




In recent years, Tecnológico de Monterrey has embraced the challenge of transforming education to meet the evolving needs of an increasingly digital and dynamic world.

Today, I am pleased to present the 2024 Educational Innovation and Digital Education Report , a testament to the most significant advancements and the profound impact of technology and innovation on our academic programs, teaching methodologies, and student learning experiences. This report not only chronicles our achievements but also reinforces our institution’s unwavering commitment to delivering cuttingedge education that prepares the leaders of tomorrow.
The integration of digital experiences into our academic programs has fundamentally reshaped the teaching-learning process. At Tecnológico de Monterrey, education has evolved into a multidimensional, interactive ecosystem where students actively participate, explore, experiment, and construct their own knowledge.
At Tecnológico de Monterrey, we believe that learning should be experiential and applied, and to this end we have integrated digital tools and advanced pedagogical techniques that facilitate this vision. With the integration of Artificial Intelligence and methodologies such as Adaptive Learning, the use of virtual laboratories and simulations, our students can now apply their knowledge in controlled environments, preparing them in a practical and effective way for the real world. In addition, the creation of Academic and Alternative Credentials allows our students to build personalized academic trajectories that reflect their growth and achievements in specific competencies that are in high demand in today’s job market.
One of the highlights of this report is the documentation of how different cutting-edge techno pedagogical strategies have been adopted, changing not only what is taught, but how it is taught.
Equally vital to this transformation is the continuous professional development of our faculty. The educator’s role has evolved from knowledge transmitter to facilitator and mentor, guiding students through discovery and knowledge construction in a technologyrich learning environment. This shift nurtures a culture of lifelong learning for both students and teachers, who continuously adapt and integrate emerging technologies and methodologies to enhance the educational experience.
Additionally, the 2024 Report highlights Tecnológico de Monterrey’s global impact on digital education. Our institution shares expertise through publications, conferences, and awards, reinforcing our position as a global leader in educational innovation. We actively engage in international digital education initiatives, collaborating with academic institutions and technology partners to develop transformative solutions that shape the future of learning worldwide.
This publication is more than a report—it is a reflection of our steadfast commitment to shaping the future of education. In a world where change is the only constant, our mission is to equip students not only to navigate the future but to lead it. Innovation and digitization
are not end goals but vital pathways to delivering truly transformative education.
I extend my deepest gratitude to the members of our community—faculty, students, collaborators, and training partners—whose dedication and passion drive this ongoing transformation. Thanks to their dedication and passion, Tecnológico de Monterrey continues to solidify its standing as a global leader in educational innovation. I invite you to explore the 2024 Educational Innovation and Digital Education Report to discover how we are actively building the future of education.
Yours sincerely,
Dra. Elsa Beatriz Palacios Corral
Director of Educational Innovation and Digital Learning
Tecnológico de Monterrey

With this compilation of data, trends, and innovative techno pedagogical experiences, the 2024 Educational Innovation and Digital Education Report serves as a vital reference for understanding and shaping the future of digital education within our institution and globally. We invite you to explore all the insights and information detailed in the pages that follow!

In an era defined by rapid technological evolution, the 2024 Educational Innovation and Digital Education Report provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of digital education and educational innovation at Tecnológico de Monterrey. This report outlines the implementation of various institutional strategies aimed at enhancing learning through technology, fostering educational practices that merge digital potential with innovative pedagogical models. These advancements are designed to ensure that each educational experience is meaningful and relevant for our students, who now face complex global challenges requiring versatile and adaptive competencies.
“ ”
We innovate with a strategic purpose and a pedagogical goal, leveraging technology to enrich learning experiences.
Our institutional culture is founded on the belief that we can always do better, and technology is a powerful enabler in this pursuit. This is the essence of educational innovation and digital education.
Juan Pablo Murra Lascurain Rector of Tecnológico de Monterrey

This annual edition covers diverse thematic areas, beginning with the strategy and relevance of Digital Education at Tecnológico de Monterrey , followed by the impact of innovative technologies and practices on teaching and learning. It highlights innovative educational experiences that incorporate emerging technologies, including Artificial Intelligence , reshaping the academic journey for both students and educators.
The report also showcases key initiatives driving cutting-edge digital educational experiences. These include the integration of Artificial Intelligence, Adaptive Learning, which tailors content to individual student needs, Immersive Learning through Extended Reality, bringing knowledge into virtual environments, and Academic and Alternative Credentials which expand the recognition of skills and competencies.
Our goal is to reach more learners of all ages, extending beyond traditional degree programs. It is vital to understand and develop the skills needed to harness the opportunities presented by new technologies, especially Artificial Intelligence.
Víctor Gutiérrez Aladro Vice President of Learning for the Future

This report also delves into crucial elements such as Faculty Development, Educational Technology Ecosystems , and Innovative Educational Spaces that redefine the design of learning environments. Moreover, it offers a global perspective on our presence in educational innovation, featuring our international publications and accolades. Through this broad vision, we aim not only to present our progress but also to inspire a commitment to education that meets the demands of a constantly evolving world.
Education is a vocation. Those who work here leave a legacy, impacting the lives of students and contributing to the development of society and the nation.
Joaquín Guerra Achem Vice Rector for Educational Innovation and Academic Policy


Digital education is becoming a fundamental pillar for the transformation of learning in cutting-edge educational institutions, and Tecnológico de Monterrey is no exception. For over 35 years, Tecnológico de Monterrey has been a pioneer in incorporating technologyenriched distance, blended and face-toface learning initiatives in its High School, Undergraduate, Graduate and Continuing Education offerings.
For Tecnológico de Monterrey, digital education is the intentional, systematic and conscious application of innovative techno pedagogies in digital learning experiences that are generated throughout a student’s journey. We consider that digital education goes beyond distance courses, since it also integrates digital learning experiences in face-to-face courses and at different moments of student life, where students learn using technology as a medium.
It was in September 2022 when the “Digital Education Strategy” was defined in the institution for the following years. Its vision, strategic objectives and priority projects focused on:
Building a portfolio that integrates learning experiences, face-to-face, blended and distance training units, as well as academic programs in digital modalities.
Supporting teachers to develop digital competencies.
Developing innovative educational solutions that ensure deep and lasting learning for students.
Designing and implementing spaces and processes that enable this digital education in all campuses of the institution.
In 2023, the eligibility framework for training units in digital mode was developed, which allows the selection of programs and courses (training units) to be designed in digital mode. Likewise, quality criteria have been defined for the design and delivery of courses and enablers, as well as a specific budget for the implementation of the strategy.
In 2024, guidelines that outline the quality criteria for the design and delivery of courses were released. These guidelines establish the key elements for the integration of digital education in face-to-face training programs and units, in digital modality training units, as well as their eligibility criteria. In addition, the integration of digital education was also defined within the curricular structure of 44 academic programs, mapping out digital experiences and the design of digital modality training units.
These guidelines establish the definitions of the institutional delivery and teaching modalities, as well as the main characteristics and general criteria that govern the design, delivery and operation of programs and training units (TUs) in digital modalities.
According to the eligibility framework, the schools defined the courses that are eligible to be taught in a digital modality (blended, distance) of the 2026 academic programs. Currently, work is being done on the design of the courses, as well as providing technopedagogical advice to the teaching teams for the development of 40 training units in digital modality, as part of an initial design stage.

Digital learning experiences were also defined, for which workshops were held with the schools to identify the experiences that add the most value to student learning.




The impact of educational innovation and digital education on learning has been a topic of growing interest in academia, especially in the current context of digital transformation. This section is dedicated to examining how these innovations have redefined teaching and learning experiences at Tecnológico de Monterrey. As technologies advance and are further integrated into the classroom, new opportunities are generated to personalize learning, foster collaboration and improve accessibility, which ultimately contribute to the integral formation of students.
This analysis not only focuses on the benefits but also considers the challenges that arise with the implementation of these innovations. When evaluating the impact of digital education, it is essential to reflect on aspects such as equal access to digital resources, teacher training and curricular adaptation. Tecnológico de Monterrey is committed to exploring these factors, seeking not only to measure the success of its initiatives, but also to identify areas for improvement to maximize the transformative potential of digital education for the benefit of the entire educational community.
In 2024, educational innovation at Tecnológico de Monterrey saw a significant increase in the design of educational experiences that transformed one or more elements of the teaching and learning process for its students. A total of 606 projects were implemented across 322 training units, representing a growth 60% compared to the 201 training units recorded in 2023.
This growth was also reflected in the participation of 1,079 unique faculty members who designed and/or adopted one or more innovative experiences, impacting over 75,000 students across High School, Undergraduate, Graduate, and Continuing Education programs in distance, hybrid, and in-person modalities.
The 606 reported projects were developed within the categories of pedagogical innovation, technological innovation, innovation management, innovative mentoring processes, and the use of innovative learning spaces. Of these, 550 projects were linked to a training unit, while the remaining 56 were related to educational innovations that had an impact on student experience and faculty development.
The following figure presents the key impact indicators for 2024.

The incorporation of transformation in elements of the teaching-learning process through educational innovation and digital education initiatives in 2024 enabled significant advancements in pedagogical, technological and experiential aspects for students. These efforts fostered meaningful experiences that contribute to their holistic development.
The following graph shows the distribution of innovative projects in 2024, according to the different educational innovation categories.


The educational innovation implemented by the teachers from the national schools and Education for Life increased the quality of the teaching-learning process both for the construction of positive emotions and for the enrichment of the new learning experiences of Tecnológico de Monterrey’s students.
The following is the number of educational innovation projects developed by the national schools and Education for Life programs during 2024, which generated efficiency, improvement and quality of the academic programs offered not only by the national schools, but also by Continuing Education, LiFE and Tec Milenio, through the different delivery modalities.
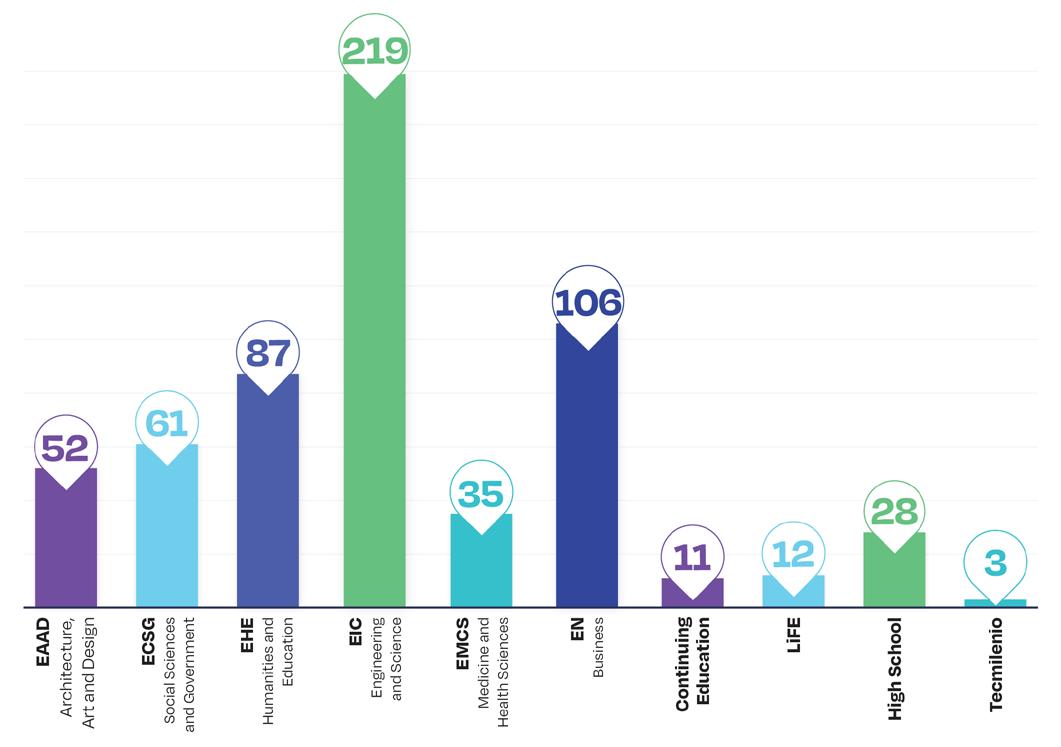
Some of the projects were developed by more than one institutional School.
The following graph shows the push for educational innovation during 2024 by national schools and Education for Life programs, based on educational innovation categories. It should be noted that some of the projects impacted more than one school or institutional initiative.
Projects per school, Continuing Education, LiFE and High School Tecmilenio based on the educational innovation categories

During 2024, different educational innovation components were incorporated into the academic levels of the national schools and Education for Life taught in distance, blended and face-to-face modalities.
The following graph shows the number of projects implemented across the institution’s different delivery modalities.
Some projects were developed by more than one institutional school.

We extend our gratitude to the faculty from the national schools and Education for Life programs, whose contributions facilitated the presentation of the current state indicators of educational innovation at Tecnológico de Monterrey. This achievement reflects their commitment to continually innovating to enrich students’ educational experiences and transform teaching practices to promote educational quality.
Digital education at Tecnológico de Monterrey is an institutional strategy that ensures meaningful learning experiences for its students through the application of innovative pedagogies that integrate digital media and technologies.
Different modalities of digital education were taught in 2024, opening the possibility of offering meaningful learning experiences in different environments. In this section, the impact of these experiences is presented.
The following figure shows student-course enrolled in groups in digital modalities, at different academic levels.
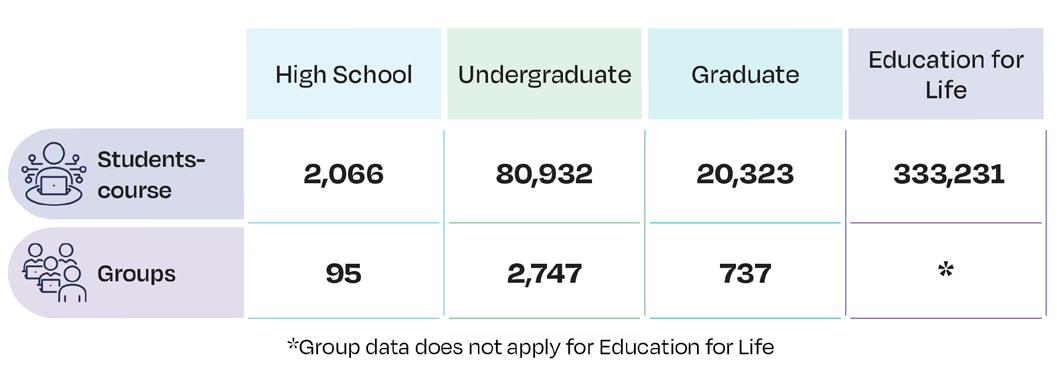


Students-course by school and modality at High School and Undergraduate level


In 2024*, 43% of undergraduate students completed at least one credit in a digital modality.
*Data from AD2024
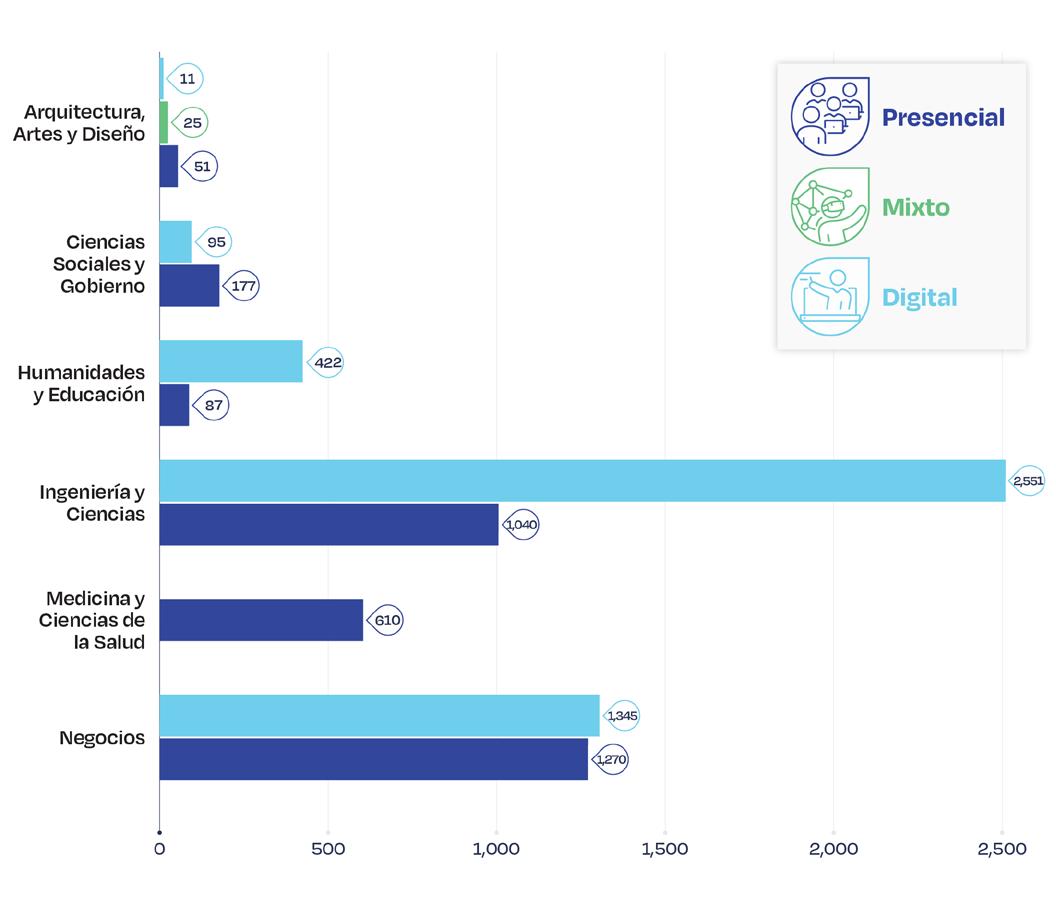
Tecnológico de Monterrey offers a wide variety of graduate programs in different modalities. In 2024, a total of 36 master’s programs and 5 specialization programs were offered, of which 20 were digital.

Distribution of graduate students enrolled in face-to-face and digital programs

In 2024, 1589 students graduated from digital programs, for a cumulative total of 39,545 graduates.
The Education for Life program encourages lifelong learning, at any time and in any form, including traditional courses or self-study. This constant preparation of individuals is essential for a comprehensive development in all aspects of life and to meet the challenges of ever-changing labor markets. The following are the different programs that Tecnológico de Monterrey offers as part of Education for Life.
In 2024, the Digital Continuing Education offerings expanded, strengthening The Learning Gate, a high-impact learning ecosystem with a flexible, on-demand model.
Currently, The Learning Gate features thematic areas in Leadership, Data Science, Marketing and Sales, Project Management, Finance, Operations, and Digital Transformation. In total, it offers more than 457 learning products and over 5,400 hours of available learning content. Additionally, it has established partnerships with leading technology companies such as IBM, Microsoft, Cisco, and AWS. This initiative was awarded the 2024 International E-Learning Award (Bronze) in the E-Learning Experience – Business Division category.
Furthermore, the Digital Learning for Employability initiative was launched, facilitated through strategic partnerships with Salesforce, Microsoft-LinkedIn, and Oracle, along with the use of the Liderly platform.
The following section presents key impact data on Digital Continuing Education.
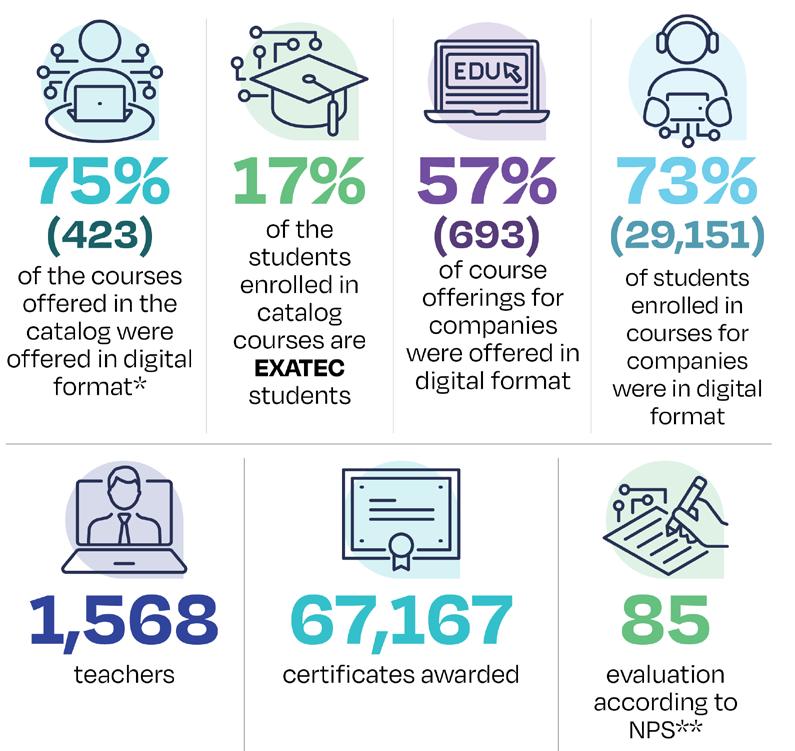
*A catalog course is a course open to the general public. **Net Promoter Score (NPS) has a scale from -100 to +100.
Source: Directorate of Planning and Effectiveness of the Vice Rector’s Office for Continuing Education (Data from January -December 2024).
MOOCs (Massive Online Open Courses) are of great importance at Tecnológico de Monterrey due to their strong impact on universal distance education. They represent both a tool for attracting students and an alternative offer for continuing education, with 233,707 students enrolled in 2024. Among the distinctive features of MOOCs, the asynchronous format and the possibility for the participant to obtain a verified digital certificate stand out. The following is a list of the most representative numbers this year of the institution’s MOOC offerings (Coursera, edX and bootcamps).

