4 minute read
The Importance of CAR T-cell Therapy
from MBMH Issue 4 English
by healcanada
CAR T-cell therapy represents a significant advancement in cancer treatment for several reasons:
1. Long-lasting Effects: Unlike traditional treatments like chemotherapy, which often need to be repeated, CAR T-cells can persist in the patient's body for months or even years. This long-term presence allows the immune system to continue fighting cancer cells, reducing the risk of recurrence.
3.
Effective for Refractory Cancers: One of the most remarkable aspects of CAR T-cell therapy is its effectiveness in treating cancers that have not responded to other forms of treatment. Patients with advanced, relapsed, or refractory cancers have seen complete remissions with CAR T-cell therapy when other treatments have failed
2. Personalized Medicine: CAR T-cell therapy is a highly personalized treatment. Since it uses a patient's own T-cells, it is tailored to the individual's specific cancer, improving the chances of success and reducing the risk of rejection or adverse immune reactions
4.
Innovative Approach to Solid Tumors: Although CAR T-cell therapy has seen the most success in treating blood cancers, there are ongoing efforts to expand its use to solid tumours, such as breast cancer, lung cancer, and glioblastoma. While solid tumours present unique challenges, advances in CAR T-cell technology hold promise for treating these more complex cancers.
Diseases Treated with CAR T-cell Therapy
CAR T-cell therapy has shown remarkable success in treating certain types of blood cancers Below are a few examples of diseases where this therapy is being used:
1. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
CAR T-cell therapy has been particularly effective in treating patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), a cancer of the blood and bone marrow that primarily affects children. Patients with relapsed or refractory ALL who have undergone CAR T-cell therapy have seen significant remission rates. For example, the FDA-approved CAR Tcell therapy Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel) was the first gene therapy available in the U.S. for ALL, demonstrating high rates of durable remission in patients (Maude et al., 2018). Health Canada approved the medication manufactured by Novartis in May 2019.
2. Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL)
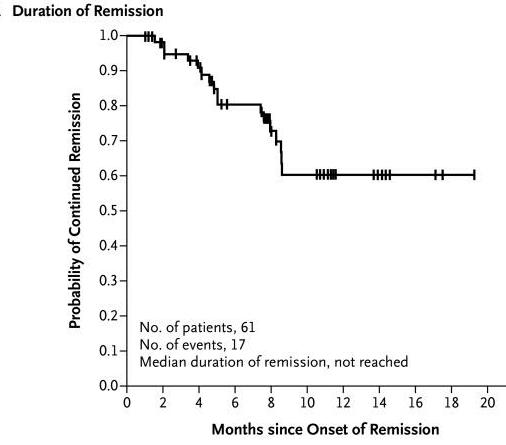
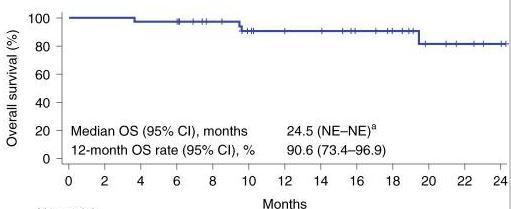
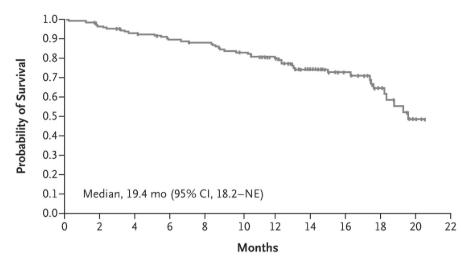
Another area where CAR T-cell therapy has made a profound impact is in treating diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. For patients who have not responded to other treatments, CAR T-cell therapies like Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel) have provided new hope, leading to high response rates (ORR) (a), prolonged response (DOR) (b) and prolonged survival (OS)(c)(Neelapu et al., 2017).
