67 minute read
5Maintenance
5.1Access doors for maintenance
5.1.1Overview of access doors
10 Motor hood 120 Left doors
11 Motor hood 140 Right door
60 Motor hood 220 Front left hood
80 Right hood 220 Front left side door
Access doorLocking mechanismAccess to:
10 or 60
Motor hoodGas pressure spring, with mechanical holding device
–Electric motor
11Radiator hoodGas pressure spring–Radiator
80Right hoodGas pressure spring and screwed part –Control oil unit –Hydraulic pump
120Left side doorsMechanical holding device –Switch cabinet
140Right side doorMechanical holding device –Control oil unit –Hydraulic pump
220Front left hoodGas pressure spring–Heating box
Tab.
Access doors
Access doorLocking mechanismAccess to:
230Front left side door Mechanical holding device –Dryer-collector unit –Heater fluid drain plug –Additionnal socket
Tab.
The machine has 8 access doors for maintenance. For safety reasons, the locks integrated in the handles 4 must be unlocked before starting to work with the machine. The right hood 80 is a screwed part which opening is not necessary in the limits of usual maintenance works.
5.1.2Door retaining rods
Caution!
Access doors can close accidentally and trap the operator or maintenance personnel.
After you have opened the access doors, latch them using the retaining rods..
To stop the access doors from moving unintentionally (eg. due to wind), open them fully and allow the door lock (see arrow) to latch in.
5.2Cleaning machine
The machine should be cleaned before carrying out any maintenance or repair work. In particular, the connections and screws should be cleaned of oil, fuel and residue of cleaning agents.
Note!
High-pressure water jet cleaners (steam cleaners) can damage the coating. Do not use high-pressure water jet cleaners during the first two months after commissioning (or after recoating).
Observe the prescribed safety distances.
Care for rubber components
Before cleaning the machine:
Before cleaning the machine with water or with a steam cleaner (high-pressure water jet cleaner), carry out the following tasks to protect the equipment against penetrating water.
Lubricate all bearing points, bolt connections and the slewing ring; if necessary, use the central lubrication system to do this.
Cover or seal all openings that must be protected against penetrating water for safety reasons (particularly at risk of damage are electric motors, electric components, switch cabinets, plug connections, measuring sensors and air filters).
Cleaning:
Use flint-free cleaning cloths.
Do not use aggressive detergents or flammable liquids.
When cleaning the engine compartment, ensure that the temperature sensor of the fire alarm and extinguishing systems (if installed) are not accidentally brought into contact with the hot cleaning solution,
After cleaning:
Remove all seals and covers. Check all fuel, engine oil and hydraulic lines for leakage, loose connections, chaffing and damage.
Repair any defects without delay.
Lubricate all bearing points, pin connections and the slewing ring to remove any water that might have been penetrated. If required, renew the preservation layer (anti-corrosion protection) on components and surfaces.
5.3Care for rubber components
The service life of rubber seals can be prolonged by treating them with a rubber care product.
Clean and regularly treat the rubber seals on doors and panelling elements with a care product. This helps prevent premature wear and protects the rubber seals during the cold season.
Recommended care products: Silicone, talcum powder, deer tallow
5.4Lubricants and fluids
5.4.1General information
Observe the instructions for lubricants and fluids. Lubricate the machine and change the oils at the prescribed intervals. For more information, see lubrication chart and inspection and maintenance schedule.
Keep workplaces for these activities clean. This enhances the service life and reliability of the machine.
All work on the machine must be carried out while it is standing on firm and level ground.
Switch off the electrical engine and open the main isolating switch, outside of the machine at the customer power supply connection.
Clean lubricating nipples before adding grease.
Clean all filling points and the area around them before opening the caps and screws.
The oil should be changed while it is at operating temperature.
After each oil change or refilling, check the fill level in the respective unit (the specified fill levels are guide values).
Collect old lubricants and fluids in suitable containers and dispose of them according to the applicable statutory regulations.
5.4.2Filling volume and lubricant chart
Recommended lubricants * = Guide values
Recommended fuels and process chemicals
SymbolDesignation
For the oil change interval, observe the instructions of the operating manual.
Filling point
Slewing gear transmission
Splitterbox
Check gear oil level
Check hydraulic oil level
Lubrication point
Carry out a manual lubrication
Carry out a semi-automatic lubrication
5.5Lubricants and fluids specification
5.5.1Lubricant for motor bearing
See type plates at the electric motor.
G1 Recommended lubricant type
G2 Lubricant quantity (cm3)
G3 Lubricant change intervals (hours) at ambient temperature (at 50 / 60 Hz)
Caution
The standard grease is ESSO UNIREX N3. We recommend using the same product for subsequent lubrication at the prescribed intervals. Never mix different lubricants
5.5.2Heating fluid system
General recommendations
The heating system works only properly when pressurised. It is therefore imperative that it is kept clean and sealed at all times and that the required heating fluid level is maintained.
Corrosion inhibitors/antifreeze agents approved by LIEBHERR ensure proper protection against frost, corrosion and cavitation without causing damage to seals and hoses and without foaming.
Heating fluids that contain unsuitable corrosion inhibitors or antifreeze agents or that have been prepared incorrectly might cause failure of assemblies and component parts in the heating circuit due to cavitation or corrosion. Heat-insulating deposits on components that conduct heat might result in overheating and consequently failure of the motor.
Water (fresh water)
Clear and clean water free of particles that meets the following chemical requirements is suitable for use as a heating fluid.
Do not use sea water, brackish water, brine or industrial wastewater.
DesignationValue / unit
Total alkaline earth metals (water hardness) 0.6 to 3.6 mmol/l (4 to 25°e) pH at 20°C6.5 to 8.5
Chloride ion concentrationmax. 80 mg/l
Sulphate ion concentrationmax. 100 mg/l
Tab. 5-3 Fresh water quality
DesignationValue / unit
Total alkaline earth metals (water hardness) 0.6 to 2.7 mmol/l (4 to 19°e) pH at 20°C6.5 to 8.0
Chloride ion concentrationmax. 80 mg/l
Sulphate ion concentrationmax. 80 mg/l
Tab. 5-4 Fresh water quality with use of DCA 4*
* = Diesel Coolant Additives
Water analysis results are available from the local authorities.
Mixing ratio for heating fluid
The heating fluid must contain min. 50% corrosion inhibitor and antifreeze agent at all times of the year
Tab. 5-5 Permissible mixing ratio (for all seasons)
Fig. 5-5 Temperature-based mixing ratio of water + corrosion inhibitor / antifreeze agent
B Corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze agent concentration in heating fluid
Permissible corrosion inhibitors/antifreeze agent
Note!
Improper mixing of different products might negatively affect the properties of the heating fluid and cause damage to the heating system.
Use only approved products. Do not mix different products.
Never mix products containing s ilicone with silicone-free products.
If the recommended LIEBHERR product is not available locally.
Concentrate
Product nameManufacturer
Liebherr Antifreeze ConcentrateLiebherr
Ready-mixed corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze agent (premix)
Product nameManufacturer
Liebherr Antifreeze MixLiebherr
Premix = ready-mixed product (50% water and 50% corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze agent)
Approved corrosion inhibitors without antifreeze agent
Note!
Improper mixing of different products might negatively affect the properties of the heating fluid and cause damage to the heating system.
Use only approved products. Do not mix different products.
Never mix products containing s ilicone with silicone-free products.
If the recommended LIEBHERR product is not available locally:
In exceptional circumstances and at ambient temperatures that are always above the freezing point, e.g. during use in tropical regions where there are no corrosion inhibitors/antifreeze agents available, the following inhibitors must be added to the heating fluid:
–DCA 4 (Diesel Coolant Additives 4)
–Caltex / Chevron / Havoline / Total product
In this case, the heating fluid must be changed annually.
As part of routine maintenance work, check the concentration and correct it, if necessary.
Product nameManufacturer
DCA 4 Diesel Coolant AdditivesFleetguard / Cummins Filtration
Caltex CL Corrosion Inhibitor ConcentrateChevron Texaco
Chevron Heavy Duty Extended Life Corrosion Inhibitor Nitrite Free (ELC)
Chevron Texaco
Havoline Extended Life Corrosion Inhibitor (XLI)Chevron Texaco
Total WT SupraTotal, Paris copyright by
5.5.3Checking heating fluid, adjusting mixing ratio
Heating fluid with corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze agent
The mixing ratio must at all times conform to a frost protection of -37°C. Take an heating fluid sample and analyse it with a suitable method for the frost protection temperature. Adjust mixing ratio, if the frost protection is not sufficient.
Determining refill volume - example for -15°C:
1 Corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze agent (concentrate), refill volume in litres
3 Max. frost protection temperature of the heating system -°C
2 Auxiliary line
4 Heating fluid volume in system in litres
Determining refill volume - example for -15°C / 50 litres of heating fluid: Based on the measured frost protection temperature (-15°C) follow the auxiliary line 2 from the left bottom corner to the vertical line 4 (heating fluid volume – 50 litres) and from there horizontally to the left scale. The refill volume 1 is 14.8 litres.
This corresponds to the refill volume of corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze agent (concentrate) to be added in order to again achieve a frost protection temperature of -37°C.
Correcting mixing ratio
The necessary refill volume is known.
To correct the mixing ratio, at least the (previously determined) volume must be drained from the heating system.
Add the determined volume of corrosion inhibitor/antifreeze agent (concentrate).
To achieve the required heating fluid level, add some of the previously drained heating fluid.
Heating fluid with corrosion inhibitor (without antifreeze agent)
When using DCA 4:
Take an heating fluid sample and analyse the concentration using a Fleetguard CC 2602 M testing kit.
If the concentration is incorrect, correct the mixing ratio (according to the values indicated by the test kit).
When using Caltex / Chevron / Havoline / Total:
The mixing ratio must always show a Brix value of 2.8-0.9+0.9 %. This corresponds to 5 to 10% of corrosion inhibitor and 90 to 95% of water.
Take an heating fluid sample and analyse with a Gefo refractometer.
Refractometer:
–Adjusting screw for adjustment to 0-line (water line)
–Adjustment of acuity by turning the eyepiece
–Soft edge of eyepiece
–Sturdy metal housing
–Safe handling thanks to rubber jacket
Measuring procedure:
Carefully clean the lid and prism.
Apply 1 to 2 drops of sample liquid onto the prism. Close the lid. The liquid is distributed. Hold the device against a light-coloured background and look through the eyepiece.
Adjust focus on scale and read the value at the blue separating line.
1 Corrosion inhibitor, refill volume in litres
2 Auxiliary line
3 Refractometer value in %Brix
4 Heating fluid volume in system in litres
Determining refill volume - example for 1% Brix / 50 litres of heating fluid: Based on the measured value (1%Brix), follow the auxiliary line 2 from the left bottom corner to the vertical line 4 (heating fluid volume – 50 litres) and from there horizontally to the left scale. The refill volume 1 is 2.4 litres.
This corresponds to the refill volume of corrosion inhibitor (concentrate) to be added in order to again achieve a value of 2.8% Brix.
Correcting mixing ratio
The necessary refill volume is known.
To correct the mixing ratio, at least the (previously determined) volume must be drained from the heating system.
Add the determined volume of corrosion inhibitor.
To achieve the required heating fluid level, add some of the previously drained heating fluid.
5.5.4Hydraulic oil
Hydraulic oils must meet the requirements outlined below.