*The satisfaction index is measured on a scale of 0 to 5, where 5 is the highest rating (Data from January -December 2024).


Social programs are aimed at promoting social inclusion and equality through social impact and transformation, with the objective of contributing to the improvement of the quality of life, the sustainable development of communities and the reduction of educational deprivation in Mexico and Latin America.
Tecnológico de Monterrey offers two distance learning social programs: Prepanet and Virtual Learning Center. Likewise, the alliance between the Tecnológico de Monterrey and the BBVA Foundation was launched in 2024 to extend the scope of “Supérate”, an initiative which provides the opportunity to level knowledge and skills for junior and high school students, through a personalized training path.
Prepanet is a program that offers high academic quality online high school education, focused on people in situations of social inequality. The following are the most representative results of Prepanet’s work during 2024:

Source: National Directorate of Prepanet (December 2024)
The Virtual Learning Center is a social program that promotes access to quality education through a virtual learning community. It provides training through free educational resources and courses, as well as through the Community Learning Centers Network (Centros Comunitarios de Aprendizaje, CCA). CCAs are physical spaces where children, young people and the broader community—primarily from remote, developing areas with limited resources and lacking educational opportunities—can develop skills and competencies to continue their academic studies, start entrepreneurial ventures, or enter the job market.
Its portal ( Centro Virtual de Aprendizaje) recorded 617,885 visits in 2024, accumulating over 17 million visits since 2009.
The Center offers two types of courses: one for self-study and the other with academic accompaniment. In the latter, students are accompanied by a faculty tutor throughout their learning process. During 2024, 9 faculty tutors and 61 students from undergraduate programs at Tecnológico de Monterrey participated as part of their social service, for a cumulative total of 398 faculty members of the institution and 5,713 students have participated in this initiative.
The following are the most representative results of the work carried out by this center during 2024:


Source: Directorate of Education for Development, School of Humanities and Education, Tecnológico de Monterrey (December 2024).



This section presents the most outstanding teaching-learning experiences that educational digitalization and innovation have generated at Tecnológico de Monterrey. This innovative approach permeates all academic levels of the institution, from High School to the various Graduate Schools, as well as specialized areas such as Continuing Education and LiFE (Leadership and Student Education), reflecting its commitment to quality education and the integral development of its students.
From virtual classrooms and immersive simulations to the use of Artificial Intelligence to personalize content and academic paths, the institution responds to the needs of a generation that demands connected and adaptive education. This report not only documents the impact of these strategies in the academic realm but also serves as a testament to Tecnológico de Monterrey’s constant evolution towards a more inclusive, accessible and effective education for all its students, promoting an environment that fosters innovation and prepares its students for the challenges of the future.

Educational Innovation and Digital Education in the School of Architecture, Art and Design
2,300
The School of Architecture, Art and Design stands out for its innovative approach to integrating technology into the creative processes of its programs. The projects developed not only apply emerging technologies in a technical manner but also encourage critical reflection on social and environmental contexts. This approach not only transforms the creative process but also provides practical solutions to real-world problems.
Additionally, the School has worked to promote the integration of these advanced technologies into academic training by implementing courses and workshops aimed at faculty development.
In the field of design and creativity, this school promotes the creation of environmentally responsible solutions while fostering students’ critical capacity to challenge established norms and explore new perspectives and approaches in design. This positioning fosters creativity, sustainability, and innovation, equipping students to face future challenges in a conscientious manner.
A key component of this strategy has been the creation of partnerships with companies and organizations that provide practical experience and expertise, enriching academic training and offering students a comprehensive view of the professional environment. These collaborations broaden the impact of education, providing graduates with valuable tools to excel in their respective fields.
1. Archie: the APA bot for Architects
Teacher-designers:
Cecilia López, Lilian Salazar, Rocío Hernández
Impact on:
81 students from Mexico City, Estado de México, and Querétaro Campuses
Archie is an assistant designed to facilitate the application of APA standards in academic figures and references; it is specifically aimed at Architecture students. Its purpose is to optimize the quality of academic work by providing accurate and accessible feedback at any time, with a special focus on annotated figures that include photographs of architectural works.
Archie’s educational innovation lies in automating the review of APA standards in a specific Architecture context, offering detailed feedback categorized as “compliant”, “partially compliant”, or “non-compliant”. This includes clear explanations and practical examples, allowing students to improve their work autonomously.
The results have reflected that it is a tool that allows consistency and clarity in citations, figures, and references, contributing significantly to the quality of academic work.


The educational innovation of the project lies in the integration of advanced technologies and the collaboration with training partners, offering students professional experience in the design and execution of large-scale architectural proposals.
The project consists of the development of an architectural proposal, carried out in collaboration with the Undersecretariat of Infrastructure of the state of Nuevo León and Gensler, a multinational firm specialized in Architecture. This proposal includes the detailed graphic representation of the design through 2D drawings, 3D modeling, photorealistic renderings, digital video tours and Virtual Reality, as well as the construction of site and project mock-ups and a programmed functional mobile prototype.
Teacher-designers:
Adalberto Tamez, Luis Campos, Juan Talamás, Marcelo Espinosa, Salvador Leal, Santiago Jasso
Impact on:
26 students from Monterrey Campus
To achieve high technical level and quality results, advanced tools such as laser cutters, 3D printing, Arduino, Mostla sensors and technologies, as well as Augmented Reality were used. These techniques and resources allowed for a comprehensive and high-quality presentation.
Teacher-designers:
Antonio Juárez, María Peña, Lesly Pliego
Impact on:
54 students from Querétaro Campus
Sketch IAAR is an educational project that combines Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Augmented Reality (AR) to transform the sensory habitat design process. The project starts with hand-drawn sketches inspired by architectural masters, which students enrich with detailed prompts in AI tools such as ChatGPT and Midjourney, generating 3D images. Subsequently, these images are combined with the original sketches to perfect the design; the final model is visualized in AR through mobile devices, allowing an immersive experience that enhances spatial, aesthetic and material understanding.
The educational innovation lies in integrating emerging technologies into architectural design, fostering creativity and experiential learning. Students develop advanced competencies in spatial design and acquire a practical vision of the materialization of creative ideas.
The project has been recognized for its impact, being highlighted at ICERI 2024. It was also offered as a workshop during the “TEC 3D” event aimed at high school students, providing them with an introduction to the use of AI and AR in design. The results demonstrate its effectiveness in connecting technological tools with learning, positioning it as an innovative benchmark in architectural design education.

This project focuses on the creation of art games, interactive video games that challenge traditional conventions by integrating art into them. Its objective is to generate experiences that transcend entertainment, impacting the player emotionally and intellectually. The proposal guides undergraduate level students in video games to design an art game, encouraging critical reflection on the limits of gameplay and aesthetic experience in video games.
The educational innovation of the project lies in using art games as a pedagogical tool to explore artistic, procedural and ideological concepts. This not only promotes creativity, but also develops the students’ critical capacity toward video games as a means of expression and cultural reference.
Teacher-designers:
Claudia Garza, Jesús Félix, Nicolás Grande, Sergio Palomino, Silvia Guerrero
Impact on:
7 students from Guadalajara Campus
The results highlight the evolution of students as designers and developers, who reflect on the conceptual impact of their proposals. In addition, the project offers valuable insights for teachers interested in integrating didactic activities that connect art and video game design.
This approach allows students to challenge the established norms in video game design, while developing advanced technical and conceptual skills, contributing to their comprehensive and critical training in the field of interactive video games.


The project’s educational innovation lies in the incorporation of biomaterials into the design process, promoting products with a sustainable life cycle that challenge traditional home aesthetics. This approach combines creativity with environmental and social responsibility, challenging students to experiment with emerging materials and apply practical solutions.
Teacher-designers:
Christian Gómez, Elena Amato, Joel Olguín, Laura Niño, Mariana Solís, Raymundo Acosta
Impact on:
39 students from Estado de México Campus
The project consisted of designing everyday household objects that were accessible and sustainable, focused on rebuilding spaces and societies affected by natural disasters, through the use of biomaterials or bio composites.
The results include products designed to foster the reintegration of affected communities, providing accessible and ecological objects that contribute to the rebuilding of livable spaces. The project stands out for its impact on the training of students, who developed competencies in sustainable design and explored new perspectives on the aesthetics and functionality of household products. This reinforces their preparation to face global challenges with innovative and responsible proposals.
Educational Innovation and Digital Education in the School of Social Sciences and Government
61 Projects
9,632 StudentsCourse 93 Teachers 17 Training Units
At Tecnológico de Monterrey’s School of Social Sciences and Government, reality is transformed through knowledge, innovation and social and political commitment. The projects developed address global and local challenges, promoting sustainable solutions with a multidisciplinary and collaborative approach. From the formulation of public policies to community development initiatives, we seek to generate a positive impact on society, training leaders capable of facing today’s world challenges.
The following are some of the School’s high-impact projects.
1. Learning methodologies and innovative spaces in the “Anti-Corruption” Course
The “Anti-Corruption” course is designed for students to explore the causes, effects and solutions to corruption in different contexts. Through five thematic sections, the course addresses corruption from ethical, economic, legal and social perspectives, encouraging critical analysis, social learning and collaboration.
The innovation in the teaching approach is grounded in Social Learning and Socratic Maieutic theories, encouraging collaboration and the development of intellectual and social skills. As part of the technological innovation incorporated into the course, sessions were designed using holograms and the interactive survey platform Menti, along with other digital resources, to enhance interaction and active learning. These tools leveraged the Tec 21 Experience framework to create more dynamic and participatory classes.
The evaluation methodology was distributed in participation in forums and discussions, quizzes, public policy projects, and video presentations. Each assignment was designed to reinforce understanding and application of key concepts in real and simulated scenarios.


This year, the National Directorate of Law designed a general education course aimed at being available to students regardless of their program. This initiative seeks to provide access to essential legal knowledge for everyday life, empowering students and fostering in them a sense of responsibility to act in accordance with the law.
Historically, law has been perceived as a complicated and exclusive language, which has limited its understanding to those who work in the legal field. This approach has represented one of the main challenges for the legal profession: the inaccessibility of law to society at large.
The new course addresses attractive topics, uses accessible language and is based on practical cases to bring the law closer to everyday life. In this way, the aim is to train professionals who exercise their rights in a socially responsible manner.
The problem posed in the course is developed from the perspective of a young person who, as an influencer, faces complex challenges related to contracts, tax payments, data protection and personal image, creation and registration of trademarks, and must understand the limits between interaction with followers and harassment in social networks. These scenarios reflect the problems of the digital environment in which students develop and seek to make them aware of the importance of knowing and applying the principles of law in their daily lives.
In a collaborative exercise, students from Tecnológico de Monterrey and Universidad de San Francisco de Quito participated in a diplomatic simulation designed to address and propose solutions to restore relations between two states. This project not only fostered critical analysis and intercultural dialogue, but also provided a platform for students to experience the complexity of international diplomacy in an academic environment.
During the simulation, key issues that impact the dynamics between nations were addressed, such as Economics, Education, culture and heritage, Human mobility and security, as well as Legal aspects.
At the end of the simulation, participants presented deliverable activities that realistically replicated the diplomatic processes, including:
An official video announcing the agreement, starring the foreign ministers of both countries.
Speeches by the presidents of Mexico and Ecuador, underlining their commitment to cooperation and building a joint future.
The symbolic signing of an official document marking the reestablishment of diplomatic relations.
This exercise not only allowed students to develop critical skills, such as negotiation, strategic analysis and teamwork, but also brought them closer to the real challenges of international politics, preparing them to be global citizens committed to cooperation and conflict resolution.

With the objective of linking the learning process of its students with a real-life labor field context, during 2024 the School of Humanities and Education developed different strategies of educational innovation. These are directly related to the students’ life processes, through the integration of innovative pedagogical approaches that, together with the implementation of cutting-edge technologies, created different learning environments. In this way, students developed and strengthened personal and social competencies to facilitate their human relationships and successfully develop in any area of their lives.
This year, the School of Humanities and Education increased the number of courses associated with workshops and activities held at the International Book Fair 2024 (FIL), to link the learning process of its students with a real-life work environment. More than 1,500 students and 35 teachers from different careers participated in these activities.
This project of innovation in the processes of student experience arises to promote the reading competency of the students of the “Hispanic Literature” program.
Teacher-designers:
Erick Tenopala, Griselda Córdova, Manuel Cebral, Miguel Muñiz, Olivia Torijano, Paloma Vargas, Rafael García, Samuel Cepeda, Sergio González, Susana Ruiz, Tanya Vázquez, Víctor Gutiérrez, Yazmín Carrizales
Impact on:
1,561 students from Monterrey Campus
The training units that participated in some activities were: “Professional internship in cultural management”, and “Creative writing concentration in the digital era”, as well as the “Discourse analysis”, “Classical texts”, “Ibero-American narrative of the 19th and 20th centuries”, “Ibero-American poetry of the 19th and 20th centuries” and “Ibero-American theater and essays of the 19th and 20th centuries” blocks. The courses “Critical analysis of texts” and “Development of publishing models and prototypes” also participated.


To improve the technical and creative competencies of students in the Undergraduate program in Music Technologies, the design of the “Music Production” course incorporated advanced technological tools such as “Ableton Live”, “Pro Tools” and “Logic Pro” for recording and mixing original compositions. The course integrated techniques like non-destructive editing, parameter automation, and real-time processing effects.
Additionally, an interdisciplinary pedagogical approach was implemented, providing students with opportunities to apply their knowledge to both the technical and creative aspects of music.
The success of this innovation was demonstrated through project presentations and feedback from international experts, who verified the appropriate and creative use of the technologies. The students’ projects showcased an advanced technical mastery of the content, and collaboration among students from different semesters fostered cooperative and active learning.
Teacher-designers:
David Calderón, Cristian Hidalgo, Edgar Torres
Impact on:
240 students from Mexico City, Estado de México, and Santa Fe Campuses
3. Use of ChatGPT as a Learning Tool in the Composition of Argumentative Essays
Teacher-designer:
Luis Moisés López
Impact on:
55 students from Estado de México Campus
This educational innovation project highlights the intentional use of ChatGPT (free version) by students to develop an argumentative essay that serves as written evidence of the acquisition of various subcompetencies, such as systemic thinking, critical thinking and written communication.
Based on Toulmin’s “Argumentation Model”, which includes 6 elements (claim, grounds, warrant, backing, qualifier and rebuttal), an essay structure is established, as well as a rubric for its evaluation.
4. Gamification as a Game Element in a Didactic Sequence, through the Tec Virtual Campus Metaverse
Teacher-designer:
Moisés Villaseñor
Impact on:
70 students from Estado de México Campus
Using Tec Virtual Campus as a learning environment, a review rally was designed with the topics seen in class (in both classroom and FIT groups), with the aim of changing the dynamics of information retrieval by students. Previously, the review was carried out with the design of “matching questions”, but the new strategy led the students to locate the data within the virtual geography to relate the findings with what was requested. The above allowed that, not having “given” the elements to relate, students had to find them, engaging more with the study contents.
Through the use of generative AI tools, students in the “Posthumanism, Ethics and Technology” training unit write a science fiction story that explores possible futures beyond traditional dystopian narratives. With the implementation of these technologies in the design of the activity, they are invited to imagine future scenarios in which the relationships between humans, technology and the environment can lead to creative, inclusive and hopeful solutions to current challenges.
The creation process includes a brainstorming phase in collaboration with the AIs to generate ideas, characters and situations. Students must integrate elements that explore technological advances and move away from the usual pessimistic view of this genre.
The activity concludes with a discussion on the possibilities and limits of AI as a creative tool, as well as an evaluation of the imagined futures, reflecting on their viability and relevance in the context of today’s world.

Educational Innovation and Digital Education in the School of Engineering and Science
219 Projects
127 Training Units
364 Teachers
19,000 StudentsCourse
In 2024, the Faculty of the School of Engineering and Sciences led several key initiatives, including:
AI allows the development of innovative teaching-learning projects and experiences. The following are some of the most representative experiences:
1. Artificial Intelligence in the development and implementation of software systems/ Artificial Intelligence applied in cyberphysical systems
The use of Artificial Intelligence in training units, both in computer science and mechatronics programs, are conformed by:
The implementation of Internet of Things (IoT) platform with Wokwi Circuits and Tinkercad for circuit simulation, integration with GeminiAI platform to support data analytics, integration of data analytics with IoT and AI solutions for mobile devices with MIT AppInventor.
In turn, implementation of Azure.DevOps for project management support, using GeminiAI for data analytics support. Firebase tool integration for authentication, realtime databases, and Google Cloud services were included.
Teacher-designers:
Antonio Bento, Elsa Torres
Impact on:
286 students from Monterrey Campus

Use of Artificial Intelligence in the teaching of supply chain management
The project consisted of applying Pecan, Artificial Intelligence to determine the demand forecast of the training partner involved for the periods required by the user, depending on the historical data available. This tool allowed students to experiment with AI applied to Industrial Engineering problems, through real challenges.
Teacher-designers:
Iván Arana, Jaime Palma, Luis Guaso
Impact on:
30 students from Monterrey Campus
Teacher-designers: Alberto Ordaz, Elvia Sánchez, Juan Aranda, Juan Sánchez, Mariel García
Impact on:
91 students from Monterrey Campus
ChatGPT was used as a tool to research, analyze and evaluate processes in the context of sustainability. Students used the tool to learn about theoretical principles of sustainability or other topics related to the training unit, cross-checking information with reliable bibliographic sources, and analyzing articles. The objective was to find out the usefulness of AI for obtaining information, as well as for learning support in more complex cognitive processes, such as analyzing, evaluating and proposing.
These initiatives with the use of AI have impacted over 380 students in 7 training units belonging to the areas of Computer Science, Mechatronics, Industrial, Bio-business and Chemical Engineering, at the Mexico City, Estado de Mexico and Monterrey campuses.

1. HibriBot to the Rescue
The project involved developing a bot powered by artificial intelligence, specialized in the topic of hybridization in organic chemistry. Its purpose is to provide students with an alternative tool to enhance their understanding of the subject.
Students interact with the bot asynchronously, engaging in a friendly conversation to express their questions on the topic. To assess their knowledge, the bot administers an evaluation and assigns scores based on their responses. At the end of the interaction, it provides the results along with feedback or references for further exploration of their areas for improvement, thereby enriching the students’ learning process.
Teacher-designers:
Araceli Florido, Irma Salgado, Victor Olvera, Tania Campos
Impact on:
107 students from Monterrey Campus
2. Use of generative AI to assist in the teaching of a new programming language: MathWorks AI Chat Playground, as a teaching assistant
The objective was to evaluate the impact of using generative AI tools in teaching a new programming language and in learning mathematics. To facilitate students’ learning of a new programming language, a methodology was designed to assess the impact of AI Chat Playground (AICP) on learning MATLAB among students with prior knowledge of Python. The results indicate that generative AI tools ease the transition to learning a new programming language, suggesting that integrating emerging technologies can enhance the learning experience.
For mathematics, a series of optional activities were designed to complement students’ learning. Through these activities, students solve mathematical exercises using artificial intelligence, compare the results with their prior knowledge, and evaluate the outcomes using other support tools, such as MATLAB.
Teacher-designers:
Julio Guillermo Arriaga Blumenkron, Alfredo Delgado Spíndola
Impact on:
76 students from Monterrey Campus
3. Using GitHub Copilot in the classroom: the impact of AI in a software construction course
Teacher-designers: Ariel Ortiz, Roberto Martínez
Impact on:
49 students from Monterrey Campus
This initiative explored the impact of GitHub Copilot in programming education, highlighting its benefits, such as increased efficiency in code generation, improved understanding of concepts, and exposure to best coding practices. However, challenges were also identified, including potential dependence on the tool and ethical concerns about code reuse. The results indicate that students found GitHub Copilot useful for addressing questions and generating code more quickly, while also recognizing the importance of critically evaluating the tool’s suggestions. Despite these challenges, GitHub Copilot emerged as a valuable resource for transforming programming education, offering support to both students and educators.
4. Use of AI in integrated process design and bio-business in circular economy systems
Teacher-designers:
Jorge Álvarez, Jorge Hidalgo, Jorge Ramírez, León Guevara, Sergio Uribe
Impact on:
+420 students from Mexico City, Estado de Mexico, Laguna, Monterrey, Querétaro and Tampico Campuses.
The GenTutor initiative was designed with Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS) to assist students by leveraging generative artificial intelligence in topics such as object-oriented programming.
Additionally, AI tools like Gradescope were implemented to strengthen assessment and feedback processes, enhancing student learning in foundational and disciplinary science training units. Another initiative, ClassAssistant, provides students with rapid and objective feedback and evaluations, offering valuable insights to support their learning process.
Some of the most outstanding projects that employed Extended Reality during 2024 are presented below.
TecDrone is an innovative authentic assessment project implemented by the School of Engineering and Science, designed to evaluate students’ sub-competencies in the field of engineering. Through this project, students have the opportunity to research, design, build, and test drones in an Extended Reality (XR) environment, enabling them to connect theoretical learning with real-world professional challenges. Additionally, students justify their decisions and actions to an expert —a character developed using artificial intelligence— simulating a professional scenario where they must defend their technical choices.
This approach not only enhances the practical application of knowledge but also strengthens key skills such as decisionmaking, problem-solving, and argumentation. According to survey results, 73% of students reported that this tool allowed them to apply their learning in a real-world context, providing an authentic assessment experience that goes beyond traditional methods.
Teacher-designers:
Roberto Rodríguez, María Ruiz, Vianney Lara
Implementation teachers:
Ivonne Yznaga, Jorge Álvarez, Jorge Hidalgo
Design team: Innovación Educativa y Aprendizaje Digital
Impact on:
51 students
Bronze Award in the QS Reimagine Education Awards 2024, Learning Assessment Category

Teacher-designers:
Dariana Rodríguez, Laura Romero, Raúl Villarreal
Impacto en:
51 students from Monterrey Campus
The objective of this project was to determine the impact of using Virtual Reality (VR) to favor the engagement and learning of students in the Biotechnology Engineering, Food Engineering and Nanotechnology Engineering programs. Through a VR environment that simulates the industrial process of tequila production, students were able to fully immerse themselves in an innovative and highly interactive educational resource.
The implementation of pilot-scale process plants in this project serves several key purposes, including:
Predict industrial-level plant behavior by operating the pilot plant under conditions similar to those expected in an immersive VR environment.
Allow students to calculate unit operations in a tequila production factory, acquiring a practical and detailed understanding of these industrial processes.
With this immersive experience, students from the three academic programs were able to apply their theoretical knowledge in a simulated environment, improving their preparation to face real challenges in their respective disciplines.

