
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Karimulla Polisetti1 , Hariprasad Chitte2
1 Assistant Professor, EEE Department, Bapatla Engineering College, Bapatla, Andhra Pradesh, India
2 Assistant Professor, EEE Department, Bapatla Engineering College, Bapatla, Andhra Pradesh, India
Abstract - Data science has become a transformative force across numerous sectors, enabling advancements in predictive modeling, personalized services, and data-driven decision-making. This paper reviews recent applications of data science in healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, social media, and the public sector. Key methods such as machinelearning,naturallanguageprocessing,andpredictive analytics are discussed in each sector, along with challenges such as data privacy, scalability, and model interpretability. Emerging trends and future directions are highlighted, emphasizing the need for ethical, transparent, and interdisciplinary approaches in deploying data science solutionsacross industries.
Keywords Machine learning, Natural language processing, Predictive analytics.
1.INTRODUCTION
In recent years, data science has rapidly evolved into a powerful field, transforming industries by enabling datadrivendecision-makingandinsights.Asthevolumeofdigital datagrowsexponentially,organizationsacrosssectorsare leveragingdata sciencetoextractvaluablepatterns,make predictions,anddriveinnovation.Thisinterdisciplinaryfield combinestechniquesfromstatistics,machinelearning,and computer science, allowing businesses and researchers to handlecomplexdatasetsandsolvecritical problems. Data scincelifecycleisasshowninfig.1.
Thisreviewpaperexplorestheimpactofdatascienceacross variousindustries,highlightingitsapplicationsinfieldssuch as healthcare, finance, retail, manufacturing, social media, and the public sector. By examining these diverse applications, we aim to provide a comprehensive understandingofthecurrent
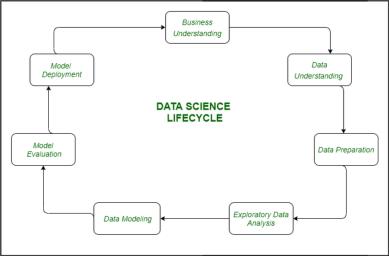
trends,methodologies,andchallengesindatascience,andto identifyareaswherefutureresearchanddevelopmentmay bringfurtheradvancements.Thisoverviewseekstoguide practitioners and researchers in harnessing data science effectivelyandethicallyacrossdomains.
In this paper optimal power flow is formulated minimizingtheoperationcostandcomparedthesemethods with respect to system loss to that of conventional power flow. Section II describes the Applications of Data Science, sectionIIIgivesthechallengesinDataScienceApplications, sectionIVpresentsfuturedirectionsandsectionVconcludes thepaper.
Here’s a detailed exploration of core applications of data scienceacrossvariousindustries.Eachsectiondescribeskey applications, data science methods used, challenges, and emergingtrends.Datacycleasshowninfig.2.
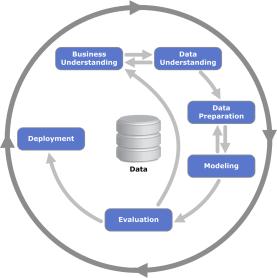
Finally, complete content and organizational editing before formatting. Please take note of the following items whenproofreadingspellingandgrammar:
2.1 Healthcare and Medicine
Applications:
Predictive Modeling for Patient Outcomes: Data sciencehelpspredictpatientoutcomes,suchasthe likelihoodofdevelopingchronicdiseases,enabling preventiveinterventions[2].
MedicalImageAnalysis:Deeplearningalgorithms areappliedtoanalyzemedicalimages(e.g.,MRIs,X-

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
rays) for detecting diseases like cancer and neurologicalconditions.
Genomics and Personalized Medicine: Machine learning algorithms analyze genetic data to tailor treatments to individual patients, enhancing the effectivenessoftherapies.
Epidemiology and Public Health: Data science modelstrackdiseaseoutbreaks,helpingtopredict the spread of infections and allocate healthcare resourcesefficiently.
MethodsUsed:
Machine Learning (ML): Used for predictive modeling and early diagnosis [4] (e.g., logistic regression,randomforests).
DeepLearning(DL):Especiallyusefulinimageand genomic data analysis (e.g., CNNs for medical imaging).
NaturalLanguageProcessing(NLP):Forprocessing unstructured medical records and extracting relevantclinicaldata.
Challenges:
Data Privacy and Security: Handling sensitive patient data while maintaining compliance with regulationslikeHIPAA.
