
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Vishram Bapat, Prof. Poonam Dharpawar, Rutuja Mahajan1 , Gayatri Aware2
123Bachelor of Technology in Department of Data Science, Usha Mittal Institute of Technology, Mumbai, India
Abstract - Autonomousdronesforsurveillancesystems represent a significant advancement in modern security technologies.Thesedronesutilizeacombinationofartificial intelligence, computer vision, and machine learning algorithmstoperformreal-timemonitoringoflargeareas without the need for human intervention. Equipped with high-resolution cameras, thermal sensors, and advanced navigationsystems,autonomousdronescandetectandtrack suspicious activities, monitor borders, or oversee critical infrastructure with high precision. The integration of GPS and AI allows drones to autonomously navigate complex environments, adapting to dynamic conditions such as weatherchangesorobstacles.Furthermore,thesesystems canrelaylivedatatocontrolcenters,enhancingsituational awareness and enabling quicker decision-making. The applicationofautonomousdronesinsurveillancepromises not only improved security but also cost-effective and scalable solutions for monitoring vast areas with minimal humanresources.
Key Words: Autonomous drone, computer vision, navigation,surveillance
Intheever-evolvinglandscapeofdefenseandsecurity,the need for intelligent, responsive, and autonomous systems has become increasingly critical. Traditional surveillance methods suchasmannedpatrols,fixedobservationposts, andcrewedaerialreconnaissance areoftenconstrainedby limitedrange,highoperationalcosts,andriskstohumanlife, especiallyinhostileorunpredictableenvironments.These limitations highlight the urgent demand for advanced technological solutions capable of enhancing situational awareness,improvingoperationalefficiency,andensuring personnelsafety.Inresponsetothesechallenges,thispaper presents AEROGLE, an autonomous surveillance drone designedspecificallytomeetthestrategicneedsofmodern defense operations. AEROGLE is a high-performance unmannedaerialvehicle(UAV)engineeredtoperformrealtimesurveillanceandreconnaissancemissionswithoutthe needforhuman intervention.Itintegratesstate-of-the-art vision-based navigation systems, machine learning algorithms,andadvancedsensors suchashigh-resolution camerasandthermal imagingmodules toautonomously monitor and analyze areas of interest from significant altitudes.ThecoreobjectiveofAEROGLEistoenablerapid dataacquisitionandsituationalanalysis,providingmilitary commanders and decision-makers with the critical intelligencenecessaryfortimelyandeffectiveresponses.
The autonomous nature of AEROGLE allows it to navigate complexterrains,avoidobstacles,tracktargets,andadaptto dynamic environmental conditions all while executing predefinedmissionparameters.Unliketraditionalremotely piloteddrones,AEROGLEeliminatestheneedforconstant operator control, thereby reducing human error and communication delays. This independence makes it particularlysuitablefordeploymentinenvironmentswhere humanpresenceisimpractical,dangerous,orimpossible such as in high-conflict zones, disaster-stricken areas, or duringadverseweatherconditions.