The Industrial Engineering Laboratory uses the KNX technology, an intelligent technology system developed for the automation of services and devices, to train students to create a better working environment for workers in a factory. This educational project seeks to show theoretically the maximum permissible working conditions that workers and laborers generally face, such as humidity, temperature, noise and brightness, in order to adapt the KNX devices to the laboratory, and thus generate comfort for the operator.
This project received recognition in 2024 by KNX as an innovative initiative.
Teacher-designers:
Ricardo Thierry, Yadira Gutiérrez
Impact on:
36 students from Monterrey Campus

This project developed an interactive three-dimensional model of a UV-VIS spectrophotometer using Augmented Reality (AR), designed for Nanotechnology and Industrial Physics students. Its purpose is to provide visual and conceptual access to the internal optics of the equipment, usually hidden inside a closed box, breaking with the limitation of traditional two-dimensional diagrams present in books and manuals.
Teacher-designers: Isaen Dzul, Mariana Elizondo
Impact on:
30 students from Monterrey Campus
Through this AR tool students were able to explore each internal component of the spectrophotometer, such as light sources, monochromators, cuvettes and detectors, visualizing their layout and operation. This approach enhanced understanding of the optical and electronic principles of the equipment, essential for spectral analysis.
It also fostered deeper learning by connecting theory and practice through an immersive and realistic experience and boosted student motivation and interest by offering a unique and accessible perspective through these advanced technologies. This model lays the foundation for incorporating AR into science education in a scalable and personalized manner.
Teacher-designers:
Edith Martínez, Linda Medina, María Lomelí
Impact on:
64 students from Monterrey Campus
An Augmented Reality game in which the calculation of volumes is applied to solve situations in outer space.
Teacher-designer:
Alfonso Serrano
Impact on:
130 students from the following campuses: Mexico City, Ciudad Juarez, Ciudad Obregon, Guadalajara, Monterrey, Morelia, Sinaloa, and Sonora North
Educational videos were designed with Advanced Video Studio (AdViS) technology, including the use of computational simulations, with the objective of improving the impact on video viewing by students in the “Motion Modeling in Engineering” training unit, which would also result in improved learning of the topics contained in the videos.

In this project, students from four universities of different cultural contexts were empowered to experience interdisciplinary and cross-cultural sustainability problem solving. The students came from different disciplines: Engineering, Medicine, Arts and Humanities. During the program, students participated in extended conversations about shared global problems, designed their own solution and developed a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) considering the four cultural contexts.
Teacher-designers:
Eduardo Juárez, Ivo Ayala
Impact on:
61 students
9 teachers over 3 learning experiences.
The 3C alliance was created as a collaboration between Tecnológico de Monterrey, Querétaro Campus, The University of Hong Kong, The International Islamic University Malaysia and Srinakharinwirot University (Thailand), which evolved over 4 years to encompass not only 2, but 4 universities.
Silver Award in the QS Reimagine Education Awards 2024, Sustainability Education Literacy category

Teacher-designers:
Adriana Martínez, Alexandro Ortiz, César Cantú, David Mastrascusa, Erick Ramírez
Impact on:
19 students from Monterrey Campus
This project introduced a new paradigm in the teaching of advanced Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies at the university level, through the FrED Factory, developed between Tecnológico de Monterrey and Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). The objective was adapting engineering education to the demands of intelligent manufacturing, prioritizing practical experience in cyber-physical systems, additive manufacturing, collaborative robotics, Virtual Reality and Artificial Intelligence, among others.
This way, it was possible to transform traditional manufacturing automation methods through real industrial challenges that integrate disciplines and emerging technologies to generate a production line focused on the production of a machine, thus integrating all the concepts of the training unit. The initiative has the potential to train engineers with integrative knowledge, emotional intelligence, and leadership and teamwork skills by being immersed in a real context.
This program has been perfected to offer an immersive experience in our “Smart Factory”. This space, part of the global Learning Factory initiative, was recognized in 2024 for its ability to prepare industrial leaders. For this experience, educational technologies such as collaborative robotics, Virtual Reality, digital simulators and 3D printing were used to enrich learning.

The educational innovation and digital education strategy of the School of Medicine and Health Sciences (EMCS) is focused on supporting the teaching-learning process, integrating cuttingedge technology and innovative pedagogical methodologies. This approach seeks to develop digital competencies, critical thinking, creativity and collaboration in students, preparing them for the challenges of an increasingly globalized and technological world.
Generation of pediatric medical simulation scenarios. Training and use of an Artificial Intelligence (AI) assistant for the generation of clinical scenarios, applied to undergraduate Medical Surgeon students during their Pediatrics (Clinical Sciences) rotation.
Multidisciplinary Clinic. In the clinical quarter of the Multidisciplinary Clinic, students used Chat GPT as support in writing a critical essay on bariatric surgery.
Two Artificial Intelligence tools, Academic GPT and SciSpace, were incorporated to teach students to limit AI ‘hallucinations’ and obtain quality advice from scientific articles. In addition, the use of Miro was incorporated as a digital tool to design a conceptual map of how the brain works.
Teacher-designer:
Daniel Mendoza, Nancy Segura, Yareni Gutiérrez, Raúl Loera
Impact on:
140 students from the Monterrey, Guadalajara, and Chihuahua Campuses.
Noodle Factory in the Classroom. In this project, the Artificial Intelligence tool “AI for student tutoring” was used to develop quizzes with immediate feedback.
Teacher-designer:
Aracely Hambleton
Impact on:
150 students from Campus Monterrey
Use of simulation with virtual patients for the development of disciplinary competencies. Through the resolution of clinical scenarios with virtual patients, students developed subcompetencies of medical care, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment.

The design of the emotional regulation activity using the Lego Serious Play (LSP) methodology in first semester students of Health Sciences fostered self-knowledge, empathy and recognition of tools for managing emotions. The experience resulted in a deep understanding of emotional regulation and established a solid foundation for students to consciously face the emotional challenges of their future in the health field, allowing them to learn to express, share and manage their emotions in a collaborative and safe environment.
Teacher-designer: Athena Flores
Impact on:
30 students from Chihuahua Campus
The project included four key phases to explore and manage basic emotions (joy, sadness, anger, fear and disgust). In the first phase, students were divided into teams and constructed individual models representing how they experienced their assigned emotion. In the second phase, they reorganized into groups according to emotion and compared their constructions, sharing their perspectives. The third phase invited modification of the individual models, adding elements of selfregulation, such as social support symbols or calming techniques. In the fourth and final phase, each team combined their individual models to create a collective representation of emotion, integrating experiences and regulation strategies.

Within the Business School, the teaching-learning process and the use of Artificial Intelligence, Virtual Reality, and competency-based assessment and feedback are key priorities for the coming years, as they can significantly enhance education. By integrating AI and VR into current learning methodologies, the School of Business aims to:
Personalize learning: Develop tailored learning activities and mechanisms for each student, aligned with their individual needs and abilities.
Analyze data: Gather and study student performance data, enabling instructors to identify areas for improvement, adjust teaching strategies, and continuously enhance curricula.
Create engaging learning experiences: Design simulations, educational games, and gamified platforms to make learning more appealing and enjoyable for students.
Increase motivation: Leverage AI, VR, and gamification to boost student motivation by making learning more fun and challenging.
Develop skills: Support the growth of transversal competencies such as problem-solving, decision-making, and collaboration.
Provide feedback: Deliver immediate insights on student progress and performance.
While the use of AI in education offers significant potential to transform teaching and learning, it also presents challenges and limitations that must be addressed thoughtfully.
This project aims to recapture the attention of the university community at Tecnológico de Monterrey through a mobile app that integrates digital tools and enabling technologies into a Mixed Reality learning experience. The app includes GPS-enabled maps, theoretical content, a learning journal, and interactive activities to enhance student-teacher engagement while providing a more dynamic and entertaining learning environment.
Teacher-designer:
Carlos Agredano
Impact on:
50 Students from Querétaro Campus
This innovation increased students’ attention, motivation, and curiosity, resulting in a significant impact on learning outcomes. It allows students to engage in activities beyond the classroom, utilizing physical spaces in combination with digital information through “phygital” geospatial projects supported by their smartphones.
Survey results showed that 95% of students better understood theoretical concepts by encountering them in real-life contexts. Additionally, they expressed a strong interest in participating in similar activities regularly. This innovation measured improvements in student attention, topic relevance, confidence in learning, and overall satisfaction.

Teacher-designer:
Gabriela Reyna
Impact on:
80 students from Monterrey Campus
The problem addressed by this initiative lies in the lack of adaptation of traditional educational methods to the diverse needs and learning styles of students. This lack of personalization leads to disengagement and low performance, particularly in developing competencies that connect theory with practice. “Green Flags” addresses this challenge by leveraging hyper-personalized learning through Artificial Intelligence and Virtual Reality. This approach enables students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations and receive direct feedback from an AI-driven expert avatar specializing in shared value creation. This enriches their learning experience while preparing them to face global challenges effectively.
This AI-enhanced VR learning experience features a storytelling component to captivate students. They virtually visit a company called Green Flags Crafts, observe its challenges, and propose shared value solutions. Their proposals are refined through interactions with an AI master consultant, who helps them identify potential challenges or limitations in their solutions.
The results of the experimental group, on average, show a usefulness of 9.1, enjoyment of 9.2, engagement of 9.1, with a significant learning of 9.3 and a user experience of 9.0. The results of the control group, on the other hand, show a usefulness of 8.5, enjoyment of 6.8, engagement of 7.2, with a meaningful learning of 7.6 and a user experience of 7.5.


This project integrated advanced Virtual Reality and Artificial Intelligence technologies into the teaching-learning process, focusing specifically on intercultural negotiations. The primary objective was to develop an interactive simulator that allows students to practice negotiation skills in a practical and immersive environment. Students assumed the roles of mayors of a Pueblo Mágico in Mexico, engaging in real-time negotiations with an AI representing an international tourism company.
This initiative provided a hands-on, immersive learning experience designed to enhance critical skills in negotiation, effective communication, and decision-making within diverse cultural contexts. It also allowed students to apply theoretical concepts in a realistic and dynamic setting, better preparing them to tackle complex intercultural challenges successfully.
Teacher-designers:
Edgar Montalvo, Horacio Carreón, Lorena Palacios, Masa Kuljis
Impact on:
250 students from Mexico City, Guadalajara and Santa Fe Campuses
Teacher-designer:
Hector Rodríguez
Impact on:
80 students from Monterrey and Saltillo Campuses
Through the design of the ChatBot, students of the International Business undergraduate program (LIN), connected previous knowledge with new learning about the legal framework of Mexican foreign trade. This experimentation promoted deeper and more applied autonomous learning.
Student engagement, user experience, and the connection between prior knowledge and new learning were enhanced. Additionally, the cognitive load was optimized through iterative assessments, which increased motivation, enthusiasm, and the overall perceived usefulness of the tool.
The success of the innovation was evidenced by:
A substantial improvement in student outcomes: the average grades increased from 32 points on the diagnostic exam to 97 points on the final exam.
Post-test survey results showed high levels of satisfaction with the use of the tool, especially in the user experience dimension (average: 64.0).

The Interview is a platform that allows students to demonstrate the development of their competencies in a playful way. It integrates gamification with the case method to simulate new candidate selection processes in companies.
The objective of this platform was to develop an environment where students were candidates applying for a job position within a company and, during the process, they were provided with feedback on their performance in both disciplinary and transversal skills. The platform presents four different dynamics: (1) challenges, which simulate problems in the areas of the organization; (2) riddles, which try to match a concept with the correct definition; (3) work situations, which allow students to reflect on ethical dilemmas that arise throughout their working life; and (4) the big challenge, which is an integrative exam of what was seen in the fourth and fifth semesters of the academic program.
This initiative allowed for an intermediate evaluation and feedback on one or up to three disciplinary competencies for the Business School programs in the focus stage, as well as transversal competencies related to communication, critical reasoning and social intelligence, providing each student with a report with their strengths and areas for improvement, which are essential for them to work on during the following semesters.
Álvaro Martínez, Anil Yasin Ar, Carlos Agredano, Claudia Ramírez, Daniel Forcada, Daniel González, Edith Tirado, Eunice Campirán, Gris Hernández, Iralis Fragiel, Iris Ruiz, Juan Bravo, Julio Borja,Lorena Palacios, Luis Camacho, Ma. del Pilar Gómez, Martha Moreno, Martín González, Paola González, Verónica Baños
3,367 Students from the following Campuses: Aguascalientes, México City, Chihuahua, Cuernavaca, Estado. de México, Guadalajara, Hidalgo, Laguna, Monterrey, Puebla, Querétaro, Saltillo, San Luis Potosí, Santa Fe, Sinaloa, Sonora North and Toluca

8,699
Considering the current and future context, the characteristics of the current generation, and the needs of our students, the High School has worked on updating its Educational-Formative Model (MEF), which will begin its implementation in August 2025. In 2024, this model impacted 24 PrepaTec campuses during its pilot phase.
During the 2024 National PrepaTec Teachers’ Meeting, the key features of this update were presented:
Strengthening the curriculum through the review of content, development of expected learning outcomes, design of activities to achieve these outcomes, and the creation of two topics per Professional School.
Optimization of the Competency Model, concretized in six transversal competencies and 16 sub-competencies.
Evolution of final projects into semester-long projects developed through the project-based learning methodology, connecting learning from various subjects through a semester concept.
Definition of semester concepts that link the learning from different subjects.
Creation of the “Problem-Solvers Training Methodology,” in collaboration with Humane Education.
Design of the “Community and Inclusion Strategy,” in collaboration with Facing History & Ourselves.
A total of 171 seed courses were designed across all courses of the PrepaTec curriculum with the help of the Digital Education team and the talent of over 100 teachers from all campuses.
The process focused on creating a new experience for students by improving aspects such as navigation routes, graphic identity, curated content, standardized structuring of submissions, and thematic links between subjects throughout the semester, promoting transversal learning.
The courses were developed in collaboration with the strategic partner, the Institute for Humane Education, which trained the course designers in a methodology called “ProblemSolvers Training.” This provided a framework for designing more meaningful strategic learning activities.
The success of this innovation was demonstrated through a pilot program conducted throughout the year in 24 high schools of various sizes and approaches. With an impact of 6,000 students and 100 teachers, the usability, user experience and implementation details of the first, third and fifth semester subjects were tested. The application was monitored through focus groups, targeted reviews, and a feedback system to identify areas for improvement in terms of structure, functionality, and clarity.
The results were evident in the continuation of the pilot program into January 2025, where over 30 high schools will continue testing these new pedagogical tools in both large-scale and focused contexts.

Teacher-designers:
Ana Laura Escamilla, Angélica Villa, Claudia Castro, Elsa Morales, Gabriela Garza, Román Martínez
Impact on:
4,577 Students
36 teachers from the following Campuses: Aguascalientes, Chiapas, Estado de México, Guadalajara, Hidalgo, Juárez, Obregón, Saltillo and Sinaloa
To learn more about the project, visit here.
Comprehensive assessment tool of the dimensions of student well-being (physical, emotional, social, intellectual, spiritual, occupational and financial). Its purpose was to provide valuable information about students’ well-being and foster self-awareness and self-management by enabling students to identify areas for personal improvement. This tool not only supported academic formation but also promoted holistic development, helping mentors better guide students.
Significant improvements were made in the personalization of support and the early identification of students’ specific needs.
The success of the innovation was evident through participation results and the impact on students’ perceptions. Among the results, there was an increase in students’ selfawareness regarding their well-being, greater engagement in key improvement areas, and a strengthened bond with their mentors. Positive changes were also observed in academic and emotional performance among students.

Noodle Factory is an AI-driven tool designed to streamline the educational process for both educators and students. Its primary objective is to provide teachers with a reliable resource to store and organize critical course content while tailoring the experience to the specific needs of their students and classes.
For students, the platform offers structured access to learning materials and unlimited, immediate feedback on quizzes and exercises conducted within the platform. These quizzes and activities are evaluated in real-time using customized criteria defined by the teachers. The platform generates detailed, content-specific feedback aligned with the knowledge the teacher has integrated into the AI system.
This learning environment provides students with more opportunities to practice and review core
concepts, while educators can optimize their time by focusing on identifying and addressing the specific learning gaps of individual students. Additionally, Noodle Factory includes an interactive chat feature, enabling students to deepen their understanding of the subject by engaging in dialogues with the ChatBot.
The tool represents a significant advancement in personalized learning and the efficiency of the educational process. Specifically, it offers reliable, curated knowledge, ensuring that students interact with trustworthy and relevant content provided by their educators or the academic institution, mitigating the risk of accessing irrelevant or unreliable information.
Teacher-designers:
Carolina Garza. Guadalupe Salazar, José Zamora, Miriam Navarrete
Impact on: 500 Students
13 teachers from Cumbres Campus
Teacher-designer:
Oswaldo Gallo
Impact on:
259 Students
4 teachers from Santa Fe Campus
To learn more about the project, visit here.
Students from the 4th semester International Baccalaureate (IB) program at Campus Santa Fe were in contact with indigenous producers to recreate a traditional cornfield that included red, blue and rainbow corn, as well as several species of beans and chili, with the objective of studying the domestication of corn by Mexican indigenous communities and how this knowledge has been passed down through generations.
Unlike previous semesters, where these themes were approached through purely theoretical instruction, this experience merged epistemological debate with the practical experience of cultivation, thereby enriching students’ learning by allowing them to physically care for a field for the first time.
The success of this educational innovation was evaluated based on three factors: first, team interviews conducted as part of mentoring for the entire cohort; second, the students’ sustained commitment to maintaining the cornfield, which involved tasks ranging from fertilization to pest control; and third, the submission of a final course essay that evaluated the “Epistemicide Project” as a case study.
At the conclusion of the six-month project, significant improvements were reported in three key areas of the teaching process: student engagement in project development, commitment to sustainability in the face of food security risks linked to climate change and enhanced critical thinking skills applied to contemporary social issues, such as food sovereignty.

This project was designed for the “Engineering and Robotics” elective course as a tool for learning and experimentation, using Amazon Web Services (AWS) technology, specifically the DeepRacer application.
Participants created “reward functions” that were input along with a series of parameters to train a “machine learning, reinforcement learning” model, which would then be simulated or run by the DeepRacer car to autonomously navigate a racetrack.
Model training was conducted using AWS cloud infrastructure. Although it is possible to train models locally, this requires additional technical expertise and equipment. The races can be virtual, remote, or in-person, with the possibility of organizing private “community races” exclusively for a closed group of participants.
As a final test, students implemented a race using scaled real-life cars, loading their pretrained models and observing the results.
The final outcomes demonstrated that students applied reinforcement learning as one of the branches of artificial intelligence, explored the use of autonomous vehicles to address problems and needs, and developed an innovative proposal applying autonomous vehicle principles to solve a real-world problem or need in alignment with certain Sustainable Development Goals.

Teacher-designer:
Arturo Mendez
Impact on:
38 Students from Santa Catarina Campus

Teacher-designer:
Ana Ángeles
Impact on:
246 Students
4 teachers from San Luis Potosí Campus
One of the core components of the course “Me and Others II” is the development of a social leadership project, where students work to improve the quality of life in their communities. During the August-December 2024 term, the use of AI was integrated into designing a workshop session for elementary school children in San Luis Potosí. Students utilized the ChatGPT and based on the AI proposal they made improvements aligned with the local community’s needs in areas such as literacy, math learning, and hygiene.
Through this activity, students exercised creativity by using the AI’s suggestions as a reference point for developing their intervention sessions. Additionally, they gained insights into the limitations of AI in practice, recognizing that not all recommendations were feasible due to the specific conditions of the community.
As a positive outcome of this initiative, more than 35 community intervention projects were created, and the community residents expressed a favorable perception of the experience.
In this project, students practiced using AI to generate content aligned with the curriculum, structuring texts and arguments through the ethical use of TecGPT. After developing their content, they engaged in realistic environments that helped enhance their communication skills and related performance indicators.
Using Oculus Meta and VirtualSpeech tools, students delivered presentations and participated in debates within virtual settings, receiving immediate feedback on key areas such as fluency, clarity, and nonverbal communication.
The application allows teachers to create rubrics to assess student performance, providing instant, detailed feedback. Throughout four implementation sessions, faculty guided students on the ethical and responsible use of AI while teaching them how to handle Virtual Reality headsets effectively. Additionally, students were encouraged to analyze and reflect on their results.
Teacher-designers: Carolina Garza. Guadalupe Salazar, José Zamora, Miriam Navarrete
Impact on:
114 Students
5 teachers from Eugenio Garza Lagüera, Irapuato, San Luis Potosí, and Tampico Campuses
To learn more about the project, visit here.