DataQualityandInteroperability:Integratingdata from different sources, such as electronic health records,poseschallengesinstandardization.
EthicalandLegalConcerns:Ethicalimplicationsof AI-drivendiagnosticsandtheneedfortransparency indecision-making.
FutureTrends:
Increased use of wearable devices for real-time patientmonitoring.
ExpansionofAI-powereddiagnosticsinresourcelimitedsettings.
Growthintelemedicine,withdata-driveninsights personalizingremotecare.
2.2. Finance and Banking
Applications:
FraudDetection:Machinelearningmodelsidentify patterns indicative of fraudulent activities,
protecting both consumers and financial institutions[2].
Credit Scoring and Risk Assessment: Algorithms evaluate a borrower’s creditworthiness, enabling lenderstomakeinformeddecisions.
AlgorithmicTrading:Datasciencemodelsprocess financial data to make high-frequency trading decisionsbasedonmarkettrends.
CustomerSegmentationandPersonalization:Data science is used to categorize clients, allowing for targetedfinancialservicesandrecommendations.
MethodsUsed:
Anomaly Detection: Techniques like isolation forestsandclusteringtoidentifyunusualpatterns intransactiondata.
Predictive Modeling: Regression models and decisiontreesforcreditscoringandloanapproval.
Sentiment Analysis: NLP techniques to analyze market sentiment based on news articles, social media,andfinancialreports.
Challenges:
Data PrivacyandSecurity: Adheringtostrictdata privacyregulations(e.g.,GDPR)whileensuringdata protection.
Model Explainability: Increasing demand for explainableAImodels,especiallyforcreditscoring andfinancialdecisions.
Handling High-Frequency Data: Processing and analyzing large volumes of real-time data in algorithmictrading.
FutureTrends:
Block chain for secure and transparent financial transactions.
Enhancedfrauddetectionandcybersecurityusing AIandmachinelearning.
AI-drivenfinancialplanningandadvisoryservices forpersonalizedfinancemanagement.
2.3. Retail and E-commerce
Applications:
Customer Segmentation: Data science clusters customers based on buying behavior,

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
demographics, and preferences to optimize marketingstrategies.
Recommendation Systems: Algorithms provide personalized product recommendations, boosting salesandenhancingcustomerexperience.
Inventory and Supply Chain Management: Forecastingmodelsoptimizestocklevels,reducing costs,andpreventingstockouts.
PricingOptimization:Data-drivendynamicpricing modelsadjustpricesbasedondemand,competition, andseasonality.
MethodsUsed:
CollaborativeFilteringandMatrixFactorization:For buildingrecommendationsystems.
Clustering:K-meansandhierarchicalclusteringto segmentcustomersbasedonbehavioralpatterns.
Time-SeriesForecasting:ARIMA,LSTMmodelsfor demandforecastingandinventorymanagement.
Challenges:
Data Integration: Combining data from various channels(in-store,online,mobile)togainaholistic customerview[1].
Privacy Concerns: Balancing personalized recommendationswithcustomerprivacy.
Handling Unstructured Data: Managing and analyzing unstructured data like product reviews andimages[3].
FutureTrends:
Use of AI-powered virtual assistants for personalizedshopping.
Augmentedreality(AR)applicationsinonlineretail forvirtualtry-ons.
Advancedsentimentanalysisforreal-timecustomer feedback.
2.4.
Applications:
PredictiveMaintenance:Analyzingmachinedatato predictfailuresandschedulemaintenance,reducing downtime.
QualityControl:Computervisionanddeeplearning modelsdetectproductdefectsonproductionlines.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization: Machine learning predicts demand, optimizing inventorylevelsandsupplychainefficiency.
Supply Chain Optimization: Data-driven insights enhancelogistics,routeoptimization,andsupplier selection.
MethodsUsed:
SensorDataAnalysis:IOTdataprocessingusingML modelstomonitormachineperformance[1].
DeepLearningforQualityControl:CNNsforvisual inspectioninautomatedqualitycontrol.
Reinforcement Learning: Applied in dynamic inventoryandsupplychainoptimization.
Challenges:
DatafromIOTDevices:Handlinglargevolumesof datageneratedbyIOTsensorsinreal-time.
Legacy Systems: Integrating new data science methodswitholderindustrialsystems.
Security Risks: Protecting IOT devices and data fromcyberthreats.
FutureTrends:
Growthindigitaltwins,creatingvirtualmodelsof productionlinesforsimulationandoptimization.