Maximum water content of hydraulic oil: <0.1%
Liebherr hydraulic oil
LIEBHERR recommends using the following hydraulic oils in its machines (depending on temperature range):
A Ambient temperature
B Cold-start range with mandatory warm-up
C Operating range
Liebherr Hydraulic Plus and Liebherr Hydraulic Plus Arctic are suitable for both long-term use and use in environmentally sensitive areas.
If LIEBHERR oils are not available locally, use one of the engine oils listed in section "Engine oils for use as hydraulic oils" (before choosing an oil, contact the respective customer service department).
Use only LIEBHERR hydraulic oils. The use of other oils is not permitted.
Warm-up instruction
The black bar B indicates ambient temperatures that are up to 20°C below the operating range C.
For cold starting at an ambient temperature below range B, the following warm-up instruction for the hydraulic oil applies:
1. Start the electrical motor.
2. Carefully activate the working hydraulics. Operate the hydraulic cylinders and move them briefly to the stop.
3. After approx. 5 minutes, actuate the travel hydraulics. Total warm-up time: approx. 10 minutes.
For cold starting at lower ambient temperatures, follow the warm-up instruction below: Before starting the motor, warm up the hydraulic oil tank. Then proceed according to the warm-up instruction in 1
Biodegradable hydraulic oils
Caution!
Do not mix hydraulic oil products!
When mixing different ester-based biodegradable hydraulic oils or mixing such products with mineral oils, aggressive chemical reactions might occur, causing damage to the hydraulic system.
Therefore never mix biodegradable hydraulic oils from different producers, and never mix bio hydraulic oils with mineral oils!
LIEBHERR recommends using the following hydraulic oils in its machines (depending on the temperature range):
Liebherr Hydraulic Plus or Liebherr Hydraulic Plus Arctic
These products are polyalphaolefins (HEPR) conforming to CEC-L-33-A-93, and are biodegradable.
When using these hydraulic oils, bypass filtration might be omitted.
If these oils are not available locally, use a fully saturated hydraulic environmental ester synthetic oil (HEES fluid) (before choosing an oil, contact the respective customer service department).
Caution!
The use of synthetic ester-based oils without bypass filter causes damage to the hydraulic system!
If synthetic ester-based oils are to be used, bypass filtration is mandatory, as the water concentration in the oil must be kept below 1000 ppm (0.1%).
Always use a bypass filter (optional equipment).
For such oils, we recommend replacing the hydraulic hoses every 4000 operating hours or at least every 4 years.
Do not use vegetable oils, as they do not possess the necessary thermal stability. The use of polyglycols is not permissible, as they cause damage to paintwork.
When using third-party products, we advise customers to request a certificate from the oil manufacturer, confirming that the product meets the above specifications.
Oil type
Oil change, oil analysis and filter change Oil change
Note!
Liebherr recommends carrying out regular oil analyses (see chapter "Oil analysis").
Oil change
LIEBHERR mineral oil
Liebherr Hydraulic HVI
Liebherr Hydraulic Basic 68
Liebherr Hydraulic Basic 100
Liebherr-PAO**
Liebherr Hydraulic Plus
Liebherr Hydraulic Plus Arctic
Not for use in environmentally sensitive areas
For use in environmentally sensitive areas (only permissible with oil analysis*) without oil analysis with oil analysis* (optional) every 3000 hevery 6000 h- *** every 4000 hevery 8000 hevery 8000 h
Third-party product - mineral oilevery 2000 hevery 2000 h- ***
Third-party product - fully saturated synthetic ester - ***- ***every 2000 h
Tab. 5-6 Oil change intervals
*If the result of the oil analysis is satisfactory, you may continue using the oil for a longer period. If the result of the oil analysis is negative, change the oil immediately.
**PAO = polyalphaolefin
***Do not mix products
Use in environmentally sensitive areas
Machines operated in such areas must be filled with biodegradable hydraulic oil.
If the machine is operated for less than 1000 hours per year, an oil sample must be taken at least once a year. If a hydraulic oil is used for a prolonged time, it must be changed at least every 4 years (mineral oils and fully saturated synthetic esters) or every 6 years (Liebherr-Plus oils).
If the machine is not in use for a period of more than 6 months, carry out an oil analysis before restarting it.
Oil analyses
For regular oil analyses, LIEBHERR recommends contracting the specialist company OELCHECK and changing the oil when indicated by the test results in the lab report.
–Yellow kit for biodegradable hydraulic oils
–Green kit for mineral oils
See also customer service and product information.
Reasons for regular oil analyses:
–Reduction of costs thanks to prolonged oil change intervals
–Detailed information regarding the hydraulic system, its component and the medium
–Better protection of resources and the environment
Oil type
Oil sampling / operating conditions
Oil sampling in machines operated under normal operating conditions
Oil sampling in machines operated under extremely dusty conditions
The oil sampling interval is determined by the actual operating conditions (for more information, see chapter "Dust-intensive applications, reduction of oil contamination")
Tab. 5-7 Symbols: Oil sampling depending on operating conditions
Oil sampling
No use in environmentally sensitive areas (oil analysis mandatory) Use in environmentally sensitive areas (oil analysis mandatory)
LIEBHERR mineral oil
Liebherr Hydraulic HVI
Liebherr Hydraulic Basic 68
Liebherr Hydraulic Basic 100
Liebherr-PAO*
Liebherr Hydraulic Plus
Liebherr Hydraulic Plus Arctic every 1000 hevery 250 h- **- ** every 1000 hevery 250 hfirst at 0 h, then every 1000 h first at 0 h, then every 250 h
Third-party product - mineral oil first after 1000 h, then every 500 h every 250 h- **- **
Third-party product - fully saturated synthetic ester - **- **first at 0 h, then every 500 h first at 0 h, then every 250 h
Tab. 5-8 Oil sampling depending on operating conditions
*PAO = polyalphaolefin
**Do not mix products
Filter change
Filter change / operating conditions
Filter change in machines operated under normal operating conditions
Filter change in machines operated under extremely dusty conditions
The filter change interval is determined by the actual operating conditions (for more information, see chapter "Dust-intensive applications, reduction of oil contamination")
Tab. 5-9 Symbols: Filter change depending on operating conditions copyright by
Change of return filter (use only LIEBHERR filters) every 1000 hevery 500 h
Tab. 5-10 Filter change depending on operating conditions
Change of bypass oil filter
LIEBHERR filterFilters from other manufacturers every 2000 h or as indicatedevery 500 hevery 250 h
Tab. 5-11 Filter change depending on operating conditions
Dust-intensive applications, reduction of oil contamination
If the machine is normally operated with a hydraulic hammer or under similar conditions (considerable dust generation), the hydraulic oil might become more contaminated than under normal working conditions.
To prevent premature wear of the hydraulic components, the oil change and sampling intervals must be shorter.
–The filter cartridge(s) in the return filter must be replaced every 500operating hours and after every hydraulic oil change.
–Use 10-µm filter cartridges instead of the standard 20/5-µm cartridges.
–The 2-µm breather filter must be replaced every 500operating hours and at every hydraulic oil change.
Machines delivered with hydraulic hammer attachment and retrofitted hydraulic hammer kits are already fitted with 10-µm filter cartridges in the return filter. Please take this into account when ordering spare parts.
5.5.5Lubricants for gearboxes
Quality
Recommended lubricant
Specification
Liebherr Gear Basic 90 LSAPI: GL-5
MIL-L: 2105 D
ZF: TE-ML 05C, 12C, 16E, 21C
Liebherr Gear Plus 20W-40API: Niveau von GL4
ZF: TE-ML 05F, 06K, 17E
Liebherr Gear Hypoid 90 EPAPI: GL 5
MIL-L: 2105 B, C, D
ZF: TE-ML 05A, 12A, 16C, 17B, 19B
Recommended lubricant Specification
Liebherr Hypoid 85W-140 EPAPI: GL-5
MIL-L: 2105 D, PRF-2105 E
ZF: TE-ML 05A, 07A, 16D, 21A
Liebherr Hydraulic-Gear ATFGM: Dexron II D
ZF: TE-ML 03D, 04D, 11A, 14A, 17C
Liebherr Syntogear Plus 75W-90API: GL-4, GL-5, MT-1
MIL-L: 2105 D, PRF-2105 E
ZF: TE-ML 02B, 05B, 07A, 12B, 16F, 17B, 19C, 21B
Tab.
If LIEBHERR oils are not available locally, use an oil that conforms to the specifications (before choosing an oil, contact our customer service department).
Viscosity
A Ambient temperature
1 Use in gearboxes
2 Use in automatic transmissions
3 Use in pump distributor gear systems
* If the pump distributor gear is equipped with an oil cooler, the oil is not suitable for the marked temperature range (shaded area).
The choice of the lubricating oil viscosity is based on the SAE classification (Society of Automotive Engineers). The SAE classification does not provide any indication as regards the quality of a lubricating oil. The relevant factor for the correct choice of SAE class is the ambient temperature. Incorrect viscosity can impair the operation of axles and gearboxes.
The temperature ranges shown in the diagram are approximate ranges that might temporarily be exceeded.
5.5.6Grease Quality
Recommended lubricant
Specification
Liebherr Universalfett 9900Soap-base grease (lithium complex)
KPF 2 N - 25 (DIN 51502)
NLGI grade: 2 (DIN 51818)
VKA welding force: > 6000 N (DIN 51350 / 4)
- Liebherr Universalfett Arctic (for low-temperature operation)
Soap-base grease (lithium complex)
KPFHC 1 N - 60 (DIN 51502)
NLGI grade: 1 (DIN 51818)
VKA welding force: > 5500 N (DIN 51350 / 4)
The grease is used for both automatic and manual machine lubrication. it is supplied by the central lubrication system or through lubrication nipples to the respective lube points.
Examples:
–Slewing ring bearings
–Crown gears, geared wheels
–Attachments
Operating temperature
A Grease temperature
* The grease is not suitable for the temperature range (shaded), if used in a central lubrication system.
** The grease may only be within the temperature range (shaded) for short periods of time. Peak temperatures of max. 200 °C (392 °F) are possible.
5.5.7Lubricants and care products for electrical and mechanical components
Medium, purposeProduct (manufacturer)
Contact spray for slip ringsCramolin
Lubricant for pistons, piston nuts and for the mounting of piston rod bearings at hydraulic cylinders
Special corrosion inhibitor for mounting recesses of sealing elements at hydraulic cylinders
Gleitmo 800
5.6Electric motor
5.6.1Type plate
5.6.2Routine maintenance
Note
Regular and preventive maintenance are describe in the attached user manual of the electric motor.
Caution
Before operating on the motor, ensure that :
–The motor is standing still and disconnected from the main power.
–There is no residual voltage.
Carefully establish the failure causes (blockage of rotor, mains phase failure, shut-down by thermal protection, lack of lubricant, etc.).
Inspection after commissioning
After approx. 50 operating hours and every 1000 operating hours, check the mounting bolts of the motor and the coupling element for proper tightening.
Mounting
DimensionClass[
Lubricating motor bearings
Note
–The greasing interval, the quantity and quality of the grease are indicated on the type plates.
–The grease to be used must be of a suitable grade, new-made and clean (no contamination by dust, water or other substances).
Caution
–The maximum interval between 2 lubrication procedures must not exceed 2 years, even if it is a storage period or an extended stop.
–The application of excessive amounts of grease can cause overheating of the bearing and can damage it.
Fig. 5-14 Lube points of the electric motor
The electric motor is switched on.
Connect the hand lubricating pump to the lube point. Every 30 seconds, release a little grease until the specified quantity is applied. Remove the hand lubricating pump
Repeat the procedure at the second lube point.