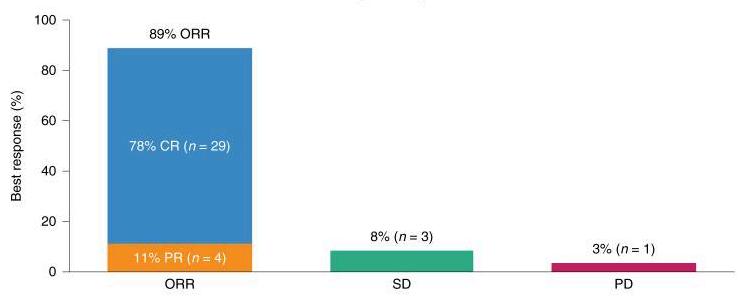
aORR:OverallResponseRate
CR:CompleteResponse
SD:Stabledisease
PR:PRogressivedisease n:numberofpatients bDOR:Durationofresponse
NR:Notreached
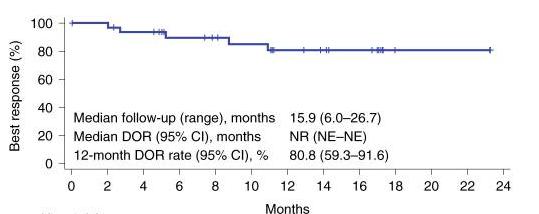
NE:Notevaluable c
OS:Overallsurvivald
NE:Notevaluable
3. Multiple Myeloma
While CAR T-cell therapy has shown the most success in B-cell malignancies, its application in multiple myeloma is gaining traction Multiple myeloma is a cancer of plasma cells, and CAR T-cell therapies targeting the B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) have shown promising results. Idecel (idecabtagene vicleucel), the first CAR T-cell therapy approved for multiple myeloma, has led to significant tumour responses in patients with relapsed or refractory disease (Munshi et al., 2021).
4. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
CAR T-cell therapy is being explored in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), a slower-growing blood cancer. Although CLL has been more resistant to CAR T-cell therapy than ALL and DLBCL, ongoing clinical trials are working to optimize CAR T-cell treatments for this patient population.
Challenges and Risks of CAR T-cell Therapy
Despite its transformative potential, CAR T-cell therapy is not without challenges and risks:
1. Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS)
One of the most serious side effects of CAR T-cell therapy is cytokine release syndrome (CRS). This occurs when the engineered T-cells trigger an intense immune response, leading to high levels of inflammatory molecules called cytokines. Symptoms can range from mild (fever, fatigue) to severe (low blood pressure, difficulty breathing), and in some cases, CRS can be lifethreatening. Early detection and prompt management are crucial for minimizing the risks associated with CRS.
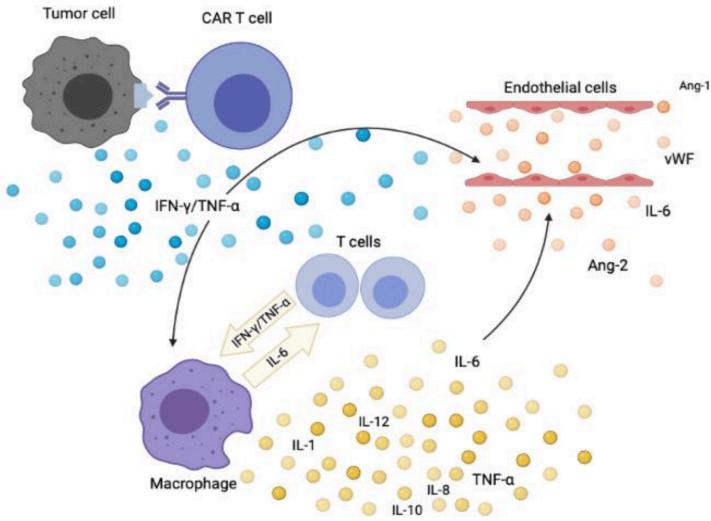
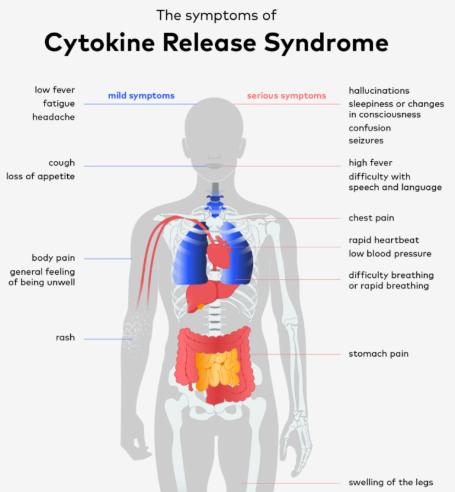
2. Neurotoxicity
Another potential side effect is neurotoxicity, which can cause confusion, seizures, and other neurological symptoms. While the exact mechanism behind CAR T-cell-induced neurotoxicity is not fully understood, it appears to be linked to the intense immune activation triggered by the therapy. Most cases of neurotoxicity are reversible with appropriate medical intervention.