AEROGLEisanautonomoussurveillancedronedesignedto addresscriticalchallengesfacedindefenseoperations.Itisa high-techsolutiontailoredtoperformreal-timesurveillance andreconnaissancetasksautonomously,withouttheneed forahumanpilot.ThemainaimofAEROGLEistoprovide enhanced situational awareness, increase safety, and improve operational efficiency in defense and security scenarios. In this research paper, the drone race autonomously. [1]. The drone is equipped with advanced sensors,includingcamerasandthermalimagingsystems,to monitor areas of interest from a significant altitude, providingcrucialdatafordecision-makinginreal-time.The design of AEROGLE focuses on integrating vision-based navigation, which allows it to operate without human intervention, navigate complexenvironmentsandexecute missionswithprecisionandreliability.Inthisrecentpaper [2]asafeandcustomizeddronesystemwasdeveloped.The abilityofAEROGLEtoflyautonomously,executepredefined tasks, and adapt to changing environments makes it a valuableassetinmoderndefensestrategies.Inthisresearch paperfocusedoncivilapplicationslikeremotesensingand mobility.[3]. The defense sector faces numerous surveillance-related challenges that require innovative solutions.Traditionalsurveillancetechniques,whichoften rely on manned aircraft, ground patrols, and fixed installations, come with several limitations, such as high operationalcosts,safetyconcerns,andtheneedforconstant human presence . In the research paper, of [4] discussed about Military Security Surveillance Applications Using Wireless Sensor Networks. These methods may not be feasible in high-risk areas or hostile environments, where humanlivesareexposedtodanger.Inthisreviewarticle,[5] discussed specific drone simulators. In addition, groundbasedsystemscanbeslow,andtheircoveragecanbelimited [6]. Drones, especially autonomous ones, offer the opportunitytoovercometheseissuesbyprovidingflexible

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
andquickresponsecapabilitiesthatcanbedeployedinreal time,eveninareasofhighriskanddifficulttoreach[7].In defense, surveillance plays a crucial role in gathering intelligence, monitoring enemy movements, securing borders,andprovidingsituationalawarenessduringcombat operations [8]. The ability to continuously monitor large areas, with- out the need for human operators, is a key advantage of autonomous drones like AEROGLE. Surveillancedronescanoperateinconditionswherehuman presence might be difficult or unsafe, such as in hostile terrain, during extreme weather conditions, or in conflict zones[9].Theycanalsocoverareasthataregeographically challenging, like mountains or forests, offering more comprehensive coverage compared to traditional surveillancemethods[10].Additionally,dronesprovidethe ad-vantageofquickdeployment,beingabletorapidlyassess the situation in real-time and provide the necessary information to ground forces, decision-makers, and commanders[11].Autonomy,inthecontextofdrones,refers totheabilityofadronetooperateindependently,without humanintervention,fortaskssuchasnavigation,obstacle avoidance,andmissionexecution[2].Autonomyisessential for drones, particularly in defense and surveillance applications, because it eliminates the need for constant human control, reducing the risk of human error and operationaldelays[6].AdronelikeAEROGLEmustbeable tonavigatecomplexenvironmentsautonomously.
The AEROGLE autonomous drone surveillance system for defense is designed with two key operational modules: SurveillanceandAutonomy.Thesemodulesworkinunison to provide a robust and intelligent solution for defense applications, ensuring real-time monitoring, threat detection, and autonomous navigation in complex environments.TheSurveillancemoduleisbuiltonstate-ofthe-art deep learning-based object detection techniques, primarily YOLO (You Only Look Once) and Faster R-CNN. YOLO is known for its speed and efficiency in detecting multipleobjectsinreal-time,makingitidealforhigh-speed aerialsurveillance.
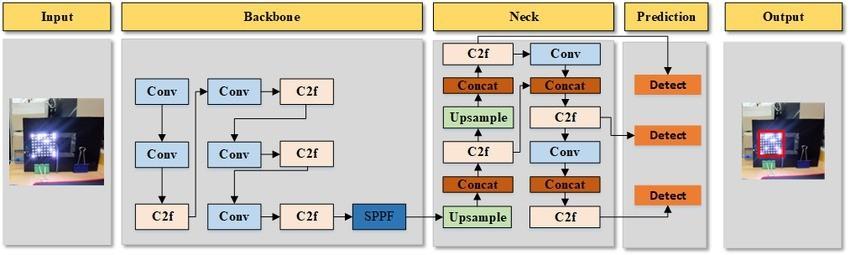
Ontheotherhand,FasterR-CNNprovideshighaccuracyin objectclassification,makingitsuitablefordetailedanalysisof potentialthreats.Thesurveillancesystemistrainedonlargescale datasetssuchas COCO(Common Objects in Context)
andcustomdatasetscontainingdefense-relatedobjectslike enemy personnel, suspicious vehicles, and hazardous materials. The annotation process for training data is performedusing theVGGImageAnnotator(VIA),ensuring precise labeling of object categories, bounding boxes, and segmentationmasks.