Inspection of bearings
Check the bearing for damage, in the event of:
–A noise or unusual vibration,
–Excessive heating of the bearing, despite of correct lubrication.
Damaged bearings must be replaced without delay in order to prevent more serious damage to the motor and the driven elements.
Cleaning
Before cleaning, ensure that the motor is completely tight (terminal box, condensate bores, etc.).
Note
–Dry cleaning (vacuum cleaner or compressed air) is always preferable to wet cleaning.
–Use a reduced pressure and clean from the centre of the motor to outwards to ensure that dust and other particles do not enter the shaft seal rings.
Ensure that the motor is free of dust and foreign objects who might block the fan hood or the cooling fins of the housing. Check that the extractor hood and the hoses are free of foreign objects and dust. Their presence in the motor aeration circuit lead to an overheating of the motor and reduce considerably its lifecycle.
5.6.3Reversible fan (option) General
The option "reversible fan" allows an easy cleaning of the cooler cores by inverting the way of rotation of the fan.
Cleaning the cooler
Danger !
Before checking the condition of the cooler, you must absolute shut off the engine and wait until the fan does not turn any more.
With running engine, depress the push button S160 and keep it depressed. The fan stops progressively (approx. 15 seconds), then the control light H90 lights up and the fan starts rotating in the opposite way.
In case of a diesel engine, bring it to high idle while keeping the push button S160 depressed.
Let the engine run at high idle for approx. 1 minute (max. 3 minutes).
Release the push button S160
The control light H90 goes out, the fan stops progressively (approx. 15 seconds), then the fan rotates in the normal way again.
Shut off the engine.
Wait until the fan does not turn any more. Check the condition of the cooler.
If necessary, repeat the cleaning procedure.
5.7Hydraulic system
Maintenance work on the hydraulic system is generally limited to the hydraulic tank. All other components of the system do not require any special maintenance or servicing.
The network of pipes and hoses must however be inspected regularly for leaks.
Note!
Cleanliness is of particular importance for the proper working of the hydraulic system.
For this reason, the prescribed intervals for –change of the return filters –cleaning of the oil cooler –oil change must be strictly adhered to.
5.7.1Depressurising the hydraulic system
Before carrying out any work on the hydraulic system, you must fully depressurise it.
Danger!
Do not use your bare hands to check the system for leaks. Fine jets of fluid escaping under high pressure can penetrate the skin and result in serious injury.
Observe the following:
Park the machine on level firm ground and place the attachment on the ground. Depressurise the high-pressure circuits. Shut down the motor.
Operate the pilot control units (joystick and pedals) in all directions (while the start key is in contact position and the safety lever is folded down).
Depressurise the pilot control circuits.
Operate the pilot control units (joystick and pedals) several times in all directions (while the start key is in contact position and the safety lever is folded down).
Fig. 5-16 Depressurising the hydraulic system
Depressurising hydraulic tank
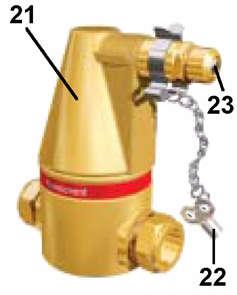
Turn out the breather filter 1 by maximum one full turn. The hydraulic system is gradually being depressurised. The breather filter 1 can be rotated by hand when the safety pin 2 is inserted. If necessary, use an open end spanner to turn the filter.
Note!
The safety pin 2 (or anti-vandalism key) should always be removed from the breather filter and attached to the machine start key.
Danger!
When at operating temperature, the hydraulic oil is hot and might be under pressure.
Avoid skin contact with hot oil or components containing hot oil.
5.7.2Checking oil level in hydraulic tank; emptying and refilling tank
Excavator position
Fig. 5-17 Machine position for the oil level check of the hydraulic system
Before checking the oil level or adding oil: –ensure that the machine is standing on level and firm ground, –the working attachment is placed on the ground and the stick and the bucket cylinders are fully extended (i.e. bucket and stick fully tilted in), –the motor is shut down, –the bucket flap (if any) is closed.
Checking oil level in hydraulic tank
Fig. 5-18 Oil level in hydraulic tank
When the machine is in inspection position, the level may not drop below the centre mark in the sight glass.
If required, add oil through the return filter until the level reaches the centre mark. The upper mark MAXI indicates the maximum oil level when all cylinders are fully retracted.
The lower mark MINI indicates the minimum oil level when all cylinders are fully extended.
If the oil level drops below the lower mark MINI, the minimum level is reached and the respective warning symbol is shown on the display.
Emptying and refilling hydraulic tank
1
3
5
7
2
4
6
R Return chamber
If possible, empty and refill the hydraulic system using a filler unit.
Draining oil:
The hydraulic system is depressurised.
Turn out the breather filter 1 by maximum one full turn. The hydraulic system is gradually being depressurised.
Remove the lid from the return filter 2
Connect the drain hose to the drain valves 5 and 6 at the hydraulic tank and to the collecting pipe.
Let the oil flow into a suitable container.
Adding hydraulic oil:
Turn out the breather filter 1 by maximum one full turn. The hydraulic system is gradually being depressurised.
Remove the lid from the return filter 2.
Add oil through the filter cartridge 2 or through the screw plug 4 at the return chamber until the level reaches the centre mark in the sight glass (see Fig. 5-18).
Tighten the breather filter 1.
Fill the tank to the upper edge. When adding oil through the filter lid, ensure that the return chamber R around the centring tube 7 is also completely filled. Replace the lid of the return filter 2 or tighten the screw 4 respectively.
Caution!
Bleed the hydraulic pumps after each hydraulic oil change.
Draining condensate:
Drain the condensate from the hydraulic tank at the intervals prescribed in the maintenance schedule.
Place a suitable container under the machine.
Connect the drain hose to the drain valves 5 and 6 (see Fig. 5-19) until the oil flowing into the container does not contain any water.
Interval: see maintenance schedule
Note!
When using biodegradable hydraulic fluids, we recommend draining of condensate each time the machine is started after a prolonged period of standstill (longer than 24 hours).
5.7.3Checking and cleaning oil cooling system
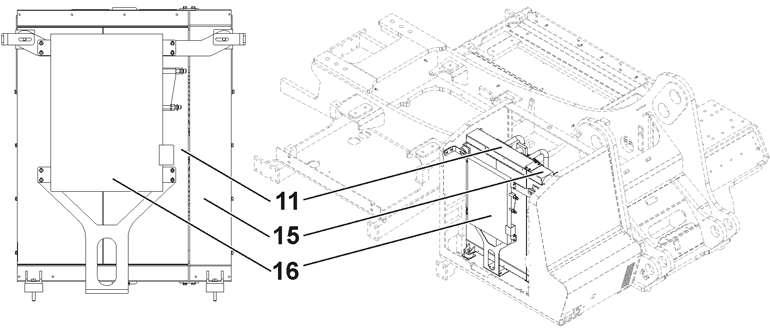
Fig. 5-20 Oil cooler
11 Hydraulic oil cooler
16 Condenser in a/c system
15 Transmission oil cooler copyright by
The hydraulic oil cooler is integrated into the combined cooler unit. A clean oil cooler is a prerequisite for optimum oil cooling.
Regularly check the fan and the cooler for damage and clean it, if necessary. If required, clean the cooling fins with compressed air or steam jet (from the inside out, see arrow). If necessary, the combined cooler might be in a tilted position (see Fig. 5-21).
Caution!
Risk of injury from crushing between the combined cooler and the catwalk.
The magnetic rod 4 of the return filter must be cleaned and the fibre glass filter cartridge 5 must be replaced at prescribed intervals (see maintenance schedule).
3 Flat gasket Note!
Cleaning the magnetic rod and/or replacing filter cartridge: The hydraulic system is depressurised.
Loosen the screws at the filter lid and lift off the lid 1 together with the magnetic rod 4
Carefully clean the magnetic rod removing any persistent dirt. Remove the spent filter cartridge 5 holding it by the bracket. Insert the new filter cartridge vertically into the tank, holding it by the bracket, and push it slightly down. Place the bracket along the side of the tank ring.
In areas with excessive dust, observe the special instructions for the filter change. Caution!
Ensure that the filter cartridge is aligned vertically in the tank and that the flat gasket 8 is not damaged.
Centre and place the lid 4 carefully on the filter cartridge 5. Ensure that the flat gasket 3 is not damaged and positioned correctly.
5.7.5Leak oil filter
The return filter 2 for leak oil of the hydraulic pumps and motors, which is attached to the rear of the hydraulic tank must also be regularly inspected and serviced. For intervals, see maintenance schedule.
When servicing the filter, replace the filter insert or clean it with cleaner's solvent or engine oil.
Note!
The filter insert can be cleaned maximum three times before it needs to be replaced.
Cleaning filter
Open the filter pot. Remove the filter cartridge. Clean the filter cartridge and the filter pot.
Inserting new or cleaned cartridge
Apply a little oil to the threads and sealing faces on the filter pot and the filter head and to the O-rings.
Carefully slide the filter cartridge onto the mounting stud. Screw the filter pot by hand to the stop and then tighten it with a spanner attached to the hexagon section at the base of the filter pot (tightening torque: 40+10 Nm).
5.7.6Control oil filter
The pressure filter 11 is an integral part of the control oil unit 1 located at the rear of the hydraulic tank.
Note!
Cleaning and re-using the filter cartridge is prohibited! Replace the cartridge each time you open the filter pot.
Replacing filter cartridge:
The hydraulic system is depressurised.
Screw off the filter pot 14 of the pressure filter 11 and pull out the filter cartridge
12
Clean the filter pot 14
Apply a little hydraulic oil to the threads and sealing faces of the filter pot 14 and the control oil unit 1 as well as to the sealing rings 13 and 15
Carefully place the new filter cartridge 12 onto the mounting stud 2
Screw in the filter pot 14 to the stop and then turn it back by hand by 1/4 revolution (90°).
5.7.7Feed line filter of the slewing gear circuit
The filter is attached to the slewing gear pump.
Unscrew the filter pot 2 of the filter and pull out the filter cartridge 3 and the O-ring 10
Clean the filter pot 2.
Apply a little oil to the threads and sealing faces of the filter pot 2 and the filter head.
Carefully mount the new filter cartridge 3, the new O-ring 10 and the spring 7 on the mounting stud.
Screw in the filter pot 2 of the filter.
5.7.8Control circuit
The control circuit does not need to be serviced.
Regularly inspect the pipelines and the connections of all units (accumulators, pressure-relief valve, pressure filter, etc.) for leakage.
Danger!
The pressure accumulator 10 (see Fig. 5-24) ensures that the control circuit remains pressurised after the motor is shut down so that a number of movements remain possible.
Prior to interfering with the control pressure circuit, it must be depressurised:
To do this, place the working attachment on the ground.
Shut down the motor.
Repeatedly actuate the two joysticks (while the start key is in contact position and the safety lever is folded down).
5.7.9Bleeding the hydraulic pumps
Caution!
The hydraulic pump and the pump regulator must be carefully bled before the first start up of the machine, after replacement of the pump or after any reparation works in the hydraulic circuit of the pump (suction line, leakage oil line, ...) and after replacement of the hydraulic oil.
The pump must also be bled after each repair work making necessary to depressurize the hydraulic tank with a vacuum pump, and especially if the fan driving pump is mounted higher or at the same height as the oil level in the hydraulic tank.
