

New HVACR Refrigerant
Requirements: Are You Ready?

BRENT FELTEN, PE
Business Development
Director



JASON CORNETT
Refrigeration Technical Manager


AIA COURSE: AIAHVACRRR01

“Henderson Engineers, Inc.” is a Registered Provider with The American Institute of Architects Continuing Education Systems (AIA/CES). Credit(s) earned on completion of this program will be reported to AIA/CES for AIA members. Certificates of Completion will also be provided to all attendees.
This program is registered with AIA/CES for continuing professional education. As such, it does not include content that may be deemed or construed to be an approval or endorsement by the AIA of any material of construction or any method or manner of handling, using, distributing, or dealing in any material or product.
Questions related to specific materials, methods, and services will be addressed at the conclusion of this presentation.
AGENDA

DUNNING-KRUGER EFFECT

“I haven’t committed every Refrigeration related regulation to memory, but I know where to look and who to ask, if I’m not able to answer your question directly.”
– Jason Cornett


ARE YOU READY FOR IT?

1. What is your company’s Refrigerant Management Program?
a. Significant fines for failure to report or comply ($57k/day)
2. Chronically leaky equipment
a. Refrigeration, air conditioning, and heat pump (RACHP)
b. ….More fines
c. Equipment replacement requirements, probation, etc.
3. Navigating Compliance
a. Proper tool adoption
b. Automation is key
c. Simplify processes and add feedback loop
d. Don’t wait

4. Do you have any NEW construction projects?
a. Any being built this year, but not grand opening until 1/1/2026?
5. Do you have any planned REMODEL projects?
6. How about CAP-EX projects? ARE YOU READY FOR IT?


The American Innovation and Manufacturing EPA (AIM) ACT

The AIM Act
Three-Legs of the EPA’s
HFC Regulating “Stool”

Phasedown of
Hydrofluorocarbons
Technology Transitions
subsection (i)
Refrigerant Management
subsection (h)

The AIM Act
Three-Legs of the EPA’s
Regulating

Phasedown of Hydrofluorocarbons
Following the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol Allocations
Prohibiting
Technology Transitions subsection (i)
Refrigerant Management subsection (h)

PHASEDOWN OF HFCs
Phasedown of Hydrofluorocarbons

Allocations for Consumption
HFC PHASEDOWN - ALLOCATIONS

2023 – Production and Consumption limited to 90% of baseline
2024-2028 – Production and Consumption limited to 60% of baseline
2029-2033 – Production and Consumption limited to 30% of baseline
2034-2035 – Production and Consumption limited to 20% of baseline
2036 – Production and Consumption limited to 15% of baseline



HFC PHASEDOWN

GWP = Global


Cost per 25LB – as of 2/27/2025





IMPLEMENTATION IMPACT

GWP of CO2 = 1

Kigali Phasedown (Schedule)
<3 (Natural Refrigerants)
R404A/R507 (Baseline)

R448A (Very Common)
<150 GWP (AIM Act – REFRIG)
<700 GWP (AIM Act – HVAC)

Significant Threshold 2029
COMPARISON – INCENTIVE TOWARDS LOWER GWP



More LBS = Lower GWP



TECHNOLOGY TRANSITION subsection
(i)
Technology Transitions
subsection (i)

Enforcement Began January 1, 2025
Prohibiting the MANUFACTURE AND IMPORT of products that use higher-GWP HFCs
Prohibiting the SALE, DISTRIBUTION, AND EXPORT of those products three years after the manufacture and import restriction
Prohibiting the INSTALLATION of new RACHP systems that use higher-GWP HFCs
TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)

Refrigeration, air conditioning, and heat pumps (RACHP) Product


RACHP
EXISTING EQUIPMENT

1. Serviceable, but expensive until end of life (EOL) $$$$ of Refrigerant
2. They can make you replace equipment, if determined “chronically leaky”


REFRIGERANT MANAGEMENT subsection (h)
Refrigerant Management subsection (h)

ALDS (Automated Leak Detection Systems)
1,500LBS or more with a GWP 53
Enforcement Begins January 1, 2026**
Pending FL appeal
Labeling, Recording, Record Keeping, Container Tracking Leak Repair 15LBS or more with a GWP 53
Reclaim and initial refrigerant charge requirements 15 percent virgin HFCs, by weight