To enhance detection efficiency, the system utilizes pretraineddeeplearningmodelsthatarefine-tunedondomainspecificdata.Thetrainingprocessinvolvesdatasetpreprocessing,augmentation,andoptimizationofhyperparameters to improve model accuracy and reduce false positive detections. The trained model is deployed on an onboard computing unit within the drone, enabling real-time processingofsurveillancefootage.Thedetectedobjectsare transmitted to a ground control station via a secure communication channel, where operators can analyze and respondtothreatsaccordingly.
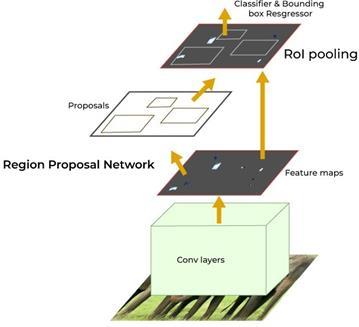
The Autonomy module is responsible for intelligent navigation and obstacle avoidance, allowing the drone to operate in complex and dynamic environments without human intervention. This module leverages PX4, an opensource flight control software that provides advanced autopilot functionalities. PX4 enables thedrone to execute predefinedmissionplans,per-formautonomoustakeoffand landing, and navigate through waypoints while avoiding obstacles.Theobstacleavoidancemechanismisimplemented usingcamera,whichprovidereal-timespatialawarenessto thedrone.Simulationandtestingarecrucialcomponentsof the devel- opment process. The AEROGLE system is rigorously tested in a virtual environment using Gazebo,a physics-basedsimulatorthatallowsforrealisticreplicationof flight dynamics and en- vironmental conditions. The simulationenvironmentincludesvariousterrains,obstacles, andweatherconditionstoevaluatethedrone’sperformance indifferentscenarios.QGroundCon-trolservesastheground control interface, providing operators with real-time telemetry,missionplanning,andsystemhealthmonitoring.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Theentiredevelopmentandprocessingworkflowiscarried outinaLinuxenvironmentusingVSCodeastheintegrated development environment (IDE). The Robot Operating System(ROS)actsasthemiddleware,facilitatingseamless com- munication between different modules, including perception,control,andnavigation.ROSnodeshandledata acquisition, sensor fusion, and decision-making processes, ensuring the autonomy and efficiency of the drone’s operations.Tooptimizereal-timeperformance,techniques suchasmodelquantizationandhardwareaccelerationusing GPUs and TPUs are employed. Quantization reduces the computationalcomplexityofdeeplearningmodels,enabling efficientinferenceonedgedevices.Additionally,theuseof lightweight neural network architectures like MobileNet further enhances processing speed while maintaining accuracy.TheintegrationofAI-poweredsurveillancewithautonomous navigation makes AEROGLE a highly effective solutionfordefenseapplications.Thesystemcanbedeployed forbordersurveillance,reconnaissancemissions,searchand rescue operations, and monitoring of high-risk areas. By combining cutting-edge object detection, real-time processing,andintelligentflightcontrol,AEROGLEenhances situationalawarenessandoperationalefficiencyindefense scenarios