5.8 LiFE
Educational Innovation and Digital Education in LiFE
12 Projects
8 Training Units
8 Teachers
12,000 StudentsCourse
The LiFE Dean’s Office for Leadership and Student Development (LiFE) aims to create a life-skills-based learning model where students can develop transversal competencies that foster self-fulfillment and strengthen their leadership potential. In line with this vision, LiFE’s educational innovation strategy in 2024 focused on developing programs targeting students’ emotional, financial, and occupational well-being at Tecnológico de Monterrey. High-impact projects were categorized into pedagogical and technological innovations.
The purpose of the “Introduction to Professional Life” Tec Week training unit was to encourage students to reflect on the career path they wish to pursue, whether as entrepreneurs, employees, graduate students, researchers, or participants in social impact projects. To enhance students’ academic experience in 2024, this training unit integrated pedagogical and technological innovations, including the implementation of Escape Room
teaching techniques and Mozilla Labs technology.
During the “Prepare for the Career of Your Life” Tec Week, students tackled common challenges they will encounter in the workforce, focusing on resource management and productivity enhancement. Escape Room-style spaces were designed and programmed within the Canvas platform. Students, working in teams, progressed through the solution development as they overcame each challenge.
Meanwhile, in the “The Art of Communicating Your Brand” Tec Week, Mozilla Labs provided practical experiences for students to hone their interview skills.
Teacher-designers:
Adriana Salgado, Alejandra Torres, Anayansi García, Eder del Ángel, Luciana Subías, Marco del Ángel
Impact on:
10,265 Students from the following Campuses: Aguascalientes, Mexico City, Chihuahua, Cuernavaca, Estado de México, Guadalajara, Hidalgo, Laguna, León, Monterrey, Morelia, Puebla, Querétaro, Saltillo, San Luis Potosí, Santa Fe, Sinaloa, Sonora North, Tampico, Toluca



This section highlights the progress and impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on educational experiences within the institution. Tecnológico de Monterrey has integrated AI as a key tool to personalize learning, enhance educational processes, and enrich student experiences.
Tecnológico de Monterrey’s AI integration strategy is built upon five fundamental pillars: enhancing the teaching-learning process, preparing professionals in their disciplines, promoting cutting-edge research, ensuring ethical AI use, and optimizing institutional operations and services. These strategic actions enable the institution to not only navigate the paradigm shift brought about by AI but also to lead in innovation, research, and organizational management. By focusing on ethical and responsible AI usage, Tecnológico de Monterrey ensures a positive impact on its students, faculty, and staff.

The Educational Artificial Intelligence Committee aims to ensure that the implementation of Artificial Intelligence in education at Tecnológico de Monterrey is both strategic and effective, contributing to the digital transformation of the teaching and learning process in alignment with institutional goals. This committee, composed of 18 members, includes the Rector, Vice-Presidents, Vice-Rectors, Deans, the Director of Educational Artificial Intelligence, and specialists in technology and ethics. It convenes monthly to coordinate AI initiatives within the institution.
The scope of the committee covers the definition of strategic lines to incorporate Artificial Intelligence in the institution, with impact in two key areas: education and management. It also approves priority projects, budgets and key issues, promoting a positive institutional impact. It monitors global trends, indicators and strategic alliances to maintain technological leadership. Its functions also include validating projects, assessing their alignment with institutional priorities and proposing improvements prior to implementation.

As a result of its student-centered learning pillars, the Educational Artificial Intelligence Directorate (IAEd) was established to focus efforts on two fundamental areas: enhancing the teaching and learning process and developing AI-related disciplinary competencies in the professionals of tomorrow.
Regarding the integration of AI in teaching and learning, the goal is to harness the transformative potential of this technology through various models, intelligent assistant architectures, and data analytics that enrich teaching practices. This strategic focus enhances the teaching experience by incorporating AI tools to design, modify, and assess personalized learning sequences tailored to meet students’ specific learning needs.
On the other hand, embedding AI-related competencies into academic curricula promotes an “AI-ready” status for students, equipping them with the skills necessary to contribute to technological advancement in their respective fields. By including both transversal competencies—core AI knowledge applicable to any professional—and disciplinary competencies—AI-specific expertise in a particular area of study—Tecnológico de Monterrey ensures that future professionals are prepared to meet the challenges of an everevolving job market.
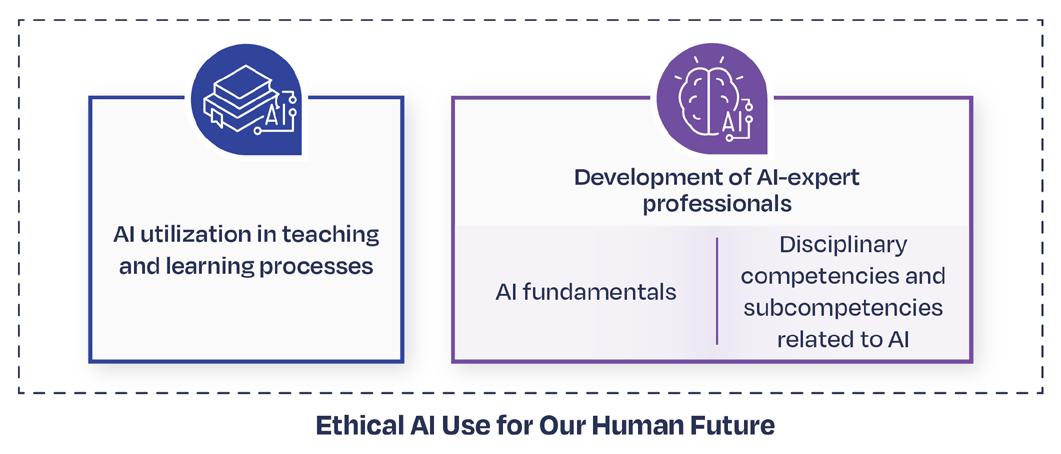
TECgpt represents an ecosystem of reusable components designed to facilitate the development of generative artificial intelligence (AI)-based products and services within Tecnológico de Monterrey. This initiative enables the implementation of multimodal approaches that generate symbolic representations of thought in various formats, such as text and images, providing user-friendly interactions tailored to specific needs.
Currently, TECgpt includes three internally developed tools: Skill Studio, access to ChatGPT through Azure OpenAI, and ChatTEC. These solutions allow the institutional community to leverage AI tools through a secure platform that prioritizes user privacy. These tools enhance instructional design, teaching practices, and access to institutional services and guidelines.
Skill Studio is a tool developed by Tecnológico de Monterrey that allows users to create generative AIpowered resources, or skills, to streamline and enrich various functions within the educational environment. Skills are programmed using natural language instructions (prompts) and can be shared and executed through a form-like interface, making them userfriendly. Since its official launch in October 2024, more than 500 teachers have accessed this tool, generating over 800 skills focused on activities such as content design, assessment, and customized pedagogical strategies. This initiative aims to transform teaching practice by automating repetitive tasks and fostering innovation.

Skill Studio is widely used for designing educational resources and training units that enhance the teaching and learning process. It played a critical role in developing the 2026 Curricular Framework at Tecnológico de Monterrey, providing a suite of eight specialized skills that support the creation of training units at every stage. Notable resources include “Create a Problem-Based Scenario,” “Design a Challenge,” “Modularize Your Block,” and “Plan a Learning Activity,” all of which address key phases of instructional design, enabling clear and efficient content structuring.
Aligned with institutional guidelines, this tool ensures the consistency and quality of educational materials, empowering teacherdesigners to optimize the teaching and learning experience. Its impact has been significant: 93% of academic programs now incorporate resources generated with Skill Studio, cementing its role as a cornerstone in AI-driven educational transformation.
The development of Skill Studio involved collaboration across various departments, including Digital Transformation, Educational Innovation and Digital Learning, Educational Technologies, CEDDIE, and the Academic ViceRector’s Office, ensuring compliance with institutional guidelines and alignment with the 2026 Curricular Framework. Additionally, a pilot program engaged 134 teachers in handson sessions to design skills, with notable examples including prompts for Pythonbased calculations, character generation, and storytelling.
Skill Studio has earned international recognition, becoming a finalist in the “2024 QS Reimagine Education Awards” in the category of Best Use of AI in Education. This year, it also received the prestigious “Netmedia ‘Most Innovative’ Award”, reflecting a commitment to global educational excellence and transformation.


Through the TECgpt ecosystem, over 30,000 faculty and staff members have access to an institutional interface powered by ChatGPT via the GPT-4o model API from Azure OpenAI. This tool enables efficient interaction with one of the most powerful AI models on the market. Key features include text generation in multiple formats and over 60 languages, supporting users in developing ideas, projects, and content. Additionally, this chatbot incorporates the DALL-E model, expanding its capabilities to generate high-quality images.
For Tecnológico de Monterrey, data protection is a top priority. All AI interactions within TECgpt take place in a secure, controlled environment, ensuring that user conversation data is not utilized for future model training.
This three-day, in-person event aimed to design enriched learning experiences through Artificial Intelligence (AI), engaging 181 educators from various educational levels, organized into 45 multidisciplinary teams. Participants were selected by their respective schools for their expertise in educational innovation and their ability to share knowledge with peers. Throughout the sessions, faculty members worked on projects integrating AI into both teaching practice and disciplinary approaches, focusing on personalized instruction, optimized assessment, and the development of skills aligned with the global AI-driven job market.
During the summit, 47 AI technologies were proposed for evaluation. Each proposal was assessed for usability, security, and data handling, resulting in 15 recommended technologies. Key topics included competency development, personalized learning, and datadriven decision-making.
Highlighted projects from AI Summit 2024 include:
InnovAItive Learning: Proposes an innovative AI integration across three phases—diagnosis, interactive teaching, and personalized feedback—using AI-powered quizzes and tutoring systems.
MediTec: ‘Virtual Patient’ that employs a language model to simulate patients for clinical interviews and case history creation.
Empathic Communication AI: Develops empathy and conflict resolution skills through AI-generated scenarios.
Executive Hot Seat AI: Enables students to interact with simulated C-level executives to receive strategic feedback.

As part of Tecnológico de Monterrey’s institutional priorities, AI-based educational technologies are being evaluated to transform teaching and learning processes. Technologies meeting institutional requirements have advanced to pilot stages to validate their impact and scalability.
The tests involved AI-driven tools designed to optimize academic processes, such as activity assessment and individualized learning support. A total of 147 faculty members participated in testing two AI-assisted evaluation tools from the Novus initiative. These tools demonstrated improvements in feedback efficiency, allowing teachers to devote more time to high-value academic interactions with students.
A pilot program was conducted in two learning units (with 40 students), using an intelligent academic assistant capable of providing realtime explanations and answering questions, thus enhancing comprehension of complex topics, such as engineering principles.
These initial tests indicate a positive impact on both teaching and learning experiences by integrating technologies that provide timely feedback and personalized learning. As a result, these tools are being assessed for scalability and potential institutional adoption, reinforcing Tecnológico de Monterrey’s commitment to academic excellence through advanced technological solutions.


The Adaptive Learning strategy aims to personalize education by leveraging AI algorithms and data analytics. In 2024, it impacted 1,107 undergraduate students and 34 faculty members. This pilot, implemented across 11 campuses and with students in Digital Education, enabled learners to practice topics based on individual needs, receive immediate feedback, and visualize real-time analytics, thereby optimizing their learning experiences.
This initiative, part of the “Path to Success” program led by the Academic Vice Rector’s Office and coordinated by the Vice Rector’s Office for Educational Innovation and Academic Policy with support from the Institute for the Future of Education, also helped teachers identify learning gaps, adjust teaching strategies, and optimize classroom time. Using specially designed leveling modules, the strategy integrated advanced technology to customize learning paths and enhance academic performance in foundational stages, marking significant progress in the continuous improvement of educational outcomes.
Tecnológico de Monterrey is developing a regulatory consultation tool to support entry-level and program directors (DEs and DPs) in providing academic guidance and resolving questions about institutional regulations. Backed by a knowledge base that integrates key regulations, including the Academic Regulations for Undergraduate Students (2019 Plans and later) and the General Student Regulations, this tool delivers quick and accurate responses. Phase 1 (2024–2025) focuses on integrating knowledge sources to generate efficient suggested responses, streamlining inquiries and optimizing student guidance.
Enhanced with AI, this tool allows immediate access to institutional policies on topics such as Tec Weeks, social service requirements, and language proficiency. It saves time on searches, ensures consistency in responses, and records frequently asked questions to continuously improve the service.
The AI Tools for Teaching Practice project evaluates and approves the institutional use of AI technologies that enhance one or more stages of the teaching and learning process. The Educational Technology team (TEDU), in collaboration with the Directorate of Educational AI, conducts rigorous reviews of criteria such as AI models, licensing, cost, and performance. Key considerations include ease of use, LMS integration, data privacy and security, and the availability of technical support.
From 47 AI technologies reviewed for potential educational use, 33 underwent detailed analysis for functionality, educational
purpose, and technical feasibility, leading to the recommendation of 15 tools. These offer capabilities in educational data analytics, personalized content generation, and resource optimization, advancing more efficient and adaptive education.
The Edutools catalog provides detailed information on AI-based educational technologies to create learning experiences applicable to teaching practice. This platform also fosters a community where educators share their use cases, enhancing technology acceptance, particularly among colleagues in Latin America.

The 2026 curricula design aims to prepare students graduating by 2030 for a future of evolving AI-driven competencies. This requires anticipating the essential skills that enable lifelong adaptability and continuous learning as current knowledge becomes obsolete. Disciplines like law, economics, computer science, and architecture demand a flexible, current approach as technological advancements rapidly redefine technical expertise. Beyond specialized skills, transversal competencies, such as critical thinking, lifelong learning, and the strategic integration of advanced technologies, especially AI, are prioritized.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence in teacher training has been promoted through various educational formats, such as: talks and podcasts, engaging over 1,219 teachers; workshops, with more than 30 different experiences that have been taught to more than 3,800 teachers, where fundamentals and brief practices of AI application in the classroom are offered; bootcamps, with 138 certified participants, designing comprehensive AI-based learning experiences; as well as hackathons, which foster innovative proposals to improve educational processes.
At the 2024 National Faculty Meeting (RNP), over 200 educators participated in AI-focused panels, courses, and discussion groups.
Course design addresses graduate profiles by incorporating competencies, sub-competencies, and key learning elements. Structured content aligns with institutional academic goals, while teaching support enhances pedagogical strategies and guarantees quality instruction. Personalized learning experiences, engagementdriven design, and tools for problem-solving, digital learning experiences, feedback processes, and student performance tracking are also included.
The impact of these initiatives is evident in their diversity and scope. In the Disciplinary Update Courses (CADis) 2024, more than 100 teachers explored topics such as teaching with AI, AI-assisted video editing, active learning scenario design and digital humanism. Popular offerings like “Building Learning with AI” and “Creating Enriched Learning Experiences with AI” highlighted growing capacity for classroom innovation, transforming educational experiences.
Tecnológico de Monterrey recognizes AI as a transformative tool for education, society, and culture. Aware of AI’s potential to automate processes and enhance human capabilities, the institution promotes an ethical framework grounded in integrity, respect, equity, and truth. This approach seeks to mitigate risks such as bias, inaccuracies, and data misuse while maximizing AI’s positive impact on learning, human development, and sustainable innovation. Guidelines emphasize transparency, responsible AI use, and critical reflection on its benefits and limitations. AI thus becomes a strategic ally in teaching and research, always in service of humanity.
The institution has developed and published “Guidelines for Ethical AI Use” for students and teachers , alongside training programs fostering both technical and ethical AI proficiency. These guidelines align with principles of honesty and justice, promoting inclusive and respectful use that advances the common good.
Tecnológico de Monterrey also collaborates with international initiatives like the Rome Call for AI Ethics and participates in specialized forums to foster interdisciplinary dialogue on AI’s role in education. These efforts reflect the institution’s commitment to cultivating ethical, responsible leaders prepared for the challenges of the digital society and building a more just and equitable future.



This section delves into the various initiatives and projects driving innovative and digital educational experiences at the institution. From Adaptive Learning, which personalizes academic content based on each student’s needs, to Immersive Learning with Extended Realities that transform education through virtual experiences, Tecnológico de Monterrey continues to lead in integrating advanced technologies into the educational landscape. These innovations not only enhance learning but also foster the development of critical skills necessary in a globalized, digital environment, positioning the institution as a trailblazer in educational innovation.
Additionally, this section highlights other key components of this innovative ecosystem, such as Academic and Alternative Credentials, faculty development, and transformative learning spaces. In addition, initiatives like the Novus project, dedicated to experimenting with and promoting techno pedagogical trends, as well as efforts in internationalization and providing access to digital laboratories, software, and information resources, reinforce Tecnológico de Monterrey’s commitment to delivering a holistic and high-quality education.

Adaptive Learning is an educational approach that uses technology to personalize the learning experience according to the needs, abilities and pace of each student. Based on data analysis, this model adjusts content, activities and
resources in real time, providing unique learning paths that optimize competency development. Its goal is to improve learning effectiveness, reduce educational gaps and foster a more dynamic, student-centered experience.
6
34
1,107
36 Groups
Control groups
4
22
827
28
In 2024, the Adaptive Learning strategy demonstrated its success by providing our students with experiences that contribute to their academic achievement in the training units during the first semesters of the Tec21 Model.

Adaptive Learning is an educational strategy where technology is employed with AI algorithms to adapt education and provide personalized learning paths.
As previously mentioned, Adaptive Learning is an educational strategy that utilizes technology, AI algorithms, and data analytics to tailor education and provide personalized learning paths.
In 2024, this educational strategy incorporated modules designed by qualified professors at Tecnológico de Monterrey to support the leveling of incoming first-year students at the Undergraduate level, enabling teachers to:
Identify gaps in students understanding.
Establish improvement actions and adjust their educational practice.
Visualize analytics in real time.
Optimize class time by analyzing the information provided by the platform.
Focus their attention on new content.
Adapting the interactions allows students to:
Generate personalized learning paths.
Level basic knowledge.
Practice the topics as many times as they consider necessary (during the period of their training unit).
Obtain immediate and personalized feedback.
The pilot program was designed by the Vice Rector’s Office for Educational Innovation and Academic Policy. Five leveling modules were designed with the Adaptive Learning strategy in Undergraduate Mathematics, Computer Science, Physics, Chemistry and Biochemistry, with the participation of 20 expert teachers within the Route to Success initiative, who incorporated the material for leveling through a strategy defined jointly with the Academic Vice Rectory.
In addition, Mathematics, Computer Science and Physics modules were taught in 6 training units, impacting a total of 1,107 students in 36 groups, thanks to the participation of 34 teachers. Pilot programs were applied in Mathematics and Computer Science, and the results showed a significant difference in the improvement of learning.
During this year, students and teachers from Digital Education, as well as from 9 campuses participated:
Mexico City
Chihuahua
Estado de México
Guadalajara
Laguna Monterrey
Puebla
Querétaro
Sonora
Tampico
Toluca
As part of the effort to enhance the 2026 curriculum, six leveling modules were designed using an Adaptive Learning strategy. These modules cover Mathematics, Computing, Physics, and Biochemistry across nine learning units.


Regarding Personalized Learning, unique route, the course “Leveling of preclinical competencies in medical care” was designed for undergraduate students of the School of Medicine and Health Sciences of the Tecnológico de Monterrey.
As this strategy gains greater successes, the focus on leveraging technology and pedagogical innovation remains clear, with the goal of optimizing learning and ensuring successful outcomes, promoting personalized and adaptive education that adjusts to individual pace and capabilities.
Immersive Learning experiences with Extended Reality technology impacted 34,742 students and 1,048 teachers during the delivery of 342 training units at the High School, Undergraduate, Graduate and Digital Continuing Education levels.
During this year, three strategic projects were implemented for the School of Business and School of Medicine and Health Sciences, as well as the first authentic assessment experience for the School of Engineering and Science, including two pilot projects that integrate Virtual Reality with Artificial Intelligence for the School of Business and the School of Engineering and Science. In addition, a strategic project called “Corona Tec” was designed and developed for the Industrial and Systems Engineering program of the School of Engineering and Science, which will be implemented in the February-June 2025 semester.
1,048 Teachers
34,742 Students 342 Training Units

Within the framework of the AIRX Strategy, several initiatives were implemented focused on promoting Immersive Learning through Extended Reality (XR) technologies, achieving progress in infrastructure, educational impact and experiences generation.
These are spaces for educational innovation, specialized environments for students and teachers to explore, develop and experiment with XR technologies. During 2024, these spaces facilitated the creation of interdisciplinary educational projects and strengthened the integration of tools such as Virtual and Mixed Reality in the teaching-learning process.


This year, the catalog of this type of resources was expanded; they were designed for different areas of knowledge, offering scalable and accessible solutions for teachers and students.
This initiative brings together innovative tools and content designed to enhance learning through Extended Reality technologies; it includes interactive simulations, immersive virtual environments and educational materials that allow teachers and students to experience teaching-learning solutions, connecting theory with practical applications in a dynamic and accessible environment.
With a structure organized by disciplines, technologies and classification by educational intent, the catalog seeks to facilitate the integration of these technologies, promoting more personalized, collaborative and meaningful learning.
Among the most relevant experiences is the presentation of projects for the different schools of the institution at different educational levels, as well as for Digital Continuing Education.
In 2024, the AIRX Strategy achieved wide international recognition thanks to its participation in important academic and educational innovation events.
As one of the most relevant activities, the paper “Learning Experience in the Business Discipline Integrating Innovative Technologies: Virtual Reality with Artificial Intelligence through an Avatar-Advisor” was presented at the ICERI 2024 International Congress, held in Seville, Spain. This work highlighted the integration of immersive
technologies and Artificial Intelligence to enrich learning experiences in the Business discipline.
Through the “Professor with hologram effect” initiative, the lecture “Leadership in Educational Innovation in Extended Reality” was given as part of the “UNAM Academic Sessions”. This event was organized by the Teacher training and professionalization center, which was attended by leaders of teaching innovation and educational development from UNAM.
These actions consolidate the AIRX Strategy as a key pillar for transforming learning, integrating emerging technologies and strengthening leadership in immersive education globally.
In addition, three projects developed under the AIRX Strategy were selected as finalists in the “QS Reimagine Education 2024” awards.
TecDrone: Assessment of STEM Competencies using VR & AI. It assesses STEM competencies using immersive technologies, which stood out as the bronze winner in the Learning Assessment category.

