1 minute read
COMPONENT OPERATION / HST Motor
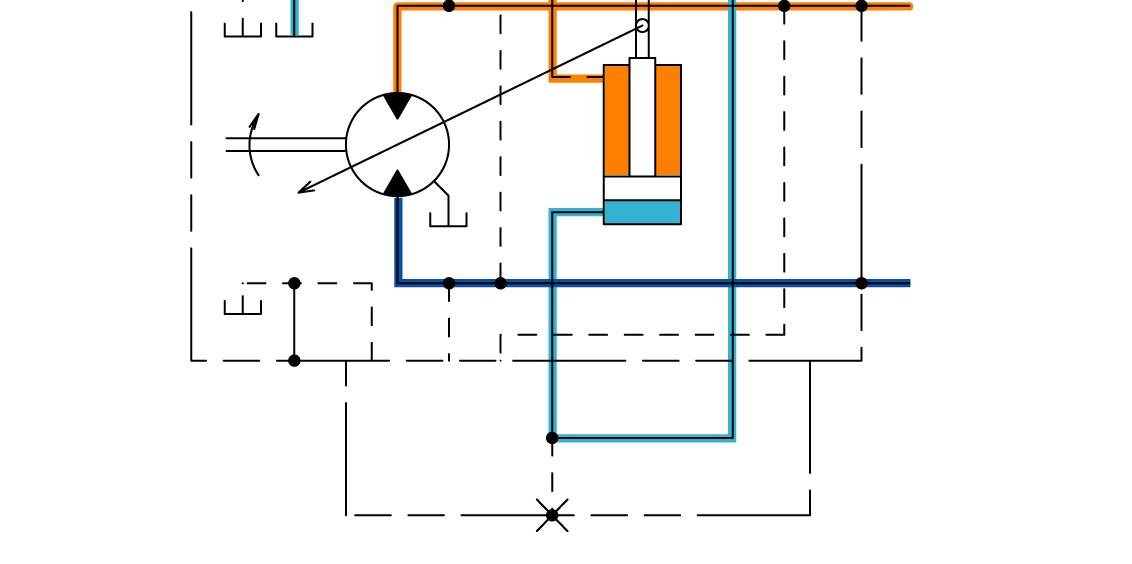
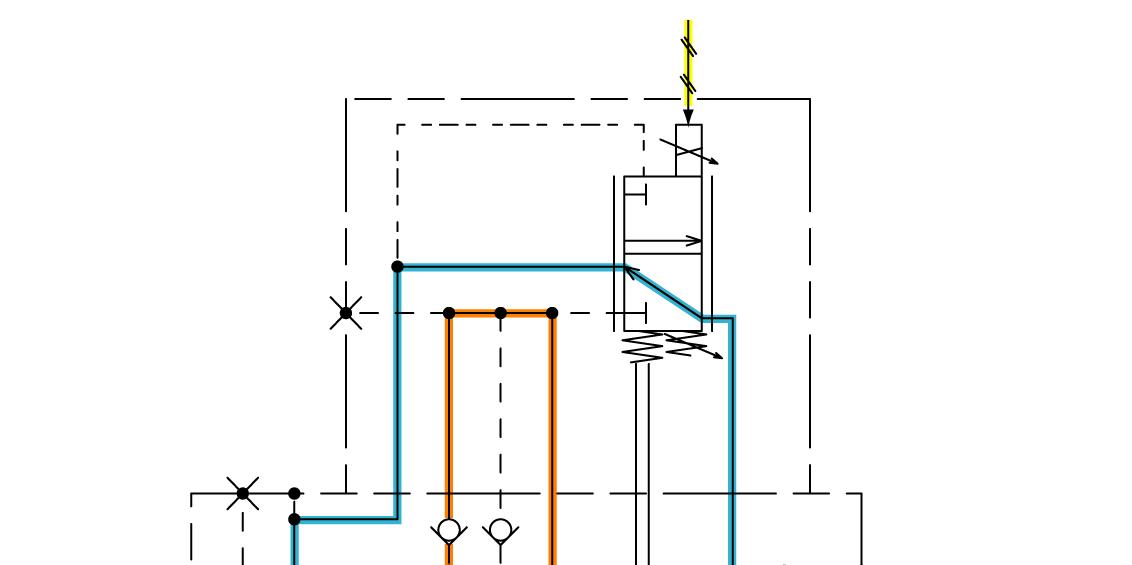
Displacement Angle Control (From Large Displacement Angle to Small Displacement Angle)
1. One pressure oil from port B (or port A) flows to the plunger through the valve plate. The other pressure oil opens the check valve, and flows to the spool and the small chamber of the servo piston.
2. The EP motor solenoid valve receives the signal from the HST control unit. When the spool moves upward, pressure oil in the large chamber of the servo piston flows to the hydraulic oil tank through the spool.
3. Therefore, the servo piston moves downward and the motor displacement angle decreases.
4. Consequently, the motor rotates at fast speed.
NOTE: The illustration shows the circuit when traveling forward.