REFRIGERANT TRANSITION
ASHRAE REFRIGERANT AND REFRIGERATION STANDARDS

ASHRAE 15 ASHRAE 34





ASHRAE 34 – REFRIGERANT NUMBERING

Synthetic Refrigerants
• R404A
• R410a – Phasing Out Production
• R448A – Above GWP Thresholds
• R513A – MT Refrigeration Only
• R454A,B,C – (A2L)
• R32 – Comfort Cooling (A2L)

Natural Refrigerants
• R744 – CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
• R290 – C3H8 (Propane)
• R600a – C4H10 (Isobutane)
• R717 – NH3 (Ammonia)
• R718 – H2O (Water)
Patented Product vs. Industrial Gas
CO2 is a biproduct from many processes (Beer Brewing & Corn Ethanol Production)

ASHRAE 34
–
TOXICITY & FLAMMABILITY

Toxicity (1st Digit)
B = Higher Toxicity
A = Lower Toxicity
Flammability (2nd Digit)
3 = Higher Flammability
2 = Lower Flammability
2L = Very Low Flammability*
1 = No Flame Propagation
ASHRAE 34 – TOXICITY & FLAMMABILITY

A1 - Lower Toxicity, No Flame Propagation
› R22, R410A, R134a,
› R404A, R407A, R448A, R513A, R744 (CO2)
A2L - Lower Toxicity, Very Low Flammability
› R455A, R454A, R454B, R454C, R457A, R32
A3 - Lower Toxicity, Higher Flammability
› R290 (Propane), R600a (Isobutane), R600 (Butane)
B2 - Higher Toxicity, Low Flammability
› R717 (Ammonia)
EPA SNAP - FINAL RULE 26


EPA SNAP - FINAL RULE 26

What is finalized in the Rule?
1. “LISTED”
a. 10 refrigerants as acceptable (subject to use conditions)
b. A2L & A3 (Modifies use conditions for R-290)
2. Incorporates
a. ASHRAE 15-2024, ASHRAE 34-2022, & UL 60335-2-89
3. Exempts R-290 from EPA Section 608 venting prohibition

A2L & A3 - REGULATORY STATUS

A2L Use in Commercial Refrigeration
UL (Underwriters Laboratory) =
EPA (SNAP 26) =
Model Codes = Incorporated into 2024 Code Cycle 5. Local Code Adoption* = TBD A3 Charge increase (From 150g currently to 500g Open case; 300g Door Case)
EPA (SNAP 26) =
Model Codes = Incorporated into 2024 Code Cycle
Local Code Adoption* = TBD * Model codes are only enforceable after they are adopted into code by a justification (Typically, but not always a State)
KEY TAKEAWAYS – A2L REFRIGERANTS
A2L System Considerations
Due to flammability more safety precautions than traditional A1 Refrigerants
1. Leak detection shutdown
2. Increased leak detection locations
3. Reduced charge limits
a. Commercial Refrigeration = 160-200LBS*
b. Commercial HVAC = 22LBS*
4. Machinery Room Provisions
5. Compressors & Electrical safety provisions to prevent ignition
6. Chemical degradation components of A2L’s are under scrutiny
a. (TFA) – Triflouroacetic acid
b. Follows the water cycle (potential contaminant to drinking water)

*Dependent upon the volume of the releasable charge
KEY TAKEAWAYS – A3 REFRIGERANTS

A3 Charge Increase
1. Pending Model Code Adoption – Local AHJ’s
2. Charge increase will allow larger R290 display cases become more practical
a. 12’ case example (allow a single condensing unit to serve, vs. 3 units)
The EPA AIM ACT
Technology Transition Rule

Okay, but what does this stuff look like?
Self-Contained Refrigerated Merchandiser

January 1, 2025

Effected Equipment
• Plug-in merchandisers
• Self-contained units
• Vending machines
Any equipment manufactured on or after 1/1/2025, must comply
• GWP of 150 or lower
• Regardless of Refrigerant Charge
*Ice Cream Machines within UL 621 are not impacted until 2028
Chillers Comfort Cooling