Fully autonomous supply chains with AI and robotics.
IncreasedadoptionofsmartfactorieswithIOTand AIintegration.
Applications:
Sentiment Analysis: NLP models analyze public sentiment on social media to gauge consumer opinionsandtrends.
Customer Engagement and Personalization: Data science identifies user preferences for targeted contentdeliveryandadvertisements.
Social Network Analysis: Mapping social connections to understand influence and reach withinnetworks.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Ad Targeting: Algorithms optimize ad delivery to relevantaudiences,improvingadengagement.
MethodsUsed:
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Sentiment analysis,textclassification,andentityrecognition.
SocialNetworkAnalysis:Graph-basedmethodsto mapandanalyzerelationshipsamongusers.
RecommendationAlgorithms:Usedtopersonalize userfeedsandsuggestcontentorproducts.
Challenges:
Data Privacy: Managing user data responsibly, especiallywithincreasingprivacyregulations.
Real-TimeAnalysis:Processingreal-timesocialdata forlivesentimentanalysis[3].
Dealing with Unstructured Data: Handling text, images,andvideosrequiresdiversemethods.
FutureTrends:
AI-poweredtoolsforreal-timesociallisteningand sentimenttracking.
Increased focus on ethical AI for personalized recommendations.
MoreadvancedvirtualinfluencersandAI-generated contentindigitalmarketing.
2.6. Public Sector and Policy Making
Applications:
Crime Prediction and Prevention: Data science models analyze crime data to identify high-risk areasandpredicttrends.
Traffic and Transportation Management: Data analytics helps optimize traffic flows and public transportationsystems.
Public Health Monitoring: Data science tracks diseasepatternsandpublichealthmetricstoguide policydecisions.
MethodsUsed:
Predictive Analytics: Time-series models and regressionanalysisforcrimeandtrafficprediction.
GISandSpatialAnalysis:Formappingandanalyzing spatialdatarelatedtourbanplanning.
Social Network Analysis: Used for tracking the spreadofinformationordiseaseinpublichealth.
Challenges:
DataPrivacy:Protectingcitizendatawhileusingit forpublicbenefit.
Bias in Decision-Making: Avoiding biases in predictive models that could lead to unfair policy decisions.
Securing Public Trust: Building transparency in data-drivenpolicies.
FutureTrends:
Greater adoption of real-time analytics in crisis management.
Use of AI for urban planning and smart city development.
Transparency-focused AI policies to build public trust[8].
Theseapplicationsdemonstratethetransformative impact of data science across different fields. The advancementsindatasciencearehelpingindustries leveragetheirdatamoreeffectively,providingnew insights and enabling more informed decisionmaking.
Theapplicationsofdatascienceacrossvariousindustries haveindeedcreatedtransformativeopportunities,butthere aresignificantchallengesthatcanhinderprogressoreven introducerisks.Belowaresomeofthemajorchallengesin datascienceapplications.
Privacy Concerns: Many data science applications rely on personal or sensitive data, such as health records,financialtransactions,oronlinebehavior. Protecting this data and complying with privacy regulations(e.g.,GDPRinEurope,HIPAAintheU.S.) is essential but can limit data availability and accessibilityforanalysis[5].
SecurityRisks:Databreachesareapersistentrisk, especiallyinsectorslikefinance,healthcare,andecommerce, wherelargeamountsofsensitivedata are stored and processed. Protecting data from cyberthreatsrequiresadvancedsecuritymeasures, whichcanaddcomplexityandcosttodatascience projects.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Privacy-Preserving Techniques: Methods like differential privacy, federated learning, and encryptionarebeingdevelopedtoprotectdata,but thesetechniquescanlimitthedepthofanalysisor complicatemodeltraining[6].
Example: In healthcare, strict regulations prevent researchers from using identifiable patient data directly, whichcanlimitthescopeofdata-driveninsightsinmedical research.
Incomplete and Inaccurate Data: Many datasets used in data science projects are incomplete, containerrors,orlacksufficientdetail.Thiscanlead to inaccurate predictions, poor insights, and unreliablemodels[3].
DataCleaningChallenges:Cleaningdatatoensure it’saccurateandconsistentacrosssourcesistimeconsumingandlabor-intensive.Datascientistsoften spend a significant amount of time on data preprocessing,whichdetractsfromtimespenton modelbuildingandanalysis.
