THEKINDERGARTENEXPERIENCE







Kindergartenisacrucialstageinachild'searlyeducation,markedbysignificantdevelopmental milestonesthatlaythefoundationforfutureacademicandsocialsuccess.Kindergartenmarks thebeginningofmoreformalliteracyandnumeracyskills,aschildrenlearntorecogniseletters, writetheirnames,readsimpleearlyreaders andcountnumbers.Socially,Kindergartenersstart tonavigatethecomplexitiesofgroupinteractions,andtheybegintodevelopgreaterlevelsof independenceinbothlifeskillsandlearning.Emotionalgrowthisalsoevidentaschildrenexpress theirfeelingsanddevelopasenseofempathy.Furthermore,theKindergartenexperiencefosters curiosityandaloveforlearning,settingthestageforalifelongjourneyofexplorationand discovery.EachmilestoneachievedinKindergartenrepresentsabuildingblockforthechild's ongoingeducationaljourneyandoverallwell-roundeddevelopment.
IntheLowerSchoolatISBwe
embracetheuniquepotentialwithineachlearner tailoreducationalexperiencestoindividualstrengths,interests&pace empowerlearnerstoexploretheirpassions integratetechnologyseamlessly cultivatecriticalthinking,andcollaborateacrossdiverseperspectives developlearnerswhoconfidentlynavigatethecomplexitiesofourworld

ISBbelievesthatinordertobeInternationalCitizens,successfulinandoutof school,studentsneedtolearnanddevelopsocialandemotionalcompetencies. ThesecompetenciesaregroundedinourCharacterStandards. C h a r a c t e r S t a n d a r d s