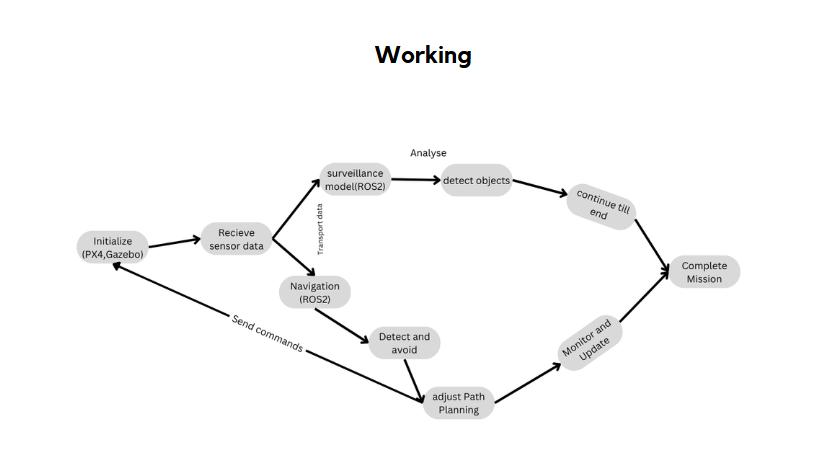
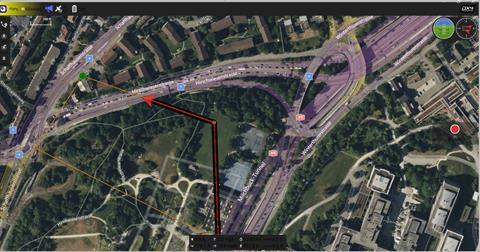
Fig.3.Flowchartforautonomousnavigation
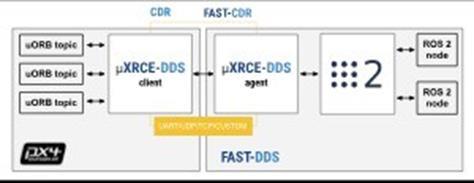
PX4Autopilotrunsontheflightcontroller(e.g.,Pixhawk)and manageslow-leveldroneoperationslikestabilization,motor control,andsensorfusionwhilesendingtelemetrydataand receiving high-level commands.ROS 2 runs on an external computer(e.g.,companioncomputer,groundstation)andis responsible for advanced AI, vision-based navigation, and pathplanning,communicatingwithPX4usingtheDDS(Data Distribution Service).The PX4-ROS 2 Bridge acts as a middlewarebetweenPX4andROS2,usingMicroXRCE-DDSto convertPX4uORBmessagesintoROS2messagesandvice versa.MAVLinkprotocolisusedforcommunicationbetween PX4 andexternal deviceslike QGroundControl,supporting telemetry,missionuploads,andcontrolcommands.PX4reads datafromonboardsensors(IMU,GPS,barometer),performs sensorfusion,andestimatesthedrone’spositionandvelocity before sending this data to ROS 2 via the PX4-ROS 2 Bridge.ROS2nodesprocessthisdataforhigh-leveltaskslike objectdetection,SLAM,andtrajectoryplanning,generating
navigationcommandsbasedonthedrone’senvironment.The PX4-ROS2Bridgetransmitsthesecommandsback toPX4, whichexecutesthemtocontrolthedrone’smovementand actions.PX4continuouslyupdatesitsstatebasedonexecuted commands and sensor feedback, forming a closed-loop systemforautonomousoperations.
TheperformanceoftheAEROGLEautonomousdronewas evaluatedthroughaseriesofsimulationtests.Theprimary metrics used for evaluation included object detection accuracy,navigationefficiency,obstacleavoidancesuccess rate,andcomputationalperformance.
ObjectDetectionPerformance:TheFasterR-CNNandYOLO models were tested on a dataset containing a variety of defense-relatedobjects,includingmilitarypersonnel,vehicles,andweapons.TheresultsdemonstratedthatFasterRCNNachievedanaverageprecision(mAP)ofapproximately 78.Duringsimulation-basedtesting,themodelssuccessfully detectedobjectswithinarangeof50meterswithaminimal false positive rate. However, in low-light conditions, detection performance slightly declined due to reduced contrast and noise in the captured images. Future improvementscouldinvolveintegratinginfraredprocessing techniquestoenhancenight-timesurveillancecapabilities.