To bleed the pump efficiently, we recommend to pressurize the tank before bleeding (0.3 to 0.5 bar air pressure). The pressurization of the tank is essential if the pump is higher or at the same height as the oil level in the hydraulic tank.
When starting the pump for the first time, and after a repair or a pump change, the oil housing must be filled with hydraulic oil. This is done through the above bleeder plugs and fittings.
Bleeding the working and slewing gear pumps
Note!
To bleed the pumps, we recommend using a special tool (ID no. 7408148) to pressurise the hydraulic tank.
If the pumps are bled without a special tool and tank pressurisation, you must switch on the motor for the duration of the bleeding process.
1 Fitting / bleeding of working pump
3 Working pump
5 Screw plug / bleeding of fan drive pump
2 Screw plug / bleeding of slewing gear pump
4 Slewing gear pump
6 Fan drive pump
To bleed a working pump 3, loosen the fitting 1 and allow the air to escape. Tighten the fitting 1 as soon as the oil escaping at the opening is free of air bubbles.
To bleed the slewing gear pump 4, loosen the screw plug 2 and allow the air to escape. Tighten the screw plug 2 as soon as the oil escaping at the opening is free of air bubbles.
Bleeding the fan drive pump
E944C and E954C
To bleed the fan drive pump 6, loosen the screw plug 5 and allow the air to escape. Tighten the screw plug 5 as soon as the oil escaping at the opening is free of air bubbles (see picture before).
E934C
Preferably unscrew a fitting on the hose on high pressure port of the pump if this port is situated near the top of the pump.
Let oil escape until it contains no more air bubbles and retighten the fitting.
Otherwise loosen (without removing) the topmost plug 28 on the pump housing, let. oil escape until it contains no more air bubbles and retighten the plug 28
Bleeding the pump regulator
The extremity of the solenoid valve Y347 is fitted with a bleeding plug 30 allowing to deaerate the pump regulator.

Insert a (2 mm) Allen wrench in the hexagon bore of the plug and unscrew of about 1/4th a turn.
Let oil escape until it contains no more air bubbles. Retighten the plug 30 (torque to 1 Nm).
Caution!
If no hydraulic tank pressurization system is available, the bleeding of the pump while turning the motor (with injection solenoid valve disconnected) is allowed only if the pump is sufficiently filled with oil. If necessary, previously fill the pump housing with oil before bleeding.
Thoroughly check the suction and leak oil lines of the pump for correct fastening and sealing, so to make sure no air entry in the hydraulic system is possible. Start the motor. Check that the fan drive motor starts (at low RPM in the cold condition of the machine).
Let the motor run for few minutes to let escape the air possibly remaining in the pump or in the hydraulic circuit.
5.7.10Bleeding the hydraulic cylinders
The cylinders must be bled after each cylinder replacement and after work carried out on the cylinders (replacement of seals, etc.) or the hydraulic circuits (replacement of hose, etc.).
3 Measuring
Bleeding procedure 1
Remove the seal plugs 2 on both sides.
Screw in two measuring necks 3 to replace the plugs and equip them with a measuring hose each.
Start the electric motor and let it run for the duration of the procedure.
If possible, move the attachment in such a way that the side to be bled (supplied side) of the cylinder is in the upper position.
The cylinder movements must be slow and carefully controlled. We recommend first bleeding one side of the cylinder without making any movements (e.g. if cylinder is already retracted, first initiate the cylinder retraction and then bleed the rod side).
The procedure is completed when the oil flowing through the measuring hose is free of air bubbles.
Actuate and bleed the other side of the cylinder.
Switch off the motor, disconnect the measuring hoses and replace the measuring necks with the seal plugs 2.
Complete bleeding procedure 2.
Bleeding procedure 2
Start the motor and let it run for the duration of the procedure.
If possible, move the attachment in such a way that the side to be bled (not-supplied side) of the cylinder is in the upper position.
Slowly extend the cylinder to the stop and then slowly retract it again to the stop. Ensure that all movements are slow and even. Repeat this process five times.
Danger!
If the cylinder is not properly bled, gas bubbles might form in the system (mixture of air and hydrocarbon). At high operating pressures in the cylinder, these gases might explode (Diesel effect).
5.7.11Disconnecting suction hose of pump
For maintenance work on the pump suction side (replacement of sight glass, removal of working pump, etc.), you can close the suction hose of the working pump by means of a stopcock so that it is disconnected from the hydraulic tank.
Stopcock at hydraulic tank
The suction hose stopcock on the hydraulic tank can be set to two positions: a open b closed
Depressurise the hydraulic system. Close the stopcock at the hydraulic tank (position b).
Draining oil from the working pumps
Loosen the screw plug 1 at the suction hose neck on the pump side. Drain the hydraulic oil from the pump and suction hose. After completion of the repair, turn the stopcock to its initial position a and engage it.
Tighten the breather filter on the hydraulic tank.
5.7.12Breather filter on hydraulic tank
Breather filter of hydraulic tank
The hydraulic system is depressurised. Replace the filter 1 together with the safety pin 2 (see inspection and maintenance schedule).
Note!
n areas with excessive dust, observe the special instructions for the filter change.
The safety pin 2 (or anti-vandalism key) should always be removed from the breather filter and attached to the machine start key.
5.7.13Bypass oil filter for hydraulic system (option)
The purpose of the bypass oil filter is to eliminate the smallest impurities and the water contained in the hydraulic system.
The bypass oil filter is mounted to the front of the hydraulic tank, resp. in the hydraulic pumps compartment.
On machine model R964 C and above, two bypass oil filters are mounted in parallel due to the oil flow to be filtered.
Note!
LIEBHERR insistently recommends to fit with a bypass oil filter the excavators which are operated with environmentally friendly hydraulic fluids.
The more the oil is contaminated, the higher the pressure in the filter housing. Depending on the machine applications and the dirt/water collection in the filter, the filter cartridge might need to be replaced before the standard change interval (2000 operating hours) is reached.
If the pressure gauge 1 indicates a value of more than 2.5 bar during operation, the filter element is too much contaminated to ensure sufficient filtering of the hydraulic oil.
Checking filter contamination
The contamination grade of the bypass oil filter must be checked at the regular intervall indicated in the maintenance chart
When checking, the hydraulic oil must be at a temperature of at least 50 °C (operating temperature) and the engine must be running.
Read the indication of the pressure gauge.
If the pressure exceeds 2.5 bar, change or get changed the filter element at once.
Replacing filter element
Switch off the engine.
copyright by
Release the pressure in the hydraulic tank.
Open and remove the tightening clamp 2
Remove the old filter element 4 and collect the oil leaking from the filter in a suitable container.
Check the inlet and outlet sections of the bypass oil filter and if necessary clean the inner side of the filter head.
Insert a new filter element 4
Replace the filter housing 3, replace and tighten the clamp 2
Start the machine and check the bypass oil filter for leakage.
5.7.14Return oil filter for hydraulic hammer (option)
In case of use of an hydraulic hammer, it is strongly advised to install an extra return oil filter.
1 Nuts
2 complete cover
3 Seal kit
4 Filter cartridge
5 Contamination indicator
6 Filter housing
The return oil filter for hydraulic hammer is mounted on the fuel tank. The intervall of maintenance depends on the indication given by the contamination indicator 5 If the indicator is green, the filter works correctly. If the indicator is red, the filter is clogged and the filter unit has to be replaced.
Replacement of the filter cartridge
The hydraulic system must be depressurized.
Unscrew the four nuts 1 on the filter cover and lift out cover 2
Remove the used filter cartridge 4
Check the seal 3 and replace it if necessary.
Carefully clean off any dirt sticking to the magnetic plug.
Insert a new filter cartridge 4.
Put the seal 3 and the cover 2
Coat the stud bolts of the filter housing 6 with anti-corrosion grease and tighten the nuts 1.
5.7.15Servicing the hydraulic cylinder
Checking the condition of the piston rod mount
Note
When a leak appears on the piston rod mount of a hydraulic cylinder (see arrow), the sealing kit must be replaced by a LIEBHERR fitter.
Protecting the piston rods
When the machine is out of service for more than 4 weeks and particularly for transportation by sea, the following measures must be taken:
Position or transport the machine in such a way that the piston rods are fully drawn into the cylinders.
Cover any loose piston rods with a thick layer of non-corrosive anti-corrosion fluid. Grease quality: see “Lubricating and operating materials”
For sea transportation, check the condition of the piston rods once more after loading.
Additionally, cover piston rods with anti-corrosion fluid if a cylinder only has a low stroke for certain work, meaning that the piston rod is not regularly moistened with hydraulic oil (eg. cylinder on slewing arm when working over ground).
Check the condition of hydraulic cylinders which are not moved a great deal re- gularly.
5.7.16Replacing hydraulic hoses
Danger!
A defective hydraulic hose can cause accidents and injuries. Replace defective hydraulic hoses (bubbles, moisture, damaged top edge etc.) immediately.
Install new hoses in such a way that torsion loading is avoided. Ensure that the hydraulic hose is not twisted when mounting.
Installed high pressure hoses with SAE connections have a nominal diameter of 16, 20, 25, 32 or 40 (5/8", 3/4", 1", 1"1/4, or 1"1/2).
You must tighten the mounting screws of the SAE fittings with the following tightening torques.:
Size of screw 4Torque value in Nm - Quality 10.9
Half flanges 5aFlat flange 5bConical flange 5c M831//
M16264170250
M20350250450
Tab. 5-14 Tightening torques for SAE fittings - Quality 10.9
Size of screw 4Torque value in Nm - Quality 8.8
Half flanges 5a
M822
M1044
M1276
M14122
M16187
Tab. 5-15 Tightening torques for SAE fittings - Quality 8.8
5.8Oil changes on components
5.8.1General
Information
The machine must be standing level. Switch off the engine.
Wait briefly until the oil has collected in the oil sump. Drain off the oil (preferably when oil is at operating temperature)
Add the oil.
Check the oil level.
Oil quality and quantity: see lubricant chart. Change intervals: see lubrication and maintenance chart.
Instructions for safe oil draining with High Rise machines
Danger!
For safety reasons, with your machine fitted with a high rise undercarriage, you must employ a lifting platform to have access to oil drain valves of the swing gear and of the pumps splitterbox. (Only authorized persons are allowed to drive a lifting platform).
Preferably employ a drain hose long enough to collect the worn oil into a container standing at ground level below the excavator.
If you attempt to drain the oil into a container placed on the lifting platform, you must in any case previously make sure that the platform is suitable (lifting capacity and stability), considering the weight of the container filled with the expected oil quantity to be drained.
5.8.2Swing gear - Oil level check and oil change
Fig.
Checking oil level and changing oil in swing gear
1 Oil reservoir
2 Cover
3
To check the oil level: When the gear oil is cold, the level in the expansion reservoir 1 should not be below the marking Min.
Otherwise add oil until the level reaches the marking Max.
To drain the oil:
Remove the cover 2
Unscrew the cover of the drain valve 3 via the opening on the upperdeck.
Screw the drain hose provided 4 to the drain valve 3 and let the oil flow out into a suitable container.
Remove the hose 4.
Screw the cover of the drain valve 3 back on.
To add the oil:
Add the oil in the reservoir until the level reaches the Max. marking.
Screw the cover 2 back on.
5.8.3Travel gear oil change
Perform the oil change at the intervals indicated in the maintenance chart. Before draining or adding oil, actuate the travel drive until one of the three drain plugs is situated straight below the central axle of the gear (Position 2). For gears having only both plugs situated on different diameters, always take the outer plug for the drain plug and turn the gear until this outer plug is straight below the centre of the gear.