Description
Connected Disciplines
Conceptual Understandings
Understandingtherelationshipbetweenmass andtheforcerequiredtomoveanobject
Science-ForcesandMotion,MathMeasurementandMathematicalThinking
Learnersunderstandthat:
Thewayobjectsmovedependsona varietyoffactors,includingtheirsizeand shape
Apushorapullaffectshowanobject movesorchangesshape
Learnersunderstandthat: Therearestagesonproductionofgoods andprovisionofservices Somegoodsandservicesareproducedin ourcommunityandsomeareproduced byothercommunitiessoweneeda systemthatallowsustobuyandsell goodsandservicestomeetourneeds Earthsresourcesareusedinavarietyof ways
Understandinghowtheneedsoflivingthings changeacrosstheirlifecycles
Science-PatternsintheNaturalWorldMathSequencing
Learnersunderstandthat:
Livingthingshavebasicsurvivalneeds includingfood,waterandshelter which aremetbytheirenvironment
Livingthingshaveavarietyofexternal features
Livingthingsgrow changeandhave offspringsimilartothemselves
Learning Engagements
Understandingoftheprinciplesofforces andmotioncanhelpusmovethingsmore efficiently Atthebeginningofthismodule, learnerssharetheirinitialideasaroundreal lifeproblems,suchasmovingalarge object Throughhands-onactivitieslearners exploreavarietyofforcesincludingpushing pulling,throwing,dropping,rollingand flying Byconductingexperimentsthey begintomanipulatevariablessuchas friction,surface,size,shapeandmassand observetheimpacttheyhaveonmoving objects Astheirexperiencegrows the learnersareencouragedtomake predictions constructandtesthypotheses Usingtheinquiryprocessenablesthe learnerstothinkofthemselvesas investigatorsandscientiststhatask questionsandseekoutanswerstoreallife problems
Inthismodule,learnersdeveloplangauge usedto describemeasurementsincluding speed,size,volumeandweight
Theresourcesthatweuseinoureveryday livescomefromarangeofdifferentsources andgothroughdifferentprocessesof production Throughoutthismodule,learners exploreavarietyofrawmaterialsandput thesematerialsthroughaprocessinorderto createproducts Learnersobservehowthe procedurecanaffecttheoutcome,for example,anapplemaybecomeapplejuiceor applesaucedependingontheprocessthe appleisputthrough Learnerslookatthe sequenceofstepsthatvariousproductsgo throughandfocusontheimportanceoforder andsequence Througharangeofcooking/ craft/constructionactivitieslearnersare providedwithmultipleopportunitiestofollow andcreatesetsofinstructionstomakevarious products Theylookatcommonitemsaround them,investigatetheiroriginsandcompare wheretheyweremade(homemadeversus factorymade,localversusimports)
Thismoduleculminatesinthecreationofa How-Tovideotosharewithawideraudience and/oraposterthatexplainsaprocedure
Exploringournaturalworldhelpsusbuilda connectiontonatureinitsvariousforms Being equippedwithgreaterknowledgeand understandingcanhelpusappreciateand protectourlivingworld Learnersobserve changesbothintheforestandintheclassroom astheywatchthelifecyclesoffrogs,butterflies andladybugsunfoldbeforethemTheyexplore bigquestionslike-Whatischange?Wheredoes itoccurinnature?Whydoesthishappen?How canoneobservethelifecycleinnature? Learnerscompleteresearchandgather informationthroughobservations,computer programmes,booksandothersourcesThe culminatingprojectendswiththelearners givingasciencepresentationonthelifecycleof ananimaltotheirparents duringagallerywalk Learnershavemultipleexperiencesorganising informationandrepresentingitusingflow charts
ThismoduleislinkedtothewritinggenreReportWriting Insmallgroupslearnerscreateareportabout ananimalorinsectandcompleteanindividual posterabouttheirlifecycle Non-fictiontext featuresareintroducedandexplored
e m a t i c s
S T E M : M a t
TheISBMathematicsprogrammeisdesignedtodevelopadeepunderstandingof mathematicalconceptswhilenurturingcriticalthinkingskillsandproblem-solvingabilities.
Strand
Counting&Cardinality
Knowsnumbernamesandthecountsequence
Countsto100byones
Countstotellthenumberofobjects
Whencountingobjects,saysthenumbernamesinthestandardorder,pairingeachobjectwithoneandonlyone numbernameandeachnumbernamewithoneandonlyoneobject
Comparesnumbers
Identifieswhetherthenumberofobjectsinonegroupisgreaterthan,lessthan,orequaltothenumberofobjects inanothergroup
Comparestwonumbersbetween1and10presentedaswrittennumerals
Patterns
Workswithpatterns
Recgnises repeatsandcreatespatterns

Operations& Algebriac Thinking
Numbers& Operationsin
Base10
Geometry
Recognisesadditionasputtingtogetherandaddingto,andrecognisessubtractionastakingapartandtakingfrom
Representsadditionandsubtractionwithobjects,fingers,mentalimages,drawings,sounds(e.g.,claps),actingout situations,verbalexplanations,expressions,orequations
Solvesadditionandsubtractionwordproblems,andaddandsubtractwithin10,e.g.,byusingobjectsordrawingsto representtheproblem Counting&
Workswithnumbers11-19togainfoundationsforplacevalue
Decomposesnumberslessthanorequalto10intopairsinmorethanoneway,eg,byusingobjectsordrawings,and recordeachdecompositionbyadrawingorequation(eg,5=2+3and5=4+1)
Foranynumberfrom1to9,findsthenumberthatmakes10whenaddedtothegivennumber,eg byusingobjectsor drawings,andrecordtheanswerwithadrawingorequation
Fluentlyaddsandsubtractswithin5
Composesanddecomposesnumbersfrom11to19intotenonesandsomefurtherones,eg,byusingobjectsor drawings,andrecordeachcompositionordecompositionbyadrawingorequation(suchas18=10+8);understand thatthesenumbersarecomposedoftenonesandone,two,three,four,five,six,seven,eight,ornineones
Identifiesanddescribesshapes
Describesobjectsintheenvironmentusingnamesofshapes,anddescribetherelativepositionsoftheseobjectsusing termssuchasabove,below,beside,infrontof,behind,andnextto Correctlynamesshapesregardlessoftheirorientationsoroverallsize
Analyses,compares,creates,andcomposesshapes
Analysesandcomparestwodimensionalshapes,indifferentsizesandorientations,usinginformallanguagetodescribe theirsimilarities,differences,parts(eg,numberofsidesandverticesandotherattributes(eg,havingsidesofequallength)
Modelsshapesintheworldbybuildingshapesfromcomponents(eg sticksandclayballs)anddrawingshapes
Describesandcomparesmeasurableattributes
Describesmeasurableattributesofobjects suchaslengthorweight
Describeseveralmeasurableattributesofasingleobject
Measurement &Data
Directlycomparestwoobjectswithameasurableattributeincommon,toseewhichobjecthas"moreof"/"lessof"theattribute, anddescribethedifference Forexample,directlycomparetheheightsoftwochildrenanddescribeonechildastaller/shorter
Classifiesobjectsandcountsthenumberofobjectsineachcategory
Classifiesobjectsintogivencategories;countsthenumbersofobjectsineachcategoryandsortthecategoriesbycount
Createmathematicalmodels
Mathematical Processes
Demonstratestheirthinkingwith pictures
R e a d i n g W r i t i n g

