



IHME measures the world's health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors. IHME's new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
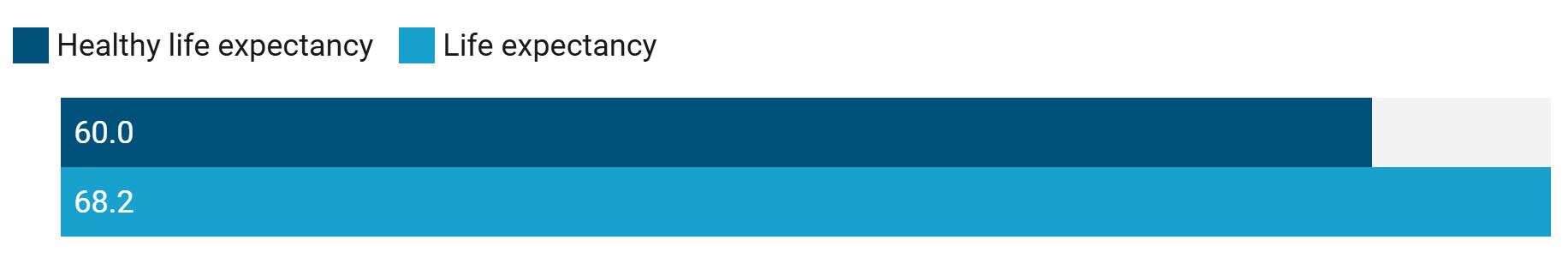
There is a gap of more than 8 years between the ASEAN region's health span and life span.1
Health span versus life span in the ASEAN region, 2021