Data Standardization: When combining data from different sources, especially in industries with legacy systems (e.g., manufacturing), achieving consistency is challenging due to varied data formatsandstandards.
Example:Inretail,customerdatafromonlineandin-store sourcesmightbeinconsistentorlackstandardformatting, complicating personalization and recommendation algorithms.
Data Bias: When the data used to train machine learningmodelsisbiased,themodelsmayinherit these biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. This is particularly problematic in sectors like finance, hiring, and criminal justice, where biased decisions can have serious consequences.
Algorithmic Fairness: Ensuring fairness in algorithms is challenging because fairness is difficult to define and measure. Different fairness metricsmaybeinconflict,andbalancingthemwith modelperformancecanbeastruggle.
SocietalImpacts:Biasedalgorithmscanperpetuate existingsocietalinequalities,leadingtoethicaland reputational risks for companies. Ensuring fair treatment across diverse demographic groups requirescarefulconsiderationandevaluation.
Example: In hiring algorithms, if the training data reflects historicalgenderbias,themodelmightunfairlyfavormale candidatesoverfemaleones,evenwhenqualificationsare similar.
DataVolume:Asdatavolumesgrow,processingand storingthisdatabecomesachallenge,particularly forapplicationslikesocialmediaanalysis,IOT,and real-time analytics. Ensuring models can handle high data throughput requires significant computationalresources.
Infrastructure Costs: Advanced data science projects often require specialized infrastructure, suchashigh-performancecomputing(HPC)clusters orcloudcomputingplatforms,whichcanbecostly andrequireskilledITsupport.
Real-Time Processing: For applications that need real-timeinsights(e.g.,frauddetection,predictive maintenance), ensuring low latency in data processingpipelinesiscriticalbutcanbetechnically demandingandcostly.
Example:Inalgorithmictrading,financialfirmsneedhighspeed processing to execute trades based on real-time marketdata,requiringsubstantialinvestmentsincomputing infrastructure.
Black-Box Models: Many advanced machine learning models, especially deep learning algorithms,areoftenconsidered“blackboxes,”asit ischallengingtounderstandthereasoningbehind theirpredictions.Thiscanbeproblematicinsectors likefinanceandhealthcare,wheretransparencyis necessary[8].
Regulatory Compliance: In regulated industries, organizations are often required to explain their models’ decisions. For instance, financial institutionsmustexplaincreditdecisionstocomply with regulations, which may be difficult with opaquemachinelearningmodels.
UserTrust:Lackofinterpretabilitycanreduceuser trustinAIapplications.Forexample,inhealthcare, physicians may be reluctant to adopt AI-based diagnostic tools if they don’t understand how the toolreachesitsconclusions.
Example: In credit scoring, a deep learning model might predictacustomer’slikelihoodofdefault,butifthereasons arenotclear,itcouldleadtoregulatoryandtrustissues.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
UnstructuredDataChallenges:Text,images,audio, andvideodataareunstructuredandoftenrequire specificpreprocessingtechniques(e.g.,NLPfortext, CNNs for images). Processing these data types is morecomplexthanstructureddataliketables[4].
DataVariety:Combiningdatafromdifferentsources (e.g.,socialmedia,CRMsystems,IOTsensors)adds complexityduetodifferingdataformatsandtypes. Harmonizing this data is essential but requires advanceddataengineeringskills.
High Storage and Processing Requirements: Unstructured data often demands more storage spaceandcomputationalresources,increasingthe costandcomplexityofdatascienceprojects.
Example:Incustomerservice,analyzingcalltranscripts,chat logs, and emails for sentiment requires processing vast amountsofunstructureddata,whichcanbechallengingto manageandanalyzeeffectively.
TalentGap:Thedemandforskilleddatascientists, engineers,andanalystsexceedsthesupply,making it challenging for organizations to find and retain qualified professionals. Additionally, data science requiresacombinationoftechnical,statistical,and domain-specificknowledge,whichishardtofindin asingleindividual.
InterdisciplinaryKnowledge:Datascientistsoften need to work closely with domain experts (e.g., doctorsinhealthcare,tradersinfinance),requiring themtohaveatleastbasicknowledgeofthefieldto createmeaningfulinsights.
Continuous Learning: The field of data science evolves rapidly, with new tools and techniques emerging frequently. Data science professionals must continuously update their skills, which requirestimeandinvestmentfrombothindividuals andorganizations.