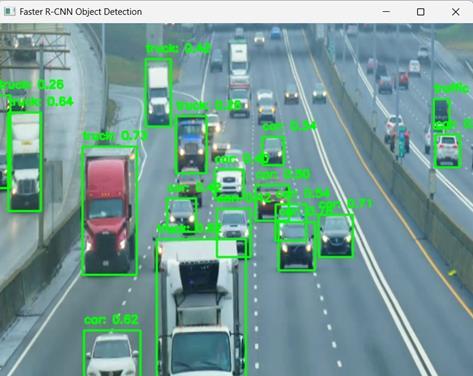

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
AutonomousNavigationandObstacleAvoidance:ThePX4basedautonomy module wastestedexclusivelyinGazebo simulations. The drone successfully navigated through prede- finedwaypointswhileavoidingstaticanddynamic obstacles with an obstacle detection success rate of 93In environments with complex terrains, such as forests and urbanareas,thedroneeffectivelyadjusteditsflightpathto avoidobstacleswhilemaintainingstability.However,inGPSdeniedenvironments,performancewasslightlyreduceddue to reliance on visual-inertial odometry. Future enhancements may involve integrating alternative localizationtechniquesforimproved performance in such conditions. Computational Efficiency: The deployment of deeplearningmodelsontheonboardcomputingunitwas optimizedthroughquantizationandhardwareacceleration.
TheuseofTensorRTformodelinferencereducedprocessing latency by approximately 40 The AEROGLE system demonstratedahighlevelofaccuracyandefficiencyinboth surveillanceandautonomousnavigation.

The combination of Faster R-CNN and YOLO provided a balancebetweendetectionaccuracyandspeed,makingthe systemsuitableforvariousdefenseapplications.Theuseof PX4 and ROS ensured seamless integration and control, while simulation-based testing in Gazebo validated the system’srobustness.
Future improvement required, in enhancing low-light detectioncapabilities,improvingGPS-deniednavigation,and integratingswarmintelligenceformulti-dronecoordination are potential directions for further research. Additionally, optimizing power consumption and increasing flight endurancewillbecrucialforlong-durationmissions.
Overall,AEROGLErepresentsasignificantadvancementin autonomous drone surveillance for defense, combining cutting-edge AI, robust navigation systems, and real-time processing to enhance situational awareness and security operations.
The AEROGLE autonomous drone surveillance system presentsahighlyeffectivesolutionfordefenseapplications byintegratingAI-drivenobjectdetectionwithautonomous flightcontrol.ThecombinationofYOLOandFasterR-CNN ensurespreciseandreal-timesurveillance,whilePX4-based autonomyenhancesoperationalefficiency.Simulation-based evaluationsvalidatethesystem’srobustness,demonstrating itspotentialforreal-worlddeploymentinbordersecurity, reconnaissance, and disaster response. Future improvementsinsensorintegration,localizationtechniques, andenduranceoptimizationwillfurtherenhanceAEROGLE’s capabilities, solidifying its role in advancing autonomous defense technology. As autonomous drone technology evolves, several areas present opportunities for further development.Thefutureofdrones,especiallyindefenseand surveillance,liesinimprovingtheirabilitytohandlemore complex, dynamic environments. Current autonomous systemsstillfacechallengesintermsoflimitedbatterylife, real-time processing power, and their ability to adapt to unpredictablevariablessuchasextremeweatherconditions or rapidly changing environments. Future advancements mayfocusonextendingbatterylifethroughbetterenergy managementandmoreefficientpowersources,whichwill enabledronestoperformlongermissionswithouttheneed for frequent recharging. Moreover, the integration of advanced AI and machine learning algorithms holds significant promise for improving the decision-making capabilitiesofdrones.Futuresystemscouldenhancetheir ability to predict and avoid unforeseen obstacles, track multipletargets,andoptimizetheirflightpathsinrealtime Additionally,thedevelopmentofmulti-dronecoordination couldpavethewayforswarmtechnologies,wheremultiple autonomousdrones work in tandemtocompletecomplex missions more efficiently. Another critical area of future research is the improvement of cybersecurity for autonomousdrones.Asdronesbecomemoreintegratedinto defenseandsecuritysystems,ensuringthattheyaresecure fromcyber-attacksbecomesincreasinglyimportant.Efforts in this direction could include the development of robust encryptionprotocols,securecommunicationchannels,and advanced threat detection systems to prevent potential breaches that could compromise missions.Finally, regulations and ethical considerations around the use of autonomousdronesinmilitaryandcivilianoperationswill continue to evolve. As these systems become more autonomous,itisessentialtoestablishclearguidelinesand frameworks to ensure their safe and responsible deployment. Future research could explore the legal and ethical implications of autonomous drones in surveillance

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 04 | Apr 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
privacy concerns, and accountability in mission-critical decisions.