Strand
AcuracyandFluency
ConceptsAbout Print
ReadsC/Dleveltextsaccurately
Readsenvironmentalprint
Manipulatesphonemes
RecallslettersandsoundsandrecallsKsightwords
Makesconnectionsandrespondstotextreadtothem
Usespicturesandcontexttounderstandguidedleveledtext
Comprehension Stragegies
Strand
TextTypes &Purposes
Participatesindiscussionsaboutatext(eg,duringwholeorsmallgroupinteractivereadalouddiscussions duringpeersharing,withinplayscenarios)
Retellsstoriesorsharesinformationfromatext
Developsandanswersquestionsaboutcharacters,majorevents,andpiecesofinformationinatext
Makesconnectionsbetweenself,text,andtheworld(eg,whatisfamiliar,whatdoesan event/picture/charactermakethemthinkof,whatdotheyremember)
Composeopinionpiecesinwhichtheytellareaderthetopicorthenameofthebooktheyarewritingaboutandstatean opinionorpreferenceaboutthetopicforthebook(eg,Myfavoritebookis )
Composeinformativetextsinwhichtheynamewhattheyarewritingaboutandsupplysomeinformationaboutthetopic Narrateasingleeventorseverallooselylinkedevents,tellabouttheeventsintheorderinwhichtheyoccurred,and provideeareactiontowhathappened
Identifynewmeaningsforfamiliarwordsandapplythemaccurately
Usethemostfrequentlyoccurringinflectionsandaffixes(eg,-ed,-s,re-,un-,pre-,-ful,-less)asacluetothemeaningof anunknownword Sortcommonobjectsintocategories(eg,shapes,foods)togainasenseoftheconceptsthe categoriesrepresent
VocabularyUse
Demonstrateunderstandingoffrequentlyoccurringverbsandadjectivesbyrelatingthemtotheiropposites(antonyms)
Identifyreal-lifeconnectionsbetweenwordsandtheiruse(eg noteplacesatschoolthatarecolorful)
Distinguishshadesofmeaningamongverbsdescribingthesamegeneralaction(eg,walk,march,strut,prance)by actingoutthemeanings
Usewordsandphrasesacquiredthroughconversations,readingandbeingreadto,andrespondingtotexts
Produceupperandlowercaselettersandusecapitalsforthestartofasentenceand“I”
Demonstratesomecontrolovertenseandgenerallyusearticlesaspointers
Understandquestionwords
Conventionsof StandardEnglish
Production ofWriting
Produceandexpandoncompletesentences
Nameendpunctuation
Writealetterorlettersformostconsonantsandshortvowelsounds
UseappropriatespellingbasedontheCommonCoreStandards
Withguidanceandsupportfromadultsparticipateinsharededitingofstudents owntextsanddiscuss possiblechanges
Exploringarangeofsoftwareand toolstodevelopcodingskillsand mathematical/computational thinking: Beebots
Osmo
Lightbot Spritbox
Asa1:1deviceschool,qualitytechnologyisavailableforallstudents. Withextensivedesign resourcessuchas3-Dprinters,laserandvinylcutters,greenscreenstudios,v-Rexrobotics, andaVRsuite,ElementarystudentsuseoneofthebestDesignTechspacesinBelgium. S T E M : D e s i g n & T e c h n o l o g y