Green Flags: Hyperpersonalization of Learning with AIRX. Presented by the Business School, it shows the educational impact on the topic of Social Responsibility.

Innovative Digital Factory: Transforming Learning through Strategic Alliances. Presented by the School of Engineering and Science, it focuses on educational transformation through strategic alliances.

In addition, the scientific article “Conceptualization, Design, Production, and Implementation of Immersive Resources: Welcome to Athens Experience as Educational Innovation to Transform the Teaching-Learning of Citizenship and Democracy” was published in the “Journal of Creative Education”, underlining the commitment to academic production and dissemination of RX experiences that transform education.
These initiatives consolidate AIRX’s impact and relevance in global educational innovation, demonstrating the commitment to excellence and the transformation of teaching through Extended Reality technologies.
Articles published in 2024:
Conceptualization, Design, Production, and Implementation of Immersive Resources: Welcome to Athens Experience as Educational Innovation to Transform the Teaching-Learning of Citizenship and Democracy.
Read the article here
Learning Experience in the Business Discipline Integrating Innovative Technologies: Virtual Reality with Artificial Intelligence Through an Avatar-Advisor.
Read the article here .

Several strategic projects were developed in collaboration with the institutional schools in 2024. These projects integrate immersive technologies and innovative methodologies to enrich learning experiences and strengthen students’ practical skills.
Among the most outstanding projects are:
My Digital Business World Hearing systems
Learning experience with Mixed Reality
ICDAS
Corona Tec
These projects reflect the institutional commitment to educational innovation, promoting meaningful learning through the use of emerging technologies and practical scenarios that connect theory with action.
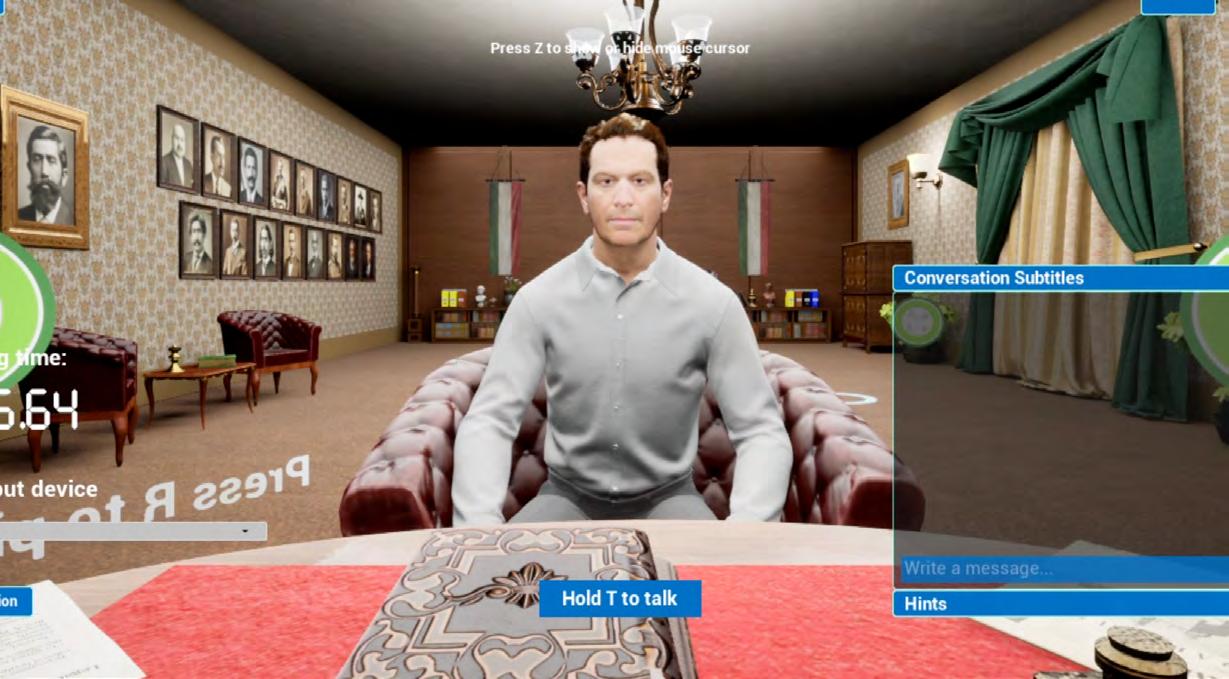
In this activity, Business students entered the My Digital Business World virtual environment, accessible from a VR Lab or a personal computer. They undertook the role of Chairman of the Legacy Village Committee, with the mission of protecting the magic of the village while promoting sustainable tourism. The challenge was to negotiate with Sir McMean, CEO of Voyage Elite Expeditions, who sought to turn Real de Platas into an exclusive destination. The students explored the immersive environment to gather key information, while the AI allowed them to interact and negotiate with the entrepreneur. At the end, in a plenary session, they evaluated their decisions, strengths and areas for improvement with their peers and teacher, consolidating their preparation to negotiate in a multicultural and global environment.
Participating campus:
and
Impact:
4 Teachers 115 Students

Participating campus:
Monterrey
Impact: 3
Teachers 39 Students
This project used interactive three-dimensional models to transform the teaching of the anatomy of the human ear, allowing students to explore in detail the different parts of the ear and understand how they function in a dynamic and immersive environment.
The integration of three-dimensional technologies in this resource fosters more visual, hands-on and in-depth learning, strengthening the understanding of complex concepts and enhancing the educational experience for students.
This project is an example of the commitment to pedagogical innovation and the use of advanced technology in the teachinglearning process.
This experience was designed specifically for the Dentistry career, allowing students to practice dental procedures for infants in an immersive environment. Using Mixed Reality technology, students were able to interact with 3D models and simulate dental procedures in a controlled scenario, providing them with the opportunity to develop technical and clinical-social skills essential for pediatric care. This experience enhances practical understanding of dental procedures and strengthens decision-making and situational management in a realistic and safe context.
The expected result is practical efficiency in diagnosis and choice of appropriate treatment with worldwide standardized criteria. The experience with Mixed Reality in Pediatric Dentistry provides an advanced and unique practice with “HoloLens 2” for immersive learning and clinical practice.

Participating campus: Monterrey
Impact:
2 Teachers 17 Students
Learn more here

This digital production plant is a virtual environment that allows the modeling of a manufacturing system with simulated scenarios, in which a user can solve challenges progressively at different stages of their academic career. It is an Immersive Learning experience with Extended Reality created for the School of Engineering and Science.




AIRX New Resource Implementation focuses on the creation and deployment of innovative tools that integrate Extended Reality technologies to transform the learning experience. Throughout 2024, a variety of immersive resources were developed and implemented, which aim to improve students’ understanding, knowledge retention and practical skills by providing them with unique opportunities to interact with content in a virtual or mixed reality environment.
TecDrone is an innovative authentic assessment project implemented in the School of Engineering and Science (EIC), designed to assess students’ sub-competencies in the area of engineering. In this project, students research, design, build and test drones in an Extended Reality (XR) environment, allowing them to connect theoretical learning with real challenges in the professional world.

In addition, students justify their decisions and actions to an expert, a character developed with artificial intelligence, which simulates a professional experience in which they must defend their technical choices. This approach not only enhances the application of knowledge, but also strengthens key skills such as decision making, problem solving and argumentation skills. According to the results of a survey, 73% of students felt that this tool allowed them to apply learning in a real context, providing them with an authentic assessment experience that goes beyond traditional methods.
Participating campus:
Monterrey
Impact:
5 Teachers 168 Students
In this space, students put their learning about Mexican politics to the test, solving various challenges that allowed them to build a shield that represents components of the country’s democracy.

This resource is a berry distribution center simulator. It consists of three sections: product selection and packaging, product packing and container assignment. In all sections, the student must perform calculations to select the correct packaging measures to reduce costs and make efficient use of resources. At the end, the student is shown the data display and the percentage of effectiveness, which will allow them to reflect and apply that experience to the solution of the challenge.

Nation wide
Learn more here


This resource allows students to put into practice the knowledge they have acquired about conscious capitalism. Throughout the tour, they must assume the role of a company executive and solve puzzles that will help them escape from each room.
Learn more here
This resource offers three leadership styles that can be presented in a work environment, such as the liberal or laissez-faire leader, the democratic leader and the autocratic leader. Through their staging, students will be able to verify the characteristics of corporate leadership; additional information is included in each scenario to reinforce the learning content.
Learn more here


Artificial Intelligence Virtual Reality Pilot Projects have been one of the main innovations in the use of emerging technologies to transform teaching and learning. These projects combine Virtual Reality with Artificial Intelligence, creating immersive and personalized learning environments that enrich the educational experience for both students and teachers.
Two pilot projects were designed and implemented: Green Flags and Engineer Xplorer.
Both projects reflect the commitment to integrate advanced technologies that transform traditional teaching, creating more dynamic, personalized and effective learning experiences. The combination of Virtual Reality and Artificial Intelligence offers invaluable support to both students and teachers, maximizing the potential of every educational interaction.
This is a unique immersive experience, where the student becomes a Jr. Consultant with the task of helping a leading company to overcome an operational crisis and regain lost trust. Through interactive 360° videos, they explore the principles of the ISO 26000 Standard and work alongside a digital mentor specialized in corporate social responsibility; in this way, they will be able to propose innovative actions that could drive a more socially responsible future. Learn

Participating campus: Monterrey
Impact: 18 Teachers 605 Students
The objective of this project was to inform students about the different engineering programs and applications, through a learning experience with Extended Reality and Artificial Intelligence, in order to contribute to clear up any doubts they might have about the choice of program.
Tecnológico de Monterrey’s Educational Model promotes the development of comprehensive competencies, preparing students to face current and future challenges. As part of their academic recognition, in addition to their degree, graduates receive Academic Credentials that validate the competencies acquired during their education. These credentials strengthen and demonstrate their professional profile and can be shared in digital format according to their interests, thus enhancing their competitiveness in the job market.
It is important to note that for the first time this year digital credentials were issued for the transversal competency “Self-knowledge and management”. These badges allow graduates to demonstrate mastery of the transversal skills acquired during their academic training and in cocurricular environments, preparing them to face a constantly changing professional and personal environments, with tools that allow them to adapt and be effective in various situations.



How many competency achievements have been recognized and of what type?
To complement the graduation profile of students, the Academic Vice Rector’s Office has launched the first offering of Alternative Credentials for undergraduate students. The Center for Evaluation and Alternative Credentials (CECA), the national body responsible for designing and managing these credentials, is supported by the Educational Learning Experiences Innovation Department, which is part of the Vice Rector’s Office for Educational Innovation and Academic Policy.
This first offering of Alternative Credentials was defined by the institutional deanships, considering their high value in the job market. The aim is to provide options that allow students to develop a differentiated profile in specific areas, such as:
Global leadership
Semiconductors
Arts and culture
Social entrepreneurship
Innovative entrepreneurship


In this offer, it is important to highlight that the “Eugenio Garza Sada Global Leadership (EGS Global)” credential is part of an independent program of the Dean’s Office of Leadership and Student Formation, starting this year, it has been formally incorporated as an Alternative Credential for undergraduate students.
Those students who meet the requirements for accreditation will receive their corresponding digital badge for the Alternative Credential upon completion.

In addition to this credential, since August 2024, the design of the Alternative Credential “Semiconductors” has been formalized in conjunction with the Dean’s Office of Engineering and Sciences. This academic program is being developed with the collaboration of highly qualified experts and will be available to students starting February 2025. The “Arts and Culture” and “Entrepreneurship” credentials are in their development phase, with enrollment open starting August 2025. Alternative Credential Sample Badge Alternative Credential Sample Badge

During 2024, the Center for Evaluation and Alternative Credentials intensified its efforts to position these credentials in the job market. This has been achieved through participation in job fairs organized by the Career Development and Outreach Centers of different campuses, attendance at international and national congresses related to the topic of competency credentials, as well as through communications directed to both internal and external audiences to guide them on the value-added benefits and effective use of the credentials and digital badges.
In order to enhance the academic experience for students, in addition to the positioning events for Tec Credentials, the Center for Evaluation and Alternative Credentials, with the support of the Learning Experience Innovation team, has launched an exclusive website to inform about the institution’s offering of Alternative Credentials. This site provides detailed and up-to-date information and offers a contact point for addressing any inquiries. The platform has allowed internal audiences to gain a better understanding of the benefits of these credentials, while also offering a space to inform interested individuals about the competencies that have guided the design of the Alternative Credentials, registration periods, duration, and modality for each credential.

The Center for Educational Development and Innovation (CEDDIE) aims to promote and facilitate educational innovation generated by teachers through its model of development and recognition of teaching, intellectual vitality and service. In order to inspire teachers to innovate in their educational practice, this center has a solid process of educational innovation.
To innovate in education, teachers drive improvements in teaching and learning from their classroom experience, through an ecosystem that fosters the generation of ideas, collaboration and dissemination.
The year 2024 has been notable for the consolidation of generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), expanding opportunities for experimentation and the creation of innovative solutions to address educational challenges more effectively.
To facilitate the design and incorporation of educational strategies based on Artificial Intelligence, activities were carried out for the following purposes:
To publicize its potential and scope.
To use tools to impact teaching and learning.
To employ tools to guide the implementation of AI when designing learning and teaching experiences.

To facilitate the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence in teaching practice, different strategies were designed and implemented, among which the following stand out:
Talks and podcasts to disseminate, inform and share best practices
As part of the strategy to use Artificial Intelligence for teaching and learning, talks were held with expert and pioneering faculty members on various perspectives. These discussions impacted 1,219 teachers. In these dialogue spaces, faculty and experts had the opportunity to interact to both increase their knowledge of AI and explore its uses in the educational field.
As part of the dissemination of this important topic, episodes have been published on the “Sintonía CEDDIE” podcast and its new format “Faculty Stories,” which have been listened to by over 550 people to date.
The offer of courses on Artificial Intelligence in education has included over 30 different development experiences that have added up to more than 3,800 participants in its different editions and formats. Among these experiences, the “Building learning with AI” bootcamp stands out, which has impacted 138 teachers in six editions. Bootcamp participants have become pioneers in Artificial Intelligence. Similarly, the
Discipline Update Course (CADi) “Generating learning experiences enriched with AI” was offered as part of the development offer during the summer period.
“AI-enriched learning” bootcamp at the National Teachers’ Meeting (RNP)
The objective of the bootcamp’s practical activity was to design specific strategies to integrate Artificial Intelligence into the teachinglearning process, focusing on improving key aspects and satisfying particular needs within the classroom. Participants reflected on when and how to incorporate Artificial Intelligence effectively, as well as on the selection of appropriate or relevant tools to enrich the educational experience.
This experience involved the participation of over 200 faculty members from the National Teachers’ Meeting (RNP) over the three days of the event’s development sessions, led by educational innovation leaders at CEDDIE.
Additionally, during the winter period, the Bootcamp “Building Learning with AI” was offered as part of the CADi program, along with the course “Creating Enriched Learning Experiences with AI” during the summer period. Together, these activities gathered over 100 participating faculty members. In both sessions, teachers learned strategies for using Artificial Intelligence in their teaching practice and also implemented quick applications.
The AI Summit is an event aimed at promoting experimentation and capturing insights on the use of AI in teaching and learning processes.
With the theme “Innovative Faculty
Transforming Education with AI (Artificial Intelligence)”, this event was held on July 29, 30 and 31, 2024, at the Mexico City Campus , and brought together High School, Undergraduate and Graduate teachers, with representation from all institutional schools. Its objective was to guide the faculty through methodologies that trigger educational innovation for the creative solution of two challenges, one with a disciplinary focus and the other with a transversal focus. During intensive collaboration sessions, 180 teachers from all levels and institutional schools developed proposals for the integration of Artificial Intelligence to improve the teaching-learning process, which were implemented during the August-December 2024 period. The documentation of these projects will allow learning to increase the responsible use of AI to address educational needs, as well as for the development of internal AI tools.
During the second semester of the year, the “AI Pioneer” badge was awarded to teachers who implemented Artificial Intelligence in their teaching practice. To date, over 240 teachers have been awarded this badge.


Dissemination and training activities: workshops and talks
To teach how to use new tools and innovative educational strategies, we continuously offer workshops and disseminate innovative practices carried out by teachers, which can also be adopted by interested colleagues. During the year, more than 290 activities were carried out that impacted over 6,000 participants. Among these, 13 learning experiences focused on the incorporation of Extended Realities as part of the learning experiences impacted more than 160 participants.
For the second time, all academic faculty members from Tecnológico de Monterrey were invited to this memorable event. A space was also created to share, celebrate, and recognize the educational innovation experiences and projects carried out by our teachers.
This year, the call aimed to identify innovative projects and implementations in the following thematic areas:
Pedagogical transformation. The project or initiative refers to the application of new methodologies to foster change in the teaching-learning process, such as the deployment of new teaching practices, learning strategies and delivery methods.
Technologies for education. Refers to the incorporation or implementation of technologies applied to the transformation and improvement of educational experiences.
Student experience management. The project or initiative implements processes for enhancing the student experience and proposes efficiencies in the design, operation, or administration of educational experiences, such as partnerships with training partners.
Artificial Intelligence in education. The project or initiative incorporates the use of Artificial Intelligence to improve the teaching-learning experience in the classroom, within an ethical framework.
Projects were recognized based on the following criteria:
They impact the transformation of the teaching-learning process.
They have the potential to generate and launch new projects.
They explore new technologies, pedagogies, or emerging educational strategies.
They multiply by involving other stakeholders in the development of ideas.
The virtual exhibition featured 116 projects created by over 220 faculty members. A total of 25 projects were recognized for excelling in one of the categories, with one project standing out across all categories.

This year, the platform “Mi Innovación Educativa” offered faculty a space for documenting initiatives through the “Registro i” initiative and a funding mechanism via the NOVUS initiative. The platform underwent a consolidation process, reaching over 3,000 active users. The documented calls that were followed up on in this space included:
NOVUS 2024 Call for Proposals
IEAD&IFE Experimentation
Registro i | Follow-up to the evidence of the classification process
“Learning from our educational innovation experiences” Festival
Hackathon
AI Summit
My VR Journey
Experiences of competency evaluation
Pioneers in Artificial Intelligence
The evaluation process for innovative practices registered by faculty provides high chances for their proposals to be accepted in various calls, including NOVUS and the faculty classification process. In addition to several calls, faculty can access badges recognizing their documented development through experiences hosted on the platform.
This year, 1,063 experiences and projects were documented on the platform, with 328 corresponding to calls associated with the NOVUS initiative and 735 related to the educational innovation recognition associated with the “Registro i” initiative.
In January, the second national hackathon was held to generate innovative solution alternatives, according to the educational challenge focused on ensuring the integration of Artificial Intelligence, so that its incorporation into the educational context translates into authentic learning for our students.
For two days, participating teachers devised solutions, received advice through interaction with experts and attended workshops on new trends, with the support of expert mentors. At the end of the event, the solutions were presented in pitch format, and the most viable and innovative ones were chosen with the objective of granting them recognition and special support for their implementation.
The lines along which the proposals were developed were:
Evaluation and feedback
Development of competencies
Production of performance evidence
A total of 52 proposals were generated by 194 teachers from 26 campuses.
First place: Mexico City Campus, with the project “Systemic AI Model for Genuine Learning (MOSIAG)”.
Second place: Monterrey Campus, with the project “ GPTeach: GPTs as a tool for the personalization of learning”.
Third place: Chihuahua Campus, “Pimp my prompt - 24/7 virtual assistant for teachers”.

The use of the Virtual Reality environment was promoted through the use of the educational metaverse of the Tecnológico de Monterrey in Virbela. The activities were mainly taught by teachers and experts on different topics. In addition, as part of the promotion of the VR Zones, 485 activities were carried out with 101 teachers and 10,861 students.
As it does every year, CEDDIE disseminated its initiatives and offered advice for the participation of teachers in calls for educational innovation, such as NOVUS and IFE Conference (formerly CIIE).
In order to promote the participation of teachers in NOVUS, 10 workshops were held, with the attendance of 125 teachers.
Also, to promote the participation of teachers in the IFE Conference , personalized and team counseling was provided.

The educational technology ecosystem developed by Tecnológico de Monterrey aims to provide students with a flexible, personalized learning environment and offer faculty an integrated platform to design teaching experiences, provide feedback, and assess competency levels—advancing the personalization of the teaching-learning process.
To enhance support for teaching and learning, several improvements were made to the ecosystem this year through the following initiatives:
Graduate Disciplinary Software Portfolio
Additionally, new technologies were integrated into Canvas to strengthen the ecosystem:
Teaching and Learning Analytics
Academic Credentials for Formative Experiences and Transversal Competencies
Turnitin Draft Coach : This tool supports academic integrity and writing feedback, helping 90,000 students improve citation skills, writing quality, and authenticity review.
Lucid: A cloud-based diagramming platform enabling realtime collaboration on diagrams, prototypes, and organizational charts. Available to 90,000 students and 11,000 faculty members, it enhances collaborative learning.
Finally, new Canvas features were released to optimize user experience, including discussion forums with AI-generated summaries, mentions, anonymous replies, and improved feedback options with video and screen recording. These updates foster effective interactions and personalized learning, enriching the academic environment.