Preferably drain the oil when it is at operating temperature.
To drain the oil:
Ensure that you have a suitable oil drainage container to hand. Place the container beneath the travel gear.
Remove the oil level plug 1.
Remove the oil drain plug 2 The oil drains into the container.
To add the oil:
Screw in the oil drain plug 2
Fill in oil until the level reaches the bore hole 1.
Screw in the oil level plug 1
Note!
The track components of the machines working with their undercarriage the most of time underwater, are exposed to increased rust and premature wear.
On these machines the oil in the travel gears must be changed every 100 working hours and an oil analysis (water content of the oil) must be performed weekly.
5.8.4Pump distributor gear - oil change
4 Lid
Checking the oil level:
5 Oil level gauge
7 Drain valve
Let the engine run for a few minutes and then shut it down.
Unscrew the dip stick 5 and clean it with a clean, lint-free cloth. Insert the dip stick 5 and screw it in to the stop , unscrew it again and remove it from the oil tank.
Check the oil level (distance to mark).
If required, add oil and repeat the above oil check.
Screw in the dip stick 5
Draining oil: Remove the lid 4.
Connect the supplied drain hose to the drain valve 7 and let the oil drain into a suitable container.
Disconnect the drain hose. Replace the lid of the drain valve 7
Adding oil:
Add oil through the filler neck 4 until the oil level reaches the "Max" mark on the dip stick 5
Replace the lid 4.
Let the engine run for a few minutes, shut it down and wait until the oil has collected in the tray. then check the oil level again.
5.9The track components
The maintenance works necessitated by the tracks assemblies mainly consist of the replacement of the worn components once they have reached their wear limits. The sealing of the carrier rollers, track rollers and idlers via slipring seals provides an increased durability to the track assemblies while making these parts widely insensitive to any intrusion of dirt or water.
5.9.1Checking the mounting screws of the track components
Regularly carry out a visual inspection for loose mounting screws on the track pads and travel drives.
Regularly check the tightening torques of some screws (take a random sample of about ten screws regularly distributed on the upper side of each chain) and retighten all the screws if you notice that at least one screw has loosened.
–The track pads mounting screws 7 must be torqued to:
•For tracks D7F, (Screws - M22 X 1,5 - 12.9) : 1070Nm (790 ft.lbs)
•For tracks D8K and B9S, (Screws - 1" - 14UNF - 12.9) : 1560Nm (1150 ft.lbs)
–The mounting screws 8 of the travel gears to the side trames must be torqued to: 960Nm (710 ft.lbs)
–The mounting screws 9 of the sprocket wheels must be torqued to:
•(Scr. - M20 - 10.9) : 560Nm (413 ft.lbs)
•(Scr. - M24 - 10.9) : 960Nm (710 ft.lbs)
–The mounting screws 10 of hydraulic motors to travel gears must be torqued to:
•(Scr. - M20 - 10.9) : 560Nm (413 ft.lbs)
•(Scr. - M24 - 10.9) : 960Nm (710 ft.lbs)
5.9.2Checking the track chains tension
Due to normal wear of the tracks, the chain tension needs to be checked regularly, and, if necessary, the chains must be tightened.
Monitoring the track tension
Relieve the track by driving the machine forwards and backwards. Place the measuring rod 1 in the area above the carrier rollers. Measure distance A between the measuring rod lower edge and the top of the track pads.
On machines with two carrier rollers per side, the track should, under operating conditions, sag 20 to 30mm between the carrier rollers.
On machines with three carrier rollers per side, the track should, under operating conditions, sag 15 to 20mm between two consecutive carrier rollers..
Note!
As an alternative, or if no correct measuring rod is available, it is possible to determine the sag A as the difference between X1 and X2 (A = X1 - X2).
X1 is the distance between lower face of a chain link and the cover sheet of the side frame measured at a carrier roller, X2 the same distance measured in the middle between two carrier rollers.
Retension the track if necessary.
5.9.3Retensioning the track
Fig. 5-42 Retensioning the track
Remove the cover 6 on the side frame of the undercarriage.
Screw high pressure hose 2 onto the manual grease gun 1
Through the opening in then side frame, connect the high pressure hose 2 to the lubricating nipple 3 of the grease tensioner 4
Inject grease until the track is sufficiently tensioned.
Check the track tension as described above.
Remove the grease gun 1, the pressure hose 2 and reattach the cover 6
5.9.4Releasing the track chain tension
Danger!
Risk of injury due to sudden dropping of the crawler or to a jet of grease under high pressure.
Because of the risk of grease jet, always wear protective gloves and glasses when releasing the chain tension
When releasing the tension of the chain, keep your head away from the opening 5 in the track side frame. Never touch the grease nipple 3 with your hand but always use an appropiate tool to unscrew or screw it in.
Before attempting to release the chain tension, loosen and remove every item which may be stucked in the chain while driving forward and backward or doing as described in the section "Cleaning the track components" thereafter.
Carefully unscrew lubricating nipple 3 (see Fig. 5-42) by several thread pitches until the grease escapes out of the releasing groove of the nipple.
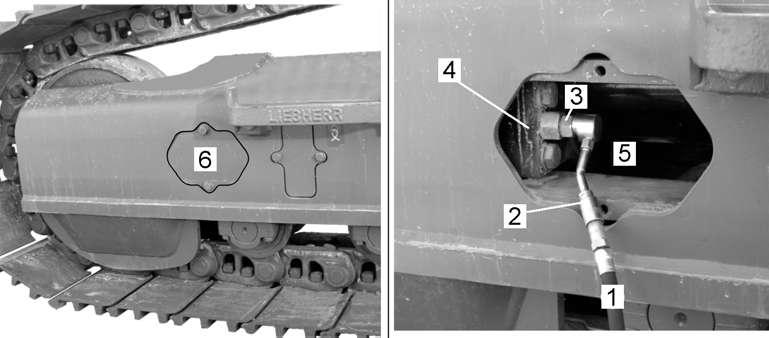
Danger!
Machines delivered up to september 2008 are possibly fitted with a lubricating nipple 3 showing two distinct hexagonal bearing areas.
To screw the grease nipple 3 in or out, always catch it at its rear part 3.1 (use a 27 mm wrench) and never at its front part 3.2
Loosening the nipple at its front hexagonal bearing area could cause the front part 3.2, to loosen and to be powerfully thrown out.
Tighten lubricating nipple 3 as soon as the desired track tension is obtained. After the adjustment procedure, drive the machine forwards and backwards and check the track tension again as described above.
5.9.5Cleaning the track components
Before working
Do not operate the machine if larger stones, pieces of wood or metal, wires or cables are wedged into the track components.
Dried or frozen mud and stones or other foreign bodies in track parts could result in considerable damage to the machine if the machine is operated or an attempt is made to free the machine using engine power.
In sub-zero temperatures, set the machine on wooden planks or logs to prevent the tracks becoming frozen to the ground.
Caution!
To avoid causing considerable damage to the frozen machine, never use force to tear it free.
A frozen track can be freed by carefully heating the track pads.
At the end of a workday
Always clean the track components from dirt accumulation before stopping the machine.
Clean the gliding surfaces of the tension units from clinging dirt or sand and apply grease.
The machine can be supported and lifted slightly on each side with the attachment, so the tracks can be cleaned.
Keep the bucket stick as vertical as possible when lifting one machine side.
Danger!
Never use this method with an high rise excavator.
Danger!
Never work from underneath on track components of the raised machine unless the track is securely blocked and supported with wooden beams. On a hard or flat soil the machine can slide away.
5.9.6Replacing track components at "High Rise" excavators
Danger!
The removal and the repair of the track chains, as well as the removal of the idler unit and of the tension spring unit are not described in this manual. These works must, for safety reasons, be performed exclusively by trained LIEBHERR Service personnel.
5.10Electrical installation
5.10.1Rotary connection
Every 500 operating hours, check the tightness of the mounting bolts of the rotary connection and of the driver components.
Bearings are lubricated for life, so relubrication is not required.
Servicing consists to clean the rotary connection every 1000 operating hours Clean the outside of dirt.
On the inside, clean the ring slip faces, the brushes and the insulators of dust to prevent leakage current between the individual slip rings.
Remove any condensate from the inside surfaces of the rotary connection. Check the surfaces of the ring slip faces for damage. Remove any beads, arc spots and oxidation.
The carbon brushes have a relatively long service life, due to the low speed and the hardness of the carbon. The carbon brushes must be replaced on time to prevent metal parts of the brush holder or the mounting bolts of the carbon brushes come into contact with the slip rings.
Every 1000 operating hours, check visually the carbon brushes.
Caution
Before carrying out any work on the rotary connection, open and lock the main switch at the power supply unit.
All work on the electrical system must be carried out by qualified persons who are aware of the risk posed by electric power.
5.10.224 V electrical system
Regularly inspect the electrical system of the excavator for defects.
Notes regarding the electrical system
Regularly inspect the electrical system of the machine for defects. Identify the cause of blown fuses and broken incandescent lamps, eliminate it and replace the fuse or the lamp.
Caution
Use only fuses. Never bypass, bridge or repair electrical fuses.
Defects such as loose connections, chaffed cables or poorly fixed clamps must be repaired without delay.
Before washing the machine, cover the electrical devices (in particular the alternator, cabling, electrical components and measurement transducers) so that they are protected against splashing water.
5.10.3Battery care (option)
Danger!
Risk of injury from sparks.
When charging batteries or carrying out other work on batteries, keep away from sparks and naked flames. Disconnect the negative pole (-) first and reconnect it last. Always wear goggles and protective gloves.
Note!
The battery might discharge itself during prolonged standstills. Prior to prolonged standstills, set the battery main switch to position 0 (off).
To ensure that the batteries work properly at all times, keep them clean. Regularly clean the pole heads and cable terminals A and protect them with a thick layer of acid-proof grease, (see Fig. 5-44).
Danger
Kinked rubber hoses of the central gas release system lead to a higher risk of explosion!
The hydrogen produced in the battery may not collect in the battery box and must be released from the enclosure through the rubber hoses. When installing the hoses of the central gas release system, ensure that they are not kinked.
Regularly check the hoses B for damage, especially after installation of the battery, (see Fig. 5-44).
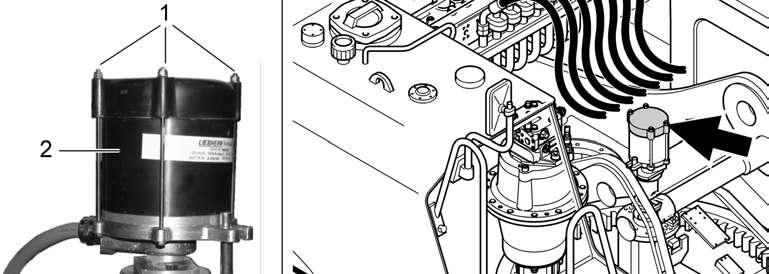
The liquid level in the cells must be about 10 to 15 mm above the upper edge of the plate. If topping up is necessary, add only distilled water.
From time to time, check the acid density using a battery tester C.
If the battery is fully charged, the density is 1.28 kg/l (31.5°Bé)
If the battery tester shows a lower value, the battery is discharged to some degree and might need to be recharged.
5.10.4Slip ring body (option)
Slip ring bodies are easily damaged by humidity, as oxide layers might form on the conducting surfaces, impairing electrical conductivity. As a consequence, the electrical consumers in the undercarriage are not sufficiently powered, which can result in malfunctions.