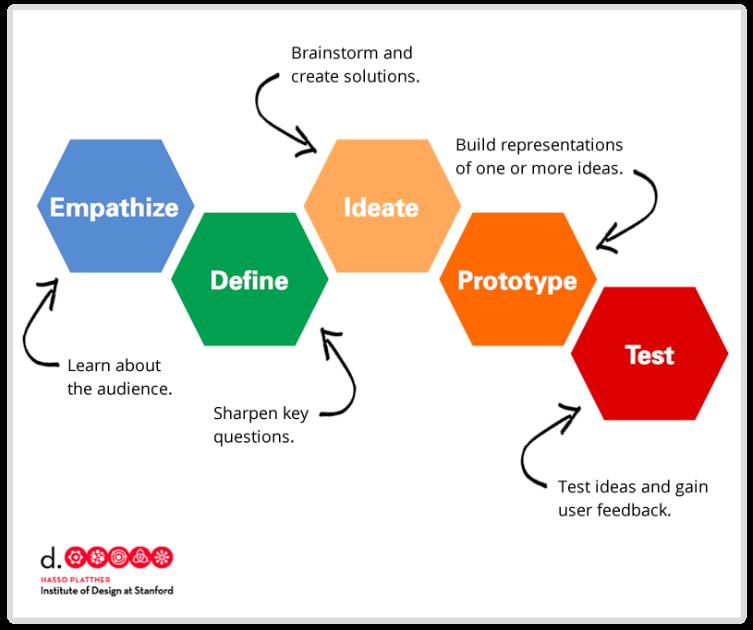
WithinDesignunitsat ISB,studentsfollowthe StanfordUniversity DesignSchoolmodel
Throughprojectsduringthe year,studentsare introducedtothedifferent designtoolsatISBandthe designprocess Weemphasiseusing technologyresponsibly andeffectivelyfor communication, collaborationand creation Becoming proficientandpostive membersinadigitalworld isaprimarygoal

Transferableskills,alsoknownasportableoruniversalskills,canbeappliedacross varioussubjectsandsituations.Theseskillsarenottiedtospecificdisciplinesbut rathercanbeadaptedandtransferredfromonecontexttoanother. T r a n s f e r a b l e S k i l l s
HowcanIactivelylistentoothers?
HowdoIsharemyideasandbuild ontheideasofothers?
HowdoIworktogethertoachieve oursharedgoals?
WhatdoIthinkIalreadyknowabout thistopic?
HowcanIdecideifinformationis helpfulandaccurate?
Howdoesinformationfromdifferent sourcesconnecttoeachother?
WhatquestionsdoIhave?
HowcanIfindthebestevidence formyquestions?
HowcanIorganiseandrecord myinformation?
HowdoIseteffectivegoalsand whereamInowinachievingthem?
HowdoIfeelandwhatis contributingtohowIfeel? DoIneedsupport?
IDENTIFYCURRENTKNOWLEDGEAND UNDERSTANDING
identifywhattheycurrentlyknowandunderstand aboutaparticularidea,conceptortopic. identifygapsintheirknowledgeand understandingofaparticularidea,conceptor topic,aswellpotentialmisconceptions
CONSTRUCTQUESTIONS: conductpreliminaryresearcharoundabroadtopic whichallowsthetopictobenarrowedappropriately. constructapowerfulresearchquestionthatrequires analysisandconceptualdepth. constructsmallerquestionsthatleadtoapossible answertoabiggerquestion.