In 2024, significant progress was made in recognizing student achievements through the issuance of three types of Academic Credentials through the Achievement Manager.
Disciplinary competencies: Acknowledge the integrated development of competencies specific to each degree program, enhancing graduate profiles for improved career opportunities.
Transversal competencies: Validate transversal skills of the educational model, acquired in academic units and extracurricular leadership activities and
student training, showcasing a unique professional profile.
Formative experiences: Reflect the development of disciplinary and transversal competencies in experiences such as concentrations or internships during the Tec Semester, enriching and broadening the students’ professional training.
Notably, for the first time, achievements in the transversal competency of “Self-knowledge and management” were reported for Tec21 Model graduates.
During 2024, the “Teaching and Learning Analytics” project has evolved significantly in personalizing the educational experience and supporting academic decision-making in the Tec21 Model. The central objective of the project is to collect and structure the data generated in various platforms of the teaching and learning ecosystem, putting this information at the service of academic leaders through information dashboards.
The impact of this project includes the automatic collection of data from more than 7 platforms, such as the student information system, competency and achievement managers, Adaptive Learning, virtual labs and curriculum design. This data is delivered to more than 750 academic leaders through information dashboards, improving the monitoring of educational initiatives.
The project was implemented nationally during the undergraduate academic periods, within a data governance framework, ensuring the quality of the information as a basis for the development of advanced analytics and personalization of learning.
In 2024, Tecnológico de Monterrey strengthened its leadership in educational innovation through initiatives aimed at transforming teaching and learning spaces to meet the demands of the digital age.
ÁGORA: Ecosystem of Spaces The ÁGORA Ecosystem of Spaces responds to the need to evolve educational spaces in an increasingly digitized and connected world by integrating advanced technologies with pedagogical models. It seeks to share the ecosystem model of cutting-edge educational environments that integrate advanced technology with innovative pedagogical models, designed to enhance student engagement and learning experience.
This ecosystem consists of four innovative spaces: XR Room, Professor with hologram effect, Hall Immersive Room, Advanced Video Studio (AdViS)
ÁGORA transforms the learning experience, making it more active, personalized and immersive. This approach not only improves student and teacher engagement, but also prepares them to face the challenges of an ever-changing global environment.
This space not only strengthens the educational ecosystem with cutting-edge technologies, but also positions Tecnológico de Monterrey as an institution that continuously innovates in order to prepare its community for a global and interconnected future. An example of this is the gold award it received at the QS Reimagine Awards 2024.
Learn more about this project, her e


Below is a description of each of the ecosystem’s spaces:
This space is designed for teachers and students to explore, design and experiment with immersive learning environments using Extended Reality (ER) technologies. Its purpose is to foster educational innovation by integrating tools such as Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR) in the teaching-learning processes.
In the XR-Room (Extended Reality Room), 94 AIRX experiences were carried out in 2024 for Undergraduate, Graduate and Digital Continuing Education levels, impacting 2,488 students, 189 teachers of Campus Monterrey from the following institutional Schools: Business, Engineering and Science; Architecture, Art and Design; Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Humanities and Education.
189 Teachers
2,488 Students
This space recreates the natural dynamics of face-to-face environments where students interact in real time with classmates and with a teacher in hologram effect, overcoming the barriers of physical distance, creating real-time connections with students in different locations. In 2024, this initiative impacted 797 students and 27 teachers, through 13 training units and 30 groups in 11 campuses.
13 Training Units
27 Teachers
797 Students
30 Groups

During the August-December 2024 semester, Tecnológico de Monterrey transferred its technological, instructional, and operational model to DUOC UC in Chile, facilitating the setup of a transmitter room and a receiver room.
Through a talk with 30 visitors from different countries, the institution’s innovation initiatives were presented simultaneously at the Mexico City, Guadalajara, Monterrey and Querétaro campuses.
Students from Monterrey Campus studying the “Concentration in Cognitive Neurosciences” training unit of the School of Humanities and Education had the opportunity to interact with Anthony Brandt, Andrew Noble and José Contreras Vidal from Rice University, Sam Houston State University and the University of Houston, experts on the subject, who gave a talk using the hologram effect.
Within the framework of the “Global Network for Advanced Management (GNAM EGADE)” week, students from various universities around the world attended the session with hologram effect hosted by Lean Foresight expert Mario Saldaña. Students from Yale University, University of Oxford, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Business School, INCAE Business School, Koç University, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile, Saïd Business School, University of British Colombia, Sauder School of Business, University of Ghana, ESSEC, among others, participated in this event.
Mario Bros. and classroom avatars
Twenty-five students of the “Pedagogical foundations applied to learning solutions” training unit of the School of Humanities and Education, led by Professor Eliud Quintero, lived experiences through the hologram effect this year. Using gamification and inverted classroom techniques in the style of video games, the students had to advance in Mario World worlds and at the same time interact with authors of the theory to interview them ‘live’.
This year this initiative evolved with the integration of advanced holographic projection solutions to transform the teaching-learning experience, through two new emerging technologies with transparent LED screens that allow optimal use of space and high visual fidelity, as well as a new audiovisual solution for the teacher to optimize attention to their remote students.
In addition, a new “Professor with multi-mode hologram effect” transmitter booth was designed and built: Holoroom I (glass screen), Holoroom II ( Holomesh screen), Holoroom III (holographic booth), and Holoroom IV (transparent LED mesh), which is located in the CEDES building of Campus Monterrey.
With the participation of more than 1,600 attendees both virtually and in person, the “PROTO Hologram” digital booth technology was premiered at the celebration of 35 years of digital and distance experiences at Tecnológico de Monterrey.
Since “Professor with hologram effect” allows the presence of renowned professors in multiple locations simultaneously, and provides a real experience without physical presence, it has been successfully presented in high-impact institutional events inside and outside the institution.
More than 400 visitors from different countries such as Mexico, Colombia, Honduras, United States of America, Colombia, Brazil, United Kingdom and Panama, among others, have had the opportunity to experience this innovative technology.

74 Teachers 55 Training Units
The Hall Immersive Room (HIR) offers an immersive experience using high-fidelity audiovisual technology that recreates an immersive environment for the teacher, allowing for greater motivation for teacher and student interaction. In 2024, the HIR became firmly established as a dynamic learning environment that enhances teacher-student interaction and motivation. It supported internationalfocused educational models, including the Global Shared Learning Classroom, Global Classroom, Global Week, Elite Courses, and Master Class. Additionally, it provided a platform for Mechanical Engineering students to develop competencies in communication skills and problem-solving.
10,522
Students
This year, more than 10,000 national and foreign students and 74 teachers from 55 training units taught by the schools of Engineering and Sciences, Social Sciences and Government, Humanities and Education, Medicine and Health Sciences, Business, EGADE and Digital Graduate were impacted. There were also 21 educational experiences of LiFE, Digital Continuing Education, CEDDIE, TecMilenio and High School.
The following are some of the most impactful experiences delivered from the Hall Immersive Room during 2024.

Through the participation of over 1,000 students and faculty members from universities including Notre Dame, Universidad Católica de Salta (UCASAL) in Argentina, Federal University of Uberlândia (UFU) in Brazil, Fatih Sultan Mehmet Vakıf University (FSMVU) in Turkey, Universidad Católica Andrés Bello in Venezuela, Universidad del Desarrollo in Chile, Bridgewater State University, University of Florida, Universidad de San Francisco in Ecuador, and Universidad del Norte in Colombia, collaborative activities were conducted using educational models such as the Global Shared Learning Classroom, Global Classroom, Global Week, and Master Class.

With the goal of creating internationalization experiences through meaningful learning, connecting students in a multicultural, collaborative, and knowledge-integrative environment, this year the international experience of the Global Shared Learning Classroom, Global Classroom, and Master Class models brought together 385 students from various universities world-wide through the Hall Immersive Room.
The Global Week program offered in Week 6 and Week 12 the training unit “Diversity in a Globalized World” , where 879 students and 10 teachers from Tecnológico de Monterrey and universities abroad had the opportunity to interact and collaborate with experts on global diversity issues.

Boosting their competencies related to communication skills and problem-solving 70 4th and 5th semester Mechanical Engineering students presented their final projects for period two in the Hall Immersive Room , with the participation of training partners Corning and Carrier de México.

For two days, the Mechanics students, accompanied by their teachers José Figueroa, Juan Molina and Nicolás Hendrichs, interacted with representatives from different areas of the corporations. The teachers, connected from their offices, appreciated the use of the Hall Immersive Room as a new format for the presentation of the students’ work, since being able to observe the physical prototype together with the theoretical presentation allowed them to provide more efficient feedback on the proposal.
Through the “Engineering in Action” program, the students of the “Design of products subjected to static loads” and “Mechanism Design” courses presented the results of the assigned challenge, as well as the physical prototype with which they showed the mechanism proposed as a solution to the challenge.

The competencies developed by the students of the School of Engineering and Science were:
Solving problems in different areas of life with ethical awareness, arguing from principles and values.
Implementing solutions to complex problems using scientific and engineering actions.
Communicating ideas, arguments and emotions orally, integrating body expression, technologies, use of space, verbal structuring and context.
With the participation of over 200 female leaders from Tecnológico de Monterrey, Tecmilenio, and TecSalud, the Summit Red Impulsa 2024: Inspiration in Motion was broadcast in April from the Hall Immersive Room.
The event encouraged network members to take charge of their professional growth, amplify the visibility of their own work and that of other women, challenge the status quo, and find their voices to inspire and transform lives and environments. It also promoted connections between women in the network and individuals who enhance their professional development.
A space of connection, respect, and admiration was fostered, encouraging reflection and deeper awareness on personal growth and development through guided interactions and active listening.
The event was led by David Garza, Executive President of Tecnológico de Monterrey, and Zinia Padilla, National Director of Alumni Relations and Co-founder of the Red Impulsa.




As part of the 35th anniversary of digital education at Tecnológico de Monterrey, Tony Bates, a pioneer in distance education, delivered a keynote session from the Hall Immersive Room to digital education faculty, focusing on the challenges and opportunities universities face with evolving educational technologies.
Speaking to nearly 100 academic attendees, Tony Bates shared key strategies to enhance student motivation and engagement in both face-to-face and virtual learning environments.
ÁGORA: Advanced Video Studio (AdViS)
In May, the Advanced Video Studio (AdViS) opened its doors as a new space for creating advanced educational videos. Since its launch, 32 faculty members have recorded over 100 videos, which have been implemented throughout 2024 and will continue into the first term of 2025. These videos have impacted 36 training units and +5,500 students across High School, Undergraduate, Graduate, and Continuing Education programs. Faculty participants came from the Monterrey, Santa Fe, Querétaro, and Toluca campuses, representing the School of Engineering and Science, Business School, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, School of Humanities and Education, EGADE Business School, and Garza Lagüera High School.
Indicadores 2024
36 Training units
32 Teachers
5,548 Students
The following activities were developed at AdViS throughout 2024, as part of its operational launch.

AdViS, located on the second floor of the CEDES building at Campus Monterrey, provides a tool that allows teachers to easily record video content in a professional studio. With self-management technology, teachers can create engaging didactic content to integrate into their courses, offering more enriching experiences tailored to the diverse learning styles of their students.
On May 2nd, the Advanced Video Studio (AdViS) was inaugurated. This facility allows teachers to efficiently and accessibly self-manage the recording of educational videos using advanced technology, optimizing the production time of this teaching resource.
Click on the video to learn more about

The recorded videos were implemented in training units related to the leveling of disciplinary competencies and leveling of preclinical competencies in medical care for students of the School of Medicine and Health Sciences. They will also be incorporated into the design of the Computer Science and Physics leveling project of the School of Engineering and Science.
Below are some of the first videos recorded in AdViS:



School: Engineering and Science
Academic level: Undergraduate
Course: Analysis of electromagnetic systems in engineered systems
Video: Magnetism: Ampere’s Law and Magnetic Force
Teacher-designer: Alfonso Serrano
Impact: 60 students
School: Medicine and Health
Academic level: Undergraduate
Course: Physiopathology of cavities
Video: Determining and modifying factors
Teacher-designer: Ernesto Ramos
Impact: 35 students
School: EGADE
Academic level: MBA and MAF Master’s degrees.
Courses: Economics for Business, Fundamentals of Business Administration (online) and Fundamentals of Business Administration (classroom).
Video: Electoral environment and the exchange rate
Teacher-designer: Jorge Velarde
Impact: 70 students

As part of the additional services offered by AdViS, synchronous sessions were also broadcasted, where the teacher presented key content in an interactive, guided, engaging, and motivating manner, fostering continuous bidirectional interaction and participation.
The real-time experiences conducted from AdViS during 2024 included the following:

Live streaming from AdViS through Tec Virtual Campus
Teacher: Martín Espitia
Business School
Impact: 73 students

Live streaming through Zoom Room
Teachers: José Figueroa y Carlos Rubio
School of Engineering and Science
Impact : 30 students

Live streaming from AdViS via the Hall Immersive Room
Teachers: José Figueroa
School of Engineering and Science
Impact: 30 students

Live streaming through Zoom Room
Teachers: José Figueroa, Alejandro García y Yeimi Arreola
School of Engineering and Science
Impact: 40 students
As part of the teacher training plan, the online course “AdViS Training: Advanced Video Recording” was designed. The course counts towards teacher classification and is accessible through Success Factors, the internal institutional platform.



In 2024, the Tec Virtual Campus solidified its role as a pioneering space for educational innovation at Tecnológico de Monterrey by evolving the academic metaverse that transforms the teaching-learning process. This year, the initiative expanded its impact by integrating a series of key services for students, such as the Virtual Library, creating a meeting and interaction point accessible nationwide.
Additionally, in 2024, the Tec Virtual Campus had a significant impact: 14,130 students from High School, Undergraduate, and Graduate programs participated in 178 academic activities, and 15 faculty members were trained in using this technology to design innovative learning experiences.
It is worth noting that this year also saw the expansion of international collaborations within the Global Shared Classroom program, with the addition of six new universities in countries such as Germany, Cyprus, Spain, and Colombia, bringing the total to 19 global institutions dynamically participating in academic metaverse activities. Below is the full list of these universities.
Duoc UC (Chile)
Florida Universitária (Spain)
Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú (Peru)
Universidad Católica de Colombia (Colombia)
Universidad Central (Chile)
Universidad de Bielefeld (Germany)
Universidad de Cardenal Herrera (Spain)
Universidad de Chile (Chile)
Universidad de Lima (Peru)
Universidad de los Andes (Colombia)
Universidad de Nicosia (Cyprus)
Universidad de Santiago de Cali (Colombia)
Universidad El Bosque (Colombia)
Universidad Javeriana (Colombia)
Universidad San Sebastián (Chile)
Universidad Uninorte (Colombia)
University of São Paulo (Brazil)
University of South Carolina (USA)
Xavier University (USA)
In summary, this evolution of the Tec Virtual Campus represents a decisive step toward an education adapted to the digital era, fostering skills and experiences that prepare students for a connected and global future.

The “VR Zones” project focuses on creating self-managed institutional spaces with content curated by faculty, positioning itself as an innovative strategy to promote Immersive Learning in Extended Realities (ER). These spaces provide an interactive and engaging learning platform available to both students and faculty, who can use them freely by identifying available stations or through an electronic agenda that allows for digital reservations to ensure station availability. Learn more here
In addition, a new VR Zone was inaugurated at PrepaTec Campus Esmeralda, bringing the total number of VR Zones to 6 at PrepaTec and 12 across various campuses nationwide. On a global scale, the use of these VR Zones facilitated 10,202 Immersive Learning in Extended Realities (AIRX) experiences, impacting 28,901 students and 468 faculty members, who used 108 Virtual Reality applications included in the institutional catalog.

Thus, VR Zones exemplifies the integration of technology into teaching and learning, generating a positive and significant impact on both faculty and students in high school and undergraduate programs.
Currently, VR Zones exist in the following campuses: Chihuahua, Mexico City, Estado de Mexico, Guadalajara, Monterrey, Puebla, Querétaro, Saltillo, San Luis Potosí, Santa Fe, Sinaloa, and Toluca; as well as at PrepaTec campuses: Cumbres, Garza Lagüera, Garza Sada, Santa Catarina, Valle Alto, and Esmeralda.
This year, VR Zones received international recognition at two major events: it was successfully presented at Educause 2024, where its model and impact were showcased, and it was also a finalist in the Education Oscars, the Reimagine Education Awards 2024.
This section highlights the key tools that strengthen the educational ecosystem of Tecnológico de Monterrey, facilitating teaching and learning in a digital environment.
Academic level: all
Academic period: all, continuous
3,005 Teachers
46,192 Students
TecDigital Labs represents the evolution of traditional computer labs at Tecnológico de Monterrey. It integrates digital and cloud-based labs within the educational technology ecosystem, with the goal of facilitating the development of competencies in face-to-face, hybrid, and distance modalities. This project transitions access to specialized software to the cloud, allowing students and faculty to experience a more convenient, flexible, and practical academic experience, both inside and outside the classroom.
In 2024, TecDigital Labs benefited 3,005 faculty members and 46,192 students across campuses nationwide. Through Canvas, users can access software anytime and anywhere, adapting to the different demands of educational models and providing usage analytics to support better decisionmaking.
The following is the usage data for TecDigital Labs in 2024.

* The use of TDL outside of class hours is higher than its use during class, which reflects that students find value in using cloud software instead of going to the computer labs.
* SolidWorks and SPSS are the most used software in the institution
* Information updated as of 12/11/2024
*Source: Apporto session report

The Academic Software Portfolio (PSA) is an initiative that consolidates technological resources through a unique catalog of academic software, defined and established by each school at the national level. This allows faculty and students to access the necessary tools to design and enrich their learning experiences. Since its implementation in 2021, the PSA has standardized the use of educational technology through an institutional software request process.
In 2024, the PSA consolidated its impact by ensuring the availability of specialized programs for High School, Undergraduate, and, for the first time, Graduate levels, benefiting over 94,000 students and 11,000 faculty members nationwide.
Additionally, as part of the 2026 Plans strategy, the PSA expanded its reach by integrating Artificial Intelligence technologies into its transversal catalog, aligning with the institutional strategy of educational leadership in an AI-driven environment. This new collection of authorized software offers secure tools aimed at enhancing the academic environment across all levels.
Currently, the PSA consists of 308 specialized software available, with a total of 263 unique software programs, classified as follows:
School of Architecture, Art and Design: 52
School of Government and Social Sciences: 9
School of Humanities and Education: 36
School of Engineering and Science: 128
School of Medicine and Health Sciences: 7
Business School: 33
High School: 43

This was one of the most notable innovations in the information and consultation services offered by the Tecnológico de Monterrey Library. In August 2024, the Digital Multiformat Library website was made available to the entire academic community on the institutional Library portal, under the “Learn” section. The purpose of this space is to highlight that the Library recognizes the existence of different learning styles and offers digital resources that cater to each of these styles: Auditory, Reading/ Writing, Visual, and Kinesthetic. In this way, not only are the different learning styles of students considered, but it also facilitates this understanding for faculty members, providing resources that help foster active learning, promote critical thinking, and offer meaningful and lasting learning experiences.
In July 2024, a significant evolution took place in the basic reference system offered to Library users: the “Online Chat,” which had been operating since March 2020 during the pandemic, evolved into a virtual assistant named “TECbot.” Starting in August 2024, all basic queries made by users can be answered by this virtual assistant, offering continuous service 24/7, without time or space restrictions. In cases where a user needs more information, “TECbot” allows direct communication with a human agent from “Tec Services,” thereby optimizing the user experience by resolving all inquiries within the same application.
This initiative is continuously updated through a database of questions and answers to address the basic information needs of all users.

The Novus initiative is designed to strengthen and promote a culture of educational innovation among our faculty. In 2024, Tecnológico de Monterrey’s focus is on facilitating the resources needed to develop innovative ideas that address key challenges related to:
Quality education
Education for sustainable development
Educational experimentation with Artificial Intelligence
Relevant teacher training for a dynamic and changing world
The main objective was to provide strategic and timely support to the faculty, helping them to transform their ideas into concrete projects that impact and improve their teaching-learning practices.
The Novus initiative supports the implementation of projects, offering significant added value to the teaching process and the learning experience by providing timely guidance to teachers during their transition to Novus. As a result, key competencies have been developed within the teaching community. With a focus
on continuous improvement, this strategy has enabled:
1. Strengthening teaching methodologies: Teachers develop and refine innovative teaching methods based on evidence and experimental results.
2. Identifying areas of opportunity : Throughout the process, educators acquire tools to assess their classroom practices and make informed decisions to foster continuous improvement.
3. Providing personalized and quality attention: Upon project completion, Novus initiatives empower teachers to offer more relevant and personalized learning experiences to their students.
Novus is not just about funding projects. It is primarily focused on developing key competencies within the teaching community, empowering educators to innovate and transform education. This initiative marks a step forward in building a community of educators equipped to tackle present challenges while enhancing a more relevant and higher-quality educational experience for their students.

Novus projects, 2022 to 2024



As part of the Experimentation team’s efforts, the Impact Measurement area carried out an investigation with the objective of identifying the competencies that our teachers develop by being part of the Novus initiative. The results revealed significant findings: not only did it show that the Novus community promotes educational innovation through experimentation, but also that, thanks to the Mentoring program integrated as a service within Novus, teachers are strengthening the following competencies.



This model was developed and validated using the “Structural Equations” statistical technique, designed to identify and evaluate the innovations with the greatest potential impact in terms of their innovative capacity. The new model is based on five main dimensions, which allow a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of each innovation. The dimensions are described below:
1. Results: Evaluates the effects achieved by the innovation, considering both direct and indirect benefits in the contexts where it is implemented.
2. Nature: Analyzes the intrinsic characteristics of the innovation, such as its originality, disruptive approach and alignment with current needs.
3. Scaling: Examines the possibility of expanding the innovation for application in other contexts or populations, considering its adaptability and potential for expansion.
4. Financial viability: Assesses the economic sustainability of the innovation, including the resources necessary for its implementation and long-term maintenance.
5. Innovation potential: Identifies the degree of novelty and creativity that the innovation brings, as well as its capacity to transform existing paradigms or generate new practices.
This model provides a robust tool for prioritizing and directing efforts towards those innovations with the highest probability of success and impact in their respective fields.

