Functions for MAI HL

by JH
CONTENTS
1. Linear
2. Quadratic
3. Radical
4. Cubic
5. Reciprocal (simple)
6. Reciprocal (others)
7. Trigonometric
8. Logistic
9. Exponential
10. Logarithmic
11. Natural exponential
12. Natural logarithmic
DNE means “Does not exist” or “Do not exist”
e.g. “The function does not exist for these values of � ” or “Zeros do not exist for this function”
Linear Function
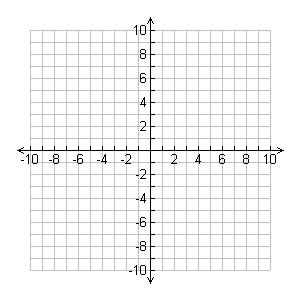
Key Features
Domain
Intervals
Intervals
Asymptote
Quadratic Function
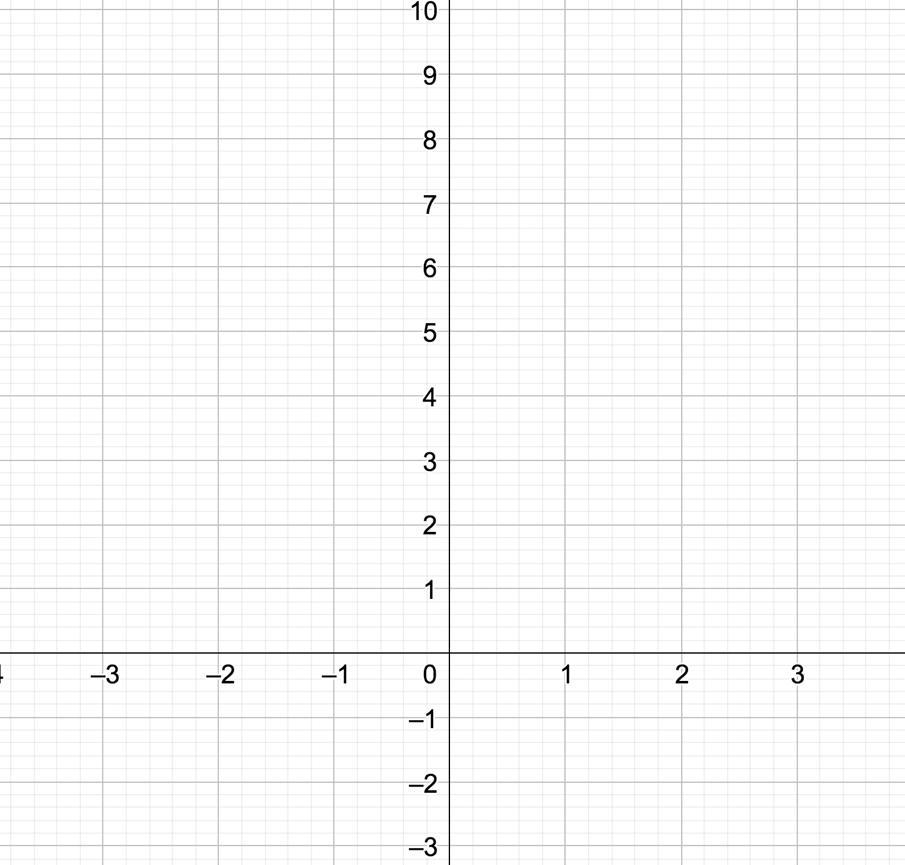
Key Features
Domain Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease Zeros
Line of symmetry

Asymptote
Radical Function

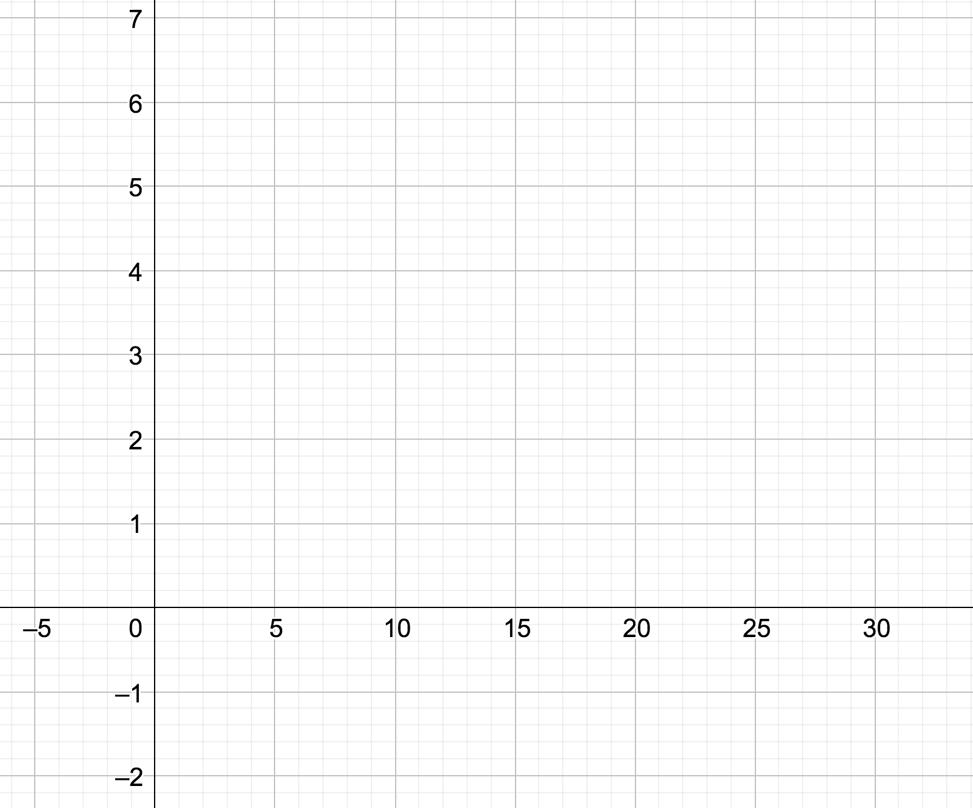
Key Features
Domain Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease DNE
Zeros � -intercepts
Line of symmetry
Asymptote
Cubic Function

Key Features
Domain Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease DNE Zeros � -intercepts
Line of symmetry DNE
Asymptote equations


Reciprocal

Key Features
Domain
Range
Intervals of increase DNE
Intervals of decrease
Zeros DNE � -intercepts DNE
Line of symmetry DNE
Asymptote equations
Reciprocal Functions

Key Features
Domain Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease Zeros
Asymptote equations
Trigonometric Function

Exponential Function
Key Features
Domain
Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease DNE
Zeros DNE � -intercepts
Line of symmetry DNE

Asymptote equations
Logarithmic Function
Key Features
Domain Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease DNE
Zeros
Line of symmetry

Asymptote equations
Natural Exponential Function
Key Features
Domain Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease DNE
Zeros DNE

Line of symmetry DNE
Asymptote equations
Natural Logarithmic Function
Key Features
Domain
Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease DNE
Zeros
Line of symmetry

Asymptote equations
Logistic Function

Key Features
Domain Range
Intervals of increase
Intervals of decrease Zeros
Line of symmetry