[1] D. Hanover, A. Loquercio, L. Bauersfeld, A. Romero, R. Penicka, Y. Song, G. Cioffi, E. Kaufmann, and D. Scaramuzza,“Autonomousdroneracing:Asurvey,”IEEE TransactionsonRobotics,2024.
[2] M. Hussein, R. Nouacer, F. Corradi, Y. Ouhammou, E. Villar,C.Tieri,andR.Castin˜eira,“Keytechnologiesfor safe and autonomous drones,” Microprocessors and Microsystems,vol.87,p.104348,2021.
[3] M. Sivakumar and N. M. Tyj, “A literature survey of unmanned aerial vehicle usage for civil applications,” JournalofAerospaceTechnologyandManagement,vol. 13,p.e4021,2021.
[4] C. Singla, R. Gill, D. Srivastava, S. Hooda, and J. Singh, “Analysisofmilitarysecuritysurveillanceapplications usingwirelesssensornetworks,”in20231stDMIHER International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education and Industry 4.0 (IDICAIEI), vol. 1. IEEE, 2023,pp.1–5.
[5] A.Mairaj,A.I.Baba,andA.Y.Javaid,“Applicationspecific drone simulators: Recent advances and challenges,” Simulation Modelling Practiceand Theory, vol.94, pp. 100–117,2019.
[6] J. Lesˇko, M. Schreiner, D. Megyesi, and L. Kova´cs, “Pixhawkpx-4autopilotincontrolofasmallunmanned airplane,” in 2019 Modern Safety Technologies in Transportation(MOSATT).IEEE,2019,pp.90–93.
[7] A. Attin and S. Bonnedahl, “Remote id and detect-andavoid in unmanned-aerial-systems: Model maximum safespeedofuas,”2024.
[8] A.V.R.Katkuri,H.Madan,N.Khatri,A.S.H.Abdul-Qawy, and K. S. Patnaik, “Autonomous uav navigation using deep learning-based computer vision frameworks: A systematicliteraturereview,”Array,vol.23,p.100361, 2024.
[9] R.CasadoandA.Bermu´dez,“Asimulationframework fordevelopingautonomousdronenavigationsystems,” Electronics,vol.10,no.1,p.7,2020.
[10] A.Patrik,G.Utama,A.A.S.Gunawan,A.Chowanda,J.S. Suroso, R. Shofiyanti, and W. Budiharto, “Gnss-based navigationsystemsofautonomousdronefordelivering items,”JournalofBigData,vol.6,pp.1–14,2019.
[11] H.X.Pham,H.M.La,D.Feil-Seifer,andL.V.Nguyen,“Autonomousuavnavigationusingreinforcementlearning,” arXivpreprintarXiv:1801.05086,2018.
[12] C.Cao,B.Wang,W.Zhang,X.Zeng,X.Yan,Z.Feng,Y.Liu, andZ.Wu,“Animprovedfasterr-cnn forsmall object detection,” Ieee Access, vol. 7, pp. 106 838–106 846, 2019.
[13] ,“Rgb-ptambasedstateestimationforunmannedaerial vehicle,”Ph.D.dissertation,,2016.