Example: In industries like manufacturing, finding data scientistswithknowledgeofbothproductionprocessesand data science methods can be difficult, which limits the successofanalyticsandIOTprojects.
Outdated Technology: Many industries, especially manufacturing and government, rely on legacy systemsthatmaynotbecompatiblewithmodern data science tools and platforms. Integrating new
analyticscapabilitieswiththeseoldersystemscan becomplexandcostly.
DataAccessIssues:Legacysystemsmightnotallow foreasyaccesstodata,limitingtheabilityofdata scienceteamstoworkwithreal-timeorlarge-scale data[3].
Technical Debt: Adapting legacy systems often involves significant modifications or custom solutions,leading totechnical debt thatcanmake futureupdatesmoredifficult.
Example:Inthepublicsector,manyagenciesuseoutdated data systems that make it challenging to implement advancedanalyticsorAI-driveninsights.
EthicalAIUse:UsingAIanddatascienceinsensitive applications, such as healthcare, finance, or law enforcement,raisesethicalquestions.Organizations must balance the benefits of data science with ethical considerations to avoid harmful consequences[3].
RegulatoryCompliance:Adheringtodataprotection regulations(e.g.,GDPR,CCPA)canbechallenging,as datascienceprojectsoftenrequirelargeamountsof dataandcross-borderdatatransfers[4].
Transparency and Accountability: Increasingly, regulators are focusing on transparency and accountability in AI applications, requiring organizations to document and audit their data sciencemodels.
Example:Inlawenforcement,predictivepolicingtoolshave faced criticism for potentially reinforcing biases and impacting certain communities unfairly, raising ethical concerns.
Resource-Intensive Models: Training complex models,particularlydeeplearningmodels,requires extensivecomputationalpower,whichcanbecostly andtime-consuming.
Environmental Impact: Large-scale data science operations consume considerable energy, contributingtotheenvironmentalfootprint.Efforts to reduce this impact include optimizing model efficiencyandusinggreenenergysources.
Sustainability Concerns: As data science becomes more widespread, there is a growing focus on sustainablepractices,suchasusingenergy-efficient

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
algorithms and optimizing code to reduce computationaldemands.
Example:Traininglargelanguagemodels(likeGPT)requires substantial GPU resources and energy, prompting discussionsontheenvironmentalcostsofAIadvancements.
These challenges are multifaceted and require careful consideration to ensure that data science applications are effective, ethical, and sustainable across industries. Addressingtheseobstacleswillhelporganizationsleverage datascienceresponsiblyandinnovativelywhileminimizing risksandmaximizingpositiveimpacts.
4. Future directions in data science
Thefieldofdatasciencecontinuestoevolverapidly,fueled by advancements in algorithms, computing power, and access to larger datasets. Below are detailed future directions in data science applications that are likely to shapetheindustryinthecomingyears.
4.1. Explainable and Interpretable AI
Importance of Transparency: With increased reliance on machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence(AI)incriticalsectors(e.g.,healthcare, finance, law), explainable AI (XAI) is becoming essential.Futuredatascienceapplicationswillfocus onmaking complexmodels moreinterpretableto ensuretrust,especiallyinregulatedindustries[8].
Emerging Techniques: Techniques such as SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations), LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations), and counterfactualexplanationsaregainingpopularity astheyhelpinterprethowmodelsmakedecisions. Thesemethodswillberefinedandintegratedinto moreapplicationstoenhanceaccountability[9].
Ethics and Fairness: Explainability also supports ethical AI by enabling developers to identify and mitigate biases in their models. This will become increasingly important as organizations work to ensurefairnessandcompliancewithregulations.
Example: In healthcare diagnostics, explainable AI would allow physicians to understand the reasoning behind AIpredicteddiagnoses,makingiteasierforthemtotrustand integratetheseinsightsintopatientcare.
4.2. Federated Learning and Privacy-Preserving Techniques
FederatedLearning:Traditionalmachinelearning models require centralized data collection, which can raise privacy concerns. Federated learning allowsmodeltrainingacrossdecentralizeddevices withoutcentralizingdata.Thisenablesdatascience
applicationstoleveragesensitivedata(e.g.,medical, financial)withoutcompromisingprivacy.
Privacy-Preserving ML: Techniques such as differentialprivacy,homomorphicencryption,and secure multi-party computation will play a larger role in data science. These methods protect individual privacy while enabling data analysis, whichisparticularlybeneficialinsectorswithstrict privacyregulations.