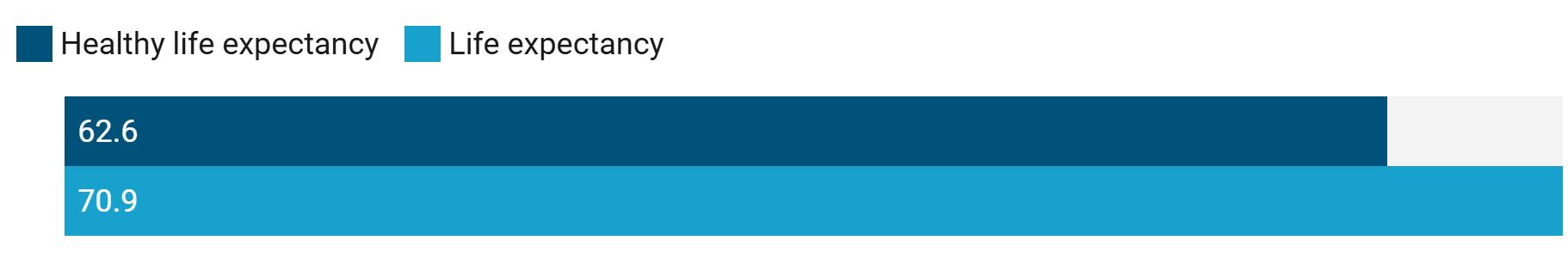
1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
Mortality from cardiovascular diseases, a top health threat in the region, exceeds the global average in most ASEAN countries.2
Cardiovascular disease deaths per 100,000 (age-adjusted), 1990-2021
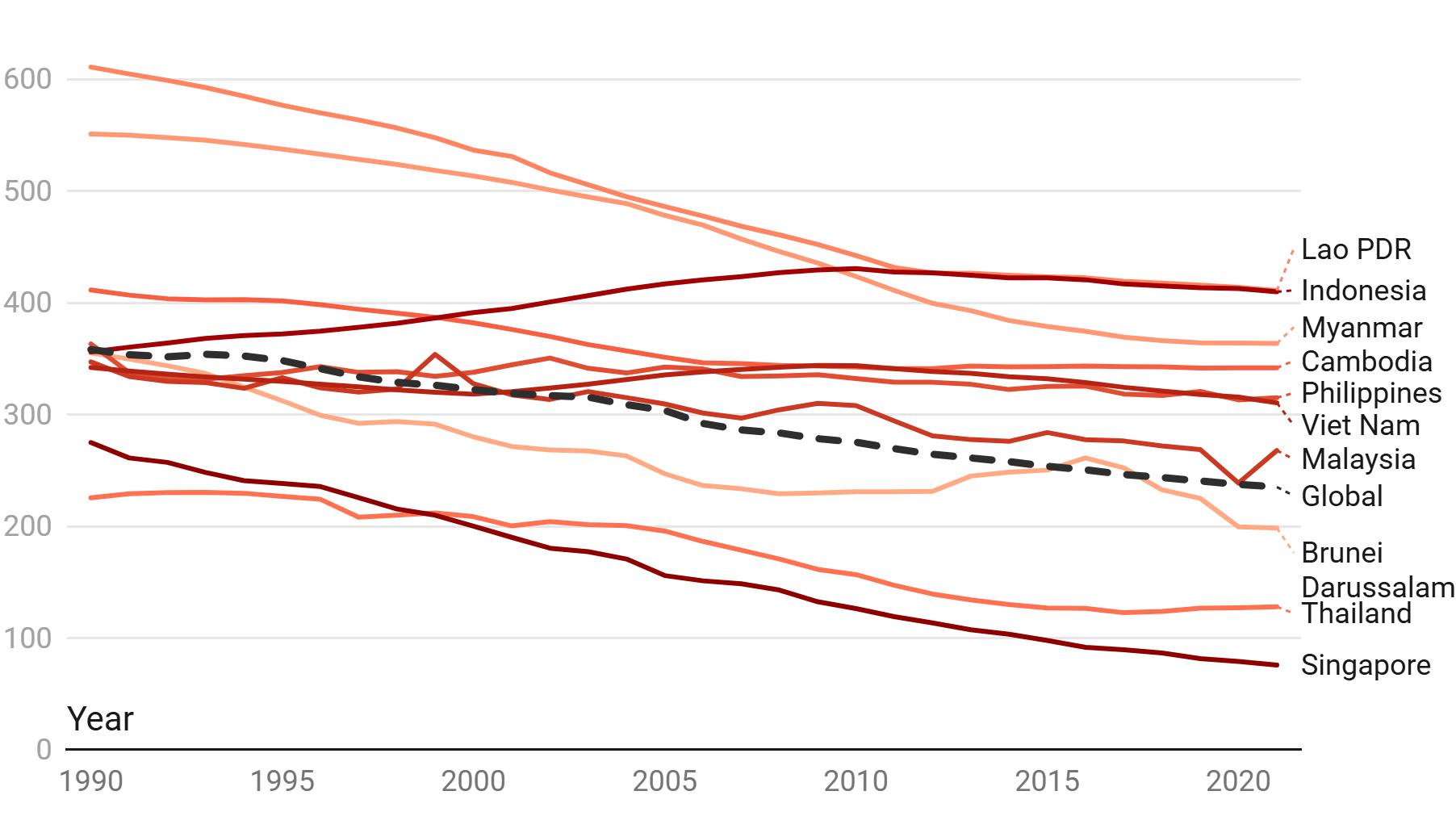