To prevent this, we recommend carrying out the following tasks every 500 operating hours:
Unscrew the lock nuts 1.
Remove the slip ring housing 2
Remove any oxidation from the slip ring body (use cleaning spray, if necessary). Replace damaged (corroded) fork terminals. Apply Cramolin contact spray to all slip ring elements.
Replace the housing 1.
Secure the housing 1 with the lock nuts 2 and tighten them all with the same torque.
5.10.5Cabinet air pressuring system (option)
Excavators operating in heavy dust conditions should be equipped with a cabinet air pressuring system. This system create an over pressure in the cabinet, so no dust can penetrate inside.
Filter maintenance
Follows the instructions indicated on cover 4
Filter removing Motor stopped.
Remove the cover 4
Remove the main element 2 with caution. Remove the safety element 3 with caution.
Filter assembling
Insert with caution the safety element 3
Insert with caution the main element 2
Reinstall the cover 4
5.11Heating and air-conditioning system
The machine is equipped with a combined heating and a/c system as standard.
5.11.1Recirculated and ambient air filters
If the filters are dirty, the air supply to the heating and a/c system is obstructed, which can result in more frequent icing and shutdown of the system.
–The recirculated and ambient air filters 1 and 3 of the heating and a/c system must be removed and cleaned every 500 operating hours.
–When working in dusty environments, the cleaning intervals must thus be shortened.
–Never operate the machine without filters, even for short periods, as the heat exchanger 6 could otherwise be quickly blocked (see Fig. 5-48).
Cleaning or replacing recirculated and ambient air filters:
To remove the ambient air filter 1, tilt the backrest of the operator seat forward. Open the quick fasteners 2 by turning them by 90 degrees and remove the recirculated air filter 1
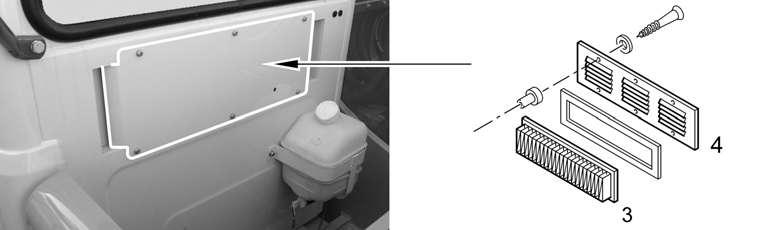
To remove the recirculated air filter 3, remove the deflector 4.
Remove the ambient air filter 3
Note!
Never clean the filter cartridges with hot water or steam!
If the filter cartridges are damaged or in poor state, replace them.
Heating and air-conditioning system
To clean the filter cartridges 1 and 3, blow them out with compressed air or wash them in cold or lukewarm water.
5.11.2Heating system
Every year at the start of the heating period, perform the following maintenance routine.
–Check the entire coolant circuit for leakage.
–Retighten the connections in the refrigerant circuit, the hose connections at the heat exchanger, the seals of the stop valves and the hose clamps.
–Filling the heating system (see "Heating and air-conditioning system" in chapter 3).
Bleeding heating system:
Through the heating unit:
To bleed the system, unscrew the red cap of the bleeder valve at opening A Press in the valve to let the air escape.
Through the air vent 21:
Air bubbles must be released manually through the bleeder valve 23, using the bleeder key 22
Screw in the bleeder valve 23
Draining the heater fluid:
Unscrew the heater fluid plug 55 with adjustable pliers.
Screw again the heater fluid plug befor refill the circuit.
Cleaning solenoid valve 5:
Every year, at the start of the heating period, dismantle and clean the solenoid valve 5 (Y46) of the hot water supply.
If the heating output is poor, also clean the solenoid valve.
Rinse the solenoid valve diaphragm with water.
Ensure that the compensation hole of the diaphragm is not blocked by dirt.
Inspecting heat exchanger:
Every 12 months, inspect the fins of the heat exchanger 6 for damage.
If they are dirty, clean them with compressed air.
If necessary, realign the fins.
5.11.3Air-conditioning system
Switch on the a/c system every 2 to 3 weeks for about 10 minutes, irrespective of the season.
During the operating period of the a/c system, the following maintenance tasks must be completed every 500 operating hours:
Inspecting condenser:
Heating and air-conditioning system
2
6
7
8
10
Inspect the condenser 2 for dirt.
If necessary, fold the condenser 2 down and clean it from the inside (blower side), using compressed air.
Ensure that the condenser fins are clean.
Dirt on the condenser might lead to excessive pressure in the coolant circuit, so that the air-conditioning system is automatically switched off.
Inspecting a/c compressor:
15
Tighten the hex nut 12 of the a/c compressor (24 Nm / 17 ft.lbs).
Maintenance of a/c compressor:
Regularly inspect the unit according to the applicable regulations and standards: Check the following:
–Electrical cable connections and fittings for proper fixture.
–Coolant level, leakage
Check coolant circuit (assembly) and its parts for leakage.
–Immediately after start-up of the lubrication of the compressor, check the following:
Oil level 1/4 to 3/4 of sight glass height S (see Fig. 5-50) (repeat check several times during the first few operating hours).
Inspecting dryer-collector unit:
While the motor is running, switch on the air-conditioning system and inspect the level of refrigerant in the sight glass 10 of the dryer-collector unit 9
Note!
If there is insufficient refrigerant in the system, the white floating ball 11 is visible at the bottom of the sight glass.
In the event of insufficient cooling output, have the system refilled by a refrigeration technician.
Determine the water content of the desiccant in the dryer-collector unit 9
Observe the colour of the indicator bead 12 in the sight glass.
If the bead is orange, the water content in the circuit is within the permitted range. A transparent bead indicates that the dryer-collector unit is saturated with water.
Immediately replace the dryer-collector unit 9
Visually inspect the dryer-collector unit 9
If the dryer-collector unit 9 shows signs of corrosion or damage (e.g.at the console fixtures, hose connection), replace the dryer-collector unit 9 (pressure vessel).
In the event of rust or damage, have the dryer-collector unit 9 replaced and filled with fresh refrigerant by a technician trained in the field of refrigeration.
For this purpose, the cooling circuit must be emptied, checked for leakage and refilled. Inspect the hose lines for chafe marks and replace any damaged hoses. Retighten the hose connections.
Additional maintenance tasks:
Fig.
Blower motor of the heating and air-conditioning unit
The following maintenance tasks must be carried out at least once every 12 months by a technician who is trained in refrigeration technology:
Functional test of the blower motor 13 (M13)
Functional test of the air flaps in the heating and air-conditioning system
Inspection of the electrical connections for proper contact
Inspection of the electrical lines for chafe marks
Inspection of the defrost thermostat 14 (B43) in the evaporator (functional test, proper fit and damage)
Functional test of the pressure switch B44 at the dryer-collector unit 9, (see Fig. 5-51)
5.12Greasing the machine
5.12.1The centralized lubrication system
The machine is serially fitted with a centralized lubrication system. With this system all or nearly all of the lube points of the machine which require at least daily lubrication are lubricated via an electrical driven grease pump which is turned on during machine operation.
This grease pump is mounted in the area behind the driver's cab.
Construction and operation of the centralized lubrication system . The grease delivered by the pump U4 is distributed to the different lubrication points LP in metered quantities, first via the main distributor 2 and further via the secondary distributors 3, 4, 5, ... mounted to the front of the upper carriage and to the working attachment.
The lubrication unit complete U4 mainly consists of a transparent grease container 13, and an electric motor 14 driving a lube pump 15.
copyright by
U4 Lubrication pump complete LP Lubrication points
During a lubricating procedure, all of the lube points LP connected to the system are lubricated one after the other in a predetermined sequence (progressive system). The flow sequence and amount of lubricant for each lubrication point depend on the combination of the distributors and lubrication lines and on the piston sizes of the different distribution elements.
Lube points connected to the central lubrication system: –the ball bearing races of the swing ring, –the housing around the output pinion of the swing ring, which contains the grease reserves for the swing ring teeth lubrication, –all (or the most of) the lubrication points of standard working attachments.
Lube points which are not connected to the central lubrication system:
Caution!
When operating a machine and especially if it is fitted with a special working attachment, make sure to lubricate daily all the lubrication points which may be installed separately, i. e. which are not connected to the central lubrication system.
–On some backhoe attachments, some grease fittings may be installed separately in the area of the connector bracket and shifting lever for the digging tool. –With special attachments (telescopic stick, hydraulic offset boom, ...) some bearing points at the attachment or at the working tool are possibly not connected to the central lubrication system. This bearing points have to be lubricated daily via separately mounted, red marked lubricating nipples and using a grease gun or a manual grease pump.
Note!
The standard undercarriages of crawler excavators do not require daily lubrication. On undercarriages with special design necessitating regular lubrication (undercarriages with adjustable track width, ...) the lubrication points are not connected to the centralized lubrication. For description of the corresponding lubrication works, see the subgroups related to the special maintenance for these undercarriages.
5.12.2Semi automatic and full automatic systems
The serially installed lubrication pump must be turned on and off via a switch in the cab by the operator (half automatic system) The lube pump is without control unit.
Full automatic system
16 Integrated control unit
The electric motor of the optional mounted full automatic system comprises an electronic control unit 16, which triggers the lubrication cycles on and off during the operation of the machine.
5.12.3Operation of the semi automatic system
In the semi – automatic system, the pump is controlled by the push button S84 on the rear control desk of the driver's cab. With the engine running, Depress the button S84 The control light in the button lights up. The lubrication procedure is started.
Centralized
Keep the lube pump running until clean grease runs out of the bearing points boom cylinders to upper carriage, then depress the button S84 again.
The control light in the button turns off and the lubrication procedure is stopped
Note!
The time necessary for the lubrication is dependent on the grease viscosity and temperature and on the design and number of connected components. At very low temperatures up to 30 minutes may be necessary for sufficient lubrication.
During lubrication, the delivery of grease can be checked visually while observing, through the transparent cap 27.2 of the stroke controller 27 mounted to the top of the main distributor 2, that the indicator stem 27.1 moves alternately in and out.
Lubrication intervals.
Under normal working conditions a semi – automatic lubrication must be performed daily.
If the machine is used under hard conditions (working under water, in very abrasive material, …) or in multi shift service, it is necessary to lubricate more often (up to once a working shift or every 4 hours).
5.12.4Operation of the full automatic system
Function of the lubrication system
After turning on the excavator the control light inside the touch S84 and the green LED 17 of the integrated control unit 16 light up for approx. 1,5 sec. to show that the electric pump is operative.
.A lubrication procedure will begin automatically after a "cycle time" is over and stop after all points have been lubricated, this without any action by the operator. During a lubricating procedure, all lube points are lubricated one after the other in a certain sequence (progressive system).
After completion of a lubrication procedure, the pump is turned off by a proximity switch B51 mounted to a distribution element of the main distributor 2
2
Grease container
14
At each stroke of a piston in this element, the switch B51 gives a pulse signal to the control unit 16, which stops the lubricating procedure as soon as the preadjusted number of strokes has been reached.
Starting an additional lubrication procedure
If the lubrication system is in working order, an additional lubricating procedure of the lube unit can be started any time by depressing either the push button S84 on the rear control desk or the touch 19 on the motor housing.
Monitoring of the automatic lubrication system
During a lubrication procedure of the lubrication unit 2, the control light inside the push button S84 and the green LED 17 are on continuously.
In case of a failure in the lube circuit (no stroke signal delivered by the proximity switch B51 about 20 minutes after begin of a lubrication procedure) both LEDs 17 and 18 and the control light inside S84 will start blinking simultaneously.