ApplicationsinIOTandEdgeComputing:Federated learningwillalsobecrucialforInternetofThings (IOT)applications,wheredatacanbeprocessedat the edge, reducing latency and bandwidth usage whilemaintaininguserprivacy.
Example:Inpersonalizedmedicine,federatedlearningcould enablecollaborativemodeltrainingacrosshospitalswithout requiringpatientdatatoleaveitsoriginallocation,ensuring compliancewithdataprotectionlaws.
AI Ethics Frameworks: As AI becomes more pervasive,thereisagrowingemphasisonethicalAI. Future data science applications will incorporate frameworks that ensure fairness, accountability, and transparency, addressing biases in data and models.
BiasDetectionandMitigation:Toolsandtechniques todetectandmitigatebiasesindataandalgorithms areadvancing.Incorporatingtheseintodatascience workflows will be essential, especially in sectors suchashiring,finance,andlawenforcement,where biasedalgorithmscanhaveseriousconsequences.
Ethical Audits and Governance: Companies are likelytoadoptregularethicalauditsofAIsystems, similar to financial audits, to ensure compliance withethicalandregulatorystandards.Thiswillhelp establishtrustandaccountability.
Example:Inhiringalgorithms,futuresystems will include built-inmechanismstodetectandadjustforbiasesrelatedto gender,ethnicity,orsocioeconomicbackgroundtopromote fairhiringpractices.
Edge Computing for Data Processing: With the proliferation of IOT devices, edge computing is gainingtractionasitenablesdataprocessingclose tothedatasource,reducinglatencyandbandwidth requirements. This is particularly useful for realtime analytics in applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial automation [10].

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Real-Time Decision-Making: Edge computing facilitatesfasterdecision-making,asdatadoesnot needtobetransmittedtoacentralizedserver.This willbeessentialinfieldslikehealthcare,whererealtime monitoring of patient vitals could trigger immediateresponses.
5G and Data Science: The roll-out of 5G networks will support edge computing by providing faster datatransfer,enablingmorecomplexanalyticsand datascienceapplicationsattheedge.
Example:Inautonomousvehicles,edgecomputingallowsfor real-time data processingdirectlyonthevehicle,enabling quick responses to changing road conditions or obstacles withoutrelyingoncloudprocessing.
4.5. Augmented Analytics and Automated Machine Learning (Auto ML)
Augmented Analytics: Augmented analytics uses machine learning and AI to automate data preparation, insight generation, and data visualization. This approach democratizes data sciencebyenablingnon-expertstoanalyzedataand gaininsightsthroughguidedanalyticsandnatural languagequeries.
AutoML:AutoMLplatformsautomatekeystagesof thedatascienceworkflow,fromfeatureengineering tomodelselectionandtuning,makingdatascience accessibletoa broaderaudience.AutoML will be especially beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises(SMEs)thatlackdedicateddatascience teams[7].
Focus on User-Friendly Interfaces: Tools that integrate Auto ML and augmented analytics with intuitiveuserinterfaceswillallowbusinessusersto performcomplexanalyses,facilitatingdata-driven decision-makingacrossorganizations.
Example:Inretail,augmentedanalyticscanempowerstore managerstogenerateinsightsintocustomerbuyingpatterns without requiring in-depth knowledge of data science, enhancinginventoryandmarketingstrategies.
4.6. Integration of Natural Language Processing (NLP) with Advanced Conversational AI
ConversationalAIExpansion:AdvancesinNLPare improving conversational AI applications, making them more sophisticated and useful for customer support,virtualassistants,andautomatedcontent creation. This will help companies provide personalizedandnaturaluserexperiencesatscale.
MultilingualandContextualUnderstanding:Future NLP models will have improved capabilities in understanding multiple languages and complex contexts, making them useful for global organizations.Techniquesliketransferlearningand few-shot learning will also enable AI systems to adapttonewlanguagesanddomainsquickly.
KnowledgeGraphsandNLP:CombiningNLPwith knowledgegraphswillenableAItoprovidericher, context-aware responses by linking relevant informationfrommultiplesources.
Example: In customer support, conversational AI with improved NLP can resolve customer queries in various languages,enhancingcustomersatisfactionandreducingthe needforhumanintervention.
Synthetic Data for Privacy and Augmentation: Generative AI techniques, like GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), are being used to create synthetic data that can mimic real data while preserving privacy. This is especially valuable in fields like healthcare and finance, where data availabilityisrestricted[12].