2Based on age-standardized deaths per 100,000 people, all sexes.
Source: https://healthdata.org/node/12445; Lancet Public Health.
Smoking, a leading risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, is high in ASEAN, particularly among males.3
Percentage of males who are smokers (age-adjusted), 2021
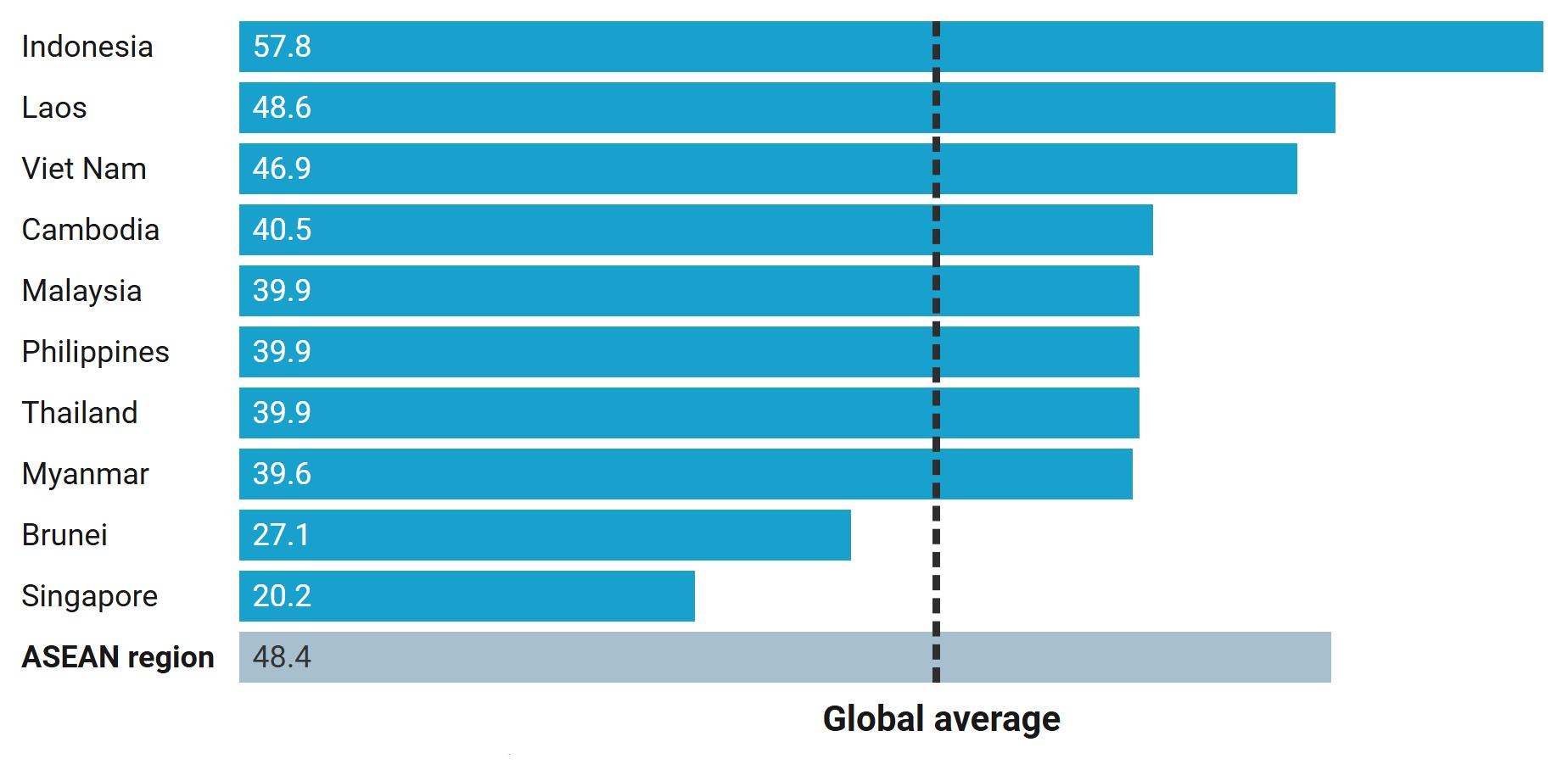
3Based on age-standardized prevalence for males age 15 and older.
Mental disorders are a major driver of poor health in ASEAN, and every country has a high burden.4
Years lived in poor health due to mental disorders, 2021

4Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all ages.

Source: https://healthdata.org/node/12445;
For young people in ASEAN, two mental disorders, anxiety and depression, are particularly burdensome.
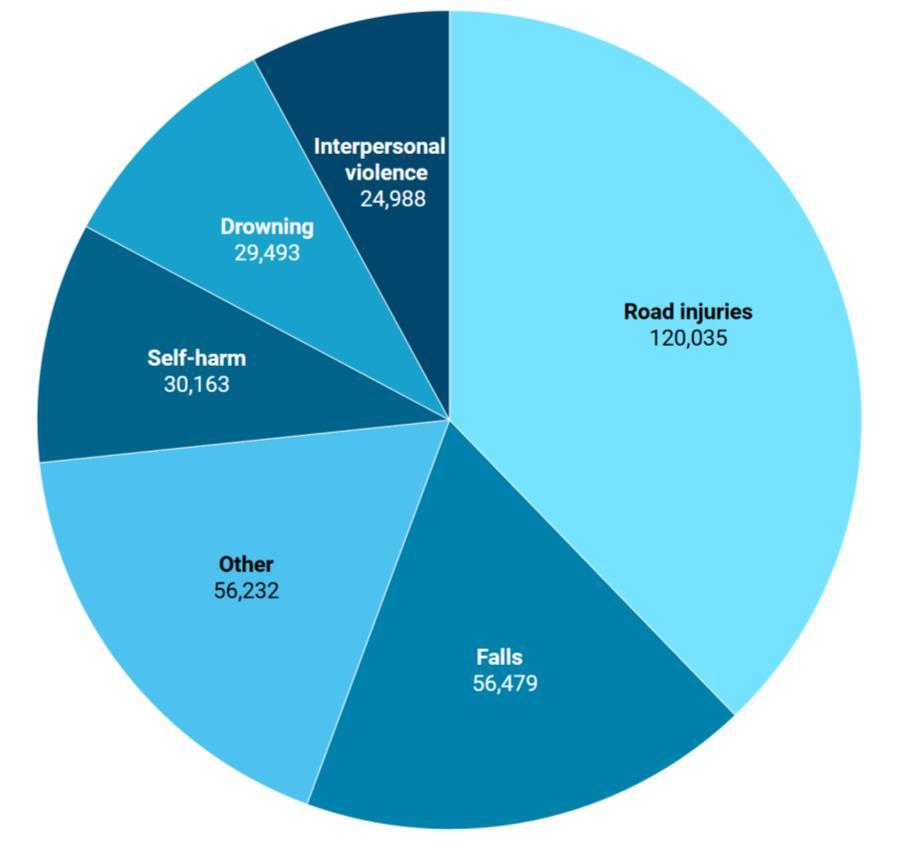
Road injuries, falls, drowning, interpersonal violence, and self-harm were the primary causes of injury in ASEAN.6
Injury deaths inASEAN, 2021
6Based on total deaths.

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice. For more information, contact:
Dr. Marie
Ng
Affiliate Associate Professor marieng@uw.edu
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.



IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of more than 9 years between Brunei Darussalam’s health span and life span.1
Health span versus life span in Brunei Darussalam, 2021

1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in Brunei Darussalam? Diabetes/high blood sugar, cardiovascular diseases, and musculoskeletal disorders rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3Includes disorders such as neck pain and arthritis.
4Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
5Body mass index greater than 25 in adults (≥18 years) and based on the International Obesity Task Force criteria for children (<18 years).

Anxiety and depression are among the top health issues for young people in Brunei Darussalam.
Leading causes 2021 ranking, ages 10-246
1 Low back pain
2 Anxiety disorders 3 Road injuries
4 Headache disorders
5 Depressive disorders
6Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.
Obesity and overweight is a rising threat to health in Brunei Darussalam.
By 2050, IHME projects that 75% of adults will be living with overweight or obesity in Brunei Darussalam.

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice. For more information, contact:
Dr. Marie Ng Affiliate Associate Professor marieng@uw.edu
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.



IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of more than 8 years between Cambodia’s health span and life span.1
Health span versus life span in Cambodia, 2021
1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in Cambodia? Cardiovascular diseases, neonatal disorders, air pollution, and smoking rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3Includes cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases.
4Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.

Anxiety and depression are among the top health issues for young people in Cambodia.
Leading causes 2021 ranking, ages 10-246
1 Road injuries
2 Headache disorders
3 Anxiety disorders
4 Tuberculosis
5 Depressive disorders
6Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.
Smoking among males in Cambodia exceeds the global average.
Percentage of males who are smokers (age-adjusted), 2021


The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice. For more information, contact:
Dr. Marie Ng Affiliate Associate Professor marieng@uw.edu
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.



IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of nearly 8 years between Indonesia’s health span and life span.1
Health span versus life span in Indonesia, 2021

1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in Indonesia? Cardiovascular diseases, neonatal disorders, high blood pressure, and smoking rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3Includes cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases.
4Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the
hierarchy. 5

Leading causes 2021 ranking, ages 10-246 1 Road injuries 2 Headache disorders 3 Anxiety disorders 4 COVID-19 5 Tuberculosis
6Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.
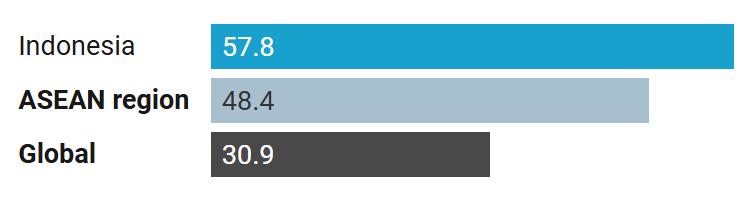
Smoking among males in Indonesia exceeds the global and ASEAN regional average.
Percentage of males who are smokers (age-adjusted), 2021

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice. For more information, contact:
Dr. Marie Ng Affiliate Associate Professor marieng@uw.edu Anxiety disorders are among the top health issues for young people in Indonesia.
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.



IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of more than 7 years between Lao PDR’s health span and life span.1
Health span versus life span in Lao PDR, 2021
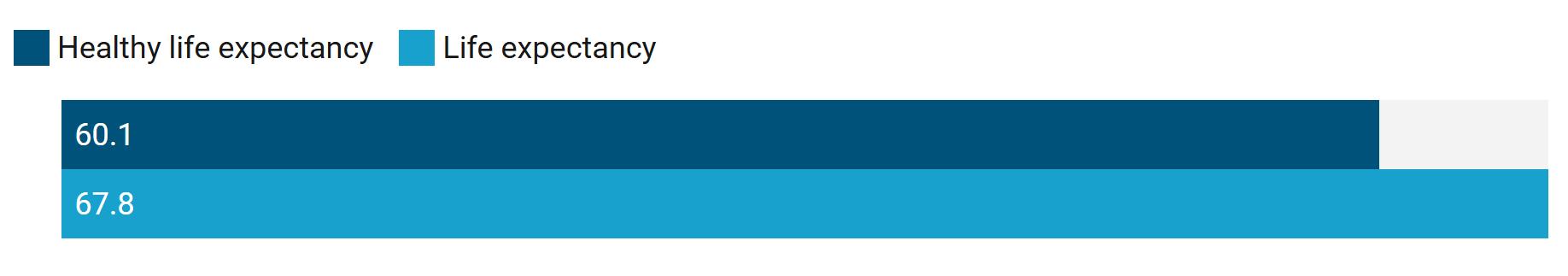
1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in Lao PDR? Neonatal disorders, cardiovascular diseases, air pollution, and high blood pressure rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3 Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
4Particulate matter.

Anxiety and depression are among the top health issues for young people in Lao PDR.
Leading causes 2021 ranking, ages 10-245 1 Road injuries
2 Headache disorders
3 Anxiety disorders
4 Interpersonal violence
5 Depressive disorders
5Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.
Smoking among males in Lao PDR exceeds the global and ASEAN regional average.
Percentage of males who are smokers (age-adjusted), 2021


The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice. For more information, contact:
Dr. Marie Ng Affiliate Associate Professor marieng@uw.edu
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.



IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of more than 8 years between Malaysia’s health span and life span.1
Health span versus life span in Malaysia, 2021
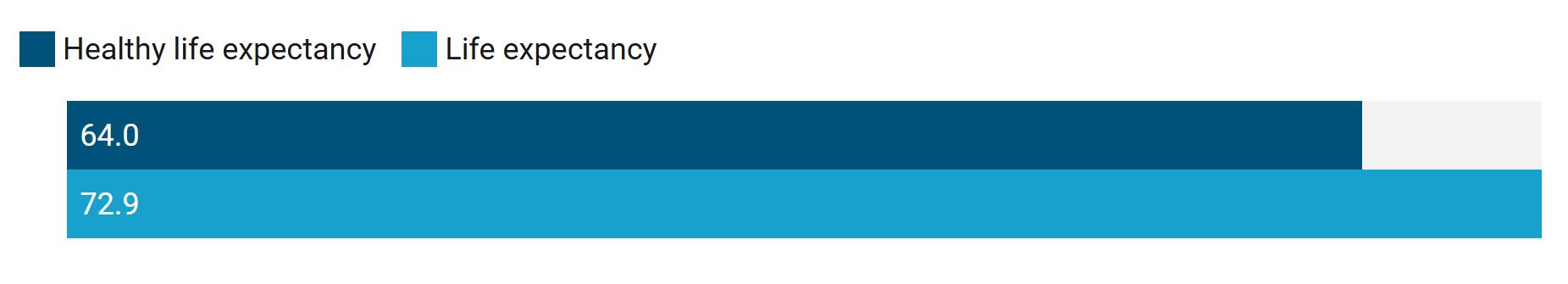
1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in Malaysia? Cardiovascular diseases, lower respiratory infections, and diabetes/high blood sugar rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
4Body mass index greater than 25 in adults (≥18 years) and based on the International Obesity Task Force criteria for children (<18 years).

5Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.
is a rising threat to health
By 2050, IHME projects that 68% of adults will be living with overweight or obesity in Malaysia.

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice. For more information, contact:
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.



IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of more than 8 years between the Philippines’ health span and life span.1
Health span versus life span in the Philippines, 2021

1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in the Philippines? Cardiovascular diseases, neonatal disorders, high blood pressure, and air pollution rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
4Particulate matter air pollution.

issues for young people in the Philippines.
Smoking among males in the Philippines
Percentage of males who are smokers (age-adjusted), 2021
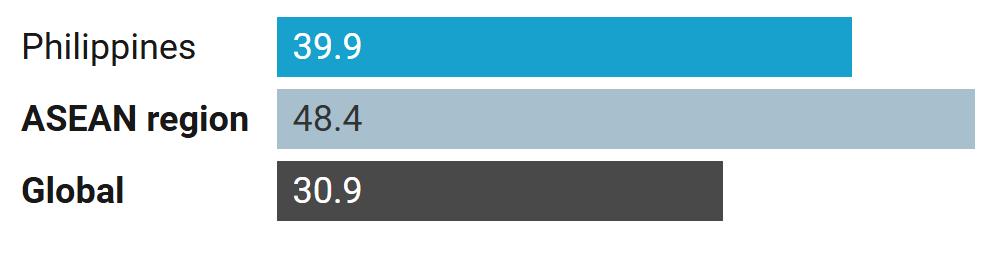
5Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice.
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.

information, contact:


IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of more than 10 years between Singapore’s health span and life span.1
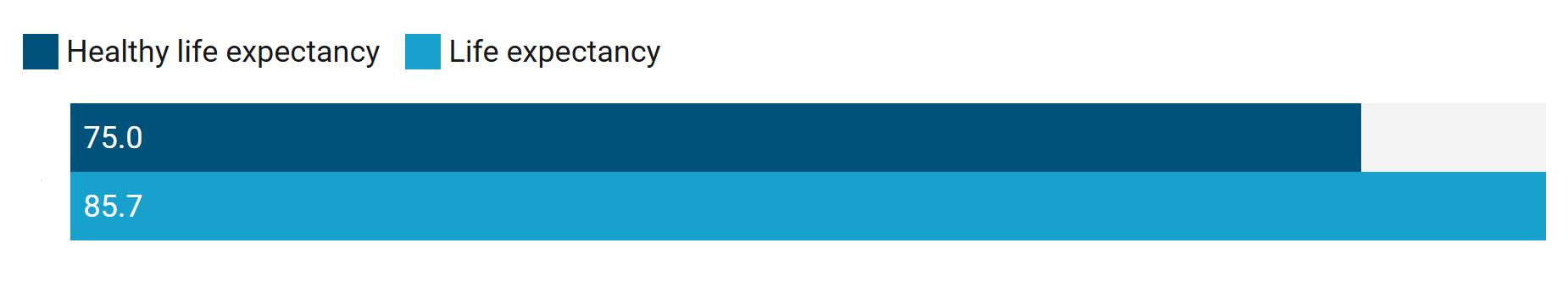
1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in Singapore? Cardiovascular diseases, musculoskeletal disorders, and diabetes/high blood sugar rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3Includes disorders such as neck pain and arthritis.
4Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
5Body mass index greater than 25 in adults (≥18 years) and based on the International Obesity Task Force criteria for
(<18 years).

in Singapore.
7Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.
By 2050, IHME projects that 63% of adults will be living with overweight or obesity in Singapore.

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice.
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.



IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of more than 9 years between Thailand’s health span and life span.1
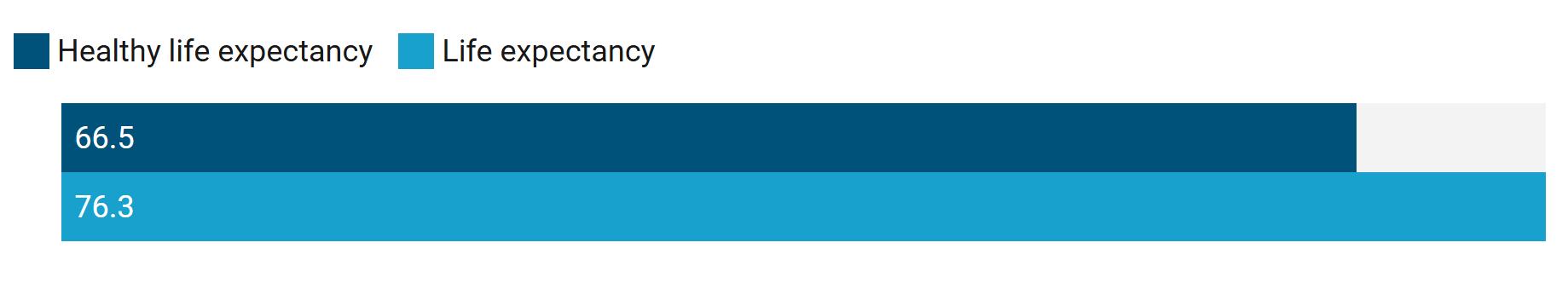
1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in Thailand? Cardiovascular diseases, road injuries, and diabetes/high blood sugar rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3Includes cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases.
4Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
5

matter.
issues for young people in Thailand.
6Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.
By 2050, IHME projects that 61% of adults will be overweight or obese in Thailand.

The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice.
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world. Obesity and overweight is a rising threat to health in Thailand.

information, contact:


IHME measures the world’s health problems in 204 countries and territories. It is the most comprehensive and comparable research on health to date, tracking 400+ diseases, injuries, and risk factors in its Global Burden of Disease (GBD) study. IHME’s new research captures the latest evidence on health in ASEAN countries.
There is a gap of more than 8 years between Viet Nam’s health span and life span.1

1Health span is the number of years someone can expect to live in good health. Estimate is based on healthy life expectancy versus life expectancy at birth for all sexes.
What drives poor health and early death in Viet Nam? Cardiovascular diseases, road injuries, and high blood pressure rank among the top health problems and risk factors.
2Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes, all ages, Level 3 of the GBD hierarchy.
3Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
4Includes cirrhosis and other chronic liver diseases
5Based on risk-attributable disability-adjusted life years in 2021 for all ages and all sexes combined, Level 3 of the

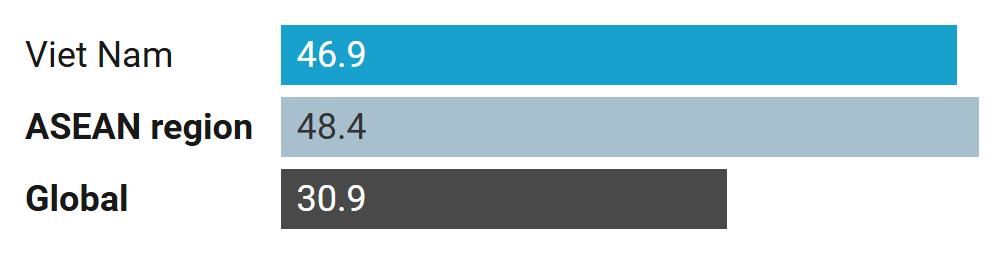
in Viet Nam.
among males in Viet Nam exceeds the
Percentage of males who are smokers (age-adjusted), 2021
7Based on disability-adjusted life years per 100,000 people, all sexes.

information,
The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation is an independent research organization at the University of Washington. Its mission is to deliver to the world timely, relevant, and scientifically valid evidence to improve health policy and practice.
The NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine is Singapore’s first and largest medical school. Its enduring mission centers on nurturing highly competent, values driven and inspired healthcare professionals to transform the practice of medicine and improve health around the world.