The possible causes are:
–a plugged or kinked lubrication line, (in this case the grease will flow out of the relief valve 26),
–not enough grease in the grease tank 13, –a problem in the 24 V electrical circuit for the motor 14 Immediately locate and remedy the cause of the trouble.
5.12.5Emergency lubrication with defective lubrication system
In case the lubrication pump 15 does not work, all lubrication points connected to the centralized system may be lubricated via the lube fitting 25 using a lubrication gun. In this case, press daily or per working shift approx. 200 cm3 grease into the fitting 25
15 Grease pump
5.12.6To refill a grease container
25 Emergency lube fitting
The grease level in the container 13 of the pump must be checked weekly, and if necessary, the container refilled.
See the lubricant chart for grease specification.
The refilling of the grease container should only be done via the special fitting 21
Note!
Avoid refilling the container 13 via the upper cover 23, since it could create an air pocket in the container and cause the pump 15 to run dry.
Insert a grease cartridge in the special filling pump 31 (Id. No. 10009239). connect the pump to the fitting 21. push the whole content of the cartridge into the container 13
For indication of ordering number of grease cartridges, refer to subgroup "lubricants specifications".
If the special filling pump 31 or the grease cartridges are not available, refill the container 13 through the grease fitting 22, using a grease gun.
5.12.7Changes in the lubrication circuit
Before you make any changes to the lubrication system (for example when changing the attachment configuration), always check with a LIEBHERR mechanic first.
Never remove a line and close off an outlet, which is not being used, or the whole lubrication system would be blocked.
Only plug an outlet after the line has been removed from the distributor and the necessary changes have been achieved at the corresponding distribution elements. This applies as well for main distributor 4 as for secondary distributors 5.
5.12.8Greasing the grab (optional extra)
The grab is not lubricated via the central greasing system. It must be regularly greased manually. The relevant oiling points are marked in red.
Greasing the grab
In normal use, each oiling point must be greased daily or per shift until clean grease flows out at the relevant bearing point.
When the machine is working hard, the greasing interval should be shortened accordingly.
Grease quality: see lubrication chart
5.13Quick-change systems
5.13.1Greasing the mechanical quick-change adapter (option)
The mechanical quick-change adapter is not lubricated via the central greasing system. The bearing points must be greased using the grease gun.
Grease the bearing points via the lubricating nipple using a grease gun. Grease quality: see “Lubricating and operating materials”
Note!
If the mechanical quick-change adapter is greased when the pin is drawn out, the hollow area between the locking pins fills with grease and the pins can no longer be reinserted.
Ensure that the locking pins are inserted when greasing.

5.13.2Hydraulic quick-change adapter (option)
Greasing the quick-change adapter
The hydraulic quick-change adapter is not lubricated via the central greasing system. The bearing points must be greased using the grease gun.
copyright by
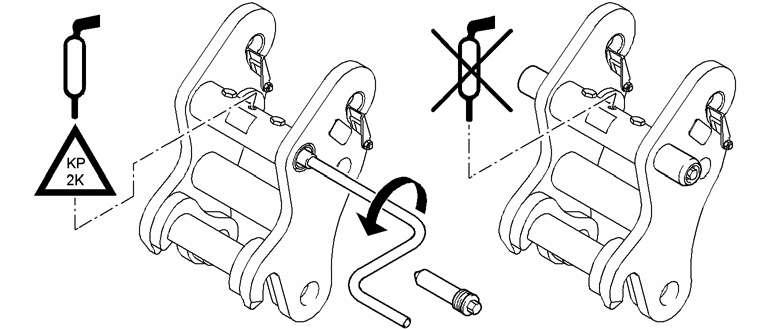
Grease the locking pins 1 via the lubricating nipple using a grease gun.
Note!
The hydraulic quick-change adapter cannot be sufficiently greased if the locking pins are drawn out.
Ensure that the locking pins are inserted when greasing.
Cleaning the sieve filter
Fig. 5-63 Cleaning the sieve filter
The filter disc 12 in the bolt connections between the connecting hoses and the hydraulic cylinder must be checked for blockages and, if necessary, cleaned every 2000operating hours.
Remove the cover 20 and the screws 21 from the quick-change adapter.
Remove bolt connections and hydraulic hoses from the hydraulic cylinder 10.
Screw out the outer mounting assembly 13 using a suitable tool (eg. a scribe).
Remove the filter disc 12 , check and if necessary clean or replace it.
Place the filter disc 12 on the inner mounting assembly 11 and mount the outer mounting assembly 13
Connect bolt connections and hydraulic hoses to hydraulic cylinder 10. Fasten the cover 20 with the screws 21 on the quick-change adapter.
5.13.3LIKUFIX (option) Cleaning LIKUFIX
The LIKUFIX hydraulic coupling system is mostly maintenance-free.
It is recommended that the system is cleaned at regular intervals and sprayed with lubricating varnish (see Workshop manual). This will prevent dirt adhering and icing up.
If the system is kept properly clean, the seals are very durable.
Check mounting bolts for tightness
Replacing the sealing ring
5-64 Replacing the sealing ring
If leaks occur at the coupler plugs (A , see arrows), the sealing rings should be replaced.
Use a screwdriver to push down the sealing washer and lever out the defective sealing ring using a pointed object (B).
Press the new sealing ring together and place it on the sealing washer with the open side down (C).
Press down the washer as far as the groove, place the screwdriver in the middle of the sealing ring and move your hand away (D).
Allow the sealing ring to jump into the groove (E).
Remove the screwdriver (F).
The sealing washer must move upwards. If necessary, press the sealingring again until the sealing washer is flexible.
5.14Check mounting bolts for tightness
The mounting bolts listed below must be regularly checked and retighten if necessary. See maintenance chart for the checks intervals.
Check mounting bolts for tightness
Caution!
The mounting bolts for all the main components (especially those listed below), and for the hydraulic hoses and pipes must be replaced after every removal.
Notice : when installing bolts of size bigger than M40 the thread of the screw must be slightly coated with a MoS2 based grease. For these bolt sizes also grease the supporting surface of the bolt head, unless hereafter otherwise specified.
5.14.1Mounting bolts of the counterweight
The mounting bolts 1 (M36 - 10.9) must be torqued to 3300 Nm (2430 ft.lbs).
5.14.2Mounting screws of the swing ring
The mounting screws 3 (M27 - 10.9) swing ring to undercarriage must be torqued to 1400 Nm (1030 ft.lbs.).
The mounting screws 4 (M27 - 10.9) swing ring to uppercarriage must be torqued to 1400 Nm (1030 ft.lbs.).
Check mounting bolts for tightness
5.14.3Mounting screws of the hydraulic oil and fuel tank
The mounting screws 5 (M20 - 10.9) must be torqued to 560 Nm (410 ft.lbs.)
5.14.4Mounting screws of the swing gear and motor
The mounting bolts 6 (M24 - 10.9) of the swing gear must be torqued to 960 Nm (710 ft.lbs).
Torque mounting bolts 7 (M20 - 10.9) of the swing motor to 560 Nm (410 ft.lbs).
5.14.5Mounting bolts central piece to side frames (option "removable side frames")
The bolts must be checked every 500 working hours, and if necessary retightened. The lower bolts M42 must be torqued to 4940 Nm (4380 ft.lbs).
The upper bolts M30 must be torqued to 1900 Nm (1400 ft.lbs).
5.14.6Fixing bolts of catwalks around the upperstructure
Every week visually check, and if necessary retighten the mounting bolts of the railer and also the ladder and suspended platform fixed around the upperstructure. Perform a general check of the tightening torque of these bolts every 1000 working hours. The bolts must be torqued to the following value:
5.15Drive unit brakes and swing gear brakes
Both the drive unit brakes and the swing gear brakes are spring-applied, pressurereleased multi-plate brakes. They are ventilated hydraulically and are fully sealed and integrated in the travel gear or swing gear transmission.
Their usage purely as parking brakes makes them wear-free and therefore maintenance free.
5.16General maintenance points
5.16.1Replacing working parts
In addition to the normal maintenance and repair work that is to be carried out at the given intervals, the machine operator and maintenance personnel can also carry out the repairs referred to below:
–Replacing worn teeth on the bucket.
–Replacing defective sealing material on the pipe and hose system and on the hydraulic unit connections (not, however, on pressure relief valves which are lead sealed at the works).
–In addition, high pressure hoses, hydraulic lines and bolt connections on the hydraulic system can be replaced.
It should be noted that only original LIEBHERR replacement parts are to be used.
This is particularly relevant for hoses and hydraulic lines, which must be preassembled at the works. For all other repairs, particularly when dismounting the ballast weight, works and dealership fitters are to be consulted.
5.16.2Checking or replacing the teeth on the bucket
Note!
Do not work with the machine if teeth on the bucket are missing or are heavily worn. With heavily worn teeth, considerably greater force will be required when using the bucket to penetrate the material to be excavated.
Determine the degree of wear of the teeth visually and at regular intervals (For intervall, refer to the maintenance chart).
Make the necessary to have heavily worn teeth replaced in good time, in any case early enough to prevent any damage occurring to the tooth fitting piece.
To attach and dismount the teeth:
Liebherr teeth system with flat locking wedge:
Fig. 5-70 Replacing the teeth
Use a hammer and ejector drift 1 to knock out the wedge 2 (A ). Remove the old tooth.
Place a new rubber wedge holder 3 onto the tooth holder (B).
Push the new tooth onto the fitting piece. Use the hammer to knock in the wedge 2 (C).
(New) Liebherr teeth system with tooth locking bolt round: To remove an old tooth
1Tooth fitting2 Tooth
3 Tooth locking bolt 4Latch
5 Expanded foam plug 10 Bolt blocking wrench
Take away the expanded foam plug 5 or the ground out of the square hole in the middle of the locking bolt 3
Set the bolt blocking wrench 10 (special tool Id. Nb. 10451202) onto the bolt 3 and turn counterclockwise to the stop (movement A - turn by approx. 30°).
Knock out the bolt 3 from the opposite side.
Take the tooth 2 off from the fitting 1 and remove the latching piece 4
To install a new tooth copyright by
Note!
Check the tooth locking bolt 3 and the latch 4 for good condition before reuse when installing a new tooth. Should this parts be distorted or strongly corroded, so they must be replaced by new ones.
Set the latch 4 in the hollow part of the tooth fitting 1 so that the flat side of the latch pushes against the fitting and slide the new tooth 2 over the tooth fitting 1
Push the tooth locking bolt 3 all the way in.
Engage the bolt blocking wrench 10 into the square hollow in the middle of the bolt 3 and lock the bolt by turning the wrench clockwise by approx. 30° (when turning, the nose 3a of the bolt is enforced over the protrusion 4a of the latch).
Take the blocking wrench away and press a new expanded foam plug 5 into the middle of the locking bolt 3.
5.16.3Welding work on the machine
Welding work on all main components or structural parts serving the power transmission (such as the undercarriage, uppercarriage, attachment parts etc.) may only be carried out by the manufacturer or by an authorized workshop.
Open the main isolator (outside the machine) before starting any electric arc welding work on the machine.
Switch off the main battery switch (option) and disconnect the batteries. Always disconnect the negative terminal (-) first and reconnect it last.
Caution!
If high currents flow through the bearings or sealing elements, these could be damaged.
Move the earthing cable of the welding tool as close as possible to the welding surface so that the welding current cannot flow over parts like the swing ring, articulations, bearings, bushings, rubber elements or seals.
5.17Inspection and maintenance schedule
Caution!