The Novus 2024 call for proposals had an increase of 6.13% (277 applications) compared to 2023 (261 applications).
After an exhaustive evaluation process by “double blind peers”, 59 proposals were selected, which make up the “Novus Generation 2024”. In this edition, 217 teachers are participating, and it is estimated that they will have an impact on 10,932 students and 418 courses. This year, projects were received from various thematic lines, which are shown in the following image.
Line

The projects were distributed in different educational technologies, receiving a greater number of projects related to the use of Artificial Intelligence (20%).

Below is an image describing the life cycle of a Novus project, which lasts approximately 18 months. This process includes several key stages that ensure the structured and complete development of each project. Throughout this process, the mentoring program plays a fundamental role, as it provides personalized accompaniment and expert guidance to the participants, ensuring that objectives and quality are met at each stage. The stages are as follows:
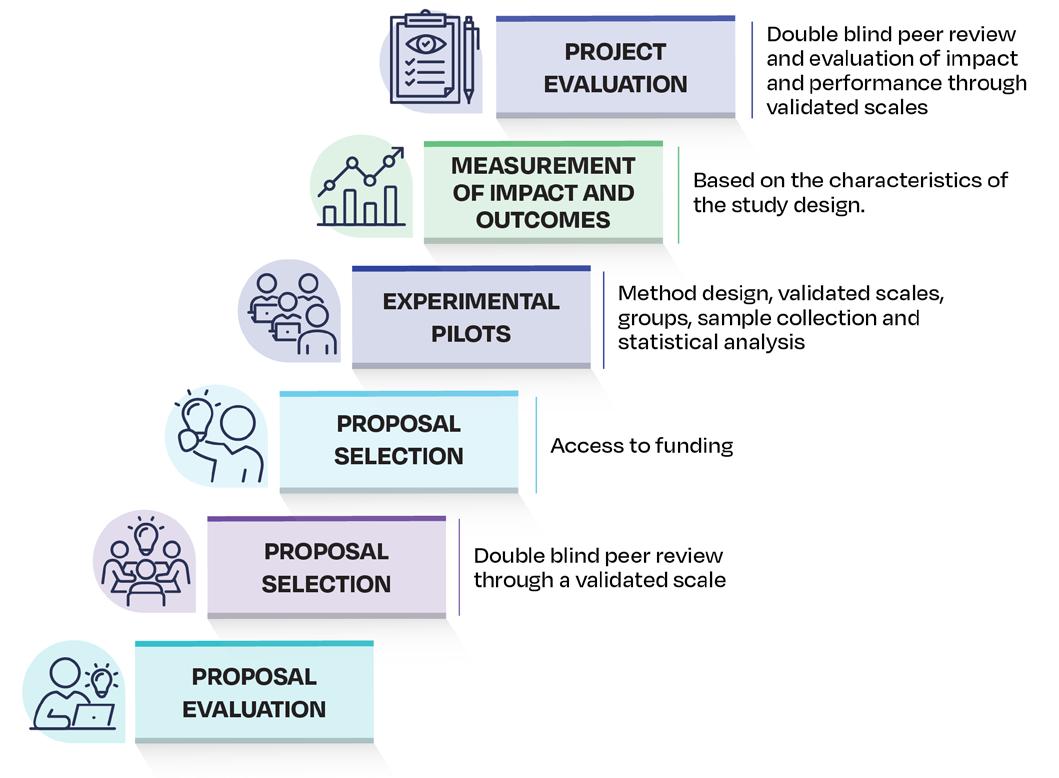

As part of the key strategies of the Novus initiative, aimed at enhancing the teachers’ competencies, a series of training sessions were conducted to transform their educational practice. These sessions focused on:
Developing educational innovation proposals: Providing tools to design projects centered on improving the teaching-learning process, promoting more effective and dynamic teaching.
Creating experimentation protocols: Offering rigorous methodologies to ensure successful and meaningful implementation of classroom innovations.
Transforming data into decisions: Training educators to measure the impact of their experimentation and transform results into practical insights for refining their teaching methodologies.
These training sessions strengthened not only the technical knowledge of teachers but also their ability to generate transformative impact within their learning environments.
Within the framework of the IFE Conference held in January 2024, an award ceremony took place to honor the projects of the “Novus Generation 2023”. The event was attended by distinguished figures, including Juan Pablo Murra, Rector of Tecnológico de Monterrey; José Escamilla, Associate Director of the Institute for the Future of Education; and Luis Portales, Leader of Experimentation, Impact Measurement, and the Writing Lab. These leaders presented certificates of recognition to the highest-rated projects. The awarded projects were:
Description: Use of Artificial Intelligence for educational dialogue, aimed at transformation through a more effective use of emotional tonalities in the academic or business feedback process.
Main Researcher: Lilia Rodríguez
Campus: Business School, Querétaro Campus
Project: App for the stimulation, development and evaluation of competencies in sustainable development.
App to promote learning and reflection, where students can learn about relevant and updated topics on sustainable development. It also has a board game for students to complement their learning.
Martha Núñez
School of Architecture, Art and Design Monterrey Campus

Project: Tec 21 car assembly plant, Augmented and Virtual Reality.
Platform that includes Virtual and Augmented Reality lessons (two lessons of each), focused on two Mecano car models belonging to the “Mx_REP” simulator products.
Carlos Alberto González Almaguer
School of Engineering and Science
Querétaro Campus
Project: Growing Together Bank, customized evaluation for the training unit “Statistical Thinking (UFPE)” through Virtual Reality.
Software in Escape Room format, which simulates a working day in a bank. The experience includes a series of activities to be performed with descriptive statistics; at the end (and immediately), the resource delivers a detailed report with feedback and level of competence development.
Gabriela Monforte García
Business School
Monterrey Campus
Project: Mixed Reality Platform for the improvement of the development of disciplinary competencies in the teaching of Control Engineering.
Virtual environment in which a plant to be controlled is represented; implementation practices of control techniques using Mixed Reality were also generated.
Alejandro Guajardo Cuéllar
School of Engineering and Science
Guadalajara Campus
Project: KUDI: financial game
Learning environment where students experience through a game the progress of their learning, as well as their financial competences.
Adriana Valle Portilla y Brenda Cruz Zamora
Business School
San Luis Potosí Campus
Boost Novus was created in response to the growing need to scale Novus projects with the potential for transferability and replication within the institutional environment. As part of a collaborative strategy with the Educational Innovation and Digital Learning Department, as well as EdTech, a comprehensive internal and external scaling process was designed. This process targets educators with completed Novus projects that have demonstrated significant impact, excelled in evaluations, and shown the potential to broaden their reach, enabling them to replicate their initiatives both within their own school and across other campuses of the institution.
Currently, three projects are being supported, providing them with the necessary resources to refine and advance their technological development. Additionally, these projects receive specialized guidance from researchers in the Impact Measurement area, focusing on demonstrating that the projects are generating positive and relevant outcomes during implementation. This guidance not only ensures an evidence-based approach but also helps establish best practices that can be adopted at an institutional level, driving educational transformation and fostering meaningful learning experiences for both students and educators.

At Novus, the power of inter-institutional collaboration is viewed as a driving force for innovation. As part of the commitment to strengthen these alliances and promote educational innovation, Novus works closely with various institutional areas—such as Educational Innovation and Digital Environments, Living Lab, and Ruta Azul—to develop strategic projects addressing key institutional needs.
Currently, several agile calls for proposals are underway, designed to explore, test, and validate new educational technologies with a focus on the use of artificial intelligence. This process aims to assess their real impact: how these tools foster student engagement, their practical utility for educators, and their contribution to the teaching-learning process within the institutional environment. Each project not only reflects the creativity and dedication of its developers but also highlights the ability to collaborate across areas, working together to achieve common goals.
With these calls, more than 400 students and 59 high school and professional teachers have been impacted.
This is a recognition and award ceremony for teachers who successfully completed their educational innovations focused on the use of Artificial Intelligence tools. The event was attended by distinguished personalities such as: Juan Pablo Murra, Rector of Tecnológico de Monterrey; Michael Fung, Director of the Institute for the Future of Education; and Joaquín Alejandro Guerra, Vice Rector of Educational Innovation and Academic Policy. The event was attended by 32 teachers, who actively participated in the experimentation with various Artificial Intelligence platforms. As a result, this initiative impacted a total of 396 students.

This section highlights cutting-edge initiatives that integrate digital tools and disruptive pedagogical approaches to enrich learning and teaching, fostering a more dynamic and interactive educational ecosystem adapted to the needs of the 21st century.
The Observatory is a unit of the Institute for the Future of Education (IFE) dedicated to the analysis and dissemination of the latest trends at the intersection of education, innovation and technology. It represents a guide for educators around the world in key areas of educational innovation, through the production and distribution of open educational resources in English and Spanish. Through the different sections of its website, newsletter and social networks, the user can consult publications such as:
Edu News : Notes and most relevant articles in the world of education.
Edu Bits : Pedagogical experiences and good practices in teaching (by teachers for teachers).
Edu Tube : The latest in educational innovation in video, webinars, interviews, conferences, among others.
Edu Reads : Reports, eBooks and readings on educational innovation and teaching strategies.
Visit the websites:
Spanish Version
English Version
In September 2024, the IFE Observatory celebrated 10 years of producing open educational resources.
A website that concentrates open educational resources related to Generative Artificial Intelligence was published.
The IFE Insights Reports were published as a series of reports aimed at decision-makers, including university rectors, administrative staff of higher education institutions, NGO directors, leaders of organizations such as UNESCO, educational policy experts, government officials, politicians, ministers, secretaries, researchers, and think tank staff, among others.
The following reports were published:
“Digital Education in Universities: A Comprehensive Implementation Guide”
This report was developed in collaboration with the Vice Rectorate for Educational Innovation and Academic Regulations, with the purpose of providing a practical guide to support educational institutions in applying and developing digital education. It offers a strategic, rather than operational, perspective, designed to help both emerging and advanced universities find potential answers to their questions.
“Teaching Engineering in the 21st Century: 4 Key Themes”
This report covers the 2023 WEEF & GEDC Summit, hosted at Tecnológico de Monterrey, a globally prestigious event for engineering schools. The summit aimed to gather insights from deans representing various countries to discuss topics related to the improvement of engineering education and its current challenges.
Publication of the “Glossary of Educational Innovation 2024”.
Broadcast of 8 webinars featuring experts from across Latin America and Spain.
Transmission of 6 panels via web in collaboration with the Universidad Oberta de Catalunya and Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú.
Production of 8 podcasts with prominent educators worldwide, addressing topics such as educational innovation, alternative credentials, artificial intelligence, access to education, the state of post-pandemic education in Latin America and the world, and workplace equity.
Collaboration with nonprofit organizations, including Ashoka Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean, Siemens Foundation, the British Council, and the Australian Embassy in Mexico, as well as international publications like EdSurge.
During 2024, the following were recorded:
Users: 3.5 million who spent an average of 2:35 minutes on our websites, consuming 5.2 million pages of content.
Suscribers: 225,000
Social media followers: 500,000


This section highlights the global impact of Tecnológico de Monterrey’s educational innovation and its recognition across various international platforms. Over the years, the institution has established a robust reputation in digital education, serving as a pioneer in adopting advanced technologies and disruptive methodologies in learning. This continuous effort has yielded numerous academic publications and prestigious awards from renowned organizations, positioning the institution as a leader in transforming higher education worldwide.
These accolades not only validate Tecnológico de Monterrey’s commitment to academic excellence and innovation but also amplify its influence within the global educational community. Through published research, articles, and case studies, the institution shares best practices and outcomes, contributing to the advancement of knowledge in digital education. This section highlights the most significant achievements in terms of publications and awards, demonstrating how these milestones have strengthened Tecnológico de Monterrey’s standing on the global map of educational innovation and reinforced its role as a reference for other institutions and a driver of change in 21st century education.


The following articles and papers were disseminated through peer-reviewed journals, digital platforms, and national and international conferences.
The publication statistics are as follows:
Publications in peerreviewed journals: 5
Articles in other media and for presentations: 13 Other publications and presentations: 55
For a detailed list of all publications, refer to Appendix
This year, 14 Tecnológico de Monterrey projects were recognized as finalists in the QS Reimagine Education Awards, often referred to as the “Oscars of education.” Of these projects, 4 received Gold, Silver and Bronze Prizes:
Category: Blended and Presence Learning
Presented by the Directorate of Educational Innovation and Digital Education, in collaboration with the institutional schools.

Cultivating Complex Reasoning Skills to Empower Lifelong Learners
Category: Lifelong Learning
Presented by the Institute for the Future of Education, in collaboration with the institutional schools.

Cross-Cultural Classroom (3C)
Category: Sustainability Education Literacy
Presented by the School of Engineering and Science.

TecDrone: Assessment of STEM Competencies using VR & AI
Category: Learning Assessment
Presented by the Directorate of Educational Innovation and Digital Education, in collaboration with the School of Engineering and Science.


Below are the award-winning and finalist projects across different categories of the QS Reimagine Education Awards 2024. Out of more than 1,200 projects submitted from around the world, an international panel of over 900 experts selected innovative programs, technologies, and pedagogical approaches that are revolutionizing education globally.
Category Project Participants Developers
Blended and Presence
Learning GOLD WINNER:
Spaces
Watch V ideo
Lifelong Learning GOLD WINNER:
Cultivating Complex
Reasoning Skills to Empower Lifelong Learners
Watch Video
Adolfo Ramírez
Ana Gabriela Pérez
Ana Gabriela Rodríguez
Beatriz Palacios
Brenda Luis
Carolina Ramírez
Ever Vázquez
Job Valdés
Leticia Castaño
Mauricio Martínez
Patricia Aldape
Verónica Pérez
Violeta Tovar
Carlos George
Carlos Vázquez
Carolina Alcántar
Edgar López
Ernesto Pacheco
Fidel Casillas
Hugo Terashima
Inés Álvarez
Irma Patiño
Jhonattan Miranda
Jorge Sanabria
José Molina
Leonardo Glasserman
Magally Martínez
María Soledad Ramírez
Miguel González
Rasikh Tariq
Educational Innovation and Digital Education, in collaboration with the Institutional Schools
Institute for the Future of Education, in collaboration with Institutional Schools
Category Project Participants Developers
Sustainability Education Literacy
Learning Assessment
SILVER AWARD:
Cross-Cultural Classroom (3C)
Watch video
BRONZE WINNER:
TecDrone: Assessment of STEM Competencies using VR & AI
Watch video
Eduardo Juárez
Ivo Neftali Ayala
Adán Graciano
Adrián Ayala
Adriana Plata
Alejandro Salas
Alfredo Ceballos
Ana Gabriela Rodríguez
Ana Mónica Turcios
Andrea Sandoval
Beatriz Palacios
Brenda Luis
Carlos Villanueva
Daniel Cantú
Daniel González
Edgar Garza
Ezel Escobar
Ivonne Yznaga
Job Valdés
Jorge Álvarez
Jorge Hidalgo
Lorena Quilantán
María Guadalupe Aguilar
María Ileana Ruiz
Mauricio Martínez
Miguel Cervantes
Obedt Figueroa
Orlando Llamas
Patricia Aldape
Roberto Rodríguez
Vianney Lara
Violeta Tovar
School of Engineering and Science, in collaboration with International Islamic University Malaysia, Srinakharinwirot University, The University of Hong Kong
Educational Innovation and Digital Education in collaboration with the School of Engineering and Science.
Best use of Generative AI GreenFlags. Hyperpersonalization of learning with AI-RX: Educational impact on social responsibility
Watch video
Best use of Generative AI Skill Studio Empowering
Educators with AIPowered Prompt Design and Sharing
Watch video
Adán Graciano
Adrián Ayala
Alberto Herrera
Alberto Sánchez
Alejandro Rocha
Alejandro Salas
Allan Acosta
Ana Gabriela Rodríguez
Beatriz Palacios
Brenda Luis
Cecilia Núñez
César Villarreal
Dulce Salas
Estrella Hernández
Evelyn González
Ezel Escobar
Gabriela Reyba
Job Valdés
Julio Mier
Lorena Quilantán
Mauricio Martínez
Nancy Cruz
Olaf Román
Orlando Llamas
Patricia Aldape
Reynaldo Contreras
Sandra Fuentes
Beatriz Palacios
Bertha Saldívar
Carmen Reyes
Eunice Ángeles
Iliana Ochoa
Irving Hidrogo
Manuel Terán
Mario Torres
Myriam Villarreal
Patricia Aldape
Úrsula Saldívar
Verónica Pérez
Educational Innovation and Digital Education in collaboration with the Business School.
Educational Innovation and Digital Education, in collaboration with the Vice-Presidency for Digital Transformation and TEDU
AI in Education VR Zones - Innovative model to enhance learning experiences
Watch video
E-Learning The Learning Gate
Watch video
Immersive Experiential Learning
Virtual Reality and AI for Entrepreneurship: Enhancing Student Competencies
Watch video
Innovation in Business Education
Conscious Enterprise Education at Tec de Monterrey
Watch video
Bertha Saldívar
Irving Hidrogo
Rogelio Hernández
Úrsula Saldívar
Verónica Castillo
Vladimir Burgos
Andrés Rivera
Lucía Juárez
Vianey Valenzuela
Clara Cobo
Daniel Forcada
Hugo Álvarez
Ján Rehák
Linda Ruiz
Nelly Salas
Víctor Jiménez
Adriana Morales
David Capistrán
Laura Guzmán
Luis Gerardo González
Marianela Adriaenséns
Nadia Covarrubias
TEDU, in collaboration with Innovative Education and Digital Education
The Learning Gate
Business School Department of Entrepreneurship
Center for Conscious Enterprises and Business School
Category Project Participants Developers
Learning Assessment Engineering empowerment: virtual factory simulations for skill enhancement
Watch video
Sustainability Education Action Beyond the Coffee Cup: Empowering Coffee-Production Communities
Watch video
Adrián Ayala
Ana Gabriela Rodríguez
Andrea Sandoval
Ángeles Aguirre
Beatriz Palacios
Blanca Benavente
Brenda Luis
Denisse Palma
Francisco Tamayo
Ingrid Benavides
Jorge Mosqueda
José Manuel Reyes
Maribell Reyes
Mauricio Martínez
Nancy Zavala
Rebeca Alvarado
Rocío Cortés
Rosario Rosas
David Mastrascusa
María del Pilar García
Nora Torres
Olga Vázquez
Educational Innovation and Digital Education, in collaboration with the School of Engineering and Science.
Institute for the Future of Education and Káapeh México
Sustainability Education Action
EGADE Action Week: Transforming Business for Sustainable Impact
Watch video
The Power of Partnerships Innovative Digital Factory: Transforming Learning through Strategic Alliances
Watch video
Cecilia Terán
Eduardo Aguiñaga
Eloísa Pérez
Eva Guerra
Gabriela Maldonado
Luciana Manfredi
Miriam García
Omar Velasco
Orla Branigan
Sonia Monárrez
Adán Graciano
Ana Gabriela Rodríguez
Armando Morales
Beatriz Palacios
Brenda Luis
Carlos VIllanueva
Claudia Hernández
Ezel Escobar
Fabiola Lima
Luis Ramírez
María Ileana Ruiz
Mónica Turcios
Orlando Llamas
Patricia Aldape
Reynaldo Contreras
Ricardo Ipiña
Vianney Lara
EGADE Business School
Educational Innovation and Digital Education, in collaboration with the School of Engineering and Science.

