5 minute read
DCS Concept
DCS CONCEPT
DCS is an electronic methane and engine-monitoring shut down system for the use on diesel engine powered machinery used for underground coal mining. The principle behind this system is to prevent the machine from operating when it may present an increased risk of igniting an explosive atmosphere. The system achieves this by monitoring a set of sensors, such as methane gas detectors, component temperature sensors, coolant flow sensors and so forth. Due to the DCS being interlinked with the engine control system on the machine the system uses this information to determine if the prevailing conditions and operating parameters are safe or unsafe, and may take action such as denying a request to start the machine, or initiating shutdown of the machine, depending on the result of this safety assessment. The system also conducts an assessment upon its own integrity. If the system cabling is damaged, any sensors are reporting invalid values, the internal battery is flat, or other abnormal conditions are detected, the system will prevent the machine from operating. The system is “fail safe” in this sense – if it cannot be positively determined that all conditions are safe, then they will assumed to be unsafe and the according actions will be taken by default. In addition to safety related assessments, the DCS system also monitors a number of operational assessments that may produce a warning to the operator, or may cause the system to shut down. These assessments are intended to avoid damage or excessive wear to the machine, and use the same shutdown mechanism as the safety assessments. The shutting down of the machine is effected via a solenoid valve that controls the pilot air pressure for the safe start shutdown valve on the machine. Should there be a malfunction in the solenoid circuit, the driver is also alerted with an indicator on the display panel in the operators cabin
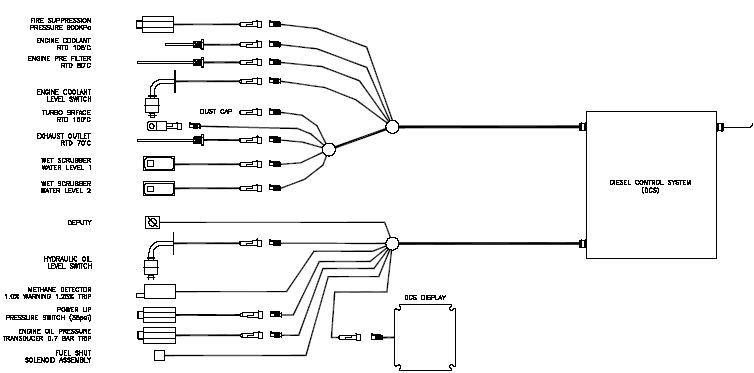
General Inputs and Outputs
Display Unit – This is the point of communication with the operator. The display consists of a small screen and keys to navigate menus, select options and so forth. The display consists of a status page, showing the current actions being taken by the system and any warnings or trip indications, along with a menu holding pages showing sensor values, log options etc. Power-Up Sensor – This sensor is used to determine when the machine is “switched on”, and hence when the DCS should start operation. The DCS will begin operation when the operator activates the air toggle switch Deputy Switch – Under certain circumstances, an appropriately authorised person may deem it necessary to operate the machine despite a high methane level being sensed. This person can unlock the Deputy Switch and engage it, causing the machine to ignore a high methane level. The machine WILL RUN DESPITE HIGH METHANE LEVEL if the Deputy switch is engaged! Ensure the Deputy Switch is disengaged when it is no longer required. Also configurable for methane reset. Methane Sensor – The Methane Sensor is used to measure the concentration of methane in the atmosphere around the machine. It is configurable for varied percentage trips. Fuel Solenoid – The Fuel Solenoid is used to control the availability of fuel to the engine by controlling the air to the fuel rack cylinder. It is engaged when the system is safe, allowing fuel to flow to the engine and the engine to run.
WARNING Deputy Switch should not be used without prior authorisation from mine management
Alternator – The Alternator is driven by the engine of the machine, and supplies current to the DCS. The DCS uses this current to maintain a battery, allowing the DCS to operate as required when the engine is not running. If the Alternator fails, the DCS will begin to discharge its own battery. This condition should be avoided. After 30
minutes the engine will shutdown if the alternator is not charging the battery. This is used as an indication that the engine is running. Engine Coolant Level – The engine may reach a high temperature if the coolant falls below a particular level. This may damage the engine and produce an unsafe condition. Engine Coolant Temperature – Under adverse circumstances, the engine coolant may reach a high temperature. This could damage the engine or produce an unsafe condition. The engine coolant is deemed to be too hot if it exceeds 105°C, and the engine will not be permitted to run. A warning will be given if it exceeds 100°C. Engine Oil Pressure – If the engine oil pressure falls too low, the engine may be damaged. In the process, excessive heat may be generated causing an unsafe condition. If the pressure falls below 0.7 Bar, the engine will be halted. Oil pressure is also used as an indication that the engine is running. Exhaust Outlet Temperature – If the exhaust leaving the machine is too hot, it may cause an unsafe condition. The temperature is measured, and if it exceeds 77°C,the engine will not be permitted to run. If it exceeds 65°C a warning will be given. Hydraulic Oil Level (Warning only) – If the hydraulic oil level falls too low, the hydraulic components of the machine may be damaged or become heated to an unsafe level. The machine will not be permitted to run in this instance. Turbo Surface Temperature – If the turbo becomes too hot, it may cause an unsafe condition. If the measured temperature exceeds 148°C the engine will not be permitted to run. If it exceeds 140°C a warning will be given. Exhaust Scrubber Temperature – If the exhaust becomes too hot, it may cause an unsafe condition. If the measured temperature exceeds 80°C the engine will not be permitted to run. If it exceeds 75°C a warning will be given. Fire suppression Pressure – If the fire suppression system pressure falls below 1100
KPa the system will issue a warning. When the fire system is activated and the pressure falls below 900 KPa the engine is shut down.
WARNING: This cable can not be removed from this enclosure. It forms part of the approval and is encapsulated in the DCS
Start /Initiate switch Run Solenoid