January 1, 2025

Effected Equipment
• Chillers used for comfort cooling
Any equipment installedon or after 1/1/2025, must comply
• GWP of 700 or lower
Heat Pumps
Light Commercial HVAC



January 1, 2026**
Effected Equipment
• Rooftop units
• Mini-splits
• Air conditioning & heat pumps
Any equipment installed* on or after 1/1/2026, must comply
• GWP of 700 or lower
**New systems with a GWP above 700 can be installed until January 1, 2026, so long as all components are manufactured or imported prior to January 1, 2025 (refer to the Interim Final Rule for additional details).
Variable Refrigerant Flow
Stationary AC & Heat Pumps

January 1, 2027**


Effected Equipment
• Rooftop units
• Air conditioning & heat pumps
Any equipment installed* on or after 1/1/2027, must comply
• GWP of 700 or lower
**New systems with a GWP above 700 can be installed until January 1, 2027, so long as all components are manufactured or imported prior to January 1, 2026. New systems with a GWP above 700 can be installed until January 1, 2028, in buildings that were issued an approved building permit prior to October 5, 2023, as long as that permit approved the use of an HFC or blend containing an HFC in such a system, and all components used in that system are manufactured or imported prior to January 1, 2026 (refer to the Variable Refrigerant Flow Air Conditioning Final Rule for additional details).
Ice Machines
Commercial
January 1, 2026

Effected Equipment
• Commercial ice machines
• Stand alone Any equipment manufactured on or after 1/1/2026, must comply
• GWP of 150 or lower
• Batch-type and continuous units
• <=1,000 & 1,200LBS /day respectively
• Larger units have a 1/1/2027 compliance date

Remote Condensing Units
Retail Food

January 1, 2026


Effected Equipment
• Remote Condensing Units (RCU)
Any equipment installed* on or after 1/1/2026, must comply
• GWP of 300 or lower for less than 200LBS
• GWP of 150 or lower for more than 200LBS
• *Field Charge completed
Rack Systems
Cold Storage Warehouses
January 1, 2026



Effected Equipment
• Centralized rack skids
• Distributed rack units
Any equipment installed* on or after 1/1/2026, must comply
• GWP of 300 or lower for less than 200LBS
• GWP of 150 or lower for more than 200LBS
• *Field Charge completed
Rack Systems
Retail Food – Supermarkets
January 1, 2027

Effected Equipment
• Centralized Rack Skids
• Distributed Rack Units
Any equipment installed* on or after 1/1/2027, must comply
• GWP of 300 or lower for less than 200LBS
• GWP of 150 or lower for more than 200LBS
• *Field Charge completed

ERA’S TOUR COMPARED TO REFRIGERANT EMISSIONS

During an NASRC training, Andre Patenaude, from Copeland, compared
• Taylor Swift’s 1st leg of the U.S. Era's Tour travel
• 37,053 miles (113 Flights)
• Equated to 39.5LBs of R404a leaked = 154,919 LBS CO2e = 77.5 Tons CO2e
• She does offset these emissions with carbon credits
Let’s see what her entire Era’s Tour looks like, compared to Refrigerant emissions
• ~240,000 miles (see link estimating total flight hours)
Grocery and cold storage systems average a ~20% leak rate per year
• A system with 2,000LBS R404a = 400LBS leaked/year
• 3,922 x 400LBS = 1,568,800 LBS CO2e = 786 Tons CO2e/year
• ~1.6x more CO2e per grocery store in just refrigerant leaks
• Equates to 255.9LBS R404a leaked = 1,003,967 LBS CO2e = 501.9 Tons CO2e R404a GWP = 3,922 24LB Cylinder for scale

The EPA AIM ACT
Technology Transition Rule

What options do I have for my facility?
The EPA AIM ACT
Technology Transition Rule