Careful maintenance is only possible, if the machine is clean. Especially visual inspections, e.g. for cracks, can only be carried out properly on a clean machine. Therefore clean the machine thoroughly before starting any maintenance work (see also chapter "Safe maintenance of machine", subchapters "Cleaning" and "Crack inspection").
Note!
The daily maintenance tasks of the machine operator include a functional test of the brakes and the electrical and hydraulic system. Also to be carried out is a daily visual inspection of the motor, hydraulic system, gearboxes and drive system.
by maintenance personnel (machine owner)
Initial and single interval
WORK TO BE CARRIED OUT ER 954 C - High-Rise
by authorised specialist technician Initial and single interval Repeat interval
ELECTRIC MOTOR AND PUMP DISTRIBUTOR GEAR
Check the terminal box cleaneliness.
Inspect and clean the fan hood and the cooling fins of the electric motor.
Lubricate the motor bearings (the lubrication interval and the quantity and quality of the lubricating grease are specified on the type plates, approx. 5400 operating hours / 2 years) (to be carried out by authorised specialist technician).
Check the oil level in the pump distributor gear.
Inspect and clean the radiator and fan.
Replace the oil in the pump distributor gear.
Check the sensor devices and cable connections.
Check the motor brackets and the pump distributor gear for proper attachment.
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
Check the oil level in the hydraulic tank.
Clean the magnetic rod in the return filter (daily during first 300operating hours).
Replace the filter cartridge in the control oil unit.
Replace the feed oil filter on the slewing gear pump.
Check the components and units for proper fixture.
Inspect and clean the hydraulic oil cooler and the fan.1)
Dewater the hydraulic tank (max. permissible water content for environmentally friendly fluids: 0.1%; use bypass filter, take oil sample).
If installed, check the hammer return filter for contamination and replace it.1) Replace the return filter cartridge (first time after 500operating hours).
Replace the leak oil filter cartridge (first time after 500operating hours). Replace the cartridge latest after 3 cleaning processes. 1)
Check the degree of contamination of the bypass oil filter (optional equipment); if required, change the filter cartridge.
Check the hydraulic system for leakage; complete a functional test. Check / readjust the servo, primary and secondary pressures.
Inspection and maintenance schedule
Maintenance/ inspection at operating hours by maintenance personnel (machine owner)
Initial and single interval
Repeat interval
Work To Be Carried Out
ER 954 C - High-Rise
by authorised specialist technician
Note
Special interval: every 250hours
Initial and single interval Repeat interval
If required, change the oil in the hydraulic system (to be carried out by specialist technical personnel; add oil through filter). For oil grades and change intervals, see fuels and lubricants, "Hydraulic oil".
Bleed the hydraulic pumps (after hydraulic oil change).
Replace the breather filter on the hydraulic tank.1)
Electrical System
Check the indicator lights and the indicating devices upon start-up.
Check the lighting system.
Check the clogging of the air filter from the electrical cabinet (option).
Empty the dust extraction valve of the air filter from the electrical cabinet (shorten or extend the interval, if necessary) (option).
Replace the main element of the air filter from the electrical cabinet (according to maintenance indicator, at least 1x per year) (option).
Replace the safety element of the air filter from the electrical cabinet (at every 3rdchange of the main element / at least 1x per year) (option).
Check the cleanness of the motor air line (during maintenance of the filter).
Check the acid density and level in the battery cells(option).
Check and clean the wire terminals and pole heads of the batteries (option).
Check the central vent tubes of the batteries for proper installation and damage (option).
Check the mounting bolts of the rotary connection and the driver for proper fixture.
Clean the rotary connection.
Carry out a visual inspection of the carbon brushes for wear. Remove the condensate from the inside surfaces.
Check the ring sliding faces for surface damage.
Carry out functional tests of the entire system and all components.
Inspect the electrical box hinges, lubricate or replace them.
Carry out functional tests of the automatic cut-outs.
Do not clean it!
WORK TO BE CARRIED OUT ER 954 C - High-Rise
by maintenance personnel (machine owner)
Initial and single interval
Repeat interval Special interval: every 250hours by authorised specialist technician
Initial and single interval Repeat interval
Slewing Gear Mechanism
Check the oil level; check the system for leakage. Change the gear oil (first time after 500operating hours).
Perform a functional test of slewing gear brake. Check the gearbox and oil motor for proper fixture.
Slewing Ring
Check the mounting bolts for proper fixture. Check the engagement of the slewing gear pinion.
Travel Gear
Check for leaks
Check transmission and oil motor mounts
Replace transmission oil (first time at 500 op. hours)
Tracks
Visual check on track tension, retension if necessary
Clean track (when work is finished)
Check mounts on track pads and sprockets
Clean and grease sliding surfaces of tensioning device
Check for leaks on idlers, carrier rollers and track rollers
OPERATOR'S CAB
Check / add detergent solution to the windscreen washer system tank.
Check the door hinges, window hinges and locks.
Heating System
Carry out a functional test of the heating system (before start of winter season).
Check the heating system for leakage.
Check / add the heaterfluid level.
Check the corrosion inhibitor and antifreeze agent concentration in the heaterfluid and adjust it, if necessary.
Note
Inspection and maintenance schedule
Maintenance/ inspection at operating hours
WORK TO BE CARRIED OUT
ER 954 C - High-Rise by maintenance personnel (machine owner)
Initial and single interval
Repeat interval
Special interval: every 250hours by authorised specialist technician
Initial and single interval Repeat interval
Change the corrosion inhibitor and antifreeze agent (every 3000operating hours or latest every 2years) (to be carried out by an authorised specialist technician).
Check the water inlet valve for dirt, and clean it, if necessary; carry out a functional test of the valve.
Bleed the Flamco vent.
Change the water of the heating system
AIR-CONDITIONING SYSTEM
Regularly switch on the air-conditioning system (at least 1x every 14days).
Check the condenser for dirt; blow it clean, if necessary.
Clean the recirculated air / fresh air filter; replace it, if necessary; shorten the interval, if there is excessive generation of dust.
Check the mounting bolts of the compressor for proper fixture.
Check the dryer-collector unit (humidity, fill level, damage); replace it, if necessary.
Check the evaporator unit; clean it, if necessary.
Check the electrical lines for chafe marks; check the plug connections for proper fixture.
Perform a functional test of the overpressure switch.
Check the cooling performance after opening/repair, or if required.
Replace the dryer-collector unit every 12 months; also check the cooling circuit for leakage and change the heaterfluid and refrigeration oil.
Every 12 months, contract a refrigeration technician to carry out a functional test of the air flaps, the pressure switches and the defrost thermostat.
UNDERCARRIAGE + UPPERCARRIAGE + WORKING ATTACHMENT
Lubricate the bearing points (undercarriage and attachments) through the lubrication system or directly at the bearing points (for points that are not integrated into the lubrication system).
Inspect the teeth visually for wear.
Check the parts for cracks.
Check the counterweight and the tank for proper fixture.
Check the lines and fittings for proper fixture.
copyright by
Note by maintenance personnel (machine owner)
Initial and single interval
Repeat interval
WORK TO BE CARRIED OUT ER 954 C - High-Rise
by authorised specialist technician
Note
Special interval: every 250hours
Initial and single interval
Repeat interval
Inspect the panelling hinges, quick fasteners and gas pressure springs of the hoods; if necessary, lubricate or replace them.
Check the lowering speed of the attachment.~ 4 sec.
Instruct the operators in the proper use of the machine.
Instruct the operator on how the machine must be lubricated according to the lubricating chart and make him aware of potential operator errors.
Hydraulic Quick Change Adapter
Perform a functional check of the visual and acoustic warning systems. Carry out a visual inspection of the extended lock bolts. Check the hydraulic hoses and the wire harness for damage. Lubricate the lock bolts.
Clean the mesh filters inside the fittings of the hydraulic hoses.
Mechanical Quick Change Adapter
Carry out a visual inspection of the extended lock bolts. Lubricate the lock bolts.
1) The maintenance intervals might have to be shortened, depending on the actual operating conditions (e.g. generation of dust, barrel fuelling).
Tab. 5-18 Maintenance chart copyright by
Inspection and maintenance schedule
Maintenance / inspection at operating hours
Additional Works To Be Carried Out On Machines Fitted With High Rise Undercarriage
By maintenance personnel (machine owner)
First and only interval
Repeat interval
Special interval every 250hours
By authorized specialist personnel
Note
First and only interval
Repeat interval
Mounting Bolts Of Undercarriage And Upperstructure
Visually check the mounting bolts undercarriage / swing ring and swing ring / upperstructure, retighten as necessary
Retighten to the prescribed tightening torques the bolts undercarriage / swing ring and swing ring / upperstructure
Visually check the mounting bolts of stairways and platforms around the upperstructure, retighten as necessary
Retighten to the prescribed tightening torques the bolts of stairways and platforms around the upperstructure
Check the mounting bolts of side frames to central piece for tightness, retighten to the prescribed tightening torque as necessary
Tab. 5-19 Chart for additional maintenance works
Maintenance works for cab adjustable on double //ogram
Maintenance of the cab elevation is limited essentially to regular visual checks of the structure and the elevation's hydraulic system.
Additionally, the machine should be washed periodically. Worn seals, cracks and other faults can be spot more easily on a well cleaned machine.
Determined malfunctions of the cab elevation are to be remedied immediately.
All repair work on the elevation is to be carried out while the cab is positioned on flat and even ground.
Depending on the repair, all the necessary parts are to be supported. Only walk, stay or work underneath the parts if they are correctly supported.
Note!
Modifications such as drilling, burning or welding on components that serve as carrying structures to the elevation may only be carried out by the manufacturer or by an authorized contracted workshop. Modifications to the adjustment of the elevation's hydraulic components may only be carried out by the manufacturer or by an authorized contracted workshop.
Before each intervention in the hydraulic circuit, the control pressure and the high pressures in the elevation's working circuits are to be released as follows : With the cab lowered to the ground, bring the start key into the contact position (safety lever must be in the down position), switch on the servo-control circuit for cab adjustment via the push button S370, briefly actuate the joystick U45 in all 4 directions (keep S370 pressed down), copyright by
Maintenance / inspection at operating hours the high pressures are released despite of the line-break protection valves installed on the hydraulic cylinders of the cab elevation, then release the push button S370 and remove the start key, ....and release the hydraulic tank pressurization as described before in this manual .
Additional Works On Machines Fitted With Cab Adjustable On Double Parallelogram
By maintenance personnel (machine owner)
First and only interval
Repeat interval
Special interval every 250hours
By
First and only interval
Repeat interval
CAB ELEVATION - STRUCTURES AND HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS
Visually check the condition of the cab elevation, inspect for parts that may have broken off, fallen off or are worn
Before working, visually check the cab elevation’s hydraulic system for leaks
Check the function of the both valves inside the cab for emergency lowering of the cab elevation
Check the function of the both valves on the elevation support for emergency lowering of the cab elevation
Check the fonction of the automatic cut-off of swing movements and lighting up of warning light
Check the fonction of the automatic cut-off of cab lowering movements
Visually check the exuding of grease at each bearing point lubricated via the central lubrication system
Check the fixing screws of the cab elevation’s base onto the uppercarriage for secure fastening. As necessary retighten these M30 fixing screws to 2300 N.m
Thorougly wash the machine in the area of the cab elevation
Visually inspect the hydraulic hoses and hydraulic components for leaks, damage and other faults
Visually inspect the steel structure parts of the cab elevation for crack formations