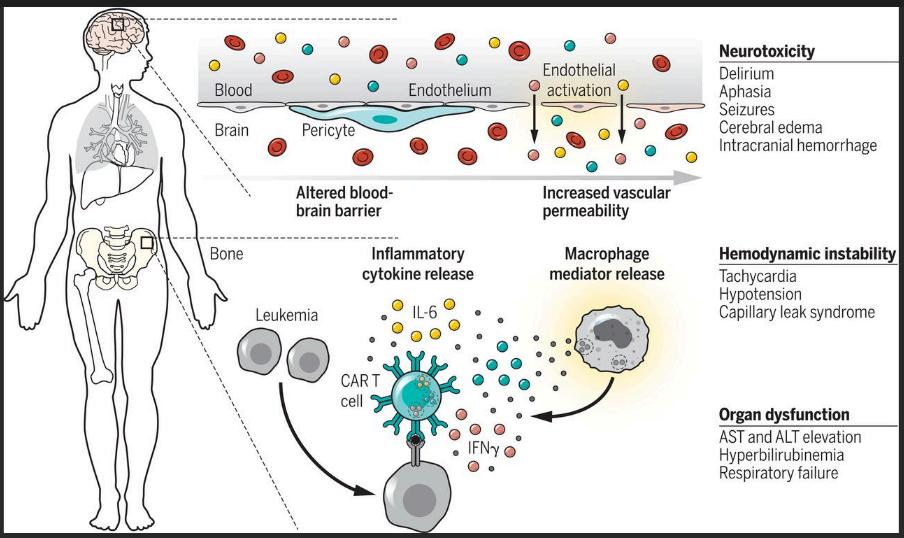
3. Access and Affordability
CAR T-cell therapy is complex and expensive, with treatment costs reaching hundreds of thousands of dollars. This raises concerns about access and affordability, particularly for patients in low-income settings or countries with limited healthcare coverage Expanding access to CAR T-cell therapy requires ongoing efforts in patient advocacy, healthcare policy, and innovative financing models.
The Future of CAR T-cell Therapy
As research advances, the future of CAR T-cell therapy looks promising. Scientists are refining CAR T-cell technology to improve its safety, effectiveness, and applicability to a broader range of cancers. Some areas of ongoing research include:
Tackling Solid Tumours: Researchers are developing new CAR T-cell therapies that can overcome the unique challenges of solid tumours, such as the dense tumour microenvironment and immune evasion mechanisms.
Reducing Side Effects: Efforts are underway to develop CAR T-cell therapies that minimize the risk of CRS and neurotoxicity One promising strategy involves using "onoff" switches that allow clinicians to control CAR T-cell activity more precisely.
Combining Therapies: Combining CAR T-cell therapy with other treatments, such as checkpoint inhibitors or traditional cancer therapies, may enhance its effectiveness and broaden its use.
The Role of Patient Advocacy
Patient advocacy is crucial in expanding access to CAR T-cell therapy and ensuring that patients understand their treatment options. Advocacy organizations can help bridge the gap between patients, healthcare providers, and researchers by promoting awareness, supporting research funding, and lobbying for policy changes that increase access to these life-saving therapies.
Additionally, advocates can work to ensure that clinical trials for CAR T-cell therapies are designed with patient needs in mind, helping to optimize treatment protocols and expand eligibility for a broader range of patients.
Conclusion
CAR T-cell therapy represents one of the most exciting advancements in cancer treatment, offering hope to patients with few remaining options Its ability to provide durable remissions in previously refractory cancers has revolutionized the treatment of blood cancers, and ongoing research is expanding its reach to other types of malignancies. While challenges remain, particularly in managing side effects and expanding access, the future of CAR T-cell therapy is bright. As patient advocates continue to push for broader access and better understanding, this therapy has the potential to save countless lives.