C-Store Example
CONVENIENCE STORE EXAMPLE –
1/1/2026

New Build
• New equipment
Refrigerant options
• RCU (GWP Under 150) CO2 or pending A2L equipment once available
• A2L Equipment is awaiting UL listings, etc.
• CO2 RCUs available but 10-30% price premium
• Central Rack System (GWP Under 150 or 300 pending Refrigerant Charge)
• CO2 Racks Available now
• Self-Contained Units (GWP Under 150)
• R290 units
• Heat rejection within the retail space is only practical for 1-5 fixtures
• Micro-Distributed Water-Cooled Equipment
• R290 or A2L Charge limitations (model code adoption slow)
• Value Proposition dependent upon 1 condensing unit per 12’ fixture
• HVAC (GWP Under 700)
The EPA AIM ACT
Technology Transition Rule

Retail Store Example
RETAIL STORE EXAMPLE –

Tenant Improvement
• New rooftop equipment (GWP under 700)
• R410a is OUT
• Manufacturer and Import Ban, 1/1/25
• R32 (A2L) – Manufacturer Dependent
• Single Component Refrigerant, able to “top-off”
• 10-Years in the market, not new, used in blends also
• R454B (A2L) – Manufacturer Dependent
• has a temperature glide, due to blend
• 69% R-32 & 31% R-1234yf
• R-1234yf = 100% TFA when leaked, within 10-14 days
• New refrigerant, not widely adopted
The EPA AIM ACT
Technology Transition Rule

Grocery Examples
GROCERY EXAMPLE –
1/1/2026

Capital Expenditure Project
• Like-For-Like
• Unit can be maintained until EOL
• Cap-ex unit cooler replacement % of fixtures not to exceed 75%
• If Rack Systems need replaced, then a refrigerant conversion would be best

GROCERY EXAMPLE –
1/1/2027

Remodel
• Existing HIGH GWP equipment
• If adding load:
• Best option is to add a CO2 condensing unit or selfcontained cases to shed load off the existing system
• Complete a refrigerant conversion to a lower GWP refrigerant

The EPA AIM ACT
Technology Transition Rule

Cold Storage Warehouse Example
COLD-STORAGE WAREHOUSE EXAMPLE
– 1/1/2027

Addition/Expansion – New Equipment
• New CO2 Rack System
• Low-charge ammonia
• Packaged units or split

LIVING IN OUR REFRIGERANTS ERA

1. INFORM, yourself and stakeholders
2. ASSESS, the impact to your business
3. PREPARE, for the regulations proactively (now is better than later)
a. Price Increases for HIGH GWP Refrigerants
4. PLAN, for worst case with supply chains and permitting, etc.
a. For NEW, REMODEL, TI, & CAP-EX construction projects, plan for equipment installation with construction schedules.
a. Work backwards from the install and compliance dates
b. Don’t risk it.
5. INVEST, in your PROCESS
a. Software solutions
b. Avoid chronically leaky RACHP equipment
a. Equipment replacement
6. IDENTIFY, who needs to be involved and at what level
7. VERIFY, your processes for Refrigerant Management are followed
8. TRUST, your partners
a. Reach out to your industry partners!
b. We are ALL in this together
I-PLAN-IT
Strategic Approach to Refrigerant Transition

I – INFORM yourself and stakeholders
P – PREPARE for regulations proactively (now is better than later)
L – LOOK AHEAD to price increases for high-GWP Refrigerants
A – ASSESS the impact on your business
N – NEW PROJECTS – Plan installation timelines for remodels, TI, and CAP-EX
I – INVEST in process improvements, leak prevention, and equipment upgrades
T – TRUST your partners – Industry collaboration is key!