L a n g u a g e s P a t h w a y s
Students,whohavedemonstratedproficiencyinEnglish,accessourFrench language.AdditionallanguagesareofferedaspartoftheISB+programme, basedondemand. ISBfollowstheCommonEuropeanFrameworkfor Languages.

English Proficiency
French FoundationsA1
IntermediateA2 InedpendentB1/C1
Grades5&6
Science& SocialStudies inFrench option
ISB+Plus Languages Opentoall regardlessof English Proficiency
StudentswhospeakHebrew,Spanish,Japanese,Korean,Dutch,orSwedish haveaccesstoonehouraweekofahomelanguageclass.For PrekindergartenandKindergartenthishasanorallanguagefocus,for studentsinGrade1and2thishasafocusonearlyliteracyskills.
c a t i o n & H e a l t h V i s u a l & P e r f o r m i n g A r t s
SpecialistprogrammesatISBareessentialcomponentsofawell-roundededucation. These programmesenhanceproblem-solving,criticalthinking,decision-making,teamwork,andself expression.
EachprogrammeistaughtbyaSpecialistintherespectivefield.
ThePhysicalEducationand Heathprogrammefocuseson thefollowingareas:
MotorSkills&Movement Patterns
Concepts,Principles, Strategies&Tactics
UnderstandingHealthy Lifestyles
MotorSkills SpacialAwaeness
ThroughouttheirjourneyinKindergarten,ourstudentsembarkonacaptivating adventureaimedatnurturingtheirphysicalandspatialunderstanding Theyimmerse themselvesinadiversearrayofobstaclecourses,daringtoconquerheightsand differentsurfaces increasingtheirdeterminationandresilience Throughbeing encouragedtochooseactivitiesthatsafelytesttheirlimits,theycourageouslyexpand theircomfortzonesandfurtherdeveloptheirmotorskillsandbodyawareness
IntheiryearofKindergarten,lessonswillalsobringanopportunitytoexplorearangeof ballactivities Witheachtossandcatch,theymastertheartofhand-eyecoordination, skilfullymaneuveringvariousobjectstopropelballswithincreasingprecision Asthey partakeinamultitudeofgames,theybegintoexplorearangeofopenspaces, discoveringtheexhilaratingfreedomofmovementandnavigation

TheArtsprogramme focusesonthefollowing areas: Creating& Performing and
Responding& Connectingto visual&musicalartworks.
OurVisualArtsprogrammeforstudentsin KindergartenthroughGrade2offersavibrant canvasforexplorationacrossarichtapestry ofartisticexpressions,spanningfrom sculptureandconstructiontopainting, drawing,textiles,anddigitalart Guidedbya curatedstudyofdiverseartists,ourstudents embarkonajourneyofdiscovery,unlocking aspectrumoftechniquesandignitingtheir imaginationstoboundlesscreativehorizons WithinourECCcommonspaceandChateau, anever-evolvinggalleryshowcasesthe masterpiecescraftedbyourstudents, createdindividuallyorcollaboratively Throughcollaborativeeffortswithbothoncampusartistsandoff-campusexcursions, includingourartist-in-residenceprogramme, ourstudentsareimmersedinadynamic exchangeofcreativeperspectives,drawing inspirationfromthevisionsofothers Ourschoolforestnotonlyprovidesa stunningbackdroptotheirlearning experiencebutallprovidesourstudentswith auniqueenpleinairexperienceenriching theirartisticjourney
Music
Whenstudentsunderstandthebuilding blocksofmusictheycanusethemto makemusictogether,express themselvesandconveysomething throughmusic Keepingasteadybeat allowsustostaytogetherwhenwesing orplayinstruments Bychangingthe volumeofmusicwecancreate surprisingeffects,andchangingthe speedofthemusiccaninfluencethe mood
Welearntheseandotherprinciples throughstories,movement,songsand playingavarietyofsmallpercussion instruments Bytheendoftheyear eachstudentisabletocreateashort melodywhichisthenperformedbya buddyfromtheUpperSchoolorchestra Inadditiontoourscheduledmusic classeswehaveregularKindergarten Singalongswhichstrengthensour senseofcommunity
L e v e l s a n d S k i l l s

