshorterschedules.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04| Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Resource Utilization: Maximizing resource utilization aims to ensure efficientallocationandutilization ofscarce resources,suchasmanpower,equipment,andmaterials.The objective function may reward schedules that utilize resources optimally while avoiding overallocation or underutilization.
Critical Path Length: Identifying and minimizing the lengthofthecriticalpath,whichrepresentsthelongestpath throughtheprojectnetworkanddeterminestheminimum projectduration,isanotherobjectiveinRCPS.Theobjective function may penalize deviations from the critical path length, encouraging optimization algorithms to focus on criticaltasks.
3.4 ADAPTATION OF PSO FOR RCPS
The study introduces modifications to traditional PSO formulations to address discrete decision variables and complex constraints. Advanced constraint-handling mechanisms such as penalties, repair operators, and constraint-aware evaluation are integrated to ensure adherence to project requirements. Adaptive parameter tuning and communication topology strategies further enhancetherobustnessofPSOinreal-worldscenarios.
3.5
The research examines PSO’s performance across diverse datasets, comparing traditional scheduling methods while exploringitspotentialforfutureoptimizationadvancements. Limitations include its applicability to datasets spanning 2005–2024 and the challenges of parameter tuning for complexconstraints.
4.1
ContinuousRigidBridgeGirderProjectinChangsha,Hunan Province
Focus: Multi-Skill Resource-Constrained MultiModalProjectScheduling
OptimizationApproach:HybridQuantumParticle Swarm Optimization (HQPSO) with JAYA optimizationsearch.
Results:HQPSOreducedprojectdurationfrom63 daysto48daysandoptimizedresourceutilization.
Cost and Duration Estimation for Government Building Projects
Focus: Accurate estimation for 60 government constructionprojectsinIraq.
Optimization Approach: PSO parameters optimizationwithdataset-drivenmodeling.
Results: Cost estimation accuracy improved to a mean absolute error of 0.97%, with significant savingsinprojectplanning.
ResidentialBuildingConstruction–GopalanAqua
Focus: Optimization of project scheduling for a residentialapartmentinBangalore.
OptimizationApproach:ImplementationofPSOto minimizecostsandreducetimelines.
Results: Cost reduced by 6.66%, with project durationshortened by46days (from484 days to 438days).

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04| Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
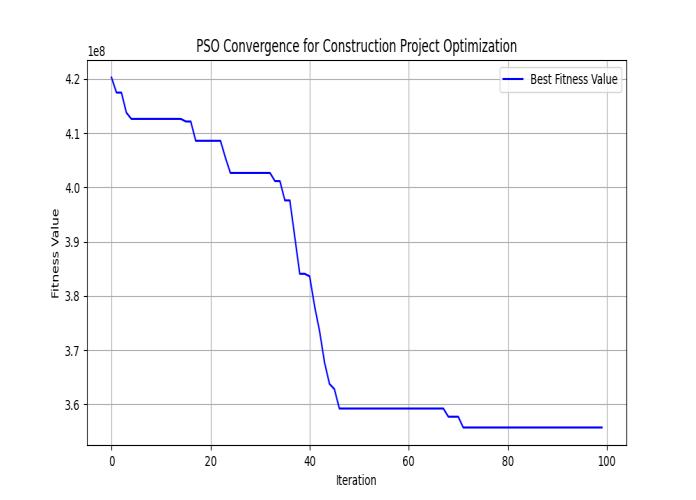
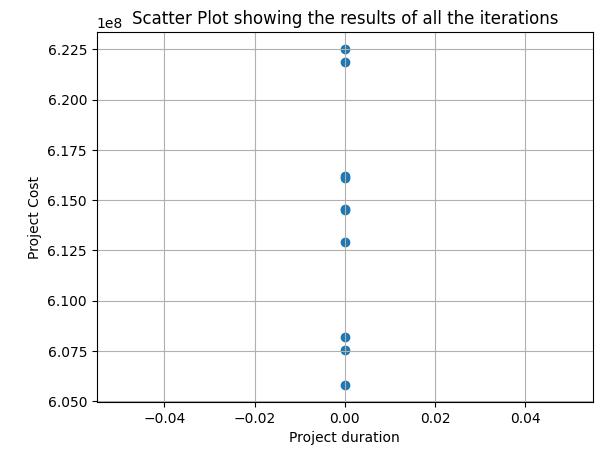
The study demonstrates the potential of Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) as an effective tool for resourceconstrainedprojectscheduling(RCPS).ImplementingPSO led to substantial improvements in both cost and time management:
Cost Reduction:
The actual cost of the residential project was ₹62,18,92,627. After optimization using PSO, this reduced to ₹58,04,47,087 a cost difference of ₹4,14,45,540(6.66%).
This reduction is attributed to the intelligent allocationofresources,whichminimizedidletime and reduced emergency expenditures caused by delaysorinefficiencies.