RESOURCES & REGULATORY LINKS

Technology Transitions Program | US EPA
Restrictions on the Use of Certain HFCs under Subsection (i) of the AIM Act | US EPA
Technology Transitions GWP Reference Table | US EPA
Fact Sheet: Final Rule 26 - Listing of Substitutes under the Significant New Alternatives Policy Program in Commercial and Industrial Refrigeration | US EPA
Protecting Our Climate by Reducing Use of HFCs | US EPA
Management of Certain HFCs and Substitutes under Subsection (h) of the AIM Act | US EPA
The Hydrofluorocarbon Phasedown and Commercial Space Conditioning: A Guide to the Transition | NREL
CODE OF FEDERAL REGULATIONS - PART 84 - PHASEDOWN OF HYDROFLUOROCARBONS
• Title 40 CFR Chapter I, Supchapter C, Part 84
• eCFR :: 40 CFR Part 84 -- Phasedown of Hydrofluorocarbons
RESTRICTIONS ON THE USE OF CERTAIN HYDROFLUOROCARBONS UNDER THE AMERICAN INNOVATION AND MANUFACTURING ACT OF 2020
• Federal Register :: Phasedown of Hydrofluorocarbons: Restrictions on the Use of Certain Hydrofluorocarbons Under the American Innovation and Manufacturing Act of 2020
ALLOWANCE ALLOCATION METHODOLOGY FOR 2024 AND LATER YEARS
• Federal Register :: Phasedown of Hydrofluorocarbons: Allowance Allocation Methodology for 2024 and Later Years
EPA AIM ACT AND SNAP FINAL RULE 26 FACT SHEETS
• https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2023-10/technology-transitions-final-rule-fact-sheet-2023.pdf
• https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2024-05/snap-final-rule-26-factsheet.pdf

The EPA AIM ACT
Technology Transition Rule

APPENDIX & RESOURCES


1. *These slides are a summary of The EPA’s Current Regulatory framework and are based on the documentation of the final rules as of 2/11/2025.
2. *These slides focus on the HVACR equipment commonly found in supermarkets & commercial applications.
3. *These slides are not meant to be a substitute for reading the regulatory text.
• The American Innovation and Manufacturing (AIM) Act represents a critical regulatory shift in how businesses handle hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), potent greenhouse gasses used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
• With the impending regulatory updates taking effect at the beginning of 2026, facility managers need to understand the steps they must take to comply.
• These slides distill the essential elements of the AIM Act, how to determine if your operations are affected, and the necessary actions to ensure compliance.
• (RACHP) – Refrigeration, air conditioning, and heat pumps
EPA AIM ACT

The AIM Act
Three-Legs of the EPA’s
HFC Regulating “Stool”
PHASEDOWN OF HFCs
Phasedown of Hydrofluorocarbons

Allocations
Following the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol
Prohibiting the manufacture and import of products that use higherGWP HFCs
Technology Transitions subsection (i)
Refrigerant Management subsection (h)
Prohibiting the sale, distribution, and export of those products three years after the manufacture and import restriction
Prohibiting the installation of new RACHP systems that use higherGWP HFCs.
Leak
Repair 15LBS or more GWP 53 ALDS, labeling, etc. HFC Refrigerant reclaim requirements

PHASEDOWN OF HFCs
KEY POINTS OF THE HFC PHASEDOWN

1. Stepwise Reduction Over 15 Years
The phasedown follows a schedule that reduces HFC supply in stages based on a baseline consumption level:
• Baseline Year: Based on average HFC usage from 2011-2013
• 2022: 10% reduction from baseline (already in effect)
• 2024: 40% reduction (major supply cut, currently in effect)
• 2029: 70% reduction (further tightening)
• 2034: 80% reduction
• 2036 & Beyond: 85% reduction (final target)
KEY POINTS OF THE HFC PHASEDOWN

2. Impact on Refrigerants & Industry
• High-GWP refrigerants like R-404A, R-410A, and R-134a are being phased down in favor of lower-GWP alternatives (e.g., A2Ls like R-454B, R-32, and natural refrigerants like CO₂ and ammonia).
• HFC supply will shrink, leading to higher prices, limited availability, and increased demand for alternatives.
• Equipment manufacturers and contractors must transition to compliant refrigerants and manage retrofits, servicing, and replacements accordingly.
KEY POINTS OF THE HFC PHASEDOWN

3. Enforcement & Regulations
• The EPA enforces the phasedown through production and consumption limits, allowances, and import/export controls.
• Violations can result in fines and penalties for non-compliance.
Why It Matters
• This phasedown affects HVACR equipment selection, refrigerant pricing, service practices, and long-term planning for businesses.
• Compliance requires strategic planning for refrigerant transitions, leak management, and equipment upgrades.