COMPONENT OPERATION / HST Motor
Displacement Angle Control (From Small Displacement Angle to Large Displacement Angle)
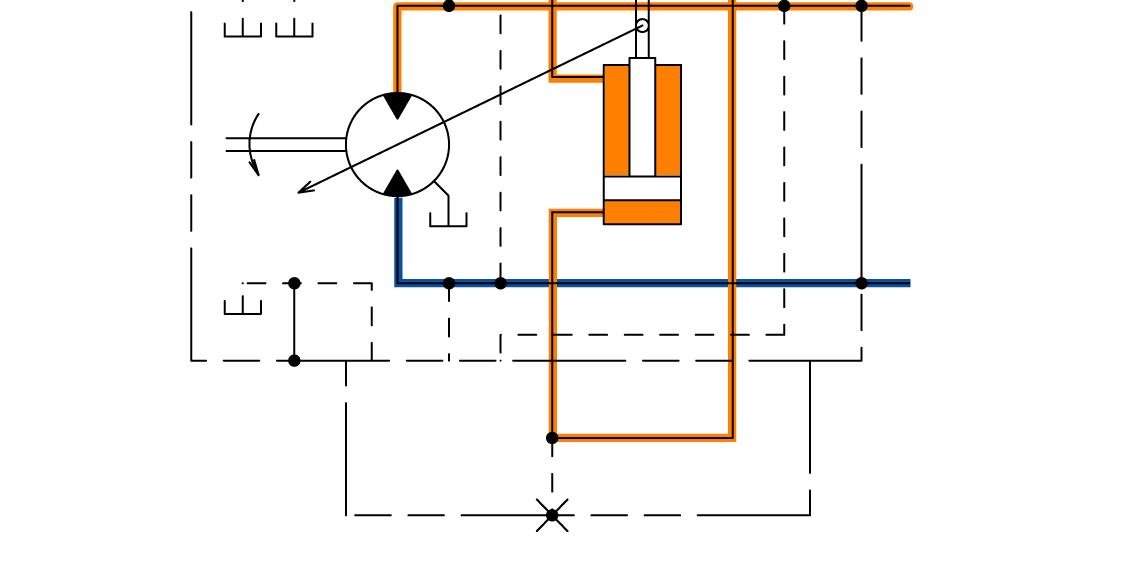
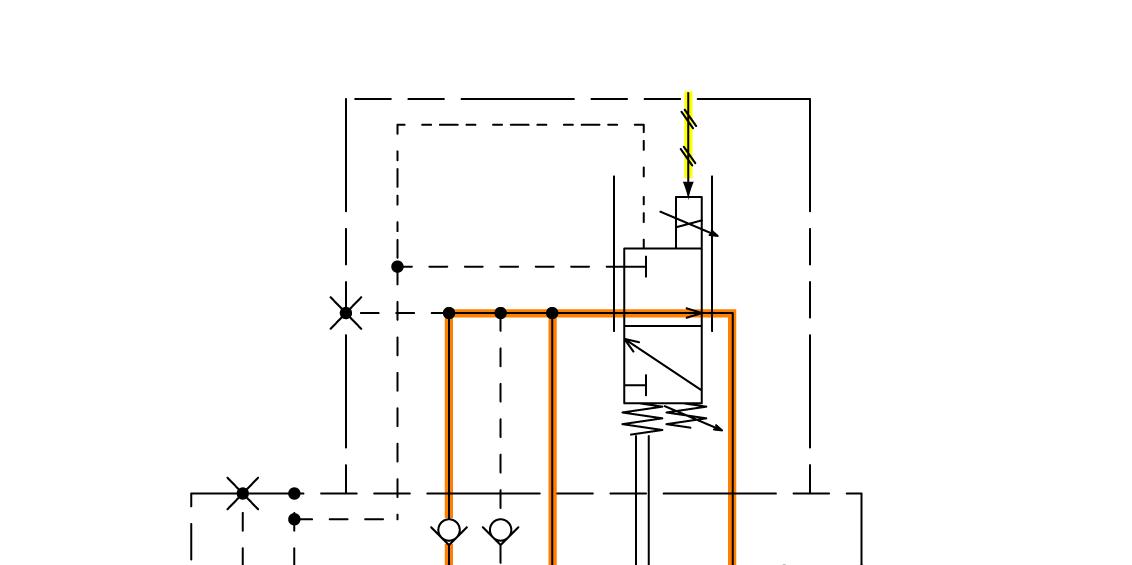
1. One pressure oil from port B (or port A) flows to the plunger through the valve plate. The other pressure oil opens the check valve, and flows to the spool and the small chamber of the servo piston.
2. The EP motor solenoid valve receives the signal from the HST control unit. When the spool moves downward, pressure oil from port B (or port A) flows to the large chamber side of the servo piston through the spool.
3. As for the pressure receiving area in the servo piston, as that in the large chamber is larger than that in the small chamber, the servo piston moves upward to the position where the servo piston balances with the balance spring so that the motor displacement angle increases.
4. Consequently, the motor rotates at slow speed.
T3-5-8