Time Efficiency:
The project's original duration was 484 days. OptimizationthroughPSOshortenedthistimeline to438days areductionof46days.
Byanalyzingdependenciesandrefiningscheduling with adaptive algorithms, PSO facilitated better handling of multi-tasking constraints and activity sequencing.
ThisstudyhighlightsthetransformativepotentialofParticle Swarm Optimization (PSO) in addressing resourceconstrainedprojectschedulingchallenges:
a) Optimization Success: The framework successfully demonstratedacostreductionof6.66%andashortened project timeline by 46 days, underscoring PSO’s efficiencyandpracticality.
b) Scalability Across Domains: From construction projects to public infrastructure, PSO consistently deliversreliableschedulingsolutionsadaptableacross variousindustriesandprojectscales.
c) Enhanced Decision-Making: Byautomating complex scheduling and optimization tasks, PSO empowers stakeholders to make data-driven decisions, ensuring higherprojectsuccessrates.
d) Environmental Benefits: Reduced resource consumption and improved scheduling contribute to sustainable construction practices, aligning projects withbroaderenvironmentalgoals.
Inconclusion,adoptingadvancedoptimizationtechniques likePSOrepresentsaforward-thinkingapproachtotackling RCPSchallenges,drivingsignificantbenefitsintermsofcost, time, resource utilization, and sustainability. This study paves the way for widespread adoption of PSO in project managementpractices.
[1] Zhang, Y., Wang, S., & Ji, G. (2015). "A Comprehensive SurveyonParticleSwarmOptimizationAlgorithmand ItsApplications."
[2] Madan,M.,&Madan,R.(2013)."GASolver-ASolutionto Resource Constrained Project Scheduling by Genetic Algorithm."
[3] Hu, W., Zhang, Y., Liu, L., & Nie, B. (2024). "Study on Multi Objective Optimization of Construction Project Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm and Particle SwarmOptimization."
[4] Vijayan, V., Achu, R., & Jayakrishnan, J. (2018). "TimeCost-RiskOptimizationinConstructionWorkbyusing AntColonyAlgorithm."
[5] Suliman, M.O., & Kumar, V.S. (2015). "Optimization of Uncertain Construction Time-Cost Trade Off Problem UsingSimulatedAnnealingAlgorithm."
[6] Hoang, N.D., Nguyen, Q.L., & Pham, Q.N. (2015). "OptimizingConstructionProjectLaborUtilizationUsing DifferentialEvolution:AComparativeStudyofMutation Strategies."
[7] Gad, A.G. (2022). "Particle Swarm Optimization AlgorithmandItsApplications:ASystematicReview."
[8] Chen,R.M.(2015)."ParticleSwarmOptimizationwith Justification and Designed Mechanisms for ResourceConstrainedProjectSchedulingProblem."
[9] Abd, A.M., Zehawi, R.N., & Ali, R.H. (2024). "Particle Swarm Optimization and Tree Models (M5P) as Cost EstimationToolforConstructionProject."
[10] Freitas, D., Lopes, L.G., & Morgado-Dias, F. (2020). "ParticleSwarmOptimisation:AHistoricalReviewUpto theCurrentDevelopments."
[11] Ye, D. (2021). "An Algorithm for Construction Project Cost Forecast Based on Particle Swarm OptimizationGuidedBPNeuralNetwork."
[12] Gad, A.G. (2022). "Particle Swarm Optimization AlgorithmandItsApplications:ASystematicReview."
e) Future Applications: ThePSOframeworkservesasa foundationforintegratingemergingtechnologies,such as AI and machine learning, to further enhance schedulingstrategiesandprojectperformance.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04| Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[13] Sahib, N.M., & Hussein, A. (2019). "Particle Swarm OptimizationinManagingConstructionProblems."
[14] Sivaraman, E., Vijayakarthick, M., & Sathishbabu, S. (2015). "Design of Model Reference Adaptive Control BasedPIControllerUsingParticleSwarmOptimization."
[15] Dhanalakshmi, C., Kalidass, P., & Suresh, S. (2023). "OptimalSitingandSizingofD-STATCOMUsingParticle SwarmOptimization."
[16] SlideShare(2019)."ComprehensiveAnalysisonOptimal Allocation and Sizing of Distributed Generation Units UsingParticleSwarmOptimizationTechnique."
[17] Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). "Particle Swarm Optimization:OriginalAlgorithmandApplications."
[18] Shi, Y., & Eberhart, R. (1998). "A Modified Particle SwarmOptimizer."
[19] Clerc,M.,&Kennedy,J.(2002)."TheParticleSwarm Explosion, Stability, and Convergence in a MultidimensionalComplexSpace."
[20] Poli, R., Kennedy, J., & Blackwell, T. (2007). "Particle SwarmOptimization:AnOverview."