Skill Studio is awarded the ‘Most Innovative’ award
The “Most Innovative” award by IT Masters Mag recognized the development of Skill Studio as one of the most groundbreaking solutions in Information Technology. This collaborative project, involving the Vice Presidency for Digital Transformation, Educational Innovation and Digital Learning, Educational Technologies, and CEDDIE, was honored in the 24th edition of the awards.
During the National Faculty Meeting of Tecnológico de Monterrey, held in July, a group of professors shared their innovative digital experiences through the institution’s metaverse.
The following are the highlighted projects:
Name
School
Laura Eugenia Romero Robles Engineering and Science Monterrey
Antonio Luis Juárez Negrete Architecture, Art and Design Queretaro
Julio Cesar Avila Romero
Engineering and Science Sonora Norte
Advantages and Risks of Using Generative Artificial Intelligence in Academic Environments
Sketch I.A.A.R: Integrating Sensory Habitat Design with Augmented Reality and Artificial Intelligence
Undergraduates’ Perceptions of Mathematics Learning Through Contextualized Problems in Professional Practice
Sascha Fürst Business Guadalajara Innovation Camp for Tackling Grand Challenges
Diana Garcia Monzalvo Business Hidalgo Learn on the Move Project
Miriam Iliana Navarrete Bear High School Tampico Learning French with Artificial Intelligence
Jorge Alvarez Ramírez
Gilberto Huesca Juárez
Engineering and Science Tampico
Engineering and Science National
Javier Armando González Lozano Business Monterrey
María Yolanda Burgos Lopez Engineering and Science Monterrey
María de la Paz Toldos Romero Business Guadalajara
Online International Collaborative Learning in the Metaverse
Effectiveness of Using ChatGPT as a Tool to Enhance the Benefits of the Flipped Learning Strategy
Educational Innovation and International Service Expansion: The Case of Axys at Tecnológico de Monterrey
MakerSpace for the Exportation of Persian Lime from Yucatán
Virtual Reality to Increase User Satisfaction in an Innovation Project
Self-Awareness as a Driver of Learning for Sustainable Behavior
Sandra Tena de la Vega High School
José Pablo Zamora Vázquez High School
State of Mexico
SocioEmotional Skills to Increase Tolerance to Frustration in First Year High School Students
San Luis Potosí Hacking AI Through Critical Thinking
Marilena Antunes Ricardo Engineering and Science Monterrey
Virtual Laboratory as a Learning Strategy in the Graduate Course Instrumental Analysis in Biotechnology
Antonio Luis Juárez Negrete Architecture, Art and Design Queretaro AI Digital Twins for Presenting the Formal Representation of Space Block
Adriana Morales Rodríguez Business Tampico Paradigm Shift and Online Learning Experience in Conscious Business
Krisztina Eva Lengyel Almos Social Sciences and Government Queretaro
Mónica Vázquez Fernández Business Santa Fe
Integration of ChatGPT and Digital Economic Atlases for Geopolitical Analysis and Future Risk Assessment
Use of Video Capsules to Strengthen Knowledge and Skills in the Financial Analysis (CF1015) Learning Unit
Adriana Diaz Marchetti Architecture, Art and Design Monterrey Vectors in Space
Rocío Elizabeth Cortez Márquez Architecture, Art and Design National
Enhancing Student Motivation, Attention, and Self-Perception of Learning Through Immersive Activities
Maria Valentina Narváez Teran Engineering and Science Monterrey A Board Game to Learn Regular Expressions
Víctor Francisco Robledo Rella Engineering and Science Mexico City Using AI to Enhance Physics Learning
The Department of Educational Innovation and Digital Learning, in collaboration with the Institute for the Future of Education, through the IFE Experimentation-Novus initiatives, the Center for Faculty Development and Educational Innovation (CEDDIE), and the national Educational Technologies (TEDU) team launched this call to transform assessment and feedback processes. This initiative invited the entire teaching community to innovate in the delivery of their courses.
These are the faculty members who presented outstanding projects:
Carlos Rafael Gijón Rivera Engineering and Science Puebla
Héctor Ramón Rodríguez Maya Business Saltillo
Ana Beatriz Salas Valdes Business Monterrey
José Guillermo Guzmán Segura High School Monterrey
Myriam Zoiree Cordero Godina High School Monterrey
Lydia Isela Garza Fernández High School Monterrey
Marcela Veazey Ochoa High School Monterrey
Eduardo Hinojosa Canseco High School Monterrey
Laura Alejandra García Cavada High School Monterrey
Edyam Alejandro Rodríguez García High School Monterrey
Paloma Villalobos Álvarez High School Monterrey
Nancy de los Angeles Segura Azuara Medicine and Health Sciences Monterrey
José Miguel Hinojosa Lezama Medicine and Health Sciences Monterrey
Rodrigo del Toro Rojas Medicine and Health Sciences Monterrey
Norma Xochitl Di Censo García Social Sciences and Government Santa Fe
Roberto Sergio García Garza High School Cumbres
Karina Esmeralda López Caballero High School Cumbres
Jesús Marcelo Aguirre Treviño High School Cumbres
Juan Francisco Soto Mendivil High School Santa Catarina
Lorena Romo Alanis High School Santa Catarina
Manuel Esquivel González High School Valle Alto
Carmen Elizabeth Tijerina Velázquez High School Eugenio Garza Sada
Silvia Elena Flores Tavitas High School Eugenio Garza Sada
Sara Camacho de la Parra Humanities and Education National
Juanita Salomón Orea High School Hidalgo
Marlety Corona García High School Hidalgo
Dania Lorenia Arriola Arteaga Online Programs
Guillermo Garrido Aguilar Online Programs
Cecilia López de la Rosa Architecture, Art and Design Mexico City
Rocío Hernández Larriba Architecture, Art and Design Queretaro
Lilian Salazar Díaz Architecture, Art and Design Mexico City
Ilssy Macchia Social Sciences and Government Puebla
Pedro Nájera García Engineering and Science Queretaro

Tecnológico de Monterrey has been a member of Quality Matters (QM) since August 2018 , establishing a partnership to adapt QM standards and evaluation rubrics for Latin America, promoting academic quality in distance education programs throughout the region.
In July 2019 , Tecnológico de Monterrey became the first institution in Latin America to earn QM certification for a course: “Foresight and Innovation.” In 2021 , three additional online graduate courses received QM certification: “Foresight and Innovation,” “Social Responsibility, Ethics, and Sustainability,” and “Leadership for Sustainable Development.” In 2022 , the institution achieved the first QM-certified Continuing Education program in Latin America.
Today, QM course design rubrics remain the standard used by Tecnológico de Monterrey for online courses, with continued faculty and instructional designer certifications in their use to enhance student learning outcomes.
In 2024, the Digital Continuing Education programs achieved quality recertification for their educational model, endorsed by ANEOR (Spanish Association for Standardization and Certification) and ANCYPEL (National Association of e-Learning Centers and Providers), leading e-learning regulatory bodies in Europe.
Obtaining this quality recertification reaffirms our commitment to academic excellence and innovation in professional training. This recognition ensures that the content, methodologies, and resources provided meet the highest international standards, guaranteeing a cutting-edge learning experience aligned with the demands of today’s dynamic environment.
This recertification not only validates the quality of our institutional educational model but also strengthens the confidence of students and organizations in the preparation of highly competitive talent capable of adapting to future challenges.


The 2024 Report on Educational Innovation and Digital Education at Tecnológico de Monterrey is the result of a collaborative effort involving multiple areas, teams and individuals dedicated to academic excellence and educational transformation.
This section recognizes the invaluable contributions and commitment of the educators, researchers, project leaders, and technical and pedagogical support staff who have driven innovation within the institution. Their dedication and vision have been instrumental in producing a report that not only documents significant advancements in educational innovation and digital learning but also inspires the academic community to continue innovating and exploring new frontiers of learning.
This publication is overseen by the Directorate of Educational Innovation and Digital Learning within the Vice Rectory of Educational Innovation and Academic Policy of Tecnológico de Monterrey.
Vice Rector’s Office for Educational Innovation and Academic Policy
Joaquín Alejandro Guerra Achem
Directorate of Educational Innovation and Digital Learning
Elsa Beatriz Palacios Corral
Directorate of Digital Education
Maribell Reyes Millán
Directorate of Learning Experience Innovation
Laura Patricia Aldape Valdés
Directorate of Content Channels and Dissemination
Norma Angélica Lara Uribe
Directorate of Strategic Planning
Silvia Catalina Farías Gaytán
Directorate of Digital Solutions Development
Lucía Caballero Morales
Content Editing
Carolina Ramírez García, Verónica Alejandra
Pérez Aguirre y Karla Verónica Cabrera
Martínez
Data Strategy
Carmen Verónica Ortiz Torres y Neidy Araceli
Torres Zúñiga
Graphic Design
María Isabel Zendejas Morales, Laura
Armida Ramírez Gutierrez y Lucía Elizabeth
Villanueva Vázquez.
Editing and proofreading
Perla Téllez Garza
Coordination
Ana Margarita Fuster Montiel

We also extend our profound gratitude to strategic partners and organizations whose support and collaboration have empowered Tecnológico de Monterrey to advance toward cutting-edge education. These allies have provided knowledge, resources, and tools that enrich our initiatives, strengthening our impact on education at both the national and international levels. Every individual and entity involved in this project has played a vital role in reflecting the institution’s commitment to transformative and inclusive education throughout these pages.
Abigail Selene López Pérez
Adriana Gabriela Gámez Garza
Alejandra Yaneth Sandoval Capetillo
Alfredo Henry Hidalgo Rasmussen
Amairani Concepción Castañón Zárate
Ana Gabriela Pérez Cantú
Ana Gabriela Rodríguez Mendoza
Ariadna Bozada Cuesta
Beatriz Meléndez Venancio
Bertha Alicia Saldívar Barboza
Brenda Aimé Luis Chavira
Cecilia Ivonne Rico Arenívar
Claudia Erika García López
Claudia Zubieta Ramírez
Crisantos Manuel Martínez
Cynthia Karyna López Botello
Dan Beltsasar Alonso Hernández
Dora Elizabeth García Olivier
Esteban Venegas Villanueva
Evelyn Garza Krause
Ever Vázquez Juárez
Feniosky Avelhermi Pena-Mora
Francisco Javier Rosales Pineda
Fresia Paloma Hernández Moreno
Homero Domínguez Perales
Horacio Arredondo Villalba
Hugo Luis López Coronel
Ingrid Gabriela Benavides García
Irving Hidrogo Montemayor
Jessica Jazmín Hernández Rodríguez
Joaquín Acevedo Mascarúa
Jorge Alfonso Rodríguez Tort
Jorge Eugenio Valdez García
José Antonio González Orta
José Luis Mata Fernández
José Rafael López Islas
José Vladimir Burgos Aguilar
Juan Pablo Nigenda Álvarez
Judith Aurora Ruiz Godoy
Karen Hinojosa Hinojosa
Laura Esther Zapata Cantú
Leticia Castaño Sánchez
Luciana Cecilia Moscoso Boedo
Luis Raúl Domínguez Blanco
Luis Alonso Herrera
Luis Omar Peña Ortega
Luis Enrique Portales Derbez
Marcela Ivonne Rodríguez Rodríguez
María del Carmen Pámanes Fernández
María Ileana Ruiz Cantisani
Mariana Aguilar Vásquez
Martha Elena Moreno Barbosa
May Iliana Portuguez Castro
Miguel Ángel Nájera
Mónica Arreola Flores
Myriam Villarreal Rodríguez
Rebeca Elizabeth Alvarado Ramírez
Rogelio Vicente Hernández Méndez
Sadie Lissette Guerrero Solis
Sandra Dennis Núñez Daruich
Yedida Betzabé López Membrila
Yesika María Arteaga León
Víctor Edrei Robles Chávez
We are especially grateful for the valuable participation of the professors who enriched their practice through digital experiences. We also extend our appreciation to all the areas involved in the definition, design, development and successful deployment of the projects implemented, always with the objective of ensuring the best experiences that add value to our students’ learning throughout their academic life.




This last section includes fundamental resources that complement the information presented in the previous sections: additional data, detailed graphs, case studies, methodological references and other materials that offer a deeper insight into the projects and initiatives of educational innovation and digital learning at Tecnológico de Monterrey.

Horizons architecture with virtual reality for complexity environments: mixed methods
Authors: María Soledad Ramírez Montoya, Sandra Martínez Pérez y Laura Patricia Zepeda Orantes.
Improving the learning-teaching process through adaptive learning strategy.
Authors: Elvira Guadalupe Rincón Flores, Leticia Castaño Sánchez, Sadie Lissette Guerrero Solís, Omar Olmos López, Carlos Felipe Rodríguez Hernández, Laura Angélica Castillo Lara y Laura Patricia Aldape Valdés.
Using an adaptive learning tool to improve student performance and satisfaction in online and face-to-face education for a more personalized approach.
Authors: Guillermo Gándara, Ana Gabriela Rodríguez Mendoza, Laura Patricia Aldape Valdés
Scientific Research an Academic Publisher: “Conceptualization, Design, Production, and Implementation of Immersive Resources: Welcome to Athens Experience as Educational Innovation to Transform the Teaching-Learning of Citizenship and Democracy” September 2024.
Authors: Guillermo Gándara, Ana Gabriela Rodríguez Mendoza, Laura Patricia Aldape Valdés
Students’ Perceived Learning Experience and Continuance Intention of Using Virtual Reality in Business Education. November 2024.
Authors: Morales-Rodriguez, A., RamírezVásquez, N., Contrino, M.F.
Tecnológico de Monterrey is a founding partner of Times Higher Education’s (THE) THE Campus initiative, whose purpose is the exchange of knowledge and experiences around technology-enhanced learning.
THE is a digital platform with over 3 million monthly visitors, which makes it ideal for integrating the expertise of universities and communicating it to the international community.
In 2024, Tecnológico de Monterrey participated by publishing 13 articles about experiences and best practices on the implementation of digital modalities and educational innovation in higher education.
Access the publications here:
1. Tips for mastering the Global Shared Learning Classroom
2. Three ways technology can make your classrooms more inclusive
3. The library’s role in digital education: content is still king
4. Using telepresence to enrich learning
5. Seven exercises to incorporate into your gender studies classes
6. Combat social injustice burnout in social sciences and humanities courses
7. Teach students to use GenAI to create characters for stories
8. Engage Gen Z students by integrating TikTok into your teaching
9. Using AI to create engaging educational games for humanities students
10. Host a competition to foster creativity and innovation at your institution
11. Strategies to enhance your online course
12. Ensuring online education is inclusive and accessible to all
13. ChatGPT and other AI tools to use in the classroom
For more information, please visit:
https://www.timeshighereducation.com/campus/institutions/monterrey-institute-technolog y
1. Adaptándonos a la IA: estrategias para preservar la integridad académica en España y América
Latina
Event: Conference for Times Higher Education
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
2. Adaptive learning in action: boosting mathematical proficiency and student engagement
Event: XVII International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation
Speaker: Leticia Castaño
3. Advancing education through AI-powered learning strategies and teaching techniques
Event: XVII International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation
Speaker: Olaf Román
4. Application of active learning techniques supported by generative AI in education
Event: XVII International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation
Speaker: Olaf Román
5. Aprendizaje activo con IA para detonar creatividad y pensamiento crítico
Event: Edutic
Speaker: Dania Arriola
6. Aprendizaje de próxima generación: exploración del impacto de los modelos de lenguaje generativo en la educación
Event: IFE Conference (featured event panel)
Speakers: Beatriz Palacios, Jordi Torras, Francisco García, Francisco Mayorga
7. Aprendizaje inmersivo en el metaverso: una nueva forma de enseñar y aprender
Event: IFE Conference
Speaker: Anahi Molina, Mónica Contrino
8. Buenas prácticas de datos enriquecidos
Media: Red Colombiana de Información Científica
Speaker: Sara Rodríguez
9. Buenas prácticas de educación mixta
Event: UAM Conference
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
10. Charla interactiva sobre IA
Event: Venture Café Conference
Speaker: Maribell Reyes
11. Clases del futuro: Tec exporta sistema de Profesor Holograma a Chile
Event: DUOC (Chile) Conference
Speakers: Beatriz Palacios, Patricia Aldape
12. Co-designing the future with generative ai: cultivating student digital competencies for tomorrow
Event: XVII International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation
Speaker: Rebeca Alvarado
13. Conferencia especial para líderes
Event: Conference for the Secretariat of Public Education, Nuevo León
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
14. Construyendo la educación del futuro: 35 años de experiencias digitales en el Tecnológico de Monterrey
Event: IFE Conference (featured event panel)
Speakers: Beatriz Palacios, Juan Pablo Murra, Ignacio de la Vega, Patricio López, Carlos Cruz
15. Desde el campus
Media: Tec Sounds Radio
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
16. Diálogo colaborativo: Potenciando sinergias
Evento: IFE Conference (mesa de networking)
Speaker: Mariana Leyva
17. Digital experiences using generative AI (ChatGPT) to enhance learning
Event: Conference for Brunel University, London
Speaker: Ingrid Benavides
18. Diseño de una estrategia de Credenciales Alternativas
Event: IFE Conference (workshop)
Speaker: Patricia Aldape, Verónica Pérez, Karla Banda
19. Driving success: strategies that enhance the higher education student’s experience in massive digital engineering courses
Event: XVII International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation
Speaker: Ingrid Benavides
20. Educational innovation applied to include students with visual disabilities in learning project management and evaluation
Event: XVII International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation
Speaker: Olaf Román
21. El uso de IA para experiencias de colaboración educativas internacionales
Event: Edutic
Speaker: Sara Camacho
22. El uso de la IA para mejorar el pensamiento crítico de los(as) estudiantes
Event: Edutic
Speaker: Martha Barba
23. Explorando el futuro de la educación: uso de ChatGPT en actividades de Ciencias Sociales y Humanidades
Event: IFE Conference
Speakers: Anahi Molina, Jessica Toro, Elizabeth Marcial, Eunice Costilla
24. EdTech Trends
Event: Roundtable at Venture Café
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
25. IA en el aula: analizando estados cognitivo-afectivos del estudiante para potenciar la educación
Event: IFE Conference
Speakers: Adriana Plata, Andrés Ayala, José Pech, Juan Graña
26. Innovación Educativa en la era de la IA
Event: Conference for Universidad de las Américas
Speakers: Ángeles Aguirre, Ingrid Benavides
27. Innovación Educativa y Educación Digital en el Tecnológico de Monterrey
Event: Conference for Universidad Rafael Landívar
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
28. Innovación educativa, retos y oportunidades de la educación superior
Event: Conference for Universidad Tecnológica Indoamérica de Ecuador
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
29. Innovación y procesos creativos
Evento: International Virtual Exchange Conference 2024
Ponente: Rebeca Alvarado
30. Innovación y transformación educativa para el contexto actual
Event: IDEAD
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
31. Inteligencia Artificial en acción: caso Tec de Monterrey
Event: IFE Conference
Speakers: Beatriz Palacios, Bertha Saldívar, Irving Hidrogo, Carmen Reyes
32. La ciencia abierta para la democratización del conocimiento científico
Media: Red Colombiana de Información Científica
Speaker: Sara Rodríguez
33. La Inteligencia Artificial como potenciador de una mejor práctica docente
Event: Edutic
Speakers: Jessica Toro, Dania Arriola, Gloria Molina, Bárbara Granados
34. ¿Las mejores prácticas hacen la perfección? Aprendizaje organizacional e intercambio de conocimientos para la transformación digital
Event: Conference for THE Campus and Universidad de Washington
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
35. Las tecnologías digitales como promotoras de la calidad y la equidad en la sociedad y la educación
Event: SENAI
Speaker: Leticia Castaño
36. Learning experience in the business discipline integrating innovative technologies: virtual reality with artificial intelligence through an avatar-advisor
Event: XVII International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation
Speaker: Ana Gabriela Rodríguez
37. Liderazgo en la innovación educativa
Event: Conferencia para UNAM
Speaker: Ana Gabriela Rodríguez
38. Mejora la motivación, atención y la percepción que los alumnos tienen sobre su propio aprendizaje utilizando actividades inmersivas y el aprendizaje basado en el metaverso
Event: IFE Conference
Speakers: Rocío Cortez, Jorge Mosqueda
39. Mejorando la experiencia de aprendizaje con la IA del Aprendizaje Adaptativo
Event: IFE Conference
Speakers: Noé Plata, Sadie Guerrero, Leticia Castaño, Laura Castillo, Prabhu
Balashanmugamruce
40. Metodología guiada para el diseño de actividades que integran herramientas de inteligencia artificial generativa en la educación: un estudio piloto que promueve el uso ético y fomenta el pensamiento crítico en estudiantes universitarios
Event: IFE Conference
Speakers: Ingrid Benavides, Yolanda Domínguez, Cynthia López, Olaf Román, Laura Zepeda
41. México a la mitad del camino de los Objetivos de Desarrollo Sostenible: tendencias, avances y retos
Event: International Book Fair (Monterrey)
Speakers: Luis Rojas, Ricardo Fernández
42. Planificación y transformación de las instituciones de educación superior del futuro
Event: Conference for Consorcio de Innovación Académica STHEM (Brasil)
Speakers: Beatriz Palacios, Maribell Reyes
43. Potenciando la innovación educativa en ciencias de la salud con Realidad Mixta
Event: IFE Conference
Speakers: Carlos Presa, Karen Reyes, Ana Gabriela Rodríguez, Mauricio Martínez, Olaf Román
44. Prácticas y estrategias de innovación educativa
Media: Tec Sounds Radio
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
45. Publicaciones EdTech Meta Red México
Event: IFE Conference (featured event panel)
Speakers: Silvia Farías, Claudia Vicario, María Zorrilla, Yara Pérez, María Solórzano
46. Reporte IFE Insights “Educación Digital: una visión estratégica y práctica”
Event: IFE Conference
Speakers: Beatriz Palacios, José Escamilla, Arturo Cherbowski
47. Retos y oportunidades de las tecnologías emergentes en la Educación Superior, líderes en innovación educativa
Event: Conference for Universidad Anáhuac
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
48. Tendencias educativas en la era de la Inteligencia Artificial
Event: Conference for Recrea Academy
Speaker: Maribell Reyes
49. Tendencias educativas para el 2024: diseñando el futuro de la educación
Event: IFE Conference (featured event conference)
Speakers: Myriam Villarreal, Elia Mendoza, Laura Zepeda, Mónica Duarte
50. Tendencias, retos y oportunidades de la educación digital en la era de la Inteligencia Artificial
Event: Conference for IFE Talks
Speakers: Beatriz Palacios, Maribell Reyes, Myriam Villarreal
51. Transformación de la educación superior a través de las estrategias de educación digital y uso de tecnologías emergentes en el contexto de la Inteligencia Artificial
Event: Conference for Association of School and Student Services Managers
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
52. Transformando la educación en el nuevo contexto
Event: Conference for Universidad Cooperativa de Colombia
Speaker: Beatriz Palacios
53. Transformando la educación para futuros visionarios
Event: Conference for OEB
Speaker: Maribell Reyes
54. Uso de IA en el desarrollo de escenarios situados para fomentar el aprendizaje interdisciplinario
Event: Edutic
Speakers: Myriam Villarreal, Noemí Villarreal
55. Uso ético y desarrollo del pensamiento crítico con IA generativa
Event: Conference for IFE Talks
Speakers: Olaf Román, Ingrid Benavides

Vice-Rectory for Educational Innovation and Academic Policy, Tecnológico de Monterrey. México 2025
If you have any questions or would like more information, send us an email to: innovacioneducativa@servicios.itesm.mx Or visit our digital space: innovacioneducativa.tec.mx