Learningtoswimatayoungageisofparamountimportanceforseveralreasons. Webelievethatthisisacruciallifeskillthatenhanceswatersafety.Earlyexposureto swimminginstillsconfidenceinthewater,helpingchildrenovercomeanyfearand buildingastrongfoundationforaquaticcompetence. Aftertheiryearofswimmingin Kindergartenchildrencanfollowthispassionthroughengagementinafterschool activitesfromGr1on.
Weofferthreedifferentlevelsofswimminginstructiontomakesure thatallstudentsexpereincesuccessandgrowth. Thelevelsinclude:
Beginnerlevel
IntermediateLevel
Advanced/IndependentSwimmer
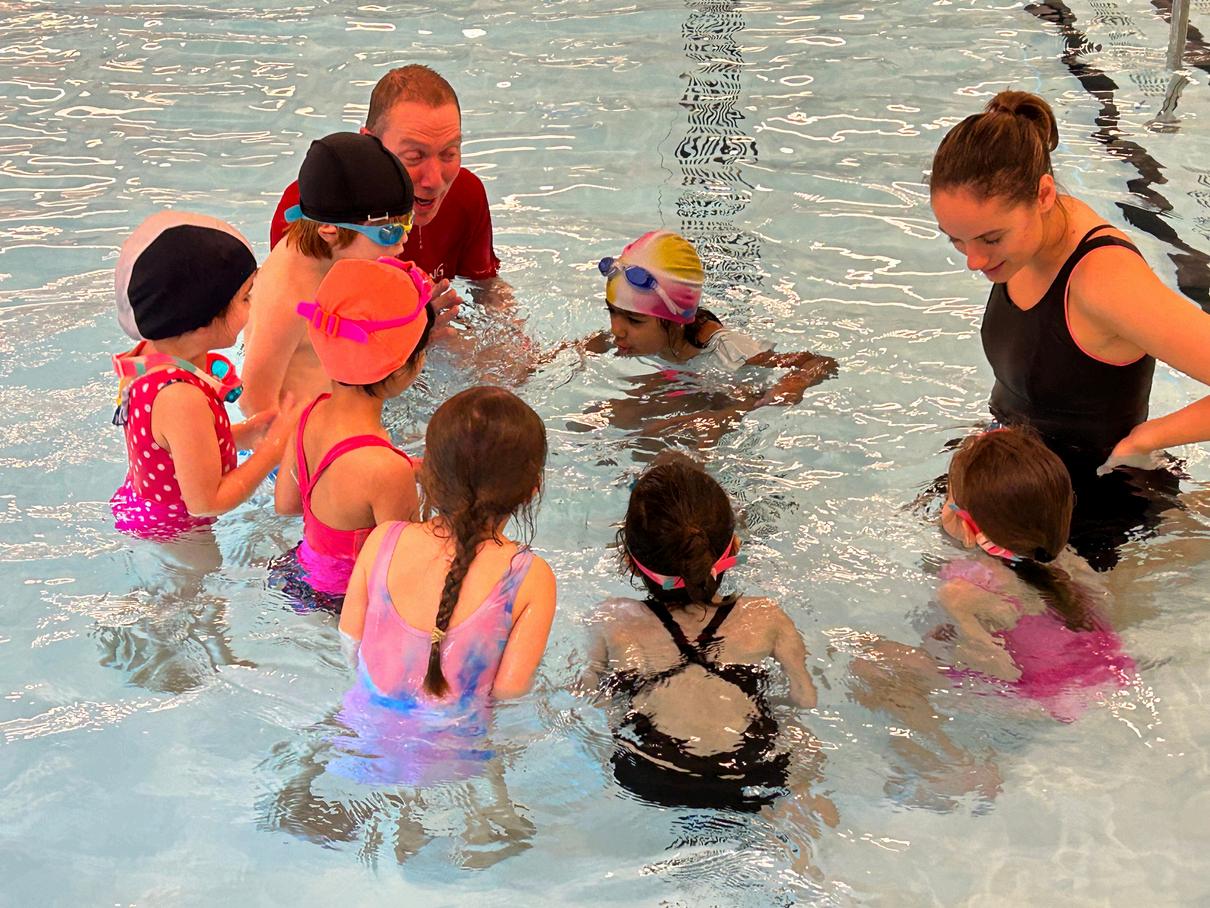