TECHNOLOGY TRANSITION subsection
(i)
TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)

Technology Transition Under the AIM Act
The Technology Transition component of the AIM Act focuses on restricting the use of high-GWP HFCs in specific applications by setting mandatory GWP limits for certain types of equipment. This is separate from the phasedown but complements it by forcing industries to adopt lower-GWP alternatives on a set timeline.
Key Dates & Compliance Deadlines:
• January 1, 2025 – Manufacturers must stop producing or importing new HVACR equipment using restricted high-GWP HFCs.
• January 1, 2026 – Installation bans take effect, meaning only compliant equipment can be installed after this date.
TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)

Affected Equipment Categories & GWP Limit
The EPA has set maximum GWP limits for different types of equipment, requiring a transition to lower-GWP refrigerants like A2Ls (e.g., R-454B, R-32), CO₂, ammonia, and hydrocarbons.
TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection
(i)

Industry Impact
• New equipment must be designed for low-GWP refrigerants, which may require changes in system components and safety protocols.
• Contractors and facility managers must prepare for the installation deadline (1/1/2026) to avoid project delays.
• Permitting & building codes must align with new refrigerants, especially A2Ls, which have different safety requirements.
Why It Matters
• The Technology Transition rules make the phasedown more than just a supply constraint—they legally prohibit certain high-GWP refrigerants in new equipment, forcing businesses to plan for compliance.
TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)

Note Differences between Manufacture & Import Compliance from Installation Date


TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)

Note Differences between Manufacture & Import Compliance from Installation Date


TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)

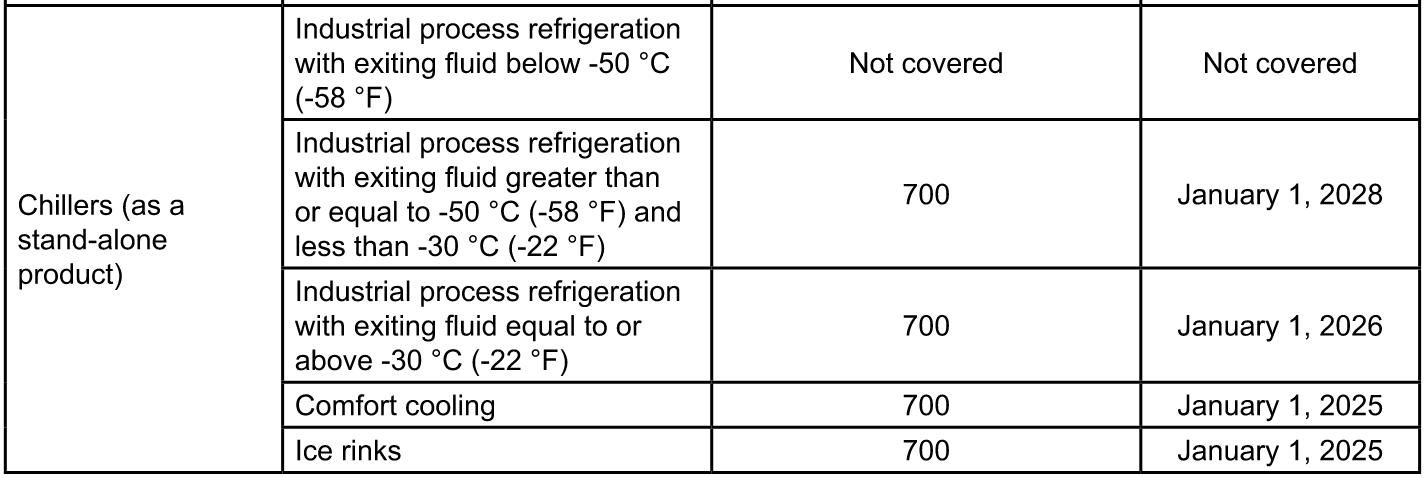
TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)



TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)

TECHNOLOGY TRANSITIONS - subsection (i)



REFRIGERANT MANAGEMENT subsection (h)
REFRIGERANT MANAGEMENT - subsection (h)

