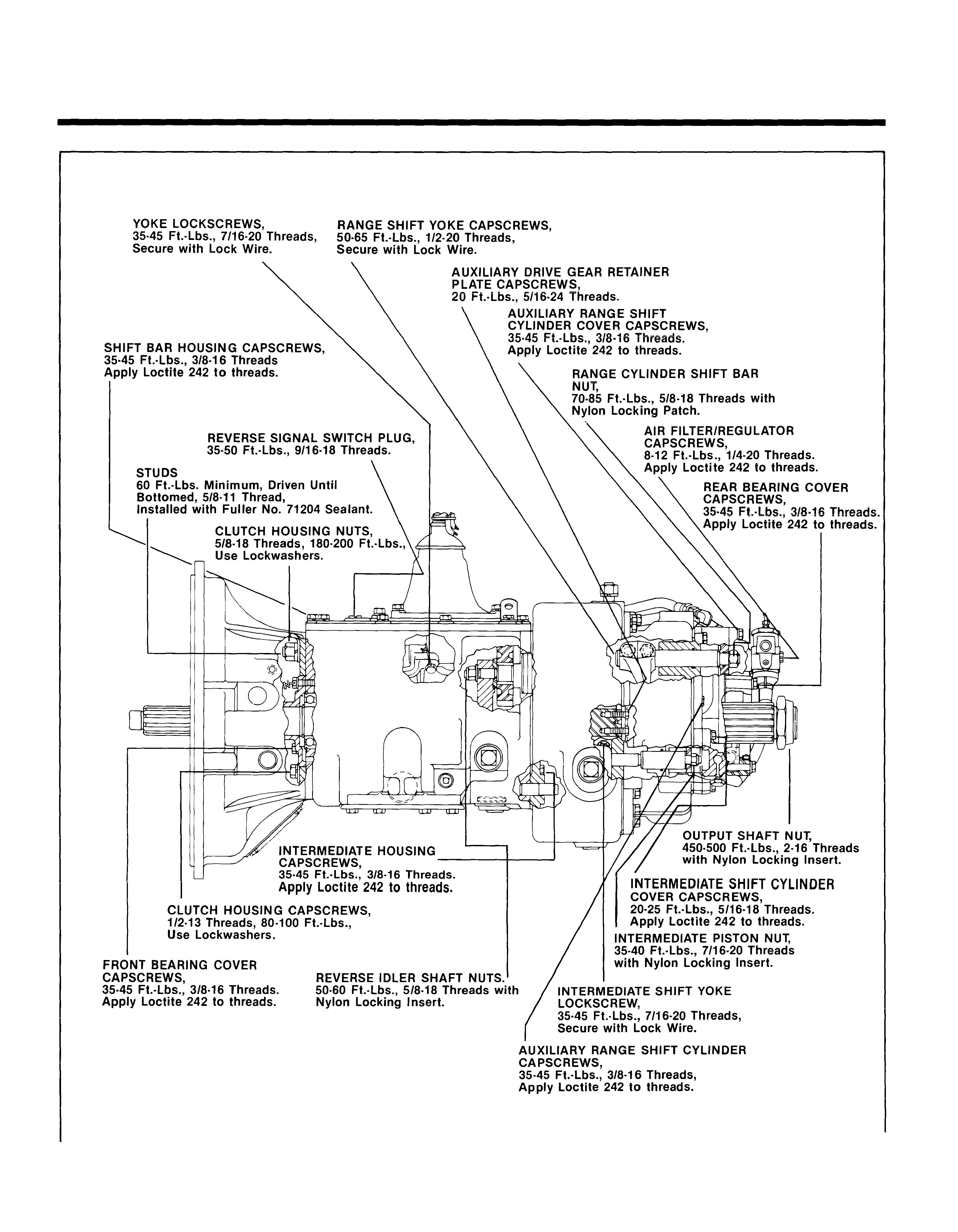
1 minute read
POWER FLOW
The transmission must efficiently transfer the engines power, in terms of torque, to the vehicles rear wheels. Knowledge of what takes place in the transmission during torque transfer is essential when troubleshooting and making repairs becomes necessary.
FRONT SECTION POWER FLOW:
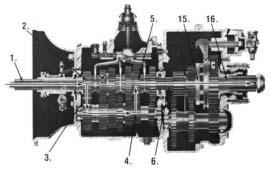
Power (torque) from the vehicles engine is transferred to the transmissions input shaft. Splines of input shaft engage internal splines in hub of main drive gear. Torque is split between the two countershaft drive gears and is delivered along countershaft to all countershaft gears. Torque is transferred to "engaged" mainshaft gear. The following cross section views illustrate a 1st/4th/9th speed gear engagement. Internal clutching teeth in hub of engaged mainshaft gear transfers torque to mainshaft through sliding clutch. Mainshaft transfers torque directly to auxiliary drive gear.
POWER FLOW
Auxiliary Section Power Flow:
7. The auxiliary drive gear splits torque between 9. Torque is transferred to output shaft through the two auxiliary countershaft drive gears. sliding clutch.
8. Torque is delivered along both countershaft to 10. Torque is delivered to driveline (LO 1st shown). the "engaged" reduction gear on output shaft.
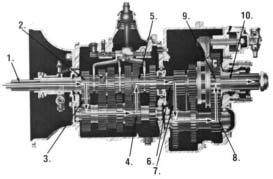
LOW - POWER FLOW
Auxiliary Section Power Flow:
11.
12.
The intermediate drive gear splits torque be- 13. tween the two auxiliary countershaft intermediate gears.
14.
Torque is delivered along both countershaft to the "engaged" reduction gear on output shaft. Torque is transferred to output shaft through sliding clutch.
Torque is delivered to driveline (INTERMEDIATE RANGE 4th shown).
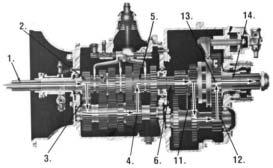
POWER FLOW
Auxiliary Section Power Flow:
15. The intermediate drive gear transfers torque 16. directly to the output shaft through "engaged" sliding clutch. Torque is delivered through output shaft to drive line (HIGH RANGE 9th shown).