IntheECCweintegratemeaningfuloutsideofschoolexperiencesintothelearningprogramme bytakingthestudentsonanumberofexcursionsthroughtheyear. OurKindergartenstudents traveltolocalmarketstopurchasefreshitemsforcooking,visitthezoo,andworkwitharange ofvisitingexpertstolearnaboutandexpereincehowthingsaremade.


Readingisthetoppriorityassignmentforhome Allstudentsshouldspendatleast20minutes pereveningreadingindependentlyorwithaparent.
Otheractivitiesmayalsobeperiodicallyassignedasrelevanttosupportandextendlearning takingplaceduringtheschoolday Theseassignmentswillbelimitedintimeandhaveaclear purpose. Examplesmayincludeinterviewingfamilymembersasconnectedtoaunitofstudy, writingtodevelopfluency,practicingmathematicsskillsforindependentmastery,reviewing languagevocabulary,etc.
IndependentReading
DuringtheirKindergartenyearchildrenwillbegintobringreadyingbookshomeduringthe week. Thesearefamiliartextsthatstudentshavereadinclass. Familiesareaskedtorevisit thesetextswiththeirchildrenasawaytobuildbothheathlyreadinghabitsandreinforcetaught readingskills.
WeencouragefamiliestoalsomaketimetoreadtotheirchildinbothEnglishandintheirown homelanguage.
S t u d e n t S e r v i c e s
TheEnglishLanguageprogrammeprovidesservicestomultilinguallearnersbysupportingtheirdevelopmentof Englishlanguageskillsandaccesstoacademiclearning.ThrougheithertheFoundational(forbeginningEnglish learners)orIntermediate(forstudentswithasolidfoundationinEnglish)programmes,studentsarewell supportedintheirdevelopingEnglishreading,writing,listeningandspeaking.
ISBprovidesservicesforstudentswithlearningneeds.Weprovideawholerangeoflevelsofsupport, makingsurethateverychildgetswhattheyneedtobesuccessful.Theteachingteamsdecideonthe mostappropriatelevelofsupporttohelpeachstudentaccessacademicsanddevelopfoundationalskills. IndividualLearningPlans(ILPs)aredevelopedforstudentswhorequiremoderatelevelsofsupporttohelp trackanddescribetheirprogresstowardsspecificgoals.SpeechandLanguageTherapyand OccupationalTherapyservicesarealsoavailalbeonourcampus.
Enrichment&Extension:throughacceleratedtargets,alternatetextsorspeciallydesignedtasksthat increasedepthofknowledge,studentshaveopportunitiestoworkwithpeersofsimilarabilitiesandhave directinstructionandfeedbackongrowthandareasforfurtherdevelopment.
Partnerships:ISBworksinpartnershipwithorganisationssuchastheCenterforTalentedYouth(John HopkinsUniversity),StanfordUniversity &NorthwesternUniversitywherequalifyingstudentshavethe opportunitytoaccesscoursestofurtherdevelopareasofhighabilityandinterest.Thesecoursestake placeoutsideofschoolhours,buttimein-schoolmaybeprovidedonacase-by-casebasis.
CounsellingServicesareavailabletoallstudentsonashort-termandneedsbasis.Althoughwedonot providelong-termtherapeuticsupport,ourCounselorcanmakerecommendationstootherprofessionals inBelgiumandabroad.
AdditionallyourCounselorleadsourinclasssocialskillslessons,andleadsparentworkshops,bookclubs andsharestimelyandpertinentresourceswithfamiliesaroundcommonissuesandparentingchallenges.