DataAugmentation:Syntheticdatacanbeusedto augmentdatasets,helpingovercomedatascarcity, especiallyforrareevents.Thisisusefulfortraining models in scenarios where collecting real-world dataischallengingorcostly.
ApplicationinCreativeIndustries:GenerativeAIis transforming fields like content creation, design, andentertainment,enabling applicationsinvideo gamedevelopment,marketing,andfilmproduction throughtheautomaticgenerationofrealisticmedia content.
Example:Inhealthcare,syntheticdatagenerationcanallow researchers to create large datasets for rare diseases, supporting model development without compromising patientprivacy.
Digital Twin Technology: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, systems, or processes.Theyareusedtosimulate,monitor,and optimize real-world counterparts in fields like manufacturing, urban planning, and healthcare. WithIOTdata,digitaltwinscanpredictandresolve potentialissuesbeforetheyoccur[11].
SimulationforDecision-Making:Simulationmodels allow businesses to test different scenarios and

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
strategies before implementing them, enabling better-informeddecisions.Thiscanbeparticularly usefulinsectorslikelogistics,wherevariablesare constantlychanging.
CombinationwithAI:AI-powereddigitaltwinscan automaticallyadjustoroptimizesystemsbasedon real-timedata,makingthemincreasinglyvaluable in industries where precision and efficiency are paramount.
Example:Inmanufacturing,digitaltwinsofproductionlines cansimulatetheimpactofchangesintheprocess,allowing manufacturers to optimize operations without disrupting actualproduction.
4.9. Integration of Data Science with Block chain Technology
Data Transparency and Integrity: Block chain’s decentralized and immutable nature provides an opportunity for secure and transparent data sharing. This is particularly useful for industries thatrelyondatatransparency,suchassupplychain management,finance,andhealthcare[13].
Block chain-Driven Data Sharing: Block chain can facilitatesecuredatasharingbetweenorganizations without compromising privacy, as records are immutableandverifiable.Thisisespeciallyuseful for collaborative research and public sector applications[16].
Smart Contracts and Data Science: Block chain smartcontractscanautomatecomplexworkflows andtransactions,whichcanbeenhancedwithdata sciencemodelstotriggerautomatedactionsbased onpredictiveanalyticsorreal-timedatainputs.
Example:Insupplychainmanagement,blockchaincanbe used to track product origin and conditions, while data science can analyze trends and predict potential supply chaindisruptions.
4.10. Focus on Sustainable AI and Green Data Science
Energy-Efficient Algorithms: Data science is increasinglyfocusedonreducingtheenvironmental footprint of large-scale model training and deployment. Future models will be optimized to reduce energy consumption, enabling more sustainableAIpractices[14].
Carbon-Neutral Cloud Computing: Many organizationsaremovingto carbon-neutral cloud providersandusingAI-driventoolstooptimizedata centerenergyusage.Thisiscrucialasdatascience
applications continue to grow and demand more computationalresources.
AI for Environmental Monitoring: Data science applicationsthemselvesarealsobeingdevelopedto address climate change and environmental protection, from monitoring deforestation to optimizing renewable energy use. These applications use predictive modeling to enhance resource efficiency and track environmental impacts[15].
Example: In agriculture, sustainable AI models are being used to monitor soil quality, predict crop yields, and optimizewaterusage,promoting.
Herearesomeconclusionsthatcapturethekeyinsightsand futureoutlookontheapplicationsofdatascience:
1. Transformative Potential Across Industries: Data science has already transformed numerous industries healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing, among others by enabling datadriven decision-making, predictive analytics, and personalizedsolutions.Theseapplicationsnotonly enhanceefficiencybutalsoopennewpathwaysfor innovationandservicedelivery.
2. GrowingNeedforEthicalandResponsibleAI:Asdata science applications become more integrated into criticalareasofsociety,thereisapressingneedfor ethical, transparent, and fair AI systems. Ensuring that algorithms are unbiased, interpretable, and secure is vital for building trust with users and maintaining regulatory compliance, especially in sensitive fields like finance, healthcare, and law enforcement.