The Emissions Reduction and Reclamation (ER&R) Program
Proposed Regulation – Beginning January 1, 2026
1. Leak repair
a. For appliances containing 15 pounds or more of an HFC Refrigerant
b. With a GWP above 53.
2. Use of automatic leak detection (ALD) Systems
a. For certain new and existing appliances containing 1,500 pounds or more of an HCF refrigerant
b. with a GWP above 53.
3. HFC refrigerant reclaim requirements
a. That are sold, identified, or reported as reclaimed refrigerant for use in the installation, servicing, and/or repair of refrigerant-containing equipment may contain no more than 15 percent virgin HFCs, by weight.
REFRIGERANT MANAGEMENT - subsection (h)

4. Reclaimed HFC – Initial Charge
a. For initial charge and servicing and/or repair of existing equipment
b. Including fire suppression equipment.
i. The servicing, repair, disposal, or installation of fire suppression equipment that contains HFCs. Including required technical training in the fire suppression sector.
5. Recovery of HFCs
a. From disposable cylinders prior to disposal.
6. Container tracking
a. For HFCs that could be used in the servicing, repair, and/or installation of equipment.
7. Recordkeeping, reporting, and labeling.
For more information on these proposed regulations see link below where each is expanded upon.
https://www.federalregister.gov/d/2023-22526
REFRIGERANT MANAGEMENT - subsection (h)

The Emissions Reduction and Reclamation (ER&R) Program
Proposed Regulations – Beginning January 1, 2026
EPA-certified reclaimers
1. Must affix a label to any container they fill that is being sold or distributed or offered for sale or distribution and that contains reclaimed HFC(s) to certify that the contents meet the reclamation standard.
2. Are required to generate a record to certify that the reclaimed HFC(s) they fill into containers that will be sold or distributed or offered for sale or distribution meet the reclamation standard. These records must be maintained at the batch level and for three years.
ASHRAE STANDARD 15 – SAFE DESIGN

Requirements before design
1. The safety group classification of the refrigerant, as defined by Standard 34
2. The occupancy classification of the room served by the refrigeration system, and
3. The refrigeration system classification, which is based on the likelihood (probability) of refrigerant leaking from a refrigeration system into an occupancyclassified area of the building.
A. Defines design, installation, and operational requirements for refrigerant safety.
B. Establishes leak detection, ventilation, charge limits, and occupancy considerations for A2Ls.
ASHRAE 34 – REFRIGERANT NUMBERING

Synthetic Refrigerants
• Man-Made
• Pure Fluids or
• Mixtures
• Azeotropic
• Zeotropic – R-4xxx
• Patented Chemical Blends
• x%, xx%, xy%
Natural Refrigerants
• Pure Fluids
• Naturally Occurring
• Sometimes called, “Industrial Gases”
• Hydrocarbons
ASHRAE 34 – TOXICITY & FLAMMABILITY


UL 60335-2-40/CSA C22.2 NO. 60335-2-40

Prepared by Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (UL) and CSA Group, UL 60335-2-40/CSA
C22.2
• No. 60335-2-40 is a product safety standard for HVAC equipment in the United States and Canada.
• Manufacturers of HVAC equipment are likely to follow the requirements of this UL/CSA standard strictly, to ensure their products are “listed” - this listing is a requirement of Section 7.6.2 in Standard 15 if a Group A2L refrigerant is used in a “high-probability” system for human comfort.
EPA SNAP - FINAL RULE 26


EPA SNAP - FINAL RULE 26

What is finalized in the Rule?
1. Lists 10 refrigerants as acceptable, subject to use conditions
• A2L’s for certain use cases
2. Modifies use conditions for R-290 (propane)
3. Incorporates by reference latest version of a. UL 60335-2-89, ASHRAE 15-2024, and ASHRAE 34-2022

4. Exempts R-290 in refrigerated food processing and dispensing equipment from the CAA section 608 venting prohibition
Which industrial sectors are included?
1. Refrigeration & Air Conditioning
Who is affected?
1. Chemical producers
2. Equipment manufacturers
3. Commercial and consumer end users of equipment and products using refrigerants
4. Service technicians
REFRIGERANT CATEGORIES




REFRIGERANT COMPARISONS



A2L & A3 REFRIGERANTS
EPA SNAP 26 – LISTED A2L REFRIGERANTS