3. AdvancementsinPrivacy-PreservingTechnologies: Privacyconcernshavebeenalongstandingchallenge indatascience,especiallywiththeincreasedfocus ondataprotectionregulationsglobally.Technologies like federated learning, differential privacy, and secure data sharing via block chain are making it possibletobalancedatautilitywithprivacy,enabling more responsible data use in highly regulated industries
4. DataScienceDemocratizationthroughAutomation: TheriseofAutoMLandaugmentedanalyticstoolsis making data science more accessible to a broader range of professionals. By lowering the technical barriers, these tools empower business users to harness data insights without requiring deep expertise,drivingamoredata-centriccultureacross organizations.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 06 | Jun 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
5. Integration of Edge Computing and Real-Time Analytics: The integration of edge computing is enabling faster and more efficient data processing, particularlyinIOT-drivenindustries.
6. SustainableandGreenDataSciencePractices:With the growing environmental concerns related to large-scale AI and data processing, sustainable practices in data science are gaining importance. Organizations are increasingly adopting energyefficientalgorithms,carbon-neutralcloudcomputing, and AI models for environmental monitoring, markingashifttowardresponsible,eco-friendlyAI practices.
7. ExpandingHorizonswithGenerativeAIandDigital Twins:GenerativeAIis notonlyreshapingcontent creationbutalsofacilitatingdatagenerationforrare events, improving model training and accuracy. Similarly,digitaltwinsareprovidingbusinesseswith advanced simulation capabilities, which optimize decision-makingprocessesbyallowingforpredictive analysisofreal-worldscenarios.
In summary, the field of data science continues to evolve, providingpowerfultoolsforinnovationandefficiencyacross awiderangeofapplications.Byaddressingethicalconcerns, privacychallenges,andenvironmentalimpacts,futuredata scienceapplicationscandrivepositivesocietalchangewhile fostering trust and sustainability. With the advent of new technologies like explainable AI, federated learning, and augmentedanalytics,thereachofdatascienceisexpanding, making it a pivotal element in the future of digital transformationacrossallsectors.
[1] Provost, F., & Fawcett, T. (2013). Data Science and its Relationship to Big Data and Data-Driven Decision Making.BigData,1(1),51–59.
[2] Dhar, V. (2013). Data Science and Prediction. CommunicationsoftheACM,56(12),64–73.
[3] Mittelstadt, B. D., Allo, P., Taddeo, M., Wachter, S., & Floridi,L.(2016). Theethicsofalgorithms:Mappingthe debate. BigData&Society.
[4] Binns,R.(2018). Fairness in machine learning: Lessons from political philosophy. Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency,149-159.
[5] Kairouz,P.,etal.(2021). AdvancesandOpenProblemsin FederatedLearning. FoundationsandTrendsinMachine Learning,14(1-2),1-210.
[6] Bonawitz,K.,etal.(2019). TowardsFederatedLearning at Scale: System Design. Proceedings of Machine LearningandSystems.
[7] He,X.,Zhao,K.,&Chu,X.(2021). AutoML:Asurveyofthe state-of-the-art. Knowledge-Based Systems, 212, 106622.
[8] Ribeiro, M. T., Singh, S., & Guestrin, C. (2016). "Why should I trust you?" Explaining the predictions of any classifier. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD InternationalConferenceonKnowledgeDiscoveryand DataMining,1135-1144.
[9] Gilpin, L. H., et al. (2018). Explaining explanations: An approach to evaluating interpretability of machine learning. IEEE 5th International Conference on Data ScienceandAdvancedAnalytics(DSAA),80-89.
[10] Deng,S.,etal.(2020).Edgeintelligence:Theconfluence of edge computing and artificial intelligence. IEEE InternetofThingsJournal,7(8),7457-7469.
[11] Tao,F.,Zhang,M.,Liu,Y.,&Nee,A.Y.C.(2019). Digital twin in industry: State-of-the-art. IEEETransactionson IndustrialInformatics,15(4),2405-2415.
[12] Frid-Adar,M.,etal.(2018).GAN-basedsyntheticmedical imageaugmentationforincreasedCNNperformancein liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing, 321, 321331.
[13] Nakamoto,S.(2008). Bitcoin: A peer-to-peer electronic cash system. [white paper]. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
[14] Strubell,E.,Ganesh,A.,&McCallum,A.(2019). Energy and policy considerations for deep learning in NLP. arXiv:1906.02243.
[15] Schwartz,R.,Dodge,J.,Smith,N.A.,&Etzioni,O.(2020). GreenAI. CommunicationsoftheACM,63(12),54–63.
[16] Zheng, Z., et al. (2017). An overview of blockchain technology:Architecture,consensus,andfuturetrends. IEEEInternationalCongressonBigData,